International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
|
|
|
- Jeremy Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN: Original Research Article A Prospective Study of the Outcome of Closed Intramedullary Fixation of Humeral Shaft Fractures Treated with Multiple K-Wires in Adults Amit Nandan Mishra 1, Sandhya Mishra 2, Shakeel Ahmad Qidwai 3, Varun Kumar Shrimal 4 1 Associate Professor, 3 Professor, 4 Senior Resident, Department of Orthopaedics, Era s Lucknow Medical College, Lucknow. 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Integral Institute of Medical and Research Sciences, Integral University, Lucknow. Corresponding Author: Sandhya Mishra Received: 26/10/2015 Revised: 20/11/2015 Accepted: 27/11/2015 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the feasibility and efficacy of management of fracture of shaft humerus in adults by closed reduction internal fixation with the help of long K-wires followed by immobilization for 3 weeks in splint and then guarded mobilization till fracture united. Methods: This was a prospective longitudinal study. The subjects with fresh diaphyseal humeral shaft fractures without injury to the same limb, transverse/oblique fractures with a large butterfly fragment, comminuted fractures/segmental fragments and long oblique or spiral fracture were included in the study. Patient was taken on the table in lateral position. The general anaesthesia was given. A midline vertical incision of about 3 cms was given on the posterior aspect of distal humerus and the soft tissue dissected. Triceps was split in line with the fibres and the bone was reached. Results: The mean age of the patients was (±13.02) years. More than half (69.6%) of the subjects were male. The RTA was among 65.2% of the subjects. The oblique with butterfly type of injury was in 30.4% of the subjects and comminuted was in 21.7%. The middle site of fracture was in 52.2% and left site of fracture was in 52.2%. The antegrade nailing was used among 69.6% of the patients. There was significant increase in the extent of union, constant score and Mayo score from 4 week to 8 and 12 week. The shoulder stiffness was among 65.2% at 4 week which became 13% at 8 and 12 week. The elbow stiffness was in 17.4% of the subjects which decreased to 13% and 8.7% at 8 and 12 week respectively. Conclusion: The present study showed that K-wire fixation for humeral shaft fractures has distinct advantages over other conservative and over operative techniques. Key words: Fracture, Humerus, K-wire fixation. INTRODUCTION Fracture of the humeral shaft are common, account for approximately 3% of all orthopaedic injuries, and result in a significant burden to society form lost productivity and wages as it affects the most productive age groups with majority of patients being affected in age group 21 to 40 years. (1-3) Treatment modalities have greatly evolved since their first description in ancient Egypt (Circa 1600 BC); however, fundamental management principles have remained consistent throughout time. Nonoperative management continues as the mainstay for treatment of the majority of these injuries, with acceptable healing in more than 90% of patients. The humeral shaft is covered with muscles and is well International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 99
2 vascularised. Slight malunion is functionally and cosmetically tolerated. (4,5) Advances in internal fixation modalities have improved surgical outcomes. (6-9) A new technique for treatment of humeral shaft fractures by closed fixation using multiple intramedullary Kirschner wires has been reported with good clinical and functional results. (10,11) This technique has been found simple and effective in providing a stable fixation of transverse and short oblique fractures of the humeral diaphysis. Considering the low-cost, universal availability and dynamic fixation without compromising stability shown in preliminary studies, K-wire fixation seems to be a perfect treatment modality for a resource scarce economy like ours. The present study was an attempt to evaluate the feasibility and efficacy of management of fracture shaft humerus in adults by closed reduction internal fixation with the help of long K-wires followed by immobilization for 3 weeks in splint and then guarded mobilization till fracture united. MATERIALS AND METHODS Study Design: This was a prospective longitudinal study. Study place: The study was conducted at the Department of Orthopaedics, Era's Lucknow Medical College and Hospital, Lucknow after the ethical approval by the ethical committee of the institute. The informed consent was taken from each of the study subjects after explaining the purpose of the study. The subjects with fresh diaphyseal humeral shaft fractures without injury to the same limb, transverse/oblique fractures with a large butterfly fragment, comminuted fractures/segmental fragments and long oblique or spiral fracture were included in the study. The subjects with old fractures either treated by other methods i.e. conservative or