The etiology, pathogenesis and natural course of
|
|
|
- Loren Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J SPORTS MED PHYS FITNESS 2009;49:171-6 Aim. The etiology, pathogenesis and natural course of Achilles tendinopathy are not yet completely known. Various forms of therapies, either conservative or surgical, have been proposed for its treatment. In the last few years, extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) has been proposed in the treatment of these tendinopathies and has shown encouraging short-term results. The purpose of this type-c study was to evaluate the effectiveness of ESWT in the symptomatic treatment of Achilles tendinopathies over time. Methods. One hundred five patients (127 tendons) aged between 18 and 74 years (mean age 47.8) were enrolled in this study. All patients underwent clinical and instrumental diagnosis (ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging and X-rays) in order to identify presence, location and seriousness of the specific tendinopathy. The symptomatology was classified using the Visual Analogical Scale (VAS) and according to a five-stage clinical evaluation range. Shock wave treatment was applied with an electromagnetic shock wave generator. The protocol consisted in an average of four sessions (minimum three, maximum five), at a 2/7-day interval. In each session impulses were administered with an energy varying between 0.08 and 0.40 mj/mm2. All patients were evaluated before therapy and two months after the last ESWT session. Also, all patients were assessed and evaluated at medium-term (6 to 12 months), and 121 patients also at long-term (13 to 24 months). Results. Authors obtained satisfactory results in 47.2% of cases (60 out of 127 tendons) at two-months follow-up, which increased to 73.2% at medium-term follow-up (93 out of 127 tendons), and then reaching 76% in the last evaluation (92 out of 121 tendons). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) in Achilles tendinopathy. A long-term follow-up observational study Orthopedic Unit and Kirk Kilgour Sports Injury Center Sant Andrea Hospital La Sapienza University, School of Medicine, Rome, Italy Conclusion. The outcome of the described shock wave treatment appears to be satisfactory and confirms the role of this alternative treatment in the management of the tendon disorders. KEY WORDS: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy - Tendinopathy - Achilles tendon - Physical therapy modalities. The etiology, pathogenesis and natural course of Achilles tendinopathy are not yet completely known. Histologically, there are no inflammatory cells, but increased amounts of interfibrillar glycosaminoglycans and changes in the collagen fibre structure and arrangement are usually seen. In situ microdialisys has confirmed the absence of inflammation. Achilles tendinopathy is most often seen among recreational male runners aged between 35 and 45 years, and it is most often considered to be associated with overuse. However, this condition is also seen in patients with a sedentary lifestyle. 1 Various forms of treatment, either conservative or surgical, have been proposed for its treatment. In the last few years extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) has been proposed in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathies and has shown encouraging short term results. ESWT has the advantage of being painless, non-invasive, well-tolerated by patients and has no collateral effects. Therefore, it could be a valid alternative to surgical treatment. 2-4 Conflicts of interest. All authors certify they did not sign any agreement with a commercial interest related to this study. Received on October 4, Accepted for publication on March 18, Corresponding author: M. C. Vulpiani, MD, Via V. Renieri 14, Rome, Italy. mariachiara.vulpiani@tin.it M. C. VULPIANI, D. TRISCHITTA, P. TROVATO, M. VETRANO, A. FERRETTI Vol No. 2 THE JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE AND PHYSICAL FITNESS 171
2 VULPIANI EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY TABLE I. Classification of Achilles tendinopathy according to symptoms. Classification Stage 0 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Symptoms No pain Pain only during sport with no limitation of sport performance Pain during sport, limiting sport participation, and sometimes at rest (particularly on rising in the morning) Pain also during daily activities Intolerable and constant pain The purpose of this type-c study (prospective study without a control group but with adequate analysis and follow-up of sufficient scope and duration) 5 was to evaluate the effectiveness of ESWT in the symptomatic treatment of Achilles tendinopathies over time. Materials and methods Between December 1997 and January 2005, 122 patients (105 males and 17 females) affected by Achilles tendinopathy were treated with ESWT. Inclusion of patients was discussed with the local Ethical Committee. A randomized placebo-controlled study could not be permitted in relation to the fact that patients were paying for ESWT treatments. Lack of a control group for ethical reasons is often found in similar published studies The inclusion criteria included a clinical history of Achilles tendon pain for at least six months and a minimum of three months conservative treatment administered without benefit for at least four weeks before shock wave treatment. Patients who underwent physical therapy in the four weeks prior to ESWT were not included in this study (three patients), as well as those who had taken non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory medication the previous week (two patients). Exclusion criteria also included other associated pathologies such as polineuropathies (one patient), previous surgical treatments of the ankle affected by Achilles tendinopathy (six patients) and patients lost at short-term follow-up (five patients). One hundred five patients were enrolled in this study (89 males and 16 females), 22 of which with bilateral pathology, for a total of 127 tendons. The patients age ranged from 18 to 74 years with an average of 47.8±12.4 years. All patients were involved in various sports activities: 10 as professionals (9.5%), 63 as amateurs (60%) and 32 practicing sports occasionally but at least once a week (30.5%). Diagnosis was made following clinical criteria and instrumental procedures (X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasonography -US-), which helped to recognise 84 cases affected by insertional tendinopathy (66.1%) and 43 cases affected by non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy (33.9%). Moreover, X-rays showed calcium deposits in 25 cases, 23 of which in the insertion region, and 2 cases observed in the context of the Achilles tendon. Evaluation methods consisted of a classification scale graded from 0 to 4 used to evaluate pre- and posttreatment subjective symptoms. All patients were requested to estimate their pretreatment subjective symptoms and the current status of their treated Achilles tendon 11 (Table I). More recent cases were evaluated with Victorian Institute of Sport Assessment-Achilles questionnaire, which is validated for Achilles tendon problems, 12 but these results could not be included in the current study for uniformity with older results. Shock wave treatment was applied using an electromagnetic shock wave generator produced by STORZ Medical AG, Tägerwilen, Switzerland). All patients underwent an average of four sessions (minimum three, maximum five), with an average two-day rest period (from two to seven days.), with an energy of mj/mm 2 for tendon belly tendinopathies and of mj/mm 2 for insertional calcific tendinopathy (optical fiber hydrophone measurements). The treatment was given with impulses for each session using an ultrasonic guidance to focus the shock waves on insertional tendinopathy or midportion tendinopathy or calcified area. Treatments were administered without anesthesia. In 11 cases, after a first standard treatment cycle, patients who did not respond adequately underwent a second identical cycle. At the end of treatment, patients were asked not to return to sports activities for a minimum of three weeks and not to assume any medical therapy. Complete return to sports activities took place in accordance with the athlete s pain tolerance and the absence of clinical signs. All patients were evaluated before therapy and two months after the last ESWT session. Also, all patients were assessed and evaluated at medium-term (6 to 12 months), and 121 patients were also evaluated at longterm (13 to 24 months). 172 THE JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE AND PHYSICAL FITNESS June 2009
