Syndromes of microcephaly, microphthalmia,
|
|
|
- Clare Chase
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
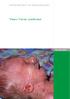
1 Journal of Medical Genetics, 1981, 18, Syndromes of microcephaly, microphthalmia, cataracts, and joint contractures ROBIN M WINTER*, DIAN DONNAIt, AND MARTIN d'a CRAWFURD* From *the Kennedy Galton Centre, Harperbury Hospital, Harper Lane, Radlett, Hertfordshire WD7 9HQ; *the Division of Inherited Metabolic Diseases, Clinical Research Centre, Northwick Park Hospital, Watford Road, Harrow, Middlesex HAI 3UJ; and tthe Department of Medical Genetics, St Mary's Hospital, Hathersage Road, Manchester M13 OJH SUMMARY Three infants are described, one with the Neu-Laxova syndrome and two with the cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal (COFS) syndrome. The relationship between these two syndromes is discussed in the light of the present cases and others in published reports. Pena and Shokeirl described ten infants with a syndrome consisting of microcephaly, microphthalmia, cataracts, and joint contractures and in most cases characteristic facial appearance. They believed that autosomal recessive inheritance was involved in what they referred to as the cerebro-oculo-facioskeletal syndrome (COFS) syndrome. A follow-up of some of the original cases and details of several new ones,2 together with other reports 3 4 which probably describe the same syndrome under different names, firmly established the existence of the COFS syndrome. However, details of other cases 5-8 have led Pena et a12 to suggest that other similar syndromes exist within the "same phenotypic syndrome community". Infants described by Neu et a19 and Laxova et al 10 had microcephaly and joint contractures but were also characterised by oedema and bizarre facial features. Similar infants were described by Lazjuk et all' who drew attention to reports in the Czech literature,12 and following a review of all known cases they suggested that the constellation of signs be called the Neu-Laxova syndrome. However, the COFS syndrome, which may itself be heterogeneous, and the Neu-Laxova syndrome have sufficient features in common for some authors to consider them to be possibly part of the same entity.7 13 In the absence of a specific biochemical or other marker it is impossible to resolve this diagnostic heterogeneity and in this report we describe three further cases, two of whom appear to conform most closely to the COFS group, and one of whom has features common to both the COFS and Neu-Laxova syndromes. Rece'ved for publication 29 May 1980 Case reports CASE 1 This was a term female infant born to a 23-year-old Caucasian primigravida. There was no family history of similar abnormalities and no known parental consanguinity. Pregnancy was uneventful and there was no history of drug ingestion. Birthweight was 1-36kg (<3rd centile) and the head circumference was 24 cm (<3rd centile). The forehead was sloping, the nasal bridge broad and prominent, and the eyes sunken and tightly closed AM FIG 1 Case
2 130 with microphthalmia and cataracts (fig 1). There was micrognathia, with the upper lip overhanging the lower, and malformed ears with abnormal antihelices. The mouth and palate were normal. The neck was short and the chest broad, and there were flexion contractures of the elbows, wrists, fingers, hips, knees, and ankles with bilateral rocker-bottom feet. The skin of the trunk was yellow, shiny, cracked with peeling in places, and resembled the collodion skin of infants with congenital ichthyosis. The baby died at 3 hours of age. A necropsy examination was refused. Investigations for intrauterine infection were negative. The karyotype (G banded) was 46,XX. CASE 2 This was a female infant who was the product of a term normal delivery to a 23-year-old Asian Indian primigravida. Pregnancy was normal and there was no history of drug ingestion or viral infections. The parents were first cousins. Birthweight was 2 2 kg (<3rd centile), head circumference was 29 5 cm (<3rd centile), and length was 53 cm (50th centile). At birth she was noted to have microcephaly, cataracts, and multiple joint contractures. On examination at 4 months of age her weight was 3 6 kg (<3rd centile), length 60 cm (25th centile), and head circumference 35-1 cm (<3rd centile). She was microcephalic with a sloping forehead, prominent root of the nose, bilateral cataracts, mild hypotelorism, and convergent strabismus (fig 2). The neck was short. There was marked scoliosis of the spine with a mongolian blue spot to the left of the sacrum Robin M Winter, Dian Donnai, and Martin d'a Crawfurd and a large (1 5 cm) pilonidal sinus. A small umbilical hernia was present, but otherwise the abdomen and external genitalia were normal. Tone of the limbs was much increased and the tendon reflexes were very brisk. There were multiple flexion contractures of the elbow, wrists, fingers, hip, knees, and ankles. The skin of the soles of the feet manifested some longitudinal folding although there was no rocker-bottom deformity. The skin was normal. Investigations for rubella, toxoplasma, and cytomegalovirus infection were negative. Urine analysis for amino-acids and reducing substances was negative. Chromosome studies (G banded) showed a 46,XX karyotype. The patient failed to thrive and had severe feeding difficulties. Development was severely retarded. She died at the age of 5 years, probably of bronchopneumonia. Her weight at death was 8 kg (<3rd centile). Necropsy examination was not carried out. CASE 3 This was a female infant, the second child born to healthy non-consanguineous Caucasian parents. The first child, at the age of 8 years, is physically and developmentally normal and there is no relevant family history. There were no illnesses in the second pregnancy and no drugs, apart from iron tablets, were taken. Delivery was by forceps and the birthweight of the infant was 3 28 kg (25th centile). The early neonatal period was uneventful but at the age of 4 months her weight was 5 67 kg and examination revealed microcephaly (head circumference J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 April Downloaded from FIG 2 Case 2. FIG 3 on 15 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
