NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL. For assessment of hand function after nerve repair
|
|
|
- Bennett Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL For assessment of hand function after nerve repair Manual for assessment of hand function after nerve repair according to Rosen score 1 Version 1, 2018
2 Documentation of hand function after nerve repair according to Rosen score, compiled in 2015 through collaboration between the Regional Hand Rehabilitation Units in Stockholm and Malmö, Sweden. Aim Our aim in writing this manual has been to promote the use of evidence-based methodology for the assessment of hand function following nerve repair in HAKIR and to create a Swedish standard for the clinical evaluation. HAKIR HAKIR is the national quality registry for hand surgery in Sweden. For more information about the registry please see If you have any questions or comments regarding the manual, please contact Birgitta Rosén ( birgitta.rosen@med.lu.se). The manual and PDF files (raw-data protocol and protocol for Rosen score) are available at and will be revised on an annual basis. 2
3 CONTENT: HAKIR Handkirurgiskt kvalitetsregister Documentation of hand function after nerve repair according to Rosen score 4 Material required 5 Scoring 5 Sensory domain Innervation Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments (SWM) 6 (pocket version with 5 filaments) Tactile gnosis Disk Criminator TM 10 Shape texture identification test (STI) 12 Dexterity Mini Sollerman test 16 Motor domain Innervation Manual muscle test (MMT) 20 Grip strength Jamar dynamometer 25 Pain/discomfort Subjective rating of Hyperaesthesia/allodynia Subjective rating of Cold sensitivity References 27 3
4 Documentation of hand function after nerve repair Rosen score ADL Identification of objects, shapes, textures Manipulation of objects Discriminination of touch Grip strength Touch thresholds Muscle function / Muscle strength Hierarchy for assessment of hand function after nerve injury. Modified from Fess (1994) 1 and Jerosch-Herold (2005) 2 4
5 The documentation is based on a standardised test battery 3,4,5. Material required: PDF files: Raw-data protocol and protocol for Rosen score Semmes-Weinstein monofilament (pocket version) Disk Criminator TM STI-test TM Mini Sollerman test or original Sollerman test (task no. 4, 8, 10) Jamar dynamometer Calculator Preparation The testing should be done in a quiet room. A screen should preferably be used for the sensory tests; otherwise the patient must have his/her eyes closed. For consistency, the same method of blinding should be used on every test occasion. During the passive sensory testing (SWM, S2PD), the patient s hand should be resting comfortably in a supine but not too extended position, e.g. on a soft pillow. During active sensory testing (STI test), the patient s hand must be able to move freely. 1. In, for example, sensory innervation, the results from the monofilament test in the marked critical sites for the relevant nerve (median nerve: tip of digit I, II, and base phalanx of digit II; ulnar nerve: tip and base of digit V and base of hypothenar) are quantified 0 5 according to instructions in the Instrument and quantification column. The results are summarised and divided by the normal value. All normal values are given in the Instrument and quantification column. The quotient is inserted into the Score column for each follow-up occasion. The maximum score for each assessment is 1.00 (two decimal places). The scoring for all assessments is done using the same procedure. 2. Since the three domains (Sensory, Motor, Pain/discomfort) do not contain an identical number of assessment instruments, the mean score for each domain is calculated. The full score for each domain is 1.00 (two decimal places). 3. The mean scores from the three domains are finally summarised as a total score, and the maximum score is therefore 3.0 (one decimal place). The total score is noted at the bottom of the Scoring key column and is also transferred to the graph to give visual feedback. 5
6 SENSORY INNERVATION Touch thresholds Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments 6 (pocketversion with 5 filaments) Material Apart from the monofilaments, coloured pens (green, blue, purple, and red) are required. The colours represent the functional interpretation of the microfilaments and can be used in the raw-data protocol 6. The original version of Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments contains 20 filaments from 8 mg to 300 g, but in most clinical assessment situations it is sufficient to use the 5 pocket filaments, which cover the entire pressure range from 70 mg to g. 6
7 Filament no. Grams ,07 Green Normal perception of light touch ,4 Blue Diminished perception of light touch Purple Diminished protective sensation Red No protective sensation Red Perception of deep pressure Striped red Cannot be tested with SW monofilament 7
8 Test procedure The test results are initially inserted into the raw-data protocol. The filaments are applied perpendicular to the skin 3 times at the highest spot of the finger pulp, and they should bend when applied (see photograph page 6). Apply for 1.5 s with an equally long pause between the three applications. Start the test distally. Apply the filaments to the areas of the hand that are indicated in the raw-data protocol. The patient says feel when he/she feels the touch (which does not have to be localised). Note a positive response in the area in the raw-data protocol if the patient answers within 3 seconds of the application. Start with filament no Show the patient the filament to emphasise that it is a very light touch that requires full concentration to feel. Demonstrate on a finger with normal feeling. To ensure that the patient is fully concentrated on the task, the examiner can randomly go back to areas with normal feeling during the test procedure. Mark with the green pen the areas where filament no is felt. Continue with filament no in the areas where the lighter filament was not felt. Mark with blue pen. Continue the testing in the unmarked areas, with filaments 4.31 (purple), 4.56 (red), and 6.65 (red). If the heaviest filament (6.65) is not felt, the area is marked with striped red. 8