3 EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY VULPIANI TABLE II. Classification of results. Results Excellent Good Fair Poor Evaluation of post-treatment results was made on the basis of the average Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score and of the subjective clinical evaluation range. The results were classified with the criteria shown in Table II. 13 In conclusion, excellent plus good results were considered as satisfactory and fair plus poor results as not satisfactory. The statistical analysis of the results (P<0.05) used Student s t test for parametric variables and U Mann- Whitney and Wilcoxon test for non-parametric variables. SPSS version 14 software package was used for data analysis. Results Symptoms Stage 0 at the time of follow-up Stage 1 with a post-treatment improvement of at least two stages Improvement but the final result was stage 2 or higher No improvement Before 2 months 6-12 months >12 months <24 Figure 1. Mean values according to the VAS scale at different stages. The mean values according to the VAS scale were evaluated at different stages and are shown in Figure 1. A significant average improvement (P<0.01) of the initial pain symptomatology (7.49±1.6) can be observed two months after the end of treatment (4.75±2.9). The mean value of the VAS scale decreases further in patients at medium-term (2.88±3.1) and is constant at long-term follow-up (2.6±3.3). Figure 2 shows mean values using subjective clinical evaluation range (Stage 0 through 4) at different stages. A noticeable improvement is shown starting two months after the end of treatment (mean 1.78±1.2) (P<0.01) and continuing at medium-term evaluation (mean 1.07±1.2), while at long-term follow-up the improvement is unchanged (mean 0.93±1.2). Finally, we obtained satisfactory results in 47.2% of cases (60 out of 127 tendons) at two-months follow-up, increasing to 73.2% at medium-term follow-up (93 out of 127 tendons), and reaching 76% in the last evaluation (92 out of 121 tendons) (Table III). We achieved better results in tendinopathies of the main body of Achilles tendon compared with those obtained in insertional tendinophaties at two-month follow-up (satisfactory results in 60.5% of non-insertional tendinophaties vs 43.7% of insertional tendinophaties; P<0.05), at medium-term follow-up (satisfactory results in 77.7% of non insertional tendinophaties vs 42.3% of insertional tendinophaties; P<0.05), and at long-term evaluation (satisfactory results in 75% of non-insertional tendinophaties vs 37.4% of insertional tendinophaties; P<0.01). Regarding calcific tendinitis, 25 cases were treated. The bone spurs remain unchanged. Mean Mean Before 2 months 6-12 months >12 months <24 Figure 2. Mean values using clinical evaluation scale at different stages. TABLE III. Results at different follow-up. Follow-up Discussion Few prospective studies are available in literature regarding conservative therapies in Achilles tendinopathy. Such conservative rehabilitation treatments have N. of Satisfac- Unsatisfactendons tory tory 2 months % 52.8% Medium term (2-12 months) % 26.8% Long term (13-24 months) %,3 24%,3 Vol No. 2 THE JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE AND PHYSICAL FITNESS 173
4 VULPIANI EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY been proposed by several authors as initial therapeutical strategy and include a combination of rest, medication (non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroid injections), orthotic treatment, stretching 17 and various forms of physiotherapy. Promising results have been obtained with eccentric training in athletic patients, with satisfactory results at medium-term follow-up. 18, 19 Eccentric exercises seem to be ineffective in sedentary patients with Achilles tendinopathy. 20 Concerning physical therapies, a recent comparative study has matched the results of cryoultrasound therapy vs those obtained with Laser CO 2 and Tecar therapy. Cases treated with cryoultrasound therapy have shown a more significant variation in VAS score than those treated with with Laser and Tecar therapy. 21 In recent studies, instrumental and immunohistochemical investigation showed neovascularization in Achilles tendons with painful tendinosis but not in normal, pain-free tendons. Neovascularization was observed in the area with tendon changes and it is probably related to the pain symptomathology. 22 Ultrasound-guided sclerosis of neovessels with polidocanol in painful chronic Achilles tendinosis has permitted a large number of cases (80%) to remain painfree for a long period of time (two years) without significant risk of tendon rupture. 23 In a recent double-blind randomized study, the efficacy of local injections of sclerosing and anesthetic substances have been compared and the sclerosing substance has been clearly demonstrated to lead to significant pain reduction. 24 Furthermore, both eccentric calf muscle training and use of sclerosing injections showed a decrease in neovascularization in a study conducted with US and color-doppler. 17 These new therapeutic frontiers, however, leave unanswered questions regarding the role and the significance of neovascularization in a region that always seemed to be hypovascular due to low oxygen supply and, therefore, with a reduced tissue regeneration potential. Further prospective work with longer follow-up is, therefore, necessary to confirm the validity of these therapies and the hypothesis that the biological stimulus of shock waves goes beyond a mere antalgic effect. In the last decade, focused ESWT has been used in the treatment of tendinopathies. Despite its success in clinical application in the treatment of soft tissues and orthopedic pathologies, the exact mechanism of ESWT is not yet fully understood. Several authors suggest that its effect can be ascribed to the transduction of the acoustic shock wave signal into a biological signal. Studies performed through the evaluation of hystological and biomechanical parameters on animals showed that ESWT induces tissue regeneration and facilitates tendon healing after trauma. These experimental studies have pointed out significant increase in neovascularization, reduced adhesion formation and increase in hydroxyproline levels on tendon tissues treated with ESWT. In addition, in the tendons treated with ESWT, a greater force is required to damage the tendon when compared with the control group. 25, 26 Biopsies performed on canine Achilles tendons 4 and 8 weeks after treatment with ESWT showed neovascularization growth and blood supply improvement, a result that was not found in the control group. 27 In a later study, neovascularization in the bone-tendon junction was confirmed by the presence of such angiogenic markers as vessel endothelial growth factor, endothelial nitric oxide synthase and by endothelial cell proliferation indicated by proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). The results showed earlier release of angiogenic growth factors and increase in neo-vessels and tissue proliferation about four weeks after treatment, that persisted for up to 12 weeks. 28 The efficacy of ESWT is strictly related to energy level and number of impulses used during treatment. 29 Effects of ESWT appear, in fact, to be dose-related. Some authors have noted that the use of energy flux densities of 0.28 mj/mm 2 on Achilles tendons treated with ESWT showed no evidence of tendon damage and that changes were reversible in four weeks, while higher energy levels (0.60 mj/mm 2 ) showed lesions of the tendon and paratendon tissue. In addition the authors revealed an increase in tendon diameter and an inflammatory reaction, which did not completely disappear after four weeks. 28 Other authors have indicated the presence of tendon lesions with the use of energy flux range between 0.42 and 0.50 mj/mm To evaluate the effects on tendon healing of different intensity impulses of extracorporeal shock wave, some authors gave a single treatment (0.16 mj/mm 2 ) to rat tendons in which Achilles tendinitis had been induced through a collagenase injection at tendon junction. The group that received ESWT with 200 impulses showed biomechanical and biochemical character- 174 THE JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE AND PHYSICAL FITNESS June 2009
