Metacarpal Lengthening in Adults With Brachymetacarpia
|
|
|
- Elfreda Arnold
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 736859HANXXX / HANDLam et al research-article2017 Surgery Article Metacarpal Lengthening in Adults With Brachymetacarpia HAND 1 7 The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav DOI: hand.sagepub.com Aaron Lam 1, Austin T. Fragomen 2, and S. Robert Rozbruch 2 Abstract Background: Metacarpal lengthening by distraction osteogenesis has been well documented in pediatric patients but limited in older patients. Fewer studies have assessed the success of the procedure through outcome measure scores. The purpose of this study is to assess the outcomes of distraction osteogenesis in skeletally mature adults with brachymetacarpia and patients perspectives on their satisfaction through outcome measure scores. Methods: Retrospective chart review of a consecutive series of metacarpal lengthenings for the treatment of brachymetacarpia was performed. Key parameters collected include starting metacarpal length, amount lengthened, range of motion of metacarpophalangeal joint, type of fixator used, distraction time, and total time in fixator. Relevant comorbidities and complications encountered were recorded as well. The Body Image Quality of Life Inventory (BIQLI) and Limb Deformity Modified Scoliosis Research Society (LD-SRS) score were given to evaluate patients perspectives on their satisfaction of surgery. Results: Seven metacarpal lengthenings were performed in 4 adult females (average age: 22.8 years) between 2005 and The average amount lengthened was 1.5 cm (range, cm), corresponding to a mean percent lengthening of 44.4% (range, 33.3%- 57.1%). The mean distraction rate was mm/day (range, mm/day). The mean distraction time was 38 days (range, days). External fixation index was 71.8 days/cm (range, days/cm). No functional loss was observed. Conclusions: Progressive distraction osteogenesis can obtain functionally successful results and improvement in aesthetics and body image without severe complications in skeletally mature adults with brachymetacarpia. Keywords: brachymetacarpia, distraction osteogenesis, adults, outcome measure scores, metacarpal lengthening Introduction Brachymetacarpia is a rare congenital hand deformity resulting in abnormal shortening of the metacarpal(s). While the incidence is unknown, brachymetacarpia occurs more often in females than in males. 13 The fourth metacarpal is the most frequently affected digit. 10 The underdevelopment of the metacarpals is due primarily to the premature closure of the epiphyseal growth plate. This may be of congenital etiology or acquired from infection or trauma to the epiphysis. Unlike other hand deformities, brachymetacarpia does not seriously compromise hand function. However, it can result in restriction of flexion at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint. 10 Severe shortening of the metacarpal(s) can alter the normal anatomy of the transverse metacarpal arch leading to weakness in grasping or difficulty in making a hard fist. 1 Therefore, surgical treatment is mainly desired because of aesthetic and body image reasons. Patients are displeased with the altered curved line formed by the tips of the fingers and altered contour of the knuckles. 12 In recent years, progressive distraction osteogenesis has been the preferred surgical intervention for brachymetacarpia. Progressive distraction osteogenesis is consider safer because the lengthening process is gradual, resulting in better outcomes and lower complication rates. 2 Although several studies have reported its high success rate in treating patients with brachymetacarpia, all the studies described pediatric patients (average age: 16.0 years). 2,3,7,8 Literature regarding metacarpal lengthening in older patients is limited. 11 In addition, few assessed the success of the procedure through outcome measure scores. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the results of distraction osteogenesis in a uniform series of older patients (average age: 22.8 years), 1 Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, USA 2 Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, USA Corresponding Author: Aaron Lam, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, 1300 Morris Park Avenue, Bronx, NY 10461, USA. alam1@mail.einstein.yu.edu
2 2 HAND 00(0) including patients perspectives on their satisfaction through outcome measure scores. Materials and Methods After obtaining institutional review board approval and informed consent from each patient, records of 4 patients who underwent 7 metacarpal lengthening for the treatment of brachymetacarpia were retrospectively reviewed by the lead author between 2005 and Patients medical charts and radiographs were reviewed. Information pertaining to the patients demographics, comorbidities, complications, and number of affected metacarpal(s) were recorded. Key parameters collected include range of motion (ROM) of the MCP joint, type of fixator used, distraction time and the total time in the fixator. Starting and ending metacarpal lengths were measured from patients radiographs. Patients completed the Body Image Quality of Life Inventory (BIQLI) 4 and Limb Deformity Modified Scoliosis Research Society (LD-SRS) score 5 both preoperatively and at the latest follow-up. Based on the measurements from the radiographs, the amount lengthened and the percentage lengthening were calculated. The lengthening rate was determined by dividing the amount lengthened by the distraction time in days. Consolidation times were indirectly calculated based on the difference between the total time in fixator and the distraction time. External fixation index (EFI) for each patient was determined by dividing the total time in fixator by the amount lengthened. To objectively determine whether the optimal amount lengthened was achieved, the mathematical relationship between the different metacarpals determined by Aydinlioglu et al was used (second metacarpal = 1.06 third metacarpal = 1.16 fourth metacarpal = 1.26 fifth metacarpal). 