Grasp and pinch strengths are
|
|
|
- Susan Bradford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pinch and Grasp Strength: Standardization of TerDlinology and Protocol (hand, prehension, tests) Roger O. Smith Margie Wadlington Benge We implemented a tridirectional survey to begin the standardization process for grasp and pinch and to improve the communication between rehabilitation professionals who assess hand strength. We surveyed the literature, occupational therapy clinics across the country, and occupational therapy educational programs. Our results reveal the current use, teachings, and recommendations of pinch and grasp strength measurement. The results confirm that the standardization ofgrasp and pinch are vitally needed. Specific recommendations to continue this standardization process are recommended. Grasp and pinch strengths are commonly measured in hand function evaluations. They have achieved a high degree of face validity because of the objectivity of measurement dev' :es, the relative simplicity of administration, and the establishment of normative data. However, grasp and pinch are not standardized and differ widely from clinic to clinic. This significantly detracts from the reliability and validity of using grasp and pinch strength tests. This study determines the consistency of terminology, equipment, and protocols used by occupational therapists in testing pinch and grasp Literature Review The literature reveals that many different protocols are available for evaluating grasp and pinch strength. For example, in 1970, Kellor and others (I) published norms for grasp and pinch, which were la tel' pu bl ished by Sister Kenny Institute (2). The protocols on which Kellor's norms are based include giving each subject two trials for grasp and then recording the highest measurement. One trial was given for pinch, and the highest measurement was recorded. Subjects could rest their forearms on the table, but could not allow the dynamometer to touch anything. Otherwise, arms could be positioned to comfort, with elbows either flexed or extended. Her terminology for pinch testing includes three-point, lateral, and palmar. In her book on physical disability, Trombly (3) uses the norms from Kellor's (I, 2) article. Their protocols for testing are basically the same; however, they are more specific in that they recommend two to three minutes of rest in between dynamometer readings. Their terminology includes tip, palmar, and lateral. The American Society for Surgery of the Hand recommends three trials for grasp and pinch (4). All three trials are recorded, along with the calculated percentage relative to pretreatment value and to Roger O. Smith, MOT, OTR, is a lecturer at the University of Wisconsin-iVladison. At the time of the study, he was Supervisor, Occupatwnal Therapy DepaTtment, and Margie Wadlington Benge, OTR, was a staff therapist; both at Salem Hospital, Salem, OR. Benge recently relocated to Dayton, OH. The American Journal ofoccupational Therapy 531
2 the other hand. Jamar dynamometer position is generally kept at the second notch, but no other instructions regarding patient positioning are provided. Pinch terminology recorded is lateral and tip. The book Rehabilitation of the Hand (5) refers to grip and pinch testing in several chapters. In chapter 8, Swanson and others recommend three trials for both tests. TheJamar dynamometer handle is spaced at 6 cm, and the extremity is not supported. Pinch terminology includes chuck pinch (threedigit pinch), pulp pinch with separate fingers, and lateral pinch. Chapter 8 also documents the use of normative data developed by Swanson and others. In chapter 5, Fess (6) recommends that three trials for both pinch and grasp testing be done and that their average be recorded. The dynamometer handle is kept at the second notch. Pinches tested include key and tip. Instructions for the Jamar dynamometer (7) do not provide any specific protocols or norms. However, they do hint at using two trials with five minutes of rest in between. Melvin (8) specifically addressed protocols for the arthritis population. She stated that every method conceivable for testing grasp has been suggested, but she recommends a specific protocol. She advocates using the sphygnomometer rather than the dynamometer and suggests three trials with a specific positioning protocol. All trials and the average are reported. A variety of grasp and pinch measurement devices are available from rehabilitation equipment distributors (9, 10), and research projects have designed other specialty meters (11-14). The literature also reveals the existence of numerous sources of normative data (2, 5, 15-18). The diverse use of terminology is also evident in the literature. AOTA's book Sample Forms for Occupational Therapy (19) shows the common use ofdifferent names for pinch. In this book, four prominent hospitals list six different names for the types of pinch they measured. The literature shows a wide variety of procedural differences regarding number of trials given, scores documented, measurement devices, normative data sources. and terminology usage. Furthermore, most references do not detail any protocol used for body placement or equipment calibration. Written sources provide little guidance in selecting the most appropriate pinch and grasp testing methods. Methods We sent a survey questionnaire to 510 occupational therapy clinics and 115 occupational therapy schools in the United States. Questionnaires were sent to all clinics listed in AOTA's 1975 Facilities Directory (20) under the categories of general medicine and surgery or physical disabilities. All schools listed in AOTA's 1983 brochure on educational programs (21) were included. The rate of return was greater than 30%. The survey included the following four specific sections: a) terminology, b) equipment, c) protocol and d) rationale. Results Demographics Of the 195 valid questionnaires returned, 31 originated in educational programs and 164 in physical disabilities clinics. from nonphysical disability occupational therapy clinical settings were omitted from the analysis. Thirty-eight states were represented, with the majority of the respondents being from California (10.8%), Texas (8.7%), New York (7.7%), Wisconsin (7.7%), and Ohio (6.7%). Clinics identified themselves as serving a general hospital (51.8%), a rehabilitation facility (39%), and a hand clinic (14.4%). The schools represented large and small occupational therapy programs and had a mean of 34 graduates per year. Responding clinics' staffing averaged 7.9 positions. with a range of 1-43 therapists. The average clinic hosted 5.8 affiliating students per year. Terminology Respondents were asked to identify pinch diagrams according to the terminology used in their setting. Table 1 shows diagram 1, for which 29 variations of terminology were listed, and gives the higher percentage responses. The many terms describing diagram 1 varied greatly from the higher percentage responses. They included a) radial digital, b) cylindrical radial palmar, and c) palmar tripod. Table 2 depicts diagram 2, for which 46 variations of terminology were listed, and gives the higher percentage responses. Varied responses included a) true pinch, b) neat tip prehension, and c) fingertip two point. Table 3 portrays diagram 3, for which 48 variations of terminology were suggested, and gives the higher percentage responses. Variations included a) terminal prehension with fingerpads, b) inferior radial, and c) superior forefinger. Seven different terms described diagram 4. Table 4 shows diagram 4 and gives the higher percentage 532 August 1985, Volume 39, Number 8
