Investigating the Temporal Course of Attentional Processing A Test of the Response-Retrieval Account of Negative Priming
|
|
|
- Maximilian George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigating the Temporal Course of Attentional Processing A Test of the Response-Retrieval Account of Negative Priming Matthias Ihrke 1,3 Jörg Behrendt 1,2 Hecke Schrobsdorff 1,3 Michael Herrman 1,3 Marcus Hasselhorn 1,2 1 Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Göttingen 2 Georg-Elias-Müller-Institute for Psychology, Göttingen 3 Max-Planck-Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization, Göttingen Teap 2008 Marburg Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
2 Outline 1 Negative Priming and Selective Attention 2 Experimental Method 3 Results 4 Conclusion & Outlook Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
3 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Negative Priming Experimental Setup Trial n Trial n + 1 Ball Buch RSI ( ms) 500 ms time Response Keys no yes no yes Distractor red, Target green Compare the green object and the grey word. Response per keyboard (Yes/No) orthogonal variation of priming and response relation possible Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
4 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Negative Priming Effect critical condition: Negative Priming Prime CO Probe Distractor object from prime trial reappears as Target in the probe NP longer reaction time ( ms) more behavioural errors Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
5 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Other Priming-Conditions Prime CO Probe Ball Bus DT (NP) Nomenclature Ball TT (PP) Bus Prime Probe Label target target = TT (PP) Ball Bus distractor target = DT (NP) DD target distractor = TD Ball Bus distractor distractor = DD TD Ball Bus Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
6 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Negative Priming Prime Probe ms 500 ms reaction stimulus onset response stimulus interval time Negative Priming is considered as the most direct indicator for attentional selection effect stems from ignored stimuli alone (as opposed to positive priming) very robust finding: different modalities (visual, auditory) different time scales (short-term vs. long-term NP) different experimental paradigms very sensitive to subtle, experimental manipulations (RSI, response,... ) Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
7 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Theories diverse theoretical discussion: Selected Theories for NP 1 Inhibition (Tipper, 1985; Houghton & Tipper, 1994; Tipper, 2001) 2 Episodic-Retrieval Approach (Neill & Valdes, 1992; Neill, 1997) 3 Response-Retrieval (Rothermund, 2005) 4 Temporal-Discrimination (Milliken et al., 1998) 5 (C)ISAM (Schrobsdorff et al., 2007) 6... Negative Priming is a complex phenomenon that is difficult to explain Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
8 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Theories Inhibition vs. Response-Retrieval target distractor Prime "Bank" retrieval Probe "Ball" conflict "Bank" time Inhibition inhibition of distractor items because of ignoring persisting inhibition delay when activating in probe Response-Retrieval retrieval of prime response in probe trial because of similarity NP depends on response (repeated or changed) Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
9 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Time-Course of a single trial What happens during a trial? complex experimental setup multiple processes measure reaction time or error rate do not resolve when the effect is triggered Hypothetical Trial Processing Additive Model Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
10 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Time-Course of a single trial What happens during a trial? complex experimental setup multiple processes measure reaction time or error rate do not resolve when the effect is triggered Hypothetical Trial Processing Additive Model Bus yes no target selection motor command response selection trial onset response time R ts R rs ζ Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
11 Negative Priming and Selective Attention Time-Course of a single trial Predictions Bus yes no target selection motor command response selection trial onset response time R ts R rs ζ Predictions from the theories Inhibition slowdown in target-selection part of the processing (abstract representation is inhibited) Response-Retrieval slowdown in response-selection or motor-command since response is then determined Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
12 Experimental Method Time-Course of a single trial Dividing the Trial introduce time-markers to analyse the processing during the trial eyemovement to distinguish target- and response-selection LRP for onset of motor command separate reaction times for target- and response-selection Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
13 Experimental Method Time-Course of a single trial Dividing the Trial introduce time-markers to analyse the processing during the trial eyemovement to distinguish target- and response-selection LRP for onset of motor command eyemovement target selection trial onset motor command response selection response LRP separate reaction times for target- and response-selection time Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
14 Experiment Two Conditions: Eyemovement Experimental Method Glance No-Glance attentional focus Bus attentional focus Eye-Movement (Glance) Bus N = 16 N = 16 Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
15 Experimental Method Experimental Method Setup Experimental Setup 36 Trials Baseline (pre/post) single-objects 30 Trials Practicing phase 924 experimental Trials (11 blocks), randomized and equally distributed across conditions RSI randomized between 500 and 1500 ms 5 Priming-Conditions (next slide) 6 objects EEG-Acquisition 60 channels (extended System, w/o O1/O2) 4 EOG channels (left/right VEOG/HEOG) Reference FCz Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
16 Glance-Extraction using EOG-data Experimental Method very reliable occurence of strong eyemovement (instruction) simple algorithm for extracting the glance 1 use signal s of one veog-channel and use sliding time-window where and W w (t) = sgn(τ max τ min ) s(τ max ) s(τ min ) τ max = arg max t S t,w and τ min = arg min S t,w t S t,w := {s(i) i {t,..., t + w}}. that gives largest difference between two points in time-window 2 find latency with largest movement as R = arg max t (W w (t)) 3 cross-validate with counter-lateral electrode Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