other surgical methods or neglected, fractures with closed head injury, segmental loss of bone, vascular injury, neurological injury, failure to reduce the fracture by closed method satisfactorily and pathological fractures were excluded from the study. Retrograde Nailing Patient was taken on the table in lateral position. The general anaesthesia was given. A midline vertical incision of about 3 cms was given on the posterior aspect of distal humerus and the soft tissue dissected. Triceps was split in line with the fibres and the bone was reached. About 2 cms proximal to the olecranon fossa a hole was drilled on the posterior aspect of the bone of about 0.5&0.5 cms diameter. Standard k-wires of 2 mm and 2.5 mm diameter and 30 cms length were bent at an angle of 45 degrees approximately 2 cms from the proximal end and was loaded on a T handle chuck and then inserted from the window into the medullary cavity crossing the fracture site into the proximal fragment under fluroscopic guidance. The tip of the wire was driven up into the humeral head and impacted. Outer end of the wire was cut 1 cm away from the entry point and was bent like a U to avoid proximal migration of the wire. Similarly a total of 2-4 K-wires were inserted in the medullary cavity depending upon the surgeon s judgement of the stability of the fixation. Proximal tip of the wires were kept divergent to have a purchase at different points in the head to achieve rotational stability at fracture site. After insertion of the k-wires the fracture was gently impacted to avoid distraction at the fracture site. Excessive force was avoided while pushing the wires into the meduallary cavity to prevent iatrogenic fracture of the greater tubercle. The wound was then irrigated with saline and closed in layers. Similarly a total 4-5 wires depending upon the size of the medullary cavity were inserted and stacked. The distal tips of the wires were kept divergent to have a purchase at different points to achieve rotational stability at fracture site. Wound was International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 100
3 irrigated with saline and closed in layers and patient was given a functional brace in the postoperative ward. All patients received broad spectrum antibiotics for a period of 2 days minimum and intravenous paracetamol 1 gm thrice daily for three days. Assisted exercises were started on the 4 th post-op day only if the VAS was 6 or less or else paracetamol was continued in the same dose for 2 more days and when the VAS and 6 or less, assisted exercises were started. Assessment criteria Patients were followed up on 4 th, 8 th and 12 th weeks. Clinical assessment in terms of:-mal alignment:-angular alignment and shortening was done. The functional assessment of shoulder and elbow joint by Constant Score and Mayo Score were evaluated. Radiological assessment in terms of sequential radiographs was done. Statistical Analysis The results are presented in mean±sd and percentages. The Paired t- test was used to compare the changes in the study parameters from 4 to 8 and weeks. The p-value<0.05 was considered significant. All the analysis was carried out by using SPSS 16.0 version (Chicago, Inc., USA). RESULTS The mean age of the patients was (±13.02) years. More than half (69.6%) of the subjects were male. The RTA was among 65.2% of the subjects. The oblique with butterfly type of injury was in 30.4% of the subjects and comminuted was in 21.7%. The middle site of fracture was in 52.2% and left site of fracture was in 52.2% (Table-1). Table-1: Basic characteristics of the study subjects No. % (n=23) Age in years 42.13±13.02 Gender Male Female Mode of injury Household Road traffic accidents Type of injury Comminuted Compound Oblique Oblique with butterfly Transverse Site of fracture Distal Middle Proximal Side of fracture Right Left The antegrade nailing was used among 69.6% of the patients (Fig.1). Fig.1: Type nailing used There was no change in extent of rotation, angulation and bone shortening from 4 week to 8 and 12 week of followup. However, there was significant increase in the extent of union, constant score and Mayo score from 4 week to 8 and 12 week (Table-2). Table-2: Comparison of parameters at follow-ups 4 week 8 week 12 week Extent of rotation 9.09± ± ±5.31 Extent of angulation 4.91± ± ±2.11 Extent of bone shortening 1.5± ± ±0.70 Extent of union cortices 2.09± ±1.00 a 3.26±1.18 a Extent of constant score 56.00± ±15.53 a 84.87±10.14 a Extent of Mayo score 58.47± ±15.70 a 93.04±14.83 a a p< (from 4 week to 8 and 12 week) International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 101
