Test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification testtm in people with chronic stroke
|
|
|
- Arthur Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification testtm in people with chronic stroke Ekstrand, Elisabeth; Lexell, Jan; Brogårdh, Christina Published in: Clinical Rehabilitation DOI: / Published: Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Ekstrand, E., Lexell, J., & Brogårdh, C. (2016). Test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification testtm in people with chronic stroke. Clinical Rehabilitation, 30(11), DOI: / General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the public portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognise and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the public portal for the purpose of private study or research. You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the public portal Take down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. L UNDUNI VERS I TY PO Box L und
2 Test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification test TM in people with chronic stroke Elisabeth Ekstrand, RPT, MSc 1,2, Jan Lexell, MD, PhD 1,2, Christina Brogårdh, RPT, PhD 1,2 From the 1 Department of Health Sciences, Lund University, Sweden, 2 Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation Medicine, Skåne University Hospital, Sweden Corresponding author: Elisabeth Ekstrand, Department of Health Sciences, Physiotherapy, Lund University, Box 157, SE Lund, Sweden. elisabeth.ekstrand@med.lu.se. Telephone number:
3 Abstract Objective: To evaluate the test-retest reliability of the Shape/Texture Identification test (STI-test TM ) in persons with chronic stroke. Design: A test-retest design. Setting: University hospital outpatient setting. Participants: Forty-five persons (mean age 65 years) with mild to moderate impairments in the arm and hand > 6 months post stroke. Interventions: Not applicable. Main Measure: The STI-test TM was used to assess active touch of the hand. It consists of two subtests: identification of shapes and identification of textures, each in three different sizes. Both hands were assessed twice, one week apart. The reliability of the data was evaluated with weighted Kappa statistics and the Svensson rank-invariant method (percentage agreement, systematic and random disagreements). Results: The median total score of the STI-test TM was 5 points (min-max 0-6 points) for the more affected hand and 6 points (min-max 3-6 points) for the less affected hand at both test occasions. The weighted Kappa coefficient was 0.94 for the more affected hand and 0.55 for the less affected hand. The percentage agreement for the more affected hand was 69% for the subtest shapes and 82% for the subtest textures, and for the less affected hand 62% and 91%, respectively. There were no systematic or random disagreements for any of the subtests. 2
4 Conclusion: The STI-test TM is reliable to assess active touch of the hand after stroke. Key words: active touch; hand; outcome assessment; reproducibility of results; somatosensory disorders; stroke. 3
5 Introduction About 65% of persons admitted to stroke rehabilitation (subacute and chronic phase) have remaining somatosensory impairments of the affected arm and hand, 1 which impact on the ability to use the hand efficiently in daily activities. 2, 3 Somatosensory function of the hand after stroke is traditionally assessed in clinical settings by the detection of light touch and proprioceptive position discrimination, which partly are included in the Fugl-Meyer Assessment of Sensorimotor Recovery After Stroke. 4, 5 However, tests of light touch and proprioception are poorly standardized and therefore there are methodological considerations about their accuracy and reliability. 4 Moreover, assessment of light touch and proprioception are performed in a passive manner (passive touch), where active hand movements are not permitted. As opposed to being touched, as in passive assessments of touch, active touch is sensing by touching. In active touch, tactile and proprioceptive information is integrated during intended hand movements. 2 Active touch is a prerequisite for exploring and identifying objects shapes, textures and sizes. The predominant sensory input to an active hand movement (for example when grasping and manipulating) is active touch. 6 Active touch has also been shown to be an essential element in the process of tactile learning after stroke. 7 One standardized outcome measure that can be used to assess active touch of the hand is the STI-test TM (Shape/Texture Identification test). 8 The test assesses active touch by 4
6 means of identification of shapes and textures of increasing grades of difficulty. The STI-test TM is easy to perform and has shown robust psychometric properties in persons with peripheral nerve injuries and peripheral nerve diseases The test is used in clinical practice to assess somatosensory function after stroke but to the best of our knowledge, no study has evaluated the test-retest reliability in this population. The aim of the present study was therefore to evaluate the test-retest reliability of the STI-test TM as an outcome measure of active touch of the hand in persons with chronic stroke. Methods This study is a part of a larger data collection evaluating the psychometric properties of outcome measures that assess different aspects of functioning and disability of the arm and hand after stroke. 12, 13 In this study data from the STI-test TM are presented. Persons with stroke were recruited from a university hospital in Sweden during April to December 2013 with the following inclusion criteria: i) at least 6 months post stroke and ii) mild to moderate paresis in their more affected arm and hand (i.e., self-reported weakness, decreased dexterity and/or difficulties to perform daily hand activities but the ability to bring the hand to the forehead and to grasp and release one block of the Box and Block test 14 ). Exclusion criteria were: i) inability to understand test instructions due 5
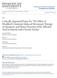
7 to impaired cognition and/or communication and ii) other diseases that could affect somatosensory function. To characterize the participants arm and hand function, assessments of sensorimotor impairments in both arms and hands were performed. Light touch and proprioception were assessed by the Fugl-Meyer Assessment of Sensorimotor Recovery After Stroke 5, grip strength was measured by the dynamometer Grippit ( Hägersten, Sweden) 13, muscle tone was assessed by the Modified Ashworth Scale 15 (classified as present if elbow, wrist or fingers had a score larger or equal to 1), and dexterity was assessed by the Modified Sollerman Hand Function Test 16 (score from 0 to 12 points, where 12 indicates normal dexterity). The less affected arm was assessed before the more affected arm and the sensorimotor assessments lasted about 25 minutes. Prior to inclusion, information about the purpose of the study was provided and each individual gave his or her written consent to participate. The principles of the Declaration of Helsinki were followed and the study was approved by the Regional Ethical Review Board, Lund, Sweden (Dnr 2012/591). The Shape/Texture Identification test (STI-test TM ) (Össur Nordic AB, Uppsala, Sweden, 8 consist of two subtests: a) identification of three shapes (cube, 6
8 cylinder or hexagon) and b) identification of three textures (one, two or three raised metal dots placed in a row) (Figure 1). The test includes three difficulty levels: decreasing sizes of the shapes (15, 8 and 5 mm), and decreasing size and distance between the dots (15, 8 and 4 mm). The score of the STI-test TM ranges from 0 to 6 points per hand, and 0 to 3 points (one point for each size) for each subtest. A maximum score of 6 points indicates normal somatosensory function. 8 Excellent test-retest reliability has been demonstrated (weighted Kappa 0.79 to 0.87) in persons with peripheral nerve injuries and diseases, and the minimally detectable change has been 8, 10, 11 defined as > 1.2 points in peripheral nerve injuries. Active touch of the hand was assessed on two occasions, one week apart, the same day of the week and the same time of the day, in a quiet separate room at the hospital by an experienced physiotherapist (first author) in agreement with the standardized protocol of the STI-test TM. 8 The participants were seated behind a screen to block their vision, and asked to identify the shapes and textures by active touch (Figure 1). Identification was performed with the pulp of the index finger with instruction not to use the nail. First the shapes of 15 mm were exposed to the less affected hand and then to the more affected hand, followed by the shapes of 8 mm and 5 mm in size. The textures were exposed in the same way. First the largest textures were exposed to the less affected hand and then to the more affected hand. Thereafter, the same procedure was used for the smaller 7