3 responses. Varied responses included a) scissor, b) inferior, and c) pad to side. Besides giving names to pinch, respondents tested different com- Table 1 Diagram 1 and the Most Common Identification Percent When Used in Conjunction Other Term Percent Terms' Three jaw or three jaw chuck Three point Palmar * Many settings responded with more than one name for this type of pinch. Table 2 Diagram 2 and the Most Common Identification Tip Tip to tip Fingertip binations of pinch. Table 5 reports the percentage of respondents standardly testing the pinch portrayed in the four diagrams. Grasp Equipment Surveyed settings listed the use of nine different brands of dynamometers. Approximately 40% of the respondents indicated they used more than one type of meter. Over 79% stated that the Jamar dynamometer was the meter most commonly used in their settings. Most dynamometers were purchased from Preston (31.3%), Fred Sammons (28.7%), and Abbey Medical (5.6%). The measurement scales used were pounds (76.9%), both pounds and kilograms (10.5%), and only kilograms (4.6%). Over two dozen sources of normative data were identified. Many respondents mentioned using more than one source. More than 54.2% of the respondents use norms from Trombly and Scott (3), Sister Kenny (2), or Kellor (1), all of which originated with Kellor. Grasp Protocol The majority of respondents indicated that they used a consistent strength testing protocol. However, 38.4% stated that thay had inconsistent use of their protocol or had none at all. Over half of the respondents stated that patient comfort was used to determine hand fit of the dynamometer. No other major percentage response was noted regarding specifications of hand fit to the grasp meter. However, some settings listed use of only certain notches of the dynamometer, with no consistency between the settings as to which notch. Other respondents explained that their determination of hand fit was based on Table 3 Diagram 3 and the Most Common Identification Palmar Pad to pad Two point Table 4 Diagram 4 and the Most Common Identification Lateral Key Table 5 Percentage of Pinches Used in Standardized Testing Diagram Diagram Diagram Diagram Other 9.2 the muscle groups they planned to evaluate. Neutral forearm placement was used by 80.5% of the settings 8.7% used patient comfort as a guide to forearm placement. Over half of the respondents said that elbows should be flexed 90 for grasp strength measurement- The American Journal ojoccupational Therapy 533
4 32.4% of these did not support the elbow and 20.5% did. Some respondents (14.1 %) said they tested with the elbow extended, and the same percentage said they used patient comfort to determine arm placement. The majority of hand strength testing was performed sitting (80.5%), some during standing (1.6%), and some without any particular instructions (14.7%). The number of grasp trials used was also varied: three trials (61.9%), two trials (14.3%). one trial (13.8%), or a combination of the above (9.5%). The strength score therapists documented varied: some documented the mean (44.4%), some documented the highest score (35.4%), and some documented multiple figures (10%). The length of rest periods in between trials was also inconsistent as follows: Some provided rest by alternating hands (35.9%), some had no protocol for rest periods (32.8%), and some listed a specific resting time frame varying from 2 to 180 seconds between trials (13.1%). Verbalizations used by the settings during testing also varied as follows: patients verbalized only instructions (34.7%), patients received encouragement through coaching (64.2%). Pinch Equipment and Protocol Pinch equipment and protocol were generally similar to grasp. Ten different pinch gauges were used with over 50% of respondents using a pinch gauge measuring 0 30 Ibs. Less than 5% of the respondents listed variations of pinch testing protocols from grasp protocols. Rationale A significant number of respondents indicated that they had no particular reason for using the specific terminology (35%), equipment (35%), or protocols (27.4%) that they used. Demographic Analysis were additionally analyzed in their relationships to demographic characteristics. Independent variables included regions, respondent types, and the existence of protocols. No important regional differences were discovered, nor were any differences noted between respondents who used protocols consistently and those who did not. However, whether a respondent was a clinic or a school, did result in differences. "Eyeballing" the data showed that generally educational programs taught a wider assortment of terms than were used by clinics. Normative data used by schools also were more varied, and a high percentage of norms were from textbooks. In contrast, clinics tended to use normative data from clinical settings. Discussion The measurement of grasp and pinch strength is in desperate need of standardized terminology and protocols. The poor continuity in grasp and pinch terminology and protocol has severe implications for the quality of occupational therapy assessment. In a clinic, this inconsistency reduces the reliability of testing between therapists. When patient records are transferred between clinics, inconsistent terms and protocols make interpretation of scores unreliable and consequently invalid. Additionally, it is becoming more frequent for hand occupational therapists to provide legal testimony. The consequences of such testimony can reach far: The professional interpretation of an "objective" occupational therapy test can alter the course of a patient's life. Our literature review, combined with survey information from occupational therapy schools and clinics nationwide, suggests strongly that specific actions are needed to standardize the methods by which therapists measure pinch and grasp strength. Dozens of terms were used to name just four diagrams of pinch. This clearly indicates that therapists throughout the country do not use or teach consistent terminology. The survey reveals not only that multiple normative data sources are used by respondents but also that a large proportion are used incorrectly. There is a significant discrepancy between the n um ber of respondents using Kellor's (1,2) normative data and the number of respondents using the protocol she used in collecting the data. More than 54.2% of respondents use norms originating from Kellor, who used the highest score of two trials. In contrast, 75% of the survey respondents use one or three trials, and only 35.4% document the highest score. In fact, many protocols overtly suggest using Kellor's norms but recommend conflicting protocols despite Kellor's specific instructions to the contrary. Furthermore, Kellor's norms are based on using a Jamar dynamometer; in practice, however, her norms are used with various types of dynamometers. The survey information points out that large numbers of schools and clinics do not have consistent protocols. Those that do have protocols differ significantly from each other. The co) lected in formation enables us to make several recommendations. First, more research is 534 August 1985, Volume 39, Number 8