1 Means were calculated for all variables. The nonparametric version Wilcoxon signed rank sum test (primary analysis approach) and paired t tests (secondary analysis approach) were used to analyze preoperative and postoperative values for the BIQLI and LD-SRS scores. Both tests were used because a sample size of 4 may not be sufficient to test the normality assumption required for paired t tests. P <.05 was considered statistically significant. Surgical Technique The upper extremity of the affected side was prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. With the help of biplanar fluoroscopy, a 1.6 mm treaded external fixation half pin was inserted into the most proximal aspect of the affected metacarpal. The pin was placed dorsal to palmar in the center of the bone and started in a slight ulnar direction to avoid the extensor tendon. Using the Orthofix Minirail frame (Orthofix, Lewisville, Texas) as a guide, the most distal pin was placed on the distal pin clamp parallel to the first pin and at the most distal aspect of the bone, just proximal to the MCP capsule. With these 2 pins placed, the orientation of the fixator was established being parallel to the metacarpal bone. An additional half pin was placed in the proximal clamp and an additional half pin was placed in the distal clamp. The external fixator was then removed from the external fixation pins and a 1.5 cm skin incision was made centered on the point just between the proximal and distal pin processes. Soft tissue dissection was carried down to the bone. The extensor tendon was retracted and the metacarpal was prepared for osteotomy using a multiple drill hole technique. A inch Kirschner wire was used to make the multiple transverse drill holes while cooled with saline. A 3-mm thin osteotome was used to complete the osteotomy. The osteotomy was completed but was left nondisplaced. The wound was irrigated, and the skin was closed with 3-0 nylon suture. The Orthofix Minirail frame was reapplied to the pins to stabilize the osteotomy and maintain it in a nondisplaced position. The MCP joint was checked to ensure that there was full ROM, from full extension to 90 of flexion, and there was no obstruction from the external fixation pins. The surgical wounds and pin sites were covered with Xeroform gauze and dry sterile dressings. The MCP joint was held in about a 60 flexed position with a Kling wrap. The lengthening process began postoperative day 5 to allow for some early healing of the osteoplasty. Postoperative physical therapy focused on stretching, active and passive ROM of the MCP joint as it is easier to lose flexion than extension. When not performing ROM exercises, the MCP joint was maintained in about 70 of flexion with a resting splint. A representative case of Patient 1 with bilateral fourth metacarpal shortening before and after is shown in Figures 1 and 2. Results Four patients undergoing 7 cases of metacarpal lengthening for brachymetacarpia were identified (Table 1). All of the patients were healthy, skeletally mature, adult females with a mean age of 22.8 years (range, years). Average follow-up was 35 months (range, 4-84 months). All lengthening procedures were performed using the Orthofix Minirail frame. On average, the lengthening rate was mm/day (range, mm/day). The mean distraction time was 38 days (range, days). Average EFI was 71.8 days/cm (Tables 2 and 3). On average, the metacarpals were lengthened by 1.5 cm (range, cm). Based on the mathematical relationship reported by Aydinlioglu et al, the average difference from the ideal length was 1.6 mm (range, cm) (Table 4). This was within our acceptable range of ±0.2 cm for achieving correct length of the affected metacarpals. The second
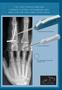
3 Lam et al 3 Figure 1. (a) Front view of the left hand showing shortening of the fourth finger. (b) When in a fist position, the absence of the knuckle (arrow) and the metacarpal shortening is apparent. (c) AP x-ray of left hand showing fourth metacarpal shortening of about 13 mm (magnification marker is 25.4 mm or 1 inch). Figure 2. (a) Two months after removal of the second hand frame. (b) Patient demonstrates excellent function and range of motion of hand. (c) Anteroposterior radiograph of left hand showing bone union, restoration of the fourth metacarpal lengths, and satisfactory alignment. Table 1. Patient Demographics. Patient (n = 4) Age (years) Comorbidities Affected metacarpal (n = 7) Starting length (cm) 1 23 None R. 4th 3.2 L. 4th None R. 5th 3.4 L. 3rd 3.8 L. 5th None L. 4th None L. 4th 3.6 Average metacarpal was used as the reference point. This was because during the surgical planning, the senior authors estimated the amount needed to be lengthened based on what fitted the normal parabola of the hand formed by the tips of the fingers. In all cases, the second metacarpal was used as the reference point. The starting length, percent lengthened, and the difference between ideal length could not be calculated for Patient 3 because the radiographs were from an outside center and they were not calibrated. At the start, 3 of the 4 patients had trouble with extension, mean of 21 (range, 0-40 ). After the lengthening procedure, all patients were able to achieve full extension of their affected
4 4 HAND 00(0) Table 2. Surgical Outcomes. Patient (n = 4) Affected metacarpal (n = 7) Amount lengthened (cm) (% lengthened) MCP ROM extension/flexion (degrees) Pre-op Post-op Complications Follow-up (months) 1 R. 4th 1.5 (46.9) 0/90 0/80 Pin site infection 36 L. 4th 1.5 (45.5) 0/90 0/90 Pin site infection 2 R. 5th 1.2 (35.3) 30/90 0/90 Break through pain/tightness 84 L. 3rd 2.1 (55.3) 30/90 0/90 Tightness L. 5th 1.3 (37.1) 30/90 0/80 Fracture at lengthening site 3 L. 4th 2.0 (57.1) 15/60 0/80 Flexion deformity at 15 osteotomy site Lack MCP flexion Lack prominent MCP on 4th finger 4 L. 4th 1.2 (33.3) 40/100 0/90 Pin site infection 2 4 Average 1.5 (44.4) 21/87 0/86 35 Note. MCP = metacarpophalangeal; ROM = range of motion. Table 3. Fixator Parameters. Patient Affected metacarpal Type of fixator Lengthening rate (mm/day) Distraction time (days) Consolidation time (days) Total time in fixator (days) EFI (days/cm) 1 R. 4th Orthofix Minirail L. 4th Orthofix Minirail R. 5th Orthofix Minirail L. 3rd Orthofix Minirail L. 5th Orthofix Minirail L. 4th Orthofix Minirail L. 4th Orthofix Minirail Average Note. EFI = external fixation index. Table 4. Comparison Between Final Length Achieved and Ideal Metacarpal Length. Patient Affected metacarpal Before (cm) After (cm) Ideal (cm) Difference (cm) 1 R. 4th L. 4th R. 5th L. 3rd L. 5th L. 4th Average 0.16 metacarpals. Similarly, flexion improved or was maintained at the normal degree of motion after the surgery for all patients except Patient 3. Overall, 5 of the 7 metacarpals healed without complications. Patient 2 had a fracture at the osteotomy site of the left fifth metacarpal during physical therapy after removal of the fixator. There was limitation of flexion of the MCP joint. This was resolved by open reduction and internal fixation with a dorsal plate and a dorsal capsulotomy of the MCP joint. After the additional surgery, patient went on to heal without further complications. In addition, Patient 3 experienced flexion deformity at the osteotomy site and was not able to achieve full flexion as compared with the other hand. While the metacarpal was lengthened to a