3 Syndromes of microcephaly, microphthalmia, cataracts, andjoint contractures 38-5 cm, <3rd centile), microphthalmia, and cataracts. Investigations for rubella, cytomegalovirus, and toxoplasmosis were negative. Urine chromatography was normal and chromosome studies (G banded) showed a 46,XX constitution. She had severe feeding difficulties, failed to thrive, and a developmental quotient on the Griffiths mental development scale was 24 at the age of 2 years. On examination at the age of 4 years, her weight was 7 25 kg (<3rd centile), length 74 cm (<3rd centile), and head circumference 40 cm (<3rd centile). Her eyes were small and deep set and cataracts were present (fig 3). The ears were large, the nasal bridge was prominent, and the upper lip overhung the lower lip. The teeth were small and brittle. There was marked camptodactyly and a thoracic kyphosis was present. She died at and acute cardiac failure. the age of 41 years from pneumonia Permission for necropsy was not granted. Discussion Infants presenting with microcephaly, cataracts, and joint contractures with associated anomalies appear to fall into three groups (table). TABLE (1) Those infants with relatively normal birthweight but with progressive postnatal growth deficiency and progressive pathology of the central nervous system, consisting of depletion of subcortical white matter and myelin, compatible with leucodystrophy. Examples of these patients include the original patients described as having the COFS syndrome by Pena and Shokeir,' some of whom were later reinvestigated,2 the patients described by Lowry et al,3 (the necropsy on one of those patients was reported by Dolman and Wright14), and those described by Scott-Emuakpor et al.4 These infants tend to have characteristic facial features consisting of microcephaly, microphthalmia, blepharophimosis, cataracts, prominent root of the nose, upper lip overhanging the lower, micrognathia, and large ear pinnas. Musculoskeletal abnormalities include camptodactyly and flexion contractures, dislocated hips with shallow acetabular angles, coxa valga, rocker-bottom feet, and a longitudinal groove on the soles. Pena et al2 suggested that the postnatal growth failure and cachexia were evidence of a primary growth deficiency. In addition to the progressive neurological pathology, some members of this group have Comparison ofpresent cases with reported cases of Neu Laxova and COFS syndromes Features Case I Case 2 Case 3 Neu-Laxova COFS COFS (early death) (classical) General Small for dates /9 4/5 8/14 Age at death±sd 3 h 5 yr 4 yr * 8 d 49 mth ±9-5 i 53 Failure to thrive NA 5/5 17/17 Mental retardation NA + + NA NA 17/17 Head and neck Microcephaly /9 4/4 16/17 Sloping forehead /6 4/5? Prominent root of nose ± + + 1/7 5/5 8/8 Flat nose and nasal bridge /7 0/5 0/8 Large ears /3 4/5 9/9 Micrognathia /6 3/5 8/9 Microphthalmia /7 3/4 11/11 Cataracts /7 3/4 11/15 Short neck /6 2/4 0/10 Trunk Kyphosis /7 2/5 13/14 Scoliosis /7 0/2 13/14 Extremities Camptodactyly/finger deformity /8 5/5 10/10 Syndactyly /6 1/5 0/9 Flexion contractures /8 5/5 14/16 Rocker-bottom feet /6 3/5 7/12 Skin Ichthyosis/collodion skin /7 0/5 0/14 Oedema of subcutis /8 0/5 0/14 CNS Hypoplasia or agenesis of the corpus callosum??? 2/5 2/3 3/7 Cerebellar hypoplasia??? 4/5 1/3 3/7 Intracranial calcification??? 1/5 0/3 2/7 *Only one live born case (Neu et al9) died at 49 days. 131
4 Robin M Winter, Dian Donnai, and Martin d'a Crawfurd also shown cerebellar hypoplasia and agenesis of the corpus callosum.4 14 The average age at death is 4 years. (2) Those infants described as being cases of the COFS syndrome who have died within the first few weeks of life. These infants in general have a low birthweight but show the facial and musculoskeletal features of the COFS syndrome.5-8 They can also have agenesis of the corpus callosum with cerebellar hypoplasia.6 8 Major visceral abnormalities are common. These include horseshoe kidney or renal agenesis, absence of the hemidiaphragm, malrotation of the colon,7 hypoplasia of the spleen and kidneys,6 and multiple foci of calcification in the heart and kidneys.8 (3) Those infants manifesting a highly lethal syndrome consisting of severe intrauterine growth retardation and often bizarre facial features with slanted forehead, retracted or absent eyelids, flattened nose, micrognathia, and low set ears. Major malformations of the brain have been reported including lissencephaly, complete or partial agenesis of the corpus callosum, and hypoplasia of the cerebellum. Some cases have ichthyosis or yellow, shiny, desquamating skin and oedema of the subcutis. In all, nine cases have been described.12 Lazjuk et al"l reviewed all the reported cases and suggested the title of the Neu-Laxova syndrome. Following the initial reports of the COFS and Neu-Laxova syndromes some authors considered them to be the same entity.7 13 However, Pena et al,2 in their follow-up report, suggested that only those patients who had a relatively normal birthweight, no major visceral malformations, and who presented with progressive failure to thrive and progressive neurological pathology should be considered to have the COFS syndrome. They considered the patients described by Lurie et a16 and Preus et a17 to have a separate disorder. Presumably, by these criteria, they would also exclude the case described by Surana et al.8 Nevertheless, there is considerable similarity between the three groups (table). In addition to the common features of microcephaly, cataracts, contractures, and failure to thrive, subjects from each group have been found to have major central nervous system malformations consisting of agenesis or hypoplasia of the corpus callosum and hypoplasia of the cerebellum. Intracranial calcification has also been a common feature. The grotesque facial features sometimes manifested in the Neu-Laxova syndrome, together with the syndactyly of hands and feet, severe oedema, and ichthyosis or yellow scaly skin seem to be peculiar to patients with this particular condition; however, no one feature serves to distinguish this syndrome completely. For example, the infants described by Taybi and Linden15 (pictures of one of whom appear in Holmes et al16), who presented with low birthweight, microcephaly, sloping forehead, flat bridge of the