5 needed to specify the advantages and disadvantages of various aspects of types of equipment and protocols. We need more empirical studies on appropriate protocols for grasp and pinch strength measurement. Second, AOTA and national rehabilitation associations need to facilitate the acquisition of the most advantageous terminology, equipment, and protocols. When adequate guidelines for pinch and grasp protocol are obtained, formal association recommendations should be adopted. Third, occupational therapy educational programs need to teach specific protocols to their students, along with the rationale for their use. This would replace the smorgasbord of information currently presen ted to students. Finally, we recommend the consideration of guidelines for pinch terminology and protocols. Because of the obvious lack of logic in pinch terminology, which results in countless numbers of actively used terms, we suggest an anatomically descriptive base for pinch terminology. The foilo\\'ing exemplifies such a descriptive and consistent base for terms: tlao-point tip pinch, three-point tip pinch, two-point pad pinch, three-point pad pinch, and lateral pinch. We do, however, acknowledge the current use of pinch terms. Thus, adopting the frequently used terms three-jaw chuck, tip pinch, and lateral pinch might be the second best choice. We abstain from recommending any specific protocol for testing as long as we do not have more data supporting certain methods. However, we strongly encourage the consistent application of the exact protocols used in obtaining t.he normative data when normat.ive dat.a charts are used. ACKNOWLEDGME TS The authors th~nk GU)' Benge, Herimina Klaus, Patti Peterson. Georgia fmhoff Smith. the Occupational Therapy Association of Oregon. Brvan Sutherland, anclthe study respondents, This study \I'as pres("j1(ed in November 1983 at the 60th Annual Session of the American Congress of Rehabilitation Medicine and the 45th Annual Assembk of the AmeriGlil Acadenl\' of Phvsical Medicine and Rehabilitation,'Los Angeles, CA, REFERE CES I, Kellor ~r. FrostJ, Silberberg N, herson I, CUllllllings R: Hand strength and dexterit\. Am J Occup Thel' , Kellor ~I, KOlldrasuk R, l\'el'soll I. frost J, Silberberg N, Hoglund M: Technical,\Ianllal: Hand Strength and Dextaity TesLL i\dinne~polis: Sister Kellll\' Institute, ) Trombh CA: Occupational Therapy for Physical Dysfunction. Baltimore: Williams 8<: Wilkins Fess FE, Gettle KS, Strickland JW: Hand Splinting.' Principles and Methods. St LOllis: Mosb\, 198 j '1. S\\illlson AB, Goran-Hagert C, S\\'~nson GD: F.\'aluation of ii"pairti,ent of hand fu"clion. In Rehabilitation of the Hand, JM Hunter, LH Schneider, Ef Mackin. AD Callahan, Editors. St Louis: Mosby, 1984, pp Fess EE: Document~tion: essential elemeills of ~n upper extremity assessment ballery. In Rehabilitation of the Hand, JM Hunter, LH Schneider, EF Ivlackin, AD Call"han, Editors. St Louis: "'[osby, 1984, pp Asimov Engineering Company: Jamar Adjustable Hand Dynamometer. Los Angeles: Asinlov Engineering 8. Melvin jl.: Rheumatic Disease: Occupational Therapy and Rehabilitation. Philadelphia: Da\'is, [ Prestoll JA: 1984/85 Catalog: Fquipment for Rehabilitation and Special Fducation. i'ic\\' York: Preston, 1982 ] O. Sammons F: 1985 Professional SelfHelp Aids Catalog. Brookfield, IL: Sammons, 1985 J I. An K, Chao EYS, Askew L.J: H~ncl strength measurement instruments. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 61: , Bechtol co: The use of a dyn~mometel' \I ith adjustable handle spacings J Bone Jomt Surg 36: , McC~leb B: Fluid squeeze dynamometer. Physiotherapy 48:3, Pronk CNA, l\iiesing R: Measuring hand-grip force, using a new application ofslr"in gauges. ivied Biol Eng Comput ,1981 I.~. Miller GE: Vigorimeter. New York: ~!iller, Schmidt RT, ToewsJV: Grip strength as nle~sured by the Jamar dynamometer. Arch l'hys Med Rehabi! 51 : , IY Thorngrell KG, Werner CO: Norm~1 grip strength. Acla Orthop Scand 50: , Agel' CL, Olivell BL: Grasp and pinch strength in children 5 to 12 years old. AmJOcwp Thn 38: , Hays CA, Kassimir J, Parkin j: Sample Forms for Occupational Therapy. Rock \ille, MD: AOTA. ) Boyer B: 1975 Facilities Directory. Rockville. MD: AOTA, i\lllcrican Occupational Therapy Association: Careers in Occupational Thprap),. Rockville, MO: AOTA, 1983 The American Journal ofoccupalional Therapy 535
INTRODUCTION SUBJECTS AND METHODS
 J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, 1
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 394-399 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.394 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Reliability of the Pinch Strength with
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 394-399 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.394 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Reliability of the Pinch Strength with
Grasp and Pinch Strength in Children 5 to 12 Years Old
 Grasp and Pinch Strength in Children 5 to 12 Years Old (hand assessment, hand function, hand rehabilitation) Charlene L. Ager Bonnie L. Olivett Connie L. Johnson The objective of this study was to establish
Grasp and Pinch Strength in Children 5 to 12 Years Old (hand assessment, hand function, hand rehabilitation) Charlene L. Ager Bonnie L. Olivett Connie L. Johnson The objective of this study was to establish
The collection of reliable and valid evaluation
 Grip and -Pinch Strength: Norms for 6- to 19-Year 1ds Virgil Mathiowetz, Diana M. Wiemer, Susan M. Federman Key Words: hand. hand strength testing. manual strength. motor skills. tests The purpose ofthis
Grip and -Pinch Strength: Norms for 6- to 19-Year 1ds Virgil Mathiowetz, Diana M. Wiemer, Susan M. Federman Key Words: hand. hand strength testing. manual strength. motor skills. tests The purpose ofthis
Adult grip strength norms for the Baseline digital dynamometer
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital epository Master s and Doctoral Projects Adult grip strength norms for the Baseline digital dynamometer Chelsey. Meek Follow this and additional
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital epository Master s and Doctoral Projects Adult grip strength norms for the Baseline digital dynamometer Chelsey. Meek Follow this and additional
Hand grip strength is a measure of. Reliability and validity of an electronic dynamometer for measuring grip strength
 Research Reliability and validity of an electronic dynamometer for measuring grip strength Deborah Allen, Fiona Barnett Aims: This article describes a study aiming to establish the concurrent validity
Research Reliability and validity of an electronic dynamometer for measuring grip strength Deborah Allen, Fiona Barnett Aims: This article describes a study aiming to establish the concurrent validity
Nutrition-Focused Physical Examination for Adults, Part 2: Grip Strength in Patient Functional Assessment
