12-14 October 2009, WHO, Geneva
|
|
|
- Rolf Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The 7 th WHO Global Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting October 2009, WHO, Geneva Summary and Recommendations Global and Regional Update The measles and rubella laboratory network (LabNet) consists of 679 laboratories serving 164 countries. A reported 239,617 samples were tested globally for measles IgM in 2008 about 6000 fewer than in Approximately 80% of the samples were also tested for rubella, resulting in an estimated 430,000 measles and rubella assays being tested in the LabNet for Timeliness and quality of the testing is high with more than 80% of laboratories reporting at least 80% of their results within 7 days. Of the 168 laboratories to receive the global annual proficiency testing panel in 2008, 98.2% passed the measles component and 94% passed the rubella component. Most of the remaining subnational laboratories participated in national proficiency testing programmes with a similar high level of accuracy. The WHO African and South East Asian Regions have developed plans for enhanced measles control and the laboratories in these regions will need to respond to a increased workload following the proposed improvement in case based surveillance. Currently, measles surveillance in India requires the collection of a representative 5 samples from each outbreak which in 2008 resulted in 1089 samples being tested by the LabNet. The number of samples required for laboratory confirmation is likely to increase to approximately 23,000 per year once "elimination" quality surveillance in implemented India. Other countries in SEAR are already meeting the expected workload for samples being tested for case confirmation, however improved molecular surveillance will be required to meet the ideal of sequence information gathered from each chain of infection. The African region as a whole tested 16,500 samples in 2008 which equates to just over the recommended surveillance goal of 2/100,000 non-measles, suspected measles cases. However, some countries in the region have yet to reach this goal but the capacity of the LabNet is adequate to meet the expected surveillance improvement in these countries. Regional Updates African region The WHO African region has established a "pre-elimination" measles control goal following early success in meeting their measles mortality goal of 95% reduction in deaths by 2010, based on 2000 baseline data. A strategic framework will be developed to guide the implementation of the pre-elimination target of 2012, including > 80% of districts investigating at least 1 suspected case per year and a non-measles febrile rash illness rate > 2/100,000. The measles LabNet was established in 1998 and currently consists of 3 regional reference and 42 national laboratories which provide diagnostic support to all 46 member states. In 2008, the measles laboratories completed 28,874 IgM serum tests, more than 90% of which were reported within 7 days of receipt in the lab. Approximately 10% of the serum tests were confirmed at one of the 3 regional reference labs and 1
2 showed more than 90% concordance. Measles virus sequencing information was obtained from nine African countries after referral to the sequencing laboratory in South Africa, however there were still many outbreaks where samples for molecular testing were not collected. The key challenges for the region include: increased workload, ensuring adequate laboratory reagents and equipment, high staff turn over, competing activities for limited resources, national ministries of health providing little support, stock outs of consumables /reagents/kits and equipment failure difficulties in shipping specimens and isolates. The region has been instrumental in trying to maintain lab capacity by holding regular training workshops with emphasis on standardizing procedures and quality control, and the reinforcing of procedures to encourage virus detection. Experienced staff are encouraged to remain in the lab through salary top ups and there is regular coordination with couriers to overcome shipping challenges. To meet the needs for enhanced surveillance following the pre elimination phase, AFRO has planned the establishment of additional laboratories, including subnational labs in Ethiopia (3), Nigeria (2), DRC (2), Cameroun (1), and Tanzania (2). Strengthening sequencing capacity in Uganda and CIV is planned and an additional Regional Reference lab is proposed for the Central African region, likely to be Cameroun. Eastern Mediterranean Region The Eastern Mediterranean region (EMR) has established a measles elimination goal targeted for All 22 EMR countries have established measles national laboratories for serological confirmation of measles and all passed the global proficiency test. Twenty labs have been fully accredited with Djibouti endeavouring to meet the minimal requirements and Somalia pending evaluation. Seventeen of the labs also have the capacity for virus isolation and detection following virus detection training workshops in 2007 and Libya, Djibouti, Somalia, UAE and Lebanon have yet to establish virus detection capacity. The Oman and Tunis regional reference laboratories have good sequencing capacity and serve the region, and the Iran, Pakistan, Morocco and Egypt national laboratories also have the sequencing capacity. EMR has more than a third of their countries which are close to elimination and the region is developing measles elimination validation guidelines to help countries confirm their success. Laboratory quality control is a critical part of this process and EMRO has strengthened monitoring QA/QC in the region through shipping serum samples dried onto filter paper for confirmatory testing. Iran, Egypt, Morocco, Sudan and Syria have all used this technique to obtain concordant results. However, two countries: Saudi Arabia and UAE have yet to participate in the external quality control programme. Drying virus infected culture material onto filter paper has also been successfully used in the region for shipping viruses between national and reference labs without the need of cold chain. Challenges for the EMR LabNet include; Meeting the increased laboratory workload as surveillance improves Ensuring H1N1 activities do not impact negatively on measles and rubella surveillance Measles validation process 2
3 Assuring quality of non-validated IgM assays Improving virological surveillance Finding sufficient external resources for laboratory supplies and training Encouraging countries to integrate lab testing costs into their surveillance programme budget Encouraging countries to focus more attention on rubella and CRS surveillance European Region The European region has seen a marked reduction in the number of measles cases in 2008 compared with previous years but outbreaks are still occurring in countries mainly in western Europe. Almost 90% of the 4301 measles cases detected in 2009 were found in countries representing 25% of the region s population. The majority of outbreaks are in Western Europe with 82% of cases found in unvaccinated individuals and 38% in over 15 years of age. The LabNet comprises 70 laboratories, including 20 sub-national laboratories, three RRLs and one Global Specialized laboratory. Laboratories tested IgM samples in 2008, 3000 fewer than 2007 due to the reduction in measles incidence. Laboratories reported 80% of the test results within the required 7 days. However, Italy is not reporting any data and Turkey has stopped reporting. All labs in the region except two (Bosnia and Herzegovina and Malta) underwent desk accreditation assessments in 2008 and all were determined to be fully accredited except Kyrgyzstan which was provisionally accredited Seventy three labs participated in the WHO Global Proficiency testing programme in 2008, including subnational labs in the Russian Federation, Turkey and Ukraine. Proficiency was excellent with only 1 laboratory failing to achieve a passing score. Russians Federation labs have started using locally produced kits and most other labs are provided with kits by their ministries, with only a small number of countries receiving kits from WHO. Key challenges identified for the EUR LabNet were; Improving M/R data quality in the Region Strengthening communication within surveillance teams to ensure linking epi and lab data Identifying a clear mechanism of laboratory reporting to a country focal person for Measles/Rubella surveillance (or an EPI manager in selected countries) in all Member States and to WHO National laboratories collaborate with the private and University diagnostic labs to ensure high quality and complete reporting of measles and rubella data, including genotyping information Address and resolve methodological challenges in achieving elimination, especially related to low PPV, false positive IgM and consideration of the wider use of PCR; automated testing systems, and alternative sampling procedures Plans to work on implementing OF and DBS where this is warranted Develop sera panels for validation purposes 3