17 100 Glance-Extraction using EOG-data 50 µv 0 Experimental Method very reliable occurence of strong eyemovement (instruction) 50 simple algorithm for extracting the glance W use signal s of w (t) s one veog-channel and use sliding time-window µv W w (t) = sgn(τ max τ min ) s(τ max ) s(τ min ) left veog Links unten where and right veog Rechts unten ms τ max = arg max t S t,w and τ min = arg min S t,w t S t,w := {s(i) i {t,..., t + w}}. that gives largest difference between two points in time-window 2 find latency with largest msmovement as R = arg max t (W w (t)) 3 cross-validate with counter-lateral electrode Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
18 Experimental Method Experiment Summary: Design Design (IV s) 1 2 Between-subjects Conditions (Glance vs. No-Glance) 2 5 Priming (CO, DT, TD, DD, TT) 3 2 Response-repetition (repetition vs. change) DV s 1 Total Reaction Time (R) condition Glance : RT until Glance (R ts ) target selection RT from Glance to response (R rs ) response-selection LRP-onset not considered here 2 (Error rates) not reported Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
19 Results Results Overall RT main effect glance vs. no-glance (trivial), F(1, 30) = 5.53, p <.03 interaction glance vs. priming F(4, 120) = 3.09, p <.02 No-Glance main effect priming, F(4, 60) = 2.64, p <.05 interaction priming response-repetition, F(4, 60) = 3.15, p <.03 pairwise comparisons not significant Glance main effect priming, F(4, 60) = 6.63, p <.001 main effect response-repetition, F(1, 15) = 19.48, p <.001 no priming response interaction Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
20 Results Results Overall RT (a) condition no-glance (b) condition glance control different response same response baseline same response baseline different response + ** ** ** DT TT TD DD control DT TT TD ** ** DD Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
21 Results Results Partial RTs Target Selection main effect priming condition for DT and TD, not for TT and DD target selection delayed for DT and TD Response Selection main effect priming condition only for TT response-selection faster for positive priming Negative priming effect due to slowing in target-selection Positive priming effect caused by faster response-selection Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
22 Results Partial RTs Results Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
23 Conclusion & Outlook Summary Summary pattern in no-glance condition largely in support for response-retrieval theory NP faster for response repetition, but slower for response-change glance-condition not consistent with response-retrieval only main effects of priming and response-repetition partial reaction times reveal: Negative priming effect occurs during target-selection Positive priming effect occurs during response-selection Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
24 Conclusion & Outlook Conclusion & Outlook Conclusions response-retrieval effect only for no-glance caused by interaction between processes? partial RTs indicate that positive and negative priming are not caused by the same mechanism results more in accordance with the inhibition framework Future Work use LRP as time marker to further separate trial processing effect caused by response-selection (comparison) or later motor processes? analyze EEG-data for correlates of in early/late portions of the ERP Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
25 Thank You Conclusion & Outlook... for your (selective) attention. Matthias Ihrke (BCCN) Temporal Course of NP / 22
ERP Correlates of Identity Negative Priming
 ERP Correlates of Identity Negative Priming Jörg Behrendt 1,3 Henning Gibbons 4 Hecke Schrobsdorff 1,2 Matthias Ihrke 1,3 J. Michael Herrmann 1,2 Marcus Hasselhorn 1,3 1 Bernstein Center for Computational
ERP Correlates of Identity Negative Priming Jörg Behrendt 1,3 Henning Gibbons 4 Hecke Schrobsdorff 1,2 Matthias Ihrke 1,3 J. Michael Herrmann 1,2 Marcus Hasselhorn 1,3 1 Bernstein Center for Computational
Unifying Negative Priming Theories
 Unifying Negative Priming Theories Hecke Schrobsdorff,2, Matthias Ihrke,3, Jörg Behrendt,3, Marcus Hasselhorn,3, Jan Michael Herrmann,2 hecke@nld.ds.mpg.de Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience
Unifying Negative Priming Theories Hecke Schrobsdorff,2, Matthias Ihrke,3, Jörg Behrendt,3, Marcus Hasselhorn,3, Jan Michael Herrmann,2 hecke@nld.ds.mpg.de Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience
The Time Course of Negative Priming
 The Time Course of Negative Priming Hendrik Degering Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Göttingen University of Göttingen, Institute for Nonlinear Dynamics 11.12.2009, Disputation Aging Effects
The Time Course of Negative Priming Hendrik Degering Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Göttingen University of Göttingen, Institute for Nonlinear Dynamics 11.12.2009, Disputation Aging Effects
Modeling Neural Correlates of Selective Attention
 Modeling Neural Correlates of Selective Attention Hecke Schrobsdorff Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Göttingen DPG Frühjahrstagung 2007 Regensburg BP12: Neuroscience 03/27/2007 Introduction
Modeling Neural Correlates of Selective Attention Hecke Schrobsdorff Bernstein Center for Computational Neuroscience Göttingen DPG Frühjahrstagung 2007 Regensburg BP12: Neuroscience 03/27/2007 Introduction
Running head: NP: ENCODING AND RETRIEVAL SPECIFIC EFFECTS. Response Retrieval and Negative Priming: Encoding and Retrieval Specific Effects
 NP: Encoding and Retrieval Specific Effects 1 Running head: NP: ENCODING AND RETRIEVAL SPECIFIC EFFECTS Response Retrieval and Negative Priming: Encoding and Retrieval Specific Effects Matthias Ihrke Max-Planck-Institute
NP: Encoding and Retrieval Specific Effects 1 Running head: NP: ENCODING AND RETRIEVAL SPECIFIC EFFECTS Response Retrieval and Negative Priming: Encoding and Retrieval Specific Effects Matthias Ihrke Max-Planck-Institute
Computational [Version of the] Imago Semantic Action Model CISAM
![Computational [Version of the] Imago Semantic Action Model CISAM Computational [Version of the] Imago Semantic Action Model CISAM](/thumbs/80/82423367.jpg) Computational [Version of the] Imago Semantic Action Model CISAM Hecke Schrobsdorff BCCN Göttingen C4 Forschungsseminar morgen früh Wed, May 3th, 27 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Imago-Semantic Action Model
Computational [Version of the] Imago Semantic Action Model CISAM Hecke Schrobsdorff BCCN Göttingen C4 Forschungsseminar morgen früh Wed, May 3th, 27 Outline 1 Introduction 2 The Imago-Semantic Action Model
priming disappear, while stays intact? Why does long-term positive long-term negative priming
 By Sandila Tanveer Dr Ewald Neumann Department of Psychology University of Canterbury, NZ Why does long-term positive priming disappear, while long-term negative priming stays intact? Priming Actions are
By Sandila Tanveer Dr Ewald Neumann Department of Psychology University of Canterbury, NZ Why does long-term positive priming disappear, while long-term negative priming stays intact? Priming Actions are
