Ipsilateral Fibular Transport Using Ilizarov Taylor Spatial Frame for a Limb Salvage Reconstruction: a Case Report
|
|
|
- Stephanie Darleen Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s CASE REPORT Ipsilateral Fibular Transport Using Ilizarov Taylor Spatial Frame for a Limb Salvage Reconstruction: a Case Report Raheel Shafi, MD& Austin T. Fragomen, MD & S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Received: 5 August 2008/Accepted: 28 October 2008 * Hospital for Special Surgery 2008 Abstract Segmental bone defects of the tibia present a challenging problem, particularly when they are associated with soft tissue injuries or instability. Various techniques have been reported to treat bone loss in the tibia. This case report describes a patient with massive segmental bone loss associated with a soft tissue injury, which required a flap for coverage. The injury was treated with an ipsilateral fibular transport utilizing an Ilizarov/Taylor spatial frame. At one and a half year follow-up, the patient was able to walk without any support at home and wore a protective shell for outdoor activities. The outcome of this case study indicates that ipsilateral fibular transport using the Ilizarov method is a valuable technique for limb salvage reconstruction. Keywords fibular transport. segmental defect. Taylor spatial frame (TSF). vascularized graft. fibular hypertrophy. Ilizarov Introduction Various techniques have been used to treat large segmental tibial defects such as autogenous cortical bone grafts [1], tibiofibular synostosis, ipsilateral fibular graft [2 8], allograft reconstruction [9], vascularized free fibula transfer [10 12], and bone transport. Ipsilateral fibular transport [13 15] is a novel option in limb salvage surgery for patients with large tibial defects. In 1904, Nichols [2] first presented the use of an ipsilateral fibular graft as a treatment for an infected tibia. R. Shafi, MD &A. T. Fragomen, MD &S. R. Rozbruch, MD Limb Lengthening and Deformity Service, Hospital for Special Surgery, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, USA S. R. Rozbruch, MD (*) 535 E 70th Street, New York, NY 10021, USA rozbruchsr@hss.edu The technique included partial dissection of muscle attachments and an osteotomy of the ipsilateral fibula, followed by medial mobilization using the intact attachments. Zahiri et al. [8] successfully used a modification of this method to treat chronic osteomylitis of the entire tibial shaft in nine children. They performed osteotomies at both metaphyses leaving the metaphyseal plates untouched. The two ends of the fibula were brought into the centers of the tibial metaphyseal stumps. Proximal fixation was achieved by locking the end of the fibula into the center of the metaphysis. Distally, an unthreaded Steinmann's pin was drilled from the heel through the calcaneum, talus, and tibial epiphysis into the medullary canal of the transferred fibula. Experiments on Macaca monkeys demonstrated that a vascularized pedicle graft of the shaft of the ipsilateral fibula could be fixed across a defect in the tibia and remain viable, even if isolated from the surrounding tissue [3, 5]. A large graft of ipsilateral fibula raised on a pedicle of peroneal tibial muscles, anterior tibial muscles, and the peroneal vessels, which are aligned and fixed with the tibia in its posterior long axis, could provide a sound mechanical and biological basis of union. However, open methods require large surgical dissections and skeletal stability could be difficult to accomplish [3, 4, 7, 13 15]. The ipsilateral and contralateral fibulae can be used to replace the missing segment using both vascularized [10] and nonvascularized grafts [16]. With vascularized grafts, specialized microvascular techniques are used to re-establish the blood supply. Free vascularized fibular grafting is a complex procedure that requires the expertise of a microvascular surgeon. Excellent results have been reported but complications of thrombosis, nonunion, and deformity have been reported [10]. In addition, complications related to the fibula harvest include hematoma, nerve injury, infection, and valgus deformity of the ankle [17, 18]. The Ilizarov method has been used to successfully transport bone and soft tissues longitudinally to treat tibial bone loss and at times to close an accompanying soft tissue
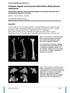
2 defect [15, 19 24]. A less common application of the Ilizarov technique is transverse bone transport [13, 15, 25]. The frame allows for gradual transport of the fibula into the adjacent tibial defect site, precise proximal and distal alignment of the fibula, and compression at tibial contact sites. This is a minimally invasive technique which requires little surgical dissection. We present a case report of a patient with massive segmental loss of tibia and an associated soft tissue injury treated with fibular transport utilizing the Ilizarov/Taylor spatial frame (TSF) (Memphis, TN, USA). Case report A 41-year-old patient (M.P.) involved in a motorcycle accident presented with a high energy right open tibia fracture with massive bone and soft tissue loss. The patient was initially treated with provisional external fixation and serial irrigation and debridement. The initial defect was 15 cm in