4 Region of the Americas The Region of the Americas' (AMR) LabNet is made up of 148 laboratories of which 124 are sub-national, 21 national, 2 regional reference and 1 global specialized. A total of 45,808 samples were tested in the region in Labs confirmed 207 measles cases from sporadic cases in a small number of countries and 3730 rubella cases. The LabNet operates at high a level of performance with all national laboratories passing the WHO global proficiency test and 86% of samples reported within 4 days of being received in the laboratory. The PAHO Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network meeting in 2009 focused on the challenges facing the region, having eliminated measles and being close to eliminating rubella. The meeting recommended increasing laboratory's sensitivity in confirming sporadic cases, improving molecular epidemiology information, and collection of additional samples for additional tests. South East Asian Region The South East Asian region has established a measles goal of 90% mortality reduction by All countries except India have implemented case based surveillance and are reporting aggregated data to the SEARO monthly. India is currently conducting outbreak investigation in 6 states and has plans to expand to more. All countries have established measles laboratories with Timor Leste's laboratory now fully operational. India has established 5 labs to cover states which have initiated surveillance and an additional 2 laboratories supporting reference activities, NIV Pune for molecular purposes and Chennai for serological testing. A further 7 state labs are planned for with priority of new labs to be established in the states of Rajasthan and Andhra Pradesh early Jakarta serves as a reference laboratory for the 3 Indonesian labs and the regional reference laboratory in Bangkok serves the remaining SEAR countries for serological and molecular reference purposes. In 2008 a regional virologist's meeting and intercountry laboratory training was conducted. Eighteen labs 18 Laboratories have been accredited with NIV Pune pending. Baseline measles genotype data is available for all countries except Bhutan and Timor Leste. Rubella baseline data has been reported for Bangladesh, India, Nepal, Thailand and Sri Lanka. It is anticipated that if the ten countries implementing case based surveillance reach expected performance indicators and India implements their planned surveillance expansions then serum samples tested could rise from the 5000 in 2009 to in In addition, it is anticipated that approximately 100 viruses will be sequenced. Sri Lanka is planning on introducing oral fluid devices as a mechanism to improve surveillance in the country. Currently there is some resistance to venipuncture and it is a challenge to collect samples from all suspected measles or rubella cases. Training of laboratory and surveillance staff is planned for Western Pacific Region The Western Pacific region (WPR) LabNet comprises 16 National laboratories, 3 regional reference laboratories and 1 global specialized laboratory. In addition China has established a network of 31 provincial and 331 prefecture laboratories which follow 4
5 the WHO standardized testing and reporting structure and have established a strong QA programme. The region has made good progress in moving towards achieving the measles elimination goal of All countries conduct case based and laboratory supported measles surveillance. Surveillance performance is improving with completeness of reporting rising from 51% in 2007 to 78% in 2009, and timeliness of reporting from 19% to 57% over the same period. In 2008, 130,580 serum samples were tested for measles IgM in the region, 121,000 from China. However, reporting of measles data to the regional office is not optimal, with 6 countries not reporting laboratory data including 2 key reporting countries (China and Japan). All China provincial labs are now trained in performing both IgM and RT-PCR techniques for measles and rubella. All national labs except for PNG were reviewed and accredited, with PNG planned to be reviewed in late All 31 Provincial labs in China will become part of the global PT testing programme in Prior to 2009 the provincial labs tested an annual PT panel compiled by the China CDC. Japan has introduced case based surveillance for all measles cases from 2008 and established 10 measles reference centres using ELISA and the Global laboratory at NIID, Japan has implemented PT and confirmatory testing. Regular communications has been established with all countries except for PNG and the PICs. A confirmatory testing mechanism was established in most national labs by The challenges and plans for 2010 include full implementation of timely, casebased laboratory reporting in those countries where it is not occurring. Implementing ELISA QC of commercial labs in countries where these are a predominant testing e.g Japan Improved communication with PIC and PNG labs Data management Molecular surveillance The tracking of virus globally can help determine whether outbreaks are caused by endemic or imported virus strains and can monitor progress with achieving measles control goals. There has been a marked improvement in the collection of measles and rubella molecular epidemiological data as more laboratories develop capacity for molecular techniques and the programmatic value in tracking viruses has been recognized. In 2006 a WHO genotype database was established to track measles viruses detected by the LabNet. By October 2009, genotype information from 7096 measles viruses had been submitted to the database comprising representatives of all 23 genotypes from 117 countries with viruses dating back to Approximately 34% of these viruses have also had sequence information submitted to GenBank. For rubella, 465 viruses have been submitted, representing all 11 genotypes from 38 countries, with 48% of them with sequence data submitted to GenBank. Genotype B3 was the predominant genotype found in Africa in 2008 and Countries with B3 genotype included Burkina Faso (>50,000 cases and 300 deaths), Cameroon, (with evidence of multiple importations), South Africa which experienced a large outbreak in Gauteng Province in 2009 with B3 virus identical to 2008 Benin B3 5
6 viruses. Other countries with B3 detected include; Benin, Cote d'ivoire, DR Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Mali, Niger, Togo and Uganda. Mali's B3 viruses were distinct from other B3s found in the region. One case in South Africa was detected with D8 virus which had epidemiological and virological links to India. The Eastern Mediterranean region reported large measles outbreaks in Egypt, Iraq and Saudi Arabia in 2008 and in Iraq (>12,000 cases) in The predominant genotype found in the region continues to be D4, (Afghanistan, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Morocco, Oman, Pakistan and Sudan). B3 was found in outbreaks in Libya and sporadic cases in Tunisia in 2009 and D8 was identified in Kuwait, Libya, Morocco and Oman. In the South East Asian Region, only 2 countries reported genotype information in 2008 and India reported D4 and D8 viruses from their molecular surveillance programme coordinated by NIV, Pune and the Thailand RRL in Bangkok reported D5 and D9 viruses identified from outbreaks in Thailand. The Western Pacific region reported genotype data from Australia (D4, D5, D8, D9, H1) China (H1, D4, D9), Hong Kong SAR (H1), Japan (D5, D8, D9, H1), Malaysia (D9), New Zealand (D9, H1) and Singapore (D4, D5, D8, D9, H1) over the period 2008 and Interestingly China reported two cases where non H1 viruses were detected and subsequently found to have epilinks to France (D4) and Thailand (D9). Both cases were thoroughly investigated and no evidence of spread was found in contacts. Australia reported H1 virus in cases with epi-links to Iran. Iran subsequently found H1 cases with epi-links to workers from China. In the European region a large outbreak of measles in the UK occurred between 2007 and 2009 where sequence analysis confirmed identical sequence in the majority of cases which was identified as D4, and labelled after the first case identified, MVs/Enfield.GBR/ Over 3,000 people within UK have been infected with same strain and at least 1,500 people in rest of Europe. An identical virus has been exported to at least 18 other countries, mostly in Europe but was also found in the Eastern Mediterranean region and the Americas. The Enfield strain has been found to have closet links to an Indian strain from 2005, with 3 nt difference. The UK reported that the Enfield strain stopped circulating in December 2008 except for an importation in March from Italy. The Luxemburg RRL reported that six hundred measles cases were notified by France in 2008 and more than 1000 cases in D4, D5, D8, D9 and H1 viruses were identified from samples tested by the national laboratory in France in 2009 including a D5 virus which spread from a school outbreak just prior to the holidays and spread over most of the country. Robert Koch Institute reported that Switzerland experienced 3 waves of measles cases since November D5 "Lucerne" virus made up the majority of the first 2 waves (2007 and 2008) and part of the 3rd (2009) wave with D4 Enfield and B3 virus also being identified in the 1149 cases identified in The D5 "Lucerne" strain also spread from Switzerland to Germany. It was reported that some countries have multiple importations with the same virus genotype but without any epi-link found, stressing the importance of collecting 6
