Unipolar Versus Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIP THE HEMIARTHROPLASTY IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL Unipolar Versus Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly Ali A. Ali, Saad M. Rashed, Mushtaq T. Hussien ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: Hip fractures are associated with high morbidity and mortality, which require a treatment plan that ensures a good outcome with minimal complications. Different treatment modalities and arthroplasty prosthesis are available and widely used. OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was to compare the short outcome of surgical treatment of femoral neck fractures in elderly using unipolar and bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Thirty four patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures ranging from Garden s class II to class IV were enrolled in the study for surgical intervention using either unipolar hemiarthroplasty (Group A: 14females, 6 males) or bipolar hemiarthroplasty (Group B: 10 females, 4 males). Patients were followed up for up to 2 years by Harris Hip Score to assess the outcome of the surgery. RESULTS: The average hip score for patients per group over the whole follow-up period showed better results in group B than in group A. Average score results were higher in all grades among group B patients. However, the difference from scores of group A patients was statistically insignificant (p>0.05). Patients of both groups had a negative correlation of age to score outcome regardless of sex and grade of fracture. In group A patients, score points for pain, stiffness, range of motion and support/locomotion were all higher during the first six months of follow up. The scores started to decline gradually after 18 months towards the end of the follow up period. In group B patients, the score points for the same parameters were all significantly lower than Group A patients during the first 3-6 months of follow up but started to increase to significantly higher levels towards the end of the follow up period. CONCLUSION: The short-term advantages of unipolar hemiarthroplasty may outweigh its long-term complications in elderly patients with limited daily activities and/or associated serious medical illnesses. In younger age patients with more ambulatory activities and greater life expectancy, bipolar hemiarthroplasty offers a better solution. KEYWORDS: femoral neck fractures, unipolar/bipolar hemiarthroplasty, austen-moore. INTRODUCTION: The hip (coxofemoral) joint is a large and stable diarthroidal ball-and-socket joint formed by the articulation between the femoral head and the acetabulum of the pelvis (1). It has a great deal of mobility, which allows normal locomotion in the performance of daily activities (2). With great stability, the joint bears the body weight and permits standing upright with little expenditure of Al-Mustansiriya University, College of Medicine, Department of Surgery. energy in the form of muscle contraction. With good range of movement, it permits bipedal movement and acceleration (3). Hip fracture refers to a fracture occurring in the area between the edge of the femoral head and 5 centimeters below the lesser trochanter. Femoral neck fractures tend to occur in elderly patients who fall. In younger individuals, femoral neck fractures generally occur as a result of major trauma due to axial loading on the femur (4). Proximal (intracapsular) femoral neck fractures are estimated THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 475
2 to be ten times more common than extracapsular fractures (5). Intracapsular femoral neck fractures have a relatively high rate of complications compared with extracapsular fractures. Potential complications following such fractures with or without surgical intervention include: infection, chronic pain, dislocation, nonunion, avascular necrosis, and posttraumatic arthritic changes (6). Because of lack of muscular attachment to the femoral neck and head, displaced femoral neck fractures are commonly associated with retinacular tearing and avascular necrosis of the femoral head (7). There is a continuous debate as to whether; open reduction with internal fixation (ORIF) or arthroplasty is the best treatment for appropriate adult surgical candidates with femoral neck fractures. Arthroplasty has three main advantages: (1) it allows early weight bearing and avoidance of complications of recumbency, (2) it eliminates avascular necrosis and nonunion as potential complications and, (3) it has significantly lower reoperation rates (8). Another ongoing controversy is related to the type of arthroplasty, partial or total, that is best suitable for a selected category of patients. Uncertainty as to which type of endoprosthesis is the ideal choice for treatment of fractures in older patients leads to significant variation in the use of each intervention internationally (9). The aim of this study was to compare the short outcome of surgical treatment of femoral neck fractures in elderly using unipolar and bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty. PATIENTS AND METHODS: The study was conducted in Al-Yarmouk Teaching Hospital, Department of orthopedic Surgery over the time period extending from February 2012 to February Thirty nine patients with femoral neck fractures were enrolled in the study but five of them passed away at different times postoperatively due to causes not related to the surgical procedure, and were excluded from the study. The 34 patients included in the study were divided into two groups according to the type of hip hemiarthroplasty. Group A patients underwent unipolar hip hemiarthroplasty surgery while group B patients had bipolar hemiarthroplasty. Group A consisted of 20 patients (14 females, 6 males) with an average age of 70.7 years. Group B consisted of 14 patients (10 females, 4 males) with an average age of 64.6 years. The selection of a patient for the type of surgery was made on the basis of age and associated medical illnesses. Patients < 60 years were excluded from the study. Those who were > 60 years and had no associated serious medical illnesses were included in group B. Those who were > 60 years and had serious chronic illnesses were included in group A, because of less operative time in unipolar surgery with less exposure to anesthesia, less bleeding risk and less reaming with subsequent less risk of fat embolism. All the patients had the same mechanism of injury, a trivial fall causing femoral neck fracture. None of the patients had acetabular fractures or other bone pathology. The fracture was graded according to Garden s classification (10) as shown in table 1. Most patients had type III or IV Garden s fracture (figure 1). THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 476
