Limb Alignment After Open-wedge High Tibial Osteotomy and Its Effect on the Clinical Outcome
|
|
|
- Dominick Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Limb Alignment After Open-wedge High Tibial Osteotomy and Its Effect on the Clinical Outcome HOSAM M. EL-AZAB, MD; MARIO MORGENSTERN, MD; PHILIP AHRENS, MD; TIBOR SCHUSTER, MSC; ANDREAS B. IMHOFF, MD; STEPHAN G.F. LORENZ, MD abstract Full article available online at ORTHOSuperSite.com. Search: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of alignment after open-wedge high tibial osteotomy and its effect on the clinical outcome. A prospective case series of 56 consecutive patients underwent open-wedge high tibial osteotomy fixed with a TomoFix plate fixator (Synthes, West Chester, Pennsylvania). The correction angle was radiologically determined preoperatively and at 6 months postoperatively. The patients were clinically and radiologically examined preoperatively and at 3, 6, and 36 months postoperatively. The mechanical axis of 50 knees was corrected from an average of 5.7 varus to 1.3 valgus. Forty-three patients had an acceptable correction with Mikulicz line crossing the tibial plateau between 50% to 70% of the tibial plateau width measured from the medial border. Undercorrection ( 50%, group II) and overcorrection ( 70%, group III) were found in 4 and 3 patients, respectively. The mean Lysholm-Gillquist score at 36 months had improved in all groups, with a statistically lower value for group II. Open-wedge high tibial osteotomy results in significant improvement of symptoms and function in all patients in the short term, even with under- and overcorrection of the osteotomy. Undercorrection was associated with a significantly lower clinical outcome in comparison to the accurate correction and overcorrection. Ligamentous laxity or soft tissue slackness of the knee can influence the overall correction after high tibial osteotomy and must be considered in preoperative planning. Patients with a high body mass index had inferior clinical results after open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Figure: Schematic drawing showing the planning for high tibial osteotomy according to Miniaci et al. 10 Line II connects the osteotomy hinge point H with the center of the ankle joint. Line III connects the hinge point H with the arc intersection with line Ia (right diagram). The angle of correction (angle ) is formed between line II and III. The proximal medical tibial angle (PMTA) is measured preoperatively and at 6 months postoperatively from the standing long-leg radiographs. Drs El-Azab, Morgenstern, Ahrens, Imhoff, and Lorenz are from the Department of Orthopedic Sports Medicine, and Mr Schuster is from the Institute for Medical Statistics and Epidemiology, Technical University Munich, Germany. Drs El-Azab, Morgenstern, Ahrens, Imhoff, and Lorenz and Mr Schuster have no relevant fi nancial relationships to disclose. Correspondence should be addressed to: Hosam M. El-Azab, MD, Department of Orthopedic Sports Medicine, Technical University Munich, Connolly St 32, Munich 80809, Germany (h.elazab@lrz.tum.de). doi: / e622
2 OPEN-WEDGE HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY EL-AZAB ET AL High tibial osteotomy is a reasonable treatment modality for unicompartmental medial osteoarthritis with varus deformity in young, active patients. 1-3 It is a realignment procedure to transfer a weight-bearing load from an affected medial compartment to a relatively intact lateral compartment of the knee. It promotes symptom relief and potential healing of damaged cartilage, 4 and it slows the progression of arthrosis in a knee with varus alignment. 5,6 Over- and undercorrection has been found by some authors to be associated with a poor clinical outcome. 6-8 Therefore, it is important to achieve and maintain accurate correction of limb alignment until complete healing. Loss of correction after adequate preoperative planning may occur intra- or postoperatively; lack of fixation and instability are the main causes Postoperative optimal alignment following valgus-producing high tibial osteotomy is controversial. Optimal correction was defined to be 8 of anatomic valgus, 11 between 3 and 6 of mechanical valgus, 3 when the weight-bearing line passed through a point between 62% and 66% 12 or 62.5% 6,13 of the tibial plateau width. With the introduction of the plate fixator for high tibial osteotomy in 2003, 14 the openwedge technique became more popular due to higher stability of the osteosynthesis and lower morbidity. 15,16 Most previous studies describing the accuracy of correction used a closed-wedge technique, 3,6,17 but few studies described this issue with the use of the openwedge technique To our knowledge, no study has described the accuracy of axis correction and its relation to clinical outcome using the TomoFix plate fixator (Synthes, West Chester, Pennsylvania). Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of correction after open-wedge high tibial osteotomy using the TomoFix plate and the correlation between the correction in the frontal plane and the clinical outcome. MATERIAL AND METHODS From September 2006 to April 2007, a consecutive series of 56 patients with varus osteoarthritis underwent an open-wedge high tibial osteotomy fixed with a TomoFix plate. Four patients (7.1%) were lost to follow-up. Two patients (3.6%) were excluded. One patient suffered a fall on ice, resulting in breakage of the plate and displacement of the osteotomy 3 months postoperatively. A revision operation was performed successfully. The second patient reported pain in the whole body, gastrointestinal pain, swelling in multiple areas of the body, and sleep problems 6 months postoperatively. The diagnosis of fibromyalgia was made, which required intensive rheumatologic treatment, biasing the clinical outcome. The average follow-up period was months (range, months). Forty (80%) men and 10 (20%) women had an average age of 43 years (range, years). Twenty-three (46%) right knees and 27 (54%) left knees were treated. Patients younger than 60 years suffering from symptomatic medial unicompartmental varus osteoarthritis or medial local cartilage damage were included in this study. Exclusion criteria include severe osteoarthritis of the knee (Kellgren-Lawrence grade III), 21 periarticular knee fractures, cruciate ligament insufficiency, patellofemoral complaints, and previous operations on the knee with arthrotomy. In addition to these selection criteria, the preosteotomy arthroscopy was considered, and meticulous intraoperative evaluation of the knee was also performed before osteotomy. As a prospective study, all patients were examined preoperatively with medical history, visual analog scale (VAS), Lysholm- Gillquist score, 22 and clinical examination of the knee. Preoperative radiologic examination included knee radiographs in 3 standard views and long-leg standing radiographs (Figure 1). Postoperatively, patients were followed up clinically at 3 (follow-up 1), 6 (follow-up 2), and an average of 36 (follow-up 3) months (range, months). A long-leg standing radiograph was performed once again at follow-up 2 (Figure 1). Hardware was removed at an average of 13 months (range, months) 1 Figure 1: Long-leg standing radiographs preoperatively (left) and 6 months postoperatively (right). Line I represents the preoperative weight-bearing line. Line Ia represents the postoperative weightbearing line passing through a point located at 62% of the tibial plateau width. postoperatively. For that reason, the patients were not evaluated at 12 months since the effect of metal removal may have an impact on the clinical results. 23 The planned correction was achieved when the weight-bearing line passed through a target point located at 62% of the tibial plateau width measured from the medial border of the tibial plateau. 6,12,13 The suggested zone of an acceptable correction OCTOBER 2011 Volume 34 Number 10 e623