nose, bulging eyes, lissencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and skeletal dysplasia, share many features common to the Neu- Laxova syndrome and to those infants described as having the COFS syndrome who died at an early age, especially the infant described by Surana et al.8 We consider our case 1 to be an example of the Neu-Laxova syndrome, phenotypically resembling case 3 of Neu et al,9 who came from a sibship where the other two affected infants were phenotypically similar to the cases reported by Laxova et al.10 However, there are considerable similarities between this patient of ours and those patients described as having the COFS syndrome who have died within the first few weeks of life. Our cases 2 and 3 appear to be like the COFS syndrome patients originally described by Pena and Shokeir,1 having relatively normal birthweights and postnatal failure to thrive in addition to the eye and musculoskeletal abnormalities. Both the Neu-Laxova syndrome and the COFS syndrome are thought to be transmitted in an autosomal recessive fashion. It remains to be seen whether they represent extreme manifestations of homozygosity for the same allele at one locus, multiple allelism, or homozygosity for abnormal alleles at different loci. The similarities between these syndromes suggest a common biochemical or pathological origin. The authors are grateful to Dr I Kessel for referring patient 1 and to Dr G Katz for referring patient 2. References Pena SDJ, Shokeir MHK. Autosomal recessive cerebrooculo-facio-skeletal (COFS) syndrome. Clin Genet 1974; 5 : Pena SDJ, Evans J, Hunter AGW. COFS syndrome revisited. Birth Defects 1978;XIV, 6B: Lowry RB, MacLean R, MacLean DM, Tischler B. Cataracts, microcephaly, kyphosis and limited joint movement in two siblings. A new syndrome. J Pediatr 1971 ;79: Scott-Emuakpor AB, Heffelfinger J, Higgins JV. A syndrome of microcephaly and cataracts in four siblings. Am J Dis Child 1977;131: Preus M, Fraser FC. The cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal syndrome. Clin Genet 1974;5: Lurie IW, Cherstvoy GI, Lazjuk MK, Usoer SS. Further evidence for the autosomal-recessive inheritance of the COFS syndrome. Clin Genet 1976;10: Preus M, Kaplan P, Kirkham TH. Renal anomalies and oligohydramnios in the cerebro-oculo-facio-skeletal syndrome. Am J Dis Child 1977;131:62-4.
5 Syndromes of microcephaly, microphthzalmia, cataracts, and joint contractures 8 Surana RB, Fraga JR, Sinkford SM. The cerebro-oculofacio-skeletal syndrome. Clin Genet 1978 ;13 : Neu RL, Lytt IG, Nagyfy SF, King S. A lethal syndrome of microcephaly with multiple congenital anomalies in three siblings. Pediatrics 1971 ;47: Laxova R, O'Hara PT, Timothy JAD. A further example of a lethal autosomal recessive condition in sibs. J Ment Defic Res 1972;16: Lazjuk GI, Lurie 1W, Ostrowskaja TI, et al. The Neu- Laxova syndrome-a distinct entity. Am J Med Genet 1979 ;3 : Povysilova V, Macek M, Salichova J, Seemanova E. Letalni Syndrom mnohocetnych malformaci u tri sourosencui. Cesk Pediatr 1976;31: Temtamy SA, McKusick, VA. The genetics of hand malformations. New York: Liss, 1978: Dolman CL, Wright VJ. Necropsy of original case of Lowry's syndrome. J Med Genet 1978 ;15 : s Taybi H, Linden D. Congenital familial dwarfism with cephaloskeletal dysplasia. Radiology 1967;89: Holmes LB, Moser HW, Halldorsson S, Maik MS, Pant SS, Matzilevich B. Mental retardation. New York: MacMillan, 1972: Requests for reprints to Dr R M Winter, Division of Inherited Metabolic Diseases, Clinical Research Centre, Watford Road, Harrow, Middlesex HAI 3UJ. J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 April Downloaded from on 15 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab
 Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Lab #10: Karyotyping Lab INTRODUCTION A karyotype is a visual display of the number and appearance of all chromosomes from a single somatic cell. A normal human karyotype would reveal 46 chromosomes (22
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Dysmorphology. Sue White. Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase. Victorian Clinical Genetics Services
 Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
Dysmorphology Sue White www.rch.unimelb.edu.au/nets/handbook Diagnostic Dysmorphology, Aase Dysmorphology Assessment Algorithm no Are the features familial? yes Recognised syndrome yes no AD/XL syndrome
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Yunis-Varon syndrome
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Yunis-Varon syndrome January 2003 2 Heyland K, Hodler C, Bänziger O, Neonatology, University Children s Hospital of Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society of Neonatology, Thomas
A Collodion Baby with Facial Dysmorphism, Limb Anomalies, Pachygyria and Genital Hypoplasia: A Mild Form of Neu-Laxova Syndrome or a New Entity?
 A Collodion Baby with Multiple Anomalies Ann Dermatol Vol. 25, No. 4, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.483 CASE REPORT A Collodion Baby with Facial Dysmorphism, Limb Anomalies, Pachygyria and
A Collodion Baby with Multiple Anomalies Ann Dermatol Vol. 25, No. 4, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.4.483 CASE REPORT A Collodion Baby with Facial Dysmorphism, Limb Anomalies, Pachygyria and
Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story
 To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story DDC Clinic mission: To enhance the quality of life for people with special needs caused by rare genetic disorders What Does It Take to Be Your Local
To Be Your Local Expert A General Pediatrician s Story DDC Clinic mission: To enhance the quality of life for people with special needs caused by rare genetic disorders What Does It Take to Be Your Local
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL. Denise LM Goh
 APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
APPROACH TO A DYSMORPHIC INDIVIDUAL Denise LM Goh Contents The dysmorphic child Incidence of congenital anomalies Suspicion for diagnosis Approach to the dysmorphic child Problem analysis history hysical
a Genetics Unit, Department of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Received 29 June 2004 Accepted 3 November 2004
 Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum?
 JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
JMed Genet 1990; 27: 169-175 Oculodentodigital dysplasia and type III syndactyly: separate genetic entities or disease spectrum? L A Brueton, S M Huson, B Farren, R M Winter Abstract A family is described
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
and duodenal atresia. Two other families reported may have had the same syndrome. Case reports CASE 1 (III.8, FAMILY 1)
 JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
JMedGenet 1991; 28: 389-394 Autosomal dominant inheritance of abnormalities of the hands and feet with short palpebral fissures, variable microcephaly with learning disability, and oesophageal/duodenal
Early onset Cockayne's syndrome: case reports with neuropathological and fibroblast studies
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 154-159 Early onset Cockayne's syndrome: case reports with neuropathological and fibroblast studies M A PATTON*, F GIANNELLIt, A J FRANCISt, M BARAITSERt, B HARDINGt,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 154-159 Early onset Cockayne's syndrome: case reports with neuropathological and fibroblast studies M A PATTON*, F GIANNELLIt, A J FRANCISt, M BARAITSERt, B HARDINGt,
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, syndrome
 Severe Silver-Russell syndrome Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 447-451 D DONNAI*, E THOMPSONt, J ALLANSONt, AND M BARAITSERt From *the Regional Genetic Service, St Mary's Hospital, Manchester M13
Severe Silver-Russell syndrome Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 447-451 D DONNAI*, E THOMPSONt, J ALLANSONt, AND M BARAITSERt From *the Regional Genetic Service, St Mary's Hospital, Manchester M13
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Stickler syndrome. Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Congenital heart malformation in Yunis-Varon syndrome
 788 77 Med Genet 1993 30: 788-792 Medical Genetics and Epidemiology, (The Centre for Medical Genetics), Adelaide, 72 King William Road, North Australia 5006, Australia. L C Ades E A Haan Organ Imaging,
788 77 Med Genet 1993 30: 788-792 Medical Genetics and Epidemiology, (The Centre for Medical Genetics), Adelaide, 72 King William Road, North Australia 5006, Australia. L C Ades E A Haan Organ Imaging,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
Limb/pelvis-hypoplasia/aplasia syndrome
 I Med Genet 1993; 30: 65-69 Centro di Genetica Umana, Ospedali Galliera, Mura Delle Cappuccine 14, 16128 Genoa, Italy. G Camera Ospedale Villa Malta, 84087 Sarno (Salerno). Italy. G Ferraiolo D Leo A Spaziale
I Med Genet 1993; 30: 65-69 Centro di Genetica Umana, Ospedali Galliera, Mura Delle Cappuccine 14, 16128 Genoa, Italy. G Camera Ospedale Villa Malta, 84087 Sarno (Salerno). Italy. G Ferraiolo D Leo A Spaziale
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL
 A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
History. History and Physical Exam of the Pediatric Patient. History of Present Illness. Chief Complaint. Past Medical History. Past Medical History
 History History and Physical Exam of the Pediatric Patient Colleen A. Kraft, M.D., FAAP Richmond Pediatric Associates, Inc. Source Who is giving the history? Is this the patient s primary caretaker? 1
History History and Physical Exam of the Pediatric Patient Colleen A. Kraft, M.D., FAAP Richmond Pediatric Associates, Inc. Source Who is giving the history? Is this the patient s primary caretaker? 1
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions
 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 2 nd Week Dr. Zakariya Al-Akri Common and Uncommon Conditions - Case (1): sunset eye appearance which occurs with increased intracranial pressure
A. Definitions... CD-157. B. General Information... CD-158
 CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
CD Part 10 Multiple Body System Disorders A. Definitions... CD-157 B. General Information... CD-158 C. Specific Listings and Residual Functional Capacity... CD-158 1. Listing 10.06: Non-Mosaic Down Syndrome
Spectrum of Features in Pterygium Syndrome
 Case Report Spectrum of Features in Pterygium Syndrome Sanjay Y. Parashar, Peter J. Anderson, Neil McLean, Marzoeki Djohansjah 1 and David J. David, Australian Craniofacial Unit and Institute, Adelaide,
Case Report Spectrum of Features in Pterygium Syndrome Sanjay Y. Parashar, Peter J. Anderson, Neil McLean, Marzoeki Djohansjah 1 and David J. David, Australian Craniofacial Unit and Institute, Adelaide,
De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 2, pp. E79-E84, 2010 De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies HADI AHMAD AHZAD 1, SITI FATIMAH RAMLI 1, TAN MAY LOONG 2, IMAN SALAHSHOURIFAR
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56, No. 2, pp. E79-E84, 2010 De novo Ring Chromosome 6 in a Child with Multiple Congenital Anomalies HADI AHMAD AHZAD 1, SITI FATIMAH RAMLI 1, TAN MAY LOONG 2, IMAN SALAHSHOURIFAR
Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis. Rodney J. Scott
 Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis Rodney J. Scott Ability to interrogate Genomic Material ~1930 Crude analyses 2012 Highly precise analyses A (very) brief history
Seven cases of intellectual disability analysed by genomewide SNP analysis Rodney J. Scott Ability to interrogate Genomic Material ~1930 Crude analyses 2012 Highly precise analyses A (very) brief history
Chromosome Disease. The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental
 Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
Medical Genetics Chapter4 Chromosome Disease Chromosome Disease Clinical feature The general features in autosome abnormalities are a triad of growth retardation, mental retardation, and specific somatic
Hirschsprung's disease
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 100-104 Interstitial deletion of distal 13q associated with Hirschsprung's disease M A LAMONT*, M FITCHETTt, AND N R DENNIS* From *the Department of Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 26, 100-104 Interstitial deletion of distal 13q associated with Hirschsprung's disease M A LAMONT*, M FITCHETTt, AND N R DENNIS* From *the Department of Child Health,
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know
 Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
Congenital anomalies of upper extremity - What Radiologist should know Poster No.: C-0955 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad; Hyderabad/IN Keywords: Congenital,
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies
 Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
Investigation of chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions in 50 patients with multiple congenital anomalies Akbar Mohammadzadeh MD, PhD candidate in Medical Genetics Genetics Research Center University
Abstract. Introduction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, September: 453-458, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Sanjad-Sakati Syndrome: A Rare Autosomal Recessive Disorder of Congenital Hypoparathyroidism-Microcephaly-Mental
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, September: 453-458, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Sanjad-Sakati Syndrome: A Rare Autosomal Recessive Disorder of Congenital Hypoparathyroidism-Microcephaly-Mental
What is Craniosynostosis?
