Index. Note: page numbers in italics refer to figures, those in bold refer to tables
|
|
|
- Reynold Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Note: page numbers in italics refer to figures, those in bold refer to tables acromial arch elevation 160 acromioclavicular joint active learner/participation role of patient 183, 184, 194 active reasoning process 50, 51 activities of daily living (ADL) 184 afferent information 190 movement efficiency 185 adjuncts to therapy 15 afferent information activities of daily living 190 hands 169 movement control afferent input manipulation 49 aids 129 walking 156 ankles sit to stand transition 87 8 standing to sitting movements 90 1 strategies 33, 136, 143 anticipatory postural adjustments (APAs) 28, 30 1, 33, 93 demand creation 159 hypothesis generation hypotonic shoulder complex 159 lack of appropriate 159, 160 standing to sitting 91 trunk stability 156, 157 upper limb motor programme 166 arm movement, limitation of range 26 armchair seating 185 assessment procedure 2, 12, 43, 44 active reasoning process 50, 51 afferent input manipulation 49 Bobath Concept 47 50, 51, 52 case study 130 1, 132, 133 functioning 66 hands improvement potential 48 9 observations 53, 54, 56, 57 potential of patient 48 problem-solving approach 3, 43, 45 recovery level prediction 48 9 assistive devices 129 walking aids 156 back pain 185 balance 31 hypotonic shoulder complex 159 improvement 197 recovery 32 strategies 33 walking aid impact 156 base of support (BOS) 185, 187 postural adaptation 196 bath, active facilitation best practice 182 biomechanics 52 bipedalism , 121, 122 upright stance 125 Bobath, Berta 1, 2 3 Bobath, Karel 1, 2 Bobath Concept clinical application of theory current theory 3 4, 12 development 1 3 body schema, stimulating body weight support treadmill training Bohannon Ordinal Sway Test 202, 203 brain injury acquired 5 6 cortical plasticity 6 7 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation 2009 Blackwell Publishing Ltd. ISBN: Edited by S. Raine, L. Meadows and M. Lynch-Ellerington 208
2 brainstem, postural control regulation 30, 31 bridging, pelvic tilt 110, 111 Canadian Occupational Performance Measure (COPM) 65, 70 3 cane use 129 ceiling effects 70 central pattern generating (CPG) circuits 119, 120 centre of mass (COM) forward transfer 85, 88, 93 sit to walk 93 standing to sitting movements 90 cervical spine, posture 159 clinical reasoning 53 60, 61 analysis 53 5 basis 52 3 hypothesis generation 53 7 models 45 7 scheduling of day cognition 28 cognitive capacity, return to work 194 Community Balance and Mobility Scale 66 compensatory strategies 25 6 constraint-induced movement therapy 15, 170 construct validity 69 contactual hand-orienting response (CHOR) 103, 104, 171, 172 3, 191 anticipatory postural adjustments 196 development improvement 196 content validity 69 contextual factors, disability impact 46 contractures, development 8 core stability 126 cortical control of locomotion 119 gait initiation cortical functional reorganisation 183 cortical plasticity 6 7 cortical reorganisation 6 7 corticospinal drive 120 corticospinal system 31 damage 124 divergence to convergence principle 168 manipulation control 164 sensory component criterion validity 69 crook, active 135 crook lying 126 facilitation 133, 134, 135 data levels 68 9 de-conditioning, secondary 194 denervation supersensitivity 6 diagnostic reasoning 45 6, 47 dialectical reasoning 47 digit, single, selectivity 200 digiti minimi muscles, abductor 175 disability definition 65 impact 46 discriminative measures 68 dorsiflexion 123 dorsolateral system, upper limb 155 dressing elbow extension 196 hand orientation for grasp 169 electromyography (EMG), sit to stand 84 endurance 35 6 energy expenditure, pacing 194 environment of patient 184 evaluative measures 68 evidence-based practice 52 3, 64 expert care 193 explicit information 27 8 extension 34 fast type muscle fibres 7 fatigue management 186, 188, 194 feedback, augmented 9 fingers activation 200 extension 196 movement 175 single digit selectivity 200 fixation, aid use 129 flexion 34 floor effects 70 foot activation 124, 136, 139 dorsiflexion 125 forward weight transfer 107, 110 position for sit to stand transition 85 sensory awareness 141 sensory input 123 sensory stimulation 106, 136, 137 sit to stand transition 85, 87 8 sit to walk 93 standing to sitting movements 90 1 weight transfer 110 force platform 123 functional activity 16 performance in sitting 186 upper limb 186, 188 functional movement accuracy
3 functional movement (Contd.) analysis 198, 199 compensatory strategies 25 6 efficient 24 5, 31 7 limitation identification 50 motor control motor learning speed 36 7 sub-optimal 34 functional reach 162, 164 9, 199 functioning assessment 66 definition 65 entirety 66 gait determinants high stepping pattern initiation , 121, 122 quantitative analysis 147 rhythmical 125 gait cycle 120, corticospinal drive 120, 121 single limb stance phase swing phase 123 gastrocnemius muscle facilitation 106 strengthening 136, 141 girdle activity 197 glenohumeral joint handling 190 mobility 159, 160 subluxation 157, 158 upper limb elevation 162 glenoid fossa 157, 158 Goal Attainment Scaling (GAS) 65, 73 8, activity goals 76, 77 8, 78 change assessment 74 expected outcomes 73 4 generic goals 76 goal setting 73 4 goal variables 74 limitations 76 measure 202, 203 scores 74, 75 standardised goals 76 stroke 76 goal oriented treatment 12 goal setting 64 Goal Attainment Scaling 73 4 grasp 164, 165, 166 aperture 169 coordination 177 functional 199 planning 169 reach to 166 and release 177 skilled strengthening 176 visual recognition 169 grip, precision/strengthening 176 ground reaction forces 123 hamstrings, strengthening 136, 138 hands afferent information 169 assessment components 171, 172 early treatment function 154 goal-orientated movement 155 grasp 166, 169 handling 171 intensive stimulation 198, 199 intrinsic muscle strength training 173 4, 175 7, 177 management mobilisation 201, 202 movement initiation 161 towards object orientation 171 position for movement between sitting and standing 97 8 post-stroke oedema 191 postural control 200 pre-shaping 169 range of movement 171 reach 166 rehabilitation 171 selectivity 201, 202 shaping 174, strengthening 201, 202 therapeutic stretch 174 upper limb function 170 4, 175 7, 177 walking aid impact on postural control/balance 156 see also contactual hand-orienting response (CHOR) heel contact 106, 107 heel strike 123 facilitation 136, 143 hemiparetic side, muscle changes 8 hip abductor strengthening 145 movement 123 hip strategies