7 representative clinical samples for sequencing which allows determination of whether viruses are imported or endemic. There are still information gaps in molecular surveillance in some countries, but these are gradually being filled as training workshops build laboratory capacity and awareness of the need for molecular surveillance occurs. Merck has provided funding for enhancing measles surveillance in AFR and 5 pilot countries (Malawi, Zimbabwe, Kenya, Benin and Cote d'ivoire) will utilize oral fluid sampling devices for collecting samples for both case confirmation and molecular surveillance. 7
8 Final Recommendations 7 th WHO Global Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting October 2009 Surveillance of molecular diversity of measles and rubella 1. Molecular data obtained from outbreaks and sporadic cases of measles and rubella, in combination with epidemiological information, can provide useful information on the likely sources of infection and differentiate between indigenous and imported viral strains. The WHO measles and rubella genotype database and MeaNS sequence databases are functioning well and are used by almost all of the sequencing laboratories in the LabNet. These databases are proving to be valuable tools for facilitating molecular surveillance, however; a. Efforts should be made to collect molecular surveillance data from all chains of infection and especially in those countries where no baseline sequence data exists. b. LabNet should utilize the well validated tools and samples available for enhancing molecular surveillance where appropriate, such as; i. Oral fluid, throat swabs, urine and PBMC as samples for virus detection ii. Detection of viral RNA in archival sera iii. Shipping of samples dried onto filter paper iv. Conventional and real time PCR for case classification and molecular surveillance Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 2. Laboratories are reminded of their requirement to submit representative genotype information on their measles and rubella strains to the WHO genotype database, preferably on a real-time basis, but at least by the end of the month the genotyping was completed. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 3. The HPA MeaNS measles sequence database now has the capacity to be used globally. It is recommended that: a. All countries are encouraged to submit measles sequence data to the HPA MeaNS measles sequence database following the WHO recommended timeliness indicators. Subnational level laboratories with sequencing capacity should submit data to their national laboratory for validation and submission. b. National laboratories with sequencing capacity should consult with their designated Regional or Global sequencing laboratory before submitting their sequences to the database to assure the quality of the data submitted. c. Regional sequencing laboratories should report data from their national measles and rubella surveillance programmes and should strongly encourage countries for which they provide sequencing support to report their own data or obtain written permission from them to submit the data on their behalf. Regional sequencing laboratories can encourage countries to report their own data by providing sequence data in a format compatible with the LabNet database needs and by assisting with preparation of MeaNS or GenBank entries. 8
9 d. HPA is encouraged to develop a similar global database for rubella and incorporating phylogenetic analysis tools. Until this has been established, rubella genotype data should continue to be submitted to the WHO genotype database. e. A small informal "steering committee" will be formed to review protocols and address ongoing issues with the sequence and genotype databases. Action: All LabNet: Timeline Ongoing. Action: Steering Committee (WHO/GSLs/RRLs) Timeline: First quarter To increase the value of sequencing information, key epidemiological information including; date of sample collection, date of rash onset, date of vaccination, unique identifiers, case location, travel history and epi-link to other cases should be provided to the network laboratories through their country surveillance teams. Action: WHO, LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 5. Sequencing laboratories are requested to share representative virus isolates with the designated strain banks for reference purposes. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 6. Countries without baseline rubella sequencing information should consider utilizing archival sera for rubella genotyping purposes. The regional laboratory coordinator should be consulted as to the appropriate procedures and site for testing these samples. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing Quality assurance 7. A standard protocol has been developed for using serum dried onto filter paper for confirmatory testing purposes. This has been evaluated under "field" conditions in the EMR and confirmed earlier evaluation results showing good concordance with liquid serum. It is recommended that regions consider introducing this technique where challenges in shipping samples to reference laboratories exist. To ensure that a gold standard reference is always available, the corresponding liquid sera should be stored at the submitting lab until confirmatory testing has been completed. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 8. National laboratories should store measles and rubella serum samples at -20 C or lower for use as; internal controls, for global proficiency test panels and for virus identification. Those laboratories with stocks of positive samples (at least 0.5 ml and preferably volumes approximating 10ml) are requested to contact their Regional laboratory coordinator to facilitate using these samples in the WHO proficiency and QC programme. Action: WHO LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing. 9. Building on the European WHO and EU initiatives the LabNet will develop a questionnaire to identify the range and scale of molecular testing within the LabNet as a preliminary step to developing a molecular QA programme. A trouble shooting guide for PCR, sequencing and analysis will also be developed. Establishing and distributing "run controls" are planned for Action: HPA, CDC, WHO. Timeline: July
10 10. The LabNet will establish a protocol and trouble shooting guide for ensuring optimal cell sensitivity testing for the isolation for measles and rubella viruses in Vero/SLAM cells. Action: GSLs, WHO. Timeline: July The volume of proficiency testing sera will be increased for those laboratories using automated IgM testing systems and consequently require larger volumes than currently distributed in the LabNet. Action: VIDRL, EUR LabNet. Timeline: Aug A more comprehensive analysis of national laboratories proficiency test results should be carried out by the regional lab coordinators to determine trends which may help identify testing issues. Action: WHO Coordinators. Timeline: Ongoing 13. Rubella virus detection methods described in the WHO measles and rubella laboratory network protocols need to be implemented more widely, including ensuring that network laboratories have access to high quality colorimetric reagents, primers and RNA controls. Action: CDC, WHO LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 14. As countries approach the elimination stage and most samples are negative for IgM, the PPV for confirmatory testing decreases. Therefore, laboratories should ensure that systematic internal quality control procedures are performed to ensure accuracy of serological testing. LabNet will develop a guideline for establishing and using in-house quality control methods to monitor accuracy of assays and the performance of the laboratory. Action: HPA, CDC, WHO. Timeline: July In countries where most measles and rubella IgM testing is performed in private/commercial laboratories, it is vital that the performance of these laboratories is monitored. Performance of these laboratories should be assessed through an external quality assurance programme and pre-existing quality assurance data should be collected by the national laboratories, where possible. These private laboratories are encouraged to share their measles and rubella data with the relevant national reference laboratory on a regular basis. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 16. Laboratory and surveillance colleagues are encouraged to meet regularly to ensure that laboratory and surveillance data are harmonized. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing Coordination 17. LabNet is concerned about the number of laboratory coordinator vacancies currently unfilled or that will become vacant in the near future. LabNet members are encouraged to apply for these positions and/or share the vacancy descriptions with potential candidates. Action: LabNet. Timeline: October- December 2009 Communication 10
