Hyperbaric Oxygen for Stage I and II Femoral Head Osteonecrosis
|
|
|
- Jessie Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hyperbaric Oxygen for and Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Lior Koren, MD; Eyal Ginesin, MD; Yehuda Melamed, MD; Doron Norman, MD; Daniel Levin, MD; Eli Peled, MD abstract Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a suggested joint-preserving treatment for symptomatic early-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Limited studies of this treatment have been published. The goal of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of this treatment in a relatively large patient cohort. The authors reviewed the files of 68 patients with 78 symptomatic joints with Steinberg stage and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. All patients were treated with hyperbaric oxygen at the authors medical health center. Pretreatment and immediate posttreatment magnetic resonance imaging (MR) findings were compared. On follow-up, a telephone interview was conducted to determine the survival of the joint. Modified Harris Hip Score and Short Form 12 health survey (SF-12) questionnaires of the start of treatment and at follow-up were obtained and evaluated for statistically significant differences. Half of the joints were stage 1 and half were stage. Seventy-four joints underwent both pre- and posttreatment MR. Eighty-eight percent of joints showed improvement posttreatment. On follow-up at a mean of 11.1±5.1 years, 54 patients (58 joints) were located and answered the questionnaires. At the time of follow-up, 93% of the joints survived. Mean Harris Hip Score improved from 21 to 81 (P<.0001), the mean physical component of the SF-12 improved from 24 to 46 (P<.0001), and the mean mental component of the SF-12 improved from 54 to 59 (P<.0001). The authors concluded that hyperbaric oxygen treatment is effective in preserving the hip joint in stage and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. [Orthopedics. 2015; 38(3):e200-e205.] The authors are from the Orthopedic Division (LK, EG, DN, DL, EP), Rambam Health Care Campus, Haifa; and the Hyperbaric Medical Unit (YM), Rambam and Elisha Hospitals, Haifa, srael. The authors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. The authors thank Mrs Ronit Leiba for conducting statistical analysis. Correspondence should be addressed to: Lior Koren, MD, Orthopedic Division, Rambam Health Care Campus, Ha alia Hashnia 8, 31096, POB 9602, Haifa, srael (koren_lior@yahoo.com). Received: February 16, 2014; Accepted: May 13, doi: / e200 Copyright SLACK ncorporated
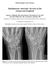
2 Osteonecrosis of the femoral head is not a rare orthopedic disorder and affects mainly young and middle-aged patients. 1 The etiology of osteonecrosis of the femoral head can be divided into 3 categories: idiopathic; secondary, mainly caused by steroid use 2 ; and trauma. 3 Patients in the idiopathic and secondary groups are relatively young, with a mean age of 47 years. 4 Young patients who undergo hip replacement are more likely to have a revision during their lifetime compared with older patients. For this reason, joint-preserving treatments in osteonecrosis of the femoral head play an important role. One treatment that has been proposed is hyperbaric oxygen treatment, which restores tissue oxygenation of the femoral head, reduces edema, and induces angiogenesis. By reducing intraosseous pressure, venous drainage is restored and the microcirculation is improved. 5 Therefore, hyperbaric oxygen treatment seems to be indicated in osteonecrosis of the femoral head because its actions address the specific needs of the endangered bone. The authors present their analysis of the results of hyperbaric oxygen treatment in patients with Steinberg stage or osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Materials and Methods Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging (MR) data were reviewed for 68 patients (78 joints) with symptomatic stage or osteonecrosis of the femoral head treated with hyperbaric oxygen from July 1996 to August Staging was done according to the criteria of Steinberg et al. 6 All patients were diagnosed and staged by MR scans reviewed by certified musculoskeletal radiologists. All patients followed a protected weight-bearing regimen for the duration of their symptoms and underwent a series of 6 daily sessions of hyperbaric oxygen treatment each week. The treatments were paid for by the patients health insurance. Treatments were continued as long as they were covered by health insurance or until symptoms resolved. The hyperbaric oxygen treatment protocol involved breathing 100% oxygen at 2 to 2.4 atmospheres absolute in a multiplace pressure chamber for 90 minutes using an overboard demand regulator with an oral nasal mask breathing system. A subsequent MR was performed within 2 months after the end of treatment. The endpoint was an improvement of immediate posttreatment MR findings compared with the pretreatment MR. On follow-up at a mean of 11.1±5.1 years, a telephone interview was conducted. Noted was the survival of the joint (hip replacement surgery or none). A modified Harris Hip Score questionnaire 7 was administered for the start of treatment and at follow-up. The same was done with the Short Form 12 health survey (SF-12), which has physical and mental components (PCS-12 and MCS-12, respectively). 8 The scoring was further analyzed for the subgroups of stage and and for the etiology groups of idiopathic, trauma, and secondary (mainly because of previous steroid treatment). Data were analyzed by a qualified statistician using SPSS software for Windows, version 18.0 (SPSS nc, Chicago, llinois). The normality of the data was tested by Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests. When the quantitative parameters were not normally distributed, nonparametric tests were used. Paired t test and Wilcoxon tests were used for differences between pre- and posttreatment results whenever necessary according to the Kolmogorov-Smirnov results. A repeated measures analysis was conducted to determine whether there was a statistically significant difference in the etiology and stage subgroups for improvement in modified Harris Hip Score, PCS- 12, and MCS-12. P<.05 was considered significant. The study was approved by the authors institutional ethics committee (reference number RMB). No funding was needed for this research. Results Table 1 details the demographic features of the study population. Mean age was 43.3±11.7 years. An equal number Table 1 Patient Characteristics Characteristic Value Patients, No. 68 Age,, y 43.3±11.7 Sex, male, No. 47 (69%) Sessions,, No. 78.3±24.2 Joints, No. 78 Side, No. Left 41 (53%) Right 27 (35%) Bilateral 10 (13%), No. 39 (50%) 39 (50%), No. 48 (62%) 14 (18%) 16 (20%) of patients had stage and stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Most of the patients had an idiopathic etiology (62%). Patients underwent 25 to 135 treatments (mean, 80±24 treatments). Table 2 summarizes the improvement seen on MR. Of 68 patients, 4 did not undergo posttreatment MR. n the remaining 74 joints (64 patients) 88% or 65 joints showed improvement (reduced lesion size) on posttreatment MR. showed 95% improvement and stage showed 81% improvement. Ninetythree percent improved in the idiopathic group, 85% improved in the trauma group, and 75% improved in the secondary group. Of 68 patients, 54 (58 joints) were located and completed the interview on follow-up. Mean follow-up was 11.1±5.1 years (range, 7 months to 16 years and 7 months). Table 3 summarizes the results of joint survival. Only 4 joints (7%) had undergone hip joint replacement at the time of follow-up, for a 93% survival rate. MARCH 2015 Volume 38 Number 3 e201