3 Table 1: Distribution of patients with femoral neck fracture undergoing unipolar (group A) or bipolar (group B) hip hemiarthroplasty according to age, sex and fracture grade. Sex Garden s Classification of femoral neck fracture Group Mean Age (years) Male Female I II III IV A (n=20) B (n=14) Garden s Classification of femoral neck fractures (10) : Garden I: incomplete or impacted fracture, in which the trabeculae of the inferior neck are still intact; femoral head is tilted in a posterolateral direction, causing vaglus angulation. Garden II: complete but undisplaced fracture with varus deformity. Garden III: complete fracture with partial displacement; the two fragments still in contact. Garden IV: complete fracture with total displacement; no continuity between proximal and distal fragments;femoral head assumes its normal position within the acetabulum. Figure 1: AP X-ray of two patients with Garden s class III (left) and class IV (right) femoral neck fractures indicated by the red arrow. Surgical Procedure All the patients underwent surgery with a standard posterior approach in lateral position under general or spinal anesthesia within two weeks of the time of injury. For the unipolar hip hemiarthroplasty, the Austin Moore approach was used. An incision was made from a point 5cm inferolateral to the posterior inferior iliac spine and extended anterior to the greater trochanter where it continued vertically downwards over the line of the femur for about 10 cm, the gluteus maximus was split in the direction of its fibers and its margins were retracted to reveal the short transverse muscles of the hip that were then divided near their insertion and reflected to expose the back of the joint capsule. The joint capsule was opened close to the greater trochanter. The fracture was shown by internal rotation of the lower limb and the head of femur became obvious. A corkscrew was used to remove the head from the acetabulum. After the femoral head was removed, the diameter of the head was measured to determine the approximate size of the head of the chosen prosthesis. The neck was then cut according to the template of the used surgical set. The femoral canal was carefully detected with a long curette and then was prepared by graduated reaming using broaches. A non-cemented Austin Moore prosthesis (TREU-INSTRUMENTE, Germany) of appropriate size was inserted with 20º of internal rotation in relation to the lesser trochanter (figure 2). Hip examination was done to ensure stability and suturing in layers was done with suction drain left. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 477
4 Figure 2: The unipolar (Austin-Moore) prosthesis inserted in position. For the bipolar hemiarthroplasty, the same surgical approach was used but with the head removed, acetabular sizers were used to verify the correct diameter of the prosthesis cup. Two types of broaches were used for preparing the femoral canal: type A for distal femoral canal reaming and type B for proximal femoral trochanteric reaming. In the last reaming broach, a trial head with different offsets has been assembled with a trial cup and reduction was done to determine the joint stability. The appropriate head offset was chosen according to this maneuver. After removal of the trial prostheses, an appropriate size cementless femoral stem and 28 mm head of appropriate offset were assembled in a modular fashion. Finally, a polyethylene acetabular shell component (B BRAUN AESCULAP, Germany) was secured (figure 3) on the assembly and the hip joint was reduced as mentioned above. All patients were encouraged to become ambulatory on the second day of the operation with the aid of a walker and minimum weight bearing. AP X-rays were taken at that day (figure 4). Figure 3: The bipolar (Aesculap) prosthesis inserted in position. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 478
5 Figure 4: Postoperative AP X-ray of the hip after unipolar (left) and bipolar (right) hemiarthroplasty. The drains were removed 48 hours postoperatively and patients were discharged. Each patient was seen one week after surgery and at two weeks for suture removal. Follow up and Hip scoring Follow up assessment started one month after surgery. Patients were assessed every month for three months and then every 3 months for up of 2 years. Harris hip scoring system (11) was used in the assessment. It covers five main aspects that include pain (0-44 points), limb length discrepancy (0-11 points), support and locomotion (0-36 points), stiffness/deformity (0 or 4 points) and range of motion (0-5 points). The score gives a maximum of 100 points and its results have been graded as shown in table 2. Table 2: Grading system for Harris hip score (11). Harris hip score Grade Excellent Good Fair < 70 Poor Radiographs were also taken with each visit to assess implant stability and look for any signs of loosening or other complications (e.g. acetabular erosion). RESULTS: The average hip score for patients per group over the whole follow-up period showed better results in group B than in group A as shown in figure 5. In group B, half the patients maintained an excellent score, 29% had good score results and only 21% had fair results. In group A, most of the patients were equally distributed between excellent and good score results (35% each), while 30% maintained fair results. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 479
6 Figure 5: Patients distribution according to average Harris Hip Score grade. The average scores for each category in each group are shown in table 3. Average score results were higher in all grade among group B patients. However, the difference from scores of group A patients was statistically insignificant (p>0.05). Table 3: Number of patients (n) and average Harris hip score results according to grade between patients treated with unipolar and bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty over a period of 2 years follow up (score represents Mean± SD). Group A (n= 20) B (n= 14) Harris Hip Score Grade Excellent Good Fair Number Score (points) Number Score (points) Number Score (points) 7 92± ± ± ± ± ±1.4 It was noted that patients of both groups had a negative correlation of age to score outcome regardless of sex and grade of fracture (figure 6). Figure 6: Correlation between patients age and Harris Hip Score outcome after unipolar or bipolar hemiarthroplasty. The hip score also showed considerable differences during the follow up period in each group. In group A patients (figure 7), score points for pain, stiffness, range of motion and support/locomotion were all higher during the first six months of follow THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 480