Prime display offset modulates negative priming only for easy-selection tasks
 Memory & Cognition 2007, 35 (3), 504-513 Prime display offset modulates negative priming only for easy-selection tasks Christian Frings Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany and Peter Wühr Friedrich
Memory & Cognition 2007, 35 (3), 504-513 Prime display offset modulates negative priming only for easy-selection tasks Christian Frings Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany and Peter Wühr Friedrich
International Journal of Psychophysiology
 International Journal of Psychophysiology 75 (2010) 339 348 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Psychophysiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ijpsycho Flanker
International Journal of Psychophysiology 75 (2010) 339 348 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Psychophysiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ijpsycho Flanker
Target localization among concurrent sound sources: No evidence for the inhibition of previous distractor responses
 Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:132 144 DOI 10.3758/s13414-012-0380-2 Target localization among concurrent sound sources: No evidence for the inhibition of previous distractor responses Malte Möller
Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:132 144 DOI 10.3758/s13414-012-0380-2 Target localization among concurrent sound sources: No evidence for the inhibition of previous distractor responses Malte Möller
Negative Priming as a Memory Phenomenon
 Zeitschrift S. Mayr & für A. Psychologie Buchner: / Negative JournalofPriming Psychology 2007as Hogrefe a 2007; Memory & Vol. Huber Phenomenon 215(1):35 51 Publishers Negative Priming as a Memory Phenomenon
Zeitschrift S. Mayr & für A. Psychologie Buchner: / Negative JournalofPriming Psychology 2007as Hogrefe a 2007; Memory & Vol. Huber Phenomenon 215(1):35 51 Publishers Negative Priming as a Memory Phenomenon
Long and Short-term Negative and Positive Priming
 Submitted for publication 19 August 2005 Do not quote without permission c 2004, 2005 by Michael A. Erickson $Id: neg-prime.tex,v 2.0 2005/08/19 17:11:21 erickson Exp $ Long and Short-term Negative and
Submitted for publication 19 August 2005 Do not quote without permission c 2004, 2005 by Michael A. Erickson $Id: neg-prime.tex,v 2.0 2005/08/19 17:11:21 erickson Exp $ Long and Short-term Negative and
Prime Retrieval of Motor Responses in Negative Priming
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2009, Vol. 35, No. 2, 408 423 2009 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/09/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0096-1523.35.2.408 Prime Retrieval
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2009, Vol. 35, No. 2, 408 423 2009 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/09/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0096-1523.35.2.408 Prime Retrieval
Experimental Design. Outline. Outline. A very simple experiment. Activation for movement versus rest
 Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
Experimental Design Kate Watkins Department of Experimental Psychology University of Oxford With thanks to: Heidi Johansen-Berg Joe Devlin Outline Choices for experimental paradigm Subtraction / hierarchical
Five shades of grey: Generalization in distractor-based retrieval of S-R episodes
 Atten Percept Psychophys (2016) 78:2307 2312 DOI 10.3758/s13414-016-1210-8 SHORT REPORT Five shades of grey: Generalization in distractor-based retrieval of S-R episodes Tarini Singh 1 & Birte Moeller
Atten Percept Psychophys (2016) 78:2307 2312 DOI 10.3758/s13414-016-1210-8 SHORT REPORT Five shades of grey: Generalization in distractor-based retrieval of S-R episodes Tarini Singh 1 & Birte Moeller
Attentional Blink Paradigm
 Attentional Blink Paradigm ATTENTIONAL BLINK 83 ms stimulus onset asychrony between all stimuli B T D A 3 N P Z F R K M R N Lag 3 Target 1 Target 2 After detection of a target in a rapid stream of visual
Attentional Blink Paradigm ATTENTIONAL BLINK 83 ms stimulus onset asychrony between all stimuli B T D A 3 N P Z F R K M R N Lag 3 Target 1 Target 2 After detection of a target in a rapid stream of visual
NSCI 324 Systems Neuroscience
 NSCI 324 Systems Neuroscience Dopamine and Learning Michael Dorris Associate Professor of Physiology & Neuroscience Studies dorrism@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/dorrislab/ NSCI 324 Systems
NSCI 324 Systems Neuroscience Dopamine and Learning Michael Dorris Associate Professor of Physiology & Neuroscience Studies dorrism@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/dorrislab/ NSCI 324 Systems
Episodic retrieval processes take place automatically in auditory negative priming
 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY 2010, 22 (8), 11921221 Episodic retrieval processes take place automatically in auditory negative priming Susanne Mayr and Axel Buchner Heinrich-Heine-Universität
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY 2010, 22 (8), 11921221 Episodic retrieval processes take place automatically in auditory negative priming Susanne Mayr and Axel Buchner Heinrich-Heine-Universität
HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION
 HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION Neural Signal Processing for Functional Neuroimaging Neuroscience Statistics Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School/MIT Division
HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION Neural Signal Processing for Functional Neuroimaging Neuroscience Statistics Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School/MIT Division
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function:
 Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance Effects of Contextual Similarity and Target-Repetition Proportion on Negative Priming in RT Distributional Analyses Chi-Shing Tse, Keith
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance Effects of Contextual Similarity and Target-Repetition Proportion on Negative Priming in RT Distributional Analyses Chi-Shing Tse, Keith
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 5: Data analysis II Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis II 6 Single
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 5: Data analysis II Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis II 6 Single
Lecture 1: Neurons. Lecture 2: Coding with spikes. To gain a basic understanding of spike based neural codes
 Lecture : Neurons Lecture 2: Coding with spikes Learning objectives: To gain a basic understanding of spike based neural codes McCulloch Pitts Neuron I w in Σ out Θ Examples: I = ; θ =.5; w=. - in = *.
Lecture : Neurons Lecture 2: Coding with spikes Learning objectives: To gain a basic understanding of spike based neural codes McCulloch Pitts Neuron I w in Σ out Θ Examples: I = ; θ =.5; w=. - in = *.
