Philos Locking plates in proximal humerus fractures literature review.
|
|
|
- Samantha Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 1 Philos Locking plates in proximal humerus fractures literature review. R Sahu Citation R Sahu. Philos Locking plates in proximal humerus fractures literature review.. The Internet Journal of Health Volume 11 Number 1. Abstract Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the results of various studies conducted on patient s world wide so far and results of proximal humerus fractures treated with the PHILOS locking plate. Results: Radio graphically union, Plate fixation was associated with minimal deformity Implant failure, Reflex sympathetic dystrophy and a vascular necrosis were observed in very few.conclusion: Fixation with the PHILOS plate is a near ideal technique with a high union rate in the treatment of proximal humeral fractures. INTRODUCTION Proximal humeral fractures (PHF) are a frequent health problem for people of various ages. They can affect quality of life, not only in acute phases, but also permanently, due to sequels. Proximal humeral fractures are common (approximately 4 5% of all fractures) and increasing in frequency, probably due to their association with osteoporosis in our increasingly aged population. 1 They represent over 70% of humeral fractures occurring over the age 40. Various treatment options of undisplaced fractures are known but are still associated with high complication rates. Over the past several decades, a wide variety of fixation devices have been developed to treat displaced and unstable proximal humerus fractures; however, there has been a lack of consensus for the optimal treatment of these complex fractures. 2,3 Treatment options include use of proximal humeral nails, plates, tension band wiring, and percutaneous or minimally invasive techniques such as pinning or screw osteosynthesis. 4-8 Moreover, the incidence of complications from operative treatment has been reported to vary between 11% and 50%. 7, 9 Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) of proximal humerus fractures with conventional plates has been associated with loss of reduction, screw loosening, and osteonecrosis Consequently, angular stable plates have been developed in recent years to preserve anatomic reduction with stronger anchorage, especially in osteoporotic bone. Among them, the 3-dimensional anatomically adjusted Philos plate (Synthes, Oberdorf, Switzerland) provides a locking system for its proximal part contacting the humeral head. To our knowledge, limited scientific evidence from only few case series studies has been published on fracture and patient outcomes after the use of this implant many different implants have been tested and investigated, thus demonstrating lack of sufficient results. Over the last years the development of angle stable, locking implants started and clinical studies demonstrated encouraging results. The locking proximal humerus plate and the PHILOS plate advanced to the implant of choice now for treatment of displaced proximal humerus fractures. There are still cases of implant failure and humerus head necrosis, but most of these complications were caused by the fracture type and not an implant specific problem. However the overall results with these new implants are encouraging. The PHILOS plate that consists of new generation of locked plates can be applied with a minimal invasive method and it is a fixating device that permits early mobility and lowers the risk of complications. And screws, has been associated with loss of reduction, screw loosening, and osteonecrosis. MATERIALS AND METHODS All of the studies were followed by standard history taking and examination of the patient with a possible shoulder injury, including neurovascular assessment, full radiological examination is required. The complete shoulder trauma radiological series consists of an anteroposterior view, scapula lateral view and an axillary view (a Velpeau view may be required if the shoulder cannot be abducted sufficiently for the axillary view).without these 3 views the fractured proximal humerus cannot be completely assessed. 1 of 9
2 The axillary view is particularly important to assess head splitting fractures, visualize posterior displacement of the greater tuberosity and to assess the relationship between the articular surfaces. Unfortunately this view is often considered articular surfaces in impression, head splitting and glenoid rim fractures. It is also useful in assessing bone stock in cases of nonunion and anatomy in malunion. Patients underwent ORIF with a Philos plate and were prospectively followed according to a predefined protocol. Exclusion criteria included pseudarthrosis, pathologic fractures and refractures open fractures, or concomitant fractures of the ipsilateral elbow or distal radius. In addition, patients with existing disorders having an effect on the healing process and function such as multiple sclerosis, paraplegia, or other relevant neurologic disorders, patients with polytrauma with an Injury Severity Score greater than 16, and patients with posttraumatic brachial plexus injury or peripheral nerve palsy were excluded. Surgery was performed in a beach chair position or prone on a radiolucent table, with side placement of an image intensifier to allow viewing of the humeral head in 2 planes. Depending on the particular need for exposure, an anterior deltopectoral or transdeltoid lateral approach was chosen. The latter approach was only appropriate for limited operations with exposure of the greater tuberosity or the most proximal part of the humeral head. After reduction, mostly with the aid of sutures, the plates were positioned using a mounted aiming device. Plates with 3 or 5 holes at shaft level were chosen based on fracture extension. Plates were placed at least 5-8 mm inferior to the upper end of the greater tuberosity to avoid subacromial impingement and 2-4 mm lateral to the bicipital groove, ensuring that a sufficient gap was maintained between the plate and the tendon of the long head of the biceps muscle. The achieved reduction was temporarily fixed with 1.6-mm K-wires through the proximal holes and checked with an image intensifier. When reduction was satisfactory, the K-wires were replaced by locked screws. Locked or standard cortical screws were inserted into the remaining holes of the humeral shaft at the discretion of the treating surgeon. During hospitalization, patient demographics (ie, sex, age, dexterity, smoking, concomitant diseases, and medication) and baseline characteristics (ie, accident type, energy level of trauma, concomitant injuries, fracture classification, delay between accident and surgery, operation time, C-arm time, use of plates with 3 or 5 holes at shaft level, distribution of used standard and locking screws, additional implants and sutures, additional medication, type and duration of immobilization, and beginning of active assisted and unrestricted mobilization) were documented. Fractures were classified according to the AO/OTA and Neer classification 46,47 by the treating surgeons. Intraoperative complications such