 Idaho Health Care Association July 18, 2018 Boise Centre Boise, Idaho Handgrip strength (HGS) is one of the clinical characteristics of protein-calorie malnutrition as described by the Academy of Nutrition
Idaho Health Care Association July 18, 2018 Boise Centre Boise, Idaho Handgrip strength (HGS) is one of the clinical characteristics of protein-calorie malnutrition as described by the Academy of Nutrition
Elastic bandage vs. neoprene thumb stabilizer splint in acute De Quervain s tenosynovitis
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 263-267 Technical report (original) DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.035 Elastic bandage vs. neoprene thumb stabilizer splint in acute De Quervain s tenosynovitis
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 263-267 Technical report (original) DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.035 Elastic bandage vs. neoprene thumb stabilizer splint in acute De Quervain s tenosynovitis
HAND GRASP DEVELOPMENT
 TYPICAL HAND GRASP DEVELOPMENT FOR FINE MOTOR SKILLS Copyright 2017, Heather Greutman - Growing Hands-On Kids, LLC www.growinghandsonkids.com All rights reserved. This book or any portion thereof may not
TYPICAL HAND GRASP DEVELOPMENT FOR FINE MOTOR SKILLS Copyright 2017, Heather Greutman - Growing Hands-On Kids, LLC www.growinghandsonkids.com All rights reserved. This book or any portion thereof may not
Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters
 Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters MARGARET ROST, SANDRA STUCKEY, LEE ANNE SMALLEY, and GLENDA DORMAN A method of measuring trunk motion and two related motions using a tape measure
Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters MARGARET ROST, SANDRA STUCKEY, LEE ANNE SMALLEY, and GLENDA DORMAN A method of measuring trunk motion and two related motions using a tape measure
Nafees Rahman, Julie Jepsen Thomas, Martin S. Rice. 78 January/February 2002, Volume 56, Number 1
 The Relationship Between Hand Strength and the Forces Used To Access Containers by Well Elderly Persons Nafees Rahman, Julie Jepsen Thomas, Martin S. Rice KEY WORDS activities of daily living hand functions
The Relationship Between Hand Strength and the Forces Used To Access Containers by Well Elderly Persons Nafees Rahman, Julie Jepsen Thomas, Martin S. Rice KEY WORDS activities of daily living hand functions
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Prosser, R., Hancock, M. J., Nicholson, L., Merry, C., Thorley, F., & Wheen, D. (2014). Rigid versus semi-rigid orthotic use following TMC arthroplasty: A randomized controlled
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Prosser, R., Hancock, M. J., Nicholson, L., Merry, C., Thorley, F., & Wheen, D. (2014). Rigid versus semi-rigid orthotic use following TMC arthroplasty: A randomized controlled
Serial Grip Strength Testing- Its Role In Assessment Of Wrist And Hand Disability
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 Serial Grip Strength Testing- Its Role In Assessment Of Wrist And Hand Disability L Ashton, S Myers Citation L Ashton, S Myers.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 5 Number 2 Serial Grip Strength Testing- Its Role In Assessment Of Wrist And Hand Disability L Ashton, S Myers Citation L Ashton, S Myers.. The Internet
Forces women with arthritis use to access or operate containers free-handed and when using wrist orthoses
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Forces women with arthritis use to access or operate containers free-handed and when using wrist orthoses
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Forces women with arthritis use to access or operate containers free-handed and when using wrist orthoses
UTILITY OF THE POWERBALL IN THE INVIGORATION OF THE MUSCULATURE OF THE FOREARM
 Hand Surgery, Vol. 13, No. 2 (2008) 79 83 World Scientific Publishing Company UTILITY OF THE POWERBALL IN THE INVIGORATION OF THE MUSCULATURE OF THE FOREARM Sebastián Axel Balan and Marc Garcia-Elias Institut
Hand Surgery, Vol. 13, No. 2 (2008) 79 83 World Scientific Publishing Company UTILITY OF THE POWERBALL IN THE INVIGORATION OF THE MUSCULATURE OF THE FOREARM Sebastián Axel Balan and Marc Garcia-Elias Institut
Testing Protocol: Grip and Pinch
 Testing Protocol: Grip and Pinch OF POWER GRIP or upright - test arm at side with elbow flexed 90 - palm facing inward Adjust handle to appropriate rung, where grip is comfortable and the thumb overlaps
Testing Protocol: Grip and Pinch OF POWER GRIP or upright - test arm at side with elbow flexed 90 - palm facing inward Adjust handle to appropriate rung, where grip is comfortable and the thumb overlaps
Ton A. R. Schreuders, 1 Marij E. Roebroeck, 1 Jean-Bart Jaquet, 2 Steven E. R. Hovius 2 and Henk J. Stam 1 INTRODUCTION
 J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: 273 278 LONG-TERM OUTCOME OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN ULNAR AND MEDIAN NERVE INJURY: COMPARING MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH TESTING, GRIP AND PINCH STRENGTH DYNAMOMETERS AND A NEW INTRINSIC
J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: 273 278 LONG-TERM OUTCOME OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN ULNAR AND MEDIAN NERVE INJURY: COMPARING MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH TESTING, GRIP AND PINCH STRENGTH DYNAMOMETERS AND A NEW INTRINSIC
PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH
 10.1515/AMB-2016-0020 PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH S. Mindova, I. Karaganova and I. Stefanova Faculty of Public Health and Health Care, University of Ruse Angel Kanchev, Ruse, Bulgaria
10.1515/AMB-2016-0020 PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH S. Mindova, I. Karaganova and I. Stefanova Faculty of Public Health and Health Care, University of Ruse Angel Kanchev, Ruse, Bulgaria
CUE-T TM. Manual of Administration. Version 1.1: July Public edition November 2018
 Capabilities of Upper Extremity Test CUE-T TM Manual of Administration Version 1.1: July 2016 Public edition November 2018 Ralph.marino@jefferson.edu 1 Copyright 2016 Thomas Jefferson University, Creative
Capabilities of Upper Extremity Test CUE-T TM Manual of Administration Version 1.1: July 2016 Public edition November 2018 Ralph.marino@jefferson.edu 1 Copyright 2016 Thomas Jefferson University, Creative
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Horng, Y. S., Hsieh, S. F., Tu, Y. K., Lin, M. C., Horng, Y. S., & Wang, J. D. (2011). The comparative effectiveness of tendon and nerve gliding exercises in patients with
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Horng, Y. S., Hsieh, S. F., Tu, Y. K., Lin, M. C., Horng, Y. S., & Wang, J. D. (2011). The comparative effectiveness of tendon and nerve gliding exercises in patients with
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Rocchi, L., Merolli, A., Morini, A., Monteleone, G., & Foti, C. (2014). A modified spica-splint in postoperative early-motion management of skier's thumb lesion: A randomized
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Rocchi, L., Merolli, A., Morini, A., Monteleone, G., & Foti, C. (2014). A modified spica-splint in postoperative early-motion management of skier's thumb lesion: A randomized