Neuroimaging Evidence for Processes Underlying Repetition of Ignored Stimuli
 Neuroimaging Evidence for Processes Underlying Repetition of Ignored Stimuli Eva Bauer*, Helge Gebhardt, Christoph Ruprecht, Bernd Gallhofer, Gebhard Sammer Cognitive Neuro Science at the Centre for Psychiatry,
Neuroimaging Evidence for Processes Underlying Repetition of Ignored Stimuli Eva Bauer*, Helge Gebhardt, Christoph Ruprecht, Bernd Gallhofer, Gebhard Sammer Cognitive Neuro Science at the Centre for Psychiatry,
IN COMPUTATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE
 IN COMPUTATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE Computational Modeling of the Negative Priming Effect Based on Inhibition Patterns and Working Memory Dongil Chung, Amir Raz, Jaewon Lee and Jaeseung Jeong Journal Name: Frontiers
IN COMPUTATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE Computational Modeling of the Negative Priming Effect Based on Inhibition Patterns and Working Memory Dongil Chung, Amir Raz, Jaewon Lee and Jaeseung Jeong Journal Name: Frontiers
SEQUENCE EFFECTS IN SIMPLE COGNITIVE TASKS: THE MULTIPLE-WEIGHTING-SYSTEMS HYPOTHESIS. Dragan Rangelov
 SEQUENCE EFFECTS IN SIMPLE COGNITIVE TASKS: THE MULTIPLE-WEIGHTING-SYSTEMS HYPOTHESIS Dragan Rangelov Dissertation at the Graduate School of Systemic Neurosciences of Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich
SEQUENCE EFFECTS IN SIMPLE COGNITIVE TASKS: THE MULTIPLE-WEIGHTING-SYSTEMS HYPOTHESIS Dragan Rangelov Dissertation at the Graduate School of Systemic Neurosciences of Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich
Target-to-distractor similarity can help visual search performance
 Target-to-distractor similarity can help visual search performance Vencislav Popov (vencislav.popov@gmail.com) Lynne Reder (reder@cmu.edu) Department of Psychology, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh,
Target-to-distractor similarity can help visual search performance Vencislav Popov (vencislav.popov@gmail.com) Lynne Reder (reder@cmu.edu) Department of Psychology, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh,
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Cognitive Neuroscience of Memory Types and Structure of Memory Types of Memory Type of Memory Time Course Capacity Conscious Awareness Mechanism of Loss Sensory Short-Term and Working Long-Term Nondeclarative
Negative priming 1985 to 2015: a measure of inhibition, the emergence of alternative accounts, and the multiple process challenge
 THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PSYCHOLOGY, 2016 Vol. 69, No. 10, 1890 1909, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17470218.2016.1173077 Negative priming 1985 to 2015: a measure of inhibition, the emergence
THE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PSYCHOLOGY, 2016 Vol. 69, No. 10, 1890 1909, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17470218.2016.1173077 Negative priming 1985 to 2015: a measure of inhibition, the emergence
Factors Affecting Speed and Accuracy of Response Selection in Operational Environments
 Factors Affecting Speed and Accuracy of Response Selection in Operational Environments Robert W. Proctor & Motonori Yamaguchi Purdue University, W. Lafayette, Indiana MURI Grant W9112NF-05-1-0153 from
Factors Affecting Speed and Accuracy of Response Selection in Operational Environments Robert W. Proctor & Motonori Yamaguchi Purdue University, W. Lafayette, Indiana MURI Grant W9112NF-05-1-0153 from
Mental representation of number in different numerical forms
 Submitted to Current Biology Mental representation of number in different numerical forms Anna Plodowski, Rachel Swainson, Georgina M. Jackson, Chris Rorden and Stephen R. Jackson School of Psychology
Submitted to Current Biology Mental representation of number in different numerical forms Anna Plodowski, Rachel Swainson, Georgina M. Jackson, Chris Rorden and Stephen R. Jackson School of Psychology
A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition
 RESEARCH ARTICLE A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition Sameer Sethi 1 *, Dr. Simon Rigoulot 2, Dr. Marc D. Pell 3 1 Faculty of Science, McGill University,
RESEARCH ARTICLE A study of the effect of auditory prime type on emotional facial expression recognition Sameer Sethi 1 *, Dr. Simon Rigoulot 2, Dr. Marc D. Pell 3 1 Faculty of Science, McGill University,
Surface Segmentation Cues Influence Negative Priming for Novel and Familiar Shapes
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Copyright 2000 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. l.,eaming, Memory, and Cognition 0278-7393/00/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//0278-7393.26.4.929 2000, Vol. 26, No.
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Copyright 2000 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. l.,eaming, Memory, and Cognition 0278-7393/00/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//0278-7393.26.4.929 2000, Vol. 26, No.
Running Head: VISUAL WORKING MEMORY LOAD AND ATTENTIONAL CONTROL
 Running Head: VISUAL WORKING MEMORY LOAD AND ATTENTIONAL CONTROL Visual working memory load disrupts template-guided attentional selection during visual search Nick Berggren* and Martin Eimer Department
Running Head: VISUAL WORKING MEMORY LOAD AND ATTENTIONAL CONTROL Visual working memory load disrupts template-guided attentional selection during visual search Nick Berggren* and Martin Eimer Department
Set-Size Effects in Identification and Localization
 Set-Size Effects in Identification and Localization Theory and Data Tom Busey Indiana University Bloomington John Palmer University of Washington Divided Attention in Search Are set-size effects in search
Set-Size Effects in Identification and Localization Theory and Data Tom Busey Indiana University Bloomington John Palmer University of Washington Divided Attention in Search Are set-size effects in search
Sequential Effects in Spatial Exogenous Cueing: Theoretical and Methodological Issues
 Sequential Effects in Spatial Exogenous Cueing: Theoretical and Methodological Issues Alessandro Couyoumdjian (alessandro.couyoumdjian@uniroma1.it) Faculty of Psychology 1, University La Sapienza via dei
Sequential Effects in Spatial Exogenous Cueing: Theoretical and Methodological Issues Alessandro Couyoumdjian (alessandro.couyoumdjian@uniroma1.it) Faculty of Psychology 1, University La Sapienza via dei
Perceptual and cognitive task difficulty has differential effects on auditory distraction
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Perceptual and cognitive task difficulty has differential effects on auditory distraction Alexandra Muller-Gass, Erich
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Perceptual and cognitive task difficulty has differential effects on auditory distraction Alexandra Muller-Gass, Erich
Novel single trial movement classification based on temporal dynamics of EEG
 Novel single trial movement classification based on temporal dynamics of EEG Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Wairagkar, M., Daly, I., Hayashi, Y. and Nasuto, S. (2014) Novel single trial movement
Novel single trial movement classification based on temporal dynamics of EEG Conference or Workshop Item Accepted Version Wairagkar, M., Daly, I., Hayashi, Y. and Nasuto, S. (2014) Novel single trial movement
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 11: Attention & Decision making Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 11: Attention & Decision making Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis
Notes and Comment. Negative priming and multiple repetition: A reply to Grison and Strayer (2001)
 Perception & Psychophysics 2002, 64 (5), 855-860 Notes and Comment Negative priming and multiple repetition: A reply to Grison and Strayer (2001) W. TRAMMELL NEILL State University of New York, Albany,
Perception & Psychophysics 2002, 64 (5), 855-860 Notes and Comment Negative priming and multiple repetition: A reply to Grison and Strayer (2001) W. TRAMMELL NEILL State University of New York, Albany,
Task Switching. Higher-Level Cognition Oct 7, 2008
 Task Switching Higher-Level Cognition Oct 7, 2008 Monsell, 2003 Task Switching Basic phenomena Reaction time (RT) cost for switching tasks Higher error rate Diminished if prepared for switch Slower RT
Task Switching Higher-Level Cognition Oct 7, 2008 Monsell, 2003 Task Switching Basic phenomena Reaction time (RT) cost for switching tasks Higher error rate Diminished if prepared for switch Slower RT
An EEG/ERP study of efficient versus inefficient visual search
 An EEG/ERP study of efficient versus inefficient visual search Steven Phillips (steve@ni.aist.go.jp) Neuroscience Research Institute (AIST), Tsukuba Central 2, 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8568
An EEG/ERP study of efficient versus inefficient visual search Steven Phillips (steve@ni.aist.go.jp) Neuroscience Research Institute (AIST), Tsukuba Central 2, 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8568
Virtual Reality Testing of Multi-Modal Integration in Schizophrenic Patients
 Virtual Reality Testing of Multi-Modal Integration in Schizophrenic Patients Anna SORKIN¹, Avi PELED 2, Daphna WEINSHALL¹ 1 Interdisciplinary Center for Neural Computation, Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
Virtual Reality Testing of Multi-Modal Integration in Schizophrenic Patients Anna SORKIN¹, Avi PELED 2, Daphna WEINSHALL¹ 1 Interdisciplinary Center for Neural Computation, Hebrew University of Jerusalem,
Does Contralateral Delay Activity Reflect Working Memory Storage or the Current Focus of Spatial Attention within Visual Working Memory?