as bleeding, hematoma, and nerve injury were documented. The radiographs were repeated postoperatively. Computed tomography evaluation was undertaken at the discretion of the treating surgeon. Follow-up Examinations After surgery, all patients were treated with a similar postoperative protocol. Isometric deltoid, bicep, and triceps strengthening were begun immediately on the first postoperative day. Patients were placed in a sling and were encouraged to start early passive range of motion exercises. Patients allowed passive range of motion exercises for the first 4 to 6 weeks postoperatively until radiographic evidence of fracture healing, and then patients began active range of motion exercises in a formal physiotherapy program. Patients were examined immediately postoperatively and after 12 weeks and 6 and 12 months, 24 and some followed it to52 months. At each follow-up, patients received shoulder radiographs in 2 planes (anterior-posterior and Neer view) to survey fracture healing. Anticipated postoperative complications included loss of reduction, fragment displacement, major varus or valgus deformation, head necrosis or implant-related problems ( screw perforation, screw loosening or backing out, plate pullout, or breakage), and surgical and other general complications such as wound infection or soft-tissue problems (rotator cuff lesions, adhesions, frozen shoulders, impingement, and nerve lesions). Complications and radiographic findings were reviewed to define if complications were implant or nonimplant related; A complication was considered as implant related if screws perforated secondary to angular stability or if implant breakage, secondary loss of reduction, or screw pullout due to insufficient purchase occurred. Patients were further interviewed concerning pain and shoulder mobility and underwent shoulder examination using a spring balance (Isobex; Curson AG, Bern, Switzerland) at 90-degree abduction. The average of these power measurements was used to assess individual Constant scores of injured and contralateral shoulders. Additionally, DASH and Neer scores were determined at the 1-year follow-up in some studies. Humeral head-to-shaft angle was measured in all anterior-posterior postoperative x- ray projections, and those specifically taken at the last follow-up were measured using the viewing software, IcoView Light (Icoserve Information Technologies, Innsbruck, Austria). The angle between shaft axis and head 2 of 9
3 axis was measured and approximated to the next 5 degrees, whereby head axis was taken as perpendicular to a line between the nearest lateral and medial visible points of the anatomic neck through the apex of the head. Head-to-shaft angle measurements were further categorized as major varus (<115 degrees), minor varus ( degrees), normal ( degrees), minor valgus ( degrees), and major valgus (>155 degrees) and compared between the postoperative and latest follow-up examination. Data Management and Analysis-Study monitoring, database management, and statistics were performed by a central monitoring organization. Complication were recorded as Plate breakage, medial varus deviation, loosening of screw and greater tuberosity displacement of greater tuberosity again; Secondary loss of reduction, with secondary impaction, secondary screw perforation, proximal screw backing out, or proximal plate pullout, complete and partial osteonecrosis, wound infection, hematoma, Soft-tissue complications mainly of impingement, adhesions leading to a frozen shoulder, after the wounds were also operatively revised. Soft-tissue complications consisted mainly of impingement, neurologic complications adhesions leading to a frozen shoulder, rotator cuff lesions and neurologic complications. 1-2 year follow-up examinations were done. Anatomic Restoration and Functional Outcomes were tabulated. DISCUSSION Methods like closed reduction and percutaneous screwing, pressure band application, intramedullary rod placement with circlage augmentation, T-buttress plate, double tubular plate, fixation with a plate having fixed angulation and primary arthroplasty are Used in the surgical treatment of displaced proximal humerus fractures. Painful and frozen shoulder, malunion and AVN are among the serious results of this clinical entity. The PHILOS plate is one of the top of the line locked compression plate used with a minimally invasive technique. It permits indirect fracture reduction thus lowering the possibility of AVN and by reducing the need of immobilization time helps diminishing the possibility of frozen shoulder. Furthermore, it is a low profile plate with the proximal screws having the capability of being applied in different directions thus making it a fixating device with a high stability in osteoporotic bones. Bulent KILIC, 32 in 2008 studied13 males and 9 females; mean age: 57; age distribution35-83, all underwent surgical therapy for proximal humerus fractures and PHILOS plate was used in all for fixation. According to Neer classification 7 patients had two piece fractures (5 were surgical collum and 2 were anatomic collum), 4 patients had valgus impaction injuries, 2 patients had fracture dislocation, 5 patients had 3 piece fracture, 1 patient had 4 piece fracture and 3 patients had 1/3 proximal fracture of the corpus. While in 8 patients a transdeltoid approach and minimal invasive method was preferred for an indirect reduction, in 14 patients open reduction with anterior deltopectoral approach was the method of treatment. Attention was given to that this guiding Kirschner wire did not pass the peak point of the greater tubercule hence the height of the plate was adjusted and impingement was prevented. Before final screwing, the height and the position of the plate were controlled under the scope and a temporary K-wire fixation was performed. The patients received antibiotic for two days for prophylaxis. All patients began passive exercises after the postoperative second day and active exercises after 4-6 weeks of surgery. All cases were invited for a control by the ends of the 2nd, 4th, 6th and 10th weeks. Cases fulfilling a 12 months of follow up (mean 14 months; distribution months) were evaluated with Constant - Murley Shoulder Scoring System 46 (0-55 points: poor, points: mean, points: good and points: very good) [5] in terms of shoulder movement clearness in every direction, pain and efficiency in performing daily activity. The Constant - Murley scores of the cases in whom open reduction was performed with deltopectoral approach and the results of the cases done with indirect reduction using the transdeltoid. In 10 of the cases both radiological and clinical union of the bones were achieved. In one case it took 16 weeks to achieve union. In another case non union was observed by the end of the 16th week and therefore it was grafted with an autologous graft. The average Constant - Murley score was 75.5 (distribution 51-93). In 8 (36.4%) of the cases the results were very good, in 7 (31.8%) of the cases the results were found to be good, in 6 (27.3%) of the cases the results were found to be mean and in 1 case (4.6%) the result was found to be poor. We were unable to put forward a significant difference between the scores of the cases in whom open reduction was performed with deltopectoral approach and the cases in whom indirect reduction was applied by using the transdeltoid lateral approach (p=0.669). Postoperative x-rays of two patients revealed a fixation in a minor varus position while in one patient the plate was placed in such a way that it would give rise to subacromial impingement (figure 1). Implant insufficiency was not 3 of 9