Overview of the FITNESSGRAM Body Composition Standards
 body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
Development and application of a hand force measurement system
 Development and application of a hand force measurement system B.D. Lowe a, Y. Kong b, and J. Han c a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, USA b Systems Management Engineering,
Development and application of a hand force measurement system B.D. Lowe a, Y. Kong b, and J. Han c a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, USA b Systems Management Engineering,
INTRODUCTION. Ayse Ozcan, Zeliha Tulum, Lamia PInar, Ferdi Baskurt. Address for correspondence. J Korean Med Sci 2004; 19: ISSN
 J Korean Med Sci 24; 19: 874-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Comparison of Pressure Pain Threshold, Grip Strength, Dexterity and Touch Pressure of Dominant and Non-Dominant
J Korean Med Sci 24; 19: 874-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Comparison of Pressure Pain Threshold, Grip Strength, Dexterity and Touch Pressure of Dominant and Non-Dominant
Spinal cord injury (SCI) and lower-extremity amputation
 Using the BTE Primus to Measure Grip and Wrist Flexion Strength in Physically Active Wheelchair Users: An Exploratory Study Orit Shechtman, Leanne MacKinnon, Catherine Locklear Key Words: hand strength
Using the BTE Primus to Measure Grip and Wrist Flexion Strength in Physically Active Wheelchair Users: An Exploratory Study Orit Shechtman, Leanne MacKinnon, Catherine Locklear Key Words: hand strength
Original Article Radial club hand deformity The continuing challenges and controversies
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 30-34 Original Article Radial club hand deformity The continuing challenges and controversies Banskota AK 1, Bijukachhe B 2, Rajbhandary
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 30-34 Original Article Radial club hand deformity The continuing challenges and controversies Banskota AK 1, Bijukachhe B 2, Rajbhandary
Humerus. Ulna. Radius. Carpals
 Posture Analysis Exercise T. Armstrong M. Ebersole 1.0 Objectives: 1. Improve skill for rating over all job and identifying specific force and posture problems 2. Learn how to characterize posture 3. Learn
Posture Analysis Exercise T. Armstrong M. Ebersole 1.0 Objectives: 1. Improve skill for rating over all job and identifying specific force and posture problems 2. Learn how to characterize posture 3. Learn
School Visits Fitness Testing
 School Visits Fitness Testing 10m Sprint Test Purpose: To measure an athlete s ability to accelerate Equipment required: timing gates or stop watch, measuring tap - Participant ready s themselves on the
School Visits Fitness Testing 10m Sprint Test Purpose: To measure an athlete s ability to accelerate Equipment required: timing gates or stop watch, measuring tap - Participant ready s themselves on the
Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain
 Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Power grip is a commonly used index to assess impairment
 Brief Report Effect of Wrist Positioning on the Repeatability and Strength of Power Grip Pauline W. K. Fong, Gabriel Y. F. Ng Key Words: hand strength testing posture and positioning evaluation wrist joint
Brief Report Effect of Wrist Positioning on the Repeatability and Strength of Power Grip Pauline W. K. Fong, Gabriel Y. F. Ng Key Words: hand strength testing posture and positioning evaluation wrist joint
ICU: Rehabilitation Programme
 Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning It can help to shape a basic fitness training programme
 Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Friedman, N., Chan, V., Reinkensmeyer, A. N., Beroukhim, A., Zambrano, G. J., Bachman, M., & Reinkensmeyer, D. J. (2014). Retraining and assessing hand movement after stroke
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Friedman, N., Chan, V., Reinkensmeyer, A. N., Beroukhim, A., Zambrano, G. J., Bachman, M., & Reinkensmeyer, D. J. (2014). Retraining and assessing hand movement after stroke
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
TEST-RETEST INTRA-RATER RELIABILITY OF GRIP FORCE IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE
 J Rehabil Med 2003; 35: 189 194 TEST-RETEST INTRA-RATER RELIABILITY OF GRIP FORCE IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE Ann Hammer 1 and Birgitta Lindmark 2 From the 1 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Örebro University
J Rehabil Med 2003; 35: 189 194 TEST-RETEST INTRA-RATER RELIABILITY OF GRIP FORCE IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE Ann Hammer 1 and Birgitta Lindmark 2 From the 1 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Örebro University
Flexor Tendons. Get a Grip on Flexor Tendons. 1) Click the arrows on the navigation panel at the bottom of the PDF page
 www. treatment2go. com & www. handtherapy. com Flexor Tendons Get a Grip on Flexor Tendons This course has active links. The index is linked so you can just click and go (page 5). To access a website click
www. treatment2go. com & www. handtherapy. com Flexor Tendons Get a Grip on Flexor Tendons This course has active links. The index is linked so you can just click and go (page 5). To access a website click
Lillian Hoyle Parent, M.A., OTR, FAOTA
 The Open Journal of Occupational Therapy OJOT Sponsor Profiles Spring 2015 Lillian Hoyle Parent, M.A., OTR, FAOTA Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.wmich.edu/sponsorprofiles Recommended
The Open Journal of Occupational Therapy OJOT Sponsor Profiles Spring 2015 Lillian Hoyle Parent, M.A., OTR, FAOTA Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.wmich.edu/sponsorprofiles Recommended
Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol
 Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Masiero, S., Boniolo, A., Wassermann, L., Machiedo, H., Volante, D., & Punzi, L. (2007). Effects of an educational-behavioral joint protection program on people with moderate
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Masiero, S., Boniolo, A., Wassermann, L., Machiedo, H., Volante, D., & Punzi, L. (2007). Effects of an educational-behavioral joint protection program on people with moderate
On behalf of Albert Einstein
 Training Guide On behalf of Albert Einstein Healthcare Network, MossRehab and Tiburon Medical Enterprises Inc., we would like to thank you for purchasing the RELEAS. RELEAS is a tension driven, hand therapy
Training Guide On behalf of Albert Einstein Healthcare Network, MossRehab and Tiburon Medical Enterprises Inc., we would like to thank you for purchasing the RELEAS. RELEAS is a tension driven, hand therapy
Tennis Elbow Assessment & Treatment Workshop
 Tennis Elbow Assessment & Treatment Workshop Ian Gatt MSc, OMT, MAACP, MCSP, BSc (Hons) 9 th Southampton Hand Course 27 th June 2014, Chilworth Manor Hotel Assessment MacDermid et al., 2010 References
Tennis Elbow Assessment & Treatment Workshop Ian Gatt MSc, OMT, MAACP, MCSP, BSc (Hons) 9 th Southampton Hand Course 27 th June 2014, Chilworth Manor Hotel Assessment MacDermid et al., 2010 References
Citation for published version (APA): Soer, R. (2009). Functional capacity evaluation: measurement qualities and normative values s.n.