5 Lam et al 5 clinically acceptable length, Patient 3 still had lack of a prominent knuckle on the fourth finger. At the latest follow-up, Patient 3 still experienced the same problem but stated that it did not affect the daily activities and did not want additional treatment. The BIQLI questionnaire and LD-SRS scores were completed by 2 of the 4 patients. Two patients were lost to follow-up. Due to the small sample size, the nonparametric version Wilcoxon signed rank sum test and paired t tests could not be used to analyze the data. Of the 2 patients that completed the surveys, the patients reported a mean BIQLI score of 1.08 prior to the surgery. After the surgery, the mean BIQLI score improved to Similarly, before the surgery, the patients reported a mean LD-SRS score of 3.8. After the surgery, the mean LD-SRS score improved to 4.2. Within the LD-SRS score, prior to the surgery, the patients reported a mean self-image/appearance score of 2.9. After the surgery, the mean self-image/appearance score improved to 4.1. The function/activity and pain scores before and after the surgery did not change, 4.2 and 4.4, respectively. Discussion Congenital shortening of the metacarpals is a rare deformity that affects women more than men. In contrast to other hand deformities, hand function is not seriously compromised. Surgery is indicated primarily for aesthetic and body image concerns. Various methods for lengthening the shortened metacarpals have been reported, including single-stage lengthening and fast distraction with bone graft. Singlestage lengthening has been reported to be limited to lengthening of less than 10 mm because of potential vascular compromise and complications include delay in union, malunion, and collapse of bone graft. 6,9 Fast distraction with bone graft allows for lengthening of more than 10 mm but requires multiple surgical stages and can result in tendon imbalance and potential flexion deformities. 6,7 Subsequently, an alternative surgical intervention is progressive distraction osteogenesis. Progressive distraction osteogenesis has been preferred in recent years because the lengthening process is gradual, requires no bone graft, and results in less pain and better aesthetic outcomes. Although studies have documented positive results with progressive distraction osteogenesis, the literature review within the last 15 years yielded case series focusing primarily on pediatric patients (Table 5). Isolated case reports were found but were excluded in the literature review. Kato et al 7 and Bulut et al 3 were case series of patients with average age of 13.3 and 14.9 years, respectively. Both reported similar outcomes from the lengthening procedure, average lengthening and average percentage lengthening of 1.52 cm (43.8%) and 1.51 cm (44.2%), respectively. In both studies, several complications were reported, including problems with the fixator, finger contracture, and hypertrophic scarring. Bulut et al especially noted that the length of metacarpals and muscles that will be affected from lengthening should be considered when determining the daily rate of distraction. In contrast, Kawoosa et al 8 documented no major complications except for mild pain and minor pin tract infection in their case series of 5 patients. In that case series, the average lengthening was 2.3 cm, which was the longest average lengthening of the 4 studies. Conversely, Bozan et al 2 had the largest sample size of the 4 case series with 8 patients and 18 affected metacarpals. Similar to the other case series, they reported an average lengthening of 1.65 cm. Bozan et al was the only study that included both pediatric and adult patients. 2 When looking at factors that influenced the healing index, Bozan et al reported that there was a linear relationship between age and corresponding healing index. 2 The healing index was defined as the time in days needed for consolidation per centimeter of distracted osteotomy site. The older the patients, the longer the healing index. In addition, both Bozan et al and Kato et al suggested that adolescence is the most appropriate time to perform distraction lengthening. 2,7 Kato et al specifically recommended lengthening when patients are between ages 10 and 15 years. 7 At that age, patients are motivated and able to safely manage the external fixator by themselves. More importantly, the final lengthening of the shortened metacarpal can be better estimated as the epiphyseal plates of the other metacarpals are almost closed. In this present case series, a uniform series of skeletally mature adults, average age 22.8 years, were evaluated. Similar to the other 4 case series where all but 1 patient were females, all of the patients in this study were also females. The average amount lengthened, average percentage of lengthening, and average follow-up were also comparable to other case series. In fact, when comparing the average healing index (HI) using the definition given by Bozan et al, the average healing index in our patients was faster than the average healing index in older patients aged 19 to 30 years in the study by Bozan et al. 2 The average healing index was 46.4 days/cm versus 58.7 days/cm. Furthermore, except for Bozan et al, where 7 of the 18 metacarpals lengthened used semicircular fixators, all other patients including this study used unilateral fixators. Unilateral fixators are preferred as they are not bulky and allow for the free use of the digit. Like the other case series, several complications were encountered during the lengthening process in this study. Patient 2 experienced a fracture at the lengthening site at the left fifth metacarpal. This was because during the lengthening process, it is easier to lose flexion than extension. During physical therapy, the patient tried to work on flexion aggressively but resulted in a fracture. To avoid subsequent problems with loss of flexion, the patients hands were kept in flexion using a splint. From there, physical therapy was
6 Table 5. Literature Review. Average follow-up (months) % lengthened EFI (* = HI) Complications Length of distraction (mm) Total time in fixator (weeks) Average age Type of fixator No. of metacarpals No. of patients Authors Year days/cm One needed bone graft Readjusting external fixator Hypertrophic scar Kato et al Hoffmann Mini Lengthener & Orthofix UMEX distractor mo/cm* Mild Pain Minor pin tract infection days days/cm Pin tract infection 23.6 Kawoosa et al Bozan et al Mini-type Semicircular Fixator & Unilateral External Fixator days day.cm Finger contracture and pain Instability and malalignment due to fixator Pin tract infection Bulut et al Unilateral External Fixator Note. EFI = external fixation index; HI = healing index; UMEX = universal mini external fixator. used to work on extension. Patient 3 experienced flexion deformity at the osteotomy site. This was attributed to early removal of frame. In addition, although the post distraction x-ray of Patient 1 in Figure 2c showed some anatomic axis angulation, the overall mechanical axis of the metacarpal was normal. No rotational deformity was present. As such, it did not adversely affect the ROM, function, or aesthetics of the patient. One unique aspect of this case series was the attempt to assess the patient s perspective in the satisfaction of the lengthening procedure using 2 different surveys, BIQLI questionnaire which measures body image and LD-SRS score which is a newly validated limb deformity score. Except for Bulut et al, 3 none of the other case series evaluated patient s satisfaction outcome. Bulut et al used the visual analog scale (VAS) to determine patient satisfaction of aesthetic outcome. Compared with preoperative and postoperative values, the VAS demonstrated a significant improvement in patient satisfaction. In this study, only 2 of the 4 patients returned the questionnaires. Therefore, the small sample size led to an inability to demonstrate statistical significance. However, of the 2 patients who responded to the surveys, both reported an increase in the scores. In the LD-SRS score, there was a marked increase in patient s self-image/appearance, from 2.9 to 4.1. This is important as positive self-image is an integral component to the overall health of a patient. Interestingly, both the function/ activity and pain scores were the same preoperatively and postoperatively, which supports the observation that brachymetacarpia does not impact hand function significantly, if at all, or cause significant pain. In this study, patients were asked to take the surveys twice, once as if before the surgery and once as if after the surgery. Although there is a possibility of recall bias, we believe the surveys were meaningful as they objectively gave the patients perspective of the surgery. If they were to do everything over again, both patients confirmed that they would choose to do the surgery. In the future, similar surveys should be used to extensively evaluate patient satisfaction with a much larger sample size. Although brachymetacarpia is a congenital deformity, some patients might not elect to treat or have the means to treat the deformity until later in their lives. Most literature recommends lengthening of the metacarpals during adolescence. As this case series illustrates, distraction osteogenesis for the treatment of shortened metacarpal is not limited to younger patients. If proper precaution is taken to prevent MCP stiffness or fracture, distraction osteogenesis can obtain functionally successful results with improvement in body image and aesthetics without severe complications in skeletally mature adults with brachymetacarpia. Ethical Approval This study was approved by our institutional review board. 6
7 Lam et al 7 Statement of Human and Animal Rights All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in Statement of Informed Consent Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Declaration of Conflicting Interests The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: AL declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. ATF reports personal fees from Smith & Nephew, personal fees from NuVasive, personal fees from Synthes, outside the submitted work. SRR reports personal fees from Smith & Nephew, personal fees from NuVasive, personal fees from Stryker, outside the submitted work. Funding The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. References 1. Aydinlioglu A, Akpinar F, Tosun N. Mathematical relations between the lengths of the metacarpal bones and phalanges: surgical significance. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1998;185(3): Bozan ME, Altinel L, Kuru I, et al. Factors that affect the healing index of metacarpal lengthening: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2006;14(2): Bulut M, Ucar BY, Azboy I, et al. Lengthening by distraction osteogenesis in congenital shortening of metacarpals. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2013;47(2): Cash TF, Fleming EC. The impact of body image experiences: development of the Body Image Quality of Life Inventory. Int J Eat Disord. 2002;31(4): Fabricant PD, Borst EW, Green SA, et al. Validation of a modified Scoliosis Research Society instrument for patients with limb deformity: the Limb Deformity-Scoliosis Research Society (LD-SRS) score. J Limb Lengthen Reconstr. 2016;2(2): Fultz CW, Lester DK, Hunter JM. Single stage lengthening by intercalary bone graft in patients with congenital hand deformities. J Hand Surg Br. 1986;11(1): Kato H, Minami A, Suenaga N, et al. Callotasis lengthening in patients with brachymetacarpia. J Pediatr Orthop. 2002;22(4): Kawoosa AA, Mir NA, Badoo AR, et al. Metacarpal lengthening by distraction osteogenesis. JK-Practitioner. 2004;11(1): Ogino T, Kato H, Ishii S, et al. Digital lengthening in congenital hand deformities. J Hand Surg Br. 1994;19(1): Rayan GM, Upton J III. Congenital Hand Anomalies and Associated Syndromes. Berlin, Germany: Springer; Rozbruch SR. Case 98: bilateral metacarpal lengthening for congenital brachymetacarpia. In: Rozbruch SR, Hamdy RC, eds. Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery Case Atlas: Adult Deformity, Tumor, Upper Extremity. Basel, Switzerland: Springer; 2015: Saito H, Koizumi M, Takahashi Y, et al. One-stage elongation of the third or fourth brachymetacarpia through the palmar approach. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;26(3): Volpi AD, Fragomen AT. Percutaneous distraction lengthening in brachymetacarpia. Orthopedics. 2011;34(8): e424-e427.
