THE INCIDENCE OF FUNCTIONAL disorders of the
|
|
|
- Adelia Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1441 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Differences in Isometric Neck Muscle Strength Between Healthy Controls and Women With Chronic Neck Pain: The Use of a Reliable Measurement Barbara Cagnie, PT, PhD, Ann Cools, PT, PhD, Veerle De Loose, PT, Dirk Cambier, PT, PhD, Lieven Danneels, PT, PhD ABSTRACT. Cagnie B, Cools A, De Loose V, Cambier D, Danneels L. Differences in isometric neck muscle strength between healthy controls and women with chronic neck pain: the use of a reliable measurement. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2007;88: Objectives: To determine the intra- and interrater reliability of the Biodex isokinetic dynamometer to measure the maximal isometric strength of the cervical flexors and extensors, to develop an age- and sex-based normative database in a healthy population, and to evaluate the differences in neck strength between women with chronic neck pain and healthy controls. Design: Cross-sectional. Setting: Physical and rehabilitation medicine department. Participants: Ninety-six healthy volunteers (4 age groups: 20 29, 30 39, 40 49, 50 59y; each consisting of 12 men and 12 women) and 30 women with chronic neck pain. Interventions: Not applicable. Main Outcome Measures: Peak isometric strength of the cervical muscles was tested for flexion and extension by using the Biodex isokinetic dynamometer. The intra- and interrater reliability of the protocol was evaluated in 12 volunteers. Results: The reliability for strength was high for both flexion and extension (intraclass correlation coefficient,.92.96). The mean peak torque for flexion and extension was significantly higher in men (24Nm, 36.4Nm, respectively) compared with women (16.6Nm, 26.5Nm, respectively) (P.001). Peak torque production for extension was significantly lower in the patient group (22.3Nm) compared with the healthy female control group (26.5Nm) (P.003). No significant differences in flexion strength between patient and female control group were found. Conclusions: Results show a high degree of intra- and interrater reliability in measuring isometric neck muscle strength when using the Biodex isokinetic dynamometer. The use of normative data for neck strength when evaluating patients with neck disorders needs to take sex into account. The current study has shown that women with chronic neck pain have lower neck muscle strength in extension than the healthy female group. Key Words: Neck pain; Rehabilitation; Reliability and validity. From the Department of Rehabilitation Sciences and Physiotherapy, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium (Cagnie, Cools, Cambier, Danneels); and Department of Physical Therapy, Centre for Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Queen Astrid Military Hospital, Brussels, Belgium (De Loose). No commercial party having a direct financial interest in the results of the research supporting this article has or will confer a benefit upon the author(s) or upon any organization with which the author(s) is/are associated. Reprint requests to Barbara Cagnie, PT, PhD, Dept of Rehabilitation Sciences and Physiotherapy, Ghent University Hospital, De Pintelaan 185, 6K3, B-9000 Ghent, barbara.cagnie@ugent.be /07/ $32.00/0 doi: /j.apmr by the American Congress of Rehabilitation Medicine and the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation THE INCIDENCE OF FUNCTIONAL disorders of the neck, typically associated with pain and muscular fatigue, is becoming a severe problem in industrial countries, even among young and middle-aged people. 1 It has considerable economic impact through sick leave and an increased use of medication, primary health care services, specialist care, laboratory tests, diagnostic imaging, and therapeutic interventions. 2 There is ample evidence that cervical strength is compromised in various cervical disorders. 2-7 The sustained muscle contraction required to hold the head in various positions and the fatigue caused by muscular weakness are suspected of being contributing factors in chronic neck pain. 2 In women, neck muscle forces are only about half those in men, despite nearly comparable head weights As a consequence, it has been suggested that in women the relatively weak neck muscles cause muscular fatigue syndrome resulting in a higher incidence of chronic neck pain. This emphasizes the need to evaluate strength in women with chronic neck pain. Assessments of cervical strength are useful in the quantification of musculoskeletal impairments and may also be used to provide a basis for assessing the efficacy of therapeutic interventions in patients with neck pain. 11,12 In recent decades, many attempts have been made to obtain an objective method of assessing cervical spine strength. Depending on the study, neck muscle strength in flexion and extension has been measured either with handheld devices 8,13 or devices attached to a solid frame or wall. 9,10,14-16 To successfully distinguish between normal and abnormal strength values in the cervical spine, 2 conditions have to be fulfilled: the derivation of age- and sex-based normative data and high reproducibility of the findings. Different studies 1,8-10,13,15,17 using different test devices have produced divergent results for cervical flexion and extension muscle strength. These discrepancies in normative data highlight the concerns regarding the comparison between different investigations as well as the published normative data and cutoff points between healthy subjects and patients. Because the results of isometric neck strength measurements are highly device dependent, it is necessary to obtain normative data with each type of device used. 12 Second, the positioning of the subjects plays a substantial role in the variation of torque values. 16 In this study, the measurements were taken in the supine position, whereas most of the past studies 1,8-10,13,15,17 were performed with the participants in the seated position. The reliability of measurements using handheld strengthtesting devices is questionable because strength measurements may vary according to the strength of the investigator. 8,13 However, non-handheld isometric neck strength measurement devices specifically built for this purpose seem to have good reliability. 10,14-17 Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) have
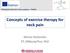
2 1442 MUSCLE STRENGTH IN NECK PAIN PATIENTS, Cagnie Fig 1. The strength testing setup for extension. been reported as ranging from.75 to.98 with different test equipment. 10,14-18 However, according to Jordan, 19 the reliability of a tool can only be inferred for the protocol used. This emphasizes the need of determination of reliability and normative data before any differentiation can be made between healthy subjects and patients. The literature is scarce about the relation between chronic neck pain and strength, and there is no consensus in the literature indicating which muscles are affected. Only a few studies 2-4,7,9,10,17 of strength measurements in cervical pathologies have been reported. Researchers 2,9,10,17 have pinpointed both the neck flexor and extensor muscles as sites of weakness, whereas others found significantly lower maximal isometric strength only in the cervical flexor 3,7 or extensor 4 muscles in patients with chronic neck pain. The first aim of this study was to determine the intra- and interrater reliability of the Biodex a isokinetic dynamometer to measure the maximal isometric strength of the cervical flexors and extensors and to develop an age- and sex-based normative database in a healthy population of 96 volunteers. The secondary objective was to evaluate whether women with chronic neck pain had lower neck strength than healthy controls. METHODS Sample Description Ninety-six healthy volunteers and 30 women with chronic neck pain took part in this study. We recruited both healthy subjects and chronic neck pain patients through local advertisement in the hospital. To be included, healthy subjects should not have had neck pain for at least 1 year before testing and should not have been engaged in training of the neck and/or shoulder muscles for at least 6 months before testing. Subjects were asked to fill in a shortened version of the standardized Dutch Musculoskeletal Questionnaire to obtain information about the absence of neck pain during the last year. 20 We divided the healthy subjects into 4 age groups (20 29, 30 39y, 40 49, 50 59y), each consisting of 12 men and 12 women. Subjects were excluded from the study if they had had an operation, were pregnant, had depression or other mental illness, and if they had any specific diseases known to cause chronic neck pain (spinal stenosis, instability or anomaly of the cervical spine, fibromyalgia, inflammatory joint diseases). Written informed consent was obtained from all the volunteers, and the study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee of the Ghent University Hospital. The study design is subdivided into 3 parts, as follows. Intra- and interrater reliability study. Of the 96 healthy volunteers, 12 volunteers (7 men, 5 women) were recruited to participate in the study of intrarater reliability. A total of 12 other healthy subjects (5 men, 7 women) volunteered to take part in the interrater reliability design. One single operator assessed the intrarater reliability, whereas, in the interrater study, 3 other investigators were involved. The investigators consisted of a manual therapist and 2 final-term manual therapy students. The investigators were trained to handle the standardized testing protocol by testing each other and by testing a volunteer not included in the study. Subjects were tested on 3 separate occasions and were scheduled to participate in the study at the same time each day to minimize the possible effects of diurnal changes. The time interval between the 2 tests was consistently 1 week. Normative database. To assess normative data and to determine if isometric cervical musculature strength is sex and age dependent, a descriptive cross-sectional study was performed. Patient study. The results obtained from the neck pain patients were compared with the healthy female data to evaluate whether patients with chronic neck pain have lower neck strength. Because the healthy subjects were tested before the neck pain patients, the raters were not blinded to the status of the subjects. Instrumentation Testing was performed by using a System 3 isokinetic dynamometer. a The isokinetic dynamometer is an electromechanical instrument controlled by a microcomputer, which offers the possibility of objectively and quantitatively evaluating physical parameters of the muscle function such as strength, power, and resistance in different joints during different angular velocities. Experimental Procedure Volunteers were positioned supine for the evaluation of extension and prone for the evaluation of flexion (figs 1, 2). A seat belt was used at shoulder height to prevent any additive strength effect from trunk musculature during the testing procedure. In the supine position, subjects were asked to cross their arms to prevent craniocaudal movements of the thorax. During the experiment, moments were resolved about axes through the midpoint of the line between the C7 spinous process and the sternal notch. Fig 2. The strength testing setup for flexion.