4 observed in any of the cases. Reflex sympathetic distrofy in one case and a vascular necrosis in another one respectively. Brunner F, 33 in 2009 operated on157 patients with 158 fractures. Occurrence of postoperative complications up to 1 year and active follow-up for 1 year with radiologic assessment to observe fracture healing, alignment, reduction, a vascular necrosis, and functional outcome measurements including Constant, Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand, and Neer scores. One-year follow-up rate was 84%. The incidence of experiencing any implant-related complication was 9% and 35% for nonimplant-related complications. Primary screw perforation was the most frequent problem (14%) followed by secondary screw perforation (8%) and a vascular necrosis (8%). After 1 year, a mean Constant score of 72 points (87% of the contra lateral noninjured side), a mean Neer score of 76 points, and mean Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand score of 16 points were achieved. Zhang H 34 in 2009 studied 35 cases with the proximal humerus and humeral shaft fractures were treated with long PHILOS locking compression plate, including 16 males and 19 females aged years old (average 54.5 years old). There were 34 cases of fresh and close fracture, and the time from injury to operation was 3-9 days. One case had delayed union of fracture 5 months after receiving T-plates and internal fixation with steel plate. For the proximal humerus fracture, 7 cases had 2 parts of fracture, 19 had 3 parts of fracture, and 9 had 4 parts of fracture according to Neer classification; while for the humeral shaft fracture, 3 cases were classified as A1, 5 as A2, 10 as B1, 3 as B2, 6 as B3, 7 as C1 and 1 as C3 according to AO classification. Postoperatively, Neer scoring system was employed to evaluate the function of shoulder joint and HSS scoring system was adopted to evaluate the function of elbow joint. All incisions healed by first intension, and 30 cases were followed up for months (average 18.2 months). Postoperatively, 2 cases had symptoms of radial nerve paralysis, which disappeared within 3 weeks; 1 case suffered from humeral head necrosis and received the secondary operation of humeral head replacement; humeral head was reduced evenly in 1 case, and 2 cases felt chronic slight pain in shoulder joints and received no further treatment. X-ray films showed 29 cases had fracture healing 6 months after operation, and all the patients had bone union 12 months after operation except 1 case receiving humeral head replacement. No such complications as screw loosening and internal fixation loosening occurred. By Neer scoring system, 6 cases were graded as excellent, 19 as good, 3 as fair, 2 as poor, and the excellent and good rate was 83.3%. By HSS scoring system, 16 cases were graded as excellent, 14 as good, and the excellent and good rate was 100%.Fazal MA 35 in 2009 conducted study on 6 men and 21 women aged 22 to 85 (mean, 56) years underwent Philos plate fixation for displaced proximal humeral fractures. 11 patients were aged 60 years or younger and 16 older than 60 years. All fractures were closed with no associated injuries and classified as 2- part (n=13), 3-part (n=12), and 4-part (n=2), according to the Neer classification. Patients were assessed radiologically and functionally using the Constant shoulder score Patients were followed up for 6 to 24 (mean, 13) months. All the fractures united except in a 76- year-old woman with a 3-part fracture in whom there was fracture collapse and screw penetration of the humeral head at 6 weeks. She subsequently developed non-union and a vascular necrosis. The mean Constant shoulder score was 70 (range, 28-88). 11 patients had a score exceeding 75, 13 were scored between 50 and 75, and 3 were below 50. Martinez AA 36 in 2009 Functional outcomes of 31 men and 27 women aged 36 to 73 (mean, 61) years who underwent Philos plate fixation for proximal humeral fractures were retrospectively reviewed. Indications for surgery were 3-part (n=33) or 4-part (n=25) closed proximal humeral fractures with angulation of more than 45 degrees or displacement of more than 1 cm. Functional outcomes and shoulder range of movement were assessed based on the Constant scoring system. Patients were followed up for 12 to 18 (mean, 15) months. All fractures healed satisfactorily, except in one patient with a valgus 4-part fracture who had malunion. No wound infections, vascular injuries, a vascular necrosis, or loss of fixation ensued. Two patients with axillary nerve palsy recovered spontaneously within 3 months. Functional outcome was excellent in 13 patients, good in 36, moderate in 8, and poor in 1. The mean Constant score was 80 (range, ) Helwig P 37 in 2009 Fractures of the proximal humerus were stabilized surgically in 87 patients (mean age 64 (16-93) years) by application of a fixed-angle plate (65 PHILOS, 22 T-LCP). There were segment fractures, 42 3-segment fractures, and 11 4-segment fractures, including 7 dislocation fractures. Follow-up assessment after a minimum of 12 months was based on the Constant, UCLA, and DASH scores and on radiographs. Postoperative complications included soft tissue problems (n = 9), humeral head necrosis (n = 9), screw perforation (n = 11), secondary displacements (n = 14), and delayed fracture healing (n = 4). Treatment outcomes recorded on the various scores were very good in 60-82% of the cases. Shahid R 38 prospectively reviewed 50 patients who had a proximal 4 of 9
5 humeral fracture treated with the PHILOS plate.clinical outcome was measured using the patient-based Oxford shoulder and DASH scoring systems. Five patients died and four were lost to follow-up. Eleven patients had 2-part, eleven 3-part and eighteen 4-part fractures. Mean follow-up time was 21.7 months (range: 6-44 months). Radiological union was achieved within 8 weeks in 40/41 fractures; complications were noted in four cases. Better results were achieved in younger than in older patients and in male than in female patients. The number of fracture fragments did not appear to affect the results, but associated dislocation of the humeral head was a pejorative factor. Their study has shown that the PHILOS plate is a reliable implant. A direct correlation was observed between Oxford shoulder and DASH scores. Kiliç B 39 study included 22 patients (13 males, 9 females; mean age 57 years; range 35 to 83 years) were treated with the PHILOS locking plate. According to the Neer classification, 13 patients had comminuted fractures, four patients had valgus impact injuries, two patients had fracture-dislocations, and three patients had fractures involving the proximal 1/3 of the humerus. The fractures were reduced by the transdeltoid lateral approach (n=8) using minimally invasive surgery, and by the anterior deltopectoral approach (n=14) using open surgery. Passive and active exercises were initiated on the second postoperative day and after 4 to 6 weeks, respectively. The results were assessed using the Constant-Murley shoulder scoring system. The mean follow up was 14 months (range 12 to 19 months). Radio graphically, union was observed in 20 patients at the end of 10 weeks. In one patient, time to union was 16 weeks. One patient underwent autogenous bone grafting because of nonunion after 16 weeks. The mean Constant-Murley score was 75.5 (range 51 to 93). There was no significant difference between Constant-Murley scores of patients undergoing the transdeltoid lateral and anterior deltopectoral approaches (p>0.05). Plate fixation was associated with minimal varus deformity in two patients, and subacromial impingement in one patient. Implant failure did not occur. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy and a vascular necrosis were observed in two patients, respectively. Krivohlávek M 40 study comprised 97 patients. The proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) plate was used in 49 patients (31 women and 18 men); with age average 57.4 years (women, 64.5 and men, 45.3 years). By the AO classification, 12 patients with type A, 15 with type B, and 22 with type C fractures. The Targon PH nail was used in 48 patients (32 women and 16 men) at an average age of 65.3 years (women, 72.2 and men, 51.4 years). Type A fractures were in 18, type B in 18 and type C in 12 patients The patients were prospectively evaluated and placed into the two groups. The post-operative range of motion was assessed by the Constant-Murley (CM) score at 6 weeks, and at 3, 6 and 12 months. The CM value was related to the healthy collateral limb and recorded as a relative CM score. In the PHILOS group, the average values were: operative time, 76.2 min; X-ray exposure, 4.2 min; and relative CM score, 74.5 points. The Targon PH group showed the average operative time of 50.2 min., X-ray exposure for 4 min. and the relative CM score 78.3 points. There were no significant differences between the groups, with the exception of shorter operative time in intramedullary nailing. Korkmaz MF 4, 41 patients who were treated with the PHILOS plate for proximal humeral fractures were evaluated in two age groups. Group A included 24 patients (12 males, 12 females; mean age 47 years; range 24 to 64 years) younger than 65 years, and group B involved 17 patients (4 males, 13 females; mean age 78 years; range 67 to 90 years) at or above 65 years. Radio graphically; all fractures were classified according to the AO/ASIF system. Surgery was performed with the deltopectoral approach in 10 and two patients, and with a deltoid split in 14 and 15 patients in group A and B, respectively. Functional and radiographic results were evaluated after a mean follow-up of 15 months (range 6 to 28 months).the mean Constant scores were 95.0 (range 74 to 100) and 92.8 (range 72 to 100) in group A and B, respectively (p>0.05). After six months of surgery, Constant scores and functional outcomes were similar in patients operated on with the deltopectoral approach or deltoid split. There was neither nonunion nor implant failure. Complications included intra-articular screw penetration (n=1), displacement of the greater tuberculum (n=1) with oblique placement of the plate (n=1), insufficient reduction (n=4), and varus displacement of the humeral head (n=3). No a vascular necrosis was seen. Egol KA patients were available for minimum 6-month follow-up (mean, 16 months; range, 6 to 45 months). Radiographically, 92% of the cases united at 3 months after surgery, and 2 fractures had signs of osteonecrosis at latest follow-up. Sixteen complications were seen in 12 patients (24%). Eight shoulders in eight patients (16%) had screws that penetrated the humeral head. Two patients developed osteonecrosis at latest follow-up. One acute fracture and one nonunion failed to unite after index surgery. Significant heterotopic bone developed in 1 patient. Early implant failure occurred in 2 patients; one was revised to a longer plate, and one underwent resection arthroplasty. There was one acute 5 of 9
6 postoperative infection The major complication reported in this study was screw penetration, suggesting that exceptional vigilance must be taken in estimating the appropriate number and length of screws used to prevent articular penetration.handschin AE 43 studied 20 female, 11 male, mean age: 62+/-16 years with two-, three- and four-part proximal humerus fractures (Neer classification) were operated using the proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS). The mean follow-up time was 19+/-3 postoperative months (range: days). Functional results (Constant score, UCLA-score) were analyzed and compared to an equivalent historic control group of 60 patients operated for the same fracture types using two one-third tubular plates. Additionally, total implant costs for each technique were compared. Complications in the PHILOS group included one implant failure with refractures, one secondary dislocation, two cases of subacromial impingement, and two cases of partial a vascular necrosis of the humeral head. The mean Constant score (age- and sex-matched) was 80+/-11% for the affected side and 104+/-13% for the healthy side. The UCLA scores were excellent in 10%, good in 67%, and fair in 23% of the patients. Complication rate and functional results did not differ significantly from the control group treated with one-third tubular plates. Implant costs were significantly higher for the PHILOS group (684+/-40 Euro vs. 158+/-20 Euro, p<0.05). Strohm PC 7 7 cases of implant failure and humerus head necrosis, but most of these complications were caused by the fracture type and not an implant specific problem. Moonot P, patients with acutely displaced three- or four-part proximal fractures of the humerus were treated by open reduction and internal fixation using the proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) plate. There were 23 women and nine men with a mean age of 59.9 years (18 to 87). Data were collected prospectively and the outcomes were assessed using the Constant score. The mean follow-up was for 11 months (3 to 24). In 31 patients (97%) the fracture united clinically and radiologically at a mean of 10 weeks (8 to 24). The mean Constant score at final review was 66.5 (30 to 92). There was no significant difference in outcome when comparing patients aged more than 60 years (18 patients) with those aged less than 60 years (14 patients) (t-test, p = ). There was one case each of nonunion, malunion and a broken screw in the elderly population. Füchtmeier B in 2007, three randomized groups were formed (n = 4 pairs) from 12 matched pairs of human cadaver humeri. The intramedullary load carriers were biomechanically superior when compared to the plating systems in the fracture model presented. Charalambous CP 44 - A chart and radiographic review of 25 cases that had proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) plate for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures was performed : Of the 25 cases, 20 went to union with a mean neck/shaft angle of degrees. Five cases required or were considered for revision surgery for non-union or implant failure. Of the 25 implants, 4 had screw protrusion into the gleno-humeral joint, 4 had screw loosening and backing out, and 1 plate broke without further trauma. Füchtmeier B in Biomechanical comparison of this implant with established systems. 