3 was defined when the weight-bearing line passed between points at 70% and 50% of the tibial plateau width (group I). 23 An undercorrection was defined when the weight-bearing line passed through a point medial to 50% of the tibial plateau width (group II), whereas an overcorrection was defined when the weight-bearing line passed through a point lateral to 70% of the tibial plateau width (group III). Furthermore, patients in group I were considered to also be in a best desired correction group (group BC) when the weight-bearing line passed through 62% 5% (range, 57%-67%) of the tibial plateau width. 19 In addition, the pure bony correction was evaluated separately on long-standing limb radiographs by subtraction of 2 measurements of the proximal medial tibial angle pre- and postoperatively (Figure 2). Body mass index (BMI) was measured and correlated with the frontal plane correction and Lysholm score. Preoperative planning was performed for every patient according to the method of Miniaci et al 10 on the long-leg standing radiographs (Figure 2). Line I represents the old weight-bearing line of the limb extending from the center of the hip through the knee to the center of the ankle joint. Line Ia is the new mechanical axis of the limb, extending from the center of the hip passing through the Fujisawa point (62% of tibial plateau width) in the knee to the level of the ankle joint. Line II connects the osteotomy hinge point H with the center of the ankle joint. With the osteotomy hinge point H as the center, an angular arc is drawn from the center of the ankle to intersect line Ia. Line III connects the osteotomy hinge point H with the arc intersection of line Ia. The angle formed between line II and III is the correction wedge angle ( angle). SURGICAL TECHNIQUE A diagnostic arthroscopy of the knee joint was performed before surgical correction to verify the preoperative clinical and radiological findings. However, in no case was an osteotomy aborted due to the appearance of severe osteoarthritic changes on arthroscopy. Concomitantly, partial meniscectomy was performed in 26 patients (52%), microfracture in 3 patients (6%), and shaving and debridement in 4 patients (8%). The procedure was performed with a medial intraligamentous open-wedge high tibial osteotomy in a biplanar fashion according to the technique published by the AO knee expert group (Figure 3). 15,24,25 The new axis was set to the 62% valgus position, which was predetermined through the preoperative planning and confirmed intraoperatively under image intensifier. Control of the alignment was performed through visual inspection together with a cable extended over the whole limb from the center of the femoral head to the center of the ankle under fluoroscopic control. 26,27 The osteotomy was fixed with a TomoFix plate, and the gap of the osteotomy was not filled with any graft material (Figure 4). Postoperative Rehabilitation Patients were mobilized on the first postoperative day. Partial weight bearing of 15 to 20 kg was allowed for 6 weeks. After radiological evaluation, the patients were 2 Figure 2: Schematic drawing showing the planning for high tibial osteotomy according to Miniaci et al. 10 Line II connects the osteotomy hinge point H with the center of the ankle joint. Line III connects the hinge point H with the arc intersection with line Ia (right diagram). The angle of correction (angle ) is formed between line II and III. The proximal medical tibial angle (PMTA) is measured preoperatively and at 6 months postoperatively from the standing long-leg radiographs. 3A 3B 3C Figure 3: Operative technique of open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Successive osteotomes are introduced in the wedge gap (A). Maintenance of the wedge gap using the arthrodesis clamp (B). Measurement of wedge height using a wedge-shape instrument in the presence of arthrodesis clamp (C). e624
4 OPEN-WEDGE HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY EL-AZAB ET AL 4A 4B Figure 4: AP (left) and lateral (right) radiographs immediately postoperatively (A). AP (left) and lateral (right) radiographs after metal removal showing complete consolidation of the osteotomy (B). allowed to increase the weight-bearing load gradually by 15 to 20 kg every week to full weight bearing. During the early postoperative period, all patients received physiotherapy in the form of mobilization, continuous passive motion, and isometric exercises. The TomoFix plate fixator is a relatively large device that sometimes causes irritation over the stretched skin, which annoys many patients. Hardware removal was routinely performed approximately 12 months postoperatively (Figure 4). Statistical Analysis Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS software package (version 17; SPSS Inc, Chicago, Illinois). Two-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was conducted to assess differences in groups about the course of follow-up. Simple comparisons of means from 2 related measurements were performed by Student t test. Bivariate correlations of quantitative data were assessed using Spearman s correlation coefficient (r). Descriptive results were displayed as a mean standard deviation. All statistical tests were conducted 2-sided, and P.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS Forty-three patients (86%) showed an acceptable correction according to our definition (group I). Undercorrection (group II) and overcorrection (group III) was found in 4 (8%) and 3 patients (6%), respectively (Tables 1, 2). The best defined correction was found in 29 patients (58%). Analysis of the pre- and postoperative axial alignment revealed an average lateral shift of the weight-bearing line of mm (range, mm). After adjustment of the differences in baseline Lysholm score, there was a significant heterogeneity in Lysholm score level in different follow-up appointments between the groups (P.017). The corresponding group differences in mean Lysholm score were: I vs II, (P.004); I vs III, (P.45); and II vs III, (P.15). Furthermore, there was a significant increase in Lysholm score within the groups (P.05 for each trend test in each group), with statistically significant changes over time in reference to preoperative Lysholm score for group I (follow-up 1, P.015; follow-up 2, P.001; follow-up 3, P.001) and for group III at follow-up 2 (P.013) (Figure 5). The mean postoperative Lysholm score for the total population at follow-up 3 was points (range, ) and classified as excellent, good, fair, and poor in 22 (44%), 17 (34%), 7 (14%), and 4 patients (8%), respectively. A test of Lysholm score trends over time revealed a significant improvement in the total study population (P.01) (Figure 6). Furthermore, the number of patients with excellent and good Lysholm scores ( points) increased from 22 (44%) at follow-up 1 to 34 (68%) at follow-up 2 and 39 (78%) at follow-up 3. According to Lysholm score, the best clinical results (excellent and good) were found at follow-up 3 in groups I and BC (Table 3). At follow-up 3, forty-four patients (88%) reported a reduction of symptoms and functional improvement during activities of daily living. Twenty patients (40%) were very satisfied with the results, 22 (44%) were satisfied, 5 (10%) were partially satisfied, and 3 (6%) were not satisfied. Thirty-eight patients (76%) required no pain medication to perform sports and recreational