11 18. A regular communication link between working sub-groups of LabNet members should be established to facilitate development of protocols and procedures for the LabNet. The key issues requiring development and deployment include; a. IgG and IgM sera panels for validating serosurveys and for evaluating the non-validated IgM assays used in a small number of countries b. Classifying sub-genotypes of rubella (specifically genotypes 2B, 1G and 1E) for the specific purpose of molecular epidemiology c. Virus culture sensitivity evaluation and trouble shooting protocols d. Internal QC protocol e. QA/QC procedures and trouble shooting guides for virus isolation and molecular techniques. Action: HPA, CDC, WHO, LabNet. Timeline: Quarterly teleconferences Enhanced Surveillance 19. Serosurveys have been demonstrated by some countries to be a useful tool for determining population immunity, especially where other data, such as laboratory based surveillance and vaccine coverage, may be limited or suspect. To validate the serosurveys a serum validation panel should be developed along the lines of the ESEN study. A protocol / guideline for the implementation, validation and interpretation of serosurveys will be developed. Action: HPA, CDC, Luxembourg, LabNet WHO. Timeline: July Point of care (POC) rapid test systems have the potential to rapidly identify outbreaks/cases. The measles POC assay data presented by HPA shows promising sensitivity and specificity compared to conventional IgM ELISA under lab conditions. The LabNet encourages the further development of POC assays and recommends evaluating these under field situations. Action: HPA, CDC WHO LabNet. Timeline: December Several WHO regions are developing protocols and indicators to document elimination of measles and/or rubella. Regional Laboratory coordinators should share laboratory-specific components of these protocols with other LabNet members for feedback and to ensure consistency within the LabNet. PAHO should share the laboratory components of their document with the LabNet before the next LabNet global meeting. Action: WHO, LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing 22. The principle of drying reagents, sera and viruses onto filter paper has been validated in reference laboratories and in the field. Laboratories should consider using this technique, following the prescribed protocols, to ship samples where appropriate. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Ongoing Advocacy 23. To ensure the LabNet has sufficient capacity to meet the enhanced laboratorybased surveillance activities in alignment with AFRO and SEARO's preelimination and mortality reduction goals, the regional coordinators are requested to identify their needs for resources and support for training activities 11
12 for the next biennium. Action: WHO AFRO, SEARO and HQ. Timeline: Ongoing 24. The LabNet should investigate strategic pairings with other laboratory based surveillance programmes (such as HIV, Flu, Polio) Action: LabNet WHO. Timeline: Ongoing 25. The LabNet endorses the Laboratory related topics proposed for the forthcoming JID review supplement and are prepared to meet the publication deadlines. Action: LabNet. Timeline: Table of contents finalized by November 2009, chapters submitted 2nd quarter
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
Global Measles and Rubella Update November 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
Global Measles and Rubella Update October 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles Cases by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug
Global Measles and Rubella Update. April 2018
 Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
Global Measles and Rubella Update April 218 Measles Number of Reported Measles by WHO Regions 218 Region Member States* Suspected cases Measles cases Clin Epi Lab Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct
The Fifth WHO Global Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting. 26 to 28 September 2007, WHO, Geneva
 The Fifth WHO Global Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting Final Summary and Recommendations Global and Regional Update 26 to 28 September 2007, WHO, Geneva The measles and rubella laboratory
The Fifth WHO Global Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting Final Summary and Recommendations Global and Regional Update 26 to 28 September 2007, WHO, Geneva The measles and rubella laboratory
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets
 Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
Update on Progress and Challenges in Achieving Measles and Rubella Targets SAGE Meeting 6 November 2013 P. Strebel, WHO/IVB/EPI Overview Global progress Regional updates Summary 2 Measles and Rubella Targets
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005
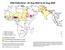 Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
What is this document and who is it for?
 Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
South-East Asia Regional Committee resolution (September 2013, New Delhi)
 South-East Asia Regional Committee resolution (September 2013, New Delhi) SEAR Member States adopted the goal of measles elimination and rubella/crs control in the South-East Asia Region by 2020. Achieving
South-East Asia Regional Committee resolution (September 2013, New Delhi) SEAR Member States adopted the goal of measles elimination and rubella/crs control in the South-East Asia Region by 2020. Achieving
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION. (indicator G2.2) Highlights
 GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
GOAL 2: ACHIEVE RUBELLA AND CRS ELIMINATION (indicator G2.2) Highlights As of December 2014, 140 Member States had introduced rubella vaccines; coverage, however, varies from 12% to 94% depending on region.
Training Workshop Report
 Training Workshop Report The 4th Regional Hands-on Training Workshop on the Laboratory Diagnosis of Measles and Rubella focusing on Molecular Diagnosis Hong Kong (China) 22 27 November 2010 (WP)/ICP/IVD/1.1/001-A
Training Workshop Report The 4th Regional Hands-on Training Workshop on the Laboratory Diagnosis of Measles and Rubella focusing on Molecular Diagnosis Hong Kong (China) 22 27 November 2010 (WP)/ICP/IVD/1.1/001-A
Comments on this bulletin are welcome. Please to Dr. Mary Agócs
 Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2010 Volume 4: October 2011 The World Health Organization
Global Invasive Bacterial Vaccine Preventable Diseases (IB-VPD) Information and Surveillance Bulletin Reporting Period: January through December 2010 Volume 4: October 2011 The World Health Organization
Status of Outbreak Vulnerable Countries
 Status of Outbreak Vulnerable Countries Hamid Jafari, WHO Robert Linkins, CDC Independent Monitoring Board Meeting 7-8 May, 2013 Outline Non-Endemic Vulnerable & At-Risk Countries Recently infected countries
Status of Outbreak Vulnerable Countries Hamid Jafari, WHO Robert Linkins, CDC Independent Monitoring Board Meeting 7-8 May, 2013 Outline Non-Endemic Vulnerable & At-Risk Countries Recently infected countries
Programmatic Feasibility of Measles Elimination
 Programmatic Feasibility of Measles Elimination World Health Organization Eastern Mediterranean Region June 2010 Acronyms: EMR Eastern Mediterranean Region of the World Health Organization 1 EMRO EPI GAVI
Programmatic Feasibility of Measles Elimination World Health Organization Eastern Mediterranean Region June 2010 Acronyms: EMR Eastern Mediterranean Region of the World Health Organization 1 EMRO EPI GAVI
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control
 The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
The Promise of Introducing Rubella Containing Vaccines on the Impact of Rubella and Measles Control GAVI Partners Forum 4 6 December 2012, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Maya van den Ent, MPH, UNICEF Peter Strebel,
Dr Ghazi Yehia OIE Regional Representative for the Middle East
 Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East The current situation Asuncion, Paraguay, 24-26 June 2009 Dr Ghazi Yehia OIE Regional Representative for the Middle East Acknowledgements
Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East The current situation Asuncion, Paraguay, 24-26 June 2009 Dr Ghazi Yehia OIE Regional Representative for the Middle East Acknowledgements
The FAO/OIE FMD Global Control Strategy Joseph Domenech, OIE on behalf of the joint FAO/OIE GF TADs PPR Working Group
 The FAO/OIE FMD Global Control Strategy Joseph Domenech, OIE on behalf of the joint FAO/OIE GF TADs PPR Working Group 5 th meeting of the GF TADs Regional Steering Committee for Europe October 8 th -9th
The FAO/OIE FMD Global Control Strategy Joseph Domenech, OIE on behalf of the joint FAO/OIE GF TADs PPR Working Group 5 th meeting of the GF TADs Regional Steering Committee for Europe October 8 th -9th
Global reductions in measles mortality and the risk of measles resurgence
 Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
Global reductions in measles mortality 2000 2008 and the risk of measles resurgence Measles is one of the most contagious human diseases. In 1980 before the use of measles vaccine was widespread, there
EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38)
 World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38) Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme, Division of Technical Support website:
World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38) Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme, Division of Technical Support website:
Pandemic H1N Dr. Maria Neira Global Influenza Programme WHO, Geneva
 Pandemic H1N1 2010 Dr. Maria Neira Global Influenza Programme WHO, Geneva WHO Role during pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Under the International Health Regulations (2005) Detect event (notification by Member States
Pandemic H1N1 2010 Dr. Maria Neira Global Influenza Programme WHO, Geneva WHO Role during pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Under the International Health Regulations (2005) Detect event (notification by Member States
Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions
 Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Core competencies in primary care: Supplement 2 Sexual and reproductive health care: A comparison of providers and delivery points between the African Region and other regions The Core competencies in
Foot and Mouth Disease Middle East situation Summary of Answers to the Questionnaire Beirut, Lebanon, 7 9 April 2009
 Foot and Mouth Disease Middle East situation Summary of Answers to the Questionnaire Beirut, Lebanon, 7 9 April 2009 Dr Pierre Primot OIE for the Middle East Purpose of the Questionnaire The purpose of
Foot and Mouth Disease Middle East situation Summary of Answers to the Questionnaire Beirut, Lebanon, 7 9 April 2009 Dr Pierre Primot OIE for the Middle East Purpose of the Questionnaire The purpose of
Yellow fever laboratory capacity on-site assessments in Africa: preliminary findings
 Yellow fever laboratory capacity on-site assessments in Africa: preliminary findings Maurice Demanou*, Barbara W. Johnson, Gamou Fall, Jean-Luc Betoulle, Chantal Reusken, Marion Koopmans, Lee Hampton,
Yellow fever laboratory capacity on-site assessments in Africa: preliminary findings Maurice Demanou*, Barbara W. Johnson, Gamou Fall, Jean-Luc Betoulle, Chantal Reusken, Marion Koopmans, Lee Hampton,
Performance of National Measles Case-Based Surveillance Systems in The WHO African Region
 Research Article Open Access Performance of National Measles Case-Based Surveillance Systems in The WHO African Region. 2012 2016 Balcha Masresha 1 *, Reggis Katsande 1, Richard Luce 2, Amadou Fall 3,
Research Article Open Access Performance of National Measles Case-Based Surveillance Systems in The WHO African Region. 2012 2016 Balcha Masresha 1 *, Reggis Katsande 1, Richard Luce 2, Amadou Fall 3,
Figure 1. Incidence rate of total (confirmed and compatible) measles cases with rash onset 1 31 December 2018, WHO Western Pacific Region
 Volume 13 Issue 1 uary 2019 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Incidence rate of total ( and compatible) measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No cases
Volume 13 Issue 1 uary 2019 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Incidence rate of total ( and compatible) measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No cases
宮村参考人提出資料 資料 2-2
 宮村参考人提出資料 資料 - Highlights of New Wild Poliovirus and cvdpv Positives Reported Globally this Week WPV cvdpv AFP other AFP other Afghanistan 5 Pakistan 3 Nigeria Location: state/province/governorate Kunar
宮村参考人提出資料 資料 - Highlights of New Wild Poliovirus and cvdpv Positives Reported Globally this Week WPV cvdpv AFP other AFP other Afghanistan 5 Pakistan 3 Nigeria Location: state/province/governorate Kunar
GLOBAL AND REGIONAL SITUATION OF AVIAN INFLUENZA
 GLOBAL AND REGIONAL SITUATION OF AVIAN INFLUENZA Dr Gounalan Pavade OIE Regional Expert Group Meeting for the Control of Avian Influenza in Asia Sapporo, Japan 3-5 October 2017 1 Avian influenza Outbreaks
GLOBAL AND REGIONAL SITUATION OF AVIAN INFLUENZA Dr Gounalan Pavade OIE Regional Expert Group Meeting for the Control of Avian Influenza in Asia Sapporo, Japan 3-5 October 2017 1 Avian influenza Outbreaks
Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case based data
 Volume 11 Issue 3 ch ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of measles cases with rash onset 1 28 ruary, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No case With case No case based data Dots are placed at random
Volume 11 Issue 3 ch ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of measles cases with rash onset 1 28 ruary, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No case With case No case based data Dots are placed at random
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua. Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2
 Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Current State of Global HIV Care Continua Reuben Granich 1, Somya Gupta 1, Irene Hall 2, John Aberle-Grasse 2, Shannon Hader 2, Jonathan Mermin 2 1) International Association of Providers of AIDS Care
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report
 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Situation Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Monthly Report October 2013 I N F O R M A T I O N S O U R C E S U S E D: Databases: OIE WAHID World Animal Health
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa
 Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case based data
 Volume 11 Issue 1 uary 2017 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case
Volume 11 Issue 1 uary 2017 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case
Figure 1. Incidence rate of total (confirmed and compatible) measles cases with rash onset 1 31 March 2018, WHO Western Pacific Region
 Volume 12 Issue 4 April ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Incidence rate of total ( compatible) measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ch, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No cases
Volume 12 Issue 4 April ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Incidence rate of total ( compatible) measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ch, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No cases
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities
 Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
ASLM Anti-microbial Resistance in Africa and Global Health Security. 9TH INTEREST WORKSHOP May 2015 Harare
 ASLM Anti-microbial Resistance in Africa and Global Health Security 9TH INTEREST WORKSHOP 2015 8 May 2015 Harare Recent Jim O Neil Report commissioned by the UK government predicts dire consequences of
ASLM Anti-microbial Resistance in Africa and Global Health Security 9TH INTEREST WORKSHOP 2015 8 May 2015 Harare Recent Jim O Neil Report commissioned by the UK government predicts dire consequences of
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF),
 Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
Analysis of Immunization Financing Indicators from the WHO-UNICEF Joint Reporting Form (JRF), 2008-2010 Claudio Politi and Oumar Sagna Department of Immunization Vaccines and Biologicals, World Health
Progress report on eradication of poliomyelitis: regional implications of the endgame strategy
 Regional Committee for the Eastern Mediterranean Sixtieth session Provisional agenda item 3 (a) August 2013 Progress report on eradication of poliomyelitis: regional implications of the endgame strategy
Regional Committee for the Eastern Mediterranean Sixtieth session Provisional agenda item 3 (a) August 2013 Progress report on eradication of poliomyelitis: regional implications of the endgame strategy
Regional Overview of the implementation of National Control Strategies for Avian Influenza. Summary review of questionnaire OIE RRAP
 Regional Overview of the implementation of National Control Strategies for Avian Influenza Summary review of questionnaire OIE RRAP The OIE Questionnaire on Influenza A surveillance in animals in the Asia
Regional Overview of the implementation of National Control Strategies for Avian Influenza Summary review of questionnaire OIE RRAP The OIE Questionnaire on Influenza A surveillance in animals in the Asia
Selected vaccine introduction status into routine immunization
 Selected introduction status into routine infant immunization worldwide, 2003 This report summarizes the current status of national immunization schedules in 2003, as reported by Member States in the /UNICEF
Selected introduction status into routine infant immunization worldwide, 2003 This report summarizes the current status of national immunization schedules in 2003, as reported by Member States in the /UNICEF
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes
 Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
Procedure for Expedited Review of imported pre-qualified vaccines for use in national immunization programmes Dr Nora Dellepiane/Dr Anil Kumar Chawla WHO/HQ-Geneva, Switzerland 1 Expedited review procedure
2004, OIE initiative Ad hoc Group on Antigen & Vaccine Banks for FMD