12 matched pairs of human humeri were employed for testing. Three randomized groups were formed (n = 4 pairs). A bending moment of 7.5 Nm and a torsional moment of 8.3 Nm were applied in a test of five loading cycles to all intact bones. Loading was consistently initiated at the distal epiphysis. The consequent deformation at the distal epiphysis was continuously recorded. Then an osteotomy with a defect of 5 mm was created to simulate an unstable subcapital humerus fracture. For paired comparison, one of each pair was stabilized with the Sirus proximal humerus nail. The other side was fixed with a reference implant. The following groups were created.: Group I: Sirus versus Proximal humerus nail (PHN) with spiral blade. Group II: Sirus versus PHILOS plate. Group III: Sirus versus 4.5 mm AO T-plate. The proximal humerus nail (Sirus) demonstrated significantly higher stiffness values than the reference implants for both bending and torsional load. The following values were recorded at a bending moment of 7.5 Nm: Sirus 14.2 mm, PHN 20.7 mm, PHILOS plate 28.1 mm, 4.5 AO T-plate 29.3 mm p < ). The values at 8.3 Nm torsional moment were: Sirus 8.5 degrees, PHN 12.3 degrees, PHILOS plate 16.4 degrees, 4.5 AO T-Platte 15.6 degrees (p < 0.002). The intramedullary load carriers were biomechanically superior when compared to the plating systems in the fracture model presented here. Supplementary, the Sirus Nail showed higher stiffness values than the PHN. CONCLUSION The Philos plate is effective in maintaining fracture reduction in proximal humerus fractures. Due to stable restoration, early functional aftercare is possible and allows the patient to regain good shoulder function and return to work earlier. Loss of reduction was rarely seen compared with other implants. Complication incidence proportions increased in older patients due to higher rates of secondary impaction, screw perforations, and humeral head necrosis, Patients older than 60 years had a 2-fold higher incidence of developing any type of complication, and those older than 70 6 of 9
7 years had a 3-fold greater incidence of experiencing platerelated complications. Osteonecrosis was mostly seen in severe fracture types. Fixation with the PHILOS plate is a near ideal technique with a high union rate in the treatment of proximal humeral fractures. References 1. Bengner U, Johnell O. Changes in the incidence of fracture of the upper end of the humerus during a 30 year period. Clin Orthop 1988; 231: Bjorkenheim JM, Pajarinen J, Savolainen V. Internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with a locking compression plate: a retrospective evaluation of 72 patients followed for a minimum of 1 year. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004; 75: [Context Link] 3. Gerber C, Werner CM, Vienne P. Internal fixation of complex fractures of the proximal humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 4. Chapman JR, Henley MB, Agel J, et al. Randomized prospective study of humeral shaft fracture fixation: intramedullary nails versus plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2000; 14: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 5. Fankhauser F, Boldin C, Schippinger G, et al. A new locking plate for unstable fractures of the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 430: [Context Link] 6. Jaberg H, Warner JJ, Jakob RP. Percutaneous stabilization of unstable fractures of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74: Bibliographic Links [Context Link] 7. Strohm PC, Kostler W, Sudkamp NP. Locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Techniques in Shoulder & Elbow Surgery. 2005; 6:8-13. Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 8. Volgas DA, Stannard JP, Alonso JE. Nonunions of the humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; 419: Ovid Full Text [Context Link 9. Wijgman AJ, Roolker W, Patt TW, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of three and four-part fractures of the proximal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 10. Wijgman AJ, Roolker W, Patt TW, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of three and four-part fractures of the proximal part of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 11. Meier RA, Messmer P, Regazzoni P, et al. Unexpected high complication rate following internal fixation of unstable proximal humerus fractures with an angled blade plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20: [Context Link] 12. Gerber C, Werner CML, Vienne P. Internal fixation of complex fractures of the proximal humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86-B: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 13. Hessmann M, Baumgaertel F, Gehling H, et al. Plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures with indirect reduction: surgical technique and results utilizing three shoulder scores. Injury. 1999;30: Bibliographic Links [Context Link] 14. Wanner GA, Wanner-Schmid E, Romero J, et al. Internal fixation of displaced proximal humeral fractures with two one-third tubular plates. J Trauma. 2003;54: Ovid Full Text Bibliographic Links [Context Link] 15. Hintermann B, Trouillier HH, Schafer D. Rigid internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus in older patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 16. Szyszkowitz R, Schippinger G. Fractures of the proximal humerus. Unfallchirurgie. 1999;102: [Context Link] 17. Kuner EH, Siebler G. Dislocation fractures of the proximal humerus-results following surgical treatment. A follow-up study of 167 cases. Unfallchirurgie. 1987; 13: [Context Link] 18. Speck M, Lang FJ, Regazzoni P. Proximal humeral multiple fragment fractures-failures after T-plate osteosynthesis. Swiss Surg. 1996;2: [Context Link] 19. Esser RD. Open reduction and internal fixation of threeand four-part fractures of the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;299: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 20. Plecko M, Kraus A. Internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the locking proximal humerus plate. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2005; 17: [Context Link] 21. Fankhauser F, Boldin C, Schippinger G, et al. A new locking plate for unstable fractures of the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;430: [Context Link] 22. Mückter H, Herzog L, Becker M, et al. Angle and rotation-stable internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures with the humerus fixator plate. Early clinical experience with a newly developed implant. Chirurg. 