7 up. The scores started to decline gradually after 18 months towards the end of the follow up period. Limb length discrepancy score points were initially slightly lower than in Group B patients and maintained an almost stable level during follow up. Figure 7: Time line changes in Harris Hip Score points categories in patients with unipolar hip hemiarthroplasty (group A). In group B patients (figure 8), the score points for pain, stiffness, range of motion and support/locomotion were all significantly lower than Group A patients during the first 3-6 months of follow up but started to increase to significantly higher levels towards the end of the follow up period (especially after months). Limb length discrepancy scores were higher than in Group A patients throughout the follow up time. However, limb length discrepancy did not exceed 1-2 cm in neither group A nor group B patients resulting in no or very slight limping. Therefore, score points for this category were not significantly different between the two groups. Figure 8: Time line changes in Harris Hip Score point s categories in patients with bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty (group B). Radiological examination follow up showed good implant fitting and bone structure in all patients during the first months of follow-up (figure 9). THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 481
8 Figure 9: Follow up AP X-ray of the hip after unipolar (left) and bipolar (right) hemiarthroplasty. However, two patients of group A showed early radiological signs of loosening after months including radiolucent line around the prosthesis and a change in the position of the implant from neutral to varus (figure 10) but neither had any clinical complaint of loosening. Three diabetic patients (2 from group A and 1 from group B) developed wound infection that was treated conservatively with antibiotics and good glycaemic control. This complication did not reach the level of implant removal nor require revision surgery. Other complications commonly encountered in hip replacement surgery like joint dislocation and acetabular protrusion did not develop in any patient during the follow up period. Figure 10: AP X-ray of a hip with unipolar hemiarthroplasty, 24 months after surgery showing a radiolucent line around the prosthesis and a change in the position of the head towards varus, considered as early radiological signs of implant loosening. THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 482
9 DISCUSSION: A hip fracture is associated with high morbidity and mortality, which necessitates a treatment plan to achieve a good outcome as soon as possible. Equally important is that evaluation of different treatment modalities (12). There is a universal agreement that unipolar or bipolar hemiarthroplasty is the preferred method for treating displaced intracapsular femoral neck fractures in elderly patients with low functional demands in the absence of degenerative disorders of the hip (13). Reported advantages of Unipolar over Bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty are less complex surgery, shorter operation times, less blood loss, and lower initial costs (14). Being the main treatment option for displaced femoral neck fractures, hemiarthroplasties are performed in great numbers worldwide. In spite of this, these procedures are seldom registered nationally and there is little evidence regarding the best choice of implant design and surgical technique (15). In the current study, the same surgical approach (posterior approach) was used for all patients. This kept discrepancies limited to the type of prosthesis used. The patient groups had an age difference of 7-8 years, but in both groups, older age was always associated with lower Harris Hip Score. This may be related to the lower activity levels and association with other medical illnesses that limit mobility and ambulation. Non-cemented prosthesis were used in all patients depending on recent reports that uncemented, modular hemiarthroplasty has given equivalent results to cemented hemiarthroplasty in terms of functional outcomes, complications, and mortality (16). In both groups, early assisted ambulation (within 48 hr of surgery) was used because it has proven to accelerate functional recovery (17). During the first 3-6 months of postoperative follow up, group A patients showed better hip scores than group B patients. The scores normalized over the following 6 months but started to decline for group A patients and improve for group B patients. These results are consistent with reports of Raia et al. & Calder et al. in most hip score aspects, especially pain (18 & 19). Pain appears to be the main influential factor on other aspects of the hip score like range of motion, stiffness, locomotion and support. Development or persistence of pain may be related to the mechanism action of each of the unipolar and bipolar prostheses. In Group A patients, pain became problematic enough to affect the hip score and its aspects in the later periods of follow up but not the early months. This is related to the proximal load transfer principle of the prosthesis. With good calcar-collar support, the stresses in the stem are small because the stem portion of the prosthesis and the bone are uncoupled and, consequently, do not share the resultant bending moment of the head and abductor forces. In later months the same load transfer principal resulted in early loosening which in turn resulted in pain and limitation of movement and support. A reduction of calcar-collar support over time with proximal fixation resulted in high stresses in the stem and stress shielding of the proximal medial cortex which may have lead to the migration of the stem tip to the valgus position (20). In group B patients, the pain factor was influential on the hip score during the early months of follow up but faded off later on. This is also related to the mechanism of action of the prosthesis which depends on bone ingrowth for support as the psrosthesis is porous coated and requires bone ingrowth for better fixation of bone. The early inability to achieve weight-bearing capacity is most likely related to the lack of mechanical support for transferring loads from the hip to the axial skeleton in the absence of bone ingrowth in the first few months postoperatively. As bone growth proceeded, enough support existed to limit pain and increase range of movement (21). Moreover, the bipolar prosthesis has two bearing surfaces; load and frictional torque can theoretically be absorbed in part by the metal on polyethylene inner bearing reducing the magnitude of forces between the implant and acetabulam and providing better range of motion and less stiffness (22). Although pain scores were lower in this group in the first few months of follow up, other score categories like range of motion and locomotion were higher compared to group A due to younger age patients with more activity and ambulation. This brought the total score nearly to the same level of group A patients. Limb length discrepancy was noticed and more pronounced in group A patients possibly due to factors related to alignment of the prosthetic stem, length of head offset and calcar seating. Individual differences exist and may be responsible for some discrepancy (23). Contradictively, Mishra et al. described more limb length discrepancy with bipolar hemiarthroplasty but, similar to our study, the discrepancy was not severe to cause THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 483