5 EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY VULPIANI istics of tendon healing, PCNA, neovascularization and elevated expression of growth factors (TGF-B1 and IGF-1) two weeks after treatment. On the other hand, ESWT treatment with 500 and impulses showed inhibitory effects on tendon repair. These studies confirm that harmful effects of ESWT on tissues are dose-related. The limitation of these studies is that results obtained on animal models cannot be utilized for human purposes, as animal soft tissues (such as rats and rabbits, etc.) could be more sensitive to ESWT. 31 In our study we used a medium-low energy flux density and different energy levels for insertional tendinopathies and tendon belly pathologies. Higher levels of energy ( mj/mm 2 ) were used in insertional tendinopathy, since the focal zone is the tendon-bone junction and related calcifications, if any, while in tendon belly pathologies a lower energy level was used ( mj/mm 2 ). While several studies are available in literature on the effects of ESWT on animal models, fewer are the clinical studies. Moreover, a comparison with studies reported in literature concerning the efficacy of ESWT in Achilles tendinopathy is difficult because treatments were administered with different generators using different levels of energy and different number of impulses. Also, clinical results were evaluated with different criteria. In a study conducted on patients with chronic Achilles tendinopathy treated with ESWT, 60% of satisfactory results were noted after three years of follow-up. 32 A recent study with control group 2 was carried out to determine the efficacy of ESWT for the treatment of adults with chronic insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Twelve months after treatment, the number of patients with successful Roles and Maudsley scores was statistically greater in the ESWT group compared with the control group (P>0.0002), with 83% of ESWT group patients having a successful result. In another study authors compared the results of ESWT with those of surgery at one year follow-up. 4 Even though the satisfactory results shown by surgery (84%) were higher than those obtained with ESWT (72%), these latter results are very encouraging. In this study satisfactory results were obtained in 77% of insertional tendinopathy cases and in 85% of tendon belly cases. In spite of some differences in the typology of patients and in follow-up, these results match those of a study carried out by La Sapienza University School of Medicine: 11 after surgery and at an average follow-up of 11.5 years (range 5-18 years) results were satisfactory in 88% of cases. The same study showed a lower percentage of satisfactory results in insertional tendinopathies (77%) when compared to tendon belly pathologies (85%), a characteristic noted in our ESWT case history, with smaller satisfactory results (excellent and good) in the insertional tendinopathies in comparison to those obtained in tendon belly pathologies at two months after the end of treatment and at medium-term follow-up (P<0.05), at mediumterm (P<0.05) and at long-term follow-up (P<0.01). In our opinion, the unsatisfactory results obtained with shock wave in treating insertional tendinopathy compared to tendon belly pathologies may be associated to the multifactorial nature of this pathology, that may include various lesions such as Haglund s heel, bursitis, upper calcanear spur, degenerative and metaplastic phenomena of the bone-tendon junction. In spite of the absence of a control group, as in other studies published in international literature, 6-10 the results obtained in our experience are encouraging for the long-lasting improvement of pain symptomatology, without collateral effects. These results would suggest to wait at least one year after treatment before considering surgery and to evaluate the possibility of administering additional treatments when satisfactory results have not been obtained. In our experience, ESWT treatment does not prejudice surgery and may even improve the tendon s condition for surgery. However, the conservative management approach is hardly tenable with serious or professional athletes, for which pressure is high to return to activity as soon as possible. These cases, if a quick response to ESWT is not observed, are normally scheduled for surgery without further wait. Presently, low- and medium-energy ESWT is used only after failure of conventional therapies while, on the basis of our experience, it can be evaluated as firstapproach therapy, due to lack of contraindications and collateral effects. In fact, patients in this study that did not respond successfully to treatment, later underwent surgery with no harm whatsoever. Finally, the response to treatment seemed not to be influenced by the presence of calcifications, which did not show any radiological evidence of modification after the treatment Vol No. 2 THE JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE AND PHYSICAL FITNESS 175
6 VULPIANI EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY Conclusions Although Achilles tendinopathy has been studied extensively, there is a clear lack of properly conducted scientific research to clarify its etiology, pathology, natural history and optimal management. As mentioned before, limitations of this study are: absence of a control group undergoing a placebo therapy and impossibility to achieve 100% patient recall. At present, this study is continuing with the adoption of a control group undergoing alternative treatment, focusing also on shock wave related modifications evidenced by diagnostic means. Despite these limitations, the study showed the positive effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of the tendinopathy, and the results obtained in our experience are encouraging in the light of the long-lasting improvement of the pain symptomatology reached without collateral effects. However, a prospective randomized, clinical trial with a control group and the standardization of physical and technical treatment parameters seems to be necessary for a classification of ESWT as evidencebased medicine. References 1. Alfredson H, Lorentzon R. Cronic Achilles tendinosis. Recommendations for treatment and prevention. Sports Med 2000;29: Furia JP. High-energy extracorporeal shock Wave therapy as a treatment for insertional achilles tendinopathy. AJSM 2006;34: Peers KH, Lysens RJ, Brys P, Bellemans J. Cross-sectional outcome analysis of athletes with chronic patellar tendinopathy treated surgically and by extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Clin J Sport Med 2003;13: Perlick L, Schiffmann R, Kraft CN, Wallny T, Diedrich O. [Extra-corporal shock wave treatment of the achilles tendinitis: Experimental and preliminary clinical results]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 2002;140: Ogden JA, Alvarez RG, Levitt R, Marlow M. Shock wave therapy (Orthotripsy) in musculoskeletal disorders. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001;(387): Jakobeit C, Winiarski B, Jakobeit S, Welp L, Spelsberg G. Ultrasoundguided, high-energy extracorporeal shock-wave treatment of symptomatic calcareous tendinopathy of the shoulder. ANZ J Surg 2002;72: Moretti B, Garofalo R, Genco S, Patella V, Mouhsine E. Mediumenergy shock wave therapy in the treatment of rotator cuff calcifying tendinitis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2005;13: Moretti B, Garofalo R, Patella V, Sisti GL, Corrado M, Mouhsine E. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in runners with a symptomatic heel spur. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2006;14: Pigozzi F, Giombini A, Parisi A, Casciello G, Di Salvo V, Santori N et al. The application of shock-waves therapy in the treatment of resistant chronic painful shoulder. A clinical experience. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2000;40: Vulpiani MC, Vetrano M, Savoia V, Di Pancrazio E, Trischitta D, Ferretti E. Jumper s knee treatment with extracorporeal shock wave therapy: a long-term follow-up observational study. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 2007;47: Chiara Vulpiani M, Guzzini M, Ferretti A. Operative treatment of chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Int Orthop 2003;27: Robinson JM, Cook JL, Purdam C, Visentini PJ, Ross J, Maffulli N et al. The VISA-A questionnaire: a valid and reliable index of the clinical severity of Achilles tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med 2001;35: Ferretti A, Conteduca F, Camerucci E, Morelli F. Patellar tendinosis: a follow-up study of surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2002;84- A: Kvist M. Achilles tendon injuries in athletes. Sports Med 1994;18: Kannus P, Jozsa L, Natri A, Jarvinen M. Effects of training, immobilization and remobilization on tendons. Scand J Med Sci Sports 1997;7: Sandmeier R, Renstrom PA. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic tendon disorders in sports. Scand J Med Sci Sports 1997;7: Alfredson H. The chronic painful Achilles and patellar tendon: research on basic biology and treatment. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2005;15: Alfredson H, Pietila T, Jonsson P, Lorentzon R. Heavy-load eccentric calf muscle training for the treatment of chronic Achilles tendinosis. Am J Sports Med 1998;26: Rompe JD, Nafe B, Furia JP, Maffulli N. Eccentric loading, shock-wave treatment, or a wait-and-see policy for tendinopathy of the main body of tendo Achillis: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 2007;35: Sayana MK, Maffulli N. Eccentric calf muscle training in non-athletic patients with Achilles tendinopathy. J Sci Med Sport 2007;10: Costantino C, Pogliacomi F, Vaienti E. Cryoultrasound therapy and tendonitis in athletes: a comparative evaluation versus laser CO 2 and Tecar therapy. Acta Biomed 2005;76: Ohberg L, Lorentzon R, Alfredson H. Neovascularisation in Achilles tendons with painful tendinosis but not in normal tendons: an ultrasonographic investigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2001;9: Ohberg L, Alfredson H. Ultrasound guided sclerosis of neovessels in painful chronic Achilles tendinosis: pilot study of a new treatment. Br J Sports Med 2002;36:173-5; discussion Alfredson H, Ohberg L. Sclerosing injections to areas of neo-vascularisation reduce pain in chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2005;13: Orhan Z, Alper M, Akman Y, Yavuz O, Yalciner A. An experimental study on the application of extracorporeal shock waves in the treatment of tendon injuries: preliminary report. J Orthop Sci 2001;6: Orhan Z, Ozturan K, Guven A, Cam K. The effect of extracorporeal shock waves on a rat model of injury to tendo Achillis. A histological and biomechanical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86: Wang CJ, Huang HY, Pai CH. Shock wave-enhanced neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction: an experiment in dogs. J Foot Ankle Surg 2002;41: Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, Weng LH, Hsu CC, Huang CS et al. Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction. A study in rabbits. J Orthop Res 2003;21: Orhan Z, Cam K, Alper M, Ozturan K. The effects of extracorporeal shock waves on the rat Achilles tendon: is there a critical dose for tissue injury? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2004;124: Rompe JD, Kirkpatrick CJ, Kullmer K, Schwitalle M, Krischek O. Dose-related effects of shock waves on rabbit tendo Achillis. A sonographic and histological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998;80: Chen YJ, Wang CJ, Yang KD, Kuo YR, Huang HC, Huang YT et al. Extracorporeal shock waves promote healing of collagenase-induced Achilles tendinitis and increase TGF-beta1 and IGF-I expression. J Orthop Res 2004;22: Buch M, Siebert W. Shockwave treatment for heel pain syndrome. A prospective investigation. In: Coombs R, Schaden W, Zhou SSH, editors. Musculoskeletal shockwave therapy. London: Greenwich Medical Media; p THE JOURNAL OF SPORTS MEDICINE AND PHYSICAL FITNESS Mese 2009
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature
 Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Plantar fasciitis: p. 1/6
 Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Pain Enduring Eccentric Exercise for the Treatment of Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy
 Pain Enduring Eccentric Exercise for the Treatment of Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Claire Dixon Laureen Holloway Janice Meier Nick Lo Teresa Lee Supervisors: W Darlene Reid Ph.D. & Sunita Mathur Ph.D.
Pain Enduring Eccentric Exercise for the Treatment of Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Claire Dixon Laureen Holloway Janice Meier Nick Lo Teresa Lee Supervisors: W Darlene Reid Ph.D. & Sunita Mathur Ph.D.
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis. American University of Beirut Medical Center
 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS
 BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
 A STUDY TO COMPARE THE EFFICACY OF ULTRASOUND WITH ECCENTRIC EXERCISES AND ULTRASOUND WITH CONCENTRIC EXERCISES ON TENDO ACHILLES TENDINITIS IN ATHELETES Ravish V. N 1, R. Raja 2, S. R. Sarala 3, Pavan
A STUDY TO COMPARE THE EFFICACY OF ULTRASOUND WITH ECCENTRIC EXERCISES AND ULTRASOUND WITH CONCENTRIC EXERCISES ON TENDO ACHILLES TENDINITIS IN ATHELETES Ravish V. N 1, R. Raja 2, S. R. Sarala 3, Pavan
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for patellar tendinopathy: a review of the literature
 Chapter 6 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for patellar tendinopathy: a review of the literature M.T. van Leeuwen J. Zwerver I. van den Akker-Scheek Br J Sports Med. 2009 Mar;43(3):163-8. 64 Chapter 6
Chapter 6 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for patellar tendinopathy: a review of the literature M.T. van Leeuwen J. Zwerver I. van den Akker-Scheek Br J Sports Med. 2009 Mar;43(3):163-8. 64 Chapter 6
Dr Hamish Osborne. Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin
 Dr Hamish Osborne Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin New Approaches to Handling Tendinopathies By Hamish Osborne Definition Tendinopathy Absence of tightly packed collagen bundles Large amount
Dr Hamish Osborne Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician Dunedin New Approaches to Handling Tendinopathies By Hamish Osborne Definition Tendinopathy Absence of tightly packed collagen bundles Large amount
SPORTS MEDICINE. Abstract In a previous uncontrolled pilot study we demonstrated very good clinical results with eccentric
 Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (2001) 9 :42 47 SPORTS MEDICINE DOI 10.1007/s001670000148 N. Mafi R. Lorentzon H. Alfredson Superior short-term results with eccentric calf muscle training compared
Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (2001) 9 :42 47 SPORTS MEDICINE DOI 10.1007/s001670000148 N. Mafi R. Lorentzon H. Alfredson Superior short-term results with eccentric calf muscle training compared
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Abstract Keywords:
 J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7: 11. Published online 2012 Mar 20. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Ching-Jen Wang1 Author information Article notes Copyright and License information
J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7: 11. Published online 2012 Mar 20. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Ching-Jen Wang1 Author information Article notes Copyright and License information
Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort.
 Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort. Poster No.: C-1680 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Morton, T. Parkes, O. Chan,
Intratendinous tears of the Achilles tendon - a new pathology? Analysis of a large 4 year cohort. Poster No.: C-1680 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Morton, T. Parkes, O. Chan,
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT)
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Gladys L.Y. Cheing, PhD 1 Hua Chang, MSc 2 Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is an emerging treatment modality for managing pain caused by various musculoskeletal
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Gladys L.Y. Cheing, PhD 1 Hua Chang, MSc 2 Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is an emerging treatment modality for managing pain caused by various musculoskeletal
@ CIC Edizioni Internazionali
 Conservative treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy: platelet-rich plasma and focused shock waves. A retrospective study Davide Erroi 1 Matilde Sigona 1 Tania Suarez 1 Donatella Trischitta 1 Antonio
Conservative treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy: platelet-rich plasma and focused shock waves. A retrospective study Davide Erroi 1 Matilde Sigona 1 Tania Suarez 1 Donatella Trischitta 1 Antonio
orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions
 orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions SANUWAVE Health, Inc. is a regenerative medicine company focused on the development and commercialization of noninvasive, biological
orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions SANUWAVE Health, Inc. is a regenerative medicine company focused on the development and commercialization of noninvasive, biological
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Min Wei, PhD* Yujie Liu, MD* Zhongli Li, PhD* Zhigang Wang, PhD*
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Clinical Efficacy Among - Assisted Radio-Frequency Ablation, Extracorporeal Shockwaves, and s in Treatment of Insertional Achilles Tendinosis Min Wei, PhD* Yujie Liu, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Clinical Efficacy Among - Assisted Radio-Frequency Ablation, Extracorporeal Shockwaves, and s in Treatment of Insertional Achilles Tendinosis Min Wei, PhD* Yujie Liu, MD*
Novel Physical Therapy Protocol Results in Increased Compressive Strain and Improved Outcomes in Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
 Novel Physical Therapy Protocol Results in Increased Compressive Strain and Improved Outcomes in Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Meghan Kelly MD PhD, Mary A Bucklin, Ruth Chimenti PhD, Rachel E Olsen,
Novel Physical Therapy Protocol Results in Increased Compressive Strain and Improved Outcomes in Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Meghan Kelly MD PhD, Mary A Bucklin, Ruth Chimenti PhD, Rachel E Olsen,
Achilles tendon injury
 Achilles tendon injury Achilles tendinopathy is highly prevalent in athletes who participate in running-based sports but can also occur in racket sports and in sedentary people. Research suggests there
Achilles tendon injury Achilles tendinopathy is highly prevalent in athletes who participate in running-based sports but can also occur in racket sports and in sedentary people. Research suggests there
Coverage Guidelines. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic Indications
 Coverage Guidelines Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic Indications Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan Coverage Guidelines may be updated throughout the
Coverage Guidelines Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic Indications Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan Coverage Guidelines may be updated throughout the
UEL. Sport Rehabilitation: Injury to Optimal Performance PTM 0114
 UEL Sport Rehabilitation: Injury to Optimal Performance PTM 0114 The role of eccentric training in the management of Achilles Tendinopathy Analysing and discussing Herrington L. and McCulloch R. (2007)
UEL Sport Rehabilitation: Injury to Optimal Performance PTM 0114 The role of eccentric training in the management of Achilles Tendinopathy Analysing and discussing Herrington L. and McCulloch R. (2007)
shaving to treat patellar tendinopathy/jumper s knee? A randomised controlled study
 1 Capio Artro Clinic, Stockholm Sports Trauma Research Centre, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden 2 Sports Medicine Unit, Department of Surgical and Perioperative Science, University of Umeå, Umeå,
1 Capio Artro Clinic, Stockholm Sports Trauma Research Centre, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden 2 Sports Medicine Unit, Department of Surgical and Perioperative Science, University of Umeå, Umeå,
Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
A 5-year follow-up study of Alfredson s heel-drop exercise programme in chronic midportion Achilles tendinopathy
 1 Sports Medicine Department, The Hague Medical Centre, Leidschendam, The Netherlands 2 Department of Orthopaedics, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, The Netherlands 3 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
1 Sports Medicine Department, The Hague Medical Centre, Leidschendam, The Netherlands 2 Department of Orthopaedics, Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, The Netherlands 3 Department of Orthopaedics, Leiden
Orthospec. ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy
 Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
Kevin Jones Medical Services Director
 Kevin Jones Medical Services Director MSK 2016 Extra Corporeal Shockwave Therapy Shock! Some Examples Of A Shockwave Atomic Bomb John Non Neumann 1945 Mathematician. Invented the WWII 1945 Atomic Bomb
Kevin Jones Medical Services Director MSK 2016 Extra Corporeal Shockwave Therapy Shock! Some Examples Of A Shockwave Atomic Bomb John Non Neumann 1945 Mathematician. Invented the WWII 1945 Atomic Bomb
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [Brunel University] On: 12 December 2008 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 773509782] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and
This article was downloaded by: [Brunel University] On: 12 December 2008 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 773509782] Publisher Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and
Citation for published version (APA): Zwerver, J. (2010). Patellar tendinopathy: Prevalence, ESWT treatment and evaluation Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy Zwerver, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy Zwerver, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Clinical Study Outcome of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy with and without Haglund s Deformity
 BioMed Research International Volume 216, Article ID 6315846, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/6315846 Clinical Study Outcome of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
BioMed Research International Volume 216, Article ID 6315846, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/6315846 Clinical Study Outcome of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
Dr abedi yekta. Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences
 Dr abedi yekta Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences Pain in midportion of Achilles tendon. Morning stiffness Tendinitis
Dr abedi yekta Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences Pain in midportion of Achilles tendon. Morning stiffness Tendinitis
AETIOLOGY TENDINOPATHY RESEARCH UPDATE - NOVEMBER Contents
 TENDINOPATHY RESEARCH UPDATE - NOVEMBER 2012 Contents AETIOLOGY... 1 A lower limb assessment tool for athletes at risk of developing patellar tendinopathy.... 1 Triceps surae activation is altered in male
TENDINOPATHY RESEARCH UPDATE - NOVEMBER 2012 Contents AETIOLOGY... 1 A lower limb assessment tool for athletes at risk of developing patellar tendinopathy.... 1 Triceps surae activation is altered in male
Lööklaineravi kasutus tendinopaatiate ravis. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopaties
 LÖÖKLAINETERAAPIA Lööklaineravi kasutus tendinopaatiate ravis Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopaties Tõnis Mandel taastusarst SA Tartu Ülikooli Kliinikum Spordimeditsiini ja taastusravi kliinik
LÖÖKLAINETERAAPIA Lööklaineravi kasutus tendinopaatiate ravis Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopaties Tõnis Mandel taastusarst SA Tartu Ülikooli Kliinikum Spordimeditsiini ja taastusravi kliinik
Citation for published version (APA): Zwerver, J. (2010). Patellar tendinopathy: Prevalence, ESWT treatment and evaluation. Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy Zwerver, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Patellar tendinopathy Zwerver, Johannes IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Confusion. Confusion. Confusion. Confusion Confusio Confusio. n Confusion Confusion. Confusion. Confusion. Confusion. Confusion.