3 Endpoint mprovement, No. Endpoint Survival, No. Score had a survival rate of 97% and stage had a survival rate of 90%. Both the idiopathic and trauma groups had a survival rate of 100%. All cases of failure occurred in the secondary group (mainly steroid treatment); this group had a survival rate of 73%. Patients who underwent joint replacement were excluded from analysis of modified Harris Hip Score and SF-12 scoring, leaving 54 joints (Tables 4-7). Pretreatment mean modified Harris Hip Score was very low, 21 points, and Table 2 Magnetic Resonance maging Results mmediately Posttreatment Compared With Pretreatment (N=74) (n=37) (n=37) (n=45) (n=13) (n=16) 65 (88%) 35 (95%) 30 (81%) 42 (93%) 11 (85%) 12 (75%) Table 3 Survival of Joints by and (N=58) (n=29) (n=29) (n=15) 54 (93%) 28 (97%) 26 (90%) 32 (100%) 11 (100%) 11 (73%) Table 4 Modified Harris Hip Score Before Treatment and at Follow-up, Excluding Replaced Joints Modified Harris Hip Score before treatment, Modified Harris Hip Score at follow-up, 21±18 19±18 23±18 22±20 16±10 17±13 81±28 87±23 75±31 79±28 81±28 87±23 P <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 it improved on follow-up to 81 points (P<.0001). n stage, the improvement was from 17 points to 79 points (P<.0001) and in stage, the improvement was from 21 points to 68 points (P<.0001). The pain component of the modified Harris Hip Score was also analyzed. t improved significantly from 7 points to 35 points (P<.0001). The mean PCS-12 score increased from 24 to 46 (P<.0001). The change was statistically significant also when comparison was made within stage and and when comparison was made by etiology. The mental component of the SF-12 also showed an overall significant change from 54 to 59 (P<.0001). The change was statistically significant when comparison was made within stage and. Concerning etiology, the difference was significant for the idiopathic group, but did not reach significance for the other groups. Discussion Survival rates of less than 60% have been reported for Steinberg stage to stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head at 5 years. 9,10 Many treatment modalities have been used in an effort to alter this natural history. Joint-preserving treatments focused on Steinberg stages and in which there is no subchondral fracture and joint surface collapse may still be avoided. These treatments included surgical procedures, such as core decompression, bone grafting, and osteotomies, and nonsurgical procedures, such as extracorporeal shock wave treatment, anticoagulative treatment, alendronate, and hyperbaric oxygen. 2 Hyperbaric oxygen treatment involves intermittent inhalation of 100% oxygen at greater than atmospheric pressure. This treatment is administered in a hyperbaric chamber, which is compressed with air, while the patient breathes oxygen at ambient pressure through a mask. nspiration of oxygen at high pressure increases the amount of oxygen dissolved in the plasma in direct proportion to the rise in ambient pressure. Thus, when oxygen is inhaled at 2 to 2.4 atmospheres absolute, the plasma oxygen content increases from 0.32 volume percent to 4.8 to 5.76 volume percent. This high dissolved oxygen concentration improves oxygen delivery to bone tissue, reduces marrow edema, and thereby reduces intraosseous pressure, improving venous drainage and microcirculation. By flooding the extracellular fluid with diffused oxygen, the oxygen becomes available to the ischemic bone cells without the need for circulat- e202 Copyright SLACK ncorporated
4 ing hemoglobin. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment also stimulates angiogenesis that is needed for healing of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. 10 Furthermore, osteoclast and osteoblast function is stimulated by the high oxygen pressure levels. 11 To the authors knowledge, this article presents the largest series of hyperbaric oxygen treatment for osteonecrosis of the femoral head to date (74 joints for MR results and 58 joints for joint survival, hip function, and quality of life) and has the longest follow-up (mean, 11.1 years for survival, hip function, and quality of life). Before MR was available, Baixe et al 12 presented a report on 41 joints with osteonecrosis of the femoral head that were treated with 20 hyperbaric oxygen sessions. All joints survived after 24 months. Strauss et al 10 presented a metaanalysis in 2008 that included stages,, and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Of 86 joints treated with hyperbaric oxygen and followed for less than 24 months, 83 (97%) survived. Of 103 other joints followed for more than 24 months, 83 (81%) survived. According to the meta-analysis by Strauss et al, 10 the results with hyperbaric oxygen were superior to the results of natural history, core decompression, bone grafting, osteotomy, and electrical stimulation. Reis et al 13 treated 16 hips with stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head with hyperbaric oxygen and compared them with the results of an observational study 14 that showed lesions of similar size on MR. n this study, 81% of joints returned to normal on MR compared with 17% in the untreated group. Camporesi et al 15 treated 10 joints with stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head with hyperbaric oxygen and compared them with 9 patients who were treated with hyperbaric air. The hyperbaric oxygen treatment group showed improved pain scores, hip joint range of motion, and stabilometry scores. n the current study, improvement on posttreatment MR was substantial, 88% in the whole group and 95% for stage and 81% for stage. These radiologic findings are in keeping with the pain reduction shown on modified Harris Hip Score and the physical and mental improvement reflected by SF-12 scores. Table 5 Pain Component of the Modified Harris Hip Score Before Treatment and at Follow-up, Excluding Replaced Joints Pain Component of the Modified Harris Hip Score Pain pretreatment, Pain at follow-up, 7±8 6±8 7±9 8±9 4±7 7±7 35±15 38±23 32±16 34±15 34±18 38±10 P <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 Score Score Table 7 MCS-12 Before Treatment and at Follow-up, Excluding Replaced Joints MCS-12 before treatment, MCS-12 at follow-up, Table 6 PCS-12 Before Treatment and at Follow-up, Excluding Replaced Joints PCS-12 pretreatment, PCS-12 at followup, 54±9 53±10 56±8 56±8 54±9 51±8 59±5 57±7 60±3 59±2 58±8 57±8 P < Abbreviation: MCS-12, mental component summary of the Short Form 12 health survey. 24±7 24±7 25±8 25±8 24±7 23±5 46±13 50±11 43±15 47±14 44±14 46±12 P <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 <.0001 Abbreviation: PCS-12, physical component summary of the Short Form 12 health survey. The authors observation at a mean of 11.1 years showed a combined survival rate for stage and stage of 93%. showed a survival rate of 97%, and stage showed a survival rate of 90%. The nat- MARCH 2015 Volume 38 Number 3 e203