4 adduction 106 7, 108 extension 125, 136, 140 locomotion initiation 107, 109 rehabilitation 196, 197, 199 holistic approach 3 home programmes humerus head 157, 158 support 190 support pillar 161 hypertonicity 10, 11 hypothesis generation 53 7 anticipatory postural adjustments case study 130 1, 132, 133 outcome evaluation 55 7 refinement 55 sit to stand impairment 101 testing 55 hypothesis-driven reasoning 46 hypothetico-deductive reasoning 45 6 index finger activation 200 movement 175 injury, neuroplastic changes 5 6 International Bobath Instructors Training Association (IBITA) 3 International Classification of Function, Disability and Health (ICF, WHO) 65 6 interossei muscles 174 activation 175 interphalangeal joint, proximal 200 interval scales 68, 69 joints, functional alignment 187, 190 kinematics/kinetics 52 sit to stand 84 kneeling, prone 136, 142 knees extension 125 forward translation 131 locking 91 movement 123, 127 locomotion 83 bipedal , 121, 122 body weight support treadmill training case study , control cortical control , 121, 122 essential requirements gait cycle initiation 125 outcome measures 147, 148, 149 pattern systems control 121 velocity lower limb alignment 54 5, 58, 60 sit to stand 88 extension 144 facilitation 58, 59, 61 linear extension 197, 198 selective movement 58, 59 swing phase 148 lumbrical muscles 174 activation 175 Maitland mobilisations 15 manipulation 166 mental imagery, hand strength training 174 mental practice 9 mesencephalic locomotor region (MLR) 120, 122 metacarpophalangeal joint extension 164 mobility scores 147 motivation, motor learning 46 Motor Club Assessment 202, 203 motor control 11 14, 26 31, 183 approach 3 11 appropriate muscle recruitment 34 repetition 13 systems approach 4 11 motor imagery, hand strength training 174 motor learning 5, 8 10, activities of daily living 184 appropriate muscle recruitment 34 engagement 46 explicit 26, 27 8 implicit 26 7 principles 10 theories 4, motor mental imagery 15 motor performance, immediate 9 motor recovery 183 motor skills, novel 9 motor unit recruitment 133, 135 movement analysis 25 6, 52 3 assistance provision 96 8 cognitive systems 24 compensation 12 13, 161 control recovery of selective 46 dysfunction hypothesis generation 53 7 observations 53, 54, 56,
5 movement (Contd.) efficiency 185, 187 critical cues 50 efficient 24 5 environment 95, 96 functional context 95 8 integrated 4, 27 neural mechanisms 27 normal 24 5 patterns 24, 33 4 abnormal coordination 2 perceptual action 24 selective 58, 59 skilled 27 stereotyped 25 strategy 10 optimisation 14 systems control 30 1 movement therapy, constraint-induced 15, 170 muscle compliance creation 15 imbalance 8 length changes 190 neural drive weakness 31 plasticity 7 8 pre-programmed activation patterns 33 range influencing by therapy 13 stiffness 8 strengthening 15, 35 weakness 13, 34 5 muscle fibre types 7 muscle length creation 15 decrease 8 influencing by therapy 13 muscle strength 34 6 training 35 6 muscle training 35 stamina 35 6 musculoskeletal system 15 narrative reasoning 46 7 nervous system plasticity 4, 5 7 regeneration 6 neural coupling, interlimb 86 neural function modification 5 neurofacilitation techniques 28 neuronal cortical connections 5 neurophysiology 2, 52 3 neuroplastic changes following injury 5 6 muscle demands 8 neuroplasticity 5 7, 53 nominal data 68 non-hemiparetic side, muscle changes 8 nucleus gigantocellularis 122 oedema, hand 191 ordinal data 68 9 orthotics 15 outcome measures 64 5, 67 data levels 68 9 locomotion 147, 148, 149 properties purpose 68 reliability responsiveness 70 selection 66, 68 sensitivity to change 70 types 70 4, 75, 76, 77 8, 78 validity 69 outcomes definition 66, 68 evaluation 202, 203 target 68 outpatient rehabilitation 194 palmar structures, shortening 200 parallel bars 129 participation domains 192 partnerships early days of rehabilitation 184 7, 188 9, 190 rehabilitation movement patients active learner 183, 184 active participation 194 environment 184 fatigue management 186, 188 leisure time 194 optimal positioning 187, 189 rehabilitation role 183 safety pattern recognition reasoning 45, 46 pelvic girdle, linear extension 197, 198 pelvic tilt 110, 111 activation 131 pelvis dynamic stability 91 weight transfer to foot 110 perception 28 perceptual disorientation 191 personal factors, disability impact 46 physiotherapy, intensive 193 plantarflexion 123 plasticity of nervous system 4, 5 7 pointing task 164 positioning optimal 187,
6 postural activity 91 enhancement 61 postural adaptation, base of support 196 postural adjustments see anticipatory postural adjustments (APAs); preparatory anticipatory postural adjustments (papas) postural alignment analysis 32 changing 187, 190 Postural Assessment Scale for Stroke 70 postural control 32 3 disruption 33 enhancement 61 feed-forward 93, 100 impairment 100 improvement 197 integrated 118 recovery 193 rehabilitation 184 5, 187 upper limb function walking aids 156 postural hypotonia 53 5 overcoming 14 postural sets 32 prone and standing down from prone lying 127 side lying 125 single leg stance supine 126 postural stability facilitation 58, 59 positive change 60 postural strategies, optimisation 14 postural support, trunk 186 postural tone regulation 119 posture analysis 32 body schema 29 feed-forward responses 30 1 integrated control 118 internal representations 28 9 management 184 5, 187 moving between 187, 190 neural mechanisms 27 systems control 30 1 walking 118 practice evaluation part task 13 specificity 27 structured 15 whole task 13 predictive measures 68 preparatory anticipatory postural adjustments (papas) 31, 33 standing to sitting 91 problem-solving approach 3, 43, 45 prone 127 facilitation 135, 136, 140 kneeling 136, 142 proprioceptive awareness 125 proprioceptive information 185 pyramidal tract lesions 2 quantitative gait analysis 147 radio-ulnar joints, hand orientation for grasp 169 range of motion (ROM) hands 171 reduced 190 shoulder complex 127, 161, 162 ratio scales 68, 69 reach acceleration phase 169 cognitive component 168 functional 162, 164 9, 199 to grasp 83, 164, hand actions 169 pattern facilitation 196, 197, 199 target location transportation phase trunk/upper limb coordination 168 reaching reasoning, active process 50, 51 recovery level prediction 48 9 recruitment 35 6 reflex inhibiting patterns/postures 2 rehabilitation 24-hour approach 182, continuum 183 day scheduling early days 184 7, 188 9, 190 home programmes intensity 193 leisure time 194 moving between postures 187, 190 outcome evaluation 202, 203 outpatient 194 patient role 183 patient safety positioning postural control 184 5, 187 return to work seating sensory 191 stroke unit