 2004, OIE initiative Ad hoc Group on Antigen & Vaccine Banks for FMD 2006, progressed by EU Funded project 2009, endorsed at OIE/FAO Global Conference on FMD, Paraguay In May 2010, Dr Jef Hammond presented
2004, OIE initiative Ad hoc Group on Antigen & Vaccine Banks for FMD 2006, progressed by EU Funded project 2009, endorsed at OIE/FAO Global Conference on FMD, Paraguay In May 2010, Dr Jef Hammond presented
Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 August 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region
 Volume 8 Issue 9 tember 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ust 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region 1 dot = 1 case Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed
Volume 8 Issue 9 tember 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ust 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region 1 dot = 1 case Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed
Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case** No case based data
 Volume 11 Issue 9 September ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of measles with rash onset 1 31 ust, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No case With case** No case based data Dots are placed at rom within
Volume 11 Issue 9 September ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of measles with rash onset 1 31 ust, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No case With case** No case based data Dots are placed at rom within
FAO GLOBAL INITIATIVES ON REGIONAL VETERINARY LABORATORY NETWORKS
 FAO GLOBAL INITIATIVES ON REGIONAL VETERINARY LABORATORY NETWORKS Gwenaelle Dauphin Laboratory Liaison Officer OFFLU focal point and several FAO colleagues Support to national laboratories Laboratory training
FAO GLOBAL INITIATIVES ON REGIONAL VETERINARY LABORATORY NETWORKS Gwenaelle Dauphin Laboratory Liaison Officer OFFLU focal point and several FAO colleagues Support to national laboratories Laboratory training
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics. Procurement for Impact P4i
 Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
Sourcing of ARVs & HIV diagnostics Procurement for Impact P4i AMDS ANNUAL STAKEHOLDERS AND PARTNERS MEETING 29 September 2014 Global Fund: Procurement for Impact: P4i Our objective was straightforward:
Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 30 September 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region
 Volume 8 Issue 10 ober 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 30 tember 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region 1 dot = 1 case Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed
Volume 8 Issue 10 ober 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 30 tember 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region 1 dot = 1 case Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed
Figure 1. Incidence rate of total (confirmed and compatible) measles cases with rash onset 1 31 December 2017, WHO Western Pacific Region
 Volume 12 Issue 1 January 2018 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Incidence rate of total ( compatible) measles with rash onset 1 31 ember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: Pacific isl countries areas No
Volume 12 Issue 1 January 2018 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Incidence rate of total ( compatible) measles with rash onset 1 31 ember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: Pacific isl countries areas No
IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES
 No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
Objectives of Rotavirus Surveillance
 Objectives of Rotavirus Surveillance Contribute data to estimate the burden of rotavirus diarrhea in children < 5 children Document circulating rotavirus strains in the AFR region Support awareness and
Objectives of Rotavirus Surveillance Contribute data to estimate the burden of rotavirus diarrhea in children < 5 children Document circulating rotavirus strains in the AFR region Support awareness and
Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 July 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region
 Volume 8 Issue 8 ust 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 y 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region 1 dot = 1 case Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed
Volume 8 Issue 8 ust 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 y 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region 1 dot = 1 case Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed
TFI Proceedings, Recommendations and implications for 2005
 January 2005 N 053 TFI 2004 - Proceedings, Recommendations and implications for 2005 The 12th meeting of the Task Force on Immunization (TFI) in Africa and the 11th meeting of the Africa Regional Inter-
January 2005 N 053 TFI 2004 - Proceedings, Recommendations and implications for 2005 The 12th meeting of the Task Force on Immunization (TFI) in Africa and the 11th meeting of the Africa Regional Inter-
Report on the 9 th WHO Global Measles Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting WHO Headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland September 2011
 Report on the 9 th WHO Global Measles Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting WHO Headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland 19-21 September 2011 Rapporteurs: J Leydon, Dr J Goodson Introduction The WHO Global Measles
Report on the 9 th WHO Global Measles Rubella Laboratory Network Meeting WHO Headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland 19-21 September 2011 Rapporteurs: J Leydon, Dr J Goodson Introduction The WHO Global Measles
Progress Towards Global Polio Eradication by 2012: Progress and Ongoing Challenges
 Progress Towards Global Polio Eradication by 2012: Progress and Ongoing Challenges European Conference on Post Polio Syndrome 31 August 2 September 2011, Copenhagen, Denmark Dr Rebecca Martin Vaccine Preventable
Progress Towards Global Polio Eradication by 2012: Progress and Ongoing Challenges European Conference on Post Polio Syndrome 31 August 2 September 2011, Copenhagen, Denmark Dr Rebecca Martin Vaccine Preventable
Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case based data
 Volume 10 Issue 4 il 2016 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ch 2016, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case
Volume 10 Issue 4 il 2016 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ch 2016, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case
Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No case based data
 Volume 11 Issue 10 ober ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of measles with rash onset 1 30 tember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No case With case No case based data Dots are placed at rom within
Volume 11 Issue 10 ober ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of measles with rash onset 1 30 tember, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No case With case No case based data Dots are placed at rom within
World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Surveillance of measles and rubella Data as of 15 March 2006
 World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Surveillance of measles and rubella Data as of 15 March 2006 WHO Regional Office for Europe Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme,
World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Surveillance of measles and rubella Data as of 15 March 2006 WHO Regional Office for Europe Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme,
Regional workshop on updating national strategic plans for the prevention of re-establishment of local malaria transmission in malaria-free countries
 Summary report on the Regional workshop on updating national strategic plans for the prevention of re-establishment of local malaria transmission in malaria-free countries Casablanca, Morocco 18 20 October
Summary report on the Regional workshop on updating national strategic plans for the prevention of re-establishment of local malaria transmission in malaria-free countries Casablanca, Morocco 18 20 October
HIV Drug Resistance Surveillance and Monitoring in the Southeast Asia Region
 HIV Drug Resistance Surveillance and Monitoring in the Southeast Asia Region Padmini Srikantiah, MD MPH HIV/AIDS Unit WHO- Regional Office for Southeast Asia The HIV epidemic in Southeast Asia Estimated
HIV Drug Resistance Surveillance and Monitoring in the Southeast Asia Region Padmini Srikantiah, MD MPH HIV/AIDS Unit WHO- Regional Office for Southeast Asia The HIV epidemic in Southeast Asia Estimated
Recommended composition of influenza virus vaccines for use in the 2007 influenza season
 Recommended composition of influenza virus vaccines for use in the 2007 influenza season September 2006 This recommendation relates to the composition of vaccines for the forthcoming winter in the southern
Recommended composition of influenza virus vaccines for use in the 2007 influenza season September 2006 This recommendation relates to the composition of vaccines for the forthcoming winter in the southern
Undiscovered progress in. in maternal mortality.