Ascension. Silicone MCP surgical technique. surgical technique Ascension Silicone MCP
 Ascension Silicone MCP surgical technique WW 2 Introduction This manual describes the sequence of techniques and instruments used to implant the Ascension Silicone MCP (FIGURE 1A). Successful use of this
Ascension Silicone MCP surgical technique WW 2 Introduction This manual describes the sequence of techniques and instruments used to implant the Ascension Silicone MCP (FIGURE 1A). Successful use of this
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia
 220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Adult Posttraumatic Reconstruction Using a Magnetic Internal Lengthening Nail S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Summary: A new generation of internal lengthening nail is now available that has
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia: Case Report and Review of the R Rose Citation R Rose. Metatarsal
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD
 Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Fibula Lengthening Using a Modified Ilizarov Method S. Robert Rozbruch, MD; Matthew DiPaola, BA; Arkady Blyakher,MD Limb Lengthening Service Hospital for Special Surgery Abstract A unique combination of
Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 1014 1019 CASE REPORT Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia Naoto Yamada*, Yoshihiro Yasuda, Nobuko Hashimoto,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 1014 1019 CASE REPORT Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia Naoto Yamada*, Yoshihiro Yasuda, Nobuko Hashimoto,
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
MiniRail System. Part B: Foot Applications. By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito
 Q U I C K R E F E R E N C E G U I D E 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ORDERING INFORMATION MiniRail System Kit, M190C Contents: M 101 Standard
Q U I C K R E F E R E N C E G U I D E 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ORDERING INFORMATION MiniRail System Kit, M190C Contents: M 101 Standard
Ascension. MCP surgical technique. surgical technique Ascension MCP PyroCarbon Total Joint
 Ascension MCP surgical technique PyroCarbon Total Joint WW 1.0 Table of Contents 2.0 Introduction............................ 2 3.0 Ascension MCP Implants................ 2 4.0 Instrumentation for MCP
Ascension MCP surgical technique PyroCarbon Total Joint WW 1.0 Table of Contents 2.0 Introduction............................ 2 3.0 Ascension MCP Implants................ 2 4.0 Instrumentation for MCP
COMPLICATIONS OF BRACHYMETATARSIA REPAIR WITH CALLUS DISTRACTION
 C H A P T E R 4 1 COMPLICATIONS OF BRACHYMETATARSIA REPAIR WITH CALLUS DISTRACTION Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Brachymetatarsia represents one of the best and most useful indications for
C H A P T E R 4 1 COMPLICATIONS OF BRACHYMETATARSIA REPAIR WITH CALLUS DISTRACTION Michelle L. Butterworth, DPM INTRODUCTION Brachymetatarsia represents one of the best and most useful indications for
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures:
 Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD. Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery
 S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Chief, Limb Lengthening & Complex Reconstruction Service Professor of Clinical Orthopedic Surgery Small Bone Innovations: consultant and royalties Smith and Nephew: consultant External
Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia. Case Report and Review of the Literature
 The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine TM ISSN: 1539-4646 Home Current Issue Archives Instructions for Authors Disclaimer Printable Version Metatarsal Lengthening By Callus Distraction For Brachymetatarsia:
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna with Distraction Osteogenesis: Three Cases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Integra. Silicone PIP Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Silicone PIP Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents Indications For Use...2 Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions...2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Assessment... 3 Step 1: Initial
Integra Silicone PIP Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents Indications For Use...2 Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions...2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Assessment... 3 Step 1: Initial
CASE REPORT. Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology
 CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
CASE REPORT Antegrade tibia lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening technology Austin T. Fragomen, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY 1 1 PR O D U CTS CONDITION Nonunion of an attempted
Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):211-5 Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand G Rajesh, WY Ip, SP Chow, BKK Fung Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):211-5 Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand G Rajesh, WY Ip, SP Chow, BKK Fung Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
Comparison between Intramedullary Nailing and Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone
 Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
The Birmingham Hook Plate Treatment Of Irreduceable Displaced Mallet Avulsion Fractures: A Technical Note
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Hand Surgery Volume 1 Number 1 The Birmingham Hook Plate Treatment Of Irreduceable Displaced Mallet Avulsion Fractures: A Technical S Tan, D Power Citation S Tan, D Power..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Hand Surgery Volume 1 Number 1 The Birmingham Hook Plate Treatment Of Irreduceable Displaced Mallet Avulsion Fractures: A Technical S Tan, D Power Citation S Tan, D Power..