7 rehabilitation team 182 clinical reasoning joint sessions 193 members 183 postural alignment change 190 return to work role 184 reliability repetition 13 cortical functional reorganisation 183 cortical plasticity 7 motor unit recruitment 135 reticulospinal neurons 122 feed-forward input 120 reach and grasp 164 rhomboid muscle 162, rotation 34 rotator cuff muscles 157, 158 rubrospinal system 31 reach and grasp 164 safety of patient sarcomeres 8 scapula assessment 131, 132 dysfunction 159 instability 135 mobility 159, movement control 131 movement direction 160 muscle interplay 162 resting position stabilisation 162, 164 stability 156, 159, 161 upper limb elevation 162 scapulohumeral rhythm 161 2, improvement 197, 198 ratio change 162 scapulothoracic joint loading 200 stability 159, 197 scheduling of day seat height 84 5 seating sensorimotor behaviour, adaptive/maladaptive 25 sensorimotor integration development 145 sensorimotor maps 27 sensory deprivation, overcoming sensory information 185 sensory loss, acquired 29 sensory rehabilitation 191 sensory systems 14 shoulder complex activation 159 alignment 158, 159 assessment 131, 132 automatic locking mechanism 158 compensatory movement 161 hemiplegic pain 190 hypotonic 159 impaired scapulohumeral rhythm 162 mobilisation 135 movement 162 muscle strengthening 162, range of movement 127, 161, 162 realignment 159 rotation 201, 202 scapula dysfunction 159 stabilisation 167 stability 164, 165 subluxation 157, 158 thoracic alignment 157 upper limb function side lying 125 hip/trunk musculature 144 single leg stance (SLS) 120, 121, 124, 195, 197, 198 case study 133, 134, 135 preparation for treadmill training 136, , 141 single limb gait cycle sit to stand (STS) transition 83 4 ageing effects 92 3 case study 133 clinical example , 104, 105 7, 108 9, , 113 contactual hand-orienting response 173 extension phase 88 flexion momentum 86 7 hand function 171 hypothesis generation 101 impairment hypothesis formation 101 hypothesis refinement 103, 105 7, treatment intervention trunk orientation 102, 103, 105 lower limb alignment 88 momentum transfer 87 8 phases 86 9 stabilisation 88 sit to walk (STW) 83, 93 ageing effects 92 sitting active posture 131 functional activity performance 186 high to stand down
8 seat height 84 5 unsupported 84 sitting and standing, movement between clinical aspects 84 6, 93 5 clinical example , 104, 105 7, 108 9, , 113 control of components 83 4 extension 107 foot position 85 functional context 95 8 hypothesis formation 101, 103, 105 7, seat height 84 5 sit to stand 83 4, 86 9, 92 3 sit to walk 83, 92, 93 standing to sitting upper limb 85 6 skills transfer 184 slow type muscle fibres 7 soft tissues, functional alignment 187, 190 soleus muscle 106 length 136 loss 124 strength loss 124 somatosensory information 28, somatosensory referencing 14 somatosensory system, stimulate it or lose it 7 spasticity definition 11 spinoreticular neurons, feedback 120 splinting 15 stamina levels 194, 197 stance linear extension 197 see also single leg stance (SLS) stand down assessment 146 standing facilitation 133, 134, 135 independent 113 standing to sitting movements stepping assessment 146 facilitated 113 sternoclavicular joint stick use 129 strength training 35 intrinsic muscle of hand 173 4, 175 7, 177 linear extension 197 motor unit recruitment 135 stretch, therapeutic 125, 174 stroke complications 190 Goal Attainment Scaling 76 postural instability 31 return to work severity 26 single leg stance 124 upper limb recovery capacity 49 stroke unit, rehabilitation 183 structured practice 15 substantia nigra pars reticularis, disinhibition 120 supine postural set 126 support conditions 32 3 fixed base 33 swing phase 124 centre of pressure 148 synapses strengthening 5 unmasking of silent 6 systems approach to motor control 4 11 target location task 9 10 task-specific training 183 task-specific treatment 12 thenar eminence muscles shortening 200 strengthening 176 therapy aims interactive 13 see also treatment intervention thoracic extension 103, 104 thoracic spine alignment 162 mobility posture 159 thoracoscapular interface, dynamic stability thumb abduction/extension 169 see also thenar eminence muscles toe-off 123 toes, extension/flexion 144 tone reduction 13 regulation 119 tonus, abnormal 2 touch, localisation assessment 171, 172 training specificity 26 task-specific 183 trapezius muscle 162, treadmill training with facilitation 144 heel strike facilitation 136,
9 treadmills 15 body weight support training preparation for training 136 treatment intervention case study , delivery intensity 193 joint sessions 193 return to work task-specific 12 tripartite control 119 trunk activity recruitment 87 antigravity activity 159 dynamic stability 91, 156 facilitation 103, 104 linear extension 197, 198 movement 26 orientation 102, 103, 105 vertical posture 108, 109 postural support 186 restraining support 156 splinting 186, 188 stabilisation 107, 109, 158, 159 standing to sitting 90, 91 unlocking 91 upper limb coordination for reach 168 Trunk Impairment Scale 68 upper limb/upper limb function activity 186, 188 improvement 158 alignment cooperative 86 for movement between sitting and standing 98 dorsolateral system 155 elevation 162 functional reach 162, hand 170 4, 175 7, 177 patient awareness 158 pointing task 164 postural control proximal stability 156 reach pattern 161 recovery capacity 49 rotation 200, 201 shoulder complex sit to stand transition 85 6 support 158, 159, 187, 190 trunk coordination for reach 168 ventromedial system 155 upper motor neuron (UMN) lesion 4 movement compensation 12 upper motor neuron (UMN) syndrome validity 69 ventromedial system, upper limb 155 verbal feedback, concurrent augmented 27 vestibular information 28, visual field arm positioning 190 hand positioning 190 target location visual information 28, visual overuse reduction 136 visual recognition for grasp 169 walking 125 body weight support treadmill training cortical control 119 essential requirements ideation of goal 120, 122 initiation 93 integrated control 118 return to work 194 walking aids, postural control/balance 156 weakness 13 weight bearing 13 weight transfer 197 wheelchairs 185 tilt-in-space 187 work, return to World Health Organization (WHO), International Classification of Function, Disability and Health 65 6 wrist activation 164, 165 contactual orientating response 103 extension 169, 196 postural control
LECTURE 8: OPTIMISING UPPER LIMB FUNCTION FOLLOWING STROKE. Understand the factors that can inhibit optimal recovery of arm function.