4 Table-3 shows the post-operative complications. The shoulder stiffness was among 65.2% at 4 week which became 13% at 8 and 12 week. The elbow stiffness was in 17.4% of the subjects which decreased to 13% and 8.7% at 8 and 12 week respectively. Table-3: Post-operative complications at follow-ups Complications 4 week 8 week 12 week No. % No. % No. % Pin tract infection with elbow stiffness Pin tract infection with shoulder stiffness Skin necrosis with elbow stiffness Elbow stiffness Shoulder stiffness No complication DISCUSSION Humerus shaft fractures affect the functional ability of an individual while at the same time restrict the social and psychological status. Full restoration of functional ability at the shortest possible time is the priority of management team. Treatment of humerus shaft fractures thus not only requires an early restoration but also requires that it is achieved completely with no restriction so as to enable the patient to take part in his/her routine activities without causing a economic or social burden. For this purpose, a prospective study was carried out in which a total of 23 patients fulfilling the inclusion criteria and not falling into the domain of exclusion criteria were enrolled. The age of patients ranged from 23 to 67 years with a mean age of 42.13±13.02 years. Majority of patients were in young and productive age group (21-40 years; 52.2%). Humerus fractures have often been reported in age group 21 to 40 years in literature too. The reason for involvement of this age group is that this is the most active age group and owing to higher level of activity has a higher risk of humerus fractures. However, in several studies average age of patients has been reported to be as high as 52 to 72 years. (12,13) however, this might be owing to the fact that they either have an inclusion criteria that includes elderly patients only or the studies are from a (13) region with higher median age. However, despite these sporadic differences, fracture humerus is generally more common in individuals with higher activity level and this is reflected in the age profile of patients in present study. On gender wise evaluation too, we observed that majority of the patients included in the study were males (69.575) and rest of the patients were females (40.43%). This finding once again endorses our earlier assumption regarding association of incidence of humerus fractures with activity level of a person. However, contrary to this, the findings in western studies suggest a higher prevalence of humeral shaft fractures among women as compared to men. (14) The reason for this as explained by the cited authors is low bone mineral density in advancing age women. The difference in etiology of humeral shaft fractures in our settings and that of western settings is that while road traffic accidents and violence are major etiologies in Indian context, in western context, the etiology is often different. In Indian studies a male predominance has often been reported with road traffic accident being the major etiology. (15,2) In present study too, we found that road traffic accident was the most common etiology (65.22%). With respect to type of fracture most common type of fracture in the present study was oblique with butterfly (30.43%), followed by comminuted (21.74%), oblique (21.74%) and transverse (17.39%). Only 8.70% suffered with compound fracture. The type of fracture International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 102
5 depends on the site, nature and intensity of the impact due to which fracture has taken place. Oblique with butterfly and oblique fractures are generally caused by an injury to the bone as the result of a fall accident or other trauma while comminuted fractures are caused mainly by high intensity trauma while transverse fractures are caused by bending forces. (16) In the present study, the most common fracture site was middle (52.17%), followed by proximal (30.43%) and least common site was distal (17.39%). In a study by Obruba et al. (13) too middle third was involved in 64%, proximal third in 30% and distal third in 6% of cases. In the present study, majority proportion of patients had involvement of left (52.17%) side. In literature no side (2) predilection has been reported. In present study, antegrade type of nailing was used in majority of the patients (68.57%) and in rest of the patients (30.43%) retrograde type of nailing was used. The selection of type of nailing depends on the site of fracture. Antegrade nailing is more suitable for proximally located fractures while retrograde nailing is used for distal fractures. (17) On follow up, in present study, all the patients had pain score between 5 and 10. Majority of the patients rate their pain score as 7 and 8 (82.61%) while 17.39% patients rated their pain score as 6. Severe pain is usually reported in pathologic (18-20) fractures of the humerus. As pathologic fractures were excluded from the present study, hence there was no case with severe pain intensity in present study. (12,21) Some studies. have shown that displacement/migration of K-wires results in a painful experience, however, the intensity of pain reported by patients in present study did not indicate any such situation. The mean extent of rotation also remained unchanged from 4 th week follow up till 12 th week follow up (9.09±5.31). Similarly direction of angulation and extent of angulation also remained unchanged throughout the study