Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 1 of 10 US 2010/ A FIG. 1
|
|
|
- Brittney Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 HSU et al. US A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) REMOTE SLEEP QUALITY DETECTING SYSTEMAND METHOD THEREOF (75) Inventors: YEH-LIANG HSU, Taoyuan City (TW); Chih-Ming Cheng, Tucheng City (TW) Correspondence Address: KILE GOEKULAN REED & MCMANUS 1200 NEW HAMPSHIRE AVE, NW, SUITE 570 WASHINGTON, DC (US) (73) Assignee: YUANZE UNIVERSITY (21) Appl. No.: 12/573,226 (22) Filed: Oct. 5, 2009 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Nov. 21, 2008 (TW) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. A61N L/04 ( ) A6IB5/08 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /42; 600/529 (57) ABSTRACT A remote sleep quality detecting system and its method pro vide a portable detecting device for detecting an examinee's physical activity while the examinee is sleeping, analyzing a detected activity signal by a signal processing module to generate a statistical value, and comparing a result of the computed Statistical value with a sleep state index to obtain sleep quality information, and then storing the activity signal and the sleep quality informationina storage unit. The system and method also provide a remote monitoring device includ ing a sleep information reading module for providing a user interface, connecting the portable detecting device via the Internet and receiving the sleep quality information produced by the portable detecting device after a command from the portable detecting device is received, such that the examin ee's sleep quality information can be examined from a remote location for a long term without disturbing the examinee's sleep. Portable detecting device Portable detecting device Remote monitoring device Remote monitoring device Portable detecting device Portable detecting device
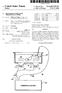
2 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 1 of 10 US 2010/ A1 detecting Portable device 6 monitoring Remote device Portable detecting device Remote monitoring device 1 2 Portable detecting device 1 1. Portable detecting device FIG. 1
3 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 2 of 10 US 2010/O131028A1 Portable detecting device Signal detector Signal processing module Signal pre-processing module 120 Analysis Memory module unit 3 Sleep quality reading module Alarm receiving unit Renote monitoring device FIG.2
4 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 3 of 10 US 2010/ A1 la Portable detecting device t activity detection pad Signal processing module Signal pre-processing module 120 or module Computation module Storage unit Memory it Network transmission unit FIG. 3
5 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 4 of 10 US 2010/ A1 b Portable detecting device M icrophone - inry. Sound 12 Signal processing module recording 120-Signal pre-processing module s device 122 Storage unit Network transmission unit JElectrical stimulator FIG. 4
6 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 5 of 10 US 2010/O131028A1 2a Remote monitoring device Sleep information reading program User interface FIG. 5A monitoring Remote device 20 Sleep quality reading module 24- Browse module 22- User interface FIG. 5B
7 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 6 of 10 US 2010/O131028A1 N N Eliterritor N N N Man : new ss t
8 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 7 of 10 US 2010/O131028A1
9 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 8 of 10 US 2010/ A1 Start S703 S701 S705 Detect a physical activity and generate an activity signal Analyze the activity signal variation r to produce a statistical value Compute the statistic value to produce sleep quality information S70T-Store the sleep quality information S709 Read and display the sleep quality information from a remote location
10 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 9 of 10 US 2010/O131028A1 S8O S803 Detect a body movement and generate a body activity Signal Digitize, filter, and sample the body activity signal S805 Analyze the activity signal variation, and produce a statistical value S807 S809 Compute a weighted Statistical value of the activity signal Compute an examinee's sleep depth S8. Classify according to the sleep depth S813 Produce sleep quality information FIG. 8
11 Patent Application Publication May 27, 2010 Sheet 10 of 10 US 2010/O131028A1 S901 S903 S905 Detect Snore, and generate a Snore signal Digitize, filter, and Sample the Snore signal Analyze the snore signal, and collect the statistics of the frequency of Snores and intermittent snores S907 S909 Compute a weighted statistical value of the intermittent snore ratio (ISR) Compare the Weighted statistical value with an intermittent snore ratio threshold to produce sleep quality information FIG. 9
12 US 2010/ A1 May 27, 2010 REMOTE SLEEP QUALITY DETECTING SYSTEMAND METHOD THEREOF CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION This application claims priority under 35 U.S.C. S119 to Taiwan Patent Application No , filed on Nov. 21, 2008, in the Taiwan Intellectual Property Office, the entire contents of which are hereby incorporated by refer CCC. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a remote sleep qual ity detecting system and a method thereof, and more particu larly to a distributed remote sleep quality detecting system and a method thereof Description of Related Art As pressure and tiredness are imposed on our work and daily life, many people have sleep disorder symptoms and need a professional medical treatment system for curing their sleep disorder. Physical activity information of a patient are collected while the patient is sleeping and used as a basis for determining the cause of the sleep disorder and performing a diagnosis to prevent a severer condition of the sleep disorder such as Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS) that may cause daytime sleepiness, chest pain, and myocardial infarc tion, or even become fatal in a serious case. Therefore, the frequency and the interval of snores measured while a patient is sleeping can be used for determining whether or not there is a probability of OSAS, so as to provide an early treatment to patients Most present sleep disorder detection systems are installed in hospitals or clinics, and special sleep centers are established in hospitals and clinics for detecting sleep infor mation. In general, an examinee has to go to a specific loca tion of the sleeping center to take a test. In the test, electrode tabs or detection circuits are attached onto the examinee's body, and the examinee sleeps in the center and allows instru ments to read data including brain wave, breathing or hemo globin concentration which are provided for medical profes sionals to evaluate and diagnose the examinee's sleep condition Since the examinee has to take the test in an unfa miliar environment and attach the detection circuits on her/his body, it may increase the examinee's psychological pressure before the examinee falls asleep, and thus resulting in an abnormal sleep condition, and causing a misjudgment on the diagnosis of a patient's sleep disorder In the situation of having increasingly more patients who require a sleeping test and need medical treatment for their sleep disorder problem, it is an important subject to let examinees take the sleep quality test at ease in a familiar environment and also allow medical professionals to control the examinee's sleep information for an accurate analysis. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Therefore, it is a primary objective of the present invention to overcome the shortcomings of the prior art by providing a remote sleep quality detecting system to achieve the effect of detecting an examinee's sleep information in a familiar sleep environment conveniently To achieve the foregoing objective, the present invention provides a remote sleep quality detecting system comprising a portable detecting device and a remote moni toring device. The portable detecting device comprises at least one signal detector, a signal processing module, a stor age unit and a network transmission unit, wherein the signal processing module further comprises an analysis module and a computation module, and the remote monitoring device further comprises a sleep quality reading module The signal detector detects the examinee's physical activity while the examinee is sleeping and generates an activ ity signal. The analysis module analyzes changes of the activ ity signal, performs a classification and collect statistics according to the variation of the activity signal, produces a statistical value required for a computation by the computa tion module, and compares a computed result with at least one sleep state index by a computation module to produce sleep quality information, transmit the sleep quality information from the network transmission unit to a network, and record and store the activity signal and the sleep quality information in the storage unit The remote monitoring device monitors the sleep quality information via the network, and the sleep quality reading module installed in the device provides a user inter face for receiving a connection instruction to connect a por table detecting device, reading the sleep quality information stored in the storage unit, and displaying the sleep quality information on the user interface The sleep quality information can be obtained from a remote location without disturbing the examinee, and the results can be observed for a long term and provided for further analyses. 0014) To achieve the foregoing objective, the present invention provides a remote sleep quality detecting method, comprising the steps of providing a signal detector for con tinuously detecting the examinee's physical activity while the examinee is sleeping and generating an activity signal; ana lyzing changes of the activity signal, and classifying and collecting statistics of the activity signal according to its variation, and producing a statistical value; comparing a com putation result obtained after the statistical value is computed with at least one sleep state index to produce sleep quality information, and storing the sleep quality information in a storage unit; and finally providing a remote monitoring device for connecting a network, and reading and displaying the sleep quality information on a user interface Therefore, the examinee's sleep information can be observed and recorded from a remote location for a long term without affecting the examinee's sleeping habits, and the sleep information obtained from the method can serve as a basis for a professional medical system to perform further evaluations The above and other objects, features and advan tages of the present invention will become apparent from the following detailed description taken with the accompanying drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0017 FIG. 1 shows a structure of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with the present invention; 0018 FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
13 US 2010/ A1 May 27, FIG. 3 is a block diagram of a portable detecting device of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention: 0020 FIG. 4 is a block diagram of a portable detecting device of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with another preferred embodiment of the present invention; 0021 FIGS. 5A and 5B are block diagrams of a remote monitoring device of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention; 0022 FIGS. 6A and 6B are schematic views of sleep qual ity information of a sleep quality detection system in accor dance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention; 0023 FIG. 7 is a flow chart of a sleep quality detection method in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention; 0024 FIG. 8 is a flow chart of detecting a physical activity in a sleep quality detection method in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention; and 0025 FIG. 9 is a flow chart of detecting snore in a sleep quality detection method in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS The present invention discloses a remote sleep qual ity detecting system and its method that provide a way or receiving a sleep quality detection of an examinee in a famil iar natural sleeping environment without disturbing the examinee's sleeping habits. In the meantime, medical profes sionals can control the examinee's sleep quality information from a remote location via a network to achieve the effects of monitoring the examinee's sleep quality information for a long term, eliminating the discomfort during the examinee's sleep quality detection, and lowering the cost of detecting the sleep quality information To make it easier for our examiner to understand the technical characteristics of the present invention, we use pre ferred embodiments together with related block diagrams and flow charts for the detailed description of the invention as follows With reference to FIG. 1 for a schematic view of a structure of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with the present invention, the remote sleep quality detecting system in this embodiment is a distributed structure that allows a portable detecting device 1 at the location of the examinee and a remote monitoring device 2 at the location of a medical and healthcare professional to be connected with each other through a network 6, so as to waive the installation of a central server. The remote monitoring device 2 with a monitoring priority can be connected to obtain information recorded in the portable detecting device 1 anytime when needed to facilitate medical and healthcare professionals to control the examinee's sleep quality information With reference to FIG. 2 for a block diagram of a remote sleep quality detecting system in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the system comprises a portable detecting device 1, a remote monitoring device 2 and an alarm receiving unit 3. The portable detecting device 1 comprises a signal detector 10, a signal processing module 12, a storage unit 14 and a network transmission unit 16. The remote monitoring device 2 comprises a sleep quality reading module 20, and a sleep quality reading module 20 provides a user interface The signal detector 10 is provided for detecting physical activity Such as body turnover, limb Swinging, or a breathing sound of the examinee while the examinee is sleep ing, generating an activity signal according to the physical activity, and transmitting the activity signal to the signal processing module 12. A signal pre-processing module 120 in the signal processing module 12 converts the analog activity signal into a digital signal and filters noises in the digital signal to provide a smoother waveform of the signal, while sampling the signals per unit time and facilitate analyzing and computing the activity signal The activity signal received and analyzed by the analysis module 122 and processed by the signal pre-process ing module 120 varies with time, such as the variation of the slope of the activity signal's waveform. The variation can be used for collecting and classifying statistics of the activity signal to produce a statistical value. The computation module 126 computes the statistical value and compares the com puted result with at least one sleep state index to produce sleep quality information. The memory unit 124 records a variation threshold, at least one computation equation and the aforementioned sleep state index, and the analysis module 122 classifies the activity signal according to the variation threshold, and the computation module 126 reads the com putation equation to compute the statistical value. The pro duced sleep quality information is transmitted to a network 6 through a network transmission unit The information