 CHAPTER 1 Undiscovered progress in maternal mortality During the early 1980s, a half-million women died every year during pregnancy, childbirth, or the postpartum period a stunning figure in a world that
CHAPTER 1 Undiscovered progress in maternal mortality During the early 1980s, a half-million women died every year during pregnancy, childbirth, or the postpartum period a stunning figure in a world that
Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 December 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region
 Volume 9 Issue 1 uary 2015 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ember 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No
Volume 9 Issue 1 uary 2015 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Distribution of confirmed measles cases with rash onset 1 31 ember 2014, WHO Western Pacific Region Legend: No confirmed case With confirmed case No
Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East the current
 1. Title, names and addresses of authors Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East the current situation G. Yehia (1), P. Primot (1) (1) OIE Regional Representation
1. Title, names and addresses of authors Foot and mouth disease control strategies in North Africa and the Middle East the current situation G. Yehia (1), P. Primot (1) (1) OIE Regional Representation
Guidance for Travelers on Temporary Work Assignment Abroad
 infected person to immediately seek medical care but, prior to arrival, notify their healthcare provider that they may have been exposed to AI. For more information about avian influenza, see www.cdc.gov/flu/avian/facts.htm,
infected person to immediately seek medical care but, prior to arrival, notify their healthcare provider that they may have been exposed to AI. For more information about avian influenza, see www.cdc.gov/flu/avian/facts.htm,
Wild Poliovirus Weekly Update
 1 of 5 12/07/2010 12:09 PM Google search this site contact links donate Home > Global Situation Wild Poliovirus Weekly Update 7 July 2010 Data as at 6 July 2010 Map of polio cases worldwide Wild poliovirus
1 of 5 12/07/2010 12:09 PM Google search this site contact links donate Home > Global Situation Wild Poliovirus Weekly Update 7 July 2010 Data as at 6 July 2010 Map of polio cases worldwide Wild poliovirus
The epidemiology of tuberculosis
 The epidemiology of tuberculosis Tuberculosis Workshop Shanghai, 12-22 May 28 Philippe Glaziou World Health Organization Outline Epidemiology refresher Estimates of tuberculosis disease burden Notifications
The epidemiology of tuberculosis Tuberculosis Workshop Shanghai, 12-22 May 28 Philippe Glaziou World Health Organization Outline Epidemiology refresher Estimates of tuberculosis disease burden Notifications
Polio Eradication and Surveillance. December
 Polio Eradication and Surveillance December 2017 1 Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) surveillance for polio eradication: >100,000 reported AFP per year December 2017 2 Global Laboratory Network for Polio Eradication
Polio Eradication and Surveillance December 2017 1 Acute Flaccid Paralysis (AFP) surveillance for polio eradication: >100,000 reported AFP per year December 2017 2 Global Laboratory Network for Polio Eradication
CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN
 CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN 2010-2012 14 Sept-10 2010 First and Second Quarters (January June) Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus (WPV)
CDC ASSESSMENT OF RISKS TO THE GLOBAL POLIO ERADICATION INITIATIVE (GPEI) STRATEGIC PLAN 2010-2012 14 Sept-10 2010 First and Second Quarters (January June) Geographic distribution of wild poliovirus (WPV)
Table 1. Measles case classification and incidence by country and area, WHO Western Pacific Region,
 Volume 7 Issue 5 May 2013 ISSN 1814 3601 Table 1. case classification and by country and area, WHO Western Pacific Region, 2008 2013 1 confirmed 2 2 009 per confirmed 2 2 010 2 011 2 012 2013 1 Confirmed
Volume 7 Issue 5 May 2013 ISSN 1814 3601 Table 1. case classification and by country and area, WHO Western Pacific Region, 2008 2013 1 confirmed 2 2 009 per confirmed 2 2 010 2 011 2 012 2013 1 Confirmed
Eligibility List 2018
 The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
The Global Fund s 2017-2022 strategy and allocation-based approach enables strategic investment to accelerate the end of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria and build resilient and sustainable systems for
VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio case
 Screening practices for infectious diseases among newly arrived migrants and Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD): strategies and coverage ISS 29 MAY 2015 VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio
Screening practices for infectious diseases among newly arrived migrants and Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD): strategies and coverage ISS 29 MAY 2015 VPD in Mediterranean Basin and Black Sea: the Polio
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts
 World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
World Health organization/ International Society of Hypertension (WH0/ISH) risk prediction charts (charts in colour) (These charts will be updated in 2014) 2 1. Introduction 2. Instructions on how to use
Proposed WHO Technical Consultation on external competence assessment for malaria microscopy
 Proposed WHO Technical Consultation on external competence assessment for malaria microscopy Malaria Policy Advisory Committee Meeting 17-19 October 2018, Executive Board meeting room World Health Organization,
Proposed WHO Technical Consultation on external competence assessment for malaria microscopy Malaria Policy Advisory Committee Meeting 17-19 October 2018, Executive Board meeting room World Health Organization,
FAOAIDEnews Animal Influenza Disease Emergency
 FAOAIDEnews Animal Influenza Disease Emergency Situation Update 82 17 November 2011 HPAI outbreaks reported in this publication refer to officially confirmed cases only. The information is compiled from
FAOAIDEnews Animal Influenza Disease Emergency Situation Update 82 17 November 2011 HPAI outbreaks reported in this publication refer to officially confirmed cases only. The information is compiled from
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011
 Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
Global Fund Results Fact Sheet Mid-2011 This fact sheet outlines some of the common questions and answers regarding results reported by Global Fund-supported programs, including the principles and approach
TB, BCG and other things. Chris Conlon Infectious Diseases Oxford
 TB, BCG and other things Chris Conlon Infectious Diseases Oxford Epidemiology Latent TB IGRA BCG >50/100000
TB, BCG and other things Chris Conlon Infectious Diseases Oxford Epidemiology Latent TB IGRA BCG >50/100000
Main global and regional trends
 I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
I N T R O D U C T I O N Main global and regional trends Promising developments have been seen in recent years in global efforts to address the AS epidemic, including increased access to effective treatment
Development of the Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategic plan
 Development of the Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategic plan SAGE Meeting 6 November 2012 Overview Process, Consultations, Development Eradication and Endgame Outcomes and Activities Legacy Planning
Development of the Polio Eradication and Endgame Strategic plan SAGE Meeting 6 November 2012 Overview Process, Consultations, Development Eradication and Endgame Outcomes and Activities Legacy Planning
ASLM Building laboratory capacity in Africa in a sustainable way
 ASLM Building laboratory capacity in Africa in a sustainable way Tsehaynesh Messele, PhD ASLM, Chief Executive Officer Annual AMDS meeting September 29-30, 2014 Geneva Laboratory capacity gaps in Africa
ASLM Building laboratory capacity in Africa in a sustainable way Tsehaynesh Messele, PhD ASLM, Chief Executive Officer Annual AMDS meeting September 29-30, 2014 Geneva Laboratory capacity gaps in Africa
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017
 THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
THE CARE WE PROMISE FACTS AND FIGURES 2017 2 SOS CHILDREN S VILLAGES INTERNATIONAL WHERE WE WORK Facts and Figures 2017 205 58 79 families and transit 31 Foster homes 162 8 3 173 214 2 115 159 136 148
Introduction to Measles a Priority Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD) in Africa
 Introduction to Measles a Priority Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD) in Africa Nigeria Center for Disease Control Federal Ministry of Health Abuja July 2015 Outline 1. Measles disease 2. Progress towards
Introduction to Measles a Priority Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD) in Africa Nigeria Center for Disease Control Federal Ministry of Health Abuja July 2015 Outline 1. Measles disease 2. Progress towards
APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS
 WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX II - TABLE 2.3 ANTI-TOBACCO MASS MEDIA CAMPAIGNS (SEE TABLE 4.9) Africa The Americas South-East Asia Europe Eastern Mediterranean Western Pacific
Rotavirus Vaccine: Supply & Demand Update. UNICEF Supply Division
 Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Rotavirus Vaccine: & Demand Update UNICEF Division July 0 Rotavirus Vaccine (RV): & Demand Update July This update provides new information on countries and their scheduled RV introductions, forecasted
Epidemiology of measles in infants younger than 6 months: analysis of surveillance data
 Epidemiology of measles in infants younger than 6 months: analysis of surveillance data 2011-2016 An analysis of the epidemiology of measles in infants younger than 6 months was conducted by the U.S. CDC
Epidemiology of measles in infants younger than 6 months: analysis of surveillance data 2011-2016 An analysis of the epidemiology of measles in infants younger than 6 months was conducted by the U.S. CDC
Figure 1. Confirmed measles cases, WHO Western Pacific Region, 1 31 March 2014
 Volume 8 Issue 4 il 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Confirmed measles cases, WHO Western Pacific Region, 1 31 ch 2014 1 dot = 1 case Confirmed cases Australia 33 Brunei Darussalam 0 Cambodia 0 China 7675
Volume 8 Issue 4 il 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Confirmed measles cases, WHO Western Pacific Region, 1 31 ch 2014 1 dot = 1 case Confirmed cases Australia 33 Brunei Darussalam 0 Cambodia 0 China 7675
Figure 1. Confirmed measles cases, WHO Western Pacific Region, 1 30 January 2014
 Volume 8 Issue 2 ruary 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Confirmed measles cases, WHO Western Pacific Region, 1 30 uary 2014 1 dot = 1 case Confirmed cases Australia 70 Brunei Darussalam 0 Cambodia 0 China
Volume 8 Issue 2 ruary 2014 ISSN 1814 3601 Figure 1. Confirmed measles cases, WHO Western Pacific Region, 1 30 uary 2014 1 dot = 1 case Confirmed cases Australia 70 Brunei Darussalam 0 Cambodia 0 China
Poliomyelitis eradication in the WHO European Region
 Provisional agenda item 6(i) EUR/RC60/16 (+EUR/RC60/Conf.Doc./9) 23 July 2010 101614 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Poliomyelitis eradication in the WHO European Region WHO Regional Committee for Europe Sixtieth session
Provisional agenda item 6(i) EUR/RC60/16 (+EUR/RC60/Conf.Doc./9) 23 July 2010 101614 ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Poliomyelitis eradication in the WHO European Region WHO Regional Committee for Europe Sixtieth session
Prohibition of importation, manufacturing and sale of Smokeless Tobacco products.