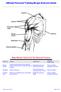
9 Scoring/Quantification Should be filled in using the Rosen score document 0 poäng = Not testable 1 poäng = SWM poäng = SWM poäng = SWM poäng = SWM poäng = SWM 2.83 Divide the result achieved from the three critical sites (0 15) by the normal value and write in the resulting value in the box marked score SWM (Semmes- Weinstein monofilament). Critical sites for median nerve and ulnar nerve 8 9
10 SENSORY FUNCTION- TACTILE GNOSIS Discriminative touch Static two-point discrimination (S2PD) 7,9 Material The Dellon-Mackinnon Disk Criminator TM 10
11 Test procedure The test results are initially inserted into the raw-data protocol. The prongs on the Discriminator are applied longitudinally and perpendicular to the finger tips (digit II or V) with one or two prongs, 10 times randomly. The pressure should be applied until the skin is just blanching. Each distance should be applied 10 times in random order (one/two prongs), and 7 answers should be correct before proceeding to a lower distance. Demonstrate first how one and two prongs feel, and be careful to apply the two prongs simultaneously. Start with 15 mm and then proceed to smaller distances (12, 10, 8 etc.). If the patient answers easily, one can proceed more quickly by omitting some distances. This is done to avoid fatigue. When the threshold for S2PD is approaching, testing should be done on each mm. Scoring/quantification in Rosen score 0 = 16 mm 1 = mm 2 = 6 10 mm 3 = 5 mm Divide the score achieved (0 3) by the normal score (3) and insert the result in the box marked Score S2PD digit II or V in the Sensory domain. 11
12 SENSORY FUNCTION - TACTILE GNOSIS The capacity to identify objects without the use of vision, which is one aspect of discriminative touch, can only be tested when the patient has some protective feeling at fingertip level, i.e. touch threshold measured with SWM at a minimum of 2 g (SWM no. 4.31). If the patient cannot feel filament no. 4.31, the score fordiscriminative touch in the Rosen score is 0. Shape Texture Identification (STI) test 2, 8-10 Material STI test Screen 12
13 Test procedure The test results are initially inserted into the raw-data protocol. Step 1 Always perform the test in the same order. Read out the following text marked in bold (but not the text in brackets) to the patient: You are now going to feel different shapes by touch (a cube, a cylinder, or a hexagon) and simple textures. (one, two or three small dots, 1 mm in diameter, and 0.5 mm in height, placed in a row). They are of varying degrees of difficulty, and your task is to identify them. You can see the shapes and textures in front of you now. There will always be one of each object and they will be presented at random. There is no time limit, so take your time when you touch them. You are only allowed to use your index finger (median nerve injuries)/ little finger (ulnar nerve injuries), and you are not allowed to use your nail. Each item will be presented to you only once, and I will tell you the result when you have finished the test. When you think you can identify the object, tell me what it is or say A, B, C, D, E, or F. (If the patient has a language problem or speech defect, he or she may point at the template disc). 13
14 Step 2 Let s start with the three different shapes. The shapes look like this. (Show the patient the disk with the 15-mm shapes). There is a cube, a cylinder, and a hexagon, all 15 mm in diameter, one of each. Don t forget that you can take as much time as you need. Step 3 Let s start with your uninjured hand. Here is the first one lift your finger here is the second one lift your finger and here is the third. Let s continue with your injured hand. Here is the first one lift your finger here is the second one lift your finger and here is the third. Steps 4 and 5 Repeat Step 3 with the smaller shapes (8 mm and 5 mm in diameter), using the same procedure. 14
15 6. Now let s go to the three different textures. There are one, two, or three dots in a row. (Show the patient the disk with the dots 15 mm apart). You should move your finger along the track (demonstrate with your own finger) all the way back and forth as many times as you need. Don t forget that you mustn t use your nail and that you can take as much time as you need. Step 7 Let s start with your uninjured hand. Here is the first one. (Make sure that the finger is in the middle of the track). Lift your finger here is the second one lift your finger and here is the third. Let s continue with your injured hand. Here is the first one lift your finger here is the second one lift your finger and here is the third. Steps 8 and 9 Repeat Step 3 with the closer-placed dots (8 mm and 4 mm apart), using the same procedure. Scoring/quantification in Rosen score 0 = 0 2 correct identifications 1 = 3 correct identifications The maximum score for the complete test is 6 Quantification in Rosen score protocol: Divide the score achieved (0 6) by the normal score (6) and insert the result in the box marked score STI test digit II or V in the Sensory domain. 15
16 SENSORY FUNCTION DEXTERITY Pulp pinch / Lateral pinch / Tripod chuck pinch 3, 11 Mini Sollerman test Material Mini Sollerman test or original Sollerman test task nos. 4, 8, and 10. The standardised Sollerman test contains 20 tasks based on the most common types of grip 13. Studies including patients with nerve injuries (median or ulnar nerve injuries) have shown that the results from 3 of the 20 tasks (4, 8, and 10) correlate strongly with the results from the full test with 20 tasks 5. Selected parts of the Sollerman hand function test (tasks 4, 8, and 10) are therefore included in the Mini Sollerman test, and are performed in accordance with the original instructions 3,13. To prepare the three selected tasks from the Sollerman test, place two coins inside each purse of task 4 and keep the zippers open; unscrew all four bolts in task 8 and place them on the table. For task 10, undo all four buttons. 16