 University of Groningen Functional capacity evaluation Soer, Remko IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Functional capacity evaluation Soer, Remko IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Flexion contracture of the proximal interphalangeal
 A Belly Gutter Splint for Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion Contracture Shin-Han Wu Key Words: contracture. splints Various splints are available for the correction of proximal interphalangeal (PiP)
A Belly Gutter Splint for Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Flexion Contracture Shin-Han Wu Key Words: contracture. splints Various splints are available for the correction of proximal interphalangeal (PiP)
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yu, J., Kang, H., & Jung, J. (2012). Effects of modified constraint-induced movement therapy on hand dexterity, grip strength and activities of daily living of children
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yu, J., Kang, H., & Jung, J. (2012). Effects of modified constraint-induced movement therapy on hand dexterity, grip strength and activities of daily living of children
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation
 An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Che Daud, A. Z., Yau, M. K., Barnett, F., Judd, J., Jones, R. E., & Muhammad Nawawi, R. F. (2016). Integration of occupation based intervention in hand injury rehabilitation:
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Che Daud, A. Z., Yau, M. K., Barnett, F., Judd, J., Jones, R. E., & Muhammad Nawawi, R. F. (2016). Integration of occupation based intervention in hand injury rehabilitation:
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Unit code: F1BE 35
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Seated Massage Therapy Unit code: F1BE 35 Unit purpose: This Unit has been designed to prepare candidates for industry by
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Seated Massage Therapy Unit code: F1BE 35 Unit purpose: This Unit has been designed to prepare candidates for industry by
Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise. Fitness Testing
 Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise Fitness Testing Importance of fitness testing Gives baseline data for monitoring/improving performance Can design training programmes based on test results and determine
Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise Fitness Testing Importance of fitness testing Gives baseline data for monitoring/improving performance Can design training programmes based on test results and determine
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT
 BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
BLOOD PRESSURE ASSESSMENT Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question How do health care skills help to promote health
Key Points for Success:
 SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
Definition of Biomechanics. Course Outline. Course Website
 Definition of Biomechanics The application of mechanical principles to the structure and function of organisms (like humans). Tony Leyland leyland@sfu.ca Structure: internal (tissue) biomechanics Function:
Definition of Biomechanics The application of mechanical principles to the structure and function of organisms (like humans). Tony Leyland leyland@sfu.ca Structure: internal (tissue) biomechanics Function:
Physical Therapist Assistant Principles of Neuromuscular Rehabilitation
 Western Technical College 10524144 Physical Therapist Assistant Principles of Neuromuscular Rehabilitation Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total
Western Technical College 10524144 Physical Therapist Assistant Principles of Neuromuscular Rehabilitation Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yin, C., Sien, N., Ying, L., Chung, S., & Leng, D. (2014). Virtual reality for upper extremity rehabilitation in early stroke: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Clinical
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yin, C., Sien, N., Ying, L., Chung, S., & Leng, D. (2014). Virtual reality for upper extremity rehabilitation in early stroke: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Clinical
Self-Transfer Assistive Device for Hip and Knee Replacement Patients
 Self-Transfer Assistive Device for Hip and Knee Replacement Patients Bita Kasra, Lars Maxfield, Niklas Menke, Sina Tautz Advisor: Dr. Michael Sracic Milwaukee School of Engineering Senior Design Project
Self-Transfer Assistive Device for Hip and Knee Replacement Patients Bita Kasra, Lars Maxfield, Niklas Menke, Sina Tautz Advisor: Dr. Michael Sracic Milwaukee School of Engineering Senior Design Project
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy an effective intervention for improving function in paralyzed upper extremities after a stroke as compared to the standard therapy? Dohle,
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy an effective intervention for improving function in paralyzed upper extremities after a stroke as compared to the standard therapy? Dohle,
Carpal tunnel syndrome
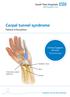 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
UK Biobank. Grip Strength Measurement. Version th April 2011
 Grip Strength Measurement Version 1.0 http://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ 15 th April 2011 This manual details the procedure for Grip Strength measurement at an Assessment Centre of the UK Biobank. Contents 1.
Grip Strength Measurement Version 1.0 http://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ 15 th April 2011 This manual details the procedure for Grip Strength measurement at an Assessment Centre of the UK Biobank. Contents 1.
How to select an age-friendly fitness facility
 How to select an age-friendly fitness facility International Council on Active Aging a division of ICAA Services inc. www.icaa.cc How to select an age-friendly fitness facility The International Council
How to select an age-friendly fitness facility International Council on Active Aging a division of ICAA Services inc. www.icaa.cc How to select an age-friendly fitness facility The International Council
RECOVERY OF ISOMETRIC GRIP STRENGTH AFTER COLLES FRACTURE: A PROSPECTIVE TWO-YEAR STUDY
 : 55 62, 1999 RECOVERY OF ISOMETRIC GRIP STRENGTH AFTER COLLES FRACTURE: A PROSPECTIVE TWO-YEAR STUDY Christel Lagerström, RPT 1,2,3, Bengt Nordgren, MD, PhD 1,2 and Hans Rahme, MD, PhD 4 From the Departments
: 55 62, 1999 RECOVERY OF ISOMETRIC GRIP STRENGTH AFTER COLLES FRACTURE: A PROSPECTIVE TWO-YEAR STUDY Christel Lagerström, RPT 1,2,3, Bengt Nordgren, MD, PhD 1,2 and Hans Rahme, MD, PhD 4 From the Departments
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 715/95. Benefit of the doubt; Nerve entrapment (ulnar).
 SUMMARY DECISION NO. 715/95 Benefit of the doubt; Nerve entrapment (ulnar). The worker appealed a decision of the Hearings Officer denying entitlement for left ulnar neuritis. The worker claimed that a
SUMMARY DECISION NO. 715/95 Benefit of the doubt; Nerve entrapment (ulnar). The worker appealed a decision of the Hearings Officer denying entitlement for left ulnar neuritis. The worker claimed that a
Occupational Therapy & Physiotherapy Assistant
 PROGRAM OBJECTIVES With increasing numbers of aging people requiring assistance, along with those recovering from surgery, health and chronic conditions, the need has never been greater for occupational
PROGRAM OBJECTIVES With increasing numbers of aging people requiring assistance, along with those recovering from surgery, health and chronic conditions, the need has never been greater for occupational
Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Survey: Let us know how this paper benefits you.
 Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Occupational Therapy Critically Appraised Papers Series Occupational Therapy 2017 Critically Appraised Paper for The Effect of Modified Constraint-Induced
Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Occupational Therapy Critically Appraised Papers Series Occupational Therapy 2017 Critically Appraised Paper for The Effect of Modified Constraint-Induced
MIE Medical Research Ltd Digital Analyser - Multi-Myometer Instruction Manual
 Instruction Manual Doc 134-03 Copyright 1998-2004 MIE Medical Research Ltd Instruction Manual Overview The Digital Analyser Multi-Myometer from MIE Medical Research Ltd is a dual function dynamometer.
Instruction Manual Doc 134-03 Copyright 1998-2004 MIE Medical Research Ltd Instruction Manual Overview The Digital Analyser Multi-Myometer from MIE Medical Research Ltd is a dual function dynamometer.