length (Figs. 1a and 2a). He had a traumatic brain injury and a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube was placed for feeding purposes. A free muscle flap was performed early to obtain soft tissue coverage and avoid infection (Fig. 1b). Subsequently, he was referred to the Limb Lengthening and Deformity Service for reconstruction of the bone defect. A month after his accident, he underwent an application of an Ilizarov/TSF along with a two level fibular osteotomy for bone transport. A two-ring frame connected with TSF struts was applied to the leg. This spanned the bone defect and stabilized the proximal and distal bone segments in line with each other. This allowed control of the proximal and distal segments on either side of the defect. A long Ilizarov plate was then connected to the frame anteromedially in preparation for the fibular transport. A two level osteotomy of the fibula was planned at the level of the tibial defect. Three pulling olive wires were placed through the fibula aiming from the posterolateral to the anteromedial (Fig. 2b). The tails of the olive wires were cut at the level of the bead and the olives were positioned against the fibula. These wires were set up as pulling wires and were attached to the anteromedial plate via three short slotted rods that had the capacity to pull all three of these olive wires. The position of these wires was such that it would pull the fibula from the posterolateral position in an anteromedial direction into the tibial defect (Fig. 2a f). Fig. 1. a This is an anteroposterior (AP) radiograph prior to the application of the Taylor spatial frame (TSF) showing the initial bony defect in a provisional external fixator. b This preop picture of the patient shows the leg in a provisional external fixator after a free muscle flap was placed to cover the soft tissue defect
3 Fig. 2. a This is an illustration of the 15-cm tibial defect. b A diagrammatic representation of the fibular transport shows the level of the fibular osteotomy and the direction of the fibular transport using three olive fibular pulling wires. c, d The AP/ lateral X-ray views of the leg were taken after the application of the two-ring frame and the fibular osteotomies. Note the three fibular wires aiming from posterolateral to anteromedial direction. e This is a diagrammatic representation of the fibular transport in the Ilizarov/TSF with three pulling olive wires. f This picture, taken in the operating room, is of the patient's leg after the application of Ilizarov/TSF2 Next, a 1-in. skin incision was made at the proximal margin of the fibula, where the proximal osteotomy was planned. Dissection was carried down between the lateral and posterior compartments, and using a microsaggital saw, an oblique osteotomy of the fibula was made. The osteotomy was completed with an osteotome. Similarly, at the distal end of the defect, a 1-in. incision was made. Dissection was carried down to the fibula, and
4 using a microsagittal saw, an oblique osteotomy was made. The osteotomy was completed with an osteotome. The osteotomies were not displaced. The wounds were irrigated and closed. The fibula transport was started 10 days postoperatively utilizing the principles of distraction osteogenesis. Twelve weeks after the application of the frame and the fibular transport, the frame was modified to optimize contact between the tibia and the transported fibula (Fig. 3a,b). The modified frame improved stability and allowed for axial compression between the tibia and the transported fibula. Bone grafting with Op-1 (Stryker, Kalamazoo, MI, USA) was used to promote healing. Four wires were placed into the transported fibula and the adjacent bone. These included a posteromedial olive wire, which was braced medially in order to bring a posteromedial tibial fragment into the alignment, a wire on the distal aspect of the fibular transport and then two opposing olive wires on the proximal main segment of the fibular transport. Two additional rings were placed as rings #3 and #4 of a five-ring construct moving from proximal to distal. All rings were connected with three or four Ilizarov rod connections. Once the rings were in place, the four wires were attached to the rings, and an arched olive wire technique was used to optimize the position, opposition, and compression of the bone. The frame fit the leg well, and the position of the fibular graft remained satisfactory. The alignment was assessed in coronal and sagittal planes using fluoroscopy. The fibular transport wires were removed. An ultrasound bone stimulator (Exogen, Smith & Nephew, Memphis, TN, USA) was used to enhance bone healing. Two weeks later at the first follow-up visit, the overall anteroposterior alignment was normal, but the lateral view showed mild procurvatum. There was a limb length discrepancy of 2.2 cm (Fig. 4). Five weeks following frame modification, a follow-up office visit revealed the graft to be in a satisfactory position. Six months following frame modification, the intermediate and middle rings were removed leaving one proximal and one distal ring connected with the rods. This was done to dynamize the fibula. At 8 months following surgery, the bone showed good alignment and progression of healing (Fig. 5a,b). The frame was further dynamized at this juncture by loosening the connection at the proximal two connection points (Fig. 5c,d). This was done to load the fibula and encourage hypertrophy. Full weight bearing was permitted after dynamization. A superficial pin track infection was noted at 9 months. It resolved with oral antibiotic therapy. The frame was removed 1 year and 10 days following the initial application. The patient was placed in a short leg cast for 2 weeks, and upon cast removal, was able to tolerate full weight bearing (Fig. 6a c). Fig. 3. a The AP view of the patient's leg shows the Ilizarov/TSF after a modification and application of additional rings. b This is a lateral view of the patient's leg after frame modification