3 MUSCLE STRENGTH IN NECK PAIN PATIENTS, Cagnie 1443 During flexion and extension, the subjects pushed directly forward or backward against the padded strain gauge of the neck strength measurement system. Subjects were verbally encouraged to exert maximal effort. Changing position took about 3 minutes. Three submaximal warmup efforts with gradually increasing force were performed in each direction to acquaint subjects with the testing position and measurement. Subjects were informed initially that to meet the objective of the project it was essential that they exert their maximal effort except in case of onset of any symptoms of pain at which time they were instructed to stop immediately and inform the investigator. Each subject was asked to perform 3 maximal efforts lasting 6 seconds each, starting gradually, building their force to maximum over the first 2 seconds, and then maintaining it over another 4 seconds with a 30-second interval. Measurements were expressed in newton meters. Peak torque was computed, and the mean result of the 3 repetitions was subjected to quantitative comparison and statistical analysis. Statistical Analysis Analysis was performed by using the SPSS statistical software. b Intra- and interrater reliability study. For analysis of intraand interrater reliability, ICCs (2-way mixed-effect model with absolute agreement) 21 with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), standard error (SE) of measurement, and smallest real difference were used. Defined with respect to a 95% level of confidence, the smallest real difference is equal to SE of measurement. Normative database. The results of flexion, extension, and extension and flexion ratios are expressed as means with standard deviations (SDs). Extension and flexion ratios are calculated by dividing the extension values by the flexion values. Two-way analysis of variance with post hoc analysis was used to determine the significance of difference in cervical flexion and extension (dependent variables) for the main factors sex and age (independent variables). An independent samples t test was used to determine the significance of difference in extension and flexion ratio between men and women. Patient study. The normality of variables was evaluated by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Statistical comparison between the groups was performed by using an independent samples t test. P less than.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS Descriptive characteristics of the healthy subjects are presented in table 1. The 30 women with chronic neck pain had a Table 1: Anthropometric Data of the Healthy Subjects (n 96) Subjects Age Groups (y) Weight (kg) Height (m) Body Mass Index (kg/m 2 ) Men (n 48) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) Women (n 48) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) NOTE. Values are mean SD. Abbreviation: BMI, body mass index. Table 2: ICC, SE of Measurement (SEM), and Smallest Detectable Difference (SDD) for Intra- and Interrater Neck Strength Measurements Rater Movement ICC (95% CI) SEM SDD Intra Flexion.96 (.91.99) Extension.94 (.85.98) Inter Flexion.92 (.79.98) Extension.94 (.82.98) NOTE. Values are 95% CI. mean age of 32.9 years, a mean height of 166.3cm, and a mean weight of 62.7kg. Intra- and Interrater Reliability Study Interrater reliability and intrarater reliability were analyzed by using the ICC, which varied from.92 to.96, depending on the direction tested (table 2). The SE of measurement ranged from 1.03 to 2.36Nm. Extension yielded higher SE estimates than flexion because of higher maximum strength values. Normative Database The multivariate analysis of variance revealed that peak values were significantly affected by sex in flexion and extension (P.001) but not by age (flexion, P.844; extension, P.408). No significant interaction effect between age and sex was found for flexion (P.122) and extension (P.522). Therefore, normative data were only distributed according to sex (table 3). The average maximum moments resolved at C7-T1 for the men were Nm for extension and Nm for flexion. The maximum moments resolved at C7-T1 for the women were Nm for extension and Nm for flexion. The mean extension and flexion ratios were for men and for women. When comparing the strength of men and women, men proved to be 40% stronger for flexion (P.001) and 44% for extension (P.001). No significant differences between men and women were found when comparing extension and flexion ratio (P.685). Patient Study When comparing the strength between the healthy subjects and the female neck pain patients, only the female healthy group (n 48) was selected because there was a significant difference in strength between men and women. The peak torque production for extension and extension and flexion strength ratios were significantly lower in the patient group compared with the female healthy control group (table 4). No Table 3: Mean Isometric Neck Muscle Strength in Flexion and Extension by Sex and Age Subjects Age Group (y) Flexion Extension Men (n 48) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) Women (n 48) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) (n 12) NOTE. Values are mean newton meters SD.
4 1444 MUSCLE STRENGTH IN NECK PAIN PATIENTS, Cagnie Table 4: Peak Neck Strength Values in Women With Chronic Neck Pain and Healthy Female Controls Movement Healthy Women (n 48) Neck Pain (n 30) Flexion (Nm) Extension (Nm) Extension/flexion ratio NOTE. Values are mean newton meters SD. significant difference emerged in the flexion strength between the patient and female control group. DISCUSSION A considerable number of reliability and validity studies 11,15-17 examining cervical strength have been identified in the literature, and, from this point of view, the present study cannot claim novelty. The strength of this study is that the results of the neck patient group are preceded by a reliability study and determination of a normative database. Discrepancies exist among similar studies 1,8-10,13,15,17 regarding normative data, which highlights the concerns regarding the comparison between different investigations as well as the published normative data and cutoff points between healthy subjects and patients. This emphasizes the need of determination of reliability and normative data before any differentiation can be made between healthy subjects and patients. We chose to measure neck strength isometrically because the major physiologic function of the neck muscles is to stabilize the neck and carry the head (postural muscles), an isometric function. However, isometric neck strength cannot be considered as a direct estimation of functional ability, which by nature is complex and influenced by several factors, such as neuromuscular function and range of motion. 15 Intra- and Interrater Reliability Study The results of the present study show high intra- and interrater reliability in cervical isometric strength measurement when using the Biodex isokinetic dynamometer. The mean ICCs calculated were at least.92. It would, therefore, appear that the methodology reported here is reliable and robust for such studies. These results are comparable to previous studies 10,14-18 in which ICC values ranged from.76 to.98. Normative Database Knowledge of normative values for cervical muscles is essential for the design and execution of rehabilitation programs. The average maximum moments resolved at C7-T1 for the men were 36.4Nm for extension and 24Nm for flexion. The maximum moments resolved at C7-T1 for the women were 26.5Nm for extension and 16.6Nm for flexion. Comparison with previous neck strength studies in which moments were expressed as newton meters revealed that in men flexion ranged from 17 to 30Nm and extension from 42 to 60Nm. In women, flexion varied from 11 to 21Nm and extension from 21 to 48Nm. 9,10,15,22 This variation in the torque values across different studies 16,23 in the literature could possibly be caused by the equipment and technique used, positioning of subjects, training effect, or ethnic differences. Although the Biodex isokinetic dynamometer is frequently used in practice and research to evaluate physical parameters of muscle function, as far as we know, it has not been used in previous studies for the measurement of cervical strength, except for the study by Seng et al. 18 The measurements were undertaken with the participants in the supine P position, although most of the studies were undertaken with the participants in the seated position. Peolsson et al 15 observed that strength in extension in the sitting position was twice as high as that previously reported in the prone position. This may explain why our results were slightly lower than most of the other results found in the literature. However, we are aware that it is more natural to test and train muscles in the positions of their use during daily activities. Differences in age. No significant difference was found in muscle strength with different age groups. These results show that the subjects in this study were able to maintain a good level of isometric neck muscle strength in all directions until their sixth decade. These findings correlate with most of the studies found in the literature, 8-10 although some others reported an age-related decrease in neck strength. 15 It is accepted generally that skeletal muscle strength increases take place until approximately the age of 30 years followed by a period of strength maintenance until age 50 or 60 years; at this time, strength begins to decline as muscle mass decreases. 