period, thus indicating that the K-wires were stabilized and did not result in any unwanted rotation. In all the cases, the angulation was less than 20 degrees and rotation was less than 30 degrees thus meeting the criteria of good outcome. (22) This stability was attained by keeping the wire tips divergent to provide rotational stability at the fracture site. (23) In present study, shortening of bone was reported in two patients and it was evident from the 4 th week follow up itself. However, the extent of shortening was 1 cm and 2 cm respectively which is within the treatment objective of achieving a shortening of 3 cm. (22) However, with respect to extent of union of cortices, a gradual and continuous increase was observed during the entire period of follow-up. K-wire induces cortical union by continuously activating the adjoining cortical tissue. Use of K-wire has been shown to provide a better cortical union in nonunited humerus shaft fractures treated by external fixator augmented by intramedullary rod. (24) In the present study, a gradual increase in functional scores of shoulder (Constant scores) was observed from 4 th week itself. Mean functional scores at the end of follow up were and median scores were 90, thus indicating that majority of patients achieved good functional restoration. Minimum functional scores at the end of follow up were 66, thus indicating that at least fair restoration of functional ability was observed in all the patients. In a study by Hoffmann et al. (12) in a minimum follow up of 12 months 60% patients showed good or excellent results, 30% had a satisfactory and 10% had an unsatisfactory or poor result. In present study, with respect to elbow performance, though at 4 th week of follow up mean scores indicative of a poor International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 103
6 performance were observed (58.47±15.91) yet by 12 th week of follow up a very highly significant change in mean scores was observed (93.04±14.83). Thus, overall mean scores indicated an excellent resumption of elbow performance. The median MAYO score at 12 th week was 100, which indicated that majority of patients had scores above 90 which indicated an excellent performance of elbow. (10) In their assessment also showed achievement of results comparable to our study with 93% patients showing good to excellent movements at shoulder and elbow. In present study too, we observed that except for 2 (8.7%) patients, all the patients achieved MAYO score above 80 which indicated that good elbow functional status was achieved in 91.3% patients. The reason for achievement of good functional status of shoulder and elbow in intramedullary wires in humeral shaft fractures could be attributed to relative freedom of movements at these ends as against conservative management and immobilization techniques. The findings thus relate with the observations of Qidwai. (10) and Khan et al. (11) who were of the view that multiple intramedullary Kirschner wires provide good clinical and functional results. In the present study, during first follow up at 4 weeks all the patients included in the study reported some complications. Shoulder stiffness only was reported by 15 (65.22%) cases and shoulder stiffness with pin tract infection was reported by 1 (4.35%) patient, this was present in cases of antegrade nailing. 4 (17.39%) patients reported elbow stiffness only, 2 (8.70%) reported elbow stiffness with skin necrosis and 1 (4.35%) patient reported elbow stiffness with pin tract infection. The stiffness of shoulder or elbow is result of immobilization and during the initial period of immobilization causes discomfort to the patient until adjustments are made. The infection and tissue necrosis was relieved by antibiotic and medical management and in subsequent follow up none of the patient had these complaints. By 12 th week, only 2 patients reported of elbow stiffness while 3 (13.04%) reported of shoulder stiffness, and the remaining 18 (78.26%) had no complication at all. Stiffness of the shoulder and elbow joints is a frequently reported disadvantage of non-operative methods. CONCLUSION The present study showed that K- wire fixation for humeral shaft fractures has distinct advantages over other conservative and over operative techniques. The low cost and universal availability of K-wires (as compared to titanium nails and the short hospital stay make this treatment cost effective and particularly suitable for developing and underdeveloped countries. This is a simple technique, and sophisticated instrumentation is not required. REFERENCES 1. Tsai CH, Fong YC, Chen YH, Hsu CJ, Chang CH, Hsu HC. The epidemiology of traumatic humeral shaft fractures in Taiwan. Int Orthop 2009;33: Singisetti K, Ambedkar M. Nailing versus plating in humerus shaft fractures: A prospective comparative study. Int Orthop April; 34 (4): Sidhu AS, Mann HS, Sidhu GDS, Banga A, Bassi A, Gupta M. management of fracture shaft of humerus open versus closed antegrade nailing. Pb Journal of Orthopaedics 2011; XII (1): Putti AB, Uppin RB, Putti BB. Locked Intramedullary nailing versus dynamic compression plating for humeral shaft fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2009; 17(2): Walker M, Palumbo B, Badman B, Brooks J, Gelderen JV, Mighell M. Humeral shaft fractures: a review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2011; 20 (5): Chapman JR, Henley MB, Agel J, Benca PJ, Randomized prospective International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 104