 LECTURE 8: OPTIMISING UPPER LIMB FUNCTION FOLLOWING STROKE Understand the factors that can inhibit optimal recovery of arm function. o Shoulder subluxation Incidence as high as 81% Downward traction leads
LECTURE 8: OPTIMISING UPPER LIMB FUNCTION FOLLOWING STROKE Understand the factors that can inhibit optimal recovery of arm function. o Shoulder subluxation Incidence as high as 81% Downward traction leads
Benefits of Weight bearing increased awareness of the involved side decreased fear improved symmetry regulation of muscle tone
 From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
NDTA BASIC ADULT COURSE KEY TO COURSE CONTENT
 Topic: Atypical Patterns of Movement Learning outcome(s) that pertain to occupational therapists 1. Identify the influence of atypical patterns of movement on: Postural alignment Transitional movements
Topic: Atypical Patterns of Movement Learning outcome(s) that pertain to occupational therapists 1. Identify the influence of atypical patterns of movement on: Postural alignment Transitional movements
Hemiplegic Shoulder. Incidence & Rationale. Shoulder Pain Assessment & Treatment
 Hemiplegic Shoulder Jeane Davis Fyfe OT, Senior Therapist Incidence & Rationale Up to 72% of stroke survivors will experience shoulder pain Shoulder pain may inhibit patient participation in rehabilitation
Hemiplegic Shoulder Jeane Davis Fyfe OT, Senior Therapist Incidence & Rationale Up to 72% of stroke survivors will experience shoulder pain Shoulder pain may inhibit patient participation in rehabilitation
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
Hemiplegic Shoulder Power Point for staff education sessions
 Appendix B Hemiplegic Shoulder Power Point for staff education sessions Jennifer Curry Physiotherapist, London Health Sciences Centre www.swostroke.ca Acknowledgements Maria Lung BSc (PT), MSc Train the
Appendix B Hemiplegic Shoulder Power Point for staff education sessions Jennifer Curry Physiotherapist, London Health Sciences Centre www.swostroke.ca Acknowledgements Maria Lung BSc (PT), MSc Train the
Rehabilitation 2. The Exercises
 Rehabilitation 2 This is the next level from rehabilitation 1. You should have spent time mastering the previous exercises and be ready to move on. If you are unsure about any of the previous exercises
Rehabilitation 2 This is the next level from rehabilitation 1. You should have spent time mastering the previous exercises and be ready to move on. If you are unsure about any of the previous exercises
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine
 Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
University of Manitoba - MPT: Neurological Clinical Skills Checklist
 Name: Site: Assessment Skills Observed Performed Becoming A. Gross motor function i. Describe movement strategies (quality, devices, timeliness, independence): supine sidelying sit stand supine long sitting
Name: Site: Assessment Skills Observed Performed Becoming A. Gross motor function i. Describe movement strategies (quality, devices, timeliness, independence): supine sidelying sit stand supine long sitting
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
Assessment Form Post Polio Syndrome and Late Effects of Polio
 FULL NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: PHONE NUMBER: CURRENT HOME ADDRESS: EMAIL ADDRESS: THERAPIST: REFERRAL SOURCE: CURRENT GP: NEXT OF KIN: ACC/NHI NUMBER: PATIENT GOALS OF TODAY S ASSESSMENT: MAIN PROBLEMS PATIENT
FULL NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: PHONE NUMBER: CURRENT HOME ADDRESS: EMAIL ADDRESS: THERAPIST: REFERRAL SOURCE: CURRENT GP: NEXT OF KIN: ACC/NHI NUMBER: PATIENT GOALS OF TODAY S ASSESSMENT: MAIN PROBLEMS PATIENT
Home Exercise Program Progression and Components of the LTP Intervention. HEP Activities at Every Session Vital signs monitoring
 Home Exercise Program Progression and Components of the LTP Intervention HEP Activities at Every Session Vital signs monitoring Blood pressure, heart rate, Borg Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) and oxygen
Home Exercise Program Progression and Components of the LTP Intervention HEP Activities at Every Session Vital signs monitoring Blood pressure, heart rate, Borg Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) and oxygen
Overview Functional Training
 Overview Functional Training Exercises with Therapist 1. Sitting 2. Standing up vs. Sitting down 3. Standing 4. Stance phase ( Static and dynamic ) 5. Swing phase 6. Gait Evaluation 7. Walking level ground
Overview Functional Training Exercises with Therapist 1. Sitting 2. Standing up vs. Sitting down 3. Standing 4. Stance phase ( Static and dynamic ) 5. Swing phase 6. Gait Evaluation 7. Walking level ground
Summary Chart 1 2 months
 NEWBORN Physiological flexion provides stability for posture & random movements Neck righting Labyrinthine righting beginning in prone & supine Primary standing reaction Movements limited by available
NEWBORN Physiological flexion provides stability for posture & random movements Neck righting Labyrinthine righting beginning in prone & supine Primary standing reaction Movements limited by available
Snow Angels on Foam Roll
 Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT
 THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
Flexibility. STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius. STRETCH: Standing gastrocnemius. STRETCH: Standing soleus. Adopt a press up position
 STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius Adopt a press up position Rest one knee on mat with the opposite leg straight Maintain a neutral spine position Push through arms to lever ankle into increased dorsiflexion
STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius Adopt a press up position Rest one knee on mat with the opposite leg straight Maintain a neutral spine position Push through arms to lever ankle into increased dorsiflexion
Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017
 Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017 Lisa Westlake www.physicalbest.com Pilates, fitball and physiotherapy blend perfectly to fine tune movement and postural awareness and provide a focus on technique,
Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017 Lisa Westlake www.physicalbest.com Pilates, fitball and physiotherapy blend perfectly to fine tune movement and postural awareness and provide a focus on technique,
Ways to make sure you achieve your handstand
 Ways to make sure you achieve your handstand What no one tells you about Lay Yong Copyright BodyTree GST Copyright 2015 2015 BodyTree GST Pte LtdPte Ltd Introduction The handstand is a challenging and
Ways to make sure you achieve your handstand What no one tells you about Lay Yong Copyright BodyTree GST Copyright 2015 2015 BodyTree GST Pte LtdPte Ltd Introduction The handstand is a challenging and
Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE. By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L
 Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L INTRODUCTION Somatic adaptation is one of the primary functions of the central
Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L INTRODUCTION Somatic adaptation is one of the primary functions of the central
Program. Neurodynamic Integration of neurodynamics into neurorehabilitation focusing on adults with a brain lesion
 Program Neurodynamic Integration of neurodynamics into neurorehabilitation focusing on adults with a brain lesion Part 1: 17 th 21 st of September 2018 Part 2: 22 nd 26 th of October 2018 Course leader
Program Neurodynamic Integration of neurodynamics into neurorehabilitation focusing on adults with a brain lesion Part 1: 17 th 21 st of September 2018 Part 2: 22 nd 26 th of October 2018 Course leader
The Proprioceptive Lumbar Spine & The role of manual therapy. Dr Neil Langridge DClinP MSc MMACP BSc (Hons) Consultant Physiotherapist
 The Proprioceptive Lumbar Spine & The role of manual therapy Dr Neil Langridge DClinP MSc MMACP BSc (Hons) Consultant Physiotherapist What do we do? Manual therapy Pain control Movement Re-educate Muscular
The Proprioceptive Lumbar Spine & The role of manual therapy Dr Neil Langridge DClinP MSc MMACP BSc (Hons) Consultant Physiotherapist What do we do? Manual therapy Pain control Movement Re-educate Muscular
VIPR and Power plate EXERCISE - 1 EXERCISE Fitness Professionals Ltd 2011 Job No. 2968
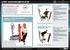 FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
Neuropathology of the Shoulder What can we learn from SCI? BESS 2009
 Neuropathology of the Shoulder What can we learn from SCI? BESS 2009 Sue Paddison Lead Clinical Specialist Physiotherapist Spinal Cord Injury Centre, RNOH,Stanmore Learning objectives Identify neural
Neuropathology of the Shoulder What can we learn from SCI? BESS 2009 Sue Paddison Lead Clinical Specialist Physiotherapist Spinal Cord Injury Centre, RNOH,Stanmore Learning objectives Identify neural
Mobility sequencing!