 Prohibition of importation, manufacturing and sale of Smokeless Tobacco products www.untobaccocontrol.org/kh/smokeless-tobacco/ BACKGROUND. Over the past decade, the WHO FCTC has served as a powerful tool
Prohibition of importation, manufacturing and sale of Smokeless Tobacco products www.untobaccocontrol.org/kh/smokeless-tobacco/ BACKGROUND. Over the past decade, the WHO FCTC has served as a powerful tool
TOBACCO USE IN OIC COUNTRIES: PROSPECTS AND CHALLENGES
 ORGANISATION OF THE ISLAMIC CONFERENCE STATISTICAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING CENTRE FOR ISLAMIC COUNTRIES OIC OUTLOOK March 2010 TOBACCO USE IN OIC COUNTRIES: PROSPECTS AND CHALLENGES
ORGANISATION OF THE ISLAMIC CONFERENCE STATISTICAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL RESEARCH AND TRAINING CENTRE FOR ISLAMIC COUNTRIES OIC OUTLOOK March 2010 TOBACCO USE IN OIC COUNTRIES: PROSPECTS AND CHALLENGES
PPR VACCINE, VACCINATION AND VACCINE QUALITY CONTROL
 Dr DIALLO ADAMA CONSULTANT FAO PPR VACCINE, VACCINATION AND VACCINE QUALITY CONTROL Lessons from rinderpest eradication 2011 was the official recognition of the world freedom from rinderpest Lessons from
Dr DIALLO ADAMA CONSULTANT FAO PPR VACCINE, VACCINATION AND VACCINE QUALITY CONTROL Lessons from rinderpest eradication 2011 was the official recognition of the world freedom from rinderpest Lessons from
Highlighting in the WHO European Region:
 No. 23(April 2012) Issue 15, April 2011 A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Highlighting in the WHO European Region: Update on measles in the European
No. 23(April 2012) Issue 15, April 2011 A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Highlighting in the WHO European Region: Update on measles in the European
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook. UNICEF Supply Division
 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table
 Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Updated 23/05/2017 מדינת ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. Exe = exempted Req = required Press the first
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration
 Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Measles cases MCV1 coverage MCV2 coverage
 Volume 7 Issue 9 tember 2013 ISSN 1814 3601 30 000 Figure 1. cases by month of onset, WHO Western Pacific Region, 2008 2013 1 Number of cases 25 000 20 000 15 000 10 000 5 000 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012
Volume 7 Issue 9 tember 2013 ISSN 1814 3601 30 000 Figure 1. cases by month of onset, WHO Western Pacific Region, 2008 2013 1 Number of cases 25 000 20 000 15 000 10 000 5 000 0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012
Overview of WRL FMD. Historical perspective. Principal activities. FMD threats. Needs/prospects. David Paton
 Tracking the emergence and global spread of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) Overview of WRL FMD David Paton Historical perspective Principal activities FMD threats Needs/prospects Historical Perspective FMD
Tracking the emergence and global spread of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) Overview of WRL FMD David Paton Historical perspective Principal activities FMD threats Needs/prospects Historical Perspective FMD
Annex 3. Meetings held in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, 2014
 Annex 3. Meetings held in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, Statutory and advisory meetings Expanded meeting for members of the Advisory Committee on Health Research to discuss integrating research in
Annex 3. Meetings held in the Eastern Mediterranean Region, Statutory and advisory meetings Expanded meeting for members of the Advisory Committee on Health Research to discuss integrating research in
מדינת ישראל. Tourist Visa Table. Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents.
 Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Updated 25/05/2015 ישראל Tourist Visa Table Tourist visa exemption is applied to national and official passports only, and not to other travel documents. (C) Bearers of official passports requiring tourist
Drug Prices Report Opioids Retail and wholesale prices * and purity levels,by drug, region and country or territory (prices expressed in US$ )
 1 / 11 Region/Subregion/ Country Africa Eastern Africa Kenya Madagascar Mauritius Uganda United Republic of Tanzania Northern Africa Algeria Egypt Libya Morocco Sudan Southern Africa Botswana Burkina Faso
1 / 11 Region/Subregion/ Country Africa Eastern Africa Kenya Madagascar Mauritius Uganda United Republic of Tanzania Northern Africa Algeria Egypt Libya Morocco Sudan Southern Africa Botswana Burkina Faso
HIV and Harm Reduction in Prisons
 HIV and Harm Reduction in Prisons School of Public Health and Community Medicine Professor Kate Dolan Program of International Research and Training National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre UNSW, Sydney,
HIV and Harm Reduction in Prisons School of Public Health and Community Medicine Professor Kate Dolan Program of International Research and Training National Drug and Alcohol Research Centre UNSW, Sydney,
Framework for Verifying Elimination of Measles and Rubella SAGE Working Group on Measles and Rubella (Draft of 18 October 2012)
 Framework for Verifying Elimination of Measles and Rubella SAGE Working Group on Measles and Rubella (Draft of 18 October 2012) Preamble The Global Vaccine Action Plan 2012-2020, established the target
Framework for Verifying Elimination of Measles and Rubella SAGE Working Group on Measles and Rubella (Draft of 18 October 2012) Preamble The Global Vaccine Action Plan 2012-2020, established the target