2001;72: [Context Link] 23. Lungershausen W, Bach O, Lorenz CO. Locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the proximal humerus. Zentralbl Chir. 2003;128: [Context Link] 24. Lill H, Hepp P, Rose T, et al. The angle stable lockingproximal-humeral-plate (LPHP) for proximal humeral fractures using a small anterior-lateral-deltoid-splittingapproach-technique and first results. Zentralbl Chir. 2004;129: [Context Link] 25. Koukakis A, Apostolou CD, Taneja T, et al. Fixation of proximal humerus fractures using the PHILOS plate: early experience. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;442: [Context Link] 26. Björkenheim JM, Pajarinen J, Savolainen V. Internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with a locking compression plate: a retrospective evaluation of 72 patients followed for a minimum of 1 year. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75: [Context Link] 27. Charalambous CP, Siddique I, Valluripalli K, et al. Proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127: Bibliographic Links [Context Link] 28. Kettler M, Biberthaler P, Braunstein V, et al. Treatment of proximal humeral fractures with the PHILOS angular stable plate: presentation of 225 cases of dislocated fractures. Unfallchirurgie. 2006;109: [Context Link] 29. Hanschin AE, Cardell M, Contaldo C, et al. Functional results of angular-stable plate fixation in displaced proximal humeral fractures. Injury. 2008;39: [Context Link] 30. Moonot P, Ashwood N, Hamlet M. Early results for treatment of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus using the PHILOS plate system. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89: [Context Link] 31. Strohm PC, Helwig P, Konrad G, et al. Locking plates in proximal humerus fractures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2007; 74: [Context Link] 32. Bulent KILIC, Mustafa UYSAL, Bekir Murat CINAR et al Early results of treatment of proximal humerus fractures with thephilos locking plate.acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2008;42(3): Brunner, Felix Sommer, Christoph Bahrs, Christian et al Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humerus Fractures Using a Proximal Humeral Locked Plate: A Prospective Multicenter Analysis Jot journal of orthopaedic trauma. Volume 22(3), March 2008, pp Zhang H, Ni W, Gao S, Liang X, Zhou A. Long PHILOS locking compression plate for treatment of proximal 7 of 9
8 humerus and humeral shaft fractures] Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi Apr; 23(4): Fazal MA, Haddad FS. Philos plate fixation for displaced proximal humeral fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) Apr; 17(1): Martinez AA, Cuenca J, Herrera A. Philos plate fixation for proximal humeral fracturesj Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) Apr; 17(1): Helwig P, Bahrs C, Epple B, Oehm J, Eingartner C, Weise K. Does fixed-angle plate osteosynthesis solve the problems of a fractured proximal humerus? A prospective series of 87 patients. Acta Orthop Feb;80(1): Shahid R, Mushtaq A, Northover J, Maqsood M.Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation. Experience of a district general hospital. Acta Orthop Belg Oct; 74(5): Kiliç B, Uysal M, Cinar BM, Ozkoç G, Demirörs H, Akpinar S.Early results of treatment of proximal humerus fractures with the PHILOS locking plateacta Orthop Traumatol Turc May-Jul;42(3): Krivohlávek M, Lukás R, Taller S, Srám JUse of anglestable implants for proximal humeral fractures: prospective studyacta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech Jun; 75(3): Korkmaz MF, Aksu N, Göğüş A, Debre M, Kara AN, Işiklar ZU The results of internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with the PHILOS locking plateacta Orthop Traumatol Turc Mar-Apr;42(2): Egol KA, Ong CC, Walsh M, Jazrawi LM, Tejwani NC, Zuckerman JD 43. J Orthop Trauma Mar; 22(3): Handschin AE, Cardell M, Contaldo C, Trentz O, Wanner GA.Functional results of angular-stable plate fixation in displaced proximal humeral fractures. Injury Mar; 39(3): Charalambous CP, Siddique I, Valluripalli K, Kovacevic M, Panose P, Srinivasan M, Marynissen H. Proximal humeral internal locking system (PHILOS) for the treatment of proximal humeral fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg Apr; 127(3): Epub 2006 Dec Füchtmeier B, May R, Fierlbeck J, Hammer J, Nerlich M. A comparative biomechanical analysis of implants for the stabilization of proximal humerus fractures. Technol Health Care. 2006;14(4-5): Müller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P, et al. The Comprehensive Classification of Fractures of Long Bones. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag; [Context Link] 48. Neer CS. Displaced proximal humeral fractures. I. Classification and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970;52: [Context Link] 49. Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; 214: Ovid Full Text [Context Link] 8 of 9
9 Author Information Ramji Lal Sahu, M. S Assistant Professor, M. M. Medical College 9 of 9
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3
 MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate NASIR AHMED 1, TARIQUE ALI KHAN 2, MUHAMMAD ABSAR ANWAR 3, AHMED ALI 4 ABSTRACT Aim: To
ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate NASIR AHMED 1, TARIQUE ALI KHAN 2, MUHAMMAD ABSAR ANWAR 3, AHMED ALI 4 ABSTRACT Aim: To
Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 602-608 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital Rizwan SHAHID, Abid MUSHTAQ,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 602-608 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital Rizwan SHAHID, Abid MUSHTAQ,
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Proximal humerus fractures operated with PHILOS plate: 4 year prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):304-309 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170790
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):304-309 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170790
Technique Guide. PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Clinical Results of Using the Proximal Humeral Internal Locking System Plate for Internal Fixation of Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures
 An Original Study Clinical Results of Using the Proximal Humeral Internal Locking System Plate for Internal Fixation of Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures Masoud Norouzi, MD, Mohammad Nasir Naderi, MD,
An Original Study Clinical Results of Using the Proximal Humeral Internal Locking System Plate for Internal Fixation of Displaced Proximal Humeral Fractures Masoud Norouzi, MD, Mohammad Nasir Naderi, MD,
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives
 Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives Diego L Fernandez M.D Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lindenhof Hospital, Berne, Switzerland www.diegofernandez.ch
Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives Diego L Fernandez M.D Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lindenhof Hospital, Berne, Switzerland www.diegofernandez.ch
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures.
 Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures. Features and Benefits Anatomic design & low profile (2.2mm) 95 No bending required Minimised soft tissue irritation Low risk of subacromial
Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. For complex and unstable fractures. Features and Benefits Anatomic design & low profile (2.2mm) 95 No bending required Minimised soft tissue irritation Low risk of subacromial
Philos Plate: Its Complications and Functional Outcome
 Original Research Article Philos Plate: Its Complications and Functional Outcome Jairam Jagiasi 1, Amit Joshi 2*, Ashish Gupta 3 1Professor And Head, 2* Senior Registrar, 3 Registrar, Department of Orthopaedics,
Original Research Article Philos Plate: Its Complications and Functional Outcome Jairam Jagiasi 1, Amit Joshi 2*, Ashish Gupta 3 1Professor And Head, 2* Senior Registrar, 3 Registrar, Department of Orthopaedics,
The Surgical And Functional Outcome In Two Part And Three Part Fracture Of The Proximal Humerus Using Proximal Humerus Locking Plate (Philos Plate).
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 2 (October. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org The Surgical And Functional Outcome
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 2 (October. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org The Surgical And Functional Outcome
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Locking Plate for Proximal Humeral Fracture in the Elderly Population: Serial Change of Neck Shaft Angle
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:209-215 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.209 Locking Plate for Proximal Humeral Fracture in the Elderly Population: Serial Change of Neck Shaft
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:209-215 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.209 Locking Plate for Proximal Humeral Fracture in the Elderly Population: Serial Change of Neck Shaft
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 214-218 ORIGINAL STUDY Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures Joseph J. CHRISTOFORAKIS, George M. KONTAKIS, Pavlos G. KATONIS, Konstantinos
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 214-218 ORIGINAL STUDY Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures Joseph J. CHRISTOFORAKIS, George M. KONTAKIS, Pavlos G. KATONIS, Konstantinos
Humerus Block. Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Outcomes of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humerus Fractures Managed With Locking Plates
 An Original Study Outcomes of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humerus Fractures Managed With Locking Plates Crispin C. Ong, MD, Young W. Kwon, MD, PhD, Michael Walsh, PhD, Roy Davidovitch,
An Original Study Outcomes of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humerus Fractures Managed With Locking Plates Crispin C. Ong, MD, Young W. Kwon, MD, PhD, Michael Walsh, PhD, Roy Davidovitch,
Proximal Humerus Fractures
 Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE
 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
Clinico-radiological outcome of closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of proximal humerus fractures
 2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
Orthopedics - Dr. Ahmad - Lecture 2 - Injuries of the Upper Limb
 The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the
PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the
Results of 131 consecutive operated patients with a displaced proximal humerus fracture: an analysis with more than two years follow-up
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2011) 21:7 12 DOI 10.1007/s00590-010-0655-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results of 131 consecutive operated patients with a displaced proximal humerus fracture: an analysis with more
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2011) 21:7 12 DOI 10.1007/s00590-010-0655-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results of 131 consecutive operated patients with a displaced proximal humerus fracture: an analysis with more
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Introduction
 Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System
 NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique The right locking option for tough fractures Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i.e. physicians in particular,
NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique The right locking option for tough fractures Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i.e. physicians in particular,
LCP Distal Humerus Plates
 The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2
 Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.004 Complex Proximal Humeral Fracture Fixation with PHILOS Plate using Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.004 Complex Proximal Humeral Fracture Fixation with PHILOS Plate using Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement.
 LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus
 The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
Integra. Proximal Humeral Fracture Plate CASE STUDY
 Integra CASE STUDY Integra Physician Profile Galen Kam, MD The Bronstein Hand Center, Las Vegas, NV Board Certification: Upper Extremity, American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical School: Creighton
Integra CASE STUDY Integra Physician Profile Galen Kam, MD The Bronstein Hand Center, Las Vegas, NV Board Certification: Upper Extremity, American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical School: Creighton
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus.
 LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures?
 NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Les séquelles traumatiques. Ph. Valenti, J. Kany, D. Katz
 Indications et Techniques Les séquelles traumatiques Ph. Valenti, J. Kany, D. Katz Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties
Indications et Techniques Les séquelles traumatiques Ph. Valenti, J. Kany, D. Katz Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties
AcUMEDr. Locking Proximal Humeral Plate. PoLARUSr PHPt
 AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 Technique Guide VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction VA-LCP Anterior
Technique Guide VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction VA-LCP Anterior
A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments.
 CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate.
 Technique Guide LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction
Technique Guide LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate. The anatomically shaped and angular stable fixation system for extraarticular fractures of the distal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction
Evaluation of the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fracture Managed By Internal Locking Plate- A Prospective Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. XI (May. 2017), PP 36-43 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Outcome of Proximal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. XI (May. 2017), PP 36-43 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Outcome of Proximal
3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates
 Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft. Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden
 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Biomechanical and Clinical Evaluation of a New Operative Technique
 27 Posterior Olecranon Plating Biomechanical and Clinical Evaluation of a New Operative Technique Nirmal C. Tejwani, M.D., Ian R. Garnham, F.R.C.S., Philip R. Wolinsky, M.D., Frederick J. Kummer, Ph.D.,
27 Posterior Olecranon Plating Biomechanical and Clinical Evaluation of a New Operative Technique Nirmal C. Tejwani, M.D., Ian R. Garnham, F.R.C.S., Philip R. Wolinsky, M.D., Frederick J. Kummer, Ph.D.,
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture
 Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Distal femoral fracture with subsequent ipsilateral proximal femoral fracture by M Agarwal, MS FRCS, AA Syed, FRCSI, PV Giannoudis (!), BSc,MB,MD,EEC(Orth) Dept. of Orthopaedics and Trauma, St.James University
Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate?