10 Because the maximum age of our studied population was 59, this could explain why no age effect was found. Second, the small sample size may represent a limitation of the data. However, Salo et al 12 evaluated a larger number of participants in a recent study (220 women divided into 4 age groups), but he also did not find a statistically significant difference in neck strength among the different age groups. Differences in sex. The men exhibited superior maximal isometric strength levels in both the flexors and the extensors of the cervical spine as compared with the women. When comparing the strength of men and women, men proved to be 40% stronger for flexion and 44% for extension. This is in accordance with the literature in which male-to-female strength values ranged from 1.2 to 2.5, 9,10,22 with a mean range from 1.7 to ,15 This strength difference corresponds well with that of other studies regarding spinal musculature. 10 Differences in maximum moments between men and women may arise from differences in posture, muscle size, or neural activation. Extension/flexion ratio. Mean extension/flexion ratio was 1.56 for men and 1.50 for women. The larger extension strength over flexion by 50% reflects the postural role of extensor musculature and obvious muscle mass difference between posterior and anterior muscles of the cervical spine. This association between the extensors and flexors of the cervical spine was found to be similar to the range of lumbar spine. 10 An explanation for this may be that the center of gravity of the head during activity, such as reading, is often located in front of the axis of rotation, leading to higher postural demands on the neck extensor muscles. Another explanation could be that the extensor muscles situated posterior to the line of rotation of the cervical spine have a longer lever arm and thereby a mechanical advantage over the flexor muscles. 15 There were no significant differences in ratio between men and women, although most of the previous studies, 10 except Peolsson s study, 15 showed that women are proportionately stronger in extension and/or proportionately weaker in the flexion as compared with men. Patient study. Peak isometric neck strength values were statistically significantly reduced in the women with chronic neck pain compared with female healthy controls in extension and extension and flexion ratio but not in flexion. A number of studies have reported that the patient populations had significantly less muscle strength than the control populations, but a consensus regarding the muscles that are affected is lacking. Researchers 2,9,10,17 have pinpointed both the neck flexor and extensor muscles as a site of weakness. Prushansky et al 4 found significantly lower maximal isometric strength of the cervical extensor muscles in patients with chronic neck pain compared with
5 MUSCLE STRENGTH IN NECK PAIN PATIENTS, Cagnie 1445 healthy matched controls, whereas Silverman et al 3 and Barton and Hayes 7 found that isometric flexion strength in patients with chronic neck pain was about 50% of that of healthy controls. It could be argued that the presence of persistent neck pain may cause patients to avoid daily activities, which may lead to specific physical deconditioning (eg, loss of strength and endurance of paraspinal muscles). This may result in even more pain and disability and so contribute to the chronicity of neck pain. 24 According to Ylinen et al, 6 part of the difference may be explained by neural inhibition caused by pain felt during test efforts, which does not normally cause any pain. A lower pressure pain threshold referring to local allodynia has been shown in patients with neck pain, which may prevent patients from producing full force because of conscious or subconscious fear of hurting themselves. Most of the pain in chronic neck pain patients is situated posteriorly, which may explain the lower extension/flexion ratio. 4 CONCLUSIONS Results show a high degree of intra- and interrater reliability in measuring isometric neck muscle strength. Establishing valid and reliable measures of neck function will enable clinicians to monitor intervention effects over time within groups of patients. The use of normative data for neck strength when evaluating patients with neck disorders needs to take gender into account. The current study has shown that women with chronic neck pain have lower neck muscle strength in extension than the healthy female group. Knowledge of the reduction in neck strength is essential in planning individually tailored neck strength training programs. References 1. Garcés G, Medina D, Milutinovic L, Garavote P, Guerado E. Normative database of isometric cervical strength in a healthy population. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2002;34: Ylinen J, Salo P, Nykanen M, Kautiainen H, Hakkinen A. Decreased isometric neck strength in women with chronic neck pain and the repeatability of neck strength measurements. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004;85: Silverman JL, Rodriquez AA, Agre JC. Quantitative cervical flexor strength in healthy subjects and in subjects with mechanical neck pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1991;72: Prushansky T, Gepstein R, Gordon C, Dvir Z. Cervical muscles weakness in chronic whiplash patients. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2005;20: Ylinen J, Savolainen S, Airaksinen O, Kautiainen H, Salo P, Hakkinen A. Decreased strength and mobility in patients after anterior cervical diskectomy compared with healthy subjects. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2003;84: Ylinen J, Takala E, Kautiainen H, et al. Association of neck pain, disability and neck pain during maximal effort with neck muscle strength and range of movement in women with chronic nonspecific neck pain. Eur J Pain 2004;8: Barton PM, Hayes KC. Neck flexor muscle strength, efficiency, and relaxation times in normal subjects and subjects with unilateral neck pain and headache. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1996;77: Staudte H, Duhr N. Age- and sex-dependent force-related function of the cervical spine. Eur Spine J 1994;3: Chiu T, Lam T, Hedley A. Maximal isometric muscle strength of the cervical spine in healthy volunteers. Clin Rehabil 2002;16: Jordan A, Mehlsen J, Bulow P, Ostergaard K, Danneskiold- Samsoe B. Maximal isometric strength of the cervical musculature in 100 healthy volunteers. Spine 1999;24: Strimpakos N, Sakellari V, Gioftsos G, Oldham J. Intratester and intertester reliability of neck isometric dynamometry. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004;85: Salo P, Ylinen J, Malkia E, Kautiainen H, Hakkinen A. Isometric strength of the cervical flexor, extensor, and rotator muscles in 220 healthy females aged 20 to 59 years. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 2006;36: Philips B, Lo S, Mastaglia F. Muscle force measured using break testing with a hand-held myometer in normal subjects aged 20 to 69 years. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000;81: Kumar S, Narayan Y, Amell T. Cervical strength of young adults in sagittal, coronal, and intermediate planes. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2001;16: Peolsson A, Oberg B, Hedlund R. Intra- and inter-tester reliability and reference values for isometric neck strength. Physiother Res Int 2001;6: Ylinen J, Rezasoltani A, Julin M, Virtapohja H, Malkia E. Reproducibility of isometric strength: measurement of neck muscles. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 1999;14: Chiu T, Lo S. Evaluation of cervical range of motion and isometric neck muscle strength: reliability and validity. Clin Rehabil 2002;16: Seng K, Peter V, Lam P. Neck muscle strength across the sagittal and coronal planes: an isometric study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2002;17: Jordan K. Assessment of published reliability studies for cervical spine range of motion measurement tools. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2000;23: Cagnie B, Danneels L, Van Tiggelen D, De Loose V, Cambier D. Individual and work related risk factors for neck pain among office workers: a cross sectional study. Eur Spine J 2007;16: Shrout P, Fleiss J. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 1979;86: Vasavada A, Li S, Delp S. Three-dimensional isometric strength of neck muscles in humans. Spine 2001;26: Suryanarayana L, Kumar S. Quantification of isometric cervical strength at different ranges of flexion and extension. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2005;20: Smeets R, Wade D, Hidding A, Van Leeuwen P, Vlaeyen J, Knottnerus J. The association of physical deconditioning and chronic low back pain: a hypothesis-oriented systematic review. Disabil Rehabil 2006;28: Suppliers a. System 3; Biodex Medical Systems Inc, 20 Ramsay Rd, Shirley, NY b. Version 11; SSPS Inc, 233 S Wacker Dr, 11th Fl, Chicago, IL
Neck pain is extremely
 Isometric Strength of the Cervical Flexor, Extensor, and Rotator Muscles in 220 Healthy Females Aged 20 to 59 Years Petri K. Salo, PT, MSc 1 Jari J. Ylinen, MD, PhD 2 Esko A. Má lkiá, PT, PhD 3 Hannu Kautiainen,
Isometric Strength of the Cervical Flexor, Extensor, and Rotator Muscles in 220 Healthy Females Aged 20 to 59 Years Petri K. Salo, PT, MSc 1 Jari J. Ylinen, MD, PhD 2 Esko A. Má lkiá, PT, PhD 3 Hannu Kautiainen,
The Reliability of Measuring Neck Muscle Strength with a Neck Muscle Force Measurement Device
 Original Article The Reliability of Measuring Neck Muscle Strength with a Neck Muscle Force Measurement Device J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 15: 7 12, 2003 ASGHAR REZASOLTANI, Ph D, PT 1, 2), AMIR AHMADI, B Sc,
Original Article The Reliability of Measuring Neck Muscle Strength with a Neck Muscle Force Measurement Device J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 15: 7 12, 2003 ASGHAR REZASOLTANI, Ph D, PT 1, 2), AMIR AHMADI, B Sc,
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer
 The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75
 The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail.