activities, 10 (20%) required occasional pain medication, and 2 (4%) required regular pain medication. The VAS decreased significantly from (range, 0-10) preoperatively to (range, 0-10) at follow-up 3 (P.01). Mean angle was 7.5, closely similar to the mean bony correction of 7.1 (mean systematic deviation ; P.008) (Table 1). Average BMI of all patients was (range, 19-32). There was no significant correlation between BMI and the frontal plane axis correction (r 0.111; P.375), but there was an inverse mild correlation between BMI and Lysholm score at final follow-up, which was statistically significant (r 0.491; P.003). Apart from the abovementioned overand undercorrection complications, 3 patients had relatively delayed healing of the osteotomy with consequent delayed plate removal (between months postoperatively). These 3 patients belong to group I. However, no significant differences in the measured outcome of these patients were found when compared with the remaining patient cohort. One patient who was excluded from our series had a metal failure and secondary displacement of the osteotomy following knee trauma and was successfully revised. OCTOBER 2011 Volume 34 Number 10 e625
5 Table 1 Analysis of Examined Parameters DISCUSSION The most important finding in this study is that an acceptable correction of the weight-bearing line was achieved in 86% of the patients. Under- or overcorrection of the weight-bearing line was found in 14% of the patients. There was a significant improvement of clinical outcome over time in the average patient cohort (Figure 6). However, the clinical outcome of the undercorrected group II was significantly lower than that of group I at follow-ups 2 and 3 (Table 2). One reason for undercorrection despite meticulous preoperative planning and intraoperative measures may be ligamentous slackness and neglection of the weight-bearing effect on the mechanical axis of the lower limb. 12 During the operation, the patients lay supine and knee ligaments were relaxed, whereas the long-leg radiograph was performed in a full weight-bearing standing position. Another explanation may be an increased medial muscle cocontraction postoperatively or increased tension of the long adductor muscle and the hamstrings as a result of their irritation by the plate. 28,29 Although the mean bony correction was nearly similar to the preoperatively determined mean angle (7.1 and 7.5, respectively) (Table 1), inaccurate correction was detected in 14% of cases, which underlines the effect of soft tissue slackness or laxity on the measurement of mechanical axis. This difference between bony and overall correction should be considered during measurement of the weight-bearing line. Preoperative planning is an important task. The presence of ligamentous laxity or rotation of the limb during standing radiographs could be a source of error. Adequate intraoperative technique is mandatory to achieve an accurate correction together with intraoperative assessment of the weight-bearing line. Many techniques were described to assess the limb alignment intraoperatively, such as visual inspection, cable method, grid board, or navigation system. 26,27 However, all of these methods ignore the effect of weight bearing and ligamentous laxity on the mechanical axis of the lower limb. Variable Mean SD Minimum Maximum Preoperative mechanical axis, deg a angle Bony correction Postoperative mechanical axis, deg a WBL Preoperative, % Postoperative, % Lysholm score Postoperative Follow-up Follow-up Follow-up BMI Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; deg, degrees; SD, standard deviation; WBL, weightbearing line. a, varus;, valgus. Table 2 Relation Between Lysholm Score and WBL at Different Time Points Lysholm Score WBL, % Mean SD Minimum Maximum Preoperatively Group I Group II Group III Group BC Follow-up 1 Group I Group II Group III Group BC Follow-up 2 Group I Group II Group III Group BC Follow-up 3 Group I Group II Group III Group BC Abbreviations: BC, best correction group; BMI, body mass index; SD, standard deviation; WBL, weight-bearing line. e626
6 OPEN-WEDGE HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY EL-AZAB ET AL 5 6 Figure 5: Diagram showing the relationship between changes in Lysholm score over time and degree of correction in the 3 groups preoperatively and during follow-up (*: P.05). Abbreviations: exam, examination; Fu, follow-up; preop, preoperatively. Figure 6: Diagram showing changes of mean Lysholm score of the total population preoperatively and during follow-up. (*: P.05). Abbreviations: exam, examination; Fu, follow-up; preoperatively. Table 3 Postoperative WBL and Lysholm Scores at Final Follow-up Mean Postoperative WBL, % No. Patients With Excellent/Good Results (%) Group (% WBL) No. Patients (%) Lysholm Score I (50-70) 43 (86) (86) II ( 50) 4 (8) (0) III ( 70) 3 (6) (67) BC (57-67) 29 (58) (86) Abbreviation: BC, best correction group; WBL, weight-bearing line. According to long-term early studies reporting the effect of high tibial osteotomy, under- or overcorrection is frequently associated with inferior clinical results. 7,8,13 Undercorrection results in a recurrence of varus deformity and is associated with persistence or recurrence of symptoms. 3,30 Overcorrection can lead to a poor cosmetic result, persistent pain, tilting of the joint line, and considerable loss of bone in case of closed wedge technique, a situation which is often difficult to treat with another osteotomy or an arthroplasty. 18,31 The improvement in groups II and III (under- and overcorrection) might be explained with changes in biomechanics and kinematics of the knee with release or decrease of the mechanical pressure on the symptomatic medial compartment, 32 lowering of the intraosseous venous pressure, and improvement of blood supply of the knee. 33 Our result concerning postoperative correction was better than that of Marti et al, 19 who found the best acceptable correction (weight-bearing line between 57%- 67%) in 50% of their patients (58% in our series). Although our radiological results were slightly inferior to those of Niemeyer et al, 23 who found an acceptable correction (weight-bearing line between 50%-70) in 90% of their patients (86% in our series), the mean Lysholm score in our series at final follow-up was superior (85 vs 78 points). We found no significant correlation between BMI and the degree of correction in the frontal plane. However, we found a mild inverse correlation between BMI and Lysholm score at follow-up, which means a deterioration of the clinical results with elevated BMI. This result is similar to Spahn et al, 34 who found a negative correlation between the clinical results and BMI. They suggested that high BMI could be implicated as a reason for loss of correction after weight bearing. This explanation can be accepted with closed-wedge or open-wedge high tibial osteotomy with conventional noninterlocking plates due to further collapse of the osteotomy. Since interlocking plate fixators were used in this series, no collapse should be expected. 15,35 However, due to the lack of immediate postoperative long-leg radiographs, this study cannot prove this thesis. In our opinion, worsening of the clinical results with increased BMI correlates to elevated biomechanical loads on the knee joint cartilage and the resulting progress of osteoarthrosis rather than loss of correction of osteotomy. Considered a limitation of our study, the follow-up time was relatively short. Longterm follow-up evaluation is mandatory to determine the outcome of open-wedge high tibial osteotomy under the use of an interlocking fixation device. OCTOBER 2011 Volume 34 Number 10 e627