17 Test procedure The test results are initially inserted into the raw-data protocol. Each test is timed and performed in the following order: 4, 8, 10. The patient is seated at a table and the test is placed in front of the patient. The patient starts with each task when you say start. Optional choice of grip. Maximum time is 60 sec. Scoring 4 points The task was completed without any difficulty within 20 s and with the prescribed hand grip of normal quality 3 points The task was completed, but with slight difficulty or The task was not completed within 20 s, but within 40 s or The task was completed with the prescribed hand grip with slight divergence from normal 2 points The task was completed, but with great difficulty or The task was not completed within 40 s but within 60 s or The task was not performed with the prescribed hand grip 1 point The task was only partially performed within 60 s 0 points The task could not be performed at all within 60 s Quantification in Rosen score The quotient between the total score achieved (0 12) and the normal (12) score is calculated and inserted into the box marked Score Sollerman test in the Sensory domain. 17
18 Task 4: Pick up the coins (optional order), one at a time from the open purses and place them on the table. Hand grip: Pulp pinch Task 8: Pick up the screw-nuts from the table, one at a time (optional order), and put them on the appropriate bolts (just so that they stay there). Hand grip: Pulp pinch, Lateral pinch, Tripod chuck pinch Task 10: Position the buttons in front of the patient (see photograph). It is optional whether the biggest button is up or down. Button the four buttons (optional order) with one hand. You are allowed to stabilize the equipment with the untested hand. Hand grip: Pulp pinch, Lateral pinch 18
19 Grip type 13 Description Pulp pinch: The object is held between the thumb and the index and/or middle finger. Tripod/Chuck pinch: The object is surrounded by the thumb, the index finger, and the middle finger. It may have (but need not have) contact with the web of the thumb. Lateral pinch: The object is held between the thumb and the radial side of the index finger. 19
20 MOTOR FUNCTION INNERVATION Manual muscle test (MMT) 0 5 (Modified MRC scale 12 ) Material Test procedure A soft pillow to support the elbow/forearm For median nerve injury, palmar abduction is tested, and for ulnar nerve injury, radial abduction dig II, abduction dig V, and adduction digit V are tested. The test results are initially inserted into the raw-data protocol. Quantification in Rosen score. The summarised MMT results (median nerve 0 5; ulnar nerve 0 15) are divided by the normal score (5 and 15, respectively), and the quotient is inserted into the box marked Score MMT in the Motor domain. The quotient between the score achieved (0 5 for median nerve and 0 15 for ulnar nerve) and the normal score (5 and 15, respectively) is calculated and inserted into the box marked Score Manual muscle test (MMT) in the Motor domain. 20
21 Median nerve Abduction of the thumb (palmar abduction) Primary muscle Position Movement Resistence M. abductor pollicis brevis. Forearm in supination, the wrist in 0 30 extension (neutral position). Palmar abduction. The patient is asked to abduct the thumb in a plane perpendicular to the plane of the palm of the hand. Resistance, when indicated, is applied at the base of the thumb at the level of the MCP joint. Grading/score Manual muscle test (MMT) = No activity 1 = Only palpable contraction 2 = Reduced movement, no resistance 3 = Normal movement, no resistance 4 = Normal movement, reduced resistance 5 = Normal movement, full resistance 21
22 Ulnar nerve Radial abduction digit II Primary muscle M. interosseus dorsalis I. Position Movement Forearm in neutral position. MCP II in slight flexion, IP joints dig II extended The patient is asked to abduct the index finger. Resistance Resistance, when indicated, is applied at the base of the index finger. Grading/score Manual muscle test (MMT) = No activity 1 = Only palpable contraction 2 = Reduced movement, no resistance 3 = Normal movement, no resistance 4 = Normal movement, reduced resistance 5 = Normal movement, full resistance 22
23 Ulnar nerve Abduction digit V Primary muscle Position Movement Resistance M. abductor digiti minimi. The examiner supports the patient s hand in supination. In this position, the tester is able to palpate the hypothenar muscles. In this way, the tester is able to judge for grade 0 or grade 1 in the case of severe paralysis, without having to change the test position. The patient is asked to abduct the little finger with the IP joints straight and the MCP joint slightly flexed, to avoid trick movements from the extensor digiti minimi. Resistance, when indicated, is given at the base of the little finger. Grading/score Manual muscle test (MMT) =No activity 1 = Only palpable contraction 2 = Reduced movement, no resistance 3 = Normal movement, no resistance 4 = Normal movement, reduced resistance 5 = Normal movement, full resistance 23
24 Ulnar nerve Adduction digit V Primary muscle Position Movement Resistance M. interosseus palmaris The forearm in supination with the hand and fingers supported. The MCP joint dig V should be held in neutral position. The patient is asked to keep the little finger adducted against the ring finger. Resistance, when trying to separate the two fingers, is applied at the base of the little finger. Grading/score Manual muscle test (MMT) = No activity 1 = Only palpable contraction 2 = Reduced movement, no resistance 3 = Normal movement, no resistance 4 = Normal movement, reduced resistance 5 = Normal movement, full resistance 24