5 ural history of survival of Steinberg stage to osteonecrosis of the femoral head is less than 60% at 5 years. 9 Modified Harris Hip Score improved significantly between the start of treatment and follow-up. This finding shows that hip joint function improved and pain was reduced. The limitation of this modified score is that patients were not examined for range of motion of the joint. The SF-12 had been shown to be reliable in evaluating the change in quality of life after hip joint treatment. 16 The survey has physical and mental components. Both showed a significant improvement at follow-up, reflecting physical and mental improvements achieved after treatment. of osteonecrosis of the femoral head affected the outcome of treatment. The secondary group (mostly steroid treatment) did not show as much improvement on MR as the other groups (75% vs 85% in the trauma group and 93% in the idiopathic group). Moreover, this group had a lower joint survival rate (73% vs 100% in the other groups). This may be related to the medical condition that necessitated steroid treatment. Further, some patients needed continued steroid treatment even after the diagnosis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Other joint-preserving treatments of early-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head also showed effectiveness. Alendronate treatment improved the survival rate of stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head to 98% and the survival rate of stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head to 92% at 8-year follow-up. 17 Core decompression led to survival of 96% of stage joints and 74% of stage joints after 10-year follow-up. 18 mplantation at the site of decompression with autologous bone marrow with or without hydroxyapatite-polyamide also proved effective. 19,20 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy and pulsed electromagnetic fields are other modalities of treatment that showed a beneficial effect on the outcome of early-stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head. 21,22 The combination of those treatments with hyperbaric oxygen might enhance the success rates of treatment and can be a focus of future research. Limitations The current study had some limitations. Analysis of MR was used for comparison of pre- and posttreatment findings to determine reduction in the size of the lesion. The study did not include the exact measurement and location of the original lesion. However, pretreatment modified Harris Hip Score and SF-12 score showed that the patients were disabled, even at stage. The number of treatment sessions given at the authors institution varied from 25 to 135 (mean, 80±24 treatments) because of variations in the coverage provided by the patients health insurance. Future studies are needed to determine the optimal number of sessions. The time of follow-up also varied from 7 months to 16 years and 7 months (mean, 11.1±5.1 years). Nevertheless, only 5 joints (8.6%) were followed for less than 2 years, and the improvement noted on the questionnaires showed that significant clinical improvement occurred. Another limitation was that 25% of patients (20 joints) were lost to follow-up for the analysis of survival, hip function, and quality of life. Those patients could not be reached by telephone. The number of patients lost to follow-up was equal between stage and stage. Sixteen cases were of idiopathic etiology, 3 were related to trauma, and only 1 had secondary etiology that had a worse prognosis in the authors analysis. Thus, the authors do not believe that the loss to follow-up affected the results. Conclusion The current study shows that hyperbaric oxygen treatment has a role in treating stage and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. References 1. Mankin HJ. Nontraumatic necrosis of bone (osteonecrosis). N Engl J Med. 1992; 326: Mont MA, Jones LC, Hungerford DS. Nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: ten years later. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88: Bachiller FG, Caballer AP, Portal LF. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head after femoral neck fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; (399): Solacoff D, Mont MA, Krackow KA. Uncemented total hip arthroplasty in patients less than 45 years with avascular necrosis. Orthop Trans. 1993; 17: Nylander G, Lewis D, Nordstrom H, Larsson J. Reduction of postischaemic edema with hyperbaric oxygen. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985; 76: Steinberg ME, Hayken GD, Steinberg DR. A quantitative system for staging avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77: Sharma S, Shah R, Draviraj KP, Bhamra MS. Use of telephone interviews to follow up patients after total hip replacement. J Telemed Telecare. 2005; 11: Gandek B, Ware JE Jr, Aaronson NK, et al. Cross-validation of item selection and scoring for the SF-12 Health Survey in nine countries: results from the QO1998; LA Project. nternational Quality of Life Assessment. J Clin Epidemiol. 1998; 51(11): Ohzono K, Sugano N, Takaoka K, et al. Natural history of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73: Strauss M, Dvorak T, Melamed Y, Reis DN. Femoral head necrosis and hyperbaric oxygen therapy. n: Hyperbaric Medicine Practice. 3rd ed. Vol. 34. North Palm Beach, FL: Best; 2008: Hunt TK, Pai MP. The effect of varying ambient oxygen tensions on wound metabolism and collagen synthesis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1972; 135: Baixe JH, Bidart J, Nicolini JC. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head by hyperbaric oxygen. Bull Med Sub Hyp. 1969; 1: Reis ND, Schwartz O, Militianu D, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a treatment for stage- avascular necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85: Van de Berg BC, Malghem JJ, Lecouvet FE, Jamart J, Maldague BE. bone marrow edema lesions of the femoral head: predictive value of MR imaging findings. Radiology. 1999; 212: Camporesi EM, Vezzani G, Bosco G, Mangar D, Bernasek TL. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in femoral head necrosis. J Arthroplasty. e204 Copyright SLACK ncorporated
6 2010; 25(6): Ostendorf M, Van Stel HF, Buskens E, et al. Patient-reported outcome in total hip replacement: a comparison of five instruments of health status. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86: Agarwala S, Shah S, Joshi VR. The use of alendronate in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: follow-up to eight years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009; 91: Fairbank AC, Bhatia D, Jinnah RH, Hungerford DS. Long-term results of core decompression for ischaemic necrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77: Wang BL, Sun W, Shi ZC, et al. Treatment of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head with the implantation of core decompression and concentrated autologous bone marrow containing mononuclear cells. Arch Orthop Surg. 2010; 130(7): Liu Y, Liu S, Su X. Core decompression and implantation of bone marrow mononuclear cells with porous hydroxyapatite composite filler for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Surg. 2013; 133(1): Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, et al. Treatment of osteonecrosis of the hip: comparison of extracorporeal shockwave with shockwave and alendronate. Arch Orthop Surg. 2008; 128(9): Massari L, Fini M, Cadossi R, Setti S, Traina GC. Biophysical stimulation with pulsed electromagnetic fields in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(suppl 2): MARCH 2015 Volume 38 Number 3 e205