9 textures. The three shapes and textures for each size were presented randomly to the participants. To score one point the participants had to identify all three shapes or textures correctly. When the score was summarized the easier level (larger size) had to be correct to get one point on a more difficult level (smaller size), otherwise that level was set to zero. The test took about 10 minutes to complete. The participants were not informed of their results until they had completed the entire test on each test occasion. Statistics Descriptive statistics, frequencies, means and standard deviations (SD) or medians and minimum and maximum (min-max), were calculated for demographic data and clinical characteristics of the participants. The STI-test TM scores (ordinal data) from the two test occasions were presented as frequencies and medians (min-max). The differences of the total sum score (test occasion two minus test occasion one) were presented as frequencies (number of persons) and percentage. The test-retest reliability data from the two test occasions were evaluated both for the total sum score and for the two subtest scores. The test-retest reliability of the total sum score was evaluated by the Kappa statistics, the proportion of agreement observed beyond the agreement expected by chance, 17 8
10 using quadratic weights. 18, 19 In the Kappa matrices of the STI-test TM seven values (0 to 6) were used for the pairs of the total sum score from the two test occasions. The Kappa coefficients were calculated using the statistical software programme MedCalc, version 15 ( The strength of the Kappa coefficients was interpreted as < 0.40 poor, 0.40 to 0.75 fair to good, and > 0.75 excellent. 20 To evaluate the test-retest reliability of the two subtests (shapes and textures), the Svensson rank-invariant method 21 was used. Analyses of the percentage agreement and disagreements (systematic and random) between the two test occasions were performed for each subtest. The systematic disagreement was analysed in relative position and in relative concentration. Relative position explains the degree of systematic change in position (higher/lower) and a positive value indicates that the participants have higher scores on the second test occasion than on the first. The relative concentration expresses the degree of systematic shift in concentration (centred/dispersed) and a positive value indicates that the participants have more centred scores at the second test occasion. 21 Possible values of relative position and relative concentration range from -1 to 1, and zero values indicate a lack of systematic disagreement. The random disagreement (i.e., the variance that cannot be explained by the systematic disagreements) is expressed as the relative rank variance. The relative rank variance ranges from 0 to 1, and the higher the value the more dispersed is the test-retest measurements. The relative position, 9
11 relative concentration and relative rank variance values together with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using a freely available programme developed by Elisabeth Svensson ( Statistically significant values were indicated by a 95% confidence interval that did not cover zero. 21 Results Forty-five persons (37 men, 8 women) with chronic stroke and mild to moderate impairments in their arm and hand participated in the study. Their mean age and standard deviation (±SD) was 65 ±7 years and the mean time from stroke onset to first test occasion was 44 ±28 months. The clinical characteristics of the participants are presented in Table 1. The median total sum score of the STI-test TM was 5 points (min-max 0 to 6) for the more affected hand and 6 points (min-max 3 to 6) for the less affected hand at both test occasions. Thirty-one (69%) participants had somatosensory impairments (total sum score < 6) in the more affected hand, 20 participants (44%) in the less affected hand and 9 participants (20%) in both hands according to the STI-test TM. 10
12 Slightly more than 50% of the participants had the same total sum score at test occasion 1 and 2 (i.e., zero point difference) for both hands, but over 90% had at most a 1-point difference in the total sum score (Table 2). The weighted Kappa coefficient was 0.94 (95% CI 0.90 to 0.98) for the more affected hand and 0.55 (95% CI 0.27 to 0.83) for the less affected hand. The agreement expected by chance was 0.21 for the more affected hand and 0.46 for the less affected hand. As can be seen in Tables 3 and 4, the scores of the STI-test TM for the more affected hand were more evenly distributed along the scale (from lower to higher values), whereas the scores for the less affected hand were more concentrated to higher values for both subtests. A majority of the participants had only a 1-point difference in scores between the two test occasions and only a few participants had a 2-point difference. The percentage agreement (Table 5) ranged from 62% to 69% for the subtest shapes and from 82% to 91% for the subtest textures. The systematic disagreements in position and concentration as well as the random disagreements for the more and less affected hand were non-significant (the CI included zero) for both subtests. 11
13 Discussion This study showed that the test-retest agreements of the STI-test TM in persons with mild to moderate impairments of the arm and hand after stroke were high for both the more affected hand and the less affected hand, without any significant systematic and random disagreements. More than 50% of the participants had no difference (zero point) in their total sum score between the two test occasions. As the minimally detectable change in peripheral nerve injuries has been defined as 1.2 points 10 it is reasonable to assume that a difference of at least one point lies within the normal variability also for persons after stroke. Over 90% of the participants had a total sum score of at most 1-point difference, which can be considered as a very high agreement between the two test occasions. The test-retest reliability, based on the weighted Kappa coefficient for the total sum scores, was excellent 20 for the more affected hand (0.94). This is in agreement with previous reliability studies of the STI-test TM in peripheral nerve injuries and diseases. 8, 11 However, the Kappa coefficient for the less affected hand (0.55) was only fair to good, 20 although 96% of the participants had at most 1-point difference between the two test occasions. The explanation for the low Kappa value for the less affected hand could be due to the scores being concentrated to the higher end of the scale (3 to 6 points) 12
14 compared to the more affected hand where the whole scale was used (0 to 6 points). The Kappa coefficient is calculated as the agreement observed beyond the agreement expected by chance. When few values in the scale are used in a test it is easier to obtain agreement just by chance. 19 The agreement by chance for the less affected hand (0.46) was higher than for the more affected hand (0.21) and, consequently, the agreement observed must be higher to obtain the same Kappa coefficient. This shows that the Kappa evaluation has limitations when the whole scale is not used, as for the less affected hand. Furthermore, the Kappa coefficient only evaluates the agreement between repeated test occasions and not if there are systematic or random disagreements. However, as previous studies have used the weighted Kappa statistics to evaluate the test-retest reliability of the total sum score of the STI-test TM, 8, 11 we also performed this analysis to enable a comparison of results. To expand our reliability analysis, we also included analyses of the subtest scores by means of the Svensson rank-invariant method. The advantage of using the Svensson method is that it provides information about the agreement between repeated measurements, but also an understanding of the size and type of disagreement. This enables the possibility to evaluate if the disagreements are large enough to affect the test-retest reliability of the measurements. The percent agreement for the identification of shapes could be considered somewhat low for both hands (more affected hand 69% 13
15 and less affected hand 62%) compared to the textures (more affected hand 82% and less affected hand 91%) (cf Table 5). 22 One explanation could be that the identification of shapes require a three-dimensional integration of tactile and proprioceptive information by active touch and is thereby more difficult for the brain to interpret compared to the more two-dimensional identification of textures. However, the dispersion of differences between the tests was small and a majority of the differences were not more than 1 point. Moreover, there were no significant disagreements, neither systematic nor random, for any of the subtests or hands. When the somatosensory impairments were assessed with the FM-UE test (passive touch), 38% of the participants had impairments in the more affected hand but no one in the less affected hand. When the somatosensory impairments were assessed with the STI-test TM (active touch) the corresponding figures were 69% for the more affected hand and 44% for the less affected hand. In clinical practice, light touch and proprioception are usually part of the standard assessment after stroke. 4 However, these tests are performed in a passive manner that is less relevant to grip control compared to active touch. 2 Thus, if only light touch and proprioception are assessed, the somatosensory impairments after stroke might be underestimated. 14