 Centre for Sports and Exercise Medicine Patellar Tendinopathy Conservative and surgical managment Nicola Maffulli Centre Lead and Professor Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon Centre for Sport and
Centre for Sports and Exercise Medicine Patellar Tendinopathy Conservative and surgical managment Nicola Maffulli Centre Lead and Professor Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon Centre for Sport and
The treatment of patellar tendinopathy
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s10195-012-0220-0 REVIEW ARTICLE The treatment of patellar tendinopathy E. C. Rodriguez-Merchan Received: 4 January 2012 / Accepted: 25 November 2012 /
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s10195-012-0220-0 REVIEW ARTICLE The treatment of patellar tendinopathy E. C. Rodriguez-Merchan Received: 4 January 2012 / Accepted: 25 November 2012 /
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
In the past decade, interest has increased. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Tendinopathies
 Perspectives on Modern Orthopaedics Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Tendinopathies Andrew Sems, MD Robert Dimeff, MD Joseph P. Iannotti, MD, PhD Dr. Sems is Consultant Surgeon,
Perspectives on Modern Orthopaedics Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in the Treatment of Chronic Tendinopathies Andrew Sems, MD Robert Dimeff, MD Joseph P. Iannotti, MD, PhD Dr. Sems is Consultant Surgeon,
Achilles Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions
 APPENDIX D Achilles Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to summarize common medical and surgical interventions which may be considered for the management of
APPENDIX D Achilles Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to summarize common medical and surgical interventions which may be considered for the management of
ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications
 ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications Extracorporeal Shock Wave Technology (ESWT) is a high energy acoustic pressure wave technology that has been demonstrated to treat a variety of musculoskeletal
ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications Extracorporeal Shock Wave Technology (ESWT) is a high energy acoustic pressure wave technology that has been demonstrated to treat a variety of musculoskeletal
Why research on tendon?
 To be or not to be Active with Painful Tendinopathy? Practical Clinical Applications Based on Current Research Using the Achilles Tendon as a Model Why research on tendon? Karin Grävare Silbernagel, PhD,
To be or not to be Active with Painful Tendinopathy? Practical Clinical Applications Based on Current Research Using the Achilles Tendon as a Model Why research on tendon? Karin Grävare Silbernagel, PhD,
C hronic tendinopathies are common in both recreational
 217 REVIEW The evolution of eccentric training as treatment for patellar tendinopathy (jumper s knee): a critical review of exercise programmes Håvard Visnes, Roald Bahr... Br J Sports Med 2007;41:217
217 REVIEW The evolution of eccentric training as treatment for patellar tendinopathy (jumper s knee): a critical review of exercise programmes Håvard Visnes, Roald Bahr... Br J Sports Med 2007;41:217
Eccentric Loading, Shock-Wave Treatment, or a Wait-and-See Policy for Tendinopathy of the Main Body of Tendo Achillis
 Eccentric Loading, Shock-Wave Treatment, or a Wait-and-See Policy for Tendinopathy of the Main Body of Tendo Achillis A Randomized Controlled Trial Jan D. Rompe,* MD, Bernhard Nafe, MD, John P. Furia,
Eccentric Loading, Shock-Wave Treatment, or a Wait-and-See Policy for Tendinopathy of the Main Body of Tendo Achillis A Randomized Controlled Trial Jan D. Rompe,* MD, Bernhard Nafe, MD, John P. Furia,
SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE
 SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety
SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety
Utility of Ultrasound for Imaging Osteophytes in Patients with Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy
 Digital Commons @ George Fox University Faculty Publications - School of Physical Therapy School of Physical Therapy 2-2015 Utility of Ultrasound for Imaging Osteophytes in Patients with Insertional Achilles
Digital Commons @ George Fox University Faculty Publications - School of Physical Therapy School of Physical Therapy 2-2015 Utility of Ultrasound for Imaging Osteophytes in Patients with Insertional Achilles
NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION
 NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION ACHILLES (Homer 800BC) When Achilles mother Thetis made her son invulnerable by submerging him in the Styx, the river
NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY IMAGE GUIDED HIGH VOLUME INJECTION ACHILLES (Homer 800BC) When Achilles mother Thetis made her son invulnerable by submerging him in the Styx, the river
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy
 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete
 Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete John P. Negrine F.R.A.C.S. Foot and Ankle Surgeon Orthosports Sydney The Bad news Maximum heart rate decreases VO2 Max decreases Runners when compared
Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete John P. Negrine F.R.A.C.S. Foot and Ankle Surgeon Orthosports Sydney The Bad news Maximum heart rate decreases VO2 Max decreases Runners when compared
3.3.1 Introduction. Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz
 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy 55 Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy Effectiveness and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disorders of the tendons: A systematic review
3.3 Shock Wave Therapy 55 Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy Effectiveness and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disorders of the tendons: A systematic review
Radial Shockwave Therapy
 Radial Shockwave Therapy New Uses for Old Technology Nick Savva FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave? Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave?
Radial Shockwave Therapy New Uses for Old Technology Nick Savva FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave? Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave?
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon
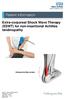 Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6459-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6459-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page
The American Journal of Sports Medicine
 The American Journal of Sports Medicine http://ajs.sagepub.com/ Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Wolf Petersen, Robert Welp and Dieter Rosenbaum Am J Sports Med 2007 35: 1659 originally published online June
The American Journal of Sports Medicine http://ajs.sagepub.com/ Chronic Achilles Tendinopathy Wolf Petersen, Robert Welp and Dieter Rosenbaum Am J Sports Med 2007 35: 1659 originally published online June
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy. Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science
 E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
Latest technology in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant tendinopathy
 Latest technology in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant tendinopathy Dr K Arjun Rao Consultant Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician FACSEP FFSEM(UK) Specialist Sportscare W.A. WA Institute of Sport School
Latest technology in the treatment of chronic recalcitrant tendinopathy Dr K Arjun Rao Consultant Sport & Exercise Medicine Physician FACSEP FFSEM(UK) Specialist Sportscare W.A. WA Institute of Sport School
TOPAZ TM What you should know
 TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
Patellar Tendinopathy
 Bulletin of the Hospital for Joint Diseases 2014;72(3):217-24 217 Patellar Tendinopathy Recent Developments toward Treatment Robert A. Christian, B.A., William H. Rossy, M.D., and Orrin H. Sherman, M.D.
Bulletin of the Hospital for Joint Diseases 2014;72(3):217-24 217 Patellar Tendinopathy Recent Developments toward Treatment Robert A. Christian, B.A., William H. Rossy, M.D., and Orrin H. Sherman, M.D.
Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy
 Acta Orthopaedica 28; 79 (2): 249 256 249 Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy A double-blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy Sten Rasmussen, Marianne Christensen, Iben Mathiesen,
Acta Orthopaedica 28; 79 (2): 249 256 249 Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy A double-blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy Sten Rasmussen, Marianne Christensen, Iben Mathiesen,
Shockwave Therapy. Leading Rehabilitation Technology
 Excellence in Shockwave Therapy Leading Rehabilitation Technology Since its foundation in 2003, REMED has tried to care for the patients suffering from different types of physical pains all over the world
Excellence in Shockwave Therapy Leading Rehabilitation Technology Since its foundation in 2003, REMED has tried to care for the patients suffering from different types of physical pains all over the world
The biological effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (eswt) on tendon tissue
 Review The biological effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (eswt) on tendon tissue Angela Notarnicola Biagio Moretti Department of Neuroscience and Organs of Sense, University of Study Aldo Moro
Review The biological effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (eswt) on tendon tissue Angela Notarnicola Biagio Moretti Department of Neuroscience and Organs of Sense, University of Study Aldo Moro
J umper s knee (chronic patellar tendinosis) is a troublesome
 423 ORIGINAL ARTICLE and pain in jumper s knee: a prospective clinical and sonographic study in elite junior volleyball players K Gisslén, H Alfredson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
423 ORIGINAL ARTICLE and pain in jumper s knee: a prospective clinical and sonographic study in elite junior volleyball players K Gisslén, H Alfredson... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Conservative management of mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy: a mixed methods study, integrating systematic review and clinical reasoning
 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 Conservative management of mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy: a mixed methods study, integrating systematic review and clinical reasoning Victoria Rowe 1, Stephanie Hemmings
1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 Conservative management of mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy: a mixed methods study, integrating systematic review and clinical reasoning Victoria Rowe 1, Stephanie Hemmings
In an adult population are eccentric exercises effective in reducing pain and improving function in Achilles tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line
 Specific Question: In an adult population are eccentric exercises effective in reducing pain and improving function in Achilles tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate quality evidence for
Specific Question: In an adult population are eccentric exercises effective in reducing pain and improving function in Achilles tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate quality evidence for
What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy?
 Specific Question: What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate evidence
Specific Question: What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate evidence
Introduction. Anatomy
 the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA History Shock waves used in human medicine as early as 1980s: Break
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA History Shock waves used in human medicine as early as 1980s: Break
New Generation Of Shockwave Devices with The Controls in the Handpiece
 New Generation Of Shockwave Devices with The Controls in the Handpiece Contents The Ultimate Shockwave Device 1 The Ultimate Shockwave Device The Tissue Regenerator is the world s most effective Shockwave
New Generation Of Shockwave Devices with The Controls in the Handpiece Contents The Ultimate Shockwave Device 1 The Ultimate Shockwave Device The Tissue Regenerator is the world s most effective Shockwave
Intelect Focus Shockwave
 Intelect Focus Shockwave A non-invasive treatment, proven effective for plantar fasciitis Intelect Focus Shockwave - the Technology Greater Power & Depth for Better Treatment In Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Intelect Focus Shockwave A non-invasive treatment, proven effective for plantar fasciitis Intelect Focus Shockwave - the Technology Greater Power & Depth for Better Treatment In Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Musculoskeletal health is a necessary component of overall
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE No Effect of Eccentric Training on Jumper s Knee in Volleyball Players During the Competitive Season A Randomized Clinical Trial Håvard Visnes, Stud Med, PT,* Aasne Hoksrud, Stud Med,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE No Effect of Eccentric Training on Jumper s Knee in Volleyball Players During the Competitive Season A Randomized Clinical Trial Håvard Visnes, Stud Med, PT,* Aasne Hoksrud, Stud Med,*
석회성건염 한양의대재활의학교실 이규훈
 석회성건염 한양의대재활의학교실 이규훈 Definition Calcifying tendinitis Acute or chronically painful condition that is caused by inflammation around calcium deposits located in or around the tendons Vascularized, viable
석회성건염 한양의대재활의학교실 이규훈 Definition Calcifying tendinitis Acute or chronically painful condition that is caused by inflammation around calcium deposits located in or around the tendons Vascularized, viable
COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS OF ULTRASOUND GUIDED INTRATENDINOUS PROLOTHERAPY INJECTION WITH CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT TO TREAT
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS OF ULTRASOUND GUIDED INTRATENDINOUS PROLOTHERAPY INJECTION WITH CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT TO TREAT FOCAL SUPRASPINATUS TENDINOSIS : RANDOMISED CONTROL STUDY 1,2
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS OF ULTRASOUND GUIDED INTRATENDINOUS PROLOTHERAPY INJECTION WITH CONVENTIONAL TREATMENT TO TREAT FOCAL SUPRASPINATUS TENDINOSIS : RANDOMISED CONTROL STUDY 1,2
EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D.
 1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
INSIGHTS INTO ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
 C H A P T E R 1 4 INSIGHTS INTO ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY Steven R. Carter, DPM TERMINOLOGY The terminology used to describe Achilles tendon pathology can be misleading and sometimes confusing. Often we use
C H A P T E R 1 4 INSIGHTS INTO ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY Steven R. Carter, DPM TERMINOLOGY The terminology used to describe Achilles tendon pathology can be misleading and sometimes confusing. Often we use
Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis.
 Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis. From the Brisbane Hand & Upper Limb Clinic, Arnold Janssen Centre, Brisbane Private Hospital, 259 Wickham Terrace, Brisbane,
Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis. From the Brisbane Hand & Upper Limb Clinic, Arnold Janssen Centre, Brisbane Private Hospital, 259 Wickham Terrace, Brisbane,
Arthroscopic treatment of chronic patellar tendinopathy in high-level athletes
 Original article Arthroscopic treatment of chronic patellar tendinopathy in high-level athletes Dimosthenis Artemis Alaseirlis 1, George Athanasios Konstantinidis 2, Nikolaos Malliaropoulos 3, Lamprini
Original article Arthroscopic treatment of chronic patellar tendinopathy in high-level athletes Dimosthenis Artemis Alaseirlis 1, George Athanasios Konstantinidis 2, Nikolaos Malliaropoulos 3, Lamprini
Tendon & Ligament Application of PRP
 Tendon & Ligament Application of PRP Sang Chul Lee, M.D, PhD. Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Myongji hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine Tendon and Ligament Low metabolic
Tendon & Ligament Application of PRP Sang Chul Lee, M.D, PhD. Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Myongji hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine Tendon and Ligament Low metabolic
Tendon Structure s Lack of Relation to Clinical Outcome After Eccentric Exercises in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 34-43 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Tendon Structure s Lack of Relation to Clinical Outcome After Eccentric Exercises in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2012, 21, 34-43 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. Tendon Structure s Lack of Relation to Clinical Outcome After Eccentric Exercises in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy
Nonoperative Treatment of Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review
 CRITICAL REVIEW Nonoperative Treatment of Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review Robert A. Magnussen, MD, Warren R. Dunn, MD, MPH, and A. Brian Thomson, MD Objective: The aim of this systematic
CRITICAL REVIEW Nonoperative Treatment of Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review Robert A. Magnussen, MD, Warren R. Dunn, MD, MPH, and A. Brian Thomson, MD Objective: The aim of this systematic
Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections as a Treatment for Refractory Patellar Tendinosis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials
 Review Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):171-177 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.16.055 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections as a Treatment
Review Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2017;29(3):171-177 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.16.055 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections as a Treatment
tissue, Interventional non-vascular /ecr2014/C-1241
 Effectiveness of Ultrasound-guided Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) injections after needle tenotomy in the treatment of chronic tendinopathies : A prospective study. Poster No.: C-1241 Congress: ECR 2014 Type:
Effectiveness of Ultrasound-guided Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) injections after needle tenotomy in the treatment of chronic tendinopathies : A prospective study. Poster No.: C-1241 Congress: ECR 2014 Type:
mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading
 Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Patellar Tendinosis A FOLLOW-UP STUDY OF SURGICAL TREATMENT
 2179 COPYRIGHT 2002 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Patellar Tendinosis A FOLLOW-UP STUDY OF SURGICAL TREATMENT BY ANDREA FERRETTI, MD, FABIO CONTEDUCA, MD, EMANUELA CAMERUCCI, MST,
2179 COPYRIGHT 2002 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Patellar Tendinosis A FOLLOW-UP STUDY OF SURGICAL TREATMENT BY ANDREA FERRETTI, MD, FABIO CONTEDUCA, MD, EMANUELA CAMERUCCI, MST,
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery
 AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
AMG Virtual CME Series Plantar Fasciitis 11-9-17 Brian T. Dix, DPM, FACFAS Board Certified in Foot and Reconstructive Hindfoot & Ankle Surgery Anatomy 3 bands of dense connective tissue, which originate
PREVALANCE. Is eccentric loading better than concentric in rehab of tendinopathy? 9/29/10. Tendinopathy - prevalance
 Is eccentric loading better than concentric in rehab of tendinopathy? Dr. Henning Langberg DMSc, PhD, PT Institute of Sports Medicine Copenhagen, Denmark PREVALANCE Tendinopathy - prevalance (Alfredson
Is eccentric loading better than concentric in rehab of tendinopathy? Dr. Henning Langberg DMSc, PhD, PT Institute of Sports Medicine Copenhagen, Denmark PREVALANCE Tendinopathy - prevalance (Alfredson
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR
 SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
Clinical Fellow, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan, Republic of China; 2
 J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(1):47-54 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Ultrasonography and clinical outcome comparison of extracorporeal shock wave therapy
J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(1):47-54 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Ultrasonography and clinical outcome comparison of extracorporeal shock wave therapy
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIITIS
 ZAGAZIG UNIVERSITY MEDICAL JOURNAL EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIITIS By Magdy Husseiny Ahmad Mansour Rheumatology &Rehabilitation Department Faculty of Medicine-Zagazig
ZAGAZIG UNIVERSITY MEDICAL JOURNAL EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIITIS By Magdy Husseiny Ahmad Mansour Rheumatology &Rehabilitation Department Faculty of Medicine-Zagazig
Shockwave Therapy. Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
 Shockwave Therapy Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy TensCare Shockwave Therapy Unit Introduction ESWT Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive therapy that uses acoustic waves
Shockwave Therapy Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy TensCare Shockwave Therapy Unit Introduction ESWT Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive therapy that uses acoustic waves
Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions
 APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH ABSTRACT
 IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF THE ADDITION OF ECCENTRICS FOR REHABILITATION OF PREVIOUSLY FAILED TREATMENTS OF GOLFERS ELBOW Timothy F. Tyler, MS, PT, ATC 1,2 Stephen J. Nicholas, MD 2 Brandon
IJSPT ORIGINAL RESEARCH CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF THE ADDITION OF ECCENTRICS FOR REHABILITATION OF PREVIOUSLY FAILED TREATMENTS OF GOLFERS ELBOW Timothy F. Tyler, MS, PT, ATC 1,2 Stephen J. Nicholas, MD 2 Brandon
Today there are several working hypothesis for the physical effects of acoustic pressure waves:
 EPAT Shockwave Therapy This scientifically proven procedure represents a breakthrough in regenerative medicine treatment options for a broad range of musculoskeletal disorders/conditions utilizing a proprietary
EPAT Shockwave Therapy This scientifically proven procedure represents a breakthrough in regenerative medicine treatment options for a broad range of musculoskeletal disorders/conditions utilizing a proprietary
Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Needle Tenotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Tendinosis
 Article Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Needle Tenotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Tendinosis Jeffrey A. Housner, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Roberta Misko, PT, PA-C Objective. Initial reports have
Article Sonographically Guided Percutaneous Needle Tenotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Tendinosis Jeffrey A. Housner, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, Roberta Misko, PT, PA-C Objective. Initial reports have
Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system
 Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system Dr. Christoph Schmitz, MD Dept. Psychiat. Neuropsychol., Div. Cell. Neurosci. Maastricht University Maastricht The
Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system Dr. Christoph Schmitz, MD Dept. Psychiat. Neuropsychol., Div. Cell. Neurosci. Maastricht University Maastricht The
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction PREDICTIVE FACTORS FOR FOR RADIAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIOPATHY
 PREDICTIVE FACTORS FOR FOR RADIAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIOPATHY JAVIER CRUPNIK, PT ALDO BUSTOS, MD Introduction Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain.
PREDICTIVE FACTORS FOR FOR RADIAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC PLANTAR FASCIOPATHY JAVIER CRUPNIK, PT ALDO BUSTOS, MD Introduction Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain.
Evidence Based Approach to the Treatment of Lower Extremity Tendinopathy. Cage SA, Gallegos DM, Eilers MA, Warner BJ
 Evidence Based Approach to the Treatment of Lower Extremity Tendinopathy Cage SA, Gallegos DM, Eilers MA, Warner BJ Thank you PICO Question Patients Subjects suffering from lower extremity tendinopathy
Evidence Based Approach to the Treatment of Lower Extremity Tendinopathy Cage SA, Gallegos DM, Eilers MA, Warner BJ Thank you PICO Question Patients Subjects suffering from lower extremity tendinopathy
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 01 Page January 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Management of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis using Hyperosmolar Dextrose Injection Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Management of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis using Hyperosmolar Dextrose Injection Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Focused Shock Waves in the Treatment of Jumper s Knee in Athletes
 AJSM PreView, published on February 13, 2013 as doi:10.1177/0363546513475345 Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Focused Shock Waves in the Treatment of Jumper s Knee in Athletes Mario Vetrano,* y MD, Anna Castorina,
AJSM PreView, published on February 13, 2013 as doi:10.1177/0363546513475345 Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Focused Shock Waves in the Treatment of Jumper s Knee in Athletes Mario Vetrano,* y MD, Anna Castorina,
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy. Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine
 Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
Protocols for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction & Achilles Tendinosis. Tara Bries, PT
 Protocols for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction & Achilles Tendinosis Tara Bries, PT Non-Operative Protocol for Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction Based on research by Alvarez et al. (2006) entitled
Protocols for Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction & Achilles Tendinosis Tara Bries, PT Non-Operative Protocol for Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction Based on research by Alvarez et al. (2006) entitled
PLATELET-RICH PLASMA FOR TREATING CHRONIC TENDINOPATHY
 PLATELET-RICH PLASMA FOR TREATING CHRONIC TENDINOPATHY Written by Jean-François Kaux, Belgium Tendinopathy is a major problem in medicine and sports traumatology 1. It is due, inter alia, to mechanical
PLATELET-RICH PLASMA FOR TREATING CHRONIC TENDINOPATHY Written by Jean-François Kaux, Belgium Tendinopathy is a major problem in medicine and sports traumatology 1. It is due, inter alia, to mechanical
Principles of Treatment. Case Studies. Principles of Treatment. Clinical Perspectives for the GP
 Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