O20 FEMORAL HEAD NECROSIS AND HYPERBARIC OXYGEN A MRI STUDY STUDY PROTOCOL ADOPTED FROM THE COST B14 WORKING GROUP
 O20 FEMORAL HEAD NECROSIS AND HYPERBARIC OXYGEN A MRI STUDY STUDY PROTOCOL ADOPTED FROM THE COST B14 WORKING GROUP "2" L. Ditri, F. Grigoletto, Y. Melamed, D. Reis, L. Cucci, P. Germonprè, T. Mesimeris,
O20 FEMORAL HEAD NECROSIS AND HYPERBARIC OXYGEN A MRI STUDY STUDY PROTOCOL ADOPTED FROM THE COST B14 WORKING GROUP "2" L. Ditri, F. Grigoletto, Y. Melamed, D. Reis, L. Cucci, P. Germonprè, T. Mesimeris,
Speaker s Disclosure Statement. Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN. Objectives. Risk Factors
 Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN Speaker s Disclosure Statement I have no industry relationships to disclose I will discuss off-label use of medications Dana-Farber/Boston Children
Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN Speaker s Disclosure Statement I have no industry relationships to disclose I will discuss off-label use of medications Dana-Farber/Boston Children
Approximately 20,000 new cases of femoral head
 A Review Paper Current Management Options for : Part 1, Diagnosis and Nonoperative Management Derek F. Amanatullah, MD, PhD, Eric J. Strauss, MD, and Paul E. Di Cesare, MD Abstract Osteonecrosis of the
A Review Paper Current Management Options for : Part 1, Diagnosis and Nonoperative Management Derek F. Amanatullah, MD, PhD, Eric J. Strauss, MD, and Paul E. Di Cesare, MD Abstract Osteonecrosis of the
Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients. Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015
 Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015 The author declares no potential conflicts of interest or financial disclosures Osteonecrosis
Screening for and Assessment of Osteonecrosis in Oncology Patients Sue C. Kaste, DO SPR Postgraduate Course 2015 The author declares no potential conflicts of interest or financial disclosures Osteonecrosis
The Natural History of Untreated Asymptomatic Hips in Patients Who Have Non-Traumatic Osteonecrosis*
 Copyright 1997 by The Journal ofbone ami Joint Surgery, Incorporated The Natural History of Untreated Hips in Patients Who Have Non-Traumatic Osteonecrosis* BY HARRY E. JERGESEN, M.D.t, AND A. SHABI KHAN,
Copyright 1997 by The Journal ofbone ami Joint Surgery, Incorporated The Natural History of Untreated Hips in Patients Who Have Non-Traumatic Osteonecrosis* BY HARRY E. JERGESEN, M.D.t, AND A. SHABI KHAN,
Noncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Elderly Patients
 Noncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Elderly Patients Ta-I Wang, MD; Shih-Hsin Hung, RN, MSN; Yu-Ping Su, MD; Chi-Quang Feng, MD; Fang-Yao Chiu, MD; Chien-Lin Liu,
Noncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Elderly Patients Ta-I Wang, MD; Shih-Hsin Hung, RN, MSN; Yu-Ping Su, MD; Chi-Quang Feng, MD; Fang-Yao Chiu, MD; Chien-Lin Liu,
The Orthopaedic In-Training Examination (OITE)
 168 Reconstructive Knee Surgery Literature as a Tool for the Orthopaedic In-Training Examination Siraj A. Sayeed, M.D., M. Eng., David R. Marker, B.S., Simon C. Mears, M.D., Ronald E. Delanois, M.D., and
168 Reconstructive Knee Surgery Literature as a Tool for the Orthopaedic In-Training Examination Siraj A. Sayeed, M.D., M. Eng., David R. Marker, B.S., Simon C. Mears, M.D., Ronald E. Delanois, M.D., and
S. Agarwala, D. Jain, V. R. Joshi and A. Sule
 Rheumatology 2005;44:352 359 Advance Access publication 24 November 2004 Efficacy of alendronate, a bisphosphonate, in the treatment of AVN of the hip. A prospective open-label study S. Agarwala, D. Jain,
Rheumatology 2005;44:352 359 Advance Access publication 24 November 2004 Efficacy of alendronate, a bisphosphonate, in the treatment of AVN of the hip. A prospective open-label study S. Agarwala, D. Jain,
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research November 28, 2017 Vol.21, No.33
 21 33 2017 11 28 Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research November 28, 2017 Vol.21, No.33 ( 100853). [J]. 2017 21(33): 5388-5393. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.33.022 ORCID: 0000-0002-3162-0662()
21 33 2017 11 28 Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research November 28, 2017 Vol.21, No.33 ( 100853). [J]. 2017 21(33): 5388-5393. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.33.022 ORCID: 0000-0002-3162-0662()
Femoral Head Osteonecrosis in Military Training Recruits: A Report of Two Cases
 MILITARY MEDICINE, 174, 11:1231, 2009 Femoral Head Osteonecrosis in Military Training Recruits: A Report of Two Cases Capt Susan M. Eckert, USAF MC * ; Maj Meredith Warner, USAF MC ; Lt Col James A. Keeney,
MILITARY MEDICINE, 174, 11:1231, 2009 Femoral Head Osteonecrosis in Military Training Recruits: A Report of Two Cases Capt Susan M. Eckert, USAF MC * ; Maj Meredith Warner, USAF MC ; Lt Col James A. Keeney,
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings
 Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SPONTANEOUS AND POST-ARTHROSCOPY OSTEONECROSIS OF THE KNEE
 THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SPONTANEOUS AND POST-ARTHROSCOPY OSTEONECROSIS OF THE KNEE Abstract Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SPONK) and osteonecrosis in the postoperative knee (ONPK) are
THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SPONTANEOUS AND POST-ARTHROSCOPY OSTEONECROSIS OF THE KNEE Abstract Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee (SPONK) and osteonecrosis in the postoperative knee (ONPK) are
Avascular necrosis of the hip treated with Metal-on-Metal. surface hip arthroplasty
 Avascular necrosis of the hip treated with Metal-on-Metal surface hip arthroplasty H Sharma ( ), C Watson, AC Campbell Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Monklands Hospital, Airdrie, Lanarkshire, ML6
Avascular necrosis of the hip treated with Metal-on-Metal surface hip arthroplasty H Sharma ( ), C Watson, AC Campbell Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Monklands Hospital, Airdrie, Lanarkshire, ML6
Long-term clinical results after iloprost treatment for bone marrow edema and avascular necrosis
 Long-term clinical results after iloprost treatment for bone marrow edema and avascular necrosis Tim Claßen, 1 Antonia Becker, 1 Stefan Landgraeber, 1 Marcel Haversath, 1 Xinning Li, 2 Christoph Zilkens,
Long-term clinical results after iloprost treatment for bone marrow edema and avascular necrosis Tim Claßen, 1 Antonia Becker, 1 Stefan Landgraeber, 1 Marcel Haversath, 1 Xinning Li, 2 Christoph Zilkens,
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis
 Rheumatology 2008;47:542 546 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken020 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis C.-J. Wang 1, F.-S. Wang 2, J.-Y. Ko 1, H.-Y. Huang 3, C.-J. Chen 4, Y.-C.