25 MOTOR FUNCTION Grip strength Jamar dynamometer 13 Material Jamar dynamometer Test procedure Grip strength Position Seated with elbow close to waist, elbow joint in 90 degrees flexion, forearm in neutral position, wrist 0 30 degrees extension. The examiner supports the dynamometer. Performance Method Grip size in position 2. Start with the uninjured hand and shift between the uninjured and injured hand. Instruction: Squeeze around the handle and press as hard as you can, a bit more, a bit more, relax. Three measurements and calculation of the mean. The test results are initially inserted into the raw-data protocol. Quantification in Rosen score The quotient between the injured and uninjured hand (considered normal) is calculated and inserted into the box marked Score Jamar dynamometer in the Motor domain. 25
26 PAIN/DISCOMFORT 3 Testprocedure The test results are initially inserted into the raw-data protocol. Ask the patient: Which of the following descriptions best describes your pain/discomfort problems from: touch of the hand? none/minor, moderate, disturbing, hinders activity. cold? none/minor, moderate, disturbing, hinders activity. Scoring/quantification in Rosen score The chosen description is marked in the raw-data protocol. 0 = hinders activity 1 = disturbing 2 = moderate 3 = none/minor The quotient between chosen description (0 3) and normal (3) is calculated and inserted into the box Score Hyperaesthesia and Cold intolerance in the Pain/discomfort domain. 26
27 REFERENCES 1. Ewing-Fess, E. Documentation: Essential elements of an upper extrremity assessment battery. In: Hunter et al (Eds). Rehabilitation of the hand and upper extremity. Elsevier, Philadelphia 1994; Jerosch-Herold C. Assessment of sensibility after nerve injury and repair: a systematic review of evidence for validity, reliability and responsiveness of tests. J Hand Surg 2005;30: Rosen B, Lundborg G. A model instrument for the documentation of outcome after nerve repair. J Hand Surg 2000;25: Rosen B, Lundborg G. A new model instrument for outcome after nerve repair. Hand Clin 2003;19: Rosén B. Recovery of sensory and motor function after nerve repair: A rationale for evaluation. J Hand Ther 1996;9: Bell-Krotoski J, Weinstein S, Weinstein C. Testing sensibility, including touch-pressure, two-point discrimination, point localization and vibration. J Hand Ther 1993;6: Lundborg G, Rosen B. The two-point discrimination test - time for a re-appraisal? J Hand Surg [Br] 2004;29: Rosén B, Lundborg G. A new tactile gnosis instrument in sensibility testing. J Hand Ther 1998;11: Rosén B, Jerosch-Herold C. Comparing the responsiveness over time of twotactile gnosis tests: two-pint discrimination and the STI-test. Br J Hand Ther 2000;5: Rosén B. Inter-tester reliability of a tactile gnosis test: STI-test. Br J Hand Ther 2003;8: Sollerman C, Ejeskar A. Sollerman hand function test. A standardised method and its use in tetraplegic patients. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 1995;29: Brandsma JW, Schreuders JA, Birke JA, Piefer A, Oostendorp RAB. Manual muscle testing. Intra-and interobserver reliability of the intrinsic muscles of the hand. J Hand Ther 1995;8: Mathiowetz V, Weber K, Volland G, Kashman N. Reliability and validity of grip and pinch strength evaluations. J Hand Surg 1984;9A:
28 Fotogruppen Södersjukhuset January
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008
 Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy
 Indian J Lepr 2011, 83 : 209-213 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy 1 2 3 Mannam Ebenezer, Kelly
Indian J Lepr 2011, 83 : 209-213 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy 1 2 3 Mannam Ebenezer, Kelly
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Evaluation of the Hand. Learning Objectives. Sitting down with the Client. Observation 2/16/2012
 Introduction to Hand & UE Rehabilitation Hand Evaluation Basics J. Robin Janson, MS, OTR, CHT Indiana University Department of Occupational Therapy Learning Objectives After actively engaging with this
Introduction to Hand & UE Rehabilitation Hand Evaluation Basics J. Robin Janson, MS, OTR, CHT Indiana University Department of Occupational Therapy Learning Objectives After actively engaging with this
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease
 Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease R.W. Selles, PhD; B.T.J. van Ginneken, MSc; T.A.R. Schreuders, PT, PhD; W.G.M. Janssen, MD; and H.J. Stam, MD, PhD, FRCP
Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease R.W. Selles, PhD; B.T.J. van Ginneken, MSc; T.A.R. Schreuders, PT, PhD; W.G.M. Janssen, MD; and H.J. Stam, MD, PhD, FRCP
Ton A. R. Schreuders, 1 Marij E. Roebroeck, 1 Jean-Bart Jaquet, 2 Steven E. R. Hovius 2 and Henk J. Stam 1 INTRODUCTION
 J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: 273 278 LONG-TERM OUTCOME OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN ULNAR AND MEDIAN NERVE INJURY: COMPARING MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH TESTING, GRIP AND PINCH STRENGTH DYNAMOMETERS AND A NEW INTRINSIC
J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: 273 278 LONG-TERM OUTCOME OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN ULNAR AND MEDIAN NERVE INJURY: COMPARING MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH TESTING, GRIP AND PINCH STRENGTH DYNAMOMETERS AND A NEW INTRINSIC
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification testtm in people with chronic stroke
 Test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification testtm in people with chronic stroke Ekstrand, Elisabeth; Lexell, Jan; Brogårdh, Christina Published in: Clinical Rehabilitation DOI: 10.1177/0269215515608512
Test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification testtm in people with chronic stroke Ekstrand, Elisabeth; Lexell, Jan; Brogårdh, Christina Published in: Clinical Rehabilitation DOI: 10.1177/0269215515608512
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Humerus. Ulna. Radius. Carpals