 This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Ylinen, Jari; Salo, Petri; Järvenpää, Salme; Häkkinen,
This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Author(s): Ylinen, Jari; Salo, Petri; Järvenpää, Salme; Häkkinen,
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device
 Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
lntertester and lntratester Reliability of a Dynamic Balance Protocol Using the Biodex Stability System
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1998, 7, 95-101 0 1998 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. lntertester and lntratester Reliability of a Dynamic Balance Protocol Using the Biodex Stability System Randy Schmitz
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1998, 7, 95-101 0 1998 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. lntertester and lntratester Reliability of a Dynamic Balance Protocol Using the Biodex Stability System Randy Schmitz
Scapulothoracic muscle strength in individuals with neck pain
 Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 29 (2016) 549 555 549 DOI 10.3233/BMR-160656 IOS Press Scapulothoracic muscle strength in individuals with neck pain Shannon M. Petersen a,,nathana.domino
Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 29 (2016) 549 555 549 DOI 10.3233/BMR-160656 IOS Press Scapulothoracic muscle strength in individuals with neck pain Shannon M. Petersen a,,nathana.domino
A Comparison of Craniocervical and Cervicothoracic Muscle Strength in Healthy Individuals
 Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2010, 26, 400-406 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. A Comparison of Craniocervical and Cervicothoracic Muscle Strength in Healthy Individuals Luke Van Wyk, Gwendolen Jull, Bill
Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2010, 26, 400-406 2010 Human Kinetics, Inc. A Comparison of Craniocervical and Cervicothoracic Muscle Strength in Healthy Individuals Luke Van Wyk, Gwendolen Jull, Bill
Influence of Lever Arm and Stabilization on Measures of Hip Abduction and Adduction Torque Obtained by Hand-Held Dynamometry
 37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of Lever Arm and Stabilization on Measures of Hip Abduction and Adduction Torque Obtained by Hand-Held Dynamometry David A. Krause, PT, MBA, DScPT, OCS, Susan J. Schlagel,
37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of Lever Arm and Stabilization on Measures of Hip Abduction and Adduction Torque Obtained by Hand-Held Dynamometry David A. Krause, PT, MBA, DScPT, OCS, Susan J. Schlagel,
Effect of Preload and Range of Motion on Isokinetic Torque in Women
 Effect of Preload and Range of Motion on Isokinetic Torque in Women By: Laurie L. Tis, David H. Perrin, Arthur Weltman, Donald W. Ball, and Joe H. Gieck * Tis, L.L., Perrin, D.H., Weltman, A., Ball, D.W.,
Effect of Preload and Range of Motion on Isokinetic Torque in Women By: Laurie L. Tis, David H. Perrin, Arthur Weltman, Donald W. Ball, and Joe H. Gieck * Tis, L.L., Perrin, D.H., Weltman, A., Ball, D.W.,
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects
 Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
CAN PARAMETERS OF THE HELICAL AXIS BE MEASURED RELIABLY DURING ACTIVE CERVICAL MOVEMENTS?
 CAN PARAMETERS OF THE HELICAL AXIS BE MEASURED RELIABLY DURING ACTIVE CERVICAL MOVEMENTS? 1 ABSTRACT Convex hull area (CHA) and mean angle (MA) have been proposed to describe the behaviour of the helical
CAN PARAMETERS OF THE HELICAL AXIS BE MEASURED RELIABLY DURING ACTIVE CERVICAL MOVEMENTS? 1 ABSTRACT Convex hull area (CHA) and mean angle (MA) have been proposed to describe the behaviour of the helical
PATIENTS WITH fibromyalgia (FM) present with diffuse
 1646 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Test-Retest Reliability of Isometric and Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion in Patients With Fibromyalgia: Evaluation of the Smallest Real Difference Jose C. Adsuar, MSc, Pedro
1646 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Test-Retest Reliability of Isometric and Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion in Patients With Fibromyalgia: Evaluation of the Smallest Real Difference Jose C. Adsuar, MSc, Pedro
Do you want to improve your Clinical Assessment?
 Do you want to improve your Clinical Assessment? An important component of the clinical examination for several conditions is the assessment of muscle strength. The standard clinical evaluation and diagnostic
Do you want to improve your Clinical Assessment? An important component of the clinical examination for several conditions is the assessment of muscle strength. The standard clinical evaluation and diagnostic
***Note: Figures may be missing for this format of the document ***Note: Footnotes and endnotes indicated with brackets
 Isokinetic Strength of the Trunk and Hip in Female Runners By: Laurie L. Tis, MEd, ATC *, David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC, David B. Snead, PhD, Arthur Weltman University of Virginia and Washington University
Isokinetic Strength of the Trunk and Hip in Female Runners By: Laurie L. Tis, MEd, ATC *, David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC, David B. Snead, PhD, Arthur Weltman University of Virginia and Washington University
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner
 Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory
 CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
Isokinetic trunk flexion extension protocol to assess trunk muscle strength and endurance: Reliability, learning effect, and sex differences
 1bs_bs_query 2bs_bs_query 3bs_bs_query 4bs_bs_query 5bs_bs_query 6bs_bs_query 7bs_bs_query 8bs_bs_query 9bs_bs_query 10bs_bs_query 12bs_bs_query 13bs_bs_query 14bs_bs_query 15bs_bs_query 16bs_bs_query
1bs_bs_query 2bs_bs_query 3bs_bs_query 4bs_bs_query 5bs_bs_query 6bs_bs_query 7bs_bs_query 8bs_bs_query 9bs_bs_query 10bs_bs_query 12bs_bs_query 13bs_bs_query 14bs_bs_query 15bs_bs_query 16bs_bs_query
Concepts of exercise therapy for neck pain
 «Therapeutic Exercise in the workplace - THEWS» Concepts of exercise therapy for neck pain Manos Stefanakis PT, MManipTher, PhD Neck pain Country 1 year incidence Reference UK 30% Palmer et al. 2001, Scand
«Therapeutic Exercise in the workplace - THEWS» Concepts of exercise therapy for neck pain Manos Stefanakis PT, MManipTher, PhD Neck pain Country 1 year incidence Reference UK 30% Palmer et al. 2001, Scand
Prevalance of Neck Pain in Computer Users
 Original Article Prevalance of Neck Pain in Computer Users Faiza Sabeen, 1 Muhammad Salman Bashir, 2 Syed Imtiaz Hussain, 3 Sarah Ehsan 4 Abstract Prolonged use of computers during daily work activities
Original Article Prevalance of Neck Pain in Computer Users Faiza Sabeen, 1 Muhammad Salman Bashir, 2 Syed Imtiaz Hussain, 3 Sarah Ehsan 4 Abstract Prolonged use of computers during daily work activities
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Disclosures. Objectives. Background. Use of Deep Cervical Flexor Exercises in Reducing Cervical Spine Pain. I have nothing to disclose.