10 troublesome limping (24). The discrepancy was seen less in group B patients possibly due to the trials of many sizes of head offsets with subsequent choosing of the most appropriate size. Dislocation of the prosthesis did not develop in the current study due to maintenance of the femoral head at 20 o anteversion in relation to the lesser trochanter which puts the prosthesis in the nearest anatomical position. Moreover, being a hemiarthroplasty, the acetabulum maintained its normal status alignment. Acetabular protrusion is commonly reported in Austin-Moore hemiarthroplasty due to the direct impaction of the metallic head on the arthritic acetabulum. It is less recorded in bipolar hemiarthroplasty due to the presence of the cup that transfers forces to the acetabular rim. The complication was not seen in any of our patients most probably due to their age which is associated with less physical activity and ambulation that is insufficient to cause acetabular damage during the period of the follow up of two years. CONCLUSION: Hemiarthroplasty is considered the optimal treatment for elderly patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures and produce satisfactory results. While bipolar prosthesis enables reduction of acetabular wear and increase in prosthesis life and function, unipolar hemiarthroplasty using the Austin Moore s remains a popular choice. The current study shows that the short-term advantages of unipolar hemiarthroplasty may outweigh its long-term complications in elderly patients with limited daily activities and/or associated medical illnesses. In less age patients with more ambulatory activities and greater life expectancy, bipolar hemiarthroplasty offers a better solution. REFERENCES: 1. Levangie PK and Norkin CC. Joint structure and function: a comprehensive analysis. In: Ch4: The hip complex, Martin RL and Kivlan B (eds.). FA Davis, PA USA. 2011: Norden M and Frankel V. Basic biomechanics of the musculoskeletal system. In: biomechanics of joints. Lippincot and Williams, PA USA, 2001: Standring S. Grey s anatomy. The anatomical basis of clinical practice. 39th ed. London: Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2005: Print. 4. Kanis JA, Odén A, McCloskey EV, Johansson H, Wahl DA & Cooper C. A systematic review of hip fracture incidence and probability of fracture worldwide. Osteoporosis International 2012;23: Guilley E, Herrmann F, Rapin CH, Hoffmeyer P, Rizzoli R &Chevalley T. Socioeconomic and living conditions are determinants of hip fracture incidence and age occurrence among community-dwelling elderly. Osteoporosis International 2011;22: Eiff MP, Hatch RL&Calmbach WL. Femur and pelvis fractures. In: Fracture Management for Primary Care, 2 nd, Saunders, Philadelphia Bachiller FG, Caballer AP& Portal LF. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head after femoral neck fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002: Parker MJ, Gurusamy K. Internal fixation versus arthroplasty for intracapsular proximal femoral fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006; CD Hopley C, Stengel D, Ekkernkamp A & Wich M. Primary total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced intracapsular hip fractures in older patients: systematic review. BMJ 2010; 340:c Canale ST & Beaty JH (editors). Campbell s operative orthopedics. 11 th edition, Mosby Co., Toronto 2008, Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51: Gjertsen JE, VinjeT, Lie SA, EngesæterLB,Havelin LI, Furnes O &Fevang JM. Patient satisfaction, pain, and quality of life 4 months after displaced femoral neck fractures: A comparison of 663 fractures treated with internal fixation and 906 with bipolar hemiarthroplasty reported to the Norwegian Hip FractureRegister. ActaOrthopaedica 2008;79: Van den Bekerom MP, Sierevelt IN, Bonke H &Raaymakers EL. The natural history of the hemiarthroplasty for displaced intracapsular femoral neck fractures: 302 patients followed until revision or death. ActaOrthopaedica 2013;84: Keating JF, Grant A, Masson M, Scott NW& Forbes JF. Displaced intracapsular hip fractures in fit, older people: a randomised comparison of reduction and fixation, bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty. HealthTechnol Assess 2005;9: THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 484
11 15. Rogmark C, Fenstad AM, Leonardsson O, Engesæter LB, KärrholmJ,Furnes O, Garellick G &Gjertsen JE. Posterior approach and uncemented stems increases the risk of reoperation after hemiarthroplasties in elderly hip fracture patients: An analysis of 33,205 procedures in the Norwegian and Swedish national registries. ActaOrthopaedica 2014; 85: Taylor F, Wright M & Zhu M. Hemiarthroplasty of the hip with and withoutcement: A randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 2012; 94: Kos N, Burger H&Vidmar G. Mobility and functional outcomes after femoral neck fracture surgery inelderly patients: a comparison between hemiarthroplasty and internal fixation. DisabilRehabil, 2011;33: Raia FJ, Chapman CB, Herrera MF, Schweppe MW, MichelsenCB, Rosenwasser MP. Unipolar or bipolar hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in the elderly? ClinOrthopRelatRes 2003; Calder SJ, Anderson GH, Jagger C, Harper WM, Gregg PJ. Unipolar or bipolar prosthesis for displaced intracapsular hip fracture in octogenarians: a randomized prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Brit 1996;78: Keaveny TM &Bartel DL. Load transfer with the Austin Moore cementless hip prosthesis. J Orthop Res. 1993;11: Chalidis BE &Ries MD. High hip center bipolar hemiarthroplasty for nonreconstructable pelvic discontinuity. ActaOrthop 2009;80: Abdelkhalek M, Abdelwahab M & Ali AM. Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr 2011;6: Sharif KM & Parker MJ. Austin Moore hemiarthroplasty: technical aspects and their effects on outcome, in patients with fractures of the neck of femur.injury. 2002; 33: MishraAK, ChalisePK, ShahSB, AdhikariV and SinghRP. Comparative study in surgical outcome of intracapsular fractures of femoral neck in active elderly patients treated with hemiarthroplasty with Austin Moore s and bipolar prosthesis. Nepal Med Coll J 2013;15: THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL JOURNAL 485