7 CONCLUSION Open-wedge high tibial osteotomy results in significant improvement of symptoms and function in all patients in the short term, even with under- and overcorrection of the osteotomy. Undercorrection was associated with a significantly lower clinical outcome in comparison to accurate correction and overcorrection. Ligamentous laxity or soft tissue slackness of the knee can influence the overall correction after high tibial osteotomy and must be considered in preoperative planning. Patients with a high BMI had inferior clinical results after openwedge high tibial osteotomy. REFERENCES 1. Coventry MB, Ilstrup DM, Wallrichs SL. Proximal tibial osteotomy. A critical long-term study of eighty-seven cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75(2): Insall JN, Joseph DM, Msika C. High tibial osteotomy for varus gonarthrosis. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984; 66(7): Hernigou P, Medevielle D, Debeyre J, Goutallier D. Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteenyear follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987; 69(3): Matsunaga D, Akizuki S, Takizawa T, Yamazaki I, Kuraishi J. Repair of articular cartilage and clinical outcome after osteotomy with microfracture or abrasion arthroplasty for medial gonarthrosis [published online ahead of print September 5, 2007]. Knee. 2007; 14(6): Ivarsson I, Myrnerts R, Gillquist J. High tibial osteotomy for medial osteoarthritis of the knee. A 5 to 7 and 11 year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72(2): Fujisawa Y, Masuhara K, Shiomi S. The effect of high tibial osteotomy on osteoarthritis of the knee. An arthroscopic study of 54 knee joints. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979; 10(3): Odenbring S, Egund N, Hagstedt B, Larsson J, Lindstrand A, Toksvig-Larsen S. Ten-year results of tibial osteotomy for medial gonarthrosis. The influence of overcorrection. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1991; 110(2): Pape D, Adam F, Rupp S, Seil R, Kohn D. Stability, bone healing and loss of correction after valgus realignment of the tibial head. A roentgen stereometry analysis [in German]. Orthopade. 2004; 33(2): Sprenger TR, Doerzbacher JF. Tibial osteotomy for the treatment of varus gonarthrosis. Survival and failure analysis to twenty-two years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85(3): Miniaci A, Ballmer FT, Ballmer PM, Jakob RP. Proximal tibial osteotomy. A new fixation device. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (246): Coventry MB. Upper tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67(7): Dugdale TW, Noyes FR, Styer D. Preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomy. The effect of lateral tibiofemoral separation and tibiofemoral length. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; (274): Noyes FR, Barber SD, Simon R. High tibial osteotomy and ligament reconstruction in varus angulated, anterior cruciate ligament-deficient knees. A two- to seven-year follow-up study. Am J Sports Med. 1993; 21(1): Staubli AE, De Simoni C, Babst R, Lobenhoffer P. TomoFix: a new LCP-concept for open wedge osteotomy of the medial proximal tibia early results in 92 cases. Injury. 2003; 34(Suppl 2):B Agneskirchner JD, Freiling D, Hurschler C, Lobenhoffer P. Primary stability of four different implants for opening wedge high tibial osteotomy [published online ahead of print November 12, 2005]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006; 14(3): Brinkman JM, Lobenhoffer P, Agneskirchner JD, Staubli AE, Wymenga AB, van Heerwaarden RJ. Osteotomies around the knee: patient selection, stability of fixation and bone healing in high tibial osteotomies. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90(12): Coventry MB. Upper tibial osteotomy for gonarthrosis. The evolution of the operation in the last 18 years and long term results. Orthop Clin North Am. 1979; 10(1): Krackow KA, Holtgrewe JL. Experience with a new technique for managing severely overcorrected valgus high tibial osteotomy at total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; (258): Marti CB, Gautier E, Wachtl SW, Jakob RP. Accuracy of frontal and sagittal plane correction in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2004; 20(4): Kim SJ, Koh YG, Chun YM, Kim YC, Park YS, Sung CH. Medial opening wedge hightibial osteotomy using a kinematic navigation system versus a conventional method: a 1-year retrospective, comparative study [published online ahead of print October 11, 2008]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009; 17(2): Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957; 16(4): Lysholm J, Gillquist J. Evaluation of knee ligament surgery results with special emphasis on use of a scoring scale. Am J Sports Med. 1982; 10(3): Niemeyer P, Koestler W, Kaehny C, et al. Twoyear results of open-wedge high tibial osteotomy with fixation by medial plate fixator for medial compartment arthritis with varus malalignment of the knee [published online ahead of print April 21, 2008]. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24(7): Lobenhoffer P, Agneskirchner J, Zoch W. Open valgus alignment osteotomy of the proximal tibia with fixation by medial plate fixator [in German]. Orthopade. 2004; 33(2): Lobenhoffer P, Agneskirchner JD. Improvements in surgical technique of valgus high tibial osteotomy [published online ahead of print January 11, 2003]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003; 11(3): Kendoff D, Citak M, Pearle A, et al. Influence of lower limb rotation in navigated alignment analysis: implications for high tibial osteotomies [published online ahead of print March 16, 2007]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007; 15(8): Kim SJ, Koh YG, Chun YM, Kim YC, Park YS, Sung CH. Medial opening wedge hightibial osteotomy using a kinematic navigation system versus a conventional method: a 1-year retrospective, comparative study [published online ahead of print October 11, 2008]. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009; 17(2): Briem K, Ramsey DK, Newcomb W, Rudolph KS, Snyder-Mackler L. Effects of the amount of valgus correction for medial compartment knee osteoarthritis on clinical outcome, knee kinetics and muscle co-contraction after opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Res. 2007; 25(3): Wang JW, Kuo KN, Andriacchi TP, Galante JO. The influence of walking mechanics and time on the results of proximal tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990; 72(6): Berman AT, Bosacco SJ, Kirshner S, Avolio A Jr. Factors influencing long-term results in high tibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (272): Grelsamer RP. Unicompartmental osteoarthrosis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77(2): Harris WR, Kostuik JP. High tibial osteotomy for osteo-arthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970; 52(2): Arnoldi CC, Lemperg K, Linderholm H. Intraosseous hypertension and pain in the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975; 57(3): Spahn G, Kirschbaum S, Kahl E. Factors that influence high tibial osteotomy results in patients with medial gonarthritis: a score to predict the results [published online ahead of print November 4, 2005]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(2): Valkering KP, van den Bekerom MPJ, Kappelhoff FM, Albers GH. Complications after TomoFix medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Knee Surg. 2009; 22(3): e628
The coronal hypomochlion
 KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
Original Article. Seong-Dae Yoon, MD 1, GuoFeng Zhang, MD 2, Hee-June Kim, MD 1, Byoung-Joo Lee, MD 1, and Hee-Soo Kyung, MD, PhD 1 1.