monitored by the remote monitor ing device 2 is the aforementioned sleep quality information, and the remote monitoring device 2 comprises a sleep quality reading module 20 for providing a user interface 22, and the user interface 22 receives a connection instruction of the portable detecting device 1. Such as receiving a network address of the portable detecting device 1, connecting to the portable detecting device 1 via the network 6, timely reading history information stored in the sleep quality information or storage unit 14 according to the monitoring requirement, and displaying the history information on the user interface If the portable detecting device 1 detects an abnor malactivity signal of the examinee Such as continuous Swings of limbs or an abnormal interrupt of Sound signals, then the network transmission unit 16 will send an alarm notice to an alarm receiving unit 3 Such as a mobile communication device or an , so that medical and healthcare profession als can handle the emergency situation immediately upon the receipt of the alarm notice With the use of the foregoing system, the examinee can carry the portable detecting device 1 home, and detect the activity signal in a sleeping environment familiar to the exam inee without the need of taking the test at a sleep center of a hospital or a clinic, so that medical and healthcare profession als can monitor the sleep quality information of the examinee who is using a portable detecting device 1 from a remote location via the network 6 anytime, without interrupting the examinee's sleep. Since the examinee's activity signal stored in the storage unit 14 is computed to produce sleep quality information, therefore, the effect of observing the examinee's sleep condition for a long term can be achieved to reduce the examinee's psychological pressure of taking the test in a sleeping center and lower the cost of medical care With reference to FIGS. 3 and 4 for block diagrams of a portable detecting device of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with preferred embodiments of the present invention, FIG. 3 shows a state of the examinee's
14 US 2010/ A1 May 27, 2010 body activity while the examinee is sleeping. In a preferred embodiment, a body activity detection pad 102 of the portable detecting device 1a is provided for detecting the examinee's upper arm movement, body movement or leg movement to generate an upperarm activity signal, a body activity signal or a leg activity signal respectively. In addition, the body activity detection pad 102 of this embodiment can detect information Such as the examinee's breathing frequency or body tempera ture In an example of detecting a body movement, a signal pre-processing module 120 digitizes, filters and samples the body activity signal generated by the body activ ity detection pad 102, and then an analysis module 122 ana lyzes variations of the slope of the body activity signals waveform (from now on referred as slope variation) and reads a variation threshold such as 0.02 from a memory unit 124, and classifies the body activity signal according to the slope variation. A statistical value UAI is produced after the time greater than a threshold is counted in every minute, wherein the statistical value UAI represents the time (such as 3.5 seconds) of a specific body movement occurred in one minute The computation module 126 receives a statistical value BAI generated by the analysis module 122 and reads a computation equation from the memory unit 124 to compute the statistical value BAI. One of the equation is a weighted computation equation that decreases the significance of the activity signal as time passes, wherein the measurement of the passing time starts after the activity signal has been detected. In other words, the statistical value BAIT received by the computation module 126 is the time period of a body move ment in the i' minute, and a statistical value BAli-1 is col lected in the previous minute, and a statistical value BAIi-2 is collected in the previous two minutes, and so forth, and the statistical values of a total of k minutes are compared. The longer the time taken for collecting the statistical value, the less is the weight given to the statistical value, and vice versa. The total sum is averaged to produce the weighted Statistical value of a time period of a body movement occurred in the recent one minute. The statistical value LAI of a leg activity signal generated by the leg movement and the weighted Sta tistical value of the time period of the leg movement are also computed as described above, and the same applies to the upper arm movement as well. Another example is taken for computing a weighted Statistical value (w3aii) of a body activity signal as follows: The computation module 126 reads another sleep depth equation from the memory unit 124, and uses the sleep depth equation and the weighted Statistical values of the upper arm activity signal and the leg activity signal to compute the examinee's sleep depth in the currently computed minute, and the sleep depth equation is given below: SleepDepth= wbAI wlAI where, wbai is the weighted statistical value of a body activ ity signal; and wall is the weighted Statistical value of a leg activity signal The computation module 126 computes the sleep depth of the examinee for every minute by the aforemen tioned equation, and compares the computed sleep depth with a sleep state index (which is the sleep depth threshold in this embodiment) recorded in the memory unit 124. The sleep depth is generally divided into two main types, wherein a value greater than the sleep depth threshold is 1, and a value smaller than the sleep depth threshold is 0. In the meantime, these values are used for comparison. Finally, sleep quality information is produced. In this embodiment, the sleep qual ity information refers to the examinee's sleep condition (as shown in FIG. 6A). If the examinee is lying in bed and the sleep depth is greater than the threshold, then the sleep con dition is Falling asleep. If the examinee is lying in bed, but the sleep depth is less than the threshold, then the sleep condition is Being awake'. If the sleep depth is less than the threshold and the examinee's index indicates that the exam inee is not in bed, then the sleep condition is No one is in bed Since the signal detector 10 of this embodiment is a body activity detection pad, the signal detector 10 can natu rally and easily detect whether or not the examinee is lying in bed, in addition to the detection of the aforementioned activ ity signals With the foregoing analysis and computation, a complete set of sleep quality information can be obtained, so that the examinee's actual sleep condition Such as whether the examinee sleeps soundly or wakes up frequently throughout the night can be observed, and the sleep condition is recorded in the storage unit 14. If it is necessary to examine the exam inee's sleep quality information, the content stored in the storage unit 14 can be transmitted and retrieved by the net work transmission module FIG. 4 shows a block diagram of a portable detect ing device of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with another preferred embodiment of the present invention, this embodiment is used for detecting the examinee Snoring condition while the examinee is sleeping, and analyzing whether or not the examinee suffers from Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS) The portable detecting device 1b of this embodi ment uses a microphone 104 to detect and receive the exam inee's Snore while the examinee is sleeping and generate a Snore signal. The signal pre-processing module 120 of the signal processing module 12 receives the Snore signal and digitizes and filters noise to take samples, and eliminate any high-frequency signal exceeding the frequency defined by the Snore from the Snore signal to avoid the case of including irrelevant Sounds into the analysis After receiving the filtered snore signal, the analysis module 122 analyzes a slope variation of the Snore signal, reads a variation threshold of the slope recorded by the memory unit 124, classifies the Snore signal into two main types according to the variation threshold, and collects the statistics. For example, if the slope is greater than the thresh old, then the snore signal is classified as 1, and if the slope is Smaller than the threshold, then the Snore signal is classified as 0, and the statistics of the time periods exceeding the threshold are collected continuously, and the time period is classified as to whether or not it falls within the time during which snore is present. For example, if the time periods exceeding the threshold continuously fall within a range from 0.8 to 1.6 seconds, then it is classified as one snore. The foregoing method is used for determining whether or not the