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 22/ Mar 16, 2015 Page 3785
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.49 Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.49 Treatment of Femoral Neck Fracture
Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip
 Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip *Hossain SN, 1 Hoque E, 2 Islam MM, 3 Rahman M, 4 Alam MS 5 Most femoral neck fractures are osteoporotic
Outcome of Replacement Hemi-arthroplasty by Non-Cemented Bipolar Prosthesis of Femoral Component of Hip *Hossain SN, 1 Hoque E, 2 Islam MM, 3 Rahman M, 4 Alam MS 5 Most femoral neck fractures are osteoporotic
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
DISCLOSURE FNFX ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? 11/21/2016 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET
 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
Aesculap Targon FN. Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures. Aesculap Orthopaedics
 Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses. Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME. Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement
 VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses VerSys
VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses Surgical Technique IMAGE TO COME Versatile solutions for total and partial hip replacement VerSys LD/Fx Cemented and Press-Fit Hip Prostheses VerSys
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 12, December ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 12, December-2015 1186 Title : A comparative study of outcomes of unipolar versus bipolar hemi-arthroplasty in geriatric age
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 12, December-2015 1186 Title : A comparative study of outcomes of unipolar versus bipolar hemi-arthroplasty in geriatric age
Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:1 6 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0100-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients Mostafa Abdelkhalek Mohamed
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:1 6 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0100-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients Mostafa Abdelkhalek Mohamed
Is there a significant difference in surgery and outcomes between unipolar and bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty? - A Prospective Study
 Mohammad Faisal and Prithviraj Nistane / International Journal of Biomedical Research 2016; 7(10): 708-712. 708 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print)
Mohammad Faisal and Prithviraj Nistane / International Journal of Biomedical Research 2016; 7(10): 708-712. 708 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print)
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
21st Century Fracture Management ETS. Surgical Protocol
 21st Century Fracture Management ETS Surgical Protocol ETS Operative Technique Step 1 Confirm that a cemented hemiarthroplasty is indicated. An X-ray template of the ETS is provided. This should be used
21st Century Fracture Management ETS Surgical Protocol ETS Operative Technique Step 1 Confirm that a cemented hemiarthroplasty is indicated. An X-ray template of the ETS is provided. This should be used
Optimizing function Maximizing survivorship Accelerating recovery
 Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
THE NATURAL FIT. Surgical Technique. Hip Knee Spine Navigation
 THE NATURAL FIT Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation MiniMAX Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation INTRODUCTION The MiniMAX TM is a cementless anatomic stem available in 9 right sizes and
THE NATURAL FIT Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation MiniMAX Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation INTRODUCTION The MiniMAX TM is a cementless anatomic stem available in 9 right sizes and
Metha Short Hip Stem System
 Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
PLR. Proximal Loading Revision Hip System
 PLR Proximal Loading Revision Hip System The PLR splined revision stem is designed to recreate the natural stresses in the revised femur, where proximal bone may be compromised. PLR Hip System Design Considerations
PLR Proximal Loading Revision Hip System The PLR splined revision stem is designed to recreate the natural stresses in the revised femur, where proximal bone may be compromised. PLR Hip System Design Considerations
Surgical Technique r5.indd 1 12/8/10 10:36 AM
 Surgical Technique The science of simplicity With more than 700,000 implantations and two and a half decades of clinical success, the Corail Total Hip System now has the most extensive experience with
Surgical Technique The science of simplicity With more than 700,000 implantations and two and a half decades of clinical success, the Corail Total Hip System now has the most extensive experience with
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique
 Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders
 ORIGINALARTICLE Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders Sanjeev Gupta, Rashid Anjum, Omeshwar Singh, Anil Gupta, Abdul Ghani, Mohammad Azhar ud din Darokhan Abstract The curent
ORIGINALARTICLE Mid Term Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty for Various Hip Disorders Sanjeev Gupta, Rashid Anjum, Omeshwar Singh, Anil Gupta, Abdul Ghani, Mohammad Azhar ud din Darokhan Abstract The curent
Cement Polished Tapered Stems of 12/14 Taper. 96 mm 98 mm 104 mm 110 mm 116 mm 122 mm 128 mm. Ceramic Femoral Head. Outer Diameter
 Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique
 Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
Cementless Tapered Femoral Stem Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning 5 Femoral neck osteotomy 5 Femoral canal preparation 5 Intra-medullary (IM) reamer 6 Sequential rasping
TaperFill. Surgical Technique
 TaperFill Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications 3 TaperFill Hip Size Charts 4-5 DJO Surgical 9800 Metric Boulevard Austin, TX (800) 456-8696 www.djosurgical.com Preoperative
TaperFill Surgical Technique Table of Contents Indications and Contraindications 3 TaperFill Hip Size Charts 4-5 DJO Surgical 9800 Metric Boulevard Austin, TX (800) 456-8696 www.djosurgical.com Preoperative
Integral 180 Surgical Technique
 Integral 180 Surgical Technique The Integral 180 and 225 are part of the Alliance Family Total Hip System. The Integral 225 femoral component is marketed for use with bone cement in the United States.