Rheumatology 2008;47:542 546 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken020 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows regeneration in hip necrosis C.-J. Wang 1, F.-S. Wang 2, J.-Y. Ko 1, H.-Y. Huang 3, C.-J. Chen 4, Y.-C.
52, 215 mg kg - 1 d - 1
 212 1218 52 215 mg kg - 1 d - 1 2 8 1/ 4 6 4 ; ; Changes of blood vessels in glucocorticoid2induced avascular necrosis of femoral head in rabbits ZHOU Qiang LI Qihong YANGLiu et al. Department of Orthopaedics
212 1218 52 215 mg kg - 1 d - 1 2 8 1/ 4 6 4 ; ; Changes of blood vessels in glucocorticoid2induced avascular necrosis of femoral head in rabbits ZHOU Qiang LI Qihong YANGLiu et al. Department of Orthopaedics
DOI: /j.issn ORCID: ( )
 20 34 2016 08 19 Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research August 19, 2016 Vol.20, No.34 ( 810001). [J]. 2016 20(34):5163-5168. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.34.023 ORCID: 0000-0003-1929-7900(
20 34 2016 08 19 Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research August 19, 2016 Vol.20, No.34 ( 810001). [J]. 2016 20(34):5163-5168. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.34.023 ORCID: 0000-0003-1929-7900(
A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Avascular Necrosis of the Hip 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
The role of electrical stimulation in the management of avascular necrosis of the femoral head in adults: a systematic review
 Al-Jabri et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:319 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1663-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of electrical stimulation in the management of avascular necrosis of the femoral head
Al-Jabri et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:319 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1663-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of electrical stimulation in the management of avascular necrosis of the femoral head
Right Hip Pain. Timothy Pelkowski, MD Saint Vincent Family Medicine Residency
 Right Hip Pain Timothy Pelkowski, MD Saint Vincent Family Medicine Residency The Case: 44 Year Old Male HPI: In August of 2015 was in the pool doing breast stroke kicking drills Noted the acute onset of
Right Hip Pain Timothy Pelkowski, MD Saint Vincent Family Medicine Residency The Case: 44 Year Old Male HPI: In August of 2015 was in the pool doing breast stroke kicking drills Noted the acute onset of
Evangelia E. Vassalou MD,PhD Radiologist Department of Medical Imaging, Heraklion University Hospital Department of Medical Imaging, Sitia General
 Evangelia E. Vassalou MD,PhD Radiologist Department of Medical Imaging, Heraklion University Hospital Department of Medical Imaging, Sitia General Hospital Osteonecrosis pathophysiology epidemiology imaging
Evangelia E. Vassalou MD,PhD Radiologist Department of Medical Imaging, Heraklion University Hospital Department of Medical Imaging, Sitia General Hospital Osteonecrosis pathophysiology epidemiology imaging
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
Case Study: David. Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip. Age Range During Treatment 16 Years
 Case Study: David Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip Age Range During Treatment 16 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of
Case Study: David Conditions Treated Femoral Neck Fracture with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip Age Range During Treatment 16 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Professor of
Interesting Case Series. Simultaneous Avascular Necrosis of the Lunate and Scaphoid
 Interesting Case Series Simultaneous Avascular Necrosis of the Lunate and Scaphoid Benson J. Pulikkottil, MD, Edward Ruane, MD, Michael E. Scott, DO, Alexandre Philipp Sater, BS, and Joseph E. Imbriglia,
Interesting Case Series Simultaneous Avascular Necrosis of the Lunate and Scaphoid Benson J. Pulikkottil, MD, Edward Ruane, MD, Michael E. Scott, DO, Alexandre Philipp Sater, BS, and Joseph E. Imbriglia,
The use of alendronate in the treatment of. of avascular necrosis of the femoral head FOLLOW-UP TO EIGHT YEARS. S. Agarwala, S. Shah, V. R.
 The use of alendronate in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head FOLLOW-UP TO EIGHT YEARS S. Agarwala, S. Shah, V. R. Joshi From the P. D. Hinduja National Hospital and Medical Research
The use of alendronate in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head FOLLOW-UP TO EIGHT YEARS S. Agarwala, S. Shah, V. R. Joshi From the P. D. Hinduja National Hospital and Medical Research
Mid-term Outcomes of Arthroscopic-Assisted Core Decompression of Pre-collapse Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Minimum of 5 Year Follow-up
 Arthroscopic-Assisted Core Decompression of Pre-collapse Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Minimum of 5 Year Follow-up Mark R. Nazal*, Ali Parsa, Scott D. Martin Sports Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic
Arthroscopic-Assisted Core Decompression of Pre-collapse Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head Minimum of 5 Year Follow-up Mark R. Nazal*, Ali Parsa, Scott D. Martin Sports Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic
Partial hip resurfacing is considered investigational/not medically necessary for all other indications not listed above.