 Does Contralateral Delay Activity Reflect Working Memory Storage or the Current Focus of Spatial Attention within Visual Working Memory? Nick Berggren and Martin Eimer Abstract During the retention of
Does Contralateral Delay Activity Reflect Working Memory Storage or the Current Focus of Spatial Attention within Visual Working Memory? Nick Berggren and Martin Eimer Abstract During the retention of
MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES
 MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES Carryl L. Baldwin and Joseph T. Coyne Department of Psychology Old Dominion University
MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES Carryl L. Baldwin and Joseph T. Coyne Department of Psychology Old Dominion University
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information ten Oever and Sack 10.1073/pnas.1517519112 SI Materials and Methods Experiment 1. Participants. A total of 20 participants (9 male; age range 18 32 y; mean age 25 y) participated
Supporting Information ten Oever and Sack 10.1073/pnas.1517519112 SI Materials and Methods Experiment 1. Participants. A total of 20 participants (9 male; age range 18 32 y; mean age 25 y) participated
Address for correspondence: School of Psychological Sciences, Zochonis Building, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, M139PL, Manchester, UK
 BBS-D-15-00891_ Mather_ Talmi & Barnacle Emotionally arousing context modulates the ERP correlates of neutral picture processing: An ERP test of the Glutamate Amplifies Noradrenergic Effects (GANE) model
BBS-D-15-00891_ Mather_ Talmi & Barnacle Emotionally arousing context modulates the ERP correlates of neutral picture processing: An ERP test of the Glutamate Amplifies Noradrenergic Effects (GANE) model
Sticky Rules: Integration Between Abstract Rules and Specific Actions
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2005, Vol. 31, No. 2, 337 350 Copyright 2005 by the American Psychological Association 0278-7393/05/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.31.2.337
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2005, Vol. 31, No. 2, 337 350 Copyright 2005 by the American Psychological Association 0278-7393/05/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0278-7393.31.2.337
Event Files: Evidence for Automatic Integration of Stimulus Response Episodes
 Ó VISUAL COGNITION, 1998, 5 (1/2), 183 216 Event Files: Evidence for Automatic Integration of Stimulus Response Episodes Bernhard Hommel Max-Planck-Institute for Psychological Research, Cognition and Action,
Ó VISUAL COGNITION, 1998, 5 (1/2), 183 216 Event Files: Evidence for Automatic Integration of Stimulus Response Episodes Bernhard Hommel Max-Planck-Institute for Psychological Research, Cognition and Action,
Templates for Rejection: Configuring Attention to Ignore Task-Irrelevant Features
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2012, Vol. 38, No. 3, 580 584 2012 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/12/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0027885 OBSERVATION Templates
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2012, Vol. 38, No. 3, 580 584 2012 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/12/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0027885 OBSERVATION Templates
The Mechanism of Valence-Space Metaphors: ERP Evidence for Affective Word Processing
 : ERP Evidence for Affective Word Processing Jiushu Xie, Ruiming Wang*, Song Chang Center for Studies of Psychological Application, School of Psychology, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong
: ERP Evidence for Affective Word Processing Jiushu Xie, Ruiming Wang*, Song Chang Center for Studies of Psychological Application, School of Psychology, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings. Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014
 Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[cdl Journals Account] [CDL Journals Account] On: 24 May 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 770849126] Publisher: Psychology Press Informa Ltd Registered in England
This article was downloaded by:[cdl Journals Account] [CDL Journals Account] On: 24 May 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 770849126] Publisher: Psychology Press Informa Ltd Registered in England
An investigation of the effect of preparation on response execution and inhibition in the go/nogo task
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2005 An investigation of the effect of preparation on response
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2005 An investigation of the effect of preparation on response
Does contralateral delay activity reflect working memory storage or the current focus of spatial attention within visual working memory?