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2016;28(4):283-288 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.16.052 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparison of Cable Method and Miniaci Method
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2016;28(4):283-288 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.16.052 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparison of Cable Method and Miniaci Method
The effect of closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope
 The effect of closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope A RETROSPECTIVE RADIOLOGICAL REVIEW OF 120 CASES H. El-Azab, A. Halawa, H. Anetzberger, A. B. Imhoff, S. Hinterwimmer From Abteilung
The effect of closed- and open-wedge high tibial osteotomy on tibial slope A RETROSPECTIVE RADIOLOGICAL REVIEW OF 120 CASES H. El-Azab, A. Halawa, H. Anetzberger, A. B. Imhoff, S. Hinterwimmer From Abteilung
Mid Term Outcome of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
 Original Research Tarun Kumar Badam 1*, Muthukumar Balaji 2, Sathish Devadoss 3, A. Devadoss 4 1 Junior Resident, 2 Junior Consultant, 3 Senior Consultant, 4 Chief, Department of Orthopaedics, IORAS Devadoss
Original Research Tarun Kumar Badam 1*, Muthukumar Balaji 2, Sathish Devadoss 3, A. Devadoss 4 1 Junior Resident, 2 Junior Consultant, 3 Senior Consultant, 4 Chief, Department of Orthopaedics, IORAS Devadoss
Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint: Comparison between the Aescula and TomoFix Plate
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:185-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.185 Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:185-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.185 Biplanar Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in the Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after High Tibial Osteotomy
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.019 Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up, MD Institute of Orthopaedics, Lerdsin Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1403.019 Clinical Outcome of Medial Opening Wedge Osteotomy with T-Locking Plate : Two Years Follow-Up, MD Institute of Orthopaedics, Lerdsin Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
21/01/10. Disclosures. Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature. Introduction. OW osteotomy and bone graft
 3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
3rd Annual Advanced Course on Knee Surgery January 17-22, 2010, Val D Isere, Results of High Tibial Osteotomy Osteotomy: Review of the Literature Disclosures Conflict of interest related to this presentation:
Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the Varus Deformity after High Tibial Osteotomy?
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 18;3():311-318 https://doi.org/1.579/ksrr.18.35 pissn 3-7 eissn 3-51 Knee Surgery & Related Research Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 18;3():311-318 https://doi.org/1.579/ksrr.18.35 pissn 3-7 eissn 3-51 Knee Surgery & Related Research Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the
Prospective 5-year survival rate data following open-wedge valgus high tibial osteotomy
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2015) 23:1949 1955 DOI 10.1007/s00167-013-2762-y KNEE Prospective 5-year survival rate data following open-wedge valgus high tibial osteotomy Gerrit Bode Johanna von
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2015) 23:1949 1955 DOI 10.1007/s00167-013-2762-y KNEE Prospective 5-year survival rate data following open-wedge valgus high tibial osteotomy Gerrit Bode Johanna von
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust
 Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust Douglas D.R. Naudie,* MD, FRCSC, Annunziato Amendola, MD, FRCSC, and Peter J. Fowler, MD, FRCSC From the Division of Orthopaedic
Opening Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy for Symptomatic Hyperextension-Varus Thrust Douglas D.R. Naudie,* MD, FRCSC, Annunziato Amendola, MD, FRCSC, and Peter J. Fowler, MD, FRCSC From the Division of Orthopaedic
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
There have been conflicting results reported in the
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
Osteotomy at the distal third of tibial tuberosity with LCP L-buttress plate for correction of tibia vara
 Huang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Osteotomy at the distal third of tibial tuberosity with LCP L-buttress plate for correction of tibia vara
Huang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Osteotomy at the distal third of tibial tuberosity with LCP L-buttress plate for correction of tibia vara
Results of arthroscopic surgery, with or without high Tibial osteotomy, in osteoarthritis of knee
 2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(3): 100-105 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(3): 100-105 Received: 17-05-2018 Accepted: 18-06-2018 Dr. Tarkik Amin Assistant Professor,
Computer-assisted High Tibial Osteotomy: Preliminary Results
 Computer-assisted High Tibial Osteotomy: Preliminary Results RAFFAELE IORIO, MD; ANTONIO VADALÀ, MD; SILVIO GIANNETTI, MD; MARCO PAGNOTTELLI, MD; PRISCILLA DI SETTE, MD; FABIO CONTEDUCA, MD; ANDREA FERRETTI,
Computer-assisted High Tibial Osteotomy: Preliminary Results RAFFAELE IORIO, MD; ANTONIO VADALÀ, MD; SILVIO GIANNETTI, MD; MARCO PAGNOTTELLI, MD; PRISCILLA DI SETTE, MD; FABIO CONTEDUCA, MD; ANDREA FERRETTI,
Navigation versus conventional high tibial osteotomy: systematic review
 Page 1 of Surgical procedures Navigation versus conventional high tibial osteotomy: systematic review KA Hasan *, D De Sa, M Khan M, T Pazionis, P Zalzal Abstract Introduction One major use for high tibial
Page 1 of Surgical procedures Navigation versus conventional high tibial osteotomy: systematic review KA Hasan *, D De Sa, M Khan M, T Pazionis, P Zalzal Abstract Introduction One major use for high tibial
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar
 Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar High Tibial Osteotomy: HTO! Valgisation HTO Intended to transfer the mechanical
Choice of spacer material for HTO! P. Landreau, MD Chief of Surgery Aspetar, Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine Hospital Doha, Qatar High Tibial Osteotomy: HTO! Valgisation HTO Intended to transfer the mechanical
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee
 DOCTYPE = ARTICLE Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee William I. Sterett, MD,* and J. Richard Steadman, MD From the Steadman Hawkins Sports Medicine Foundation, Vail, Colorado
DOCTYPE = ARTICLE Chondral Resurfacing and High Tibial Osteotomy in the Varus Knee William I. Sterett, MD,* and J. Richard Steadman, MD From the Steadman Hawkins Sports Medicine Foundation, Vail, Colorado
Despite the expanding indications for knee arthroplasty,
 Prospective Outcomes of Young and Middle-Aged Adults With Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis Treated With a Proximal Tibial Opening Wedge Osteotomy Robert F. LaPrade, M.D., Ph.D., Stanislav I. Spiridonov,
Prospective Outcomes of Young and Middle-Aged Adults With Medial Compartment Osteoarthritis Treated With a Proximal Tibial Opening Wedge Osteotomy Robert F. LaPrade, M.D., Ph.D., Stanislav I. Spiridonov,
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 410 417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis C. Catier, M.