 What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
What is Craniosynostosis? Craniosynostosis is defined as the premature closure of the cranial sutures (what some people refer to as soft spots). This results in restricted and abnormal growth of the head.
Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 488-492 Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome I D YOUNG AND J R MOORE From the Department of Child Health, University of Leicester, Leicester LE2 7LX. SUMMARY
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 488-492 Intrafamilial variation in Cohen syndrome I D YOUNG AND J R MOORE From the Department of Child Health, University of Leicester, Leicester LE2 7LX. SUMMARY
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider TEST DISEASE/CONDITION POPULATION TRIAD Submitting laboratory: Manchester RGC Approved: September 2013
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier/Additional Provider TEST DISEASE/CONDITION POPULATION TRIAD Submitting laboratory: Manchester RGC Approved: September 2013
Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information
 Jame5. L.Jma5, ~reuiry Medical Conditions Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information I Not Listed later Children with medical conditions which
Jame5. L.Jma5, ~reuiry Medical Conditions Medical Conditions Resulting in High Probability of Developmental Delay and DSCC Screening Information I Not Listed later Children with medical conditions which
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University
 Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
Faravareh Khordadpoor (PhD in molecular genetics) 1- Tehran Medical Genetics Laboratory 2- Science and research branch, Islamic Azad University 1395 21 مشاوره ژنتیک و نقش آن در پیش گیری از معلولیت ها 20
Clinical Guidance. Neonatal Manual Chapter 10: Musculoskeletal problems
 Clinical Guidance Neonatal Manual Chapter 10: Musculoskeletal problems Summary This manual contains clinical guidelines developed by the Neonatal Unit multidisciplinary team over recent years. This chapter
Clinical Guidance Neonatal Manual Chapter 10: Musculoskeletal problems Summary This manual contains clinical guidelines developed by the Neonatal Unit multidisciplinary team over recent years. This chapter
I have no disclosures
 I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
I have no disclosures Provide an overview of the spectrum of congenital upper extremity anomalies Describe the key imaging findings of these abnormalities Discuss the important clinical features of these
Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye. Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine
 Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine Why Make A Syndrome Diagnosis? Why did it happen? What does the future hold? How can you treat/manage it?
Dysmorphology And The Paediatric Eye Jill Clayton-Smith Manchester Centre For Genomic Medicine Why Make A Syndrome Diagnosis? Why did it happen? What does the future hold? How can you treat/manage it?
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ)
 Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
Glossary of medical terms (grouped by affected system or organ) Atrial septal defect (ASD) disorder of the heart that is present at birth involving a hole in the wall (septum) separating the two upper
Further delineation of Nevo syndrome
 v.. \. #/ 3666JMed Genet 1997;34:366-370 Further delineation of Nevo syndrome L I Al-Gazali, D Bakalinova, E Varady, J Scorer, M Nork Abstract A Nevo syndrome is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterised
v.. \. #/ 3666JMed Genet 1997;34:366-370 Further delineation of Nevo syndrome L I Al-Gazali, D Bakalinova, E Varady, J Scorer, M Nork Abstract A Nevo syndrome is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterised
Elements of Dysmorphology I. Krzysztof Szczałuba
 Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Elements of Dysmorphology I Krzysztof Szczałuba 9.05.2016 Common definitions (1) Dysmorphology: recognition and study of birth defects (congenital malformations) and syndromes [David Smith, 1960] Malformation:
Miller-Dieker syndrome. William B Dobyns, MD
 Miller-Dieker syndrome William B Dobyns, MD MDS phenotype Early clinical course Prenatal Prenatal growth DEF 11/26 Polyhydramnios 13/24 Neonatal Neonatal resuscitation 06/20 Neonatal jaundice 08/21 Growth
Miller-Dieker syndrome William B Dobyns, MD MDS phenotype Early clinical course Prenatal Prenatal growth DEF 11/26 Polyhydramnios 13/24 Neonatal Neonatal resuscitation 06/20 Neonatal jaundice 08/21 Growth
Renal Study Day Case Presentation. Dr. Aoife Owens ST2 November 2018
 Renal Study Day Case Presentation Dr. Aoife Owens ST2 November 2018 Mum 17yrs old Normally fit and well O negative Non-smoker Unemployed Dad 17yrs old Normally fit and well Unemployed Background Parents
Renal Study Day Case Presentation Dr. Aoife Owens ST2 November 2018 Mum 17yrs old Normally fit and well O negative Non-smoker Unemployed Dad 17yrs old Normally fit and well Unemployed Background Parents
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010
 Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Bench to Bassinet Pediatric Cardiac Genomics Consortium: CHD GENES Form 105: Congenital Extracardiac Findings Version: B - 11/01/2010 SECTION A: ADMINISTRATIVE INFORMATION A1. Study Identification Number:
Preferred language: PATIENT INFORMATION. Date of birth (dd/mm/yyyy): Age: Sex: Male Female. City: State: Country: Zip code:
 ADULT INTAKE QUESTIONNAIRE Please fill out this form as completely as possible. This information will help us to better assess whether you are a good candidate for the program. Today s date (dd/mm/yyyy):
ADULT INTAKE QUESTIONNAIRE Please fill out this form as completely as possible. This information will help us to better assess whether you are a good candidate for the program. Today s date (dd/mm/yyyy):
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
The Floppy Baby. Clare Betteridge
 The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
TERMS: Neonatal Period: Birth --> 28 days of life. Term Infant: weeks of gestation
 Normal newborn objectives Quickly identify any danger signs Assess the normal adaptations of a newborn after birth Identify conditions requiring special care or follow-up observation. Identify any birth
Normal newborn objectives Quickly identify any danger signs Assess the normal adaptations of a newborn after birth Identify conditions requiring special care or follow-up observation. Identify any birth
Klippel Trenaunay and Proteus Syndrome overlap--a diagnostic dilemma
 Klippel Trenaunay and Proteus Syndrome overlap--a diagnostic dilemma Puri K.J.P.S. (MD)*, Malhotra S.K. (MD)**, Akanksha Jain (MBBS)*** Professor& Head* Professor& Head** Resident*** Department of Dermatology,
Klippel Trenaunay and Proteus Syndrome overlap--a diagnostic dilemma Puri K.J.P.S. (MD)*, Malhotra S.K. (MD)**, Akanksha Jain (MBBS)*** Professor& Head* Professor& Head** Resident*** Department of Dermatology,
Early Identification of Young Children with Deaf-Blindness
 Early Identification of Young Children with Deaf-Blindness Jerry G. Petroff & Madeline Appell Based on the work of.. Dr. Sarah Cawthon, M.D. What is Deaf-Blindness? the term deaf-blind, with respect to
Early Identification of Young Children with Deaf-Blindness Jerry G. Petroff & Madeline Appell Based on the work of.. Dr. Sarah Cawthon, M.D. What is Deaf-Blindness? the term deaf-blind, with respect to
Case 1B. 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21)
 Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Case 1B 46,XY,-14,+t(14;21) G-banded Chromosome telomere centromere G-dark bands AT-rich few genes G-pale bands GC-rich many genes telomere ideograms ideograms Conventional (light microscopy) p = short
Objectives See course web page for full objectives Read : , (not Bayes theorem section)
 An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
An Approach to Birth Defects: Perspectives in Dysmorphology Cassatt children, Mary Cassatt Adam and Eve Romulus Vuia (1922) Elizabeth M. Petty, MD Associate Professor Molecular Medicine and Genetics epetty@umich.edu
The study of hereditary traits
 Hereditary traits The study of hereditary traits Traits determined by phenotypic expression of one or several genes, ± interaction with environment factors; The weight of hereditary factors in phenotype
Hereditary traits The study of hereditary traits Traits determined by phenotypic expression of one or several genes, ± interaction with environment factors; The weight of hereditary factors in phenotype
HEALTH. Doctors. Level: Materials Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None. Technology Needed:
 HEALTH Doctors Level: Materials Needed: Technology Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None Santa Ana College, School of Continuing Education Parts of the Body Directions: Write
HEALTH Doctors Level: Materials Needed: Technology Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None Santa Ana College, School of Continuing Education Parts of the Body Directions: Write
Ring 18. Our Mission: To help individuals. they face so they might lead healthy, happy, and productive lives. Normal Chromosomes
 The Chromosome 18 Registry & Research Society Ring 18 There are five major conditions involving large changes of chromosome 18. Each of these conditions has a wide variety of characteristics. Additionally,
The Chromosome 18 Registry & Research Society Ring 18 There are five major conditions involving large changes of chromosome 18. Each of these conditions has a wide variety of characteristics. Additionally,
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Normal development & reflex
 Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS
 UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
UNIT IX: GENETIC DISORDERS Younas Masih Lecturer New Life College Of Nursing Karachi 3/4/2016 1 Objectives By the end of this session the Learners will be able to, 1. Know the basic terms related genetics
Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients
 Original Research Article Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients Kataria Sushma K 1, Gurjar Anoop S 2,*, Parakh Manish 3, Gurjar Manisha 4, Parakh
Original Research Article Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients Kataria Sushma K 1, Gurjar Anoop S 2,*, Parakh Manish 3, Gurjar Manisha 4, Parakh
Case Report A Case with Mega Cisterna Magna Renal and Ear Anomalies: Is This a New Syndrome?