15 US 2010/ A1 May 27, 2010 time period is for one Snore, and selectively recording the time period in the memory unit 124 for the use by the analysis module 122. Finally, the frequency of snores per minute is counted to produce a Snore frequency statistical value In this embodiment, the analysis module 122 ana lyzes the time interval and the frequency of Snores occurred per minute, and divides the examinee's Snore into a general Snore and an intermittent Snore according to the time interval between two snores. For example, if the time interval between two snore falls within a range from 10 seconds to 60 seconds, then the Snore is considered as an intermittent Snore, and if the time interval between two snores is less than 10 seconds, then the Snore is considered as a general Snore, and the frequency of intermittent Snores per minute is counted to produce an intermittent Snore frequency statistical value The computation module 126 computes an intermit tent snore ratio (ISR) of snores occurred in one minute according to the Snore frequency statistical value and the intermittent Snore frequency statistical value. In addition, the computation module 126 reads a computation equation from the memory unit 124, and the computation equation is a weighted computation equation of significance of the Snore signals decremented with time after the Snore signals are detected. In other words, the computation module 126 com pares the intermittent snore ratio ISRi in the recent minute with the intermittent snore ratio ISRi-1 of the previous minute, the intermittent snore ratio ISRi-2 of the previous two minutes, up to the intermittent snore ratio ISRi-k+1 of the previous k minutes. The longer the time of the intermittent Snore ratio, the less is the weight, and vice versa. The total Sum is averaged to produce the weighted Statistical value of the intermittent Snore ratio in the recent minute. For example, the weighted statistical value (wlsri) of the intermittent Snore ratio occurred in recent five minutes is computed as follows: wisr ISR = is ISR, ISK+ + is i ISR ISK-1 + is 3. ISR ISR-2+ is 3. ISR ISR-3+ is * ISR ISR The larger the weighted statistical value (wlsri), the higher is the intermittent Snore ratio of the examinee, and the higher is the probability for the examinee to suffer from Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS) After the computation module 126 computes the weighted statistical value of the intermittent snore ratio, the result is compared with an intermittent snore ratio threshold recorded in the memory unit 124 to produce the examinee's sleep quality information relating to Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS). For example, if the weighted statistical value of the intermittent snore ratio is greater than 0.25, then the examinee is considered to suffer from OSAS', and if the weighted statistical value of the intermittent snore ratio is smaller than 0.25, then the examinee is considered not to suffer from OSAS' as shown in FIG. 6B. Thus, this method allows the examinee to know whether or not there is any OSAS symptom occurred while the examinee is sleeping and determine whether or not to seek for medical treatment according to the information. Finally, the detected Snore sig nal and sleep quality information are recorded in the storage unit 14, and selectively transmitted to the network transmis sion unit 16 via the network 6, if needed This embodiment further comprises a sound record ing device 4 and an electrical stimulator 5 coupled to the signal processing module 12. The sound recording device 4 records and provides contents of Snores produced by the examinee as a reference information for a medical treatment according to the instruction of the signal processing module 12. The electrical stimulator 5 such as a transcutaneous elec trical nerve stimulator produces a slight electric current to stimulate the examinee if the examinee is diagnosed to Suffer from OSAS and helps the examinee to restore a normal breathing and saves the examinee from the danger of a pos sible OSAS From the embodiment as described above, we know that the present invention can detect the examinee's sleep information continuously for a long term without affecting the examinee's sleep, and recording objective and accurate information which is absolutely helpful to the diagnosis of the examinee's sleep disorder In the foregoing embodiment, the body activity and the snore are detected separately for the simplicity of illus trating the present invention, but they can be combined in actual implementation as well. The invention has the function of detecting the body activity and Snore simultaneously to provide complete sleep quality information detected by the portable detecting device The remote monitoring device 2 reads the activity signal and the sleep quality information stored in the storage unit 14 of the portable detecting device 1 via the network 6. With reference to FIGS.5A and 5B for block diagrams of a remote monitoring device of a sleep quality detection system in accordance with preferred embodiments of the present invention, FIG. 5A shows a remote monitoring device 2a comprising a sleep information reading program 202, which is a VB application program and provides a user interface 22, and FIG. 5B shows another preferred embodiment of a sleep quality reading module 20 of a remote monitoring device 2b, comprising a browse module 24 Such as a webpage browser for accessing an application server system (not shown in the figure) to obtain the user interface The remote monitoring device 2a or 2b receives a connection instruction for connecting the portable detecting device 1 through the user interface 22, Such as entering a network address of the portable detecting device 1, connect ing the portable detecting device 1 via a distributed network according to the connection instruction, and reading the sleep quality information (such as the aforementioned sleep condi tion information or Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSAS) information collected while the examinee is sleep ing) stored in the storage unit 14, and displaying the sleep quality information on the user interface 22 timely for medi cal and healthcare professionals to monitor and control the sleep information or reading history information recorded in the storage unit 14 back to the user interface 22 according to another operation instruction received by the user interface 22 after the portable detecting device 1 is connected, so that medical and healthcare professionals can observe the exam inee's past sleep information and take necessary actions From the description above, we know that a sleep quality detection system is constructed by a distributed struc ture, so that both of the examinee and medical and healthcare professionals can obtain the detected and monitored informa tion by the most convenient method. The invention reduces the examinee's psychological and monetary burdens and pro vides accurate successive data which are very helpful to related medial professionals for diagnosing and curing the examinee's sleep disorder.