 Subject: Policy #: Current Effective Date: 11/13/2006 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 09/14/2006 Description/Scope Hip resurfacing can be categorized in two ways: as a partial (hemi) hip resurfacing
Subject: Policy #: Current Effective Date: 11/13/2006 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 09/14/2006 Description/Scope Hip resurfacing can be categorized in two ways: as a partial (hemi) hip resurfacing
Yohei Tomaru 1, Tomokazu Yoshioka 2*, Hisashi Sugaya 2, Katsuya Aoto 1, Hiroshi Wada 1, Hiroshi Akaogi 1, Masashi Yamazaki 1 and Hajime Mishima 1
 Tomaru et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:292 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1652-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hip preserving surgery with concentrated autologous bone marrow aspirate transplantation
Tomaru et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:292 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1652-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hip preserving surgery with concentrated autologous bone marrow aspirate transplantation
Evaluation of femoral head necrosis using a volumetric method based on MRI
 1 of 4 Evaluation of femoral head necrosis using a volumetric method based on MRI A. Bassounas 1, D. I. Fotiadis 2, K. N. Malizos 3 MD 1 Medical Physics Division, Medical School, University of Ioannina,
1 of 4 Evaluation of femoral head necrosis using a volumetric method based on MRI A. Bassounas 1, D. I. Fotiadis 2, K. N. Malizos 3 MD 1 Medical Physics Division, Medical School, University of Ioannina,
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
Porous tantalum rods for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head
 of the femoral head Z.H. Liu, W.S. Guo, Z.R. Li, L.M. Cheng, Q.D. Zhang, D.B. Yue, Z.C. Shi, B.L. Wang, W. Sun and N.F. Zhang Department of Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
of the femoral head Z.H. Liu, W.S. Guo, Z.R. Li, L.M. Cheng, Q.D. Zhang, D.B. Yue, Z.C. Shi, B.L. Wang, W. Sun and N.F. Zhang Department of Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing, China
Kienböck s disease stage II in an adolescent with benign outcome
 Kienböck s disease stage II in an adolescent with benign outcome A. Schweizer¹( ), F. Denzler¹, G. Kohler² ¹University Children s Hospital Basel, Orthopaedic Department UKBB, Basel, Switzerland ²Kantonsspital
Kienböck s disease stage II in an adolescent with benign outcome A. Schweizer¹( ), F. Denzler¹, G. Kohler² ¹University Children s Hospital Basel, Orthopaedic Department UKBB, Basel, Switzerland ²Kantonsspital
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Bone 49 (2011) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Bone. journal homepage:
 Bone 49 (2011) 1005 1009 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Bone journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bone Original Full Length Article Autologous bone marrow cell implantation in the treatment
Bone 49 (2011) 1005 1009 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Bone journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bone Original Full Length Article Autologous bone marrow cell implantation in the treatment
Removing the Rust-A Seminar for the Seasonal Runner. David Bernhardt, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Orthopedics and Rehab
 Removing the Rust-A Seminar for the Seasonal Runner David Bernhardt, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Orthopedics and Rehab Objectives Formulate a plan to start running, improving your fitness Understand
Removing the Rust-A Seminar for the Seasonal Runner David Bernhardt, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Orthopedics and Rehab Objectives Formulate a plan to start running, improving your fitness Understand
MRI Evaluation of Post Core Decompression Changes in Avascular Necrosis of Hip
 Original Article MRI Evaluation of Post Core Decompression Changes in Avascular Necrosis of Hip DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/13995.6967 Radiology Section Madhavi Nori 1, Sravan Kumar Marupaka 2, Swathi Alluri
Original Article MRI Evaluation of Post Core Decompression Changes in Avascular Necrosis of Hip DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/13995.6967 Radiology Section Madhavi Nori 1, Sravan Kumar Marupaka 2, Swathi Alluri
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology
 Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia
 Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
Hyperbaric Oxygen Utilization in Wound Care
 Hyperbaric Oxygen Utilization in Wound Care Robert Barnes, MD, CWS Hyperbaric Center Sacred Heart Medical Center Riverbend Springfield, Oregon No relevant disclosures Diabetes and lower extremity wounds
Hyperbaric Oxygen Utilization in Wound Care Robert Barnes, MD, CWS Hyperbaric Center Sacred Heart Medical Center Riverbend Springfield, Oregon No relevant disclosures Diabetes and lower extremity wounds
Core decompression with bone grafting combined with arterial perfusion in treating early osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (7): 3237-3241 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Core decompression with bone grafting combined with arterial perfusion in treating early osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (7): 3237-3241 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Core decompression with bone grafting combined with arterial perfusion in treating early osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Topical Oxygen Wound Therapy (MEDICAID)
 Topical Oxygen Wound Therapy (MEDICAID) Last Review Date: September 8, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.15C8v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Topical Oxygen Wound Therapy (MEDICAID) Last Review Date: September 8, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.15C8v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or
Prediction of posttraumatic femoral head osteonecrosis by quantitative intraosseous aspirate and core biopsy analysis: A prospective study
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 486-492 ORIGINAL STUDY Prediction of posttraumatic femoral head osteonecrosis by quantitative intraosseous aspirate and core biopsy analysis: A prospective study Ramesh Kumar
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 486-492 ORIGINAL STUDY Prediction of posttraumatic femoral head osteonecrosis by quantitative intraosseous aspirate and core biopsy analysis: A prospective study Ramesh Kumar
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Marrow Edema of the Medial Compartment of the Knee: A Comparative Study
 Original Paper Received: February 10, 2016 Accepted: October 25, 2016 Published online: October 25, 2016 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Marrow Edema of the Medial
Original Paper Received: February 10, 2016 Accepted: October 25, 2016 Published online: October 25, 2016 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Is Effective in the Treatment of Bone Marrow Edema of the Medial
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature
 Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments.
 CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
A bone preserving solution... to help recapture a patient s way of life.
 A bone preserving solution... to help recapture a patient s way of life. Biomet s ReCap Femoral Resurfacing System offers: Time-buying bridge between hemi and total hip arthroplasty for the patient suffering
A bone preserving solution... to help recapture a patient s way of life. Biomet s ReCap Femoral Resurfacing System offers: Time-buying bridge between hemi and total hip arthroplasty for the patient suffering
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Treatment of Venous ulcers utilizing n-butyl Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue)
 Treatment of Venous ulcers utilizing n-butyl Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue) Awais Siddique MD Endovascular Radiologist AZH WAVE CENTERS Milwaukee WI Venous disease Etiology Are the result of Venous valvular
Treatment of Venous ulcers utilizing n-butyl Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue) Awais Siddique MD Endovascular Radiologist AZH WAVE CENTERS Milwaukee WI Venous disease Etiology Are the result of Venous valvular
Plate Exposure after Reconstruction by Plate and Anterolateral Thigh Flap in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with composite mandibular Defects
 Plate Exposure after Reconstruction by Plate and Anterolateral Thigh Flap in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with composite mandibular Defects Chia-Hsuan Tsai/ Huang-Kai Kao M. D. Introduction Malignant
Plate Exposure after Reconstruction by Plate and Anterolateral Thigh Flap in Head and Neck Cancer Patients with composite mandibular Defects Chia-Hsuan Tsai/ Huang-Kai Kao M. D. Introduction Malignant
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Isolated Subtalar Arthrodesis for Avascular Necrosis of the Talus
 Isolated Subtalar Arthrodesis for Avascular Necrosis of the Talus Travis J. Dekker, MD Manuel J. Pelligrini, MD Adam P. Schiff, MD James K. DeOrio, MD Mark E. Easley, MD James A. Nunley, MD Samuel B. Adams,
Isolated Subtalar Arthrodesis for Avascular Necrosis of the Talus Travis J. Dekker, MD Manuel J. Pelligrini, MD Adam P. Schiff, MD James K. DeOrio, MD Mark E. Easley, MD James A. Nunley, MD Samuel B. Adams,
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
THE ADVANTAGES OF INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION AND CRYOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR POST-OPERATIVE PATIENT CARE
 THE ADVANTAGES OF INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION AND CRYOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR POST-OPERATIVE PATIENT CARE WWW.GAMEREADY.COM 1.888.426.3732 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION SURGERIES THAT BENEFIT FROM INTERMITTENT
THE ADVANTAGES OF INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION AND CRYOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR POST-OPERATIVE PATIENT CARE WWW.GAMEREADY.COM 1.888.426.3732 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION SURGERIES THAT BENEFIT FROM INTERMITTENT
Hip Resurfacing.