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 149656, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/149656 Case Report A Case with Mega Cisterna Magna Renal and Ear Anomalies: Is This a New Syndrome? Çapan
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 149656, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/149656 Case Report A Case with Mega Cisterna Magna Renal and Ear Anomalies: Is This a New Syndrome? Çapan
Four weeks of Intrauterine life
 Objective Congenital & Developmental Malformation Overview of Musculoskeletal dev. Abnormal pattern of dev. Common upper & lower ext. abnormalities READ : SPINE and more information in text book Definition
Objective Congenital & Developmental Malformation Overview of Musculoskeletal dev. Abnormal pattern of dev. Common upper & lower ext. abnormalities READ : SPINE and more information in text book Definition
Dextrocardia in patients with Poland syndrome: Phenotypic characterization provides insight into the pathogenesis
 Dextrocardia in patients with Poland syndrome: Phenotypic characterization provides insight into the pathogenesis Anwar Baban Dipartimento Medico Chirurgico di Cardiologia Pediatrica. Ospedale Pediatrico
Dextrocardia in patients with Poland syndrome: Phenotypic characterization provides insight into the pathogenesis Anwar Baban Dipartimento Medico Chirurgico di Cardiologia Pediatrica. Ospedale Pediatrico
CRANIOFACIAL MORPHOLOGY AND DENTAL FINDINGS OF SECKEL SYNDROME: CASE REPORTS OF TWO SIBLINGS
 CRANIOFACIAL MORPHOLOGY AND DENTAL FINDINGS OF SECKEL SYNDROME: CASE REPORTS OF TWO SIBLINGS Zuhal Kirzioglu 1, M. Semra Ozay Erturk 2, Yildirim Erdogan 3 * 1. Professor, Süleyman Demirel University, Faculty
CRANIOFACIAL MORPHOLOGY AND DENTAL FINDINGS OF SECKEL SYNDROME: CASE REPORTS OF TWO SIBLINGS Zuhal Kirzioglu 1, M. Semra Ozay Erturk 2, Yildirim Erdogan 3 * 1. Professor, Süleyman Demirel University, Faculty
Feeding Disorders and Growth in Williams Syndrome
 Feeding Disorders and Growth in Williams Syndrome Sharon M. Greis M.A., CCC/SLP BRS-S and Paige Kaplan M.B.B.Ch. Williams Syndrome Clinic The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Pediatric Feeding & Swallowing
Feeding Disorders and Growth in Williams Syndrome Sharon M. Greis M.A., CCC/SLP BRS-S and Paige Kaplan M.B.B.Ch. Williams Syndrome Clinic The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Pediatric Feeding & Swallowing
The Baller-Gerold syndrome: phenotypic and cytogenetic overlap with Roberts syndrome
 I Med Genet 1990; 27: 371-375 The Baller-Gerold syndrome: phenotypic and cytogenetic overlap with Roberts syndrome 371 S M Huson, C S Rodgers, C M Hall, R M Winter Abstract A case is reported where the
I Med Genet 1990; 27: 371-375 The Baller-Gerold syndrome: phenotypic and cytogenetic overlap with Roberts syndrome 371 S M Huson, C S Rodgers, C M Hall, R M Winter Abstract A case is reported where the
An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification. Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization
 An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization What are the problems? When did they happen? How did they arise? Why
An Introduction to Dysmorphology Clinical Approach and Classification Dr. malek nia Genetic consulting center Of welfare organization What are the problems? When did they happen? How did they arise? Why
Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal
 Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
Journal of Medical Genectics (1976). 13, 136-141. Camptodactyly, with muscular hypoplasia, skeletal dysplasia, and abnormal palmar creases: Tel Hashomer camptodactyly syndrome* RCHARD M. GOODMAN,t MARASSA
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE
 CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
CHROMOSOMAL NUMERICAL ABERRATIONS INSTITUTE OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICAL GENETICS OF THE 1 ST FACULTY OF MEDICINE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATIONS NUMERICAL STRUCTURAL ANEUPLOIDY POLYPLOIDY MONOSOMY TRISOMY TRIPLOIDY
Klinefelter syndrome ( 47, XXY )
 Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Sex Chromosome Abnormalities, Sex Chromosome Aneuploidy It has been estimated that, overall, approximately one in 400 infants have some form of sex chromosome aneuploidy. A thorough discussion of sex chromosomes
Polycystic Kidneys Associated with Malformations
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 285. Polycystic Kidneys Associated with Malformations of the Brain, Polydactyly, and Other Birth Defects in Newborn Sibs A Lethal Syndrome Showing the Autosomal-recessive
Journal of Medical Genetics (1971). 8, 285. Polycystic Kidneys Associated with Malformations of the Brain, Polydactyly, and Other Birth Defects in Newborn Sibs A Lethal Syndrome Showing the Autosomal-recessive
Teratology and. Early Pregnancy
 Teratology and Early Pregnancy Wolfgang E. Paulus Institute for Reproductive Toxicology Institute of Reproductive Toxicology St. Elisabeth Hospital Ravensburg, Germany Academic Teaching Hospital of the
Teratology and Early Pregnancy Wolfgang E. Paulus Institute for Reproductive Toxicology Institute of Reproductive Toxicology St. Elisabeth Hospital Ravensburg, Germany Academic Teaching Hospital of the
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 2: 16, December Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma
 Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia with Arachnodactyl and Palmoplanter Keratoderma Taseer Ahmed Bhatt Department of Dermatology, STD & Leprosy Govt. Medical College Srinagar, Kashmir Egyptian Dermatology
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS
 wjpls, 2015, Vol. 1, Issue 1, 175-181 Case Reports ISSN 2454-2229 WJPLS www.wjpls.org WAARDENBURG SYNDROME TYPE I A CASE SERIES FROM A SINGLE FAMILY Dr. D. Manikyamba 1*, Dr. S. Chandra Sekhar 2, Dr. G.
wjpls, 2015, Vol. 1, Issue 1, 175-181 Case Reports ISSN 2454-2229 WJPLS www.wjpls.org WAARDENBURG SYNDROME TYPE I A CASE SERIES FROM A SINGLE FAMILY Dr. D. Manikyamba 1*, Dr. S. Chandra Sekhar 2, Dr. G.