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 410 417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis C. Catier, M.
High tibial valgus osteotomy using the Tomofix plate Medium-term results in young patients
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 360-367 ORIGINAL STUDY High tibial valgus osteotomy using the Tomofix plate Medium-term results in young patients Saeed H. ZAKI, Paul J. RAE From the Wrightington Hospital
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 360-367 ORIGINAL STUDY High tibial valgus osteotomy using the Tomofix plate Medium-term results in young patients Saeed H. ZAKI, Paul J. RAE From the Wrightington Hospital
Su Chan Lee, MD, Kwang Am Jung, MD, Chang Hyun Nam, MD, Soong Hyun Jung, MD, Seung Hyun Hwang, MD
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:47-54 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.47 The Short-term Follow-up Results of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Using an Aescula Open Wedge Plate and
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2010;2:47-54 doi:10.4055/cios.2010.2.1.47 The Short-term Follow-up Results of Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy with Using an Aescula Open Wedge Plate and
Reliability of computer-assisted surgery as an intraoperative ruler in navigated high tibial osteotomy
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:297 302 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1145-9 ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Reliability of computer-assisted surgery as an intraoperative ruler in navigated high tibial osteotomy Florian
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:297 302 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1145-9 ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Reliability of computer-assisted surgery as an intraoperative ruler in navigated high tibial osteotomy Florian
Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy, MD 1,2 * ; Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan, MD 1 ; Meir Liebergall, MD 2; Andrew D. Pearle, MD 1 1Hospital for Special Surgery, Weill Medical
Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy, MD 1,2 * ; Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan, MD 1 ; Meir Liebergall, MD 2; Andrew D. Pearle, MD 1 1Hospital for Special Surgery, Weill Medical
High tibial osteotomy with Puddu plate for the treatment of varus gonarthrosis
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 948 954 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-006-0074-1 Mehmet Asik Cengiz Sen Bulent Kilic S. Bora Goksan Feyyaz Ciftci Omer F. Taser High tibial osteotomy with Puddu
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 948 954 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-006-0074-1 Mehmet Asik Cengiz Sen Bulent Kilic S. Bora Goksan Feyyaz Ciftci Omer F. Taser High tibial osteotomy with Puddu
Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity
 ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate. 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique
 Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning HTO Body weight < 100 kg, Non smoker. For preoperative planning be aware of potential femoral
Opening Wedge Osteotomy System using PEEKPower HTO Plate 2 nd Generation Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning HTO Body weight < 100 kg, Non smoker. For preoperative planning be aware of potential femoral
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Computer-Assisted Navigation in High Tibial Osteotomy: A Systematic Review of the Literature
 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 2: M8) 305-312 305 Open Access Computer-Assisted Navigation in High Tibial Osteotomy: A Systematic Review of the Literature Natasha E. Picardo *,1, Wasim
The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, (Suppl 2: M8) 305-312 305 Open Access Computer-Assisted Navigation in High Tibial Osteotomy: A Systematic Review of the Literature Natasha E. Picardo *,1, Wasim
Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain
 DOI 10.1007/s11420-019-09670-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain Rachael J. Da Cunha, MD,
DOI 10.1007/s11420-019-09670-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Biomechanical and Functional Improvements Gained by Proximal Tibia Osteotomy Correction of Genu Varum in Patients with Knee Pain Rachael J. Da Cunha, MD,
The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information
 The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information The Treatment Gap Increasing numbers of young, active OA patients with longer life expectancy and higher activity demands. 1 Large increase in arthroplasty
The KineSpring Knee Implant System Product Information The Treatment Gap Increasing numbers of young, active OA patients with longer life expectancy and higher activity demands. 1 Large increase in arthroplasty
Original Article. Introduction
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):34-41 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.035 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Clinical and Radiological Results with Second-Look
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):34-41 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.035 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Clinical and Radiological Results with Second-Look
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Technique Guide. TomoFix Medial Distal Femur (MDF). For closed-wedge varus femoral osteotomies.
 Technique Guide TomoFix Medial Distal Femur (MDF). For closed-wedge varus femoral osteotomies. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits of the TomoFix Knee 2 Osteotomy System Osteotomy Principles
Technique Guide TomoFix Medial Distal Femur (MDF). For closed-wedge varus femoral osteotomies. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits of the TomoFix Knee 2 Osteotomy System Osteotomy Principles
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy (average 6 years follow-up)
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2003) 11 : 139 144 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-003-0344-0 Cengiz Sen Mehmet Kocaoglu Levent Eralp The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2003) 11 : 139 144 KNEE DOI 10.1007/s00167-003-0344-0 Cengiz Sen Mehmet Kocaoglu Levent Eralp The advantages of circular external fixation used in high tibial osteotomy
2/7/2018. Osteotomies About the Knee. Editorial Board AJSM Social Media. Consultant. <55 yrs old 55 yrs old >75 yrs old
 21st Annual Orthopaedic & Sports Medicine Conference February 9 2018 February 10 2018 Disclosures Osteotomies About the Knee Dr Alan Getgood MD MPhil FRCS(Tr&Orth) DipSEM Assistant Professor Complex Knee
21st Annual Orthopaedic & Sports Medicine Conference February 9 2018 February 10 2018 Disclosures Osteotomies About the Knee Dr Alan Getgood MD MPhil FRCS(Tr&Orth) DipSEM Assistant Professor Complex Knee
TomoFix Medial High Tibial Plate (MHT). For Medial High Tibial Osteotomies.