 Mobility sequencing When practicing joint mobility drills we have the opportunity to improve our movement. The muscles associated with the joint being mobilised as well as the joint itself will improve
Mobility sequencing When practicing joint mobility drills we have the opportunity to improve our movement. The muscles associated with the joint being mobilised as well as the joint itself will improve
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization
 Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Bench Press (free weights) Pullover (dumbbell) Prone-grip pull-up (tower/assisted platform
 When exercising always incorporate a warm-up for at least 5 minutes. Typically a warm-up should be a whole body exercise i.e. jumping jacks, jogging, calisthenics, etc The repetitions represent how much
When exercising always incorporate a warm-up for at least 5 minutes. Typically a warm-up should be a whole body exercise i.e. jumping jacks, jogging, calisthenics, etc The repetitions represent how much
Case History in The Bobath Concept in Adult Neurology
 Case History in The Bobath Concept in Adult Neurology 동의의료원재활치료센터 서성우. 김경모 About the Author School of Physiotherapy, New castle-upon-tyne, England, in 1978 Trained as a Bobath Instructor with BBTA Bente
Case History in The Bobath Concept in Adult Neurology 동의의료원재활치료센터 서성우. 김경모 About the Author School of Physiotherapy, New castle-upon-tyne, England, in 1978 Trained as a Bobath Instructor with BBTA Bente
Sensory. Physical. Cognitive. Language 4/12/2016 LEARNING OBJECTIVES AT ASSESSMENT: SKILLS EVALUATION OVERVIEW
 ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT: SEATING AND POSITIONING FOR ACCESS Anne Cronin 2016 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the principles related to assessment and intervention in assistive technology (AT) service
ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT: SEATING AND POSITIONING FOR ACCESS Anne Cronin 2016 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the principles related to assessment and intervention in assistive technology (AT) service
Introduction of mat activity 국립재활원물리치료실장영민
 Introduction of mat activity 국립재활원물리치료실장영민 Content 1. Why do mat activity? 2. Supine progression 3. Prone progression 4. Theraputic mat activity Why do mat activity? 1. Wide BOS & lower GOG: security and
Introduction of mat activity 국립재활원물리치료실장영민 Content 1. Why do mat activity? 2. Supine progression 3. Prone progression 4. Theraputic mat activity Why do mat activity? 1. Wide BOS & lower GOG: security and
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual
 Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Exploring the Rotator Cuff
 Exploring the Rotator Cuff Improving one s performance in sports and daily activity is a factor of neuromuscular efficiency and metabolic enhancements. To attain proficiency, reaction force must be effectively
Exploring the Rotator Cuff Improving one s performance in sports and daily activity is a factor of neuromuscular efficiency and metabolic enhancements. To attain proficiency, reaction force must be effectively
Berg Balance Scale. Name: Date of Test:.
 Berg Balance Scale Name: Date of Test:. 1. Sit to Stand Instructions: Please stand up. Try not to use your hands for support ( ) 0: Needs moderate or maximal assistance to stand ( ) 1: Needs minimal assistance
Berg Balance Scale Name: Date of Test:. 1. Sit to Stand Instructions: Please stand up. Try not to use your hands for support ( ) 0: Needs moderate or maximal assistance to stand ( ) 1: Needs minimal assistance
Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses?
 Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses? Basics of Gait Analysis Gait cycle: heel strike to subsequent heel strike,
Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses? Basics of Gait Analysis Gait cycle: heel strike to subsequent heel strike,
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire
 Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
Evaluating the Athlete Questionnaire Prior to developing the strength and conditioning training plan the coach should first evaluate factors from the athlete s questionnaire that may impact the strength
THE STRATEGIES FOR CONNECTION IN CHILDREN WITH CP
 2015 한국보바스소아학술대회 THE STRATEGIES FOR CONNECTION IN CHILDREN WITH CP KYOUNG SOOK PARK INSTRUCTOR THE BOBATH CONCEPT The NDT/Bobath Concept offers a forward looking interdisciplinary problem solving approach
2015 한국보바스소아학술대회 THE STRATEGIES FOR CONNECTION IN CHILDREN WITH CP KYOUNG SOOK PARK INSTRUCTOR THE BOBATH CONCEPT The NDT/Bobath Concept offers a forward looking interdisciplinary problem solving approach
Issues in Cerebral Palsy Part 1: Physical Handling Assessment by Christine A. Nelson, Ph.D., OTR with contribution by W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR
 The following article is granted 1 Contact Hour/ equivalent to.15 CEU/equivalent to 1.25 PDUs. To receive CEU credit you must complete the CEU Exam after reading the article. Close the PDF file after reading
The following article is granted 1 Contact Hour/ equivalent to.15 CEU/equivalent to 1.25 PDUs. To receive CEU credit you must complete the CEU Exam after reading the article. Close the PDF file after reading
copyrighted material by PRO-ED, Inc.