 Running Head: Visual Working Memory and the CDA Does contralateral delay activity reflect working memory storage or the current focus of spatial attention within visual working memory? Nick Berggren and
Running Head: Visual Working Memory and the CDA Does contralateral delay activity reflect working memory storage or the current focus of spatial attention within visual working memory? Nick Berggren and
OBJECTIVE METHODS OF SOCIAL COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE FOR SOCIAL ATTUNEMENT AGNIESZKA WYKOWSKA
 OBJECTIVE METHODS OF SOCIAL COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE FOR SOCIAL ATTUNEMENT AGNIESZKA WYKOWSKA Engineering Psychology, Luleå University of Technology & Institute for Cognitive Systems, Technical University
OBJECTIVE METHODS OF SOCIAL COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE FOR SOCIAL ATTUNEMENT AGNIESZKA WYKOWSKA Engineering Psychology, Luleå University of Technology & Institute for Cognitive Systems, Technical University
The relative attractiveness of distractors and targets affects the coming and going of item-specific control: Evidence from flanker tasks
 Atten Percept Psychophys (2015) 77:373 389 DOI 10.3758/s13414-014-0752-x The relative attractiveness of distractors and targets affects the coming and going of item-specific control: Evidence from flanker
Atten Percept Psychophys (2015) 77:373 389 DOI 10.3758/s13414-014-0752-x The relative attractiveness of distractors and targets affects the coming and going of item-specific control: Evidence from flanker
Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system
 Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system Jonathan Pillow Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Lec. 3 Outline for today: psychophysics Weber-Fechner Law Signal Detection
Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system Jonathan Pillow Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Lec. 3 Outline for today: psychophysics Weber-Fechner Law Signal Detection
ERROR PROCESSING IN CLINICAL POPULATIONS IN CONTRAST TO ADHD J.J.VAN DER MEERE
 ERROR PROCESSING IN CLINICAL POPULATIONS IN CONTRAST TO ADHD J.J.VAN DER MEERE 1 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK OF ERROR PROCESSING Mean RT x error x 500 ms x x x RTe+1 2 CEREBRAL PALSY an umbrella term covering
ERROR PROCESSING IN CLINICAL POPULATIONS IN CONTRAST TO ADHD J.J.VAN DER MEERE 1 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK OF ERROR PROCESSING Mean RT x error x 500 ms x x x RTe+1 2 CEREBRAL PALSY an umbrella term covering
The speed of voluntary and priority-driven shifts of visual attention. *Corresponding Author. Malet Street, London, WC1E 7HX, UK
 The speed of voluntary and priority-driven shifts of visual attention Michael Jenkins 1 *, Anna Grubert, & Martin Eimer 1 *Corresponding Author 1 Department of Psychological Sciences, Birkbeck, University
The speed of voluntary and priority-driven shifts of visual attention Michael Jenkins 1 *, Anna Grubert, & Martin Eimer 1 *Corresponding Author 1 Department of Psychological Sciences, Birkbeck, University
Rapid Resumption of Interrupted Visual Search New Insights on the Interaction Between Vision and Memory
 PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Report Rapid Resumption of Interrupted Visual Search New Insights on the Interaction Between Vision and Memory Alejandro Lleras, 1 Ronald A. Rensink, 2 and James T. Enns
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Report Rapid Resumption of Interrupted Visual Search New Insights on the Interaction Between Vision and Memory Alejandro Lleras, 1 Ronald A. Rensink, 2 and James T. Enns
Congruency Effects with Dynamic Auditory Stimuli: Design Implications
 Congruency Effects with Dynamic Auditory Stimuli: Design Implications Bruce N. Walker and Addie Ehrenstein Psychology Department Rice University 6100 Main Street Houston, TX 77005-1892 USA +1 (713) 527-8101
Congruency Effects with Dynamic Auditory Stimuli: Design Implications Bruce N. Walker and Addie Ehrenstein Psychology Department Rice University 6100 Main Street Houston, TX 77005-1892 USA +1 (713) 527-8101
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance Item and Category-Based Attentional Control During Search for Real-World Objects: Can You Find the Pants Among the Pans? Rebecca Nako,
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance Item and Category-Based Attentional Control During Search for Real-World Objects: Can You Find the Pants Among the Pans? Rebecca Nako,
Dissociation of attentional processes in patients with focal frontal and posterior lesions
 Neuropsychologia 37 (1999) 1005±1027 Dissociation of attentional processes in patients with focal frontal and posterior lesions Donald T. Stuss a, *, Je rey P. Toth a, b, 1, Dina Franchi a, Michael P.
Neuropsychologia 37 (1999) 1005±1027 Dissociation of attentional processes in patients with focal frontal and posterior lesions Donald T. Stuss a, *, Je rey P. Toth a, b, 1, Dina Franchi a, Michael P.
The Role of Probe-Trial Distractors in the Production/Removal of the Spatial Negative Priming Effect
 Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2013 The Role of Probe-Trial Distractors in the Production/Removal of the Spatial Negative Priming Effect Peter
Western University Scholarship@Western Electronic Thesis and Dissertation Repository August 2013 The Role of Probe-Trial Distractors in the Production/Removal of the Spatial Negative Priming Effect Peter
Visual Selective Attention and the Effects of Monetary Rewards Chiara Della Libera and Leonardo Chelazzi
 PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Article Visual Selective Attention and the Effects of Monetary Rewards Chiara Della Libera and Leonardo Chelazzi Department of Neurological and Vision Sciences, Section of
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE Research Article Visual Selective Attention and the Effects of Monetary Rewards Chiara Della Libera and Leonardo Chelazzi Department of Neurological and Vision Sciences, Section of
Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling
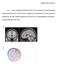 Supplementary materials 1 Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling analyses placed the source of the No Go N2 component in the dorsal ACC, near the ACC source
Supplementary materials 1 Figure 1. Source localization results for the No Go N2 component. (a) Dipole modeling analyses placed the source of the No Go N2 component in the dorsal ACC, near the ACC source
Dissociable neural correlates for familiarity and recollection during the encoding and retrieval of pictures
 Cognitive Brain Research 18 (2004) 255 272 Research report Dissociable neural correlates for familiarity and recollection during the encoding and retrieval of pictures Audrey Duarte a, *, Charan Ranganath
Cognitive Brain Research 18 (2004) 255 272 Research report Dissociable neural correlates for familiarity and recollection during the encoding and retrieval of pictures Audrey Duarte a, *, Charan Ranganath
SAMENESS AND REDUNDANCY IN TARGET DETECTION AND TARGET COMPARISON. Boaz M. Ben-David and Daniel Algom Tel-Aviv University
 SAMENESS AND REDUNDANCY IN TARGET DETECTION AND TARGET COMPARISON Boaz M. Ben-David and Daniel Algom Tel-Aviv University boazb@post.tau.ac.il Abstract Searching for targets, people perform better and reap
SAMENESS AND REDUNDANCY IN TARGET DETECTION AND TARGET COMPARISON Boaz M. Ben-David and Daniel Algom Tel-Aviv University boazb@post.tau.ac.il Abstract Searching for targets, people perform better and reap
The Adaptive Character of the Attentional System: Statistical Sensitivity in a Target Localization Task
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2003, Vol. 29, No. 3, 631 649 Copyright 2003 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0096-1523/03/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0096-1523.29.3.631
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2003, Vol. 29, No. 3, 631 649 Copyright 2003 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0096-1523/03/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0096-1523.29.3.631
Are Retrievals from Long-Term Memory Interruptible?