 TomoFix Medial High Tibial Plate (MHT). For Medial High Tibial Osteotomies. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
TomoFix Medial High Tibial Plate (MHT). For Medial High Tibial Osteotomies. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
The Learning Curve for Biplane Medial Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy in 100 Consecutive Cases Assessed Using the Cumulative Summation Method
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 8;(4):- https://doi.org/.579/ksrr.7.64 pissn 4-76 eissn 4-45 Knee Surgery & Related Research The Learning Curve for Biplane Medial Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 8;(4):- https://doi.org/.579/ksrr.7.64 pissn 4-76 eissn 4-45 Knee Surgery & Related Research The Learning Curve for Biplane Medial Open Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
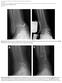 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Modern High Tibial Osteotomy. Medial Compartment OsteoArthritis of Knee
 Modern High Tibial Osteotomy Medial Compartment OsteoArthritis of Knee Dr. Milind Chaudhary Director Int. Deformity & Lengthening Inst. Akola Consultant, Jaslok Hospital, Mumbai Imm.Past President ASAMI
Modern High Tibial Osteotomy Medial Compartment OsteoArthritis of Knee Dr. Milind Chaudhary Director Int. Deformity & Lengthening Inst. Akola Consultant, Jaslok Hospital, Mumbai Imm.Past President ASAMI
Open-wedge HTO with a locking plate (TomoFix ) for treatment of medial monocompartment osteoarthritis
 Open-wedge HTO with a locking plate (TomoFix ) for treatment of medial monocompartment osteoarthritis Introduction The combination of malalignment and unicompartmental osteoarthritis, more often encountered
Open-wedge HTO with a locking plate (TomoFix ) for treatment of medial monocompartment osteoarthritis Introduction The combination of malalignment and unicompartmental osteoarthritis, more often encountered
Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist
 Knee Prosthesis Models & Materials, Surgical Techniques and Approaches Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist INTRODUCTION VARUS VALGUS 46 Y OLD MALE Pain in the medial compartment left more than
Knee Prosthesis Models & Materials, Surgical Techniques and Approaches Stefan Rahm MD University Hospital Balgrist INTRODUCTION VARUS VALGUS 46 Y OLD MALE Pain in the medial compartment left more than
Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Takuya Konno, MD 1, Tomohiro Onodera, MD, PhD 1, Yasuhiko Kasahara, MD, PhD 1, Daisuke Takahashi 1, Norimasa
Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Takuya Konno, MD 1, Tomohiro Onodera, MD, PhD 1, Yasuhiko Kasahara, MD, PhD 1, Daisuke Takahashi 1, Norimasa
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
High Tibial Osteotomy Using the Tomofix Plating System: Short Term Outcomes in Young Adults
 International Journal of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation, 2014, 1, 39-43 39 High Tibial Osteotomy Using the Tomofix Plating System: Short Term Outcomes in Young Adults Laurence Dodd *, Ryan Wood, Oliver
International Journal of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation, 2014, 1, 39-43 39 High Tibial Osteotomy Using the Tomofix Plating System: Short Term Outcomes in Young Adults Laurence Dodd *, Ryan Wood, Oliver
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
High tibial osteotomy in Sweden,
 244 Acta Orthopaedica 212; 83 (3): 244 248 High tibial osteotomy in Sweden, 1998 27 A population-based study of the use and rate of revision to knee arthroplasty Annette W-Dahl 1,2, Otto Robertsson 1,2,
244 Acta Orthopaedica 212; 83 (3): 244 248 High tibial osteotomy in Sweden, 1998 27 A population-based study of the use and rate of revision to knee arthroplasty Annette W-Dahl 1,2, Otto Robertsson 1,2,
Return to work and clinical outcome after open wedge HTO
 Return to work and clinical outcome after open wedge HTO Steffen Schröter, Johannes Mueller, Ronald van Heerwaarden, Philipp Lobenhoffer, Ulrich Stöckle & Dirk Albrecht Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology,
Return to work and clinical outcome after open wedge HTO Steffen Schröter, Johannes Mueller, Ronald van Heerwaarden, Philipp Lobenhoffer, Ulrich Stöckle & Dirk Albrecht Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology,
Surgical Considerations:
 Knee Osteoarthritis / Defects of the Articular Cartilage Articular cartilage defects are variable in their presentation, in terms of location as well as severity. Several surgical procedures have been
Knee Osteoarthritis / Defects of the Articular Cartilage Articular cartilage defects are variable in their presentation, in terms of location as well as severity. Several surgical procedures have been
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016
 SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
SCIENTIFIC POSTER #28 Tibia OTA 2016 Effectiveness of Complex Combined Nonunion/Malunion Correction, Utilizing a Hexapod External Fixator John Arvesen, MD 1 ; J. Tracy Watson, MD 2 ; Heidi Israel, PhD,
Cheng Jin 1, Eun-Kyoo Song 2, Quan-He Jin 2, Nam-Hun Lee 2 and Jong-Keun Seon 2*
 Jin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:228 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2161-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcomes of simultaneous high tibial osteotomy and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Jin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:228 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2161-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcomes of simultaneous high tibial osteotomy and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis
 Clinical Report Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(1)
Clinical Report Proximal fibular osteotomy: a new surgery for pain relief and improvement of joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(1)
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Technique Guide. TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee.
 Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Jail Technique for the Fixation of Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Jail Technique for the Fixation of Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures Operative Management of Split Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Jail Technique for the Fixation of Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fractures Operative Management of Split Unicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture
Meniscal Tears/Deficiency in Athletes
 Meniscal Tears/Deficiency in Athletes A. Amendola MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Sports Medicine Duke University 1 2 Meniscal tears Introduction Meniscal tears are one of the most frequent
Meniscal Tears/Deficiency in Athletes A. Amendola MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Director of Sports Medicine Duke University 1 2 Meniscal tears Introduction Meniscal tears are one of the most frequent
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
Role of osteotomy in multiligament knee injuries
 Review Article Page 1 of 11 Role of osteotomy in multiligament knee injuries Taher Abdelrahman 1, Alan Getgood 2 1 Clinical Fellow Orthopaedic Sport Medicine, 2 Department of Surgery, Fowler Kennedy Sport
Review Article Page 1 of 11 Role of osteotomy in multiligament knee injuries Taher Abdelrahman 1, Alan Getgood 2 1 Clinical Fellow Orthopaedic Sport Medicine, 2 Department of Surgery, Fowler Kennedy Sport
Anterior Tibial Subluxation with ACL Deficient Knees influences the Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction.
 Anterior Tibial Subluxation with ACL Deficient Knees influences the Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction. RYOTA TAKASE 1), KAZUHISA HATAYAMA 1), MASANORI TERAUCHI 1) KENICHI SAITO 2), HIROTAKA CHIKUDA
Anterior Tibial Subluxation with ACL Deficient Knees influences the Knee Stability after ACL Reconstruction. RYOTA TAKASE 1), KAZUHISA HATAYAMA 1), MASANORI TERAUCHI 1) KENICHI SAITO 2), HIROTAKA CHIKUDA
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Massive Varus- Overview. Massive Varus- Classification. Massive Varus- Definition 07/02/14. Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR
 07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and Varus Knee Deformity Based on Two-Dimensional Assessment of Side-to-Side Differences
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy
 Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy Hamamatsu University School of Medicine Mitsuru Hanada, Shoichi
Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy Hamamatsu University School of Medicine Mitsuru Hanada, Shoichi
Keywords Osteotomy; Knee; Osteoarthritis; Tibia/surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Roberto da Cunha Luciano 1, Getúlio Danival de Moura Souza 2, Juliano Rispoli 3, Rodrigo Galvão Cardoso 4, Marcus Vinícius Martins do Nascimento 5, Gustavo Gontijo Domingos 6, Dyego Vilela
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Roberto da Cunha Luciano 1, Getúlio Danival de Moura Souza 2, Juliano Rispoli 3, Rodrigo Galvão Cardoso 4, Marcus Vinícius Martins do Nascimento 5, Gustavo Gontijo Domingos 6, Dyego Vilela
H.P. Teng, Y.J. Chou, L.C. Lin, and C.Y. Wong Under general or spinal anesthesia, the knee was flexed gently. In the cases of limited ROM, gentle and
 THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
Complications of Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:365-372 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.365 Complications of Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Jong Hun Ji, MD, Sang Eun Park, MD,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:365-372 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.365 Complications of Medial Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Jong Hun Ji, MD, Sang Eun Park, MD,
ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play
 ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play Seth Gasser, MD Director of Sports Medicine Florida Orthopaedic Institute Introduction Return to Play: the point in recovery from an injury when a person is safely
ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play Seth Gasser, MD Director of Sports Medicine Florida Orthopaedic Institute Introduction Return to Play: the point in recovery from an injury when a person is safely
HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS
 Original Article HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS Roger Avakian 1, Nilson Roberto Severino 2, Ricardo de Paula Leite Cury 3, Victor Marques de Oliveira 1, Tatsuo Aihara 4, Osmar Pedro
Original Article HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMY IN PATIENTS WITH KNEE ARTHROSIS Roger Avakian 1, Nilson Roberto Severino 2, Ricardo de Paula Leite Cury 3, Victor Marques de Oliveira 1, Tatsuo Aihara 4, Osmar Pedro
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury
 Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement
 016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique
 Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique W-Dahl, Annette; Toksvig-Larsen, Sören Published in: Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica
Cigarette smoking delays bone healing: A prospective study of 200 patients operated on by the hemicallotasis technique W-Dahl, Annette; Toksvig-Larsen, Sören Published in: Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica
High tibial osteotomy with a dynamic axial fixator
 KNEE High tibial osteotomy with a dynamic axial fixator PRECISION IN ACHIEVING ALIGNMENT V. Bachhal, S. S. Sankhala, N. Jindal, M. S. Dhillon From Sawai Man Singh Medical College and Hospital, Jaipur,
KNEE High tibial osteotomy with a dynamic axial fixator PRECISION IN ACHIEVING ALIGNMENT V. Bachhal, S. S. Sankhala, N. Jindal, M. S. Dhillon From Sawai Man Singh Medical College and Hospital, Jaipur,
Axial and torsional stability of an improved single-plane and a new bi-plane osteotomy technique for supracondylar femur osteotomies
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2011) 19:1090 1098 DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1349-0 KNEE Axial and torsional stability of an improved single-plane and a new bi-plane osteotomy technique for supracondylar
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2011) 19:1090 1098 DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1349-0 KNEE Axial and torsional stability of an improved single-plane and a new bi-plane osteotomy technique for supracondylar
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Influence of High Tibial Osteotomy on Bone Marrow Edema in the Knee
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 454, pp. 155 162 26 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Influence of High Tibial Osteotomy on Bone Marrow Edema in the Knee A. H. Kröner, MD * ; C. E. Berger,
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 454, pp. 155 162 26 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Influence of High Tibial Osteotomy on Bone Marrow Edema in the Knee A. H. Kröner, MD * ; C. E. Berger,
Principles Starting Point Trajectory L/A/R Stable Construct. DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS 5/16/2017
 DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS Medical/Orthopaedic Publications Editorial/Governing Board OTA Newsletter Editor OsteoSynthesis, The JOT Online Discussion Forum Editor JOT Associate Editor JAAOS
DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS Medical/Orthopaedic Publications Editorial/Governing Board OTA Newsletter Editor OsteoSynthesis, The JOT Online Discussion Forum Editor JOT Associate Editor JAAOS
TomoFix. Application Notes. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
 TomoFix Application Notes This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of Contents Introduction 2 Case Examples 4 Features
TomoFix Application Notes This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Table of Contents Introduction 2 Case Examples 4 Features
Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes
 Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes William M Weiss, MD MSc FRCSC Orthopedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy & Extremity Reconstruction
Knee Dislocation: Spectrum of Injury, Evolution of Treatment & Modern Outcomes William M Weiss, MD MSc FRCSC Orthopedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy & Extremity Reconstruction
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
Malalignment can affect any of the three
 ch05_anbari:layout 1 8/20/2009 2:12 PM Page 47 C H A P T E R 5 Osteotomies: High Tibial, Distal Femoral, and Tibial Tubercle Ammar Anbari, MD Malalignment can affect any of the three compartments of the
ch05_anbari:layout 1 8/20/2009 2:12 PM Page 47 C H A P T E R 5 Osteotomies: High Tibial, Distal Femoral, and Tibial Tubercle Ammar Anbari, MD Malalignment can affect any of the three compartments of the
The knee is a complex and dynamic joint that is
 87 Sagittal and Coronal Biomechanics of the Knee A Rationale for Corrective Measures Harlan B. Levine, M.D., and Joseph A. Bosco III, M.D. The knee is a complex and dynamic joint that is subjected to many
87 Sagittal and Coronal Biomechanics of the Knee A Rationale for Corrective Measures Harlan B. Levine, M.D., and Joseph A. Bosco III, M.D. The knee is a complex and dynamic joint that is subjected to many
Patellofemoral Joint. Question? ANATOMY
 Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