16 Several factors can influence the test-retest reliability. In the present study, the test situation was carefully standardized and the test protocol was thoroughly described. A one-week interval between the test occasions was chosen to avoid fatigue, minimize learning effects and to standardize the testing. The participants were tested at the same location, at the same time and day of the week at both test occasions. All participants were in the chronic phase after stroke when spontaneous recovery no longer is expected and therefore considered stable with regard to their somatosensory function. There is no accepted method to decide the sample size when using the Svensson rankinvariant method. 21 About 30 participants are considered sufficient in test-retest reliability studies of parametrical data, 23 but when non-parametric data is used it is suggested that the sample size should be larger. 24 Therefore, we included 45 participants, which we believe can be considered sufficiently large to evaluate the reliability of the STI-test TM. Study Limitations In the present study, persons with major cognitive impairments or difficulties to communicate were excluded, and more men than women agreed to participate. As the STI-test TM assesses active touch, persons with no motor function in their more affected 15
17 hand cannot perform the test. Therefore, the results cannot be generalized to the entire stroke population. As this study was part of a larger data collection comprising assessments of function, activity of the arm and hand, perceived participation and life satisfaction after stroke we had to limit the number of somatosensory outcome measures and variables assessed. We only had three somatosensory measures in the present study and it had been valuable to also include other measures of active touch. However, there is a lack of simple and standardized outcome measures to assess somatosensory function after stroke. In the present study, we therefore aimed to evaluate the psychometric properties of the STItest TM as a measure of active touch. In the future it would be valuable to investigate other psychometric properties, such as validity and responsiveness, but also how the STI-test TM is associated with motor function (dexterity) of the hand. Clinical Messages The STI-test TM is reliable to assess active touch of the hand in persons with chronic stroke. 16
18 Acknowledgements We thank the persons who volunteered to participate and Associate Professor Birgitta Rosén, OT, PhD, Lund University, Lund, Sweden for valuable discussions about the STI-test TM. Funding The study was supported by grants from Skåne county council s research and development foundation, Vårdakademin at Skåne University Hospital, the Norrbacka Eugenia Foundation and the Swedish Stroke Association. Conflict of Interest No part of this work has been published elsewhere and is not under consideration for publication in any other journal. No conflict of interest exists. 17
19 References 1. Carey LM, Matyas TA. Frequency of discriminative sensory loss in the hand after stroke in a rehabilitation setting. J Rehabil Med. 2011;43(3): Blennerhassett JM, Matyas TA, Carey LM. Impaired discrimination of surface friction contributes to pinch grip deficit after stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2007;21(3): Hermsdorfer J, Hagl E, Nowak DA, Marquardt C. Grip force control during object manipulation in cerebral stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003;114(5): Winward CE, Halligan PW, Wade DT. Current practice and clinical relevance of somatosensory assessment after stroke. Clin Rehabil. 1999;13(1): Fugl-Meyer AR, Jaasko L, Leyman I, Olsson S, Steglind S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. A method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand J Rehabil Med. 1975;7(1): Gibson JJ. Observations on active touch. Psychol Rev. 1962;69: Carey L, Macdonell R, Matyas TA. SENSe: Study of the Effectiveness of Neurorehabilitation on Sensation: a randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2011;25(4): Rosen B, Lundborg G. A new tactile gnosis instrument in sensibility testing. J Hand Ther. 1998;11(4):
20 9. Rosén B, Jerosch-Herold C. Comparing the responsiveness over time of two tactile gnosis tests: two-point discrimination and the STI-test. Brit J Hand Ther. 2000;5(4): Rosén B. Inter-Tester Reliability of a Tactile Gnosis Test: the STI-Test. Brit J Hand Ther. 2003;8(3): Svensson E, Hager-Ross C. Hand function in Charcot Marie Tooth: test retest reliability of some measurements. Clin Rehabil. 2006;20(10): Ekstrand E, Lindgren I, Lexell J, Brogardh C. Test-retest reliability of the ABILHAND questionnaire in persons with chronic stroke. PM R. 2014;6(4): Ekstrand E, Lexell J, Brogardh C. Isometric and isokinetic muscle strength in the upper extremity can be reliably measured in persons with chronic stroke. J Rehabil Med. 2015;47: Mathiowetz V, Volland G, Kashman N, Weber K. Adult norms for the Box and Block Test of manual dexterity. Am J Occup Ther. 1985;39(6): Bohannon RW, Smith MB. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys Ther. 1987;67(2): Rosen B. Recovery of sensory and motor function after nerve repair. A rationale for evaluation. J Hand Ther. 1996;9(4): Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ Psychol Meas. 1960;20:
21 18. Cohen J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol Bull. 1968;70(4): Sim J, Wright CC. The kappa statistic in reliability studies: use, interpretation, and sample size requirements. Phys Ther. 2005;85(3): Fleiss JL. Statistical methods for rates and proportions. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley; Svensson E. Different ranking approaches defining association and agreement measures of paired ordinal data. Stat Med. 2012;31(26): Kazdin AE. Artifact, bias, and complexity of assessment: the ABCs of reliability. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977;10(1): Hobart JC, Cano SJ, Warner TT, Thompson AJ. What sample sizes for reliability and validity studies in neurology? J Neurol. 2012;259(12): Lehmann EL, D'Abrera HJ. Nonparametrics: statistical methods based on ranks. New York: Springer;
22 Table 1. Characteristics of the 45 participants with chronic stroke. Type of stroke, n (%) Cerebral infarction 32 (71) Cerebral haemorrhage 13 (29) Paretic side, n (%) Right 25 (56) Handedness, n (%) Right handedness 42 (93) Light touch absent or diminished, more affected arm and hand, n (%) a 17 (38) Arm (upper arm, forearm) 12 (27) Hand (palmar surface) 17 (38) Proprioception absent or diminished, more affected arm and hand, n (%) a 9 (20) Wrist 5 (11) Thumb 9 (20) Grip strength, more affected hand, newton (SD) b 238 (112) Grip strength ratio, more affected hand/less affected hand, newton (SD) 0.71 (0.28) Spasticity, more affected arm and hand 1, n (%) c 15 (33) Dexterity (score 0-12), more affected hand, median (min-max) d 7 (0-11) n: number of participants; a Fugl-Meyer Assessment of Sensorimotor Recovery After Stroke; b assessed by the dynamometer Grippit ( Hägersten, Sweden); c Modified Ashworth Scale; d Modified Sollerman Hand Function Test. 21
23 22
24 Table 2. Number (%) of participants with differences in the total STI-test TM score between the two test occasions (n=45). Differences in scores T2 minus T More affected hand 1 (2) 6 (13) 26 (58) 10 (22) 2 (4) Less affected hand 0 (0) 6 (13) 25 (56) 12 (27) 2 (4) T1: test occasion one; T2: test occasion two; zero indicates that participants had the same total STI-test TM score at both test occasions; a positive or negative value indicates that the ratings at T2 were higher or lower, respectively, than at T1. 23
25 Table 3. The subtest shapes: pairs of data from the two test occasions for the more affected hand and the less affected hand (n=45). More affected hand T1 Less affected hand T T T1: test occasion one; T2: test occasion two. Numbers in bold print represent the pairs of identical total scores of the STI-test TM at both test occasions. 24
26 Table 4. The subtest textures: pairs of data from the two test occasions for the more affected hand and the less affected hand (n=45). More affected hand T1 Less affected hand T T T1: test occasion one; T2: test occasion two. Numbers in bold print represent the pairs of identical total scores of the STI-test TM at both test occasions. 25
27 Table 5. Percentage agreement, and systematic and random disagreements between test occasion 1 and 2 for the two subtests of STI TM (n=45). PA % RP RC RV 95% CI 95% CI 95% CI More affected hand Subtest shapes to 0.12 Subtest textures to 0.13 Less affected hand Subtest shapes to 0.29 Subtest textures to to to to to to to to to 0.00 PA: percentage agreement; RP: relative position (systematic disagreement); RC: relative concentration (systematic disagreement); RV: relative rank variance (random disagreement); CI: confidence interval 26
28 a) b) c) Figure 1: The Shape/Texture Identification test (a-b) and the testing position (c) 27
Grip strength is a representative measure of muscle weakness in the upper extremity after stroke
 Grip strength is a representative measure of muscle weakness in the upper extremity after stroke Ekstrand, Elisabeth; Lexell, Jan; Brogårdh, Christina Published in: Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation DOI:
Grip strength is a representative measure of muscle weakness in the upper extremity after stroke Ekstrand, Elisabeth; Lexell, Jan; Brogårdh, Christina Published in: Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation DOI:
Upper extremity disability after stroke. Psychometric properties of outcome measures and perceived ability to perform daily hand activities.