7 study of humeral shaft fracture fixation: intramedullary nails versus plates. J Orthop Trauma 2000; 14: Martinez AA, Cuenca J, Herrera A. Treatment of humeral shaft nonunions: nailing versus plating. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2004; 124: Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, McKee MD, Schemitsch EH. Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: a meta analysis. Acta Orthop 2006;77: Singisetti K, Ambedkar M. Nailing versus plating in humerus shaft fractures: A prospective comparative study. Int. Orthop. 2010; 34(4): Qidwai SA. Treatment of human shaft fractures by closed fixation using multiple intramedullary Kirschner wires. J Trauma Jul;49(1): Khan AQ, Iraqi AA, Sherwani MK, Abbas M.Sharma A. Percutaneous multiple K-wire fixation for humeral shaft fractures. Saudi Med J Jan;28(1): Hoffmann R, Khodadadyan C, Raschke M, Melcher I, Maitino PD, Haas NP. Retrograde intramedullary nailing in proximal fracture of the humerus in the elderly patient. Results of minimally invasive management concept. Zentralbl Chir. 1998;123(11): Obruba P, Kopp L, Edelmann K. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures using Hackethal s technique of intramedullary bundle nailing. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2012;79(4): Kim SH, Szabo RM, Marder RA. Epidemiology of humerus fractures in the United States: nationwide emergency department sample, Arthritis Care & Research 2012; 64(3): Putti AB, Uppin RB. Locked intramedullary nailing versus dynamic compression plating for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) Aug;17(2): Newton CD. Etiology, Classification and Diagnosis of Fractures. In: Small Animal Orthopedics. Newton CD, Nunamaker DM, (eds.). Lipincott Philadelphia, Lin J, Inoue N, Valdevit A, et al.. Biomechanical comparison of antegrade and retrograde nailing of humeral shaft fracture. Clin Orthop. 1998;351: Flinkkila T, Hyvonen P, Leppilahti J, Hamalainen M. Pathological fractures of the humeral shaft. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1998;87(4): Anselmetti GC, Manca A, Chiara G, Tutton S, Iussich G, Gino G, Grignani G, Ortega C, Moselli N, Regge D. Painful pathologic fracture of the humerus: percutaneous osteoplasty with bone marrow nails under hybrid computer tomography and fluoroscopic guidance. J Vasc Interv Radiol Jul;22(2): Jindal N, Gupta P, Gupta RK, Kumar A, Jindal A. Pucker sign in proximal humeral fractures: implications on management. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr August; 8(2): Fang RH, Chang TL. Watch out for the K-wire: painful experiences in two cases. Br J Plast Surg Dec;55(8): Sarmiento A, Kinman PB, Galvin EG, et al.. Functional bracing of fractures of the shaft of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1977;59-A(5): Qidwai SA. Treatment of proximal humeral fractures by intramedullary Kirschner wires. J Trauma Jun;50(6): EI-Rosasy MA. Nonunited humerus shaft fractures treated by external fixator augmented by intramedullary rod. Ind. J. Orthop. 2012;46(1): How to cite this article: Mishra AN, Mishra S, Qidwai SA et al. A prospective study of the outcome of closed intramedullary fixation of humeral shaft fractures treated with multiple K- wires in adults. Int J Health Sci Res. 2015; 5(12): *********** International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 105
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Dr. Raja Rathnam Korani
 2018; 2(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 06-10 Received: 12-11-2017 Accepted: 15-12-2017 Civil Surgeon Specialist, District
2018; 2(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 06-10 Received: 12-11-2017 Accepted: 15-12-2017 Civil Surgeon Specialist, District
Modified extra rotator-cuff entry point in antegrade humeral nailing
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2005) 125: 27 32 DOI 10.1007/s00402-004-0757-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Panayiotis Dimakopoulos Æ Andreas X. Papadopoulos Michalis Papas Æ Andreas Panagopoulos Æ Elias Lambiris Modified
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2005) 125: 27 32 DOI 10.1007/s00402-004-0757-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Panayiotis Dimakopoulos Æ Andreas X. Papadopoulos Michalis Papas Æ Andreas Panagopoulos Æ Elias Lambiris Modified
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Journal of College of Medical Sciences-Nepal, 2012, Vol-8, No-1,13-17 Original Article Results of lateral pin fixation for the displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children H.K. Gupta 1, K.D.
Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF DIAPHYSEAL FEMUR FRACTURE WITH INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL AND K. NAIL
 International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
International Journal of Innovation and Applied Studies ISSN 2028-9324 Vol. 15 No. 3 Apr. 2016, pp. 560-564 2016 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijias.issr-journals.org/ COMPARATIVE
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
EVOS MINI with IM Nailing
 Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
Case Series Dr. John A. Scolaro EVOS MINI with IM Nailing A series of studies Introduction Intramedullary nailing has become the standard for many long bone fractures. Fracture reduction prior to nail
陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長
 陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長 2012-12-25 1 30 y/o male, TA no radial nerve injury 2 s/p splint arrange functional brace 3 1 month 4 2 months 5 3 months 6 4 months 7 One year 8 Conservative Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures
陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長 2012-12-25 1 30 y/o male, TA no radial nerve injury 2 s/p splint arrange functional brace 3 1 month 4 2 months 5 3 months 6 4 months 7 One year 8 Conservative Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series
 Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
UP. EXTREMITY DYNAMIC HUMERAL NAIL. Supple pinning of humeral fractures
 UP. EXTREMITY BEHAC DYNAMIC HUMERAL NAIL Supple pinning of humeral fractures BEHAC nail Surgical Technique 1. PRINCIPLE : Behac nails apply the principle of elastic osteosynthesis using a cluster of ascending
UP. EXTREMITY BEHAC DYNAMIC HUMERAL NAIL Supple pinning of humeral fractures BEHAC nail Surgical Technique 1. PRINCIPLE : Behac nails apply the principle of elastic osteosynthesis using a cluster of ascending
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 76/ Sept. 21, 2015 Page 13162
 A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
A CLINICAL STUDY OF MANAGEMENT OF FRACTURE BOTH BONES FOREARM WITH INTERNAL FIXATION BY TWO DIFFERENT METHODS D. Venkateswara Rao 1, Chinta Shyam Kumar 2, Anvesh Sangepu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: D.
Biomechanical and Clinical Evaluation of a New Operative Technique
 27 Posterior Olecranon Plating Biomechanical and Clinical Evaluation of a New Operative Technique Nirmal C. Tejwani, M.D., Ian R. Garnham, F.R.C.S., Philip R. Wolinsky, M.D., Frederick J. Kummer, Ph.D.,
27 Posterior Olecranon Plating Biomechanical and Clinical Evaluation of a New Operative Technique Nirmal C. Tejwani, M.D., Ian R. Garnham, F.R.C.S., Philip R. Wolinsky, M.D., Frederick J. Kummer, Ph.D.,
Surgical Technique. Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90
 Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
CiSE. PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Humerus through an Anterolateral Approach. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
Functional outcome of antegrade interlocking intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rajagopal HP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1127-1131 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174147
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rajagopal HP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1127-1131 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174147
Złamania trzonu kości ramiennej kiedy nie operować?