5 Fig. 4. The 51-in. long X-ray shows leg length and alignment The patient continued to improve, and at the one and a half year follow-up visit, the patient showed a well healed fibula transport. This was assessed by clinical and radiographic measures. The patient continues to walk without any support in his home, and he wears a protective shell for outdoor activities. M.P. tolerates full weight bearing (Fig. 7a c). Discussion A large segmental defect of the tibia is a difficult problem to treat [2 8, 10, 13, 15, 24]. These patients will often present with other traumatic injuries, and treatment options become limited if soft tissue defects are combined with segmental bone loss. Various methods to fill segmental bone defects such as microsurgical transport of vascularized bone, e.g., rib, iliac crest, fibula, and allograft reconstruction, have also been employed. A below knee amputation is a reasonable alternative solution. However, it is not preferable, particularly in patients who have a normal foot and ankle and do not require vascular repair [26]. Each of these methods is effective depending on the circumstances. They have drawbacks including the possibility of donor site morbidity, deep infection [13], peroneal nerve injury [1], and ankle instability on the contralateral previously unaffected limb. They may be at a high risk of failure [1, 9, 10] as infection, rejection, fracture, and nonunion all have been described with these techniques. A limb salvage reconstruction was chosen with understanding that an amputation could be performed if this failed. In 1877, Albert [6] first proposed the use of the fibula as a substitute for the tibia. He obtained fusion between the fibula and the femur in a patient with congenital absence of the proximal tibia. Since then, the fibula has been used as a substitute for a missing segment of tibia or to reinforce a weakened section. The major advantage of a perfused transplant is to retain the biological potential of living bone. This gives a shorter time for consolidation, increases potential for remodeling, confers greater resistance to infection, and has better long-term mechanical properties [3 6, 23]. Furthermore, in contrast to an allograft, it has no immunogenicity [5, 9]. The fibula is a straight cortical bone and is long enough to bridge most defects. While it normally carries only one sixth of the static loading of the leg [7], the fibula will undergo hypertrophy [5, 6, 10, 13, 16] when it is subjected to greater loading stresses. This was our rationale for maintaining the patient in a dynamized frame for an extended period of time. This allowed remodeling of the tibia fibula docking sites and fibula hypertrophy while protecting the fibula from fracture. Ilizarov described two methods [13, 25] for treating large defects with his fine wire fixator. In the first method, the fibular segment is translated medially, creating a proximal and distal, side-to-side tibiofibular synostosis. This is the method that we used. In the second method, the fibula is split longitudinally and transverse distraction osteogenesis is performed. This technique is complex and no mention is made of the clinical results. Ipsilateral fibular bone transport using an Ilizarov/TSF is a successful approach to safely and effectively fill a tibial defect [3, 5, 7, 13, 15, 25]. It has the advantage of a vascularized fibular graft but does not require large dissection; there is no need for microvascular surgery, and there is no donor site morbidity. A tibia fibula synostosis and bony healing is achieved at both ends of the defect. The Ilizarov/TSF allows for stability and longitudinal compression without internal fixation [13, 14, 19, 21]. Furthermore, operative dissection of the fibula is minimal, and the bone remains well vascularized as both sources of blood supply are neither defined nor dissected [22 24]. Muscle attachments are maintained without dissection and the overlying free flap remains undisturbed. The fibular segment is central and is held by the tibial remnants in a mechanically advantageous position in the line of the axis of the tibia. Weight bearing can begin almost immediately after surgery, and the proximal and distal joints are mobilized satisfactorily. Further, limb lengthening may be carried out through a separate corticotomy of either the proximal or distal tibial remnant. However, this procedure has its limitations. It requires a suitable length of uninjured fibula to be available in the same leg, and although this may be present in most tumor cases, it is not always the case in trauma-related injuries.