 Upper extremity disability after stroke. Psychometric properties of outcome measures and perceived ability to perform daily hand activities. Ekstrand, Elisabeth Submitted: 2016-01-01 Document Version Other
Upper extremity disability after stroke. Psychometric properties of outcome measures and perceived ability to perform daily hand activities. Ekstrand, Elisabeth Submitted: 2016-01-01 Document Version Other
ISOMETRIC AND ISOKINETIC MUSCLE STRENGTH IN THE UPPER EXTREMITY CAN BE RELIABLY MEASURED IN PERSONS WITH CHRONIC STROKE
 J Rehabil Med 2015; 47: 706 713 ORIGINAL REPORT ISOMETRIC AND ISOKINETIC MUSCLE STRENGTH IN THE UPPER EXTREMITY CAN BE RELIABLY MEASURED IN PERSONS WITH CHRONIC STROKE Elisabeth Ekstrand, RPT, MSc 1,2,
J Rehabil Med 2015; 47: 706 713 ORIGINAL REPORT ISOMETRIC AND ISOKINETIC MUSCLE STRENGTH IN THE UPPER EXTREMITY CAN BE RELIABLY MEASURED IN PERSONS WITH CHRONIC STROKE Elisabeth Ekstrand, RPT, MSc 1,2,
Ten recommendations for Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (OAC) manuscript preparation, common for all types of studies.
 Ten recommendations for Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (OAC) manuscript preparation, common for all types of studies. Ranstam, Jonas; Lohmander, L Stefan Published in: Osteoarthritis and Cartilage DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2011.07.007
Ten recommendations for Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (OAC) manuscript preparation, common for all types of studies. Ranstam, Jonas; Lohmander, L Stefan Published in: Osteoarthritis and Cartilage DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2011.07.007
NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL. For assessment of hand function after nerve repair
 NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL For assessment of hand function after nerve repair Manual for assessment of hand function after nerve repair according to Rosen score 1 Version 1, 2018 Documentation of hand
NATIONAL ASSESSMENT MANUAL For assessment of hand function after nerve repair Manual for assessment of hand function after nerve repair according to Rosen score 1 Version 1, 2018 Documentation of hand
Augmented reflection technology for stroke rehabilitation a clinical feasibility study
 Augmented reflection technology for stroke rehabilitation a clinical feasibility study S Hoermann 1, L Hale 2, S J Winser 2, H Regenbrecht 1 1 Department of Information Science, 2 School of Physiotherapy,
Augmented reflection technology for stroke rehabilitation a clinical feasibility study S Hoermann 1, L Hale 2, S J Winser 2, H Regenbrecht 1 1 Department of Information Science, 2 School of Physiotherapy,
Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Survey: Let us know how this paper benefits you.
 Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Occupational Therapy Critically Appraised Papers Series Occupational Therapy 2017 Critically Appraised Paper for The Effect of Modified Constraint-Induced
Dominican University of California Dominican Scholar Occupational Therapy Critically Appraised Papers Series Occupational Therapy 2017 Critically Appraised Paper for The Effect of Modified Constraint-Induced
Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures
 Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures Collin, David; Dunker, Dennis; Gothlin, Jan H.; Geijer, Mats Published in: Acta Radiologica
Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures Collin, David; Dunker, Dennis; Gothlin, Jan H.; Geijer, Mats Published in: Acta Radiologica
Interrater and Intrarater Reliability of the Assisting Hand Assessment
 Interrater and Intrarater Reliability of the Assisting Hand Assessment Marie Holmefur, Lena Krumlinde-Sundholm, Ann-Christin Eliasson KEY WORDS hand pediatric reliability OBJECTIVE. The aim of this study
Interrater and Intrarater Reliability of the Assisting Hand Assessment Marie Holmefur, Lena Krumlinde-Sundholm, Ann-Christin Eliasson KEY WORDS hand pediatric reliability OBJECTIVE. The aim of this study
Life Satisfaction in Persons with Late Effects of Polio
 Life Satisfaction in Persons with Late Effects of Polio Lund, Maria Larsson; Lexell, Jan Published in: Applied Research in Quality of Life DOI: 10.1007/s11482-010-9116-4 2011 Link to publication Citation
Life Satisfaction in Persons with Late Effects of Polio Lund, Maria Larsson; Lexell, Jan Published in: Applied Research in Quality of Life DOI: 10.1007/s11482-010-9116-4 2011 Link to publication Citation
Significance of a notch in the otoacoustic emission stimulus spectrum.
 Significance of a notch in the otoacoustic emission stimulus spectrum. Grenner, Jan Published in: Journal of Laryngology and Otology DOI: 10.1017/S0022215112001533 Published: 2012-01-01 Link to publication
Significance of a notch in the otoacoustic emission stimulus spectrum. Grenner, Jan Published in: Journal of Laryngology and Otology DOI: 10.1017/S0022215112001533 Published: 2012-01-01 Link to publication
What's on the Horizon: Defining Physiatry Through Rehabilitation Methodology.
 What's on the Horizon: Defining Physiatry Through Rehabilitation Methodology. Lexell, Jan Published in: PM&R DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.03.009 2012 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
What's on the Horizon: Defining Physiatry Through Rehabilitation Methodology. Lexell, Jan Published in: PM&R DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.03.009 2012 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Lars Jacobsson 1,2,3* and Jan Lexell 1,3,4
 Jacobsson and Lexell Health and Quality of Life Outcomes (2016) 14:10 DOI 10.1186/s12955-016-0405-y SHORT REPORT Open Access Life satisfaction after traumatic brain injury: comparison of ratings with the
Jacobsson and Lexell Health and Quality of Life Outcomes (2016) 14:10 DOI 10.1186/s12955-016-0405-y SHORT REPORT Open Access Life satisfaction after traumatic brain injury: comparison of ratings with the
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effectiveness of a modified constraint-induced therapy (mcit) intervention compared to conventional rehabilitation methods for the rehabilitation
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION What is the effectiveness of a modified constraint-induced therapy (mcit) intervention compared to conventional rehabilitation methods for the rehabilitation
TEST-RETEST INTRA-RATER RELIABILITY OF GRIP FORCE IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE
 J Rehabil Med 2003; 35: 189 194 TEST-RETEST INTRA-RATER RELIABILITY OF GRIP FORCE IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE Ann Hammer 1 and Birgitta Lindmark 2 From the 1 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Örebro University
J Rehabil Med 2003; 35: 189 194 TEST-RETEST INTRA-RATER RELIABILITY OF GRIP FORCE IN PATIENTS WITH STROKE Ann Hammer 1 and Birgitta Lindmark 2 From the 1 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Örebro University
Increased mortality after fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus: a case-control study of 253 patients with a 12-year follow-up.