 Disclosures Use of Deep Cervical Flexor Exercises in Reducing Cervical Spine Pain I have nothing to disclose. Sarah Pawlowsky, PT, DPT, OCS Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Core Faculty UCSF/SFSU Graduate
Disclosures Use of Deep Cervical Flexor Exercises in Reducing Cervical Spine Pain I have nothing to disclose. Sarah Pawlowsky, PT, DPT, OCS Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Core Faculty UCSF/SFSU Graduate
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris
 Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
Cervical Range of Motion Discriminates Between Asymptomatic Persons and Those With Whiplash
 1 Cervical Range of Motion Discriminates Between Asymptomatic Persons and Those With Whiplash SPINE 2001;26:2090-2094 (October 1, 2001) Paul T. Dall Alba, Michele M. Sterling, Julia M. Treleaven, Sandra
1 Cervical Range of Motion Discriminates Between Asymptomatic Persons and Those With Whiplash SPINE 2001;26:2090-2094 (October 1, 2001) Paul T. Dall Alba, Michele M. Sterling, Julia M. Treleaven, Sandra
Scapular Muscle Strengthening
 Original Research Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1995, 4, 244-252 O 1995 Human Kinetics Publ~shers, Inc. Scapular Muscle Strengthening Thomas Zmierski, Sam Kegerreis, and James Scarpaci The purposes
Original Research Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1995, 4, 244-252 O 1995 Human Kinetics Publ~shers, Inc. Scapular Muscle Strengthening Thomas Zmierski, Sam Kegerreis, and James Scarpaci The purposes
Peak Torque Comparison between isam 9000 and Biodex Isokinetic Devices
 International Journal of Health Sciences September 2016, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 7-13 ISSN: 2372-5060 (Print), 2372-5079 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
International Journal of Health Sciences September 2016, Vol. 4, No. 3, pp. 7-13 ISSN: 2372-5060 (Print), 2372-5079 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
Obesity is associated with reduced joint range of motion (Park, 2010), which has been partially
 INTRODUCTION Obesity is associated with reduced joint range of motion (Park, 2010), which has been partially attributed to adipose tissues around joints limiting inter-segmental rotations (Gilleard, 2007).
INTRODUCTION Obesity is associated with reduced joint range of motion (Park, 2010), which has been partially attributed to adipose tissues around joints limiting inter-segmental rotations (Gilleard, 2007).
Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
Three-Dimensional Isometric Strength of Neck Muscles in Humans
 Three-Dimensional Isometric Strength of Neck Muscles in Humans SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1904 1909 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Anita N. Vasavada, PhD,* Siping Li, PhD, and Scott L. Delp,
Three-Dimensional Isometric Strength of Neck Muscles in Humans SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1904 1909 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Anita N. Vasavada, PhD,* Siping Li, PhD, and Scott L. Delp,
Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain
 Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Reliability of hand-held dynamometer for strength testing of knee musculature in healthy Indian pediatric population: a cross-sectional study.
 Han d-h eld Dyn amo met er Kne e mus cle Strengt h Chi ldre n Reliability of hand-held dynamometer for strength testing of knee musculature in healthy Indian pediatric population: a cross-sectional study.
Han d-h eld Dyn amo met er Kne e mus cle Strengt h Chi ldre n Reliability of hand-held dynamometer for strength testing of knee musculature in healthy Indian pediatric population: a cross-sectional study.
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles
 Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger
 Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Original Article. MUNENORI KATOH, PT, PhD 1), YUKINOBU HIIRAGI, PT, PhD 2), MANABU UCHIDA, PT, PhD 3)
 Original Article Validity of Isometric Muscle Strength Measurements of the Lower Limbs Using a Handheld Dynamometer and Belt: a Comparison with an Isokinetic Dynamometer J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 23: 553 557,
Original Article Validity of Isometric Muscle Strength Measurements of the Lower Limbs Using a Handheld Dynamometer and Belt: a Comparison with an Isokinetic Dynamometer J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 23: 553 557,
Abstract. A novel device to improve sitting posture. Hoda Dalimi (1) Ali Ghorbani (2) Anoushirvan Kezam nejad (3) Mohammad Hossein Alizadeh (4)
 A novel device to improve sitting posture Hoda Dalimi (1) Ali Ghorbani (2) Anoushirvan Kezam nejad (3) Mohammad Hossein Alizadeh (4) (1) Msc of Sports Science, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran (2) Msc
A novel device to improve sitting posture Hoda Dalimi (1) Ali Ghorbani (2) Anoushirvan Kezam nejad (3) Mohammad Hossein Alizadeh (4) (1) Msc of Sports Science, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran (2) Msc
Exercise for Reducing Neck Pain and Enhancing Dynamic Stability.
 Exercise for Reducing Neck Pain and Enhancing Dynamic Stability www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Presentation Outline Compare/Contrast Lumbar Exercise Literature to Cervical Spine Discuss Neck Musculature and
Exercise for Reducing Neck Pain and Enhancing Dynamic Stability www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Presentation Outline Compare/Contrast Lumbar Exercise Literature to Cervical Spine Discuss Neck Musculature and
S3 EFFECTIVE FOR SHOULDER PATHOLOGIES -Dr. Steven Smith
 S3 EFFECTIVE FOR SHOULDER PATHOLOGIES -Dr. Steven Smith Introduction: Scapular function and its role in shoulder biomechanics has gained increased notoriety in the pathogenesis of shoulder dysfunction
S3 EFFECTIVE FOR SHOULDER PATHOLOGIES -Dr. Steven Smith Introduction: Scapular function and its role in shoulder biomechanics has gained increased notoriety in the pathogenesis of shoulder dysfunction
DUAL POSITION BACK EX/FLEX ATTACHMENT
 DUAL POSITION BACK EX/FLEX ATTACHMENT OPERATION MANUAL 830-450 FN: 08-261 Rev A 11/15 BIODEX Biodex Medical Systems, Inc. 20 Ramsey Road, Shirley, New York, 11967-4704 Tel: 800-224-6339 (Int l 631-924-9000),
DUAL POSITION BACK EX/FLEX ATTACHMENT OPERATION MANUAL 830-450 FN: 08-261 Rev A 11/15 BIODEX Biodex Medical Systems, Inc. 20 Ramsey Road, Shirley, New York, 11967-4704 Tel: 800-224-6339 (Int l 631-924-9000),
Cervico-Thoracic Management Exercise and Manual Therapy. Deep Neck Flexor Training. Deep Neck Flexor Training. FPTA Spring 2011 Eric Chaconas 1
 Cervico-Thoracic Management Exercise and Manual Therapy Eric Chaconas PT, DPT, CSCS, FAAOMPT Deep Neck Flexor Training Evidence of dysfunction in the longus coli and longus capitus. Chronic Neck Pain Idiopathic
Cervico-Thoracic Management Exercise and Manual Therapy Eric Chaconas PT, DPT, CSCS, FAAOMPT Deep Neck Flexor Training Evidence of dysfunction in the longus coli and longus capitus. Chronic Neck Pain Idiopathic
Tung-Wu Lu, DPhil 1, Horng-Chaung Hsu, MD 2, Ling-Ying Chang, MS, PT 3 and Hao-Ling Chen, PhD 4 ORIGINAL REPORT. J Rehabil Med 2007; 39:
 J Rehabil Med 2007; 39: 679 684 ORIGINAL REPORT ENHANCING THE EXAMINER S RESISTING FORCE IMPROVES THE RELIABILITY OF MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS: COMPARISON OF A NEW DEVICE WITH HAND-HELD DYNAMOMETRY
J Rehabil Med 2007; 39: 679 684 ORIGINAL REPORT ENHANCING THE EXAMINER S RESISTING FORCE IMPROVES THE RELIABILITY OF MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS: COMPARISON OF A NEW DEVICE WITH HAND-HELD DYNAMOMETRY
OBJECTIVE AND ACCURATE measurements of lumbar