Integral 180 Surgical Technique The Integral 180 and 225 are part of the Alliance Family Total Hip System. The Integral 225 femoral component is marketed for use with bone cement in the United States.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
76 F: Plays tennis, lives independently, told she has weak bone
 Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Preoperative Planning. The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to:
 Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION
 EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Encina HA Stem Table of Contents Introduction 3 Encina HA Stem Features 4 Surgical
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Encina HA Stem Table of Contents Introduction 3 Encina HA Stem Features 4 Surgical
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Alpine Cementless Hip Stem
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Alpine Cementless Hip Stem The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Alpine Cementless Hip Stem. It is expected that the surgeon is already familiar with
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Alpine Cementless Hip Stem The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Alpine Cementless Hip Stem. It is expected that the surgeon is already familiar with
Surgical Technique. Hip System
 Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
Surgical Technique Hip System INDICATIONS FOR USE The TaperSet Hip System is designed for total or partial hip arthroplasty and is intended to be used with compatible components of the Consensus Hip System.
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT:
 THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY. Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA
 DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA Disclosures None Direct Superior Approach History and development of the approach
DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA Disclosures None Direct Superior Approach History and development of the approach
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Anterior Approach Surgical Technique. Paragon Stem System. enabling people to enjoy life
 Anterior Approach Surgical Technique Paragon Stem System enabling people to enjoy life Contents Pre-Operative Planning... 2 Suggested Templating Method... 2 Surgical Technique... 3 Surgical Approach...
Anterior Approach Surgical Technique Paragon Stem System enabling people to enjoy life Contents Pre-Operative Planning... 2 Suggested Templating Method... 2 Surgical Technique... 3 Surgical Approach...
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
Design Rationale. ECHELON Primary Hip System
 Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
28 Surgical Technique
 Surgical Technique 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 28 26 Technique described by James L. Guyton, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee James W. Harkess, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee David G. LaVelle,
Surgical Technique 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 28 26 Technique described by James L. Guyton, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee James W. Harkess, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee David G. LaVelle,
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2011 Vol 5 No 1 doi: /MOJ
 doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
operative technique Kent Hip
 operative technique Kent Hip The Kent Hip Operative Technique The Kent Hip was developed by Mr Cliff Stossel, FRCS in Maidstone, Kent, UK and first implanted in 1986. It was designed to deal with problems
operative technique Kent Hip The Kent Hip Operative Technique The Kent Hip was developed by Mr Cliff Stossel, FRCS in Maidstone, Kent, UK and first implanted in 1986. It was designed to deal with problems
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Bi-Polar 22.2mm & 28mm System - Operative technique
 Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Introduction...2 Preoperative Planning...3 Preoperative Planning...3 Templating and Radiographs...4 Determination of Leg Length Discrepancy...5 Determining Acetabular Cup
Introduction. Femoral neck fracture in the elderly
 Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
Fll Fellow: 姜智偉 Introduction Femoral neck fracture in the elderly 14 50 % mortality tlit rate in the first year Highest in the first 6 months, then gradually reduced Affect mortality: Age, gender, comitant
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty
![Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty](/thumbs/90/102636395.jpg) Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Progeny Hip Stem. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications
 Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Taperloc Complete Hip System. Surgical Technique
 Taperloc Complete Hip System Surgical Technique One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized care to one patient. The science and art of medical
Taperloc Complete Hip System Surgical Technique One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1 million times per year, Biomet helps one surgeon provide personalized care to one patient. The science and art of medical
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY
 ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
Hip Replacement - Anterior
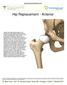 Hip Replacement - Anterior Anterior hip replacement surgery is an alternative to hip replacements where the surgeon accesses the hip joint from the side or through the buttocks. The anterior procedure
Hip Replacement - Anterior Anterior hip replacement surgery is an alternative to hip replacements where the surgeon accesses the hip joint from the side or through the buttocks. The anterior procedure
AML Hip System. Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique
 AML Hip System Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique Design Rationale Evolution In 1977, DePuy Synthes Companies introduced the original cementless total hip. The AML Hip launched in order to solve one
AML Hip System Design Rationale/ Surgical Technique Design Rationale Evolution In 1977, DePuy Synthes Companies introduced the original cementless total hip. The AML Hip launched in order to solve one
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 04 Page April 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i4.176 Functional Outcome of Fracture Neck of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i4.176 Functional Outcome of Fracture Neck of