6 Fig. 5. a, b The AP/lateral views of the leg show progression of healing and alignment of the fibular transport. This is a dynamized frame. c, d Pictures of the patient standing and full weight bearing after frame modification and dynamization HSSJ
7 Fig. 6. a A diagrammatic representation of the healed fibular transport is shown after removal of the frame. b, c AP/lateral X-ray views of the healed fibular transport are shown after removal of frame
8 Fig. 7. a c These photographs display front, back, and side views of the patient standing without support. He is full weight bearing at this one and a half year follow-up HSSJ
9 Acknowledgment The authors would like to thank Craig Fryman, BS (Research Coordinator). References 1. Enneking WF, Eady JL, Burchardt H (1980) Autogenous cortical bone grafts in the reconstruction of segmental skeletal defects. J Bone Joint Surg Am 62: Huntington TW (1905) Case of bone transference. Use of a segment of fibula to supply a defect in the tibia. Ann Surg 41: Chacha PB, Ahmed M, Daruwalla JS (1981) Vascular pedicle graft of the ipsilateral fibula for non-union of the tibia with a large defect: an experimental and clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 63: Agiza AR (1981) Treatment of tibial osteomyelitic defects and infected pseudarthroses by the Huntington fibular transference operation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 63: Shapiro MS, Endrizzi DP, Cannon RM et al (1993) Treatment of tibial defects and nonunions using ipsilateral vascularized fibular transposition. Clin Orthop Relat Res 296: Hertel R, Pisan M, Jakob RP (1995) Use of the ipsilateral vascularised fibula for tibial reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Br 77: Date AS, Solanki SB, Badhe NP et al (1996) Management of gap non-union of tibia by tibialisation of ipsilateral vascular fibula. J Postgrad Med 42: Zahiri CA, Zahiri H, Tehrany F (1997) Limb salvage in advanced chronic osteomyelitis in children. Int Orthop 21: Mankin HJ, Hornicek FJ, Raskin KA (2005) Infection in massive bone allografts. Clin Orthop Relat Res 432: Wood MB (2007) Free vascularized fibular grafting 25 years' experience: tips, techniques and pearls. Orthop Clin North Am 38: Carr AJ, Macdonald DA, Waterhouse N (1988) The blood supply of the osteocutaneous free fibular graft. J Bone Joint Surg Br 70: Mozzafarian K, Lascombes P, Dautel G (2008) Vascular basis of free transfer of proximal epiphysis and diaphysis of fibula: an anatomical study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (in press) 13. Atkins RM, Madhaven P, Sudhaker J et al (1999) Ipsilateral vascularized fibular transport for massive defects of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81: Goren D, Sapir O, Stern A et al (2005) Ipsilateral fibular transfer for a large tibial defect caused by a gunshot injury. Mil Med 170: Catagni MA, Ottaviani G, Camagni M (2007) Treatment of massive tibial bone loss due to chronic draining osteomyelitis: fibula transport using the Ilizarov frame. Orthopedics 30: May JW, Jupiter JB, Weiland AJ et al (1989) Current concepts review clinical classification of post-traumatic tibial osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71: Minami A, Kasashima T, Iwasaki N et al (2000) Vascularized fibular grafts an experience of 102 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 82-B: Pederson WC, Person DW (2007) Long bone reconstruction with vascularized bone grafts. Orthop Clin North Am 38: Mullen JE, Rozbruch SR, Blyakher A et al (2004) Ilizarov method for wound closure and bony union of an open grade IIIB tibia fracture. Case Rep Clin Pract Rev 5: Shane JN, Helfet DL, Rozbruch SR (2006) Temporary intentional leg shortening and deformation to facilitate wound closure using the Ilizarov/Taylor spatial frame. J Orthop Trauma 20: Rozbruch SR, Adam M, Weitzman BA et al (2006) Simultaneous treatment of tibial bone and soft-tissue defects with the Ilizarov method. J Orthop Trauma 20: Rozbruch SR, Pugsley JS, Fragomen AT et al (2008) Repair of tibial nonunions and bone defects with the Taylor spatial frame. J Orthop Trauma 22: Cattaneo R, Catagni M, Johnson EE (1992) The treatment of infected nonunions and segmental defects of the tibia by the methods of Ilizarov. Clin Orthop Relat Res 280: Sen C, Kocaoglu M, Eralp L et al (2004) Bifocal compression distraction in the acute treatment of grade III open tibial fractures with bone and soft-tissues: a report of cases. J Orthop Trauma 18: Ilizarov GA (1992) Pseudoarthroses and defects of long tubular bones: treatment of marked defects. In: Ilizarov GA (ed) Transosseous osteosynthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp Lange RH (1989) Limb reconstruction versus amputation decision making in massive lower extremity trauma. Clin Orthop Relat Res 243:92 99
The ipsilateral and contralateral fibulae have been
 Ipsilateral vascularised fibular transport for massive defects of the tibia R. M. Atkins, P. Madhavan, J. Sudhakar, D. Whitwell From the Bristol Royal Infirmary, Bristol, England The ipsilateral and contralateral
Ipsilateral vascularised fibular transport for massive defects of the tibia R. M. Atkins, P. Madhavan, J. Sudhakar, D. Whitwell From the Bristol Royal Infirmary, Bristol, England The ipsilateral and contralateral
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
Acute emergency tibialization of the fibula: reconstruction of a massive tibial defect in a type IIIC open fracture