 99 Strapped Versus Unstrapped Technique of the Prone Press-Up for Measurement of Lumbar Extension Using a Tape Measure: Differences in Magnitude and Reliability of Measurements William D. Bandy, PhD, PT,
99 Strapped Versus Unstrapped Technique of the Prone Press-Up for Measurement of Lumbar Extension Using a Tape Measure: Differences in Magnitude and Reliability of Measurements William D. Bandy, PhD, PT,
Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve
 Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve By: Daniel J. LaPlaca *, Douglas R. Keskula, Kristinn I. Heinrichs, and David H. Perrin LaPlaca, D.J., Keskula, D., Heinrichs,
Comparison of N-K Table Offset Angles with the Human Knee Flexor Torque Curve By: Daniel J. LaPlaca *, Douglas R. Keskula, Kristinn I. Heinrichs, and David H. Perrin LaPlaca, D.J., Keskula, D., Heinrichs,
ATLANTOAXIAL (AA) disorders are common consequences
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Decreased Muscle Strength and Mobility of the Neck in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Atlantoaxial Arja Häkkinen, PhD, Marko Henrik Neva, MD, PhD, Markku Kauppi, MD, PhD, Pekka
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Decreased Muscle Strength and Mobility of the Neck in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Atlantoaxial Arja Häkkinen, PhD, Marko Henrik Neva, MD, PhD, Markku Kauppi, MD, PhD, Pekka
A comparison of training methods to increase neck muscle strength
 Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 2011 2005 A comparison of training methods to increase neck muscle strength Angus Burnett Fiona Naumann Ryan Price Ross Sanders This article was originally published
Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 2011 2005 A comparison of training methods to increase neck muscle strength Angus Burnett Fiona Naumann Ryan Price Ross Sanders This article was originally published
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS. I. Devreux
 EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS I. Devreux To determine the extent and degree of muscular weakness resulting from disease, injury or disuse. The records obtained from these tests provide a base for planning
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS I. Devreux To determine the extent and degree of muscular weakness resulting from disease, injury or disuse. The records obtained from these tests provide a base for planning
Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters
 Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters MARGARET ROST, SANDRA STUCKEY, LEE ANNE SMALLEY, and GLENDA DORMAN A method of measuring trunk motion and two related motions using a tape measure
Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters MARGARET ROST, SANDRA STUCKEY, LEE ANNE SMALLEY, and GLENDA DORMAN A method of measuring trunk motion and two related motions using a tape measure
Relationship of the Penn Shoulder Score with Measures of Range of Motion and Strength in Patients with Shoulder Disorders: A Preliminary Report
 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 16: 39 44, 2003 2003 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal Relationship of the Penn Shoulder Score with Measures of Range of Motion and Strength
The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 16: 39 44, 2003 2003 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal Relationship of the Penn Shoulder Score with Measures of Range of Motion and Strength
Reliability of Stationary Dynamometer Muscle Strength Testing in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
 1128 Reliability of Stationary Dynamometer Muscle Strength Testing in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Cheryl D. Ford-Smith, PT, MS, NCS, Jean F. Wyman, PhD, RN, R.K. Elswick Jr, PhD, Theresa Fernandez,
1128 Reliability of Stationary Dynamometer Muscle Strength Testing in Community-Dwelling Older Adults Cheryl D. Ford-Smith, PT, MS, NCS, Jean F. Wyman, PhD, RN, R.K. Elswick Jr, PhD, Theresa Fernandez,
SLAP LESION REPAIR PROTOCOL
 SLAP LESION REPAIR PROTOCOL Clarkstown Division This rehabilitation protocol has been developed for the patient following a SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior) repair. It is extremely important to
SLAP LESION REPAIR PROTOCOL Clarkstown Division This rehabilitation protocol has been developed for the patient following a SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior) repair. It is extremely important to
performance in young jumpers
 BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
BIOLOGY OF EXERCISE VOLUME 5.2, 2009 Isokinetic muscle strength and running long jump performance in young jumpers D.O.I: http:doi.org/10.4127/jbe.2009.0030 YIANNIS KOUTSIORAS, ATHANASIOS TSIOKANOS, DIMITRIOS
THE PRO-POSTURE NECK EXERCISER
 EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE PRO-POSTURE NECK EXERCISER The following are a list of six different exercises that can be performed with the Pro- Posture Neck Exerciser. 1) Basic Pro-Posture Neck Pump Exercise
EXERCISE INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE PRO-POSTURE NECK EXERCISER The following are a list of six different exercises that can be performed with the Pro- Posture Neck Exerciser. 1) Basic Pro-Posture Neck Pump Exercise
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN
 STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
Contents INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1. SECTION 1 Data collection methodology 2
 Contents Page No INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1 SECTION 1 Data collection methodology 2 SECTION 2 5 DATASHEETS. 1. Push and pull strength 5 2. Push with the thumb or 2 or more fingers 11 3. Push with the
Contents Page No INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1 SECTION 1 Data collection methodology 2 SECTION 2 5 DATASHEETS. 1. Push and pull strength 5 2. Push with the thumb or 2 or more fingers 11 3. Push with the
Improving Thoracic Mobility
 Improving Thoracic Mobility By William J. Hanney DPT, PhD, ATC, CSCS Course Description A lack of thoracic mobility can have broad clinical implications and evidence suggests addressing mobility in this
Improving Thoracic Mobility By William J. Hanney DPT, PhD, ATC, CSCS Course Description A lack of thoracic mobility can have broad clinical implications and evidence suggests addressing mobility in this
The Effect of Inter-Trial Rest Interval on the Assessment of lsokinetic Thigh Muscle Torque
 The Effect of Inter-Trial Rest Interval on the Assessment of lsokinetic Thigh Muscle Torque PAUL W. STRATFORD, MSc,' ANNETTE BRUULSEMA,2 BILL MAXWELL,= TIM BLACK, BSc,' BEVERLY HARDING, BSc4 Journal of
The Effect of Inter-Trial Rest Interval on the Assessment of lsokinetic Thigh Muscle Torque PAUL W. STRATFORD, MSc,' ANNETTE BRUULSEMA,2 BILL MAXWELL,= TIM BLACK, BSc,' BEVERLY HARDING, BSc4 Journal of
BANKART REPAIR PROTOCOL
 BANKART REPAIR PROTOCOL Clarkstown Division This rehabilitation protocol has been developed for the patient following Bankart surgical procedure for anterior shoulder instability. The protocol is divided
BANKART REPAIR PROTOCOL Clarkstown Division This rehabilitation protocol has been developed for the patient following Bankart surgical procedure for anterior shoulder instability. The protocol is divided
Resistive Eccentric Exercise: Effects of Visual
 Resistive Eccentric Exercise: Effects of Visual Feed back on Maximum Moment of Knee Extensors and Flexors Eleftherios Kellis, BScl Vasilios Baltzopoulos, Ph D, M Phil, BSc2 Copyright 1996. All rights reserved.
Resistive Eccentric Exercise: Effects of Visual Feed back on Maximum Moment of Knee Extensors and Flexors Eleftherios Kellis, BScl Vasilios Baltzopoulos, Ph D, M Phil, BSc2 Copyright 1996. All rights reserved.
CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE. Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA
 CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA Stepping Back What are the goals? What is the value? Is it Sport Specific
CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA Stepping Back What are the goals? What is the value? Is it Sport Specific
Cost Reduction Technology. Simplifying the Management of Post-injury Musculoskeletal Disorder Injuries
 Cost Reduction Technology Simplifying the Management of Post-injury Musculoskeletal Disorder Injuries 312.960.9273 Soft-Tissue Injury Management OBJECTIVE Introduce attendees to isokinetic testing and
Cost Reduction Technology Simplifying the Management of Post-injury Musculoskeletal Disorder Injuries 312.960.9273 Soft-Tissue Injury Management OBJECTIVE Introduce attendees to isokinetic testing and
The following pages constitute the final, accepted and revised manuscript of the article:
 The following pages constitute the final, accepted and revised manuscript of the article: Flansbjer, Ulla-Britt and Holmbäck, Anna Maria and Downham, David and Lexell, Jan What change in isokinetic knee
The following pages constitute the final, accepted and revised manuscript of the article: Flansbjer, Ulla-Britt and Holmbäck, Anna Maria and Downham, David and Lexell, Jan What change in isokinetic knee
SLAP LESION REPAIR PROTOCOL Dr. Steven Flores
 SLAP LESION REPAIR PROTOCOL Dr. Steven Flores This rehabilitation protocol has been developed for the patient following a SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior) repair. It is extremely important to
SLAP LESION REPAIR PROTOCOL Dr. Steven Flores This rehabilitation protocol has been developed for the patient following a SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior) repair. It is extremely important to
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Measuring the Strength and Endurance Capacity of Deep Cervical Flexor Muscles in Parmar Smitul
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Measuring the Strength and Endurance Capacity of Deep Cervical Flexor Muscles in Parmar Smitul
Test-Retest Reliability of Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion
 626 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TestRetest Reliability of Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion Gisela Sole, BSc(Physio), MSc(Med), Jonas Hamrén, BSc(Physio), Stephan Milosavljevic, BAppSc(Physio), PhD, Helen Nicholson,
626 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TestRetest Reliability of Isokinetic Knee Extension and Flexion Gisela Sole, BSc(Physio), MSc(Med), Jonas Hamrén, BSc(Physio), Stephan Milosavljevic, BAppSc(Physio), PhD, Helen Nicholson,
Comparing Dominant and Non-Dominant Torque and Work using Biodex 3 Isokinetic Protocol for Knee Flexors and Extensors INTRODUCTION PURPOSE METHODS
 Comparing Dominant and Non-Dominant Torque and Work using Biodex 3 Isokinetic Protocol for Knee Flexors and Extensors Joshua R. Sparks B.S., ACSM HFS, BACCHUS PHE KINE 533C, Louisiana Tech University INTRODUCTION
Comparing Dominant and Non-Dominant Torque and Work using Biodex 3 Isokinetic Protocol for Knee Flexors and Extensors Joshua R. Sparks B.S., ACSM HFS, BACCHUS PHE KINE 533C, Louisiana Tech University INTRODUCTION
NZQA Expiring unit standard 7026 version 4 Page 1 of 7. Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics
 Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH
 10.1515/AMB-2016-0020 PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH S. Mindova, I. Karaganova and I. Stefanova Faculty of Public Health and Health Care, University of Ruse Angel Kanchev, Ruse, Bulgaria
10.1515/AMB-2016-0020 PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH S. Mindova, I. Karaganova and I. Stefanova Faculty of Public Health and Health Care, University of Ruse Angel Kanchev, Ruse, Bulgaria
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 A STUDY TO ANALYSE THE ISOMETRIC STRENGTH AND ISOKINETIC PEAK TORQUES OF HAMSTRING AND QUADRICEPS AT DIFFERENT ANGLES AND ANGULAR VELOCITY OF KNEE USING ISOKINETIC DEVICE IN NORMAL INDIVIDUALS SHANTHI
A STUDY TO ANALYSE THE ISOMETRIC STRENGTH AND ISOKINETIC PEAK TORQUES OF HAMSTRING AND QUADRICEPS AT DIFFERENT ANGLES AND ANGULAR VELOCITY OF KNEE USING ISOKINETIC DEVICE IN NORMAL INDIVIDUALS SHANTHI
Reliability and validity of the Biodex system 3 pro isokinetic dynamometer velocity, torque and position measurements
 Reliability and validity of the Biodex system 3 pro isokinetic dynamometer velocity, torque and position measurements By: Joshua M. Drouin 1, Tamara C. Valovich-McLeod 2, Sandra J. Shultz 3, Bruce M. Gansneder
Reliability and validity of the Biodex system 3 pro isokinetic dynamometer velocity, torque and position measurements By: Joshua M. Drouin 1, Tamara C. Valovich-McLeod 2, Sandra J. Shultz 3, Bruce M. Gansneder
Measuring Muscle Strength for People With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Retest Reliability of Hand-Held Dynamometry
 32 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Measuring Muscle Strength for People With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Retest Reliability of Hand-Held Dynamometry Simone D. O Shea, PT, Nicholas F. Taylor, PhD, PT, Jennifer
32 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Measuring Muscle Strength for People With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Retest Reliability of Hand-Held Dynamometry Simone D. O Shea, PT, Nicholas F. Taylor, PhD, PT, Jennifer
Research Report. Abdominal Muscle Response During Curl-ups on Both Stable and Labile Surfaces
 Research Report Abdominal Muscle Response During Curl-ups on Both Stable and Labile Surfaces Background and Purpose. With the current interest in stability training for the injured low back, the use of
Research Report Abdominal Muscle Response During Curl-ups on Both Stable and Labile Surfaces Background and Purpose. With the current interest in stability training for the injured low back, the use of
Chapter 4B: Reliability Trial 2. Chapter 4B. Reliability. General issues. Inter-rater. Intra - rater. Test - Re-test
 Chapter 4B: Reliability Trial 2 Chapter 4B Reliability General issues Inter-rater Intra - rater Test - Re-test Trial 2 The second clinical trial was conducted in the spring of 1992 using SPCM Draft 6,
Chapter 4B: Reliability Trial 2 Chapter 4B Reliability General issues Inter-rater Intra - rater Test - Re-test Trial 2 The second clinical trial was conducted in the spring of 1992 using SPCM Draft 6,
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
Return to play after shoulder injury and high performance training in the overhead athlete
 Return to play after shoulder injury and high performance training in the overhead athlete Dr Ann Cools, PT, PhD Dept Rehab. Sciences & Physiotherapy Ghent University, Belgium Shoulder and scapular measurements
Return to play after shoulder injury and high performance training in the overhead athlete Dr Ann Cools, PT, PhD Dept Rehab. Sciences & Physiotherapy Ghent University, Belgium Shoulder and scapular measurements
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity
 Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Analysis of the functional biomechanics of different chair types during esports activity Final Report December 2017 Dr. Frank Emrich Scientific Consultant Biomechanics & Ergonomics 1 Introduction The esports
Session 4: Exercise Prescription for Musculoskeletal Disorders: Low Back Pain
 Session 4: Exercise Prescription for Musculoskeletal Disorders: Low Back Pain Course: Designing Exercise Prescriptions for Normal/Special Populations Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI
Session 4: Exercise Prescription for Musculoskeletal Disorders: Low Back Pain Course: Designing Exercise Prescriptions for Normal/Special Populations Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI
Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs
 Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs Chapter Five: Movement Examination of the Lumbar Spine Time) (45 minutes
Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs Chapter Five: Movement Examination of the Lumbar Spine Time) (45 minutes
Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Head, Neck, and Cervical Spine Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS Pre- Chapter Case Study
 Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS (20 minutes CEU Time) Subjective A 43-year-old male, reported a sudden onset of left-sided neck and upper extremity
Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS (20 minutes CEU Time) Subjective A 43-year-old male, reported a sudden onset of left-sided neck and upper extremity
Rebecca Courtney, PT, DPT. Supervisor, Ochsner HealthyBack
 Rebecca Courtney, PT, DPT Supervisor, Ochsner HealthyBack What is the Healthy Back Program? A comprehensive treatment approach for patients with sub-acute chronic neck and back pain Includes MD assessment,
Rebecca Courtney, PT, DPT Supervisor, Ochsner HealthyBack What is the Healthy Back Program? A comprehensive treatment approach for patients with sub-acute chronic neck and back pain Includes MD assessment,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION
 Interexaminer Reliability of Three Methods of Combining Test Results to Determine Side of Sacral Restriction, Sacral Base Position, and Innominate Bone Position Henry C. Tong, MD; Oscar G. Heyman, DO;
Interexaminer Reliability of Three Methods of Combining Test Results to Determine Side of Sacral Restriction, Sacral Base Position, and Innominate Bone Position Henry C. Tong, MD; Oscar G. Heyman, DO;
Anneli Peolsson, M. Peolsson, G. Jull, T. Loefstedt, J. Trygg and S. OLeary. Linköping University Post Print
 Preliminary evaluation of dorsal muscle activity during resisted cervical extension in patients with longstanding pain and disability following anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery Anneli
Preliminary evaluation of dorsal muscle activity during resisted cervical extension in patients with longstanding pain and disability following anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery Anneli
Isometric cervical extension force and dimensions of semispinalis capitis muscle
 Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 39 No. 3, May/June 2002 Pages 423 428 Isometric cervical extension force and dimensions of semispinalis capitis muscle Asghar Rezasoltani, PhD; Jari
Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 39 No. 3, May/June 2002 Pages 423 428 Isometric cervical extension force and dimensions of semispinalis capitis muscle Asghar Rezasoltani, PhD; Jari
Chapter 7. Inter-rater reliability of a video-analysis method measuring low-back load in a field situation.