16 US 2010/ A1 May 27, With reference to FIG. 7 for a flow chart of a sleep quality detection method in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the method comprises the following steps: A signal detector 10 detects the examin ee's physical activity while the examinee is sleeping and generates an activity signal (S701). An analysis module 122 analyzes the activity signal varied with time, and classifies and collects the statistics of the activity signals to produce a statistical value (S703). A computation module 126 computes the statistical value and compares the result with a sleep state index to produce sleep quality information (S705). The sleep quality information is stored in a storage unit 14 (S707). A sleep quality reading module 20 is provided for reading the sleep quality information from a remote location via a net work 6 and displaying the sleep quality information on a user interface 22 of the remote monitoring device 20 (S709). Therefore, medical and healthcare professionals can monitor and observe the examinee's sleep quality information in the long term from the remote location, without disturbing the examinee's sleep, and further analyze or evaluate the exam inee's sleep quality according to the observed sleep quality information, and cure the examinee's sleep disorder Before the activity signal is analyzed, a signal pre processing module 120 digitizes and filters noises of the detected activity signal and takes samples for the analysis. The step for the sleep quality reading module 20 to read the sleep quality information further comprises the steps of pro viding a browse module 24 to access an application server system to obtain the user interface 22, and connecting the user interface 22 to obtain the sleep quality information after a connection instruction is received The method of this embodiment further comprises the steps of recording the activity signal in the storage unit 14: and providing a memory unit 124 for recording a variation threshold provided for the analysis module 122 to classify the activity signal according to its variation, and also recording a computation equation for computing a statistical value by the computation module 126, and recording a sleep state index which is compared with the computed result and provided for the operation of the aforementioned steps. The computation equation includes a weighted computation equation which is a computation equation of significance of the activity signal decremented with time after the activity signal is detected, so that the level of physical activity represented by the most recently detected activity signal becomes more significant. This embodiment further comprises the steps of providing an alarm receiving unit 3 Such as a mobile communication device or an ; receiving an alarm notice and transmitting the alarm notice to a medical or healthcare professional via the network 6 for taking an emergency action if an abnormal activity signal of the examinee is detected With reference to FIG.8 for a flow chart of detecting a physical activity in a sleep quality detection method in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the method comprises the steps of providing a body activity detection pad 102 to detect the examinee's upper arm movement, body movement or leg movement and generate an upper arm activity signal, a body activity signal or a leg activity signal respectively (S801); providing a signal pre processing module 120 to digitize, filter and sample the activ ity signal (S803); analyzing a slope variation of the activity signal varied with time by an analysis module 122 to classify the activity signal according to the slope variation and a variation threshold recorded in the memory unit 124 and collect the statistics of the time greater than the threshold in a minute, and generate a statistical value of the time period of the body, leg, or upper arm movement (S805). A computation module 126 reads a weighted computation equation from the memory unit 124 and computes the weighted Statistical value of the time period of the upper arm movement and the time period of the leg movement (S807), and reads a sleep depth computation equation, such that the sleep depth computation equation and the weighted Statistical values of the upper arm activity signal and the leg activity signal can be used for computing the examinee's sleep depth in the recent minute (S809). The sleep depth threshold is compared and divided into two types: a sleep depth greater than the threshold and a sleep depth smaller than the threshold (S811). Finally, an index indicating whether or not the examinee is lying in bed is provided for producing sleep quality information, and the examinee's sleep condition Such as falling asleep, being awake' and no one is in bed is displayed (S813). The detailed computing procedure of the computation module 126 is illustrated in FIG. 3. The remote monitoring device 20 reads the examinee's sleep condition while the examinee is sleeping and provides the sleep condition for the examinee to determine whether or not the examinee has an insomnia prob lem With reference to FIG.9 for a flow chart of detecting Snore in a sleep quality detection method in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the method comprises the steps of providing a microphone 104 for detecting snore produced by the examinee while the exam inee is sleeping, and generating a Snore signal (S901); digi tizing, filtering the portion with a too-high frequency, and sampling the Snore signal by a signal pre-processing module 120 (S903); analyzing a slope variation of the snore signal varied with time by an analysis module 122, and classifying the Snore signal according to the slope variation and the variation threshold recorded in the memory unit 124 and collecting the statistics of the frequency of intermittent Snores occurred in a minute (S905), wherein the detailed analysis procedure is illustrated in FIG The computation module 126 computes a statistical value produced by the analysis module 122 according to a computation equation stored in the memory unit 124, and uses the computation equation as disclosed in FIG. 4 to pro duce a weighted statistical value of the intermittent snore ratio (ISR) (S907), wherein the larger the weighted statistical value, the higher is the probability for the examinee to suffer from Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OAS), and then the intermittent snore ratio threshold recorded in the memory unit 124 is used for comparing the computed weighted Statistical value to produce sleep quality information (S909), and a weighted statistical value greater than the threshold is recorded as OSAS', and a weighted statistical value greater than the threshold is recorded as No OSAS', and these values are provided for medical and healthcare professionals to monitor the examinee's condition In addition, the present invention also records the examinee's Snores, uses a Sound recording device 4 to record the examinee's Snores while the examinee is sleeping, and provides an electrical stimulator 5 for transmitting a slight current to stimulate an examine to resume a normal breathing and avoid the danger of OSAS when an abnormal Snore signal of the examinee is detected In summation of the description of the aforemen tioned preferred embodiments, the present invention provides