 Posture Analysis Exercise T. Armstrong M. Ebersole 1.0 Objectives: 1. Improve skill for rating over all job and identifying specific force and posture problems 2. Learn how to characterize posture 3. Learn
Posture Analysis Exercise T. Armstrong M. Ebersole 1.0 Objectives: 1. Improve skill for rating over all job and identifying specific force and posture problems 2. Learn how to characterize posture 3. Learn
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand)
 MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
PHYSICAL FUNCTION TESTS
 ?Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 15 minutes per response, including the time for reviewing instructions, searching existing data sources, gathering
?Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 15 minutes per response, including the time for reviewing instructions, searching existing data sources, gathering
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Hands on Nerve Conduction Studies
 Hands on Nerve Conduction Studies N. CUTANEUS ANTEBRACHII LATERALIS Type of measurement: Antidromic. Position of limb: Subject supine, elbow extended, and forearm supinated. Type of recording electrodes:
Hands on Nerve Conduction Studies N. CUTANEUS ANTEBRACHII LATERALIS Type of measurement: Antidromic. Position of limb: Subject supine, elbow extended, and forearm supinated. Type of recording electrodes:
Testing Protocol: Grip and Pinch
 Testing Protocol: Grip and Pinch OF POWER GRIP or upright - test arm at side with elbow flexed 90 - palm facing inward Adjust handle to appropriate rung, where grip is comfortable and the thumb overlaps
Testing Protocol: Grip and Pinch OF POWER GRIP or upright - test arm at side with elbow flexed 90 - palm facing inward Adjust handle to appropriate rung, where grip is comfortable and the thumb overlaps
Structure and Function of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Shoulder Exercises Phase 1 Phase 2
 Shoulder Exercises Phase 1 1. Pendulum exercise Bend over at the waist and let the arm hang down. Using your body to initiate movement, swing the arm gently forward and backward and in a circular motion.
Shoulder Exercises Phase 1 1. Pendulum exercise Bend over at the waist and let the arm hang down. Using your body to initiate movement, swing the arm gently forward and backward and in a circular motion.
Key Points for Success:
 SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
General Information - Exercise
 General Information - Exercise To maximize the potential for prevention and recovery, it is important to make a commitment to daily stretching and cardiovascular exercise and to perform strengthening exercises
General Information - Exercise To maximize the potential for prevention and recovery, it is important to make a commitment to daily stretching and cardiovascular exercise and to perform strengthening exercises
A New Tactile Gnosis Instrument in Sensibility Testing
 ( SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLESJ A New Tactile Gnosis Instrument in Sensibility Testing B. Rosen, OT, MSc G. Lundborg, MD, PhD Department of Hand Surgery Malmo University Hospital Lund University Malmo,
( SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLESJ A New Tactile Gnosis Instrument in Sensibility Testing B. Rosen, OT, MSc G. Lundborg, MD, PhD Department of Hand Surgery Malmo University Hospital Lund University Malmo,
Examination of the Hand
 1 Examination of the Hand R E Page History 3 Examination 4 Movement 8 Features of Specific Conditions Affecting the Hand and Special Tests 8 Examination of the Hand 3 History General Establish important
1 Examination of the Hand R E Page History 3 Examination 4 Movement 8 Features of Specific Conditions Affecting the Hand and Special Tests 8 Examination of the Hand 3 History General Establish important
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical Therapy for Your Oncologic Shoulder Replacement
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Physical Therapy for Your Oncologic Shoulder Replacement This handout has information about your oncologic shoulder replacement and the exercises you will need
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Physical Therapy for Your Oncologic Shoulder Replacement This handout has information about your oncologic shoulder replacement and the exercises you will need
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Shoulder Exercises. Wall Press Up with Gym Ball
 Shoulder Exercises The exercises listed below are part of a treatment regime for patients attending The Police Rehabilitation Centre. They are reproduced here as an aide memoire for those patients. The
Shoulder Exercises The exercises listed below are part of a treatment regime for patients attending The Police Rehabilitation Centre. They are reproduced here as an aide memoire for those patients. The
Electrical stimulation of the upper limb. Paul Taylor
 Electrical stimulation of the upper limb Paul Taylor Three upper limb Pathways Shoulder subluxation Upper Limb Active Function Upper limb Passive All differ in aims but follow a similar 6 month protocol
Electrical stimulation of the upper limb Paul Taylor Three upper limb Pathways Shoulder subluxation Upper Limb Active Function Upper limb Passive All differ in aims but follow a similar 6 month protocol
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
An Illustrated Guide For Peripheral Nerve Examination. Bedside Teaching for 2 nd year medical Students
 An Illustrated Guide For Peripheral Nerve Examination Bedside Teaching for 2 nd year medical Students Prepared by: Dr. Farid Ghalli Clinical Teacher (Hon) November 2016 Before Examination : Wash hands
An Illustrated Guide For Peripheral Nerve Examination Bedside Teaching for 2 nd year medical Students Prepared by: Dr. Farid Ghalli Clinical Teacher (Hon) November 2016 Before Examination : Wash hands
LSUHSC Occupational Therapy Carpal Tunnel Treatment Protocol
 LSUHSC Occupational Therapy Carpal Tunnel Treatment Protocol SpringerImages Carla Saulsbery LOTR,CHT Dr. A. Hollister, MD Carpal Tunnel * Impingement of the Median nerve under the transverse carpal ligament