Bone Conserving Hip Replacement Surgical technique
 MiniHip Bone Conserving Hip Replacement Surgical technique MiniHip Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Pre-operative templating 6 Operative technique 7 Neck resection 7 Femoral canal preparation 7
MiniHip Bone Conserving Hip Replacement Surgical technique MiniHip Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Pre-operative templating 6 Operative technique 7 Neck resection 7 Femoral canal preparation 7
Tradition Hip Primary Surgical Technique
 Design Rationale Many total hip designs in today s marketplace do not take advantage of the known forces present in the femur. Long term stability of a total hip prosthesis requires an implant design and
Design Rationale Many total hip designs in today s marketplace do not take advantage of the known forces present in the femur. Long term stability of a total hip prosthesis requires an implant design and
FLH /11
 FLH 225 04/11 This publication has been issued by: European Central Marketing Waterton Industrial Estate Bridgend, South Wales CF31 3XA, United Kingdom Tel: +44 (0)1656 655221 Fax: +44 (0)1656 645454 www.biomet.com
FLH 225 04/11 This publication has been issued by: European Central Marketing Waterton Industrial Estate Bridgend, South Wales CF31 3XA, United Kingdom Tel: +44 (0)1656 655221 Fax: +44 (0)1656 645454 www.biomet.com
Posterior approach and uncemented stems increases the risk of reoperation after hemiarthroplasties in elderly hip fracture patients
 18 Acta Orthopaedica 2014; 85 (1): 18 25 Posterior approach and uncemented stems increases the risk of reoperation after hemiarthroplasties in elderly hip fracture patients An analysis of 33,205 procedures
18 Acta Orthopaedica 2014; 85 (1): 18 25 Posterior approach and uncemented stems increases the risk of reoperation after hemiarthroplasties in elderly hip fracture patients An analysis of 33,205 procedures
PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS *Ibrahim M., Shah Sachin and Kothadia Pradeep Department of Orthopaedics, KBNIMS, Gulbarga, Karnataka,
PRIMARY BIPOLAR ARTHROPLASTY IN TREATMENT OF UNSTABLE INTERTROCHANTERIC FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS *Ibrahim M., Shah Sachin and Kothadia Pradeep Department of Orthopaedics, KBNIMS, Gulbarga, Karnataka,
VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis. Surgical Technique
 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique 1 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative
VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique 1 VerSys Fiber Metal Taper Hip Prosthesis Surgical Technique Table of Contents Preoperative
S U R G I C A L T E C H N I Q U E
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total hip replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and survivorship. The DePuy PROXIMA Hip System
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(2):166-71 Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures Stefan Bauer, 1 Patrick Isenegger, 1 Oliver P Gautschi, 1 Kwok M Ho, 2 Piers
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(2):166-71 Cemented Thompson versus cemented bipolar prostheses for femoral neck fractures Stefan Bauer, 1 Patrick Isenegger, 1 Oliver P Gautschi, 1 Kwok M Ho, 2 Piers
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH
 DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
DIRECT ANTERIOR APPROACH JOINT REPLACEMENT PROGRAM 2301 25TH STREET SOUTH FARGO ND 58103 CENTER FOR MINIMAL INVASIVE JOINT SURGERY (p) 701-241-9300 (tf) 866-887-9300 www.jointpain.md FARGO FERGUS FALLS
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
Total Hip Replacement. Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you.
 Total Hip Replacement Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of the Direct Anterior Approach to total hip arthroplasty.
Total Hip Replacement Find out why the Anterior Approach may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of the Direct Anterior Approach to total hip arthroplasty.
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 08 Page August 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.08 Study of Functional and Radiological Outcome
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i8.08 Study of Functional and Radiological Outcome
Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients
 Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement
 Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
CC TRIO VERSAFITCUP. Surgical Technique. each to their own. Hip Knee Spine Navigation
 VERSAFITCUP CC TRIO each to their own Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation Versafitcup CC TRIO Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation EACH TO THEIR OWN The Versafitcup CC Trio is a range
VERSAFITCUP CC TRIO each to their own Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation Versafitcup CC TRIO Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation EACH TO THEIR OWN The Versafitcup CC Trio is a range
APS Natural-Hip System
 APS Natural-Hip System Surgical Technique Bone conserving, anatomic fit APS Natural-Hip System Surgical Technique APS Natural-Hip System Surgical Technique Developed in conjunction with Jay Butler, MD
APS Natural-Hip System Surgical Technique Bone conserving, anatomic fit APS Natural-Hip System Surgical Technique APS Natural-Hip System Surgical Technique Developed in conjunction with Jay Butler, MD
9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas
 rev. A Encore Orthopedics, Inc. 1998 www.encoremed.com 9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas 78758 512-832-9500 1 contents How to use the Foundation Hip 1 2 Plan your approach Select your hardware Preparing
rev. A Encore Orthopedics, Inc. 1998 www.encoremed.com 9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas 78758 512-832-9500 1 contents How to use the Foundation Hip 1 2 Plan your approach Select your hardware Preparing
Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay
 Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay Pelvis anatomy Pelvis function - axial load bearing - protection: abdominal, pelvic structures Pelvic injury mechanism Falling from
Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay Pelvis anatomy Pelvis function - axial load bearing - protection: abdominal, pelvic structures Pelvic injury mechanism Falling from
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
The Hip Joint. Exercises and Injuries
 The Hip Joint Exercises and Injuries Pelvis Abnormalities To appreciate the abnormalities that may occur, picture a box around the pelvis. The two most common situations are: 1.the pelvis is tilted forward