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic. Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack
 Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
S E L E C T I O N. Adjustable Bench. User manual. All equipment T H E S T R E N G T H E V O L U T I O N
 S E L E C T I O N T H E S T R E N G T H E V O L U T I O N User manual All equipment 1 Contents Identification of the manufacturer and equipment... 3 Description of the equipment... 4 Technical data...
S E L E C T I O N T H E S T R E N G T H E V O L U T I O N User manual All equipment 1 Contents Identification of the manufacturer and equipment... 3 Description of the equipment... 4 Technical data...
Measurement Error in Grip and Pinch Force Measurements in Patients With Hand Injuries
 Research Report Measurement Error in Grip and Pinch Force Measurements in Patients With Hand Injuries Background and Purpose. There is limited documentation of measurement error of grip and pinch force
Research Report Measurement Error in Grip and Pinch Force Measurements in Patients With Hand Injuries Background and Purpose. There is limited documentation of measurement error of grip and pinch force
Effectiveness of adaptive utensils on hand and finger range of motion in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis
 University of Tennessee at Chattanooga UTC Scholar Honors Theses Student Research, Creative Works, and Publications 5-2019 Effectiveness of adaptive utensils on hand and finger range of motion in individuals
University of Tennessee at Chattanooga UTC Scholar Honors Theses Student Research, Creative Works, and Publications 5-2019 Effectiveness of adaptive utensils on hand and finger range of motion in individuals
Among the non-operative methods, serial or wedge casting of the patient's arm in forced extension has been used with success. However, the weight and
 A Modular, Prefabricated Orthosis for Treatment of Elbow Flexion Contractures 1 S.I. REGER, PH.D., C.P. 2 J. O'REAGAN 2 M.H. BO-BLITZ2 R.W. ROSENBERGER, C.P. 2 A simple and adjustable orthosis has been
A Modular, Prefabricated Orthosis for Treatment of Elbow Flexion Contractures 1 S.I. REGER, PH.D., C.P. 2 J. O'REAGAN 2 M.H. BO-BLITZ2 R.W. ROSENBERGER, C.P. 2 A simple and adjustable orthosis has been
Hand of Hope. For hand rehabilitation. Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited
 Hand of Hope For hand rehabilitation Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Over 17 Million people worldwide suffer a stroke each year A stroke is the largest cause of a disability with half of all
Hand of Hope For hand rehabilitation Member of Vincent Medical Holdings Limited Over 17 Million people worldwide suffer a stroke each year A stroke is the largest cause of a disability with half of all
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition
 A Comparison of Treatment Approaches Used After Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Elin J. Groves, Barbara A. Rider Key Words: carpal tunnel syndrome. hand function hand occupational therapy. progressive resistive
A Comparison of Treatment Approaches Used After Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery Elin J. Groves, Barbara A. Rider Key Words: carpal tunnel syndrome. hand function hand occupational therapy. progressive resistive
CoastalHealth OSTEOARTHRITIS AND YOUR THUMBS WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS? HOW DOES OA AFFECT MY THUMBS? Vancouver 43-
 Vancouver 43- CoastalHealth Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy OSTEOARTHRITIS AND YOUR THUMBS WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS? Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative
Vancouver 43- CoastalHealth Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy OSTEOARTHRITIS AND YOUR THUMBS WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS? Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Focused Question For individuals with Grade II and III osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapeziometacarpal (CMC) joint in the dominant hand, is using a short oppenens orthosis
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Focused Question For individuals with Grade II and III osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapeziometacarpal (CMC) joint in the dominant hand, is using a short oppenens orthosis
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
 Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) Community Exercise Transition Program Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 2. Eligibility Criteria... 4 3. Location... 4 Parking... 4 4. Intake Procedures...
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) Community Exercise Transition Program Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 2. Eligibility Criteria... 4 3. Location... 4 Parking... 4 4. Intake Procedures...
PTA Applied Kinesiology 2
 Western Technical College 10524157 PTA Applied Kinesiology 2 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3 Applies basic principles from PTA Kinesiology
Western Technical College 10524157 PTA Applied Kinesiology 2 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3 Applies basic principles from PTA Kinesiology
How to select an age-friendly fitness facility
 How to select an age-friendly fitness facility How to select an age-friendly fitness facility The International Council on Active Aging (ICAA), the world s largest senior fitness association, has created
How to select an age-friendly fitness facility How to select an age-friendly fitness facility The International Council on Active Aging (ICAA), the world s largest senior fitness association, has created
Sarah E. Collier, Julie Jepsen Thomas
 Range of Motion at the Wrist: A Comparison Study of Four Wrist Extension Orthoses and the Free Hand Sarah E. Collier, Julie Jepsen Thomas KEY WORDS hand occupational therapy (treatment) wrist splint OBJECTIVE.
Range of Motion at the Wrist: A Comparison Study of Four Wrist Extension Orthoses and the Free Hand Sarah E. Collier, Julie Jepsen Thomas KEY WORDS hand occupational therapy (treatment) wrist splint OBJECTIVE.
Cambridge TECHNICALS. OCR Level 2 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL SPORT R/502/5410 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 30
 Cambridge TECHNICALS OCR Level 2 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA in SPORT Fitness Testing and Training R/502/5410 LEVEL 2 UNIT 3 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 30 UNIT CREDIT VALUE: 5 Fitness Testing and
Cambridge TECHNICALS OCR Level 2 CAMBRIDGE TECHNICAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA in SPORT Fitness Testing and Training R/502/5410 LEVEL 2 UNIT 3 GUIDED LEARNING HOURS: 30 UNIT CREDIT VALUE: 5 Fitness Testing and
9/18/2017. Getting a Grip! Disclosures. Disclosures. Agenda. Learning Outcomes. Handgrip strength, muscle function and malnutrition
 Getting a Grip! Handgrip Strength Examination for Malnourished Populations DPG Spotlight www.cnmdpg.org Barbara Lusk, MFCS. RD, LDN, FAND Chair 2017-2018 Disclosures Julie McGuire, MS, RDN, LD Clinical
Getting a Grip! Handgrip Strength Examination for Malnourished Populations DPG Spotlight www.cnmdpg.org Barbara Lusk, MFCS. RD, LDN, FAND Chair 2017-2018 Disclosures Julie McGuire, MS, RDN, LD Clinical
Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery
 Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation
Rehabilitation programme after cannulated hip screw surgery Information for patients at Princess Royal University Hospital This leaflet gives you advice about the things you can do after your operation
Goniometric Reliability in a Clinical Setting
 Goniometric Reliability in a Clinical Setting Elbow and Knee Measurements JULES M. ROTHSTEIN, PETER J. MILLER, and RICHARD F. ROETTGER Reliability of goniometric measurements has been examined only under
Goniometric Reliability in a Clinical Setting Elbow and Knee Measurements JULES M. ROTHSTEIN, PETER J. MILLER, and RICHARD F. ROETTGER Reliability of goniometric measurements has been examined only under
Moving and Handling Guidance
 NIPEC/19/03 (replacing NIPEC/14/21) NORTHERN IRELAND PRACTICE AND EDUCATION COUNCIL FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY Moving and Handling Guidance February 2019 Review date: April 2021 Centre House 79 Chichester
NIPEC/19/03 (replacing NIPEC/14/21) NORTHERN IRELAND PRACTICE AND EDUCATION COUNCIL FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY Moving and Handling Guidance February 2019 Review date: April 2021 Centre House 79 Chichester
34b Chair Massage! Technique Review and Practice!