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2013) 8:127 131 DOI 10.1007/s11751-013-0167-6 CASE REPORT Acute emergency tibialization of the fibula: reconstruction of a massive tibial defect in a type IIIC open fracture Fatih
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2013) 8:127 131 DOI 10.1007/s11751-013-0167-6 CASE REPORT Acute emergency tibialization of the fibula: reconstruction of a massive tibial defect in a type IIIC open fracture Fatih
Small-wire circular fixators and hybrid external fixation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correction of Tibial Malunion and Nonunion With Six-Axis Analysis Deformity Correction Using the Taylor Spatial Frame David S. Feldman, MD, Steven S. Shin, MD, Sanjeev Madan, MD, and Kenneth
USE OF THE IPSILATERAL VASCULARISED FIBULA FOR
 USE OF THE IPSILATERAL VASCULARISED FIBULA FOR TIBIAL RECONSTRUCTION R. HERTEL, M. PISAN, R. P. JAKOB From the University of Berne, Switzerland Between 1989 and 1994 we used a vascularised ipsilateral
USE OF THE IPSILATERAL VASCULARISED FIBULA FOR TIBIAL RECONSTRUCTION R. HERTEL, M. PISAN, R. P. JAKOB From the University of Berne, Switzerland Between 1989 and 1994 we used a vascularised ipsilateral
Temporary Intentional Leg Shortening and Deformation to Facilitate Wound Closure Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame
 TECHNICAL TRICK Temporary Intentional Leg Shortening and Deformation to Facilitate Wound Closure Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame Shane J. Nho, MD, David L. Helfet, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
TECHNICAL TRICK Temporary Intentional Leg Shortening and Deformation to Facilitate Wound Closure Using the Ilizarov/Taylor Spatial Frame Shane J. Nho, MD, David L. Helfet, MD, and S. Robert Rozbruch, MD
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions?
 Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions? James J Hutson Jr MD Professor Orthopedic Trauma Ryder
Is Distraction Histiogenesis a Reliable Method to Reconstruct Segmental Bone and Acquired Leg Length Discrepancy in Tibia Fractures and Non Unions? James J Hutson Jr MD Professor Orthopedic Trauma Ryder
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Treatment of large diaphyseal bone defect of the tibia by the fibula pro tibia technique : application in developing countries
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 17-23 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of large diaphyseal bone defect of the tibia by the fibula pro tibia technique : application in developing countries René Castro Gayito, Giambattista
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 17-23 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of large diaphyseal bone defect of the tibia by the fibula pro tibia technique : application in developing countries René Castro Gayito, Giambattista
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
The space shuttle docking at the international space station
 Docking Tips The space shuttle docking at the international space station Bone gap after component fracture tibia A standard distal to proximal bone transport Apparently simple pictures of the bone transport
Docking Tips The space shuttle docking at the international space station Bone gap after component fracture tibia A standard distal to proximal bone transport Apparently simple pictures of the bone transport
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Large segmental defects of the tibia caused by highenergy. Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 3 & 4 2003-2004 101 Ten Year Experience with Use of Ilizarov Bone Transport for Tibial Defects Gene D. Bobroff, M.D., Stuart Gold, M.D., and Daniel
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis
 Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Management of Nonunion of Tibia by Ilizarov Technique Haque MA 1, Islam SM 2, Chowdhury MR 3
 ...Original Article Management of Nonunion of Tibia by Ilizarov Technique Haque MA 1, Islam SM 2, Chowdhury MR 3 Abstract This prospective study was carried out during the period of January 2007 to December
...Original Article Management of Nonunion of Tibia by Ilizarov Technique Haque MA 1, Islam SM 2, Chowdhury MR 3 Abstract This prospective study was carried out during the period of January 2007 to December
Pilon fractures. Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota
 Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
Debate: I Do Bone Transport. Disclosures. Bone Defects 5/10/2017
 Debate: I Do Bone Transport David W. Lowenberg, M.D. Clinical Pressor Department Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University School Medicine Disclosures Board Directors: Foundation for Orthopaedic Trauma (FOT)
Debate: I Do Bone Transport David W. Lowenberg, M.D. Clinical Pressor Department Orthopaedic Surgery Stanford University School Medicine Disclosures Board Directors: Foundation for Orthopaedic Trauma (FOT)
Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery
 Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016
 SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
abstract n Feature Article Chun-Cheng Lin, MD; Chuan-Mu Chen, MD; Fang-Yao Chiu, MD; Yu-Pin Su, MD; Chien-Lin Liu, MD; Tain-Hsiung Chen, MD
 Staged Protocol for the Treatment of Chronic Tibial Shaft Osteomyelitis With Ilizarov s Technique Followed by the Application of Intramedullary Locked Nail Chun-Cheng Lin, MD; Chuan-Mu Chen, MD; Fang-Yao