 Are Retrievals from Long-Term Memory Interruptible? Michael D. Byrne byrne@acm.org Department of Psychology Rice University Houston, TX 77251 Abstract Many simple performance parameters about human memory
Are Retrievals from Long-Term Memory Interruptible? Michael D. Byrne byrne@acm.org Department of Psychology Rice University Houston, TX 77251 Abstract Many simple performance parameters about human memory
A Race Model of Perceptual Forced Choice Reaction Time
 A Race Model of Perceptual Forced Choice Reaction Time David E. Huber (dhuber@psych.colorado.edu) Department of Psychology, 1147 Biology/Psychology Building College Park, MD 2742 USA Denis Cousineau (Denis.Cousineau@UMontreal.CA)
A Race Model of Perceptual Forced Choice Reaction Time David E. Huber (dhuber@psych.colorado.edu) Department of Psychology, 1147 Biology/Psychology Building College Park, MD 2742 USA Denis Cousineau (Denis.Cousineau@UMontreal.CA)
Electrophysiological Substrates of Auditory Temporal Assimilation Between Two Neighboring Time Intervals
 Electrophysiological Substrates of Auditory Temporal Assimilation Between Two Neighboring Time Intervals Takako Mitsudo *1, Yoshitaka Nakajima 2, Gerard B. Remijn 3, Hiroshige Takeichi 4, Yoshinobu Goto
Electrophysiological Substrates of Auditory Temporal Assimilation Between Two Neighboring Time Intervals Takako Mitsudo *1, Yoshitaka Nakajima 2, Gerard B. Remijn 3, Hiroshige Takeichi 4, Yoshinobu Goto
Task Preparation and the Switch Cost: Characterizing Task Preparation through Stimulus Set Overlap, Transition Frequency and Task Strength
 Task Preparation and the Switch Cost: Characterizing Task Preparation through Stimulus Set Overlap, Transition Frequency and Task Strength by Anita Dyan Barber BA, University of Louisville, 2000 MS, University
Task Preparation and the Switch Cost: Characterizing Task Preparation through Stimulus Set Overlap, Transition Frequency and Task Strength by Anita Dyan Barber BA, University of Louisville, 2000 MS, University
Author's personal copy
 Mem Cogn (2017) 45:1384 1397 DOI 10.3758/s13421-017-0734-z Components of competitor priming in task switching Morgan L. Teskey 1 & Michael E. J. Masson 1 Published online: 17 July 2017 # Psychonomic Society,
Mem Cogn (2017) 45:1384 1397 DOI 10.3758/s13421-017-0734-z Components of competitor priming in task switching Morgan L. Teskey 1 & Michael E. J. Masson 1 Published online: 17 July 2017 # Psychonomic Society,
Grace Iarocci Ph.D., R. Psych., Associate Professor of Psychology Simon Fraser University
 Grace Iarocci Ph.D., R. Psych., Associate Professor of Psychology Simon Fraser University Theoretical perspective on ASD Where does attention and perception fit within the diagnostic triad of impairments?
Grace Iarocci Ph.D., R. Psych., Associate Professor of Psychology Simon Fraser University Theoretical perspective on ASD Where does attention and perception fit within the diagnostic triad of impairments?
Multiphoton Imaging of Neuronal Activity in vivo in Behavioral Paradigms
 Multiphoton Imaging of Neuronal Activity in vivo in Behavioral Paradigms 2 Outline Surgical preparation Experimental apparatus Synchronization of behavioral trials with imaging Off axis imaging 3 Multiphoton
Multiphoton Imaging of Neuronal Activity in vivo in Behavioral Paradigms 2 Outline Surgical preparation Experimental apparatus Synchronization of behavioral trials with imaging Off axis imaging 3 Multiphoton
Priming of Pop-out provides reliable measures of target activation and distractor inhibition in selective attention q
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Vision Research 48 (2008) 30 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Priming of Pop-out provides reliable measures of target activation and distractor inhibition in
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Vision Research 48 (2008) 30 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Priming of Pop-out provides reliable measures of target activation and distractor inhibition in
Event-Related Potentials Recorded during Human-Computer Interaction
 Proceedings of the First International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME2005) May 15-18, 2005, Takamatsu, Japan (Organized Session No. 20). Paper No. 150, pp. 715-719. Event-Related Potentials
Proceedings of the First International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering (CME2005) May 15-18, 2005, Takamatsu, Japan (Organized Session No. 20). Paper No. 150, pp. 715-719. Event-Related Potentials
Negative priming and perceptual fluency: More than what meets the eye
 Perception & Psychophysics 2001, 63 (6), 1063-1071 Negative priming and perceptual fluency: More than what meets the eye SARAH GRISON University of Wales, Banger, Wales and DAVID L. STRAYER University
Perception & Psychophysics 2001, 63 (6), 1063-1071 Negative priming and perceptual fluency: More than what meets the eye SARAH GRISON University of Wales, Banger, Wales and DAVID L. STRAYER University
Schizophrenia as a disorder of thought, or language? Evidence from brain and behavioral investigations
 Schizophrenia as a disorder of thought, or language? Evidence from brain and behavioral investigations Karen Froud Teachers College, Columbia University New York City Outline Big questions, and why this
Schizophrenia as a disorder of thought, or language? Evidence from brain and behavioral investigations Karen Froud Teachers College, Columbia University New York City Outline Big questions, and why this
The attentional selection of spatial and non-spatial attributes in touch: ERP evidence for parallel and independent processes
 Biological Psychology 66 (2004) 1 20 The attentional selection of spatial and non-spatial attributes in touch: ERP evidence for parallel and independent processes Bettina Forster, Martin Eimer School of
Biological Psychology 66 (2004) 1 20 The attentional selection of spatial and non-spatial attributes in touch: ERP evidence for parallel and independent processes Bettina Forster, Martin Eimer School of
Processing of attended and ignored words in the parafovea: Inhibitory aspects of semantic processing
 Psicológica (2000), 21, 233-257 Processing of attended and ignored words in the parafovea: Inhibitory aspects of semantic processing Juan Lupiáñez *, María Rosario Rueda, María Ruz and Pío Tudela Universidad
Psicológica (2000), 21, 233-257 Processing of attended and ignored words in the parafovea: Inhibitory aspects of semantic processing Juan Lupiáñez *, María Rosario Rueda, María Ruz and Pío Tudela Universidad
ERP Components and the Application in Brain-Computer Interface
 ERP Components and the Application in Brain-Computer Interface Dr. Xun He Bournemouth University, 12 th July 2016 The 1 st HCI and Digital Health Forum: Technologies and Business Opportunities between
ERP Components and the Application in Brain-Computer Interface Dr. Xun He Bournemouth University, 12 th July 2016 The 1 st HCI and Digital Health Forum: Technologies and Business Opportunities between