LSUHSC Occupational Therapy Carpal Tunnel Treatment Protocol SpringerImages Carla Saulsbery LOTR,CHT Dr. A. Hollister, MD Carpal Tunnel * Impingement of the Median nerve under the transverse carpal ligament
Research Article The Thermal Sensitivity Test in Evaluating Outcome after Peripheral Nerve Injury
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 528356, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/528356 Research Article The Thermal Sensitivity Test in Evaluating Outcome after Peripheral Nerve Injury
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 528356, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/528356 Research Article The Thermal Sensitivity Test in Evaluating Outcome after Peripheral Nerve Injury
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Ton A. R. Schreuders, Marij E. Roebroeck, PhD, Jean-Bart Jaquet, MD, Steven E. R. Hovius, MD, PhD, Henk J. Stam, MD, PhD, Rotterdam, the Netherlands
 Measuring the Strength of the Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand in Patients with Ulnar and Median Nerve Injuries: Reliability of the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) Ton A. R. Schreuders, Marij E.
Measuring the Strength of the Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand in Patients with Ulnar and Median Nerve Injuries: Reliability of the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) Ton A. R. Schreuders, Marij E.
TASC Manual and Scoresheet Printing Suggestions
 TASC Manual and Scoresheet Printing Suggestions The manual (pages 2-21 of this packet) is meant to be printed in booklet form so that the final form is 8.5x5.5 inches in size (achieved by folding the printed
TASC Manual and Scoresheet Printing Suggestions The manual (pages 2-21 of this packet) is meant to be printed in booklet form so that the final form is 8.5x5.5 inches in size (achieved by folding the printed
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
Performing a Physical Demands Analysis
 Performing a Physical Demands Analysis A Physical Demands Analysis (PDA) is a systematic procedure to quantify and evaluate the physical, cognitive, and environmental demands of the essential and non-essential
Performing a Physical Demands Analysis A Physical Demands Analysis (PDA) is a systematic procedure to quantify and evaluate the physical, cognitive, and environmental demands of the essential and non-essential
ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting)
 ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting) Position (A) Patient: Place arm against side of trunk. Helper: Hold elbow to stabilize. (B) - Lift hand toward shoulder, palm up. - Keep wrist straight. Do sessions
ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting) Position (A) Patient: Place arm against side of trunk. Helper: Hold elbow to stabilize. (B) - Lift hand toward shoulder, palm up. - Keep wrist straight. Do sessions
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Arthritis at the Base of the Thumb. Pain
 Arthritis at the Base of the Thumb Arthritis at the base of the thumb is a very common condition. Pain is often one of the primary presenting symptoms but you may find this varies depending on activity,
Arthritis at the Base of the Thumb Arthritis at the base of the thumb is a very common condition. Pain is often one of the primary presenting symptoms but you may find this varies depending on activity,
CUE-T TM. Manual of Administration. Version 1.1: July Public edition November 2018
 Capabilities of Upper Extremity Test CUE-T TM Manual of Administration Version 1.1: July 2016 Public edition November 2018 Ralph.marino@jefferson.edu 1 Copyright 2016 Thomas Jefferson University, Creative
Capabilities of Upper Extremity Test CUE-T TM Manual of Administration Version 1.1: July 2016 Public edition November 2018 Ralph.marino@jefferson.edu 1 Copyright 2016 Thomas Jefferson University, Creative
Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol
 Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance,
79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Demo and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance,
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
PAB Test Manual. Introduction
 PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
Ultimate Personal Training Biceps Exercise Guide
 Ultimate Personal Training Biceps Exercise Guide Major Muscles That Act At The Elbow and Forearm MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION Biceps brachii Brachialis Pronator teres Long head from tubercle above glenoid cavity;
Ultimate Personal Training Biceps Exercise Guide Major Muscles That Act At The Elbow and Forearm MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION Biceps brachii Brachialis Pronator teres Long head from tubercle above glenoid cavity;
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, 1
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 394-399 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.394 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Reliability of the Pinch Strength with
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 394-399 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.394 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Reliability of the Pinch Strength with
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance,
80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 80b Orthopedic Massage: Technique Review and Practice! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance,
 www.fitnessfirst-usa.com Chest Fly Shoulders, elbows and wrists aligned in same plane with elbows at 90 degrees Feet should be staggered, and body leaning slightly forward for leverage Step far enough
www.fitnessfirst-usa.com Chest Fly Shoulders, elbows and wrists aligned in same plane with elbows at 90 degrees Feet should be staggered, and body leaning slightly forward for leverage Step far enough
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players.
 Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Arthritis of the Base of the Thumb. Advice and Exercises
 Arthritis of the Base of the Thumb Advice and Exercises Arthritis at the base of the thumb is very common. It is a progressive condition. At any state in time, symptoms can vary and at times, your thumb
Arthritis of the Base of the Thumb Advice and Exercises Arthritis at the base of the thumb is very common. It is a progressive condition. At any state in time, symptoms can vary and at times, your thumb
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Scapular Protraction in Sitting
 9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
SMALL GROUP SESSION 8 October 21st or October 23 rd. Narratives Discussion/ OSCE Practice
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 8 October 21st or October 23 rd Narratives Discussion/ OSCE Practice Readings: Review your upper extremity, blood pressure and chest/lung OSCEs; Read Rita Charon s Narrative Medicine:
SMALL GROUP SESSION 8 October 21st or October 23 rd Narratives Discussion/ OSCE Practice Readings: Review your upper extremity, blood pressure and chest/lung OSCEs; Read Rita Charon s Narrative Medicine:
Throwers Ten Exercise Program
 The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition, all exercises included are
The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition, all exercises included are
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
SUSPECTS THE UNUSUAL. Often-Overlooked Muscles. Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis. Flexor pollicis longus.
 THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
On The Road. Training Manual
 On The Road Training Manual ST - 1 Standing External Rotation Strength Training Injury prevention Strengthening the rotator cuff Attach the tubing to a secure location like a fence or the net post. Start
On The Road Training Manual ST - 1 Standing External Rotation Strength Training Injury prevention Strengthening the rotator cuff Attach the tubing to a secure location like a fence or the net post. Start
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation
 An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill. patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry
 Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
A Clinicians Guide To The Active Movement Scale (AMS) An Evaluative Tool For Infants With Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy
 A Clinicians Guide To The Active Movement Scale (AMS) An Evaluative Tool For Infants With Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy Table of Contents Introduction.. 3 Active Movement Scale 4 AMS Evaluation Form.
A Clinicians Guide To The Active Movement Scale (AMS) An Evaluative Tool For Infants With Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy Table of Contents Introduction.. 3 Active Movement Scale 4 AMS Evaluation Form.
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection
 The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS
 YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
Therapy Manual DO NOT PRINT
 Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
Exercise Library. Exercise Image Description. Air Squats. Assisted Dips. Assisted Pull- Ups
 Exercise Library Exercise Image Description Air Squats Start in standing position with arms by side or in front of you. Squat down until your thighs are parallel to the ground, then return to standing.
Exercise Library Exercise Image Description Air Squats Start in standing position with arms by side or in front of you. Squat down until your thighs are parallel to the ground, then return to standing.
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017
 Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
Effect of Sensory Re-Education after Low Median Nerve Complete Transection and Repair
 Balkan Military Medical Review 14, 253-262 (2011) Original Article Effect of Sensory Re-Education after Low Median Nerve Complete Transection and Repair Dimitrios K. ANTONOPOULOS 1, Andreas F. MAVROGENIS
Balkan Military Medical Review 14, 253-262 (2011) Original Article Effect of Sensory Re-Education after Low Median Nerve Complete Transection and Repair Dimitrios K. ANTONOPOULOS 1, Andreas F. MAVROGENIS
Starting a Strength Training Program
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Starting a Strength Training Program About This Kit The key to improving strength is applying resistance to the muscle
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Starting a Strength Training Program About This Kit The key to improving strength is applying resistance to the muscle
INTRODUCTION. Ayse Ozcan, Zeliha Tulum, Lamia PInar, Ferdi Baskurt. Address for correspondence. J Korean Med Sci 2004; 19: ISSN
 J Korean Med Sci 24; 19: 874-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Comparison of Pressure Pain Threshold, Grip Strength, Dexterity and Touch Pressure of Dominant and Non-Dominant
J Korean Med Sci 24; 19: 874-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Comparison of Pressure Pain Threshold, Grip Strength, Dexterity and Touch Pressure of Dominant and Non-Dominant
Shoulder Arthroscopic Capsular Release Rehabilitation
 Shoulder Arthroscopic Capsular Release Rehabilitation Phase two: 3 to 6 weeks after surgery Goals: 1. Improve range of motion of the shoulder 2. Begin gentle strengthening Activities 1. Sling Your sling