 Hip Resurfacing http://www.birminghamhipresurfacing.com/hipresurfacing/technology.cfm The end of the femur is capped somewhat like a tooth cap The hip socket receives a cupped implant to move together
Hip Resurfacing http://www.birminghamhipresurfacing.com/hipresurfacing/technology.cfm The end of the femur is capped somewhat like a tooth cap The hip socket receives a cupped implant to move together
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmission Following Hip Arthroscopy
 Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmission Following Hip Arthroscopy Matthew Hartwell, MD Allison Morgan, BA Daniel Johnson, MD Richard Nicolay, MD Ryan Selley, MD Michael Terry, MD Vehniah Tjong, MD Disclosures
Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmission Following Hip Arthroscopy Matthew Hartwell, MD Allison Morgan, BA Daniel Johnson, MD Richard Nicolay, MD Ryan Selley, MD Michael Terry, MD Vehniah Tjong, MD Disclosures
CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS
 CASE REPORT CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS Bruno Dutra Roos 1, Milton Valdomiro Roos 2, Antero
CASE REPORT CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS Bruno Dutra Roos 1, Milton Valdomiro Roos 2, Antero
Dr. Mont Interview, Baltimore, MD
 Dr. Mont Interview, Baltimore, MD Interviewed by Vicky Marlow on September 1, 2008 1.) How did you get started with Hip Resurfacing and tell us about your background and experience as a surgeon. Where
Dr. Mont Interview, Baltimore, MD Interviewed by Vicky Marlow on September 1, 2008 1.) How did you get started with Hip Resurfacing and tell us about your background and experience as a surgeon. Where
Effect of age, sex, co morbidities, delay in surgery and complications on outcome in elderly with proximal femur fractures
 2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
2018; 4(3): 498-506 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 498-506 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 27-05-2018 Accepted: 28-06-2018 P Venu Gopala Reddy Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Metha Short Hip Stem System
 Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Operations about Hip in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Patients
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:22-27 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.22 Operations about Hip in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Patients Jeong Joon Yoo, MD, Sae Hyung Chun, MD, Young
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:22-27 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.22 Operations about Hip in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Positive Patients Jeong Joon Yoo, MD, Sae Hyung Chun, MD, Young
Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Treatment and evolution.
 Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Treatment and evolution. J. R. Valentí Nín; M. Leyes; D. Schweitzer ABSTRACT We performed a retrospective study on 21 patients affected by unilateral spontaneous
Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Treatment and evolution. J. R. Valentí Nín; M. Leyes; D. Schweitzer ABSTRACT We performed a retrospective study on 21 patients affected by unilateral spontaneous
PROGRESSION OF AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF FEMORAL HEAD AND CHOICE OF TREATMENT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 54. 00-00, 1992 Invited Article PROGRESSION OF AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF FEMORAL HEAD AND CHOICE OF TREATMENT HISASHI IWATA, YUKIHARU HASEGAWA, MASANORI MIZUNO, EIICHI GENDA, YUJI KATAOKA
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 54. 00-00, 1992 Invited Article PROGRESSION OF AVASCULAR NECROSIS OF FEMORAL HEAD AND CHOICE OF TREATMENT HISASHI IWATA, YUKIHARU HASEGAWA, MASANORI MIZUNO, EIICHI GENDA, YUJI KATAOKA
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29800 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moojen, Wouter Anton Title: Introducing new implants and imaging techniques for
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29800 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moojen, Wouter Anton Title: Introducing new implants and imaging techniques for
Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improve Bone Regeneration With Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improve Bone Regeneration With Mesenchymal Stem Cells Johannes Schneppendahl, MD 1, Jan Grassmann, MD 1, Marcel Betsch, M.D. 2, Michael Wild, MD, PhD 3, Mohssen Hakimi, MD,
Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improve Bone Regeneration With Mesenchymal Stem Cells Johannes Schneppendahl, MD 1, Jan Grassmann, MD 1, Marcel Betsch, M.D. 2, Michael Wild, MD, PhD 3, Mohssen Hakimi, MD,
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria
 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Date of origin: 1995 Last review date: 2009 Clinical Condition: Variant 1: Avascular Necrosis (steonecrosis) of the Hip Initial study when avascular
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Date of origin: 1995 Last review date: 2009 Clinical Condition: Variant 1: Avascular Necrosis (steonecrosis) of the Hip Initial study when avascular
Osteochondritis Dissecans
 Osteochondritis Dissecans Introduction Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a problem that affects the knee, mostly at the end of the big bone of the thigh (the femur). A joint surface damaged by OCD doesn't
Osteochondritis Dissecans Introduction Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a problem that affects the knee, mostly at the end of the big bone of the thigh (the femur). A joint surface damaged by OCD doesn't
Unique MRI Findings as an Early Predictor of Osteonecrosis in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Sansgiri et al. MRI of Osteonecrosis Associated With Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pediatric Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Rakhee Kisan Sansgiri 1 Michael
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Sansgiri et al. MRI of Osteonecrosis Associated With Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pediatric Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Rakhee Kisan Sansgiri 1 Michael
Plantar fasciitis: p. 1/6
 Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT. Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad
 Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006
 The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
Relationship of Idiopathic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head to Perfusion Changes in the Proximal Femur by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Chan et al. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI of Femoral Idiopathic Osteonecrosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Wing P. Chan 1,2 Yi-Jui Liu 3 Guo-Shu Huang
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Chan et al. Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI of Femoral Idiopathic Osteonecrosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Wing P. Chan 1,2 Yi-Jui Liu 3 Guo-Shu Huang
pissn: , eissn: Yonsei Med J 54(2): , 2013
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.510 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(2):510-515, 2013 Clinical Results of Auto-Iliac Cancellous Bone Grafts Combined with Implantation
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.510 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(2):510-515, 2013 Clinical Results of Auto-Iliac Cancellous Bone Grafts Combined with Implantation
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs)
 Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
What Is the Radiographic Prevalence of Incidental Kienböck Disease?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:808 813 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4541-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Is the
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2016) 474:808 813 DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4541-1 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Is the
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...)
 Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Subchondral Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Head in a Pregnant Woman with Pre-existing Anorexia Nervosa
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2018, 245, 1-5 SIF of the Femoral Head in Pregnancy 1 Subchondral Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Head in a Pregnant Woman with Pre-existing Anorexia Nervosa Kyoko Kasahara,
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2018, 245, 1-5 SIF of the Femoral Head in Pregnancy 1 Subchondral Insufficiency Fracture of the Femoral Head in a Pregnant Woman with Pre-existing Anorexia Nervosa Kyoko Kasahara,
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa
 Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa Hywel Davies BSc ( ),Andrew J Unwin BSc, Nick P H Morgan BSc Windsor Knee Clinic, Windsor, United Kingdom Correspondence: Hywel Davies, Windsor
Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa Hywel Davies BSc ( ),Andrew J Unwin BSc, Nick P H Morgan BSc Windsor Knee Clinic, Windsor, United Kingdom Correspondence: Hywel Davies, Windsor
ARTICLE IN PRESS. All-Patient Refined Diagnosis- Related Groups in Primary Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2009 All-Patient Refined Diagnosis- Related Groups in Primary Arthroplasty Carlos J. Lavernia, MD,*y Artit Laoruengthana, MD,y Juan S. Contreras, MD,y and Mark
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2009 All-Patient Refined Diagnosis- Related Groups in Primary Arthroplasty Carlos J. Lavernia, MD,*y Artit Laoruengthana, MD,y Juan S. Contreras, MD,y and Mark
Blood Transfusion Practice Indicated by Paediatric Intensive Care Specialists in Response to Four Clinical Scenarios
 Original articles Blood Transfusion Practice Indicated by Paediatric Intensive Care Specialists in Response to Four Clinical Scenarios E. NAHUM, J. BEN-ARI, T. SCHONFELD Paediatric Intensive Care Unit,
Original articles Blood Transfusion Practice Indicated by Paediatric Intensive Care Specialists in Response to Four Clinical Scenarios E. NAHUM, J. BEN-ARI, T. SCHONFELD Paediatric Intensive Care Unit,
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis. American University of Beirut Medical Center
 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/30/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 79 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Functional Outcomes After Fracture-dislocation Of The Ankle
 Functional Outcomes After Fracture-dislocation Of The Ankle Direk Tantigate, MD, Gavin Ho, BA, Joshua Kirschenbaum, Christina E Freibott, BA, Benjamin Ascherman, BA, Justin K Greisberg, MD, J. Turner Vosseller,
Functional Outcomes After Fracture-dislocation Of The Ankle Direk Tantigate, MD, Gavin Ho, BA, Joshua Kirschenbaum, Christina E Freibott, BA, Benjamin Ascherman, BA, Justin K Greisberg, MD, J. Turner Vosseller,
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder a Risk for Kohler s Disease? Osteonecrosis of Navicular Bone of Foot
 Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder a Risk for Kohler s Disease? Osteonecrosis of Navicular Bone of Foot Ozgur Basal, Halil Burc, Tolga Atay Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Faculty
Is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder a Risk for Kohler s Disease? Osteonecrosis of Navicular Bone of Foot Ozgur Basal, Halil Burc, Tolga Atay Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Faculty
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
The rate of success of transtrochanteric rotational
 Trochanteric rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head THE USE OF MRI IN THE SELECTION OF PATIENTS K.-H. Koo, H.-R. Song, J.-W. Yang, P. Yang, J.-R. Kim, Y.-M. Kim From the Gyeong-Sang
Trochanteric rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head THE USE OF MRI IN THE SELECTION OF PATIENTS K.-H. Koo, H.-R. Song, J.-W. Yang, P. Yang, J.-R. Kim, Y.-M. Kim From the Gyeong-Sang
Coverage Guideline. BioniCare System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) DEFINITION COVERAGE CRITERIA MEDICAL BACKGROUND
 Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Are You Living with. Hip Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you.
 Are You Living with Hip Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Hip pain shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Understanding Common Causes of Hip Pain If you are one of
Are You Living with Hip Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Hip pain shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Understanding Common Causes of Hip Pain If you are one of
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Core Decompression for Avascular
 Page 1 of21 Aetna Better Health 2000 Market Street, Suite 850 Philadelphia, PA 19103 AETNA BETTER HEALTH Clinical Policy Bulletin: Core Decompression for Avascular Necrosis Revised April 2014 Number: 0753
Page 1 of21 Aetna Better Health 2000 Market Street, Suite 850 Philadelphia, PA 19103 AETNA BETTER HEALTH Clinical Policy Bulletin: Core Decompression for Avascular Necrosis Revised April 2014 Number: 0753
Osteoporosis. Overview
 v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
Are There Clinical Meaning on Asymptomatic Pulmonary Embolism After Total Knee Arthroplasty?
 Are There Clinical Meaning on Asymptomatic Pulmonary Embolism After Total Knee Arthroplasty? * 1,2 ATSUSHI SATO, MD, PhD, * 1,2 Takayuki Koya, * 2,3 Hiroshi Takagi, * 2 Jun Oike,, * 2 Saki Yagura, * 2
Are There Clinical Meaning on Asymptomatic Pulmonary Embolism After Total Knee Arthroplasty? * 1,2 ATSUSHI SATO, MD, PhD, * 1,2 Takayuki Koya, * 2,3 Hiroshi Takagi, * 2 Jun Oike,, * 2 Saki Yagura, * 2
Whole body MR in patients with multiple myeloma
 Whole body MR in patients with multiple myeloma Alina Piekarek, Piotr Sosnowski, Adam Nowicki, Mieczysław Komarnicki Received: 11.05.2009 Accepted: 13.07.2009 Subject: original article Clinical Radiology
Whole body MR in patients with multiple myeloma Alina Piekarek, Piotr Sosnowski, Adam Nowicki, Mieczysław Komarnicki Received: 11.05.2009 Accepted: 13.07.2009 Subject: original article Clinical Radiology
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion
 Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Long Term Re-Operation Rate After Open Versus Endoscopic Release Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 24 Number 1 Long Term Re-Operation Rate After Open Versus Endoscopic Release Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome D Ip, N Fu Citation D Ip, N Fu. Long Term
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 24 Number 1 Long Term Re-Operation Rate After Open Versus Endoscopic Release Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome D Ip, N Fu Citation D Ip, N Fu. Long Term