Verbruggen, F., & Logan, G. D. (2009). Proactive adjustments of response strategies in the
 1 Verbruggen, F., & Logan, G. D. (2009). Proactive adjustments of response strategies in the stop-signal paradigm. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 35(3), 835-54. doi:10.1037/a0012726
1 Verbruggen, F., & Logan, G. D. (2009). Proactive adjustments of response strategies in the stop-signal paradigm. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 35(3), 835-54. doi:10.1037/a0012726
Temporal attention enhances early visual processing: A review and new evidence from event-related potentials
 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Temporal attention enhances early visual processing: A review and new evidence from event-related potentials Ángel Correa,
available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Temporal attention enhances early visual processing: A review and new evidence from event-related potentials Ángel Correa,
The effect of asymmetrical association on positive and negative semantic priming
 Memory & Cognition 2002, 30 (8), 1263-1276 The effect of asymmetrical association on positive and negative semantic priming KEITH A. HUTCHISON State University of New York, Albany, New York One s actively
Memory & Cognition 2002, 30 (8), 1263-1276 The effect of asymmetrical association on positive and negative semantic priming KEITH A. HUTCHISON State University of New York, Albany, New York One s actively
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus)
 EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus) Introduction 17 subjects were tested to measure effects of a Brain.fm focus session on cognition. With 4 additional subjects, we recorded EEG data during baseline and while
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus) Introduction 17 subjects were tested to measure effects of a Brain.fm focus session on cognition. With 4 additional subjects, we recorded EEG data during baseline and while
Bioscience in the 21st century
 Bioscience in the 21st century Lecture 2: Innovations and Challenges Dr. Michael Burger Outline: Review of last lecture Organization of the nervous system (in brief) The mapping concept Bionic implants
Bioscience in the 21st century Lecture 2: Innovations and Challenges Dr. Michael Burger Outline: Review of last lecture Organization of the nervous system (in brief) The mapping concept Bionic implants
Concurrent Learning of Temporal and Spatial Sequences
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2002, Vol. 28, No. 3, 445 457 Copyright 2002 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0278-7393/02/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//0278-7393.28.3.445
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 2002, Vol. 28, No. 3, 445 457 Copyright 2002 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0278-7393/02/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//0278-7393.28.3.445
Studying the time course of sensory substitution mechanisms (CSAIL, 2014)
 Studying the time course of sensory substitution mechanisms (CSAIL, 2014) Christian Graulty, Orestis Papaioannou, Phoebe Bauer, Michael Pitts & Enriqueta Canseco-Gonzalez, Reed College. Funded by the Murdoch
Studying the time course of sensory substitution mechanisms (CSAIL, 2014) Christian Graulty, Orestis Papaioannou, Phoebe Bauer, Michael Pitts & Enriqueta Canseco-Gonzalez, Reed College. Funded by the Murdoch
Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
Competition in visual working memory for control of search
 VISUAL COGNITION, 2004, 11 6), 689±703 Competition in visual working memory for control of search Paul E. Downing and Chris M. Dodds University of Wales, Bangor, UK Recent perspectives on selective attention
VISUAL COGNITION, 2004, 11 6), 689±703 Competition in visual working memory for control of search Paul E. Downing and Chris M. Dodds University of Wales, Bangor, UK Recent perspectives on selective attention
Limits to the Use of Iconic Memory
 Limits to Iconic Memory 0 Limits to the Use of Iconic Memory Ronald A. Rensink Departments of Psychology and Computer Science University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4 Canada Running Head: Limits
Limits to Iconic Memory 0 Limits to the Use of Iconic Memory Ronald A. Rensink Departments of Psychology and Computer Science University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4 Canada Running Head: Limits
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion
 Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
The EEG Analysis of Auditory Emotional Stimuli Perception in TBI Patients with Different SCG Score
 Open Journal of Modern Neurosurgery, 2014, 4, 81-96 Published Online April 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojmn http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojmn.2014.42017 The EEG Analysis of Auditory Emotional
Open Journal of Modern Neurosurgery, 2014, 4, 81-96 Published Online April 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojmn http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojmn.2014.42017 The EEG Analysis of Auditory Emotional
A Race Model of Perceptual Forced Choice Reaction Time
 A Race Model of Perceptual Forced Choice Reaction Time David E. Huber (dhuber@psyc.umd.edu) Department of Psychology, 1147 Biology/Psychology Building College Park, MD 2742 USA Denis Cousineau (Denis.Cousineau@UMontreal.CA)
A Race Model of Perceptual Forced Choice Reaction Time David E. Huber (dhuber@psyc.umd.edu) Department of Psychology, 1147 Biology/Psychology Building College Park, MD 2742 USA Denis Cousineau (Denis.Cousineau@UMontreal.CA)
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University
 Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
Working Memory (Goal Maintenance and Interference Control) Edward E. Smith Columbia University Outline Goal Maintenance Interference resolution: distraction, proactive interference, and directed forgetting
October 2, Memory II. 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome. 9 Recent/Remote Distinction. 11 Frontal/Executive Contributions to Memory
 1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
1 Memory II October 2, 2008 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 The Human Amnesic Syndrome Impaired new learning (anterograde amnesia), exacerbated by increasing retention delay Impaired recollection of events learned prior
Cognitive Control as Alternation of Activation and Suppression in the Stroop Task
 Cognitive Control as Alternation of Activation and Suppression in the Stroop Task Ion Juvina (ijuvina@andrew.cmu.edu) Niels A. Taatgen (taatgen@cmu.edu) Daniel Dickison (danieldickison@cmu.edu) Department
Cognitive Control as Alternation of Activation and Suppression in the Stroop Task Ion Juvina (ijuvina@andrew.cmu.edu) Niels A. Taatgen (taatgen@cmu.edu) Daniel Dickison (danieldickison@cmu.edu) Department