 34b Chair Massage! Technique Review and Practice! 34b Chair Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Class Outline" 5 minutes "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes
34b Chair Massage! Technique Review and Practice! 34b Chair Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Class Outline" 5 minutes "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes
SaeboStretch (Patented)
 SaeboStretch (Patented) Product Manual A Dynamic Solution for a Dynamic Problem No Plateau In Sight Introduction Saebo Inc. is pleased to provide you with the most innovative resting hand splint available.
SaeboStretch (Patented) Product Manual A Dynamic Solution for a Dynamic Problem No Plateau In Sight Introduction Saebo Inc. is pleased to provide you with the most innovative resting hand splint available.
34b Chair Massage! Technique Review and Practice!
 34b Chair Massage! Technique Review and Practice! 34b Chair Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Class Outline" 5 minutes "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes
34b Chair Massage! Technique Review and Practice! 34b Chair Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Class Outline" 5 minutes "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes
Hand Therapy Protocols
 Hand Therapy Protocols Post Repair Therapy Protocols Page 1 of 10 Following are representative protocols for each of the three basic approaches to flexor tendon post repair management: immobilization,
Hand Therapy Protocols Post Repair Therapy Protocols Page 1 of 10 Following are representative protocols for each of the three basic approaches to flexor tendon post repair management: immobilization,
Ergonomics and therapy- An introduction DR.AYESHA BSPT, PPDPT
 Ergonomics and therapy- An introduction DR.AYESHA BSPT, PPDPT Ergonomics The study of work performance with an emphasis on worker safety and productivity Occupational therapy Skilled treatment that helps
Ergonomics and therapy- An introduction DR.AYESHA BSPT, PPDPT Ergonomics The study of work performance with an emphasis on worker safety and productivity Occupational therapy Skilled treatment that helps
ATTENTION TRAINING EXERCISES USING BRAINWAVE-R
 ATTENTION TRAINING EXERCISES USING BRAINWAVE-R Aim To understand why attention training is needed by some service users. To be able to safely and effectively carry out prescribed attention training exercises
ATTENTION TRAINING EXERCISES USING BRAINWAVE-R Aim To understand why attention training is needed by some service users. To be able to safely and effectively carry out prescribed attention training exercises
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow)
 EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers. Contusion Injuries to the Forearm. Forearm Fractures 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases
 Eur Orthop Traumatol (2012) 3:89 93 DOI 10.1007/s12570-012-0086-x CASE REPORT Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases İsmail Bülent Özçelik & Samet Vasfi Kuvat
Eur Orthop Traumatol (2012) 3:89 93 DOI 10.1007/s12570-012-0086-x CASE REPORT Heterotopic replantations in mutilating hand injuries, presentation of three cases İsmail Bülent Özçelik & Samet Vasfi Kuvat
Effect of hand dominance and body mass index on maximal isometric hand grip strength in normal young adults
 Original article: Effect of hand dominance and body mass index on maximal isometric hand grip strength in normal young adults 1 Dr Sonali S. Pande, 2 Dr Nazish Shaikh, 3 Dr Arun Chutani 1Associate Prof,
Original article: Effect of hand dominance and body mass index on maximal isometric hand grip strength in normal young adults 1 Dr Sonali S. Pande, 2 Dr Nazish Shaikh, 3 Dr Arun Chutani 1Associate Prof,
Physical Therapist Assistant Program Guide
 Physical Therapist Assistant Program Guide Program Director: Jeffrey Coon, MPT 970-542-3225 Email:Jeffrey.Coon@MorganCC.edu Program Information Thank you for your interest in the Physical Therapist Assistant
Physical Therapist Assistant Program Guide Program Director: Jeffrey Coon, MPT 970-542-3225 Email:Jeffrey.Coon@MorganCC.edu Program Information Thank you for your interest in the Physical Therapist Assistant
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION For stroke patients, in what ways does robot-assisted therapy improve upper extremity performance in the areas of motor impairment, muscle power, and strength?
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION For stroke patients, in what ways does robot-assisted therapy improve upper extremity performance in the areas of motor impairment, muscle power, and strength?
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Effects of Grip Power Training on Elbow Flexion Strength after Oberlin Transfer in Upper Arm Type Brachial Plexus Injuries
 Effects of Grip Power Training on Elbow Flexion Strength after Oberlin Transfer in Upper Arm Type Brachial Plexus Injuries Yi-Jung Tsai 1, Chih-Kun Hsiao 2, Yuan-Kun Tu 2, Chin-Hsien Wu 2, Fong-Chin Su
Effects of Grip Power Training on Elbow Flexion Strength after Oberlin Transfer in Upper Arm Type Brachial Plexus Injuries Yi-Jung Tsai 1, Chih-Kun Hsiao 2, Yuan-Kun Tu 2, Chin-Hsien Wu 2, Fong-Chin Su
NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL. For assessment of hand function after nerve repair
 NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL For assessment of hand function after nerve repair Manual for assessment of hand function after nerve repair according to Rosen score 1 Version 1, 2018 Documentation of hand
NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL For assessment of hand function after nerve repair Manual for assessment of hand function after nerve repair according to Rosen score 1 Version 1, 2018 Documentation of hand
Therapy Manual DO NOT PRINT
 Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
Muscle Size & Strength
 Muscle Size & Strength 1 Name Muscle Size & Strength PURPOSE: To compare muscle size and strength MATERIALS: Tape measure Bathroom scale PROCEDURE: Part 1 Measuring the size of your muscles: 1. Work with
Muscle Size & Strength 1 Name Muscle Size & Strength PURPOSE: To compare muscle size and strength MATERIALS: Tape measure Bathroom scale PROCEDURE: Part 1 Measuring the size of your muscles: 1. Work with