 Contents Preparation for Functional Sitting Partial Pull to Sit.......................................................... 2 Pull to Sit................................................................ 3
Contents Preparation for Functional Sitting Partial Pull to Sit.......................................................... 2 Pull to Sit................................................................ 3
Considerations in the selection of patients for Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy
 Considerations in the selection of patients for Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy The best and the worst surgery I have ever been associated with. A therapist's perspective Dean Morgan, PT Disclosure Statement
Considerations in the selection of patients for Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy The best and the worst surgery I have ever been associated with. A therapist's perspective Dean Morgan, PT Disclosure Statement
Building Better Balance
 Building Better Balance The Effects of MS on Balance Individuals with MS experience a decline in their balance due to various MS related impairments. Some of these impairments can be improved with exercise
Building Better Balance The Effects of MS on Balance Individuals with MS experience a decline in their balance due to various MS related impairments. Some of these impairments can be improved with exercise
Issues in Cerebral Palsy Part 2: Physical Handling Treatment by Christine A. Nelson, Ph.D., OTR with contribution by W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR
 The following article is granted 1 Contact Hour/ equivalent to.15 CEU/equivalent to 1.25 PDUs. To receive CEU credit you must complete the CEU Exam after reading the article. Close the PDF file after reading
The following article is granted 1 Contact Hour/ equivalent to.15 CEU/equivalent to 1.25 PDUs. To receive CEU credit you must complete the CEU Exam after reading the article. Close the PDF file after reading
DOES IMPROVING THE STRENGTH OF THE KINETIC CHAIN OF STANCE RESULT IN INCREASED GAIT SPEED? (First published by Synapse Autumn/Winter 2013)
 DOES IMPROVING THE STRENGTH OF THE KINETIC CHAIN OF STANCE RESULT IN INCREASED GAIT SPEED? (First published by Synapse Autumn/Winter 2013) Michael Walsh 1 Introduction One of the main impairments after
DOES IMPROVING THE STRENGTH OF THE KINETIC CHAIN OF STANCE RESULT IN INCREASED GAIT SPEED? (First published by Synapse Autumn/Winter 2013) Michael Walsh 1 Introduction One of the main impairments after
SUBMARINE SERIES - LEVEL 3
 SUBMARINE SERIES - LEVEL 3 Navy Operational Fitness Series submarine Series navy operational fitness 3 Simple Steps to Get Started! Step : Choose a Level This card series progresses you through 3 levels
SUBMARINE SERIES - LEVEL 3 Navy Operational Fitness Series submarine Series navy operational fitness 3 Simple Steps to Get Started! Step : Choose a Level This card series progresses you through 3 levels
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players.
 Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Chapter 8 8/23/2016. Body Mechanics and Patient Mobility. Introduction to Body Mechanics and Patient Mobility
 Chapter 8 Body Mechanics and Patient Mobility All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction to Body Mechanics and Patient Mobility
Chapter 8 Body Mechanics and Patient Mobility All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction to Body Mechanics and Patient Mobility
GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
GENERAL EXERCISES KNEE BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only are not to be
A B C. Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow
 Session Two A B C Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow Will be based on your group of participants. Ensure that your lesson plan content links to objectives What is the reason for prep?
Session Two A B C Breathing Concentration Control Centring Precision Flow Will be based on your group of participants. Ensure that your lesson plan content links to objectives What is the reason for prep?
Standing Shoulder Internal Rotation with Anchored Resistance. Shoulder External Rotation Reactive Isometrics
 Standing Shoulder Row with Anchored Resistance Begin standing upright, holding both ends of a resistance band that is anchored in front of you at chest height, with your palms facing inward. Pull your
Standing Shoulder Row with Anchored Resistance Begin standing upright, holding both ends of a resistance band that is anchored in front of you at chest height, with your palms facing inward. Pull your
Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author]
![Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author] Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author]](/thumbs/89/101009847.jpg) Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author] Overall description Programme duration: 2 years/8 quarters Weekly frequency: 1 group session
Appendix 1: Description of the Ossébo fall and injury prevention exercise programme [posted as supplied by author] Overall description Programme duration: 2 years/8 quarters Weekly frequency: 1 group session
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises
 Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP. Sets Reps Weight Notes DB ALTERNATING BICEP CURLS WITH TWIST
 Jump Start Week # DAY WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP DUMBBELL STIFF LEG DEAD LIFT ***This Week -we are doing circuits. - sets of reps moving from exercise A-B-C-D-E-F and then back round again to A. So A- reps,
Jump Start Week # DAY WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP DUMBBELL STIFF LEG DEAD LIFT ***This Week -we are doing circuits. - sets of reps moving from exercise A-B-C-D-E-F and then back round again to A. So A- reps,
ORTHOPEDIC PHYSIOTHERAPY EVALUATION FORM. Age: Gender: M/F IP/OP
 ORTHOPEDIC PHYSIOTHERAPY EVALUATION FORM NAME: DATE: Age: Gender: M/F IP/OP Occupation: Referred by: Address: Phone Number: Registration Number: Civil Status: Diagnosis: Chief Complaints: Past Medical
ORTHOPEDIC PHYSIOTHERAPY EVALUATION FORM NAME: DATE: Age: Gender: M/F IP/OP Occupation: Referred by: Address: Phone Number: Registration Number: Civil Status: Diagnosis: Chief Complaints: Past Medical
Lower Extremity Physical Performance Testing. Return to Function (Level I): Core Stability
 Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
BIOFEEDBACK AND HIPPOTHERAPY, FROM THE BOBATHCONCEPT, AS. HYPERTHERAPY WITH CONGENITAL HEMIPARESIS. (Daniël BENS, Belgium)
 BIOFEEDBACK AND HIPPOTHERAPY, FROM THE BOBATHCONCEPT, AS HYPERTHERAPY WITH CONGENITAL HEMIPARESIS. (Daniël BENS, Belgium) Many techniques of treatment for the child with cerebral palsy have developed over
BIOFEEDBACK AND HIPPOTHERAPY, FROM THE BOBATHCONCEPT, AS HYPERTHERAPY WITH CONGENITAL HEMIPARESIS. (Daniël BENS, Belgium) Many techniques of treatment for the child with cerebral palsy have developed over
ACTIVE AGING.
 Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Coaching the Injury Prone Athlete
 Coaching the Injury Prone Athlete Rob Thickpenny National Coach Mentor - Physical Preparation High Knee Drill Foot cocked, heel to butt, knee high, step over opposite knee, tall hips, extend hips in drive,
Coaching the Injury Prone Athlete Rob Thickpenny National Coach Mentor - Physical Preparation High Knee Drill Foot cocked, heel to butt, knee high, step over opposite knee, tall hips, extend hips in drive,
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Throwing Athlete Rehabilitation. Brett Schulz LAT/CMSS Sport and Spine Physical Therapy
 Throwing Athlete Rehabilitation Brett Schulz LAT/CMSS Sport and Spine Physical Therapy Disclosure No conflicts to disclose Throwing Athlete Dilemma The shoulder must have enough range of motion to allow
Throwing Athlete Rehabilitation Brett Schulz LAT/CMSS Sport and Spine Physical Therapy Disclosure No conflicts to disclose Throwing Athlete Dilemma The shoulder must have enough range of motion to allow
Pilates for golfers. SoonHong Min CTTC Seoul, Korea
 Pilates for golfers SoonHong Min CTTC 2015.6 Seoul, Korea Abstract Whether twisting the body on a drive or leaning over to pick up a ball, golfers constantly torqueing their bodies. Golf also requires
Pilates for golfers SoonHong Min CTTC 2015.6 Seoul, Korea Abstract Whether twisting the body on a drive or leaning over to pick up a ball, golfers constantly torqueing their bodies. Golf also requires
Bone-Patellar tendon-bone Autograft ACL Recon. Date of Surgery: Patient Name:
 Dx: o Right o Left Bone-Patellar tendon-bone Autograft ACL Recon Date of Surgery: Patient Name: PT/OT: Please evaluate and treat. Follow attached protocol. 2-3 x per week x 6 weeks. Signature/Date: GENERAL
Dx: o Right o Left Bone-Patellar tendon-bone Autograft ACL Recon Date of Surgery: Patient Name: PT/OT: Please evaluate and treat. Follow attached protocol. 2-3 x per week x 6 weeks. Signature/Date: GENERAL
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 th edition
 ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 th edition Chapter 7: Functional Assessments: Posture, Movement, Core, Balance, and Flexibility 1 Learning Objectives This session, which is based on Chapter 7 of the ACE
ACE Personal Trainer Manual, 4 th edition Chapter 7: Functional Assessments: Posture, Movement, Core, Balance, and Flexibility 1 Learning Objectives This session, which is based on Chapter 7 of the ACE
Daily. Workout Workout Focus: Bodyweight strength, power, speed, mobility MOBILITY WARM UP. Exercise Descriptions.