 Increased mortality after fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus: a case-control study of 253 patients with a 12-year follow-up. Olsson, Christian; Petersson, Claes; Nordquist, Anders Published in:
Increased mortality after fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus: a case-control study of 253 patients with a 12-year follow-up. Olsson, Christian; Petersson, Claes; Nordquist, Anders Published in:
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill. patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry
 Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Use of mental imagery to improve task generalisation after a stroke
 HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH FUND Use of mental imagery to improve task generalisation after a stroke Key Messages Patients who received mental imagery intervention showed better performance on 15 daily tasks
HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH FUND Use of mental imagery to improve task generalisation after a stroke Key Messages Patients who received mental imagery intervention showed better performance on 15 daily tasks
Teaching A Way of Implementing Statistical Methods for Ordinal Data to Researchers
 Journal of Mathematics and System Science (01) 8-1 D DAVID PUBLISHING Teaching A Way of Implementing Statistical Methods for Ordinal Data to Researchers Elisabeth Svensson Department of Statistics, Örebro
Journal of Mathematics and System Science (01) 8-1 D DAVID PUBLISHING Teaching A Way of Implementing Statistical Methods for Ordinal Data to Researchers Elisabeth Svensson Department of Statistics, Örebro
Many upper extremity motor function outcome measures do
 Assessing Wolf Motor Function Test as Outcome Measure for Research in Patients After Stroke Steven L. Wolf, PhD, PT; Pamela A. Catlin, EdD, PT; Michael Ellis, MPT; Audrey Link Archer, MPT; Bryn Morgan,
Assessing Wolf Motor Function Test as Outcome Measure for Research in Patients After Stroke Steven L. Wolf, PhD, PT; Pamela A. Catlin, EdD, PT; Michael Ellis, MPT; Audrey Link Archer, MPT; Bryn Morgan,
1 Miller RP, Kori SH, Todd DD. The Tampa Scale. Unpublished
 J Rehabil Med 2005; 37: 330 334 EVALUATING THE RELIABILITY OF MULTI-ITEM SCALES: A NON-PARAMETRIC APPROACH TO THE ORDERED CATEGORICAL STRUCTURE OF DATA COLLECTED WITH THE SWEDISH VERSION OF THE TAMPA SCALE
J Rehabil Med 2005; 37: 330 334 EVALUATING THE RELIABILITY OF MULTI-ITEM SCALES: A NON-PARAMETRIC APPROACH TO THE ORDERED CATEGORICAL STRUCTURE OF DATA COLLECTED WITH THE SWEDISH VERSION OF THE TAMPA SCALE
On the physiological location of otoacoustic emissions
 On the physiological location of otoacoustic emissions Brännström, Jonas; Lantz, Johannes Published: 2001-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Brännström, J., & Lantz, J. (2001).
On the physiological location of otoacoustic emissions Brännström, Jonas; Lantz, Johannes Published: 2001-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Brännström, J., & Lantz, J. (2001).
End-of-life care in oxygen-dependent COPD and cancer: a national population-based study.
 End-of-life care in oxygen-dependent COPD and cancer: a national population-based study. Ahmadi, Zainab; Lundström, Staffan; Janson, Christer; Strang, Peter; Emtner, Margareta; Currow, David C; Ekström,
End-of-life care in oxygen-dependent COPD and cancer: a national population-based study. Ahmadi, Zainab; Lundström, Staffan; Janson, Christer; Strang, Peter; Emtner, Margareta; Currow, David C; Ekström,
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION: Will use of low-level functional electrical stimulation improve accuracy of active reaching with the upper extremity better than traditional occupational
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION: Will use of low-level functional electrical stimulation improve accuracy of active reaching with the upper extremity better than traditional occupational
Inter-rater reliability and validity of the Action Research arm test in stroke patients
 Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 107-1 I 3 Inter-rater reliability and validity of the Action Research arm test in stroke patients CHING-LJN HSIEH, I-PING HSUEH, FU-MEI CHIANG 1, PO-HSIN LJN School of Occupational
Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 107-1 I 3 Inter-rater reliability and validity of the Action Research arm test in stroke patients CHING-LJN HSIEH, I-PING HSUEH, FU-MEI CHIANG 1, PO-HSIN LJN School of Occupational
Abdul-Alim A. Atteya, PhD, PT. ABSTRACT
 Articles Abdul-Alim A. Atteya, PhD, PT. ABSTRACT Objectives: To examine the feasibility and efficacy of a modified constraint induced therapy protocol on stroke patients. Methods: This study was carried
Articles Abdul-Alim A. Atteya, PhD, PT. ABSTRACT Objectives: To examine the feasibility and efficacy of a modified constraint induced therapy protocol on stroke patients. Methods: This study was carried
Change in health-related quality of life over 1 month in cancer patients with high initial levels of symptoms and problems
 Syddansk Universitet Change in health-related quality of life over 1 month in cancer patients with high initial levels of symptoms and problems Lund Rasmussen, Charlotte; Johnsen, Anna Thit; Petersen,
Syddansk Universitet Change in health-related quality of life over 1 month in cancer patients with high initial levels of symptoms and problems Lund Rasmussen, Charlotte; Johnsen, Anna Thit; Petersen,
MINERVA MEDICA COPYRIGHT
 EUR J PHYS REHABIL MED 2008;44:431-5 Robot-assisted therapy for neuromuscular training of sub-acute stroke patients. A feasibility study Aim. Several studies have described the contribution of robotics
EUR J PHYS REHABIL MED 2008;44:431-5 Robot-assisted therapy for neuromuscular training of sub-acute stroke patients. A feasibility study Aim. Several studies have described the contribution of robotics
Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients.
 Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients. Isaksson, Marléne Published in: Contact Dermatitis DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.00959.x
Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients. Isaksson, Marléne Published in: Contact Dermatitis DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.00959.x
A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy
 Indian J Lepr 2011, 83 : 209-213 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy 1 2 3 Mannam Ebenezer, Kelly
Indian J Lepr 2011, 83 : 209-213 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy 1 2 3 Mannam Ebenezer, Kelly
LUP. Lund University Publications. Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. This paper has
LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. This paper has
Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma
 Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma Gunnel Sandqvist and Mona Eklund Objective. Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) is a hand function test for persons who have systemic sclerosis
Validity of HAMIS: A Test of Hand Mobility in Scleroderma Gunnel Sandqvist and Mona Eklund Objective. Hand Mobility in Scleroderma (HAMIS) is a hand function test for persons who have systemic sclerosis
INTRODUCTION SUBJECTS AND METHODS
 J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
Strengths of the Nordic monitoring system
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 12, 2018 Strengths of the Nordic monitoring system Fagt, Sisse; Matthiessen, Jeppe Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 12, 2018 Strengths of the Nordic monitoring system Fagt, Sisse; Matthiessen, Jeppe Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of
Puschmann, Andreas; Dickson, Dennis W; Englund, Elisabet; Wszolek, Zbigniew K; Ross, Owen A
 CHCHD2 and Parkinson's disease Puschmann, Andreas; Dickson, Dennis W; Englund, Elisabet; Wszolek, Zbigniew K; Ross, Owen A Published in: Lancet Neurology DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00095-2 2015 Link to
CHCHD2 and Parkinson's disease Puschmann, Andreas; Dickson, Dennis W; Englund, Elisabet; Wszolek, Zbigniew K; Ross, Owen A Published in: Lancet Neurology DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00095-2 2015 Link to
Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease
 Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease R.W. Selles, PhD; B.T.J. van Ginneken, MSc; T.A.R. Schreuders, PT, PhD; W.G.M. Janssen, MD; and H.J. Stam, MD, PhD, FRCP
Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease R.W. Selles, PhD; B.T.J. van Ginneken, MSc; T.A.R. Schreuders, PT, PhD; W.G.M. Janssen, MD; and H.J. Stam, MD, PhD, FRCP
A New Tactile Gnosis Instrument in Sensibility Testing
 ( SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLESJ A New Tactile Gnosis Instrument in Sensibility Testing B. Rosen, OT, MSc G. Lundborg, MD, PhD Department of Hand Surgery Malmo University Hospital Lund University Malmo,
( SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLESJ A New Tactile Gnosis Instrument in Sensibility Testing B. Rosen, OT, MSc G. Lundborg, MD, PhD Department of Hand Surgery Malmo University Hospital Lund University Malmo,
The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function
 The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function Raviraj Nataraj, Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, William H. Seitz, MD, Zong-Ming Li. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA. Disclosures:
The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function Raviraj Nataraj, Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, William H. Seitz, MD, Zong-Ming Li. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA. Disclosures:
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy an effective intervention for improving function in paralyzed upper extremities after a stroke as compared to the standard therapy? Dohle,
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy an effective intervention for improving function in paralyzed upper extremities after a stroke as compared to the standard therapy? Dohle,
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008
 Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
FLT3 mutations in patients with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
 FLT3 mutations in patients with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) Kabir, Nuzhat N.; Rönnstrand, Lars; Uddin, Kazi Published in: Medical Oncology DOI: 10.1007/s12032-013-0462-6 Published: 2013-01-01
FLT3 mutations in patients with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) Kabir, Nuzhat N.; Rönnstrand, Lars; Uddin, Kazi Published in: Medical Oncology DOI: 10.1007/s12032-013-0462-6 Published: 2013-01-01
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy more effective in a, or individually, on sensorimotor function, activities of daily living, quality of life, and visuospatial neglect
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is mirror therapy more effective in a, or individually, on sensorimotor function, activities of daily living, quality of life, and visuospatial neglect
The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity
 863 The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity Tetsuya Tsuji, MD, Meigen Liu, MD, DMSc, Shigeru Sonoda, MD, DMSc, Kazuhisa Domen, MD, DMSc, Naoichi Chino, MD,
863 The Stroke Impairment Assessment Set: Its Internal Consistency and Predictive Validity Tetsuya Tsuji, MD, Meigen Liu, MD, DMSc, Shigeru Sonoda, MD, DMSc, Kazuhisa Domen, MD, DMSc, Naoichi Chino, MD,
Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis
 Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis Milos R. Popovic* 1,2, Vlasta Hajek 2, Jenifer Takaki 2, AbdulKadir Bulsen 2 and Vera Zivanovic 1,2 1 Institute
Restoration of Reaching and Grasping Functions in Hemiplegic Patients with Severe Arm Paralysis Milos R. Popovic* 1,2, Vlasta Hajek 2, Jenifer Takaki 2, AbdulKadir Bulsen 2 and Vera Zivanovic 1,2 1 Institute
Comparing Vertical and Horizontal Scoring of Open-Ended Questionnaires
 A peer-reviewed electronic journal. Copyright is retained by the first or sole author, who grants right of first publication to the Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation. Permission is granted to
A peer-reviewed electronic journal. Copyright is retained by the first or sole author, who grants right of first publication to the Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation. Permission is granted to
The Effects of Hand Strength on Pointing Performance
 Chapter 1 The Effects of Hand Strength on Pointing Performance P. Biswas and P. Robinson 1.1 Introduction Pointing tasks form a significant part of human-computer interaction in graphical user interfaces.
Chapter 1 The Effects of Hand Strength on Pointing Performance P. Biswas and P. Robinson 1.1 Introduction Pointing tasks form a significant part of human-computer interaction in graphical user interfaces.
Reliability of the Modified Motor Assessment Scale and the Barthel Index
 Reliability of the Modified Motor Assessment Scale and the Barthel Index SANDY C. LOEWEN and BRIAN A. ANDERSON Many physical therapists use descriptive and functional assessments of motor recovery for
Reliability of the Modified Motor Assessment Scale and the Barthel Index SANDY C. LOEWEN and BRIAN A. ANDERSON Many physical therapists use descriptive and functional assessments of motor recovery for
The potential for faking on the Mississippi Scale for Combat-Related PTSD
 The potential for faking on the Mississippi Scale for Combat-Related PTSD Lyons, J.A.; Caddell, J.M.; Pittman, R.L.; Rawls, R.; Perrin, Sean Published in: Journal of Traumatic Stress DOI: 10.1007/BF02102788
The potential for faking on the Mississippi Scale for Combat-Related PTSD Lyons, J.A.; Caddell, J.M.; Pittman, R.L.; Rawls, R.; Perrin, Sean Published in: Journal of Traumatic Stress DOI: 10.1007/BF02102788
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Smania, N., Gandolfi, M., Paolucci, S., Iosa, M., Ianes, P., Recchia, S., & Farina, S. (2012). Reduced-intensity modified constraint-induced movement therapy versus conventional
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Smania, N., Gandolfi, M., Paolucci, S., Iosa, M., Ianes, P., Recchia, S., & Farina, S. (2012). Reduced-intensity modified constraint-induced movement therapy versus conventional
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION For stroke patients, in what ways does robot-assisted therapy improve upper extremity performance in the areas of motor impairment, muscle power, and strength?
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION For stroke patients, in what ways does robot-assisted therapy improve upper extremity performance in the areas of motor impairment, muscle power, and strength?
University of Dundee. Volunteering Scott, Rosalind. Publication date: Link to publication in Discovery Research Portal
 University of Dundee Volunteering Scott, Rosalind Publication date: 2009 Link to publication in Discovery Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Scott, R. (2009). Volunteering: does our
University of Dundee Volunteering Scott, Rosalind Publication date: 2009 Link to publication in Discovery Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Scott, R. (2009). Volunteering: does our
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Wu, C., Huang, P., Chen, Y., Lin, K., & Yang, H. (2013). Effects of mirror therapy on motor and sensory recovery in chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Archives
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Wu, C., Huang, P., Chen, Y., Lin, K., & Yang, H. (2013). Effects of mirror therapy on motor and sensory recovery in chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Archives
The variable risk of colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
 The variable risk of colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Lindgren, Stefan Published in: European Journal of Internal Medicine DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2004.12.001 Published: 2005-01-01
The variable risk of colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Lindgren, Stefan Published in: European Journal of Internal Medicine DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2004.12.001 Published: 2005-01-01
The Relationship among COPD Severity, Inhaled Corticosteroid Use, and the Risk of Pneumonia.
 The Relationship among COPD Severity, Inhaled Corticosteroid Use, and the Risk of Pneumonia. Rennard, Stephen I; Sin, Donald D; Tashkin, Donald P; Calverley, Peter M; Radner, Finn Published in: Annals
The Relationship among COPD Severity, Inhaled Corticosteroid Use, and the Risk of Pneumonia. Rennard, Stephen I; Sin, Donald D; Tashkin, Donald P; Calverley, Peter M; Radner, Finn Published in: Annals
Evaluation of New Parameters for Assessment of Stroke Impairment
 Evaluation of New Parameters for Assessment of Stroke Impairment Kathrin Tyryshkin a, Janice I. Glasgow a and Stephen H. Scott b a School of Computing, Queen s University, Kingston, ON. Canada; b Department
Evaluation of New Parameters for Assessment of Stroke Impairment Kathrin Tyryshkin a, Janice I. Glasgow a and Stephen H. Scott b a School of Computing, Queen s University, Kingston, ON. Canada; b Department
William C Miller, PhD, FCAOT Professor Occupational Science & Occupational Therapy University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada
 William C Miller, PhD, FCAOT Professor Occupational Science & Occupational Therapy University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada THE L TEST MANUAL Version: November 2014 Table of Contents Introduction...
William C Miller, PhD, FCAOT Professor Occupational Science & Occupational Therapy University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada THE L TEST MANUAL Version: November 2014 Table of Contents Introduction...
Does organic food intervention in the Danish schools lead to change dietary patterns? He, Chen; Mikkelsen, Bent Egberg
 Aalborg Universitet Does organic food intervention in the Danish schools lead to change dietary patterns? He, Chen; Mikkelsen, Bent Egberg Published in: Like what you get? Is it good for you? Organic food,
Aalborg Universitet Does organic food intervention in the Danish schools lead to change dietary patterns? He, Chen; Mikkelsen, Bent Egberg Published in: Like what you get? Is it good for you? Organic food,
Reliability of the Box and Block Test of Manual Dexterity for Use With Patients With Fibromyalgia
 Brief Report Reliability of the Box and Block Test of Manual Dexterity for Use With Patients With Fibromyalgia Mark L. Canny, Jeffrey M. Thompson, Mikel J. Wheeler KEY WORDS disability evaluation fibromyalgia
Brief Report Reliability of the Box and Block Test of Manual Dexterity for Use With Patients With Fibromyalgia Mark L. Canny, Jeffrey M. Thompson, Mikel J. Wheeler KEY WORDS disability evaluation fibromyalgia
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is the combination of occupational therapy (OT) and mental practice (MP), from either an internal or an external perspective, an effective intervention
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION Is the combination of occupational therapy (OT) and mental practice (MP), from either an internal or an external perspective, an effective intervention
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs
 Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Professions and occupational identities
 Professions and occupational identities Sundin, Olof; Hedman, Jenny Published in: Theories of information behavior: a researcher s quide Published: 2005-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published
Professions and occupational identities Sundin, Olof; Hedman, Jenny Published in: Theories of information behavior: a researcher s quide Published: 2005-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published
Assessment of Somatosensory
 Rivermead Assessment of Somatosensory Performance Charlotte E Winward 1, Peter W Halligan 2, Derick T Wade 3 2 nd EDITION (2012) OPERATOR MANUAL 1 Movement Science Group, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford,
Rivermead Assessment of Somatosensory Performance Charlotte E Winward 1, Peter W Halligan 2, Derick T Wade 3 2 nd EDITION (2012) OPERATOR MANUAL 1 Movement Science Group, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford,
Date: December 4 th, 2012 CLINICAL SCENARIO:
 1 Title: There is strong support for the effectiveness of mcimt compared to conventional therapy in improving physical function and occupational performance of the affected upper extremity in adults 0
1 Title: There is strong support for the effectiveness of mcimt compared to conventional therapy in improving physical function and occupational performance of the affected upper extremity in adults 0
Modified constraint induced therapy: A randomized feasibility and efficacy study
 Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 38 No. 5, September/October 2001 Pages 583 590 CLINICAL REPORT Modified constraint induced therapy: A randomized feasibility and efficacy study Stephen
Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development Vol. 38 No. 5, September/October 2001 Pages 583 590 CLINICAL REPORT Modified constraint induced therapy: A randomized feasibility and efficacy study Stephen
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Cui, B. J., Wang, D. Q., Qiu, J. Q., Huang, L. G., Zeng, F. S., Zhang, Q.,... Sun, Q. S. (2015). Effects of a 12-hour neuromuscular electrical stimulation treatment program
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Cui, B. J., Wang, D. Q., Qiu, J. Q., Huang, L. G., Zeng, F. S., Zhang, Q.,... Sun, Q. S. (2015). Effects of a 12-hour neuromuscular electrical stimulation treatment program
Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain
 Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
MANY DIFFERENT OUTCOME measures have been developed
 14 The Intra- and Interrater Reliability of the Action Research Arm Test: A Practical Test of Upper Extremity Function in Patients With Stroke Johanna H. Van der Lee, MD, Vincent De Groot, MD, Heleen Beckerman,
14 The Intra- and Interrater Reliability of the Action Research Arm Test: A Practical Test of Upper Extremity Function in Patients With Stroke Johanna H. Van der Lee, MD, Vincent De Groot, MD, Heleen Beckerman,
Clinical Evaluation of Closed-Loop Administration of Propofol Guided by the NeuroSENSE Monitor in Children
 Clinical Evaluation of Closed-Loop Administration of Propofol Guided by the van Heusden, Klaske; Dumont, Guy A.; Soltesz, Kristian; Petersen, Christian; West, Nicholas; Umedaly, Aryannah; Ansermino, J.
Clinical Evaluation of Closed-Loop Administration of Propofol Guided by the van Heusden, Klaske; Dumont, Guy A.; Soltesz, Kristian; Petersen, Christian; West, Nicholas; Umedaly, Aryannah; Ansermino, J.
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Effect of time period of data used in international dairy sire evaluations Citation for published version: Weigel, KA & Banos, G 1997, 'Effect of time period of data used in
Edinburgh Research Explorer Effect of time period of data used in international dairy sire evaluations Citation for published version: Weigel, KA & Banos, G 1997, 'Effect of time period of data used in
Test-retest reliability of the ABILHAND Questionnaire in persons with chronic stroke.
 Test-retest reliability of the ABILHAND Questionnaire in persons with chronic stroke. Ekstrand, Elisabeth; Lindgren, Ingrid; Lexell, Jan; Brogårdh, Christina Published in: PM&R DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2013.09.015
Test-retest reliability of the ABILHAND Questionnaire in persons with chronic stroke. Ekstrand, Elisabeth; Lindgren, Ingrid; Lexell, Jan; Brogårdh, Christina Published in: PM&R DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2013.09.015
Akita J Med 44 : , (received 11 December 2017, accepted 18 December 2017)
 Akita J Med 44 : 111-116, 2017 (33) Takashi Mizutani 1), Toshiki Matsunaga 2), Kimio Saito 2), Takehiro Iwami 3), Satoru Kizawa 4), Toshihiko Anbo 3) and Yoichi Shimada 1) 1) Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Akita J Med 44 : 111-116, 2017 (33) Takashi Mizutani 1), Toshiki Matsunaga 2), Kimio Saito 2), Takehiro Iwami 3), Satoru Kizawa 4), Toshihiko Anbo 3) and Yoichi Shimada 1) 1) Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
ii. Reduction of tone in upper limb Lycra arm splints improve movement fluency in children with cerebral palsy.
 Guidelines for the Provision of Dynamic Compression for people diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis The use of Lycra garments in patients with the diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis has been initiated with very
Guidelines for the Provision of Dynamic Compression for people diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis The use of Lycra garments in patients with the diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis has been initiated with very
Aalborg Universitet. CLIMA proceedings of the 12th REHVA World Congress Heiselberg, Per Kvols. Publication date: 2016
 Aalborg Universitet CLIMA 2016 - proceedings of the 12th REHVA World Congress Heiselberg, Per Kvols Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link to publication
Aalborg Universitet CLIMA 2016 - proceedings of the 12th REHVA World Congress Heiselberg, Per Kvols Publication date: 2016 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Link to publication
Clinical application of computerized evaluation and re-education biofeedback prototype for sensorimotor control of the hand in stroke patients
 Hsu et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2012, 9:26 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Open Access Clinical application of computerized evaluation and re-education
Hsu et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2012, 9:26 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Open Access Clinical application of computerized evaluation and re-education
Efficacy of mirror therapy in subacute stroke: A case-control study
 Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(2):84-89 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Efficacy of mirror therapy in subacute stroke: A case-control
Al Am een J Med Sci 2016; 9(2):84-89 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Efficacy of mirror therapy in subacute stroke: A case-control
PERSISTENT LOSS OF upper-extremity (UE) motor function
 660 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An Evaluation of the Wolf Motor Function Test in Motor Trials Early After Stroke Dorothy F. Edwards, PhD, Catherine E. Lang, PT, PhD, Joanne M. Wagner, PT, PhD, Rebecca Birkenmeier,
660 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An Evaluation of the Wolf Motor Function Test in Motor Trials Early After Stroke Dorothy F. Edwards, PhD, Catherine E. Lang, PT, PhD, Joanne M. Wagner, PT, PhD, Rebecca Birkenmeier,
A profiling system for the assessment of individual needs for rehabilitation with hearing aids
 A profiling system for the assessment of individual needs for rehabilitation with hearing aids WOUTER DRESCHLER * AND INGE BRONS Academic Medical Center, Department of Clinical & Experimental Audiology,
A profiling system for the assessment of individual needs for rehabilitation with hearing aids WOUTER DRESCHLER * AND INGE BRONS Academic Medical Center, Department of Clinical & Experimental Audiology,
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Friedman, N., Chan, V., Reinkensmeyer, A. N., Beroukhim, A., Zambrano, G. J., Bachman, M., & Reinkensmeyer, D. J. (2014). Retraining and assessing hand movement after stroke
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Friedman, N., Chan, V., Reinkensmeyer, A. N., Beroukhim, A., Zambrano, G. J., Bachman, M., & Reinkensmeyer, D. J. (2014). Retraining and assessing hand movement after stroke
BACKGROUND. Paul Taylor. The National Clinical FES Centre Salisbury UK. Reciprocal Inhibition. Sensory Input Boosted by Electrical Stimulation
 The REAcH project. A Randomised Controlled Trial of an Accelerometer Triggered Functional Electrica Stimulation Device For Recovery of Upper Limb Function in Chronic Stroke Patients. Paul Taylor The National
The REAcH project. A Randomised Controlled Trial of an Accelerometer Triggered Functional Electrica Stimulation Device For Recovery of Upper Limb Function in Chronic Stroke Patients. Paul Taylor The National
(77, 72, 74, 75, and 81).