 Inter-rater reliability of a video-analysis method measuring low-back load in a field situation. P. Coenen I. Kingma C.R. Boot P.M. Bongers J.H. van Dieën Applied Ergonomics, 213, 44(5): 828-834 ABSTRACT
Inter-rater reliability of a video-analysis method measuring low-back load in a field situation. P. Coenen I. Kingma C.R. Boot P.M. Bongers J.H. van Dieën Applied Ergonomics, 213, 44(5): 828-834 ABSTRACT
Validity and Reliability of a Hand-Held Dynamometer for Dynamic Muscle Strength Assessment
 40 Validity and Reliability of a Hand-Held Dynamometer for Dynamic Muscle Strength Assessment Lan Le-Ngoc 1 and Jessica Janssen 2 1 Industrial Research Ltd, Christchurch 2 Burwood Academy of Independent
40 Validity and Reliability of a Hand-Held Dynamometer for Dynamic Muscle Strength Assessment Lan Le-Ngoc 1 and Jessica Janssen 2 1 Industrial Research Ltd, Christchurch 2 Burwood Academy of Independent
Faulty Movement Patterns
 Faulty Movement Patterns Functional Evaluation and Prague School Test (part 1) Instructor: Dr. Craig Liebenson, DC Quantitative Functional Capacity Evaluation: 1. Side Plank Endurance 2. Forward Plank
Faulty Movement Patterns Functional Evaluation and Prague School Test (part 1) Instructor: Dr. Craig Liebenson, DC Quantitative Functional Capacity Evaluation: 1. Side Plank Endurance 2. Forward Plank
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill. patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry
 Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
ISOKINETIC TESTING AND DATA INTERPRETATION
 ISOKINETIC TESTING AND DATA INTERPRETATION PRINCIPLES OF ISOKINETIC The principle behind Isokinetic exercise and testing is that the lever arm moves at a preset fixed speed allowing for accommodating resistance
ISOKINETIC TESTING AND DATA INTERPRETATION PRINCIPLES OF ISOKINETIC The principle behind Isokinetic exercise and testing is that the lever arm moves at a preset fixed speed allowing for accommodating resistance
Title: Rotational strength, range of motion, and function in people with unaffected shoulders from various stages of life
 Author's response to reviews Title: Rotational strength, range of motion, and function in people with unaffected shoulders from various stages of life Authors: Jean-Sébastien Roy (jean-sebastien.roy.1@ulaval.ca)
Author's response to reviews Title: Rotational strength, range of motion, and function in people with unaffected shoulders from various stages of life Authors: Jean-Sébastien Roy (jean-sebastien.roy.1@ulaval.ca)
Anterior Stabilization of the Shoulder: Distal Tibial Allograft
 Anterior Stabilization of the Shoulder: Distal Tibial Allograft Name: Diagnosis: Date: Date of Surgery: Phase I Immediate Post Surgical Phase (approximately Weeks 1-3) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory
Anterior Stabilization of the Shoulder: Distal Tibial Allograft Name: Diagnosis: Date: Date of Surgery: Phase I Immediate Post Surgical Phase (approximately Weeks 1-3) Minimize shoulder pain and inflammatory
differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
 CHAPTER 6 Muscles at Work After completing this chapter you should be able to: differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
CHAPTER 6 Muscles at Work After completing this chapter you should be able to: differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
Biceps Tenodesis Protocol
 Biceps Tenodesis Protocol A biceps tenodesis procedure involves cutting of the long head of the biceps just prior to its insertion on the superior labrum and then anchoring the tendon along its anatomical
Biceps Tenodesis Protocol A biceps tenodesis procedure involves cutting of the long head of the biceps just prior to its insertion on the superior labrum and then anchoring the tendon along its anatomical
Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance
 Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Introduction Rubber resistance was originally used to train
Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Introduction Rubber resistance was originally used to train
Most Dangerous Man! FACTS ON STREGNTH. Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
 FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
Downloaded from umj.umsu.ac.ir at 22: on Friday March 22nd 2019
 * 91/06/07 : 91/04/02 : :.. -. :. ICC. ICC.. :. // // :. : - - : :.(-) - (SLR) Email: eterafoskouei@tbzmed.ac.ir.(). (ULTT).().. ( ) Straight Leg Raise Upper Limb Tension Tests .().(-) Hough.().() ULTT1.()
* 91/06/07 : 91/04/02 : :.. -. :. ICC. ICC.. :. // // :. : - - : :.(-) - (SLR) Email: eterafoskouei@tbzmed.ac.ir.(). (ULTT).().. ( ) Straight Leg Raise Upper Limb Tension Tests .().(-) Hough.().() ULTT1.()
IS THERE A LINK BETWEEN SPINE AND HIP MOBILITY?
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 4, No. 2, 2012, 1-5 UDC 796.012.23 Research article IS THERE A LINK BETWEEN SPINE AND HIP MOBILITY? Miroslav Saviè and S2P, Laboratory for Motor Control and Motor Learning,
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 4, No. 2, 2012, 1-5 UDC 796.012.23 Research article IS THERE A LINK BETWEEN SPINE AND HIP MOBILITY? Miroslav Saviè and S2P, Laboratory for Motor Control and Motor Learning,
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE)
 Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards.
 Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards. Prepared by Engineering and Human Performance Lab Department of
Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards. Prepared by Engineering and Human Performance Lab Department of
Hakan Giir, MD, PhD, Bedrettin Akova, MD, Selfuk Kiifiiko~lu, MD
 1024 Continuous Versus Separate Isokinetic Test Protocol: The Effect of Estradiol on the Reproducibility of Concentric and Eccentric Isokinetic Measurements in Knee Muscles Hakan Giir, MD, PhD, Bedrettin
1024 Continuous Versus Separate Isokinetic Test Protocol: The Effect of Estradiol on the Reproducibility of Concentric and Eccentric Isokinetic Measurements in Knee Muscles Hakan Giir, MD, PhD, Bedrettin