Semiology of musculoskeletal system in children:
 Semiology of musculoskeletal system in children: CS 1. Name what represente the anterior fontanelle: a) Serosanguine bosa b) An ossified membranous area localized between the frontal and parietal bones
Semiology of musculoskeletal system in children: CS 1. Name what represente the anterior fontanelle: a) Serosanguine bosa b) An ossified membranous area localized between the frontal and parietal bones
further evidence for autosomal recessive inheritance
 J Med Genet 1991; 28: 695-700 Miller syndrome (postaxial acrofacial dysostosis): further evidence for autosomal recessive inheritance and expansion of the phenotype A L Ogilvy-Stuart, A C Parsons Abstract
J Med Genet 1991; 28: 695-700 Miller syndrome (postaxial acrofacial dysostosis): further evidence for autosomal recessive inheritance and expansion of the phenotype A L Ogilvy-Stuart, A C Parsons Abstract
Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 313-321 Sorsby syndrome: a report on further generations of the original family E M THOMPSON AND M BARAITSER From the Clinical Genetics Unit, The Hospitals for Sick
Program Script. Nursing Assessment The Head-to-Toe Assessment
 Program Script Nursing Assessment The Head-to-Toe Assessment This document comprises the complete script for this program including chapter titles. This is provided to instructors to enhance the educational
Program Script Nursing Assessment The Head-to-Toe Assessment This document comprises the complete script for this program including chapter titles. This is provided to instructors to enhance the educational
By: Dr. Doaa Khater Yassin, MM and M.D Paed Sr. specialist of Pediatrics SQUH
 By: Dr. Doaa Khater Yassin, MM and M.D Paed Sr. specialist of Pediatrics SQUH Born SGA with birth weight of 2.4 kg, had IUGR Hospitalized at the age of 2 month with severe dehydration Diagnosed as DKA
By: Dr. Doaa Khater Yassin, MM and M.D Paed Sr. specialist of Pediatrics SQUH Born SGA with birth weight of 2.4 kg, had IUGR Hospitalized at the age of 2 month with severe dehydration Diagnosed as DKA
A. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis. B. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis.
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print)
 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2017; 5(9):626-630 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2017; 5(9):626-630 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Case History Report Form
 Child details ( * required) Name (first name only) or *Code John *Chronological age (CA) Actual age since birth *Diagnosis and/or presenting problems 18-27 mos Joubert Syndrome - a rare brain malformation
Child details ( * required) Name (first name only) or *Code John *Chronological age (CA) Actual age since birth *Diagnosis and/or presenting problems 18-27 mos Joubert Syndrome - a rare brain malformation
ISSN CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR
 J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
J. Adv. Zool. 2018: 39(1): 32-36 ISSN-0253-7214 CHROMOSOME STUDY IN SUSPECTED CASES OF TURNER S SYNDROME FROM JAMMU REGION OF JAMMU & KASHMIR Wahied Khawar Balwan and Neelam Saba *Department of Zoology,
THE COSTELLO SYNDROME: A BOY WITH THICK MITRAL VALVES AND ARRHYTHMIAS
 Jpn J Human Genet 38, 329-334, 1993 Case Report THE COSTELLO SYNDROME: A BOY WITH THICK MITRAL VALVES AND ARRHYTHMIAS Yoshinori IZUMIKAWA,* Kenji NARITOMI, Takaya TOHMA, Noboru SHIROMA, and Kiyotake HIRAYAMA
Jpn J Human Genet 38, 329-334, 1993 Case Report THE COSTELLO SYNDROME: A BOY WITH THICK MITRAL VALVES AND ARRHYTHMIAS Yoshinori IZUMIKAWA,* Kenji NARITOMI, Takaya TOHMA, Noboru SHIROMA, and Kiyotake HIRAYAMA
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24,
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Rare Case Series of Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
 Case Report: Rare Case Series of Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Dr. D.Y.Shrikhande ***,Dr. Jayshree Jadhav**, Dr. AmitGarg*,Dr.BhavikaSingla*, Dr. Vivek Singh* ***Professor and Head of Department of
Case Report: Rare Case Series of Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita Dr. D.Y.Shrikhande ***,Dr. Jayshree Jadhav**, Dr. AmitGarg*,Dr.BhavikaSingla*, Dr. Vivek Singh* ***Professor and Head of Department of
Quick Reference Guide
 This index may help determine a clinical diagnosis. Fairly common dysmorphic features are listed with corresponding syndromes in which the characteristic is a frequent finding. The syndrome features are
This index may help determine a clinical diagnosis. Fairly common dysmorphic features are listed with corresponding syndromes in which the characteristic is a frequent finding. The syndrome features are
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities
 ISUOG Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the planes required
ISUOG Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the planes required
A summary of guidance related to viral rash in pregnancy
 A summary of guidance related to viral rash in pregnancy Wednesday 12 th July 2017 Dr Rukhsana Hussain Introduction Viral exanthema can cause rash in pregnant women and should be considered even in countries
A summary of guidance related to viral rash in pregnancy Wednesday 12 th July 2017 Dr Rukhsana Hussain Introduction Viral exanthema can cause rash in pregnant women and should be considered even in countries
Yorkshire and Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline
 Yorkshire and Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline Title: Author: NEONATAL BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURY Rebecca Musson Date written: January 2011, reviewed January 2016 Review date: January 2019 This
Yorkshire and Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline Title: Author: NEONATAL BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURY Rebecca Musson Date written: January 2011, reviewed January 2016 Review date: January 2019 This
Human Genetic Disorders
 Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Human Genetic Disorders HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Human somatic cells have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes 23 are inherited from the mother and 23 from the father HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Autosomes o Are
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia
 JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
Syndromic X Linked Mental Retardation
 Syndromic X Linked Mental Retardation Introduction : Dr. Yousef.A. Assaleh Dept. of Pediatric - faculty of medicine Zawia University Mental retardation is defined as incomplete or insufficient general
Syndromic X Linked Mental Retardation Introduction : Dr. Yousef.A. Assaleh Dept. of Pediatric - faculty of medicine Zawia University Mental retardation is defined as incomplete or insufficient general