Shoulder Arthroscopic Capsular Release Rehabilitation Phase two: 3 to 6 weeks after surgery Goals: 1. Improve range of motion of the shoulder 2. Begin gentle strengthening Activities 1. Sling Your sling
INTRODUCTION SUBJECTS AND METHODS
 J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
Daily. Workout MOBILITY WARM UP Exercise Descriptions. (See Below)
 MOBILITY WARM UP Pelvic Tilt Lateral Pelvic Tilt Hip Circles Lateral Spine Glide Spinal Flexion and Extension Lateral Spinal Flexion Neck Juts and Tucks Neck Glides Arm Screws Arm Circles Elbow Circles
MOBILITY WARM UP Pelvic Tilt Lateral Pelvic Tilt Hip Circles Lateral Spine Glide Spinal Flexion and Extension Lateral Spinal Flexion Neck Juts and Tucks Neck Glides Arm Screws Arm Circles Elbow Circles
Resistance Training Program
 Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM
 THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition,
THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition,
Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength
 Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength Objectives After participating in this lesson students will: Be familiar with why we stretch. Develop a stretching routine to do as a pre-activity before
Lesson Sixteen Flexibility and Muscular Strength Objectives After participating in this lesson students will: Be familiar with why we stretch. Develop a stretching routine to do as a pre-activity before
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES
 LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
Subacromial Bursa Injection
 Subacromial Bursa Injection 5 cc syringe, 21 gauge 1.5 inch needle 1% lidocaine - 4cc 40mg triamcinolone - 1 cc of 40mg/ml identify site-seat the patient with weight of arm hanging down, palpate the lateral
Subacromial Bursa Injection 5 cc syringe, 21 gauge 1.5 inch needle 1% lidocaine - 4cc 40mg triamcinolone - 1 cc of 40mg/ml identify site-seat the patient with weight of arm hanging down, palpate the lateral
Human Anatomy and Physiology - ANAT 14 Sensory System Lab Goals Activities
 Sensory System Human Anatomy and Physiology - ANAT 14 Lab Goals Observe many characteristics of our somatic and special senses. Activity descriptions noted in your lab manual are specified. Activities
Sensory System Human Anatomy and Physiology - ANAT 14 Lab Goals Observe many characteristics of our somatic and special senses. Activity descriptions noted in your lab manual are specified. Activities
Inhibition Associated with somatic dysfunctions, no matter which components are impaired Implies consideration of all components in treatment planning
 Somatic Dysfunction Impaired or altered function of related components of the somatic system including the skeletal, arthrodial, myofascial structures and their related vascular, lymphatic and neural elements.
Somatic Dysfunction Impaired or altered function of related components of the somatic system including the skeletal, arthrodial, myofascial structures and their related vascular, lymphatic and neural elements.
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Anatomy - Hand. Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics. Osteology. Carpal Arch. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Side Split Squat. The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time
 GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
Accepted for publication 15 March Lepr Rev (2007) 78,
 Lepr Rev (2007) 78, 122 130 Ensuring inter-tester reliability of voluntary muscle and monofilament sensory testing in the INFIR Cohort Study ANNE E. ROBERTS*, PETER G. NICHOLLS**, PRANAVA MADDALI* & WIM
Lepr Rev (2007) 78, 122 130 Ensuring inter-tester reliability of voluntary muscle and monofilament sensory testing in the INFIR Cohort Study ANNE E. ROBERTS*, PETER G. NICHOLLS**, PRANAVA MADDALI* & WIM
Patients First. Upper Body Exercises: Back, Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, & Hands. To obtain the best results, please perform each exercise as shown.
 Patient Education ABOUT YOUR THERAPY Upper Body Exercises: Back, Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, & Hands To obtain the best results, please perform each exercise as shown. The goal of these exercises is to regain
Patient Education ABOUT YOUR THERAPY Upper Body Exercises: Back, Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, & Hands To obtain the best results, please perform each exercise as shown. The goal of these exercises is to regain
Routine For: OT Wrist - Assistive/Active
 WRIST - 3 Extension (Assistive) Arm on table with thumb-up. Bend hand back at wrist. Alternate way: Use other hand to bring hand up, then let go. WRIST - 10 Flexion (Assistive) Place forearm on table,
WRIST - 3 Extension (Assistive) Arm on table with thumb-up. Bend hand back at wrist. Alternate way: Use other hand to bring hand up, then let go. WRIST - 10 Flexion (Assistive) Place forearm on table,
Table Of Contents. Complete Guide To Muscle Building MUSCLE BUILDING INTRODUCTION... 3 TRAINING EXERCISES...
 Table Of Contents MUSCLE BUILDING INTRODUCTION... 3 TRAINING EXERCISES... 7 EXTENSIVE WORKOUTS... 21 POWER FOODS DEFINED... 29 MEAL PLANS: PRINT OUT... 48 RESTED PERFORMANCE... 71 THE TRUTH ABOUT SUPPLEMENTS...
Table Of Contents MUSCLE BUILDING INTRODUCTION... 3 TRAINING EXERCISES... 7 EXTENSIVE WORKOUTS... 21 POWER FOODS DEFINED... 29 MEAL PLANS: PRINT OUT... 48 RESTED PERFORMANCE... 71 THE TRUTH ABOUT SUPPLEMENTS...
Resistance Training Program
 Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