 Złamania trzonu kości ramiennej kiedy nie operować? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fractures when not to operate? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fx general considerations Incidence
Złamania trzonu kości ramiennej kiedy nie operować? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fractures when not to operate? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fx general considerations Incidence
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6251-6255 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparison study of the clinical effect and biomechanics between locking compression plate and interlocking intramedullary
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6251-6255 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Comparison study of the clinical effect and biomechanics between locking compression plate and interlocking intramedullary
InternationalJournalofAgricultural
 www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
www.ijasvm.com IJASVM InternationalJournalofAgricultural SciencesandVeterinaryMedicine ISSN:2320-3730 Vol.5,No.2,May2017 E-Mail:editorijasvm@gmail.com oreditor@ijasvm.comm@gmail.com Int. J. Agric.Sc &
Original Research Article
 TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
TREATMENT OF COMPLEX TIBIAL FRACTURES TYPES V AND VI OF SCHATZKER CLASSIFICATION BY DOUBLE PLATE FIXATION WITH SINGLE ANTERIOR INCISION Thoguluva Chandra Sekaran Prem Kumar 1, M. N. Karthi 2 1Senior Assistant
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
Humerus shaft - Reduction & Fixation - Compression plate - AO Surgery Reference. Compression plating
 Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus Fractures with Tens - A Retrospective Analysis.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2017), PP 82-86 www.iosrjournals.org Surgical Management of Paediatric Humerus
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Internal fixation of fracture both bone forearm: Comparison of dynamic compression plate and IM nail
 2017; 3(3): 508-513 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 508-513 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 12-05-2017 Accepted: 13-06-2017 Dr. Ranjan Kumar Gupta Collage Loni. Taluka-Rahata, Dr. Mahammad Akram
2017; 3(3): 508-513 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 508-513 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 12-05-2017 Accepted: 13-06-2017 Dr. Ranjan Kumar Gupta Collage Loni. Taluka-Rahata, Dr. Mahammad Akram
Percutaneous pinning in displaced supracondylar fracture of humerus in children
 2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
2017; 3(3): 156-160 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 156-160 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 25-05-2017 Accepted: 26-06-2017 Dr. Anvesh Gattu Assistant Professor, Dr. BLS Kumar Babu Associate Professor,
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Segmental tibial fractures treated with unreamed interlocking nail A prospective study
 2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails
 Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre
 Original article : Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre Chandra Prakash Singh Associate Professor, Department
Original article : Study of Evaluation of Lateral Surgical Approach for Diaphyseal Fractures of Distal 2/3rd of Radius at a Tertiary Care Teaching Centre Chandra Prakash Singh Associate Professor, Department
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Antigrade Humerus Interlocking Nailing for Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus: A Study of Clinical Outcomes
 Original Article Antigrade Humerus Interlocking Nailing for Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus: A Study of Clinical Outcomes Prasanth Ganji *, PR Naidu Pothula, Nandam Ramarao, Raj Kumar Vijay, Bharath chandra
Original Article Antigrade Humerus Interlocking Nailing for Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus: A Study of Clinical Outcomes Prasanth Ganji *, PR Naidu Pothula, Nandam Ramarao, Raj Kumar Vijay, Bharath chandra
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft. Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden
 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture
 Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
A clinical study of minimal invasive anterior bridge plating for humerus shaft fractures
 2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 02 Page February 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Comparative Study of Functional Outcome of Compression Plating and Interlocking Nailing For Fracture Shaft Humerus in Adults Authors Dr.
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Comparative Study of Functional Outcome of Compression Plating and Interlocking Nailing For Fracture Shaft Humerus in Adults Authors Dr.
Surgical Technique. Distal Humerus Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
AcUMEDr. Locking Proximal Humeral Plate. PoLARUSr PHPt
 AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4
 Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Relationship between the Apex of Flexible Nail and the Level of Fracture: A Biomechanical Study Ahmed N* 1, Gakhar H 2, Cheung G 3, Sharma A 4 Abstract Background Centre of Orthopaedic biomechanics, Bath
Surgical Technique. Intramedullary locked Nailing With Screws for Humerus Fractures Solid/Cannulated. Humeral Interlocking Nail.
 Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
EXTRAARTICULAR ANTEGRADE FIXATION OF PROXIMAL PHALYNX FRACTURES WITH BENT K WIRE
 EXTRAARTICULAR ANTEGRADE FIXATION OF PROXIMAL PHALYNX FRACTURES WITH BENT K WIRE Research article Orthopaedics Mohammed Sadiq 1, Raju Kulkarni 2 1 - Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, ESIC
EXTRAARTICULAR ANTEGRADE FIXATION OF PROXIMAL PHALYNX FRACTURES WITH BENT K WIRE Research article Orthopaedics Mohammed Sadiq 1, Raju Kulkarni 2 1 - Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, ESIC
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures
 TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
TENS in paediatrics both bone forearm fractures Dr.Ajit Singh, Associate Professor, Department of orthopedics, IMS, BHU, Varanasi. Abstract Context: Diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna are common
THE NANCY NAIL. The End Caps ADVANTAGES OF NANCY NAIL
 NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3
 MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing
 Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Original Article A comparative study of 30 cases of trochanteric fracture femur treated with dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing Jaswinder Pal Singh Walia *, Himanshu Tailor**, H S Mann ***,
Clinico-radiological outcome of closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of proximal humerus fractures
 2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and
 Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
Original Article Functional and radiological outcome after closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and children Amin Kumar Shrestha 1, Suresh Uprety 2, Govinda K.C. 2, Sharma Paudel
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE
 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
Humerus Block. Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur *
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
humerus InSafeLOCK Nail
 humerus InSafeLOCK Nail Introduction Content Humerus InSafeLOCK Nail is an innovative intramedullary nailing system, developed for humerus problems. Humerus fractures have 5-6 % incidence of all bone fractures.