 Workout 5.18.18 Workout Focus: Bodyweight strength, power, speed, mobility Pelvic Tilt Lateral Pelvic Tilt Hip Circles Lateral Spine Glide Spinal Flexion and Extension Lateral Spinal Flexion Neck Juts
Workout 5.18.18 Workout Focus: Bodyweight strength, power, speed, mobility Pelvic Tilt Lateral Pelvic Tilt Hip Circles Lateral Spine Glide Spinal Flexion and Extension Lateral Spinal Flexion Neck Juts
Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed.
 Session 1 Details Cardio - Choose one of the following Elliptical Slow to Moderate Cardio Intervals (1) Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed. Treadmill
Session 1 Details Cardio - Choose one of the following Elliptical Slow to Moderate Cardio Intervals (1) Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed. Treadmill
TPW 's Upper Back Menu
 TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand)
 MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Functional Movement Test. Deep Squat
 Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
LEAPS (Locomotor Experience Applied Post-Stroke) Home Exercise Program (HEP) Therapist Intervention Manual
 LEAPS (Locomotor Experience Applied Post-Stroke) Home Exercise Program (HEP) Therapist Intervention Manual Brooks Rehabilitation Center, Jacksonville, FL Florida Hospital, Orlando, FL Long Beach Memorial
LEAPS (Locomotor Experience Applied Post-Stroke) Home Exercise Program (HEP) Therapist Intervention Manual Brooks Rehabilitation Center, Jacksonville, FL Florida Hospital, Orlando, FL Long Beach Memorial
2017 COS ANNUAL MEETING AND EXHIBITION HOME EXERCISES
 UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
Masters Swimming Dryland Training Program. November-December
 Masters Swimming Dryland Training Program November-December Staggered Stance High Kneeling Chop with Theraband (1 minute each side) Engage core. Pull Theraband down toward knee that is on the ground keeping
Masters Swimming Dryland Training Program November-December Staggered Stance High Kneeling Chop with Theraband (1 minute each side) Engage core. Pull Theraband down toward knee that is on the ground keeping
Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year
 Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year 1. Overview the most common age-related risk factors
Presented by Maureen Hagan BScPT (Physiotherapist), BA PE ACE, Can-Fit-Pro Certified 2006 IDEA Fitness Instructor & 1998 Program Director of the Year 1. Overview the most common age-related risk factors
Exercise Therapy for Patients with Knee OA Knee Exercise Protocol Knee Home Exercise Programme
 Chapter FOUR Exercise Therapy for Patients with Knee OA Knee Exercise Protocol Knee Home Exercise Programme Chris Higgs Cathy Chapple Daniel Pinto J. Haxby Abbott 99 n n 100 General Guidelines Knee Exercise
Chapter FOUR Exercise Therapy for Patients with Knee OA Knee Exercise Protocol Knee Home Exercise Programme Chris Higgs Cathy Chapple Daniel Pinto J. Haxby Abbott 99 n n 100 General Guidelines Knee Exercise
ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY REHABILITATION PROTOCOL MENISCUS REPAIR
 GENERAL GUIDELINES ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY REHABILITATION PROTOCOL MENISCUS REPAIR - The local anesthetic (similar to novacaine) in your knee lasts 6-12 hours - Start taking the pain medication as soon
GENERAL GUIDELINES ARTHROSCOPIC KNEE SURGERY REHABILITATION PROTOCOL MENISCUS REPAIR - The local anesthetic (similar to novacaine) in your knee lasts 6-12 hours - Start taking the pain medication as soon
Multi-Segmental Rotation Corrective Exercises
 Multi-Segmental Rotation Corrective Exercises Side Lying Thoracic Rotation keep one knee on a folded pillow or small ball with the hip flexed at least 90 degrees. Place the hand on the stomach/ribs and
Multi-Segmental Rotation Corrective Exercises Side Lying Thoracic Rotation keep one knee on a folded pillow or small ball with the hip flexed at least 90 degrees. Place the hand on the stomach/ribs and
EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION FOR A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE
 EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION FOR A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE Benefits of Regular Exercise Improve musculoskeletal health Increase strength Activities of daily living, quality of life Increase endurance Improve functional
EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION FOR A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE Benefits of Regular Exercise Improve musculoskeletal health Increase strength Activities of daily living, quality of life Increase endurance Improve functional
Scapular Protraction in Sitting
 9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
REMINDER. an exercise program. Senior Fitness Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning
 Functional Forever: Exercise for Independent Living REMINDER Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns. What
Functional Forever: Exercise for Independent Living REMINDER Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns. What
Spinal Alignment and corrective exercise: The importance of posture in the frailer older adult.
 Later Life Training 2013 Conference Spinal Alignment and corrective exercise: The importance of posture in the frailer older adult. PRESENTED BY SHEILA DONE We are all aware why posture and muscle balance
Later Life Training 2013 Conference Spinal Alignment and corrective exercise: The importance of posture in the frailer older adult. PRESENTED BY SHEILA DONE We are all aware why posture and muscle balance
P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine:
 P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: Circuit Training Exercises Side Deltoid Raise w/ band Triceps Extensions Ball Pushups: Ball Squat: (hold dumbbells on your side
P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: P3 Week One - M-W-F Workout Routine: Circuit Training Exercises Side Deltoid Raise w/ band Triceps Extensions Ball Pushups: Ball Squat: (hold dumbbells on your side
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology ROM & GONIOMETRY
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology & GONIOMETRY MSAK201-II Session 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology & GONIOMETRY MSAK201-II Session 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will
Pre and Post pool sessions. County Camps
 Pre and Post pool sessions County Camps Key themes of the session PREPOOL Health and safety Environmental factors Swimmers clothing Why warm up? RMAP Which exercises? POST POOL Why do it? Good technique
Pre and Post pool sessions County Camps Key themes of the session PREPOOL Health and safety Environmental factors Swimmers clothing Why warm up? RMAP Which exercises? POST POOL Why do it? Good technique
SPT1 Module 1 Questions
 SPT1 Module 1 Questions Clinical Reasoning 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect A. Diagnostic reasoning is the formation of a diagnosis based purely on physical disability and impairment.