Integra. Silicone MCP Joint Prosthesis SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Silicone MCP Joint Prosthesis SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents Introduction Indications For Use...2 Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions... 2 System Overview... 3 Surgical Technique
Integra Silicone MCP Joint Prosthesis SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents Introduction Indications For Use...2 Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions... 2 System Overview... 3 Surgical Technique
Acu-Loc Wrist Spanning Plate System. Surgical Technique
 Acu-Loc Wrist Spanning Plate System Surgical Technique Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches
Acu-Loc Wrist Spanning Plate System Surgical Technique Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches
THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES
 THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES Intramedullary Nail & Slotted Awl Proximal Locking Device New Radio Opaque Soft Tissue Protection Cap Pre Operative Post
THE FIRST PERCUTANEOUS LOCKED FLEXIBLE INTRAMEDULARY NAIL SYSTEM FOR HAND FRACTURES Intramedullary Nail & Slotted Awl Proximal Locking Device New Radio Opaque Soft Tissue Protection Cap Pre Operative Post
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. MiniRail System. Part B: Foot Applications. By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ALWAYS INNOVATING
 14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ALWAYS INNOVATING ORDERING INFORMATION Sterilization box, empty M190 Can accommodate: M101 Standard MiniRail
14 MiniRail System Part B: Foot Applications By Dr. B. Magnan, Dr. E. Rodriguez and Dr. G. Vito ALWAYS INNOVATING ORDERING INFORMATION Sterilization box, empty M190 Can accommodate: M101 Standard MiniRail
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are
 The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are inserted in a multiplanar and multi-directional fashion
The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are inserted in a multiplanar and multi-directional fashion
Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL
 C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
Silicone PIP, MCP & MCP-X (PreFlex)
 Silicone PIP, MCP & MCP-X (PreFlex) Finger Joint Arthroplasty Operative Technique Silicone PIP Silicone MCP Silicone PreFlex (MCP-X) Stryker Disclaimer This publication sets forth detailed recommended
Silicone PIP, MCP & MCP-X (PreFlex) Finger Joint Arthroplasty Operative Technique Silicone PIP Silicone MCP Silicone PreFlex (MCP-X) Stryker Disclaimer This publication sets forth detailed recommended
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results in 24 Cases Treated by In Situ Osteotomy
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org 468 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 468-472 Open Access Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org 468 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 468-472 Open Access Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results
Lengthening of fourth brachymetatarsia by three different surgical techniques
 Lengthening of fourth brachymetatarsia by three different surgical techniques W.-C. Lee, J. H. Yoo, J.-S. Moon From Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea W.-C. Lee, Md, PhD, Professor J.-S. Moon, MD, Orthopaedic
Lengthening of fourth brachymetatarsia by three different surgical techniques W.-C. Lee, J. H. Yoo, J.-S. Moon From Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea W.-C. Lee, Md, PhD, Professor J.-S. Moon, MD, Orthopaedic
Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL
 Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
Technique Guide. Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges.
 Technique Guide Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges. Table of Contents Introduction Rotation Correction Plates 1.5
Technique Guide Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges. Table of Contents Introduction Rotation Correction Plates 1.5
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
CableFIX Xpress Carpometacarpal Fixation System. Operative technique
 CableFIX Xpress Carpometacarpal Fixation System Operative technique CableFIX Xpress Carpometacarpal Fixation System CableFIX Xpress Carpometacarpal Fixation System Contents 1. Indications and contraindications...
CableFIX Xpress Carpometacarpal Fixation System Operative technique CableFIX Xpress Carpometacarpal Fixation System CableFIX Xpress Carpometacarpal Fixation System Contents 1. Indications and contraindications...
Integra. Spider and Mini Spider Limited Wrist Fusion System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Spider and Mini Spider Limited Wrist Fusion System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Description... 02 Indications... 02 Contraindications... 02 Surgical Technique... 03 Spider Introduction-Four
Integra Spider and Mini Spider Limited Wrist Fusion System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of contents Description... 02 Indications... 02 Contraindications... 02 Surgical Technique... 03 Spider Introduction-Four
Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger Flaps and Vigorous Postoperative Exercises
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity
 Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery
 Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE MCP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Summary provided by designing surgeon Arnold-Peter C.
NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE MCP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Summary provided by designing surgeon Arnold-Peter C.
Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy
 METATARSAL BONES LENGTHENING WITH LAKI MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy alexander@kirienko.com Alexander KIRIENKO, MD
METATARSAL BONES LENGTHENING WITH LAKI MINI EXTERNAL FIXATOR Kirienko Alexander Peccati Andrea, Portinaro Nicola Istituto Clinico Humanitas, Milano, Italy alexander@kirienko.com Alexander KIRIENKO, MD
Visualize, stabilize, mobilize. Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique
 Visualize, stabilize, mobilize Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique Wristore Distal Radius Fracture Fixator 1 Pin Placement Identify anatomy and make a direct (open)
Visualize, stabilize, mobilize Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique Wristore Distal Radius Fracture Fixator 1 Pin Placement Identify anatomy and make a direct (open)
DFS Hip Distractor. Surgical Technique
 DFS Hip Distractor Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Hip Distractor Associated... Page 2 Components And Instrumentation Radiographs... Page 4 Fixator Orientation... Page 5 Initial Screw
DFS Hip Distractor Surgical Technique Contents Introduction... Page 1 Hip Distractor Associated... Page 2 Components And Instrumentation Radiographs... Page 4 Fixator Orientation... Page 5 Initial Screw
Distal Radius Plate 2.4/2.7 dorsal and volar
 Distal Radius Plate 2.4/2.7 dorsal and volar Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Distal Radius Plate
Distal Radius Plate 2.4/2.7 dorsal and volar Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Distal Radius Plate
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
Finger Mobility Deficits Fracture of metacarpal Fracture of phalanx of phalanges
 1 Finger Mobility Deficits ICD-9-CM codes: 715.4 Osteoarthrosis of the hand 815.0 Fracture of metacarpal 816.0 Fracture of phalanx of phalanges ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4301 Carrying
1 Finger Mobility Deficits ICD-9-CM codes: 715.4 Osteoarthrosis of the hand 815.0 Fracture of metacarpal 816.0 Fracture of phalanx of phalanges ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4301 Carrying
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Epidemiology in USA: Metacarpal fractures: Page 1
 Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
TABLE E-1 Complications and Clinical Remarks for Pediatric Humeral Lengthening Procedures Study Complications (No.) Clinical Remarks*
 Page 1 TABLE E-1 Complications and Clinical Remarks for Pediatric Humeral Lengthening Procedures Study Complications (No.) Clinical Remarks* Janovec 12 Infection (4), radial nerve palsy (1), radial and
Page 1 TABLE E-1 Complications and Clinical Remarks for Pediatric Humeral Lengthening Procedures Study Complications (No.) Clinical Remarks* Janovec 12 Infection (4), radial nerve palsy (1), radial and
MICRONAIL. Intramedullary Distal Radius System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 MICRONAIL II Intramedullary Distal Radius System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Introduction 3 4 Chapter 1 5 Chapter 2 6 Appendix A 18 Appendix B 19 Surgeon Design Team Introduction Product Information Surgical
MICRONAIL II Intramedullary Distal Radius System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Introduction 3 4 Chapter 1 5 Chapter 2 6 Appendix A 18 Appendix B 19 Surgeon Design Team Introduction Product Information Surgical
Research Article. Abstract
 Research Article Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/jaaos by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3XGJiJSDa6kLdjliRzOOsR+bI3gZWJ99prwiH9JOuTYY=
Research Article Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/jaaos by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3XGJiJSDa6kLdjliRzOOsR+bI3gZWJ99prwiH9JOuTYY=
Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement: Case Series
 737481FAIXXX10.1177/1071100717737481Foot & Ankle InternationalDa Cunha et al research-article2017 Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement:
737481FAIXXX10.1177/1071100717737481Foot & Ankle InternationalDa Cunha et al research-article2017 Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis and Fusion for Failed First Metatarsophalangeal Joint Replacement:
Technique Guide. 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot.
 Technique Guide 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot. Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot. Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Hand Fracture System with Small Bone External Fixation System. Product Overview
 Hand Fracture System with Small Bone External Fixation System Product Overview Acumed Hand Fracture System The Acumed Hand Fracture System is designed to provide both standard and fracture-specific fixation
Hand Fracture System with Small Bone External Fixation System Product Overview Acumed Hand Fracture System The Acumed Hand Fracture System is designed to provide both standard and fracture-specific fixation
Technique Guide Hammertoe Correction System
 Technique Guide Hammertoe Correction System TM The ToeMATE Hammertoe Correction System is an easy to implant bone screw system intended for the correction of hammertoe deformity. It is provided in a complete
Technique Guide Hammertoe Correction System TM The ToeMATE Hammertoe Correction System is an easy to implant bone screw system intended for the correction of hammertoe deformity. It is provided in a complete
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate
 The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate PROCEDURE GUIDE www.flowerortho.com The Flower Foot & Ankle Application NC FUSION PLATE 2-HOLE COMPRESSION PLATE TMT FUSION PLATE LAPIDUS FUSION PLATE COMPRESSION
The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate PROCEDURE GUIDE www.flowerortho.com The Flower Foot & Ankle Application NC FUSION PLATE 2-HOLE COMPRESSION PLATE TMT FUSION PLATE LAPIDUS FUSION PLATE COMPRESSION
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria
 TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
TRANSPOSITION OF THE LATERAL SLIPS OF THE APONEUROSIS IN TREATMENT OF LONG-STANDING " BOUTONNIERE DEFORMITY " OF THE FINGERS By IVAN MATEV Institute of Reconstructive Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria RUPTURE of
PALMAR SKIN CONTRACTURE of congenital clasped
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE New Flap for Widening of the Web Space and Correction of Palmar Contracture in Complex Clasped Thumb Mostafa Mahmoud, MD, Hisham Abdel-Ghani, MD, John C. Elfar, MD In our experience,
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE New Flap for Widening of the Web Space and Correction of Palmar Contracture in Complex Clasped Thumb Mostafa Mahmoud, MD, Hisham Abdel-Ghani, MD, John C. Elfar, MD In our experience,
S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2013) 37:1995 2000 DOI 10.1007/s00264-013-1962-x ORIGINAL PAPER S-osteotomy with lengthening and then nailing compared with traditional Ilizarov method Xia Lan & Lihai
A Patient s Guide to Adult Metacarpal Fractures of the Hand
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Metacarpal Fractures of the Hand 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
A Patient s Guide to Adult Metacarpal Fractures of the Hand 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is
A Dynalllic Splint for U se After Total Wrist Arthroplasty
 A Dynalllic Splint for U se After Total Wrist Arthroplasty (active-assistive therapy, post-operative splinting, rheumatoid arthritis) Barbara M. Johnson Mary Jean Gregory Flynn Robert D. Beckenbaugh Total
A Dynalllic Splint for U se After Total Wrist Arthroplasty (active-assistive therapy, post-operative splinting, rheumatoid arthritis) Barbara M. Johnson Mary Jean Gregory Flynn Robert D. Beckenbaugh Total
Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures.
 Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame When to use The
Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame When to use The
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
The Wrist Fusion Set. Stainless Steel and Titanium TECHNIQUE GUIDE. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
 The Wrist Fusion Set Stainless Steel and Titanium TECHNIQUE GUIDE Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Three Plate Options Stainless Steel or Titanium* Standard Bend Stainless Steel [242.510]
The Wrist Fusion Set Stainless Steel and Titanium TECHNIQUE GUIDE Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Three Plate Options Stainless Steel or Titanium* Standard Bend Stainless Steel [242.510]
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/577 Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis R Senthilkumar 1, E Kovarthini 2, Heber
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/577 Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis R Senthilkumar 1, E Kovarthini 2, Heber
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion
 Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
FINGER INJURIES. Chapter 24, pgs ,
 FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
PIPR Proximal Interphalangeal Replacement. Operative Technique
 PIPR Proximal Interphalangeal Replacement Operative Technique Contents PIPR Proximal Interphalangeal Replacement Developed in association with Mr I Trail and The Wrightington Hospital. Contents Section
PIPR Proximal Interphalangeal Replacement Operative Technique Contents PIPR Proximal Interphalangeal Replacement Developed in association with Mr I Trail and The Wrightington Hospital. Contents Section
Soft Tissue Rebalancing Procedures for the Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformities
 Soft Tissue Rebalancing Procedures for the Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformities NO DISCLOSURES Objectives The main objectives of any procedure in hallux abducto valgus surgery are to correct the deformity,
Soft Tissue Rebalancing Procedures for the Treatment of Hallux Valgus Deformities NO DISCLOSURES Objectives The main objectives of any procedure in hallux abducto valgus surgery are to correct the deformity,
Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions)
 Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Online Supplementary Material to: Complex angular and torsional deformities (distal femoral malunions) Preoperative planning using stereolithography and surgical correction with locking plate fixation
Modified Bilhaut-Cloquet Procedure for Wassel Type-II and III Polydactyly of the Thumb. Surgical Technique
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Modified Bilhaut-Cloquet Procedure for Wassel Type-II and III Polydactyly
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Modified Bilhaut-Cloquet Procedure for Wassel Type-II and III Polydactyly
Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Hoffmann II Micro External Fixation System
 Trauma Hoffmann II Micro External Fixation System Indications for the Hand Components 9 3 4 5 1 2 7 8 6 1 Hoffmann II Micro Multi-Pin Clamp 2 Hoffmann II Micro 90 Multi-Pin Clamp 3 Hoffmann II Micro Rod
Trauma Hoffmann II Micro External Fixation System Indications for the Hand Components 9 3 4 5 1 2 7 8 6 1 Hoffmann II Micro Multi-Pin Clamp 2 Hoffmann II Micro 90 Multi-Pin Clamp 3 Hoffmann II Micro Rod
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER cop2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION 1 FEATURES OF SHOULDER COMPONENTS 2 EQUIPMENT REQUIRED 5 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING 6 SURGICAL PROCEDURE 8 POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER cop2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION 1 FEATURES OF SHOULDER COMPONENTS 2 EQUIPMENT REQUIRED 5 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING 6 SURGICAL PROCEDURE 8 POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures
 The THAI Journal of SURGERY 2009; 30:5-10. Official Publication of the Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures Somboon
The THAI Journal of SURGERY 2009; 30:5-10. Official Publication of the Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures Somboon
Technique Guide. Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator. Part of the Synthes External Fixation Systems.
 Technique Guide Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator. Part of the Synthes External Fixation Systems. Table of Contents Introduction Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator 2 Indications 3 Surgical Technique Configure
Technique Guide Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator. Part of the Synthes External Fixation Systems. Table of Contents Introduction Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator 2 Indications 3 Surgical Technique Configure
Mini External Fixator.
 Mini External Fixator. Assembly and Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier control Warning
Mini External Fixator. Assembly and Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier control Warning
Forearm Fracture Solutions. Product Overview
 Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set. Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1)
 Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1) The Distal Radius Plates Indications For fixation of fractures and osteotomies, including
Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1) The Distal Radius Plates Indications For fixation of fractures and osteotomies, including
Clover Staple. Surgical Technique
 Clover Staple Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Clover Staple is a permanent implant that removes minimal cross-sectional fusion area, allows easy radiographical monitoring and may permit
Clover Staple Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Clover Staple is a permanent implant that removes minimal cross-sectional fusion area, allows easy radiographical monitoring and may permit
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM
 3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