humerus InSafeLOCK Nail Introduction Content Humerus InSafeLOCK Nail is an innovative intramedullary nailing system, developed for humerus problems. Humerus fractures have 5-6 % incidence of all bone fractures.
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on Surgical Management of Distal Tibial Fractures by Using Minimally Invasive Technique
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on Surgical Management of Distal Tibial Fractures by Using Minimally Invasive Technique
Olecranon fracture. Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital
 Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale
 Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale Overview 1. What is IM Nailing? 2. History 3. Design Rationale & Evolution 4. Modern IM Nails 5. The Future What is IM Nailing? Method of internal fixation in
Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale Overview 1. What is IM Nailing? 2. History 3. Design Rationale & Evolution 4. Modern IM Nails 5. The Future What is IM Nailing? Method of internal fixation in
A comparative study of locking plate by MIPO versus closed interlocking intramedullary nail in extraarticular distal tibia fractures
 2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
2018; 4(3): 145-149 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 145-149 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 26-05-2018 Accepted: 27-06-2018 Kanachur Institute of Medical Sciences Mangalore University Road, Natekal,
Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study
 Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Original article: Assessment of Prognosis of Patients with Intertrochanteric Fractures Undergoing Treatment with PFN: An Observational Study Gajraj Singh 1, Sandhya Gautam 2 1Assistant Professor, Department
Case Presentation: Comminuted Fractures of the Proximal Ulna 11/28/2017. Disclosures. Surgical Strategy. Implant Choice. Melvin P.
 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for Proximal and Distal Fractures of The Tibia: A Biological Approach
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1603.006 Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for Proximal and Distal Fractures of The Tibia: A Biological Approach Gupta P, MS Orth, Tiwari A, MS Orth, Thora A,
http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1603.006 Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) for Proximal and Distal Fractures of The Tibia: A Biological Approach Gupta P, MS Orth, Tiwari A, MS Orth, Thora A,
Evaluation of the functional outcome in open tibial fractures managed with an Ilizarov fixator as a primary and definitive treatment modality
 2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
2017; 3(2): 436-440 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 436-440 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. SK Irfan Ali Assistant Professor, Dr. Sujai S Associate Professor,
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
LCP Distal Tibia Plate
 Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Fractures (Broken Bones)
 Fractures (Broken Bones) A fracture is a broken bone. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces). Types of Fractures Bones
Fractures (Broken Bones) A fracture is a broken bone. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces). Types of Fractures Bones
Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace
 18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
18 Fracture Shaft of Femur in Children with Newly Designed Femoral Brace Mahara D P, Lamichhane A, Acharya P, Shrestha G C Department of Orthopaedics, Tribhuvan University Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu,
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
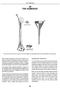 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia
 Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90.
 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of Contents Introduction
Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of Contents Introduction
Bi-columnar Plating For Supracondylar Fracture Extending Into Humeral Shaft : A Report Of Three Case And Literature Review
 Article ID: WMC001214 2046-1690 Bi-columnar Plating For Supracondylar Fracture Extending Into Humeral Shaft : A Report Of Three Case And Literature Review Corresponding Author: Dr. Chander Bhushan, Postgraduate
Article ID: WMC001214 2046-1690 Bi-columnar Plating For Supracondylar Fracture Extending Into Humeral Shaft : A Report Of Three Case And Literature Review Corresponding Author: Dr. Chander Bhushan, Postgraduate
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION
 C H A P T E R 3 0 COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most common fixation for proximal interphalangeal fusion
C H A P T E R 3 0 COMPARING KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION TO A NEW DEVICE USED FOR PROXIMAL INTERPHALANGEAL FUSION Scott R. Roman, DPM INTRODUCTION The most common fixation for proximal interphalangeal fusion