Staged Protocol for the Treatment of Chronic Tibial Shaft Osteomyelitis With Ilizarov s Technique Followed by the Application of Intramedullary Locked Nail Chun-Cheng Lin, MD; Chuan-Mu Chen, MD; Fang-Yao
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/383 Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation T Suresh Kumar 1, Swagat Mahapatra 2 1 Assistant
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/383 Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation T Suresh Kumar 1, Swagat Mahapatra 2 1 Assistant
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Lengthening & Deformity correction with. Fixator Assisted Nailing
 Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Lengthening & Deformity correction with Fixator Assisted Nailing External Fixation Used as *Intra-Op Alignment tool * for lengthening with the main intention of reducing External fixation time! Advantages
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Comparison of acute compression distraction and segmental bone transport techniques in the treatment of tibia osteomyelitis
 Comparison of acute compression distraction and segmental bone transport techniques in the treatment of tibia osteomyelitis Eralp Levent 1, Sen Cengiz 1, Dikmen Goksel 1, Tomak Yılmaz 2, Gulsen Mahir 3,
Comparison of acute compression distraction and segmental bone transport techniques in the treatment of tibia osteomyelitis Eralp Levent 1, Sen Cengiz 1, Dikmen Goksel 1, Tomak Yılmaz 2, Gulsen Mahir 3,
Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy
 METATARSAL BONES LENGTHENING WITH LAKI MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy alexander@kirienko.com Alexander KIRIENKO, MD
METATARSAL BONES LENGTHENING WITH LAKI MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy alexander@kirienko.com Alexander KIRIENKO, MD
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Of approximately 2 million long bone fractures
 Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS
 ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS M. N. Tahmasebi * and Sh. Jalali Mazlouman Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS M. N. Tahmasebi * and Sh. Jalali Mazlouman Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Tibia T-Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
Composite Bone and Soft Tissue Loss Treated With Distraction Histiogenesis
 Composite Bone and Soft Tissue Loss Treated With Distraction Histiogenesis CPT Michael J. Beltran, MD, 1 CPT Leah M. Ochoa, MD, 2 MAJ Richard M. Graves, MD, 2 MAJ(P) Joseph R. Hsu, MD, 3 and the Skeletal
Composite Bone and Soft Tissue Loss Treated With Distraction Histiogenesis CPT Michael J. Beltran, MD, 1 CPT Leah M. Ochoa, MD, 2 MAJ Richard M. Graves, MD, 2 MAJ(P) Joseph R. Hsu, MD, 3 and the Skeletal
Reconstruction of Segmental Bone Defects Due to Chronic Osteomyelitis with Use of an External Fixator and an Intramedullary Nail Surgical Technique
 183 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Reconstruction of Segmental Bone Defects Due to Chronic Osteomyelitis with Use of an External Fixator and an Intramedullary Nail
183 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Reconstruction of Segmental Bone Defects Due to Chronic Osteomyelitis with Use of an External Fixator and an Intramedullary Nail
We present a series of ten hypertrophic nonunions
 MANAGEMENT OF NONUNION OF FRACTURES BY DISTRACTION WITH CORRECTION OF ANGULATION AND SHORTENING MICHAEL SALEH, SIMON ROYSTON From the Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, England We present a series of
MANAGEMENT OF NONUNION OF FRACTURES BY DISTRACTION WITH CORRECTION OF ANGULATION AND SHORTENING MICHAEL SALEH, SIMON ROYSTON From the Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, England We present a series of
Kocaoglu, Mehmet MD; Eralp, Levent MD; Sen, Cengiz MD; Cakmak, Mehmet MD; Dincyürek, Hakan MD; Göksan, S. Bora MD
 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Volume 17(8), September 2003, pp 543-548 Management of Stiff Hypertrophic Nonunions by Distraction Osteogenesis: A Report of 16 Cases [Original Articles] Kocaoglu,
The Use of Ilizarov External Fixation Following Failed Internal Fixation
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 17(4):490 505 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia The Use of Ilizarov External Fixation Following Failed Internal Fixation Mark R. Brinker, M.D.*, and Daniel
Techniques in Orthopaedics 17(4):490 505 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia The Use of Ilizarov External Fixation Following Failed Internal Fixation Mark R. Brinker, M.D.*, and Daniel
Treatment of septic non-union of tibia using compression and distraction technique with ilizarov circular fixator
 Original Article Treatment of septic non-union of tibia using compression and distraction technique with ilizarov circular fixator Muhammad Ayaz Khan, Muhammad Salman, Muhammad Imran Khan, Tamjeed Gul,
Original Article Treatment of septic non-union of tibia using compression and distraction technique with ilizarov circular fixator Muhammad Ayaz Khan, Muhammad Salman, Muhammad Imran Khan, Tamjeed Gul,
Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Neurologic Damage. The most common neurologic injury following intramedullary tibial nailing is injury to the peroneal nerve.
 COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
COMPLICATIONS Knee Pain Anterior knee pain was present in 55% Affects younger more than older patients A significant number of the patients with anterior knee pain had pain with kneeling [90%] They also
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring Fixator
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement: Case Series
 737481FAIXXX10.1177/1071100717737481Foot & Ankle InternationalDa Cunha et al research-article2017 Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement:
737481FAIXXX10.1177/1071100717737481Foot & Ankle InternationalDa Cunha et al research-article2017 Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement:
Galal Zaki Said 1, *, Osama Ahmed Farouk 1, Hatem Galal Said 1
 KOWSAR Two-Stage Surgical Treatment for Non-Union of a Shortened Osteoporotic Femur Galal Zaki Said 1, *, Osama Ahmed Farouk 1, Hatem Galal Said 1 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine,
KOWSAR Two-Stage Surgical Treatment for Non-Union of a Shortened Osteoporotic Femur Galal Zaki Said 1, *, Osama Ahmed Farouk 1, Hatem Galal Said 1 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine,
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS
 FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA MORTISE INHERENTLY UNSTABLE LATERAL MALLEOLUS ACTS AS BUTTRESS / POST RESIST LATERAL TRANSLATION OF TALUS
FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA MORTISE INHERENTLY UNSTABLE LATERAL MALLEOLUS ACTS AS BUTTRESS / POST RESIST LATERAL TRANSLATION OF TALUS
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
ARMS. Reconstruction of Large Femur and Tibia Defect with Free Vascularized Fibula Graft and Locking Plate INTRODUCTION.
 Original Article ARMS Archieves of Reconstructive Microsurgery pissn 2383-5257 eissn 2288-6184 Arch Reconstr Microsurg 2015;24(2):68-74 http://dx.doi.org/10.15596/arms.2015.24.2.68 Reconstruction of Large
Original Article ARMS Archieves of Reconstructive Microsurgery pissn 2383-5257 eissn 2288-6184 Arch Reconstr Microsurg 2015;24(2):68-74 http://dx.doi.org/10.15596/arms.2015.24.2.68 Reconstruction of Large
Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 611-615 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of non-union of forearm bones with a free vascularised cortico - periosteal flap from the medial femoral condyle Luc DE SMET From the University
Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics
 MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
Pilon Fractures Pearls of Treatment Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSOT November 2017, Tampa
 Pilon Fractures Pearls of Treatment Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSOT November 2017, Tampa Disclosures No relevant disclosures There is more literature
Pilon Fractures Pearls of Treatment Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSOT November 2017, Tampa Disclosures No relevant disclosures There is more literature
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
Outcome of Treatment of Nonunion Tibial Shaft Fracture by Intramedullary Interlocking Nail augmentated with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft.
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2014; 16(1): 58-62 Outcome of Treatment of Nonunion Tibial Shaft Fracture by Intramedullary Interlocking Nail augmentated with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft. Shah SB,
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2014; 16(1): 58-62 Outcome of Treatment of Nonunion Tibial Shaft Fracture by Intramedullary Interlocking Nail augmentated with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft. Shah SB,
Reintroducing the latissimus-rib free flap as a long bone substitute in the reconstruction of lower extremity injuries
 Case report Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 2, August 2008. pp.104-110 Reintroducing the latissimus-rib free flap as a long bone substitute in the reconstruction of lower extremity
Case report Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 2, August 2008. pp.104-110 Reintroducing the latissimus-rib free flap as a long bone substitute in the reconstruction of lower extremity
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique
 TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot)
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS
 TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
GREENS SURGICALS. Redefining Excellence INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR
 GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
GREENS SURGICALS Redefining Excellence TIBIA AND FEMUR INSTRUMENT SYSTEM PREPARED BY: DR. VINAY KUMAR OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES INDEX SR.NO CONTENTS 1 LIST OF INSTRUMENT FOR TIBIA AND FEMUR. 2 RADIO GRAPH OF
Clinical. Solutions. Synthes Solutions. Foot and Ankle.
 Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Schedule Of Anaesthetic Rates Applicable To Podiatry. Procedure List. As Of. 01 April Government of Alberta
 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
We carried out a randomised, controlled trial in
 Vascular injuries in compound fractures of the leg with initially adequate circulation Saranatra Waikakul, Somjet Sakkarnkosol, Vichai Vanadurongwan From Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand We carried
Vascular injuries in compound fractures of the leg with initially adequate circulation Saranatra Waikakul, Somjet Sakkarnkosol, Vichai Vanadurongwan From Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand We carried
6/5/2018. Open Fractures and Dislocations around the Foot and Ankle: Disclosures. Talking Points. Soft-Tissue Strategies
 Open Fractures and Dislocations around the Foot and Ankle: Soft-Tissue Strategies 16 th Annual Trauma 101 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST AND ORTHOPAEDIC PA & NP Clearwater, FL May 11, 2018
Open Fractures and Dislocations around the Foot and Ankle: Soft-Tissue Strategies 16 th Annual Trauma 101 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST AND ORTHOPAEDIC PA & NP Clearwater, FL May 11, 2018
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Maquet: Maquet: Biomechanics. Maquet: /21/10. Philippe Landreau, MD
 Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
Mohammed H. Salal*, Isam H.Ali**
 MANAGEMENTS THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE OF TIBIAL MEDICAL HEMIMELIA JOURNAL Managements of Type 2 Tibial Hemimelia; Short Review on Treatment of Tibial Defects and The Results of Four Patient Treated Using
MANAGEMENTS THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE OF TIBIAL MEDICAL HEMIMELIA JOURNAL Managements of Type 2 Tibial Hemimelia; Short Review on Treatment of Tibial Defects and The Results of Four Patient Treated Using
Acute compression and lengthening by the Ilizarov technique for infected nonunion of the tibia with large bone defects
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2006;14(3):273-9 Acute compression and lengthening by the Ilizarov technique for infected nonunion of the tibia with large bone defects MP Magadum, CM Basavaraj Yadav, MS
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2006;14(3):273-9 Acute compression and lengthening by the Ilizarov technique for infected nonunion of the tibia with large bone defects MP Magadum, CM Basavaraj Yadav, MS
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized
 Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized autologous bone graft in leg reconstruction for patients with osteosarcoma Names of authors Masataka Noguchi, Hiroo Mizobuchi,
Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized autologous bone graft in leg reconstruction for patients with osteosarcoma Names of authors Masataka Noguchi, Hiroo Mizobuchi,
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques
 TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
Internal bone transport using a cannulated screw as a mounting device in the treatment of a post-infective ulnar defect
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2016) 11:63 67 DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0246-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Internal bone transport using a cannulated screw as a mounting device in the treatment of a post-infective ulnar defect
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2016) 11:63 67 DOI 10.1007/s11751-016-0246-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Internal bone transport using a cannulated screw as a mounting device in the treatment of a post-infective ulnar defect
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate
 The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate PROCEDURE GUIDE www.flowerortho.com The Flower Foot & Ankle Application NC FUSION PLATE 2-HOLE COMPRESSION PLATE TMT FUSION PLATE LAPIDUS FUSION PLATE COMPRESSION
The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate PROCEDURE GUIDE www.flowerortho.com The Flower Foot & Ankle Application NC FUSION PLATE 2-HOLE COMPRESSION PLATE TMT FUSION PLATE LAPIDUS FUSION PLATE COMPRESSION
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
The pilon tibiale fracture
 The pilon tibiale fracture Thomas Beck Spitalzentrum Oberwallis OTC Trauma course september 2017 xxx I have no financial relationships with commercial entities that produce healthcare related products.
The pilon tibiale fracture Thomas Beck Spitalzentrum Oberwallis OTC Trauma course september 2017 xxx I have no financial relationships with commercial entities that produce healthcare related products.
Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using Circular External Fixation with Six-Axis Deformity Correction of the Distal Tibia
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2011.0986 Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using Circular External Fixation with Six-Axis Deformity Correction of the Distal Tibia Daniel M. Horn, MD 1 ; Austin T. Fragomen,
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2011.0986 Supramalleolar Osteotomy Using Circular External Fixation with Six-Axis Deformity Correction of the Distal Tibia Daniel M. Horn, MD 1 ; Austin T. Fragomen,