 Jung et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:102 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? Woo-Bin
Jung et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:102 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? Woo-Bin
 Use of a partial humeral head resurfacing system for management of an osseous mechanic... Page 1 of 12 Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011 Jan-Mar; 5(1): 17 20. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.80465. PMCID: PMC3109768 Copyright
Use of a partial humeral head resurfacing system for management of an osseous mechanic... Page 1 of 12 Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011 Jan-Mar; 5(1): 17 20. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.80465. PMCID: PMC3109768 Copyright
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Proximal Humerus Fractures/Dislocations.
 Proximal Humerus Fractures/Dislocations www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz History/Demographics Bimodal: young-high energy, elderly-low energy(osteoporosis) 45% of all humerus fx. elderly females 4:1 over males
Proximal Humerus Fractures/Dislocations www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz History/Demographics Bimodal: young-high energy, elderly-low energy(osteoporosis) 45% of all humerus fx. elderly females 4:1 over males
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
Humeral SuturePlate. Surgical Technique
 Humeral SuturePlate Surgical Technique The humeral SuturePlate is an anatomically designed, low profile, titanium polyaxial locking plate and screw system. Multiple chamfered suture eyelets along the margin
Humeral SuturePlate Surgical Technique The humeral SuturePlate is an anatomically designed, low profile, titanium polyaxial locking plate and screw system. Multiple chamfered suture eyelets along the margin
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT. By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg
 MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
TREATMENT OF DISPLACED PROXIMAL HUMERAL FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 TREATMENT OF DISPLACED PROXIMAL HUMERAL FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS KAROL ZYTO, LEIF AHRENGART, ANDERS SPERBER, HANS TÖRNKVIST From Söder Hospital and the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden We randomised
TREATMENT OF DISPLACED PROXIMAL HUMERAL FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS KAROL ZYTO, LEIF AHRENGART, ANDERS SPERBER, HANS TÖRNKVIST From Söder Hospital and the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden We randomised
LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER
 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER cop2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION 1 FEATURES OF SHOULDER COMPONENTS 2 EQUIPMENT REQUIRED 5 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING 6 SURGICAL PROCEDURE 8 POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE GALAXY FIXATION SHOULDER cop2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION 1 FEATURES OF SHOULDER COMPONENTS 2 EQUIPMENT REQUIRED 5 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING 6 SURGICAL PROCEDURE 8 POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
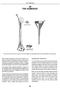 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
FRACTURE OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS & SHAFT MANAGED WITH CLOSED REDUCTION & EXTERNAL FIXATION BY JOSHI EXTERNAL STABILISATION SYSTEM (JESS) A CASE REPORT
 FRACTURE OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS & SHAFT MANAGED WITH CLOSED REDUCTION & EXTERNAL FIXATION BY JOSHI EXTERNAL STABILISATION SYSTEM (JESS) A CASE REPORT 1 1 2 3 4 Prakriti Raj Kandel, Rajiv Baral, Abhishek Kumar
FRACTURE OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS & SHAFT MANAGED WITH CLOSED REDUCTION & EXTERNAL FIXATION BY JOSHI EXTERNAL STABILISATION SYSTEM (JESS) A CASE REPORT 1 1 2 3 4 Prakriti Raj Kandel, Rajiv Baral, Abhishek Kumar
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2014) 15:111 115 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0273-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2014) 15:111 115 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0273-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
Olecranon fracture. Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital
 Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
WINSTA-C. Clavicle Plating System
 Clavicle Plating System Clinical Advisor Michael Kurer FRCS FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic and Shoulder Surgeon North Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust Table of Contents Introduction Indication
Clavicle Plating System Clinical Advisor Michael Kurer FRCS FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic and Shoulder Surgeon North Middlesex University Hospital NHS Trust Table of Contents Introduction Indication
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Upper limb fractures. Mithun Nambiar Orthopaedic Resident Royal Melbourne Hospital
 Upper limb fractures Mithun Nambiar Orthopaedic Resident Royal Melbourne Hospital http://janeaustensworld.files.wordpress.com/2010/10/17_skeleton.jpg Principles of fracture management Restoration of anatomy
Upper limb fractures Mithun Nambiar Orthopaedic Resident Royal Melbourne Hospital http://janeaustensworld.files.wordpress.com/2010/10/17_skeleton.jpg Principles of fracture management Restoration of anatomy
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do?
 Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Locking Plates for Extremity Fractures A Technology Overview EVIDENCE TABLES
 Locking Plates for Extremity Fractures A Technology Overview EVIDENCE TABLES Adopted by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Board of Directors December 6, This document is a supplement to the
Locking Plates for Extremity Fractures A Technology Overview EVIDENCE TABLES Adopted by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Board of Directors December 6, This document is a supplement to the
PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017
 PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017 ANIL DUTTA, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Displacement > 1 cm Angulation > 45 degree SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER SAN ANTONIO DISCLOSURE
PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017 ANIL DUTTA, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Displacement > 1 cm Angulation > 45 degree SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER SAN ANTONIO DISCLOSURE
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Shoulder Arthroplasty for Proximal Humerus Fracture
 Arthroplasty in Upper Limb Trauma AADO/HKSSH Conjoint Scientific Meeting 2012 Shoulder Arthroplasty for Proximal Humerus Fracture Dr TSE Lung Fung Department of O&T, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese
Arthroplasty in Upper Limb Trauma AADO/HKSSH Conjoint Scientific Meeting 2012 Shoulder Arthroplasty for Proximal Humerus Fracture Dr TSE Lung Fung Department of O&T, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese
Surgical Technique. Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90
 Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
 LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Technique Guide. DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone.
 Technique Guide DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Clinical Cases 5 Surgical Technique Implantation 6 Implant
Technique Guide DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Clinical Cases 5 Surgical Technique Implantation 6 Implant
Technique Guide. LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia
 Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 8. DISTAL GUIDED LOCKING FOR PROXIMAL NAIL PROXIMAL LOCKING FOR LONG NAIL 13
 Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