17 US 2010/ A1 May 27, 2010 a natural and comfortable way of detecting the examinee's sleep information in an environment familiar to the examinee. The present invention not only saves the trouble of going to a specific hospital or clinic, but also avoids disturbing the examinee during the processes of performing the detection and connecting information by the portable detecting device, so that the examinee can take a test without a burden. The invention detects and obtains more accurate information, and also saves the cost for the examinee to go to a hospital or a clinic to take the test. More importantly, medical and health care professionals can observe the examinee's sleep condi tion anytime and read the examinee's sleep information to determine and make further diagnoses and treatment, so as to enhance the accuracy of analyzing the sleep disorder Symp toms and the efficiency of curing the examinee's sleep disor der Although the present invention has been described with reference to the preferred embodiments thereof, it will be understood that the invention is not limited to the details thereof, Various substitutions and modifications have been Suggested in the foregoing description, and others will occur to those of ordinary skill in the art. Therefore, all such sub stitutions and modifications are intended to be embraced within the scope of the invention as defined in the appended claims. What is claimed is: 1. A remote sleep quality detecting system, comprising: a portable detecting device, comprising: at least one signal detector for continuously detecting a physical activity of an examinee while the examinee is sleeping, and for generating an activity signal; a signal processing module for receiving the activity signal, and for analyzing and computing the activity signal, the signal processing module comprising: an analysis module for analyzing changes of the activ ity signal, and generating a statistical value accord ing to the classification and statistics of the varia tion of the activity signal; and a computation module for receiving and computing the statistical value, and comparing a computed result with at least one sleep state index to produce sleep quality information; a storage unit for storing the activity signal and the sleep quality information received by the signal processing module; and a network transmission unit for transmitting the sleep quality information via a network; and a remote monitoring device for monitoring the sleep qual ity information of the examinee from a remote location via the network, and comprising: a sleep quality reading module for providing a user interface to receive a connection instruction to con nect the portable detecting device, reading and dis playing the sleep quality information at the user inter face, whereby the sleep quality information of the examinee can be observed from a remote location by a distributed network structure, and the sleep quality of the examinee can be analyzed further according to the sleep quality information. 2. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 1, wherein the signal processing module further comprises: a signal pre-processing module for digitizing and filtering the activity signal, and sampling the activity signal; and a memory unit for storing a variation threshold, at least one computation equation and a sleep state index, wherein the analysis module classifies the activity signal accord ing to the variation threshold, and the computation mod ule computes the statistical value according to the com putation equation. 3. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 1, wherein the sleep quality reading module further comprises: a browse module for accessing an application server sys tem to provide the user interface. 4. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 1, wherein the signal detector is a body activity detection pad provided for detecting body activity while the examinee is sleeping, and the activity signal is a body activity signal. 5. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 4. wherein the body activity detection pad detects an upper arm movement, a body activity or a leg movement of the exam inee, and the body activity signal is an upper arm activity signal, a body activity signal or a leg activity signal. 6. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 1, wherein the signal detector is a microphone provided for detecting Snore produced by the examinee while the exam inee is sleeping, and the activity signal is a Snore signal. 7. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 6. further comprising: a Sound recording device, coupled to the signal processing module for recording Snore produced by the examinee, and storing the Snore in the storage unit; and an electrical stimulator, coupled to the signal processing module for transmitting a current to stimulate the exam inee to breathe normally. 8. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 1, wherein the analysis module analyzes variations of the slope of the activity signal's waveform. 9. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 1, further comprising: an alarm receiving unit for receiving an alarm notice trans mitted from the network transmission unit through the portable detecting device. Such that an abnormal occur rence of the activity signal during the examinee's sleep is known. 10. The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 9. wherein the alarm receiving unit is a mobile communication device or an The remote sleep quality detecting system of claim 1, wherein the sleep quality information read by the sleep qual ity reading module is the current sleep quality information or history sleep quality information. 12. A remote sleep quality detecting method, comprising the steps of: providing a signal detector for continuously detecting a physical activity of an examinee while the examinee is sleeping, and generating an activity signal; analyzing changes of the activity signal variation with time, and producing a statistical value according to the variation classification and Statistics of the activity sig nal; computing the statistical value, and comparing the com puted result with at least one sleep state index to produce sleep quality information; recording the sleep quality information in a storage unit; and
18 US 2010/ A1 May 27, 2010 providing a remote monitoring device, and displaying the sleep quality information read via a network at a user interface, whereby the sleep quality information of the examinee can be observed at a remote location for a long term, and the sleep quality of the examinee can be analyzed further according to the sleep quality information. 13. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 12, further comprising a procedure before the step of analyzing the activity signal, and the procedure comprising the steps of digitizing and filtering the activity signal; and sampling the activity signal. 14. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 12, further comprising the steps of recording the activity signal in the storage unit; and providing a memory unit for storing a variation threshold, at least one computation equation and the sleep state index, classifying the activity signal according to the classification of the variation threshold, and computing the statistical value according to the computation equa tion. 15. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 14, wherein the computation equation is a weighted computation equation according to the level of significance of the activity signal decreasing with time after the detection takes place. 16. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 12, further comprising a procedure during the step of detecting a physical activity by the signal detector while the examinee is sleeping, and the procedure comprising the steps of the signal detector detecting body activity while the exam inee is sleeping; and generating a body activity signal. 17. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 16, wherein the signal detector is a body activity detection pad, and the body activity signal is an upper arm activity signal, a body activity signal or a leg activity signal. 18. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 12, further comprising a procedure during the step of detecting a physical activity by the signal detector while the examinee is sleeping, and the procedure comprising the steps of the signal detector detecting Snore while the examinee is sleeping; and generating a Snore signal, wherein the signal detector is a microphone. 19. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 18, further comprising a procedure after the step of detecting the Snore by the signal detector while the examinee is sleeping, and the procedure comprising the steps of: providing a sound recording device for recording Snore produced by the examinee, and storing the Snore in the storage unit; and providing an electrical stimulator for transmitting a current to stimulate the examinee, and drive the examinee to breathe normally. 20. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 12, further comprising a procedure during the step of reading the sleep quality information by the sleep quality reading mod ule, consisting of: accessing an application server system from a browse unit for providing the user interface. 21. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 12, further comprising the step of providing an alarm receiving unit for receiving an alarm notice when an occurrence of an abnormal activity signal is detected. 22. The remote sleep quality detecting method of claim 21, wherein the alarm receiving unit is a mobile communication device or .