 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 RESEARCH DESIGN A descriptive study using a cross sectional design was used to establish norms on the JHFT for an ethnically diverse South African population between the ages
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 RESEARCH DESIGN A descriptive study using a cross sectional design was used to establish norms on the JHFT for an ethnically diverse South African population between the ages
Development of the Hand Active Sensation Test: Reliability and Validity
 1471 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Development of the Hand Active Sensation Test: Reliability and Validity Petra S. Williams, MS, D. Michele Basso, EdD, Jane Case-Smith, EdD, Deborah S. Nichols-Larsen, PhD ABSTRACT.
1471 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Development of the Hand Active Sensation Test: Reliability and Validity Petra S. Williams, MS, D. Michele Basso, EdD, Jane Case-Smith, EdD, Deborah S. Nichols-Larsen, PhD ABSTRACT.
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/23532
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/23532
Development of a self-reported Chronic Respiratory Questionnaire (CRQ-SR)
 954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
Online Journal Club-Article Review
 Online Journal Club-Article Review Article Citation Study Objective/Purpose (hypothesis) Brief Background (why issue is important; summary of previous literature) Study Design (type of trial, randomization,
Online Journal Club-Article Review Article Citation Study Objective/Purpose (hypothesis) Brief Background (why issue is important; summary of previous literature) Study Design (type of trial, randomization,
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis.
 Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
Cluster headache associated with acute maxillary sinusitis. Edvardsson, Bengt Published in: SpringerPlus DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-509 2013 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Edvardsson,
The device for upper limb rehabilitation that supports patients during all the phases of neuromotor recovery A COMFORTABLE AND LIGHTWEIGHT GLOVE
 SINFONIA The device for upper limb rehabilitation that supports patients during all the phases of neuromotor recovery A COMFORTABLE AND LIGHTWEIGHT GLOVE The key feature of Gloreha Sinfonia is a rehabilitation
SINFONIA The device for upper limb rehabilitation that supports patients during all the phases of neuromotor recovery A COMFORTABLE AND LIGHTWEIGHT GLOVE The key feature of Gloreha Sinfonia is a rehabilitation
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yu, J., Kang, H., & Jung, J. (2012). Effects of modified constraint-induced movement therapy on hand dexterity, grip strength and activities of daily living of children
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yu, J., Kang, H., & Jung, J. (2012). Effects of modified constraint-induced movement therapy on hand dexterity, grip strength and activities of daily living of children
LUP. Lund University Publications. Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. This paper has
LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. This paper has
Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report.
 Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report. Brogren, Elisabeth; Dahlin, Lars Published in: Journal of Hand Surgery DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.09.014
Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report. Brogren, Elisabeth; Dahlin, Lars Published in: Journal of Hand Surgery DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.09.014
Aalborg Universitet. Statistical analysis plan Riis, Allan; Karran, E. L. ; Jørgensen, Anette; Holst, S.; Rolving, N. Publication date: 2017
 Aalborg Universitet Statistical analysis plan Riis, Allan; Karran, E. L. ; Jørgensen, Anette; Holst, S.; Rolving, N. Publication date: 2017 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
Aalborg Universitet Statistical analysis plan Riis, Allan; Karran, E. L. ; Jørgensen, Anette; Holst, S.; Rolving, N. Publication date: 2017 Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record
Chapter 4B: Reliability Trial 2. Chapter 4B. Reliability. General issues. Inter-rater. Intra - rater. Test - Re-test
 Chapter 4B: Reliability Trial 2 Chapter 4B Reliability General issues Inter-rater Intra - rater Test - Re-test Trial 2 The second clinical trial was conducted in the spring of 1992 using SPCM Draft 6,
Chapter 4B: Reliability Trial 2 Chapter 4B Reliability General issues Inter-rater Intra - rater Test - Re-test Trial 2 The second clinical trial was conducted in the spring of 1992 using SPCM Draft 6,
Arm function after stroke. An evaluation of grip strength as a measure of recovery and a prognostic indicator
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:1267-1272 Arm function after stroke. An evaluation of grip strength as a measure of recovery and a prognostic indicator ALAN SUNDERLAND, DEBORAH
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:1267-1272 Arm function after stroke. An evaluation of grip strength as a measure of recovery and a prognostic indicator ALAN SUNDERLAND, DEBORAH
Effects on facial dysfunction and swallowing capacity of intraoral stimulation early and late after stroke
 NeuroRehabilitation 36 (2015) 101 106 DOI:10.3233/NRE-141197 IOS Press 101 Effects on facial dysfunction and swallowing capacity of intraoral stimulation early and late after stroke Mary K.D. Hägg a,b,
NeuroRehabilitation 36 (2015) 101 106 DOI:10.3233/NRE-141197 IOS Press 101 Effects on facial dysfunction and swallowing capacity of intraoral stimulation early and late after stroke Mary K.D. Hägg a,b,
Upper limb and stroke. Mobilisation and Tactile Stimulation to enhance upper limb recovery after stroke. Upper limb and stroke.
 Mobilisation and Tactile Stimulation to enhance upper limb recovery after stroke Investigation of acceptable dose and efficacy Linda Hammett Research Physiotherapist ACPIN London 7 November 2009 Upper
Mobilisation and Tactile Stimulation to enhance upper limb recovery after stroke Investigation of acceptable dose and efficacy Linda Hammett Research Physiotherapist ACPIN London 7 November 2009 Upper
Published in: Proceedings of 15th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA'95, Trondheim, Norway, June 26-30, 1995
 Aalborg Universitet Comparison of eight psychometric methods for measuring threshold of hearing Sørensen, Michael Friis; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Lydolf, Morten; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings
Aalborg Universitet Comparison of eight psychometric methods for measuring threshold of hearing Sørensen, Michael Friis; Frandsen, Peder Christian; Lydolf, Morten; Møller, Henrik Published in: Proceedings
Evaluation of dual-arc VMAT radiotherapy treatment plans automatically generated via dose mimicking.
 Evaluation of dual-arc VMAT radiotherapy treatment plans automatically generated via dose mimicking. Petersson, Kristoffer; Nilsson, Per; Engström, Per; Knoos, Tommy; Ceberg, Crister Published in: Acta
Evaluation of dual-arc VMAT radiotherapy treatment plans automatically generated via dose mimicking. Petersson, Kristoffer; Nilsson, Per; Engström, Per; Knoos, Tommy; Ceberg, Crister Published in: Acta
The potential effect of a vibrotactile glove rehabilitation system on motor recovery in chronic post-stroke hemiparesis
 Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) 1183 1187 1183 DOI 10.3233/THC-171001 IOS Press Technical Note The potential effect of a vibrotactile glove rehabilitation system on motor recovery in chronic post-stroke
Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) 1183 1187 1183 DOI 10.3233/THC-171001 IOS Press Technical Note The potential effect of a vibrotactile glove rehabilitation system on motor recovery in chronic post-stroke
SENSe Implement: Changing clinical practice in sensory rehabilitation of the arm after stroke
 SENSe Implement: Changing clinical practice in sensory rehabilitation of the arm after stroke Leeanne Carey, Liana Cahill, Natasha Lannin and the SENSe Implement team. latrobe.edu.au CRICOS Provider 00115M
SENSe Implement: Changing clinical practice in sensory rehabilitation of the arm after stroke Leeanne Carey, Liana Cahill, Natasha Lannin and the SENSe Implement team. latrobe.edu.au CRICOS Provider 00115M