The Hip Joint Exercises and Injuries Pelvis Abnormalities To appreciate the abnormalities that may occur, picture a box around the pelvis. The two most common situations are: 1.the pelvis is tilted forward
ZMR CROSSOVER INSTRUMENTS AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Surgical Technique for Revision Hip Arthroplasty
 ZMR CROSSOVER INSTRUMENTS AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Surgical Technique for Revision Hip Arthroplasty A MULTITUDE OF OPTIONS Several fixation options are offered within the ZMR Hip System. Spout, Cone, and
ZMR CROSSOVER INSTRUMENTS AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Surgical Technique for Revision Hip Arthroplasty A MULTITUDE OF OPTIONS Several fixation options are offered within the ZMR Hip System. Spout, Cone, and
The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification D Iyer Citation D Iyer. The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification. The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification D Iyer Citation D Iyer. The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification. The
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP. Dr Károly Fekete
 DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
Primary hip arthroplasty through a limited posterior trochanteric osteotomy
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 548-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary hip arthroplasty through a limited posterior trochanteric osteotomy Joaquin SANCHEZ-SOTELO, John GIPPLE, Daniel BERRY, Charles ROWLAND, Robert
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 548-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary hip arthroplasty through a limited posterior trochanteric osteotomy Joaquin SANCHEZ-SOTELO, John GIPPLE, Daniel BERRY, Charles ROWLAND, Robert
EVOLVING OUR HERITAGE, MEETING YOUR NEEDS. Surgical Technique
 EVOLVING OUR HERITAGE, MEETING YOUR NEEDS Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med Mpact DM Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med INTRODUCTION The Mpact DM is part of the Mpact Acetabular System and
EVOLVING OUR HERITAGE, MEETING YOUR NEEDS Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med Mpact DM Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med INTRODUCTION The Mpact DM is part of the Mpact Acetabular System and
ZMR Crossover Instruments. Abbreviated Surgical Technique
 ZMR Crossover Instruments Abbreviated Surgical Technique ZMR Crossover Instruments Surgical Technique Introduction ZMR Crossover Instruments facilitate the combination of any Porous Proximal Body with
ZMR Crossover Instruments Abbreviated Surgical Technique ZMR Crossover Instruments Surgical Technique Introduction ZMR Crossover Instruments facilitate the combination of any Porous Proximal Body with
CeramTec Medical Products. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
Move Ahead with Confidence. Hip Replacement Solutions from DePuy Orthopaedics
 Move Ahead with Confidence Hip Replacement Solutions from DePuy Orthopaedics The Healthy Hip Joint Pelvis Acetabulum (hip socket) Head of femur Neck of femur Femur (thigh bone) Head of femur in the acetabulum
Move Ahead with Confidence Hip Replacement Solutions from DePuy Orthopaedics The Healthy Hip Joint Pelvis Acetabulum (hip socket) Head of femur Neck of femur Femur (thigh bone) Head of femur in the acetabulum
CORAIL HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 CORAIL HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE SCIENCE OF SIMPLICITY With 2,000,000 stems provided for patients worldwide 1 and thirty years of clinical history, the CORAIL Total Hip System now has a very extensive
CORAIL HIP SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE SCIENCE OF SIMPLICITY With 2,000,000 stems provided for patients worldwide 1 and thirty years of clinical history, the CORAIL Total Hip System now has a very extensive
MITCH TRH System Modular Head Operative Technique
 MITCH TRH System Modular Head Operative Technique Manufactured by: Pending Pending Approval - - Pending Approval Introduction The MITCH TRH System is an evolutionary design, comprising of traditional resurfacing
MITCH TRH System Modular Head Operative Technique Manufactured by: Pending Pending Approval - - Pending Approval Introduction The MITCH TRH System is an evolutionary design, comprising of traditional resurfacing
Comparative study in surgical management of fracture neck femur treated with Austin Moore prosthesis and bipolar prosthesis
 2017; 3(4): 571-577 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(4): 571-577 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 20-08-2017 Accepted: 21-09-2017 Dr. Takshay Gandhi Dr. Dhruven Kosada Dr. Parth Thakor Dr. Jainish Patel
2017; 3(4): 571-577 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(4): 571-577 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 20-08-2017 Accepted: 21-09-2017 Dr. Takshay Gandhi Dr. Dhruven Kosada Dr. Parth Thakor Dr. Jainish Patel
RECOVERY. P r o t r u s i o
 RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Displaced intra-capsular neck femur fractures in elderly: Austin Moore s prosthesis or Cemented Modular Bipolar Prosthesis
 Original Research Article Displaced intra-capsular neck femur fractures in elderly: Austin Moore s prosthesis or Cemented Modular Bipolar Prosthesis Bijith Balan 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3,
Original Research Article Displaced intra-capsular neck femur fractures in elderly: Austin Moore s prosthesis or Cemented Modular Bipolar Prosthesis Bijith Balan 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3,
Inspiring people, Enriching lives
 TM Inspiring people, Enriching lives Encore Medical, L.P. 9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas 78758 512-832-9500 www.encoremed.com Encore Medical, L.P. Cat. # 0177-170 1000 12/04 rev. A Encore and Revelation
TM Inspiring people, Enriching lives Encore Medical, L.P. 9800 Metric Blvd. Austin, Texas 78758 512-832-9500 www.encoremed.com Encore Medical, L.P. Cat. # 0177-170 1000 12/04 rev. A Encore and Revelation
Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication?
 CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
Medical Products Division. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Approach Patients with CONFIDENCE
 Design Rationale Approach Patients with CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Design Rationale Approach Patients with CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