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.02451 05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245105 A1 HO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR NETWORK TRANSMISSION (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2009.02451 05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245105 A1 HO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR NETWORK TRANSMISSION (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
1 ADJUSTMENT THRESHOLD-N. United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. 5,660,184. Aug. 26, 1997 PATIENT'S HEARTBEAT PACEMAKEREVENT QRS DETECTION THRESHOLD
 United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
Chapter 2. Development of a portable device for tele-monitoring. of physical activities during sleep
 Author: Chih-Ming Cheng (2007-07-11); recommended: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2007-07-). Note: This article is Chapter 2 of Chih-Ming Cheng s PhD thesis Development of a portable system for tele-monitoring of sleep
Author: Chih-Ming Cheng (2007-07-11); recommended: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2007-07-). Note: This article is Chapter 2 of Chih-Ming Cheng s PhD thesis Development of a portable system for tele-monitoring of sleep
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0267,527 A1
 (19) United States US 2004O267527A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0267,527 A1 Creamer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2004 (54) VOICE-TO-TEXT REDUCTION FOR REAL TIME IM/CHAT/SMS
(19) United States US 2004O267527A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0267,527 A1 Creamer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 30, 2004 (54) VOICE-TO-TEXT REDUCTION FOR REAL TIME IM/CHAT/SMS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150254235A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0254235 A1 Whitley (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) SIGN LANGUAGE TRANSLATION (57) ABSTRACT The instant
US 20150254235A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0254235 A1 Whitley (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) SIGN LANGUAGE TRANSLATION (57) ABSTRACT The instant
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1
 USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0113348 A1 Douskey et al. US 2015O113348A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) IMPLEMENTING MISR COMPRESSION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0113348 A1 Douskey et al. US 2015O113348A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) IMPLEMENTING MISR COMPRESSION
(12) United States Patent
 USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
(12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008O1771.57A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0177157 A1 Pasricha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIE DETECTION VIA ELECTROGASTROGRAPHY (76) Inventors: Pankaj
(19) United States US 2008O1771.57A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0177157 A1 Pasricha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LIE DETECTION VIA ELECTROGASTROGRAPHY (76) Inventors: Pankaj
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0193020 A1 Krissman et al. US 2014O193020A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) HEADPHONE ASSEMBLY Applicant: THE KETCHUM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0193020 A1 Krissman et al. US 2014O193020A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) HEADPHONE ASSEMBLY Applicant: THE KETCHUM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al.
 United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,744,043 B2
 USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
y 2. (12) United States Patent VbOt W N 35 (10) Patent No.: US 8,855,348 B2 HAD CIRCUIT ACTIVE TELECOIL (45) Date of Patent: Oct.
 USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 2008022721 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0227210 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) HOME TEST FOR GLYCATED ALBUMIN IN Publication Classification
US 2008022721 OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0227210 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2008 (54) HOME TEST FOR GLYCATED ALBUMIN IN Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8584.853B2 (12) United States Patent Knight et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,584.853 B2 Nov. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORAN ORTHOPEDCFXATION SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Adam T.
USOO8584.853B2 (12) United States Patent Knight et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,584.853 B2 Nov. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORAN ORTHOPEDCFXATION SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Adam T.
(12) United States Patent
 US00895.3827B2 (12) United States Patent Sacha et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,953,827 B2 Feb. 10, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) HEARNGAD WITH INTEGRATED
US00895.3827B2 (12) United States Patent Sacha et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,953,827 B2 Feb. 10, 2015 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) HEARNGAD WITH INTEGRATED
IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE UTILITY APPLICATION FOR UNITED STATES PATENT FOR
 IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE UTILITY APPLICATION FOR UNITED STATES PATENT FOR Fully-Implantable Cochlear Implant with Nasal Insertion Capability Inventor(s): Hugh Emmanuel 24 Wallalong
IN THE UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE UTILITY APPLICATION FOR UNITED STATES PATENT FOR Fully-Implantable Cochlear Implant with Nasal Insertion Capability Inventor(s): Hugh Emmanuel 24 Wallalong
(12) United States Patent Clapp et al. US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 US B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O23O254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230254A1 Harrison et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) HYBRID IMPLANTABLE COCHLEAR STIMULATOR HEARING
(19) United States US 2004O23O254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230254A1 Harrison et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) HYBRID IMPLANTABLE COCHLEAR STIMULATOR HEARING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 US 20020055857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0055857 A1 Mault (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF ASSISTING INDIVIDUALS IN Publication Classification LIFESTYLE
US 20020055857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0055857 A1 Mault (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD OF ASSISTING INDIVIDUALS IN Publication Classification LIFESTYLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,282,443 B1
 USOO6282443B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,282,443 B1 Mann et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) METHOD OF TREATMENT OF (56) References Cited DYSMENORRHEA OR RELIEVING MENSTRUAL
USOO6282443B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,282,443 B1 Mann et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) METHOD OF TREATMENT OF (56) References Cited DYSMENORRHEA OR RELIEVING MENSTRUAL
United States Patent (19) Lidow
 United States Patent (19) Lidow 54 SLEEP STATE INHIBITED WAKE-UP ALARM (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Derek Lidow, Beverly Hills, Calif, International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Lidow 54 SLEEP STATE INHIBITED WAKE-UP ALARM (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Derek Lidow, Beverly Hills, Calif, International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. (21) Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0054940A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/005494.0 A1 Almen (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (57) ABSTRACT MONITORING HEART
(19) United States US 2005.0054940A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/005494.0 A1 Almen (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR (57) ABSTRACT MONITORING HEART
IIII. United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,776,150 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
1, 2021,22) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. (19) United States. Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep.