SPT1 Module 1 Questions Clinical Reasoning 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect A. Diagnostic reasoning is the formation of a diagnosis based purely on physical disability and impairment.
Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol
 Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol GENERAL GUIDELINES - Use the cryotherapy cuff continuously for the first 72 hours, then as needed thereafter - Ensure that the cuff never contacts the skin directly
Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol GENERAL GUIDELINES - Use the cryotherapy cuff continuously for the first 72 hours, then as needed thereafter - Ensure that the cuff never contacts the skin directly
Southern Sports & Orthopaedics
 Knee conditioning program This knee conditioning program is designed to help you rehabilitate from your knee injury. In some cases, the program is being used as pre-habilitation, that is strengthening
Knee conditioning program This knee conditioning program is designed to help you rehabilitate from your knee injury. In some cases, the program is being used as pre-habilitation, that is strengthening
Respiration & Trunk control The Great Connection. Brief Review of Normal Development of the Rib Cage
 Respiration & Trunk control The Great Connection. are part of a complex combination of interactive systems. Muscles of respiration are part of the musculature of dynamic postural control. First 3 Years
Respiration & Trunk control The Great Connection. are part of a complex combination of interactive systems. Muscles of respiration are part of the musculature of dynamic postural control. First 3 Years
Module Goals. An Introduction to Seating and Positioning for Individuals Who Use Assistive Technology. To answer the following questions:
 An Introduction to Seating and Positioning for Individuals Who Use Assistive Technology Aileen Costigan, MSc-OT Communication Sciences and Disorders The Pennsylvania State University fac3@psu.edu Module
An Introduction to Seating and Positioning for Individuals Who Use Assistive Technology Aileen Costigan, MSc-OT Communication Sciences and Disorders The Pennsylvania State University fac3@psu.edu Module
Role Of The Fitness Professional. Causes of Fitness Related Injuries. The Assessments. Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach 2/9/2016
 Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach Role Of The Fitness Professional Fitness professionals must assess clientele, but need to understand the difference between medical diagnosis vs fitness limitations.
Screening & Assessing: A Holistic Approach Role Of The Fitness Professional Fitness professionals must assess clientele, but need to understand the difference between medical diagnosis vs fitness limitations.
ANTERIOR CRUCTIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCION/REPAIR AND MENISCUS REPAIR REHABILITATION PROTOCOL
 ANTERIOR CRUCTIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCION/REPAIR AND MENISCUS REPAIR REHABILITATION PROTOCOL GENERAL GUIDELINES - The local anesthetic (similar to novacaine) in your
ANTERIOR CRUCTIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCION/REPAIR AND MENISCUS REPAIR REHABILITATION PROTOCOL GENERAL GUIDELINES - The local anesthetic (similar to novacaine) in your
Viking Strong Exercise & Stretch Ebook
 Viking Strong Exercise & Stretch Ebook Lower Body Exercises. 2 Abductor. Training the abductors and adductors improves muscular imbalances, strengthens your core and prevents injury. We've all seen the
Viking Strong Exercise & Stretch Ebook Lower Body Exercises. 2 Abductor. Training the abductors and adductors improves muscular imbalances, strengthens your core and prevents injury. We've all seen the
ETS EXERCISE SHEETS EXPLAINED
 ETS EXERCISE SHEETS EXPLAINED Exercises 4pt kneeling Supermans Extend opposite arm/leg whilst maintaining neutral spine. Hips are to remain parallel to the floor during movement. Core. Also assists in
ETS EXERCISE SHEETS EXPLAINED Exercises 4pt kneeling Supermans Extend opposite arm/leg whilst maintaining neutral spine. Hips are to remain parallel to the floor during movement. Core. Also assists in
Older Adult Advanced
 Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
IFAST Assessment. Name: Date: Sport: Review Health Risk Assessment on initial consult form. List Client Goals (what brings you here?
 IFAST Assessment Name: Date: Sport: Review Health Risk Assessment on initial consult form List Client Goals (what brings you here?) Cardiovascular Measurements Blood Pressure Resting Heart Rate Body Composition
IFAST Assessment Name: Date: Sport: Review Health Risk Assessment on initial consult form List Client Goals (what brings you here?) Cardiovascular Measurements Blood Pressure Resting Heart Rate Body Composition
Preventing Shoulder Pain
 International Clinical Educators, INC. By Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L About the Author & Presenter Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L, is an internationally recognized leader in educational programs developed for health care
International Clinical Educators, INC. By Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L About the Author & Presenter Jan Davis, MS, OTR/L, is an internationally recognized leader in educational programs developed for health care
Physical Sense Activation Programme
 Flexion extension exercises for neck and upper back Sitting on stool Arms hanging by side Bend neck and upper back Breathe out Extend your neck and upper back Lift chest to ceiling Squeeze shoulder blades
Flexion extension exercises for neck and upper back Sitting on stool Arms hanging by side Bend neck and upper back Breathe out Extend your neck and upper back Lift chest to ceiling Squeeze shoulder blades
Postural instability Hypokinesia Rigidity Tremor Forward flexed posture. pain million people 50+ years old 10 most populated countries
 4.1-4.6 million people 50+ years old 10 most populated countries Cyndi Robinson, PT, PhD University of Washington Seattle, Washington, USA Progressive neurodegenerative disorder Selective neuronal loss
4.1-4.6 million people 50+ years old 10 most populated countries Cyndi Robinson, PT, PhD University of Washington Seattle, Washington, USA Progressive neurodegenerative disorder Selective neuronal loss
Mind-body Balance Training for Special Populations
 ACE Pro Source Mind-body Balance Training for Special Populations By Elizabeth Kovar Individuals who are balance challenged, such as those with Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis, require a method
ACE Pro Source Mind-body Balance Training for Special Populations By Elizabeth Kovar Individuals who are balance challenged, such as those with Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis, require a method
PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE
 PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE Published by: Physiotherapist RUKIYE KORUCU Istanbul, Turkey Sep 2007 English translation by R.Schoenbohm WHY PHYSIOTHERAPY? Preserve the breathing capacity Strengthen the chewing
PHYSIOTHERAPY IN SSPE Published by: Physiotherapist RUKIYE KORUCU Istanbul, Turkey Sep 2007 English translation by R.Schoenbohm WHY PHYSIOTHERAPY? Preserve the breathing capacity Strengthen the chewing