 (19) United States US 20110224481A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0224481 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SPHENO-TEMPORAL BONE CONDUCTION COMMUNICATION EOUIPMENT AND/OR
(19) United States US 20110224481A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0224481 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SPHENO-TEMPORAL BONE CONDUCTION COMMUNICATION EOUIPMENT AND/OR
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,112,065 B2 Kopelman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006
 United States Patent US007 112065B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,112,065 B2 Kopelman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR DEFINING A FINISH LINE 5,372,502 A 12/1994 Massen et al. OF
United States Patent US007 112065B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,112,065 B2 Kopelman et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 26, 2006 (54) METHOD FOR DEFINING A FINISH LINE 5,372,502 A 12/1994 Massen et al. OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100142740A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/014274.0 A1 Roerup (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 10, 2010 (54) HEARING AID WIRELESS Related U.S. Application Data COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 20100142740A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/014274.0 A1 Roerup (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 10, 2010 (54) HEARING AID WIRELESS Related U.S. Application Data COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. s 8
 (19) United States US 2007.0049567A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0049567 A1 Wiley (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) HORMONE REPLACEMENT COMPOSITION AND METHOD (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2007.0049567A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0049567 A1 Wiley (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) HORMONE REPLACEMENT COMPOSITION AND METHOD (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO823 1533B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,231,533 B2 Buchalter (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 31, 2012 (54) ULTRASOUND COUPLING DEVICE 2003/0149359 A1 8/2003 Smith... 600/437 2003/O195420
(12) United States Patent USOO823 1533B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,231,533 B2 Buchalter (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 31, 2012 (54) ULTRASOUND COUPLING DEVICE 2003/0149359 A1 8/2003 Smith... 600/437 2003/O195420
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060074454A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0074454 A1 Freeberg (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR SELECTION OF CARDAC PACING ELECTRODE CONFIGURATIONS
(19) United States US 20060074454A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0074454 A1 Freeberg (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR SELECTION OF CARDAC PACING ELECTRODE CONFIGURATIONS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O175192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0175192 A1 Cheng (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2016 (54) ADJUSTABLE ACUPOINT AND ORGAN (52) U.S. Cl. PRESSING DEVICE
(19) United States US 2016O175192A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0175192 A1 Cheng (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2016 (54) ADJUSTABLE ACUPOINT AND ORGAN (52) U.S. Cl. PRESSING DEVICE
Development of a portable device for home monitoring of. snoring. Abstract
 Author: Yeh-Liang Hsu, Ming-Chou Chen, Chih-Ming Cheng, Chang-Huei Wu (2005-11-03); recommended: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2005-11-07). Note: This paper is presented at International Conference on Systems, Man and
Author: Yeh-Liang Hsu, Ming-Chou Chen, Chih-Ming Cheng, Chang-Huei Wu (2005-11-03); recommended: Yeh-Liang Hsu (2005-11-07). Note: This paper is presented at International Conference on Systems, Man and
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
available as a signal. The considerable data reduction asso
 USOO5928.6A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Krumbiegel et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1999 54 PROCESS AND DEVICE FOR THE 4,428,381 1/1984 Hepp... 128/773 AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF ABNORMAL
USOO5928.6A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Krumbiegel et al. () Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1999 54 PROCESS AND DEVICE FOR THE 4,428,381 1/1984 Hepp... 128/773 AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF ABNORMAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160337769A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0337769 A1 Siddhartha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) A METHOD FOR FITTING A HEARING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICE AS WELL
(19) United States US 20160337769A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0337769 A1 Siddhartha et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) A METHOD FOR FITTING A HEARING (52) U.S. Cl. DEVICE AS WELL
A Sleeping Monitor for Snoring Detection
 EECS 395/495 - mhealth McCormick School of Engineering A Sleeping Monitor for Snoring Detection By Hongwei Cheng, Qian Wang, Tae Hun Kim Abstract Several studies have shown that snoring is the first symptom
EECS 395/495 - mhealth McCormick School of Engineering A Sleeping Monitor for Snoring Detection By Hongwei Cheng, Qian Wang, Tae Hun Kim Abstract Several studies have shown that snoring is the first symptom
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004.0024334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0024334 A1 Boncompte (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2004 (54) ULTRASOUND ENDOMASSAGE DEVICE (76) Inventor: Joan
(19) United States US 2004.0024334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0024334 A1 Boncompte (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2004 (54) ULTRASOUND ENDOMASSAGE DEVICE (76) Inventor: Joan
United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974
 United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974 (54) BoNE CONDUCTION MICROPHONE ASSEMBLY Primary Examiner-Ralph D. Blakeslee 75 Inventor: Charles - M. Santori, San Jose, Calif., Attorney,
United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974 (54) BoNE CONDUCTION MICROPHONE ASSEMBLY Primary Examiner-Ralph D. Blakeslee 75 Inventor: Charles - M. Santori, San Jose, Calif., Attorney,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
(12) United States Patent
 US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1
 USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090156363A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0156363 A1 GUID et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXERCISE MACHINE WITH ADAPTIVE INTERFACE (75) Inventors: JARNO
(19) United States US 20090156363A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0156363 A1 GUID et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) EXERCISE MACHINE WITH ADAPTIVE INTERFACE (75) Inventors: JARNO
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O063621A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0063621 A1 NAUMANN (43) Pub. Date: (54) CONNECTOR FOR HEARING INSTRUMENT, HEARING INSTRUMENT AND HEARING INSTRUMENT
(19) United States US 2012O063621A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0063621 A1 NAUMANN (43) Pub. Date: (54) CONNECTOR FOR HEARING INSTRUMENT, HEARING INSTRUMENT AND HEARING INSTRUMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
Inspire Therapy for Sleep Apnea
 Inspire Therapy for Sleep Apnea Patient Guide Giving You the FREEDOM TO SLEEP Like Everyone Else Take Comfort. Inspire therapy can help. Inspire therapy is a breakthrough implantable treatment option for
Inspire Therapy for Sleep Apnea Patient Guide Giving You the FREEDOM TO SLEEP Like Everyone Else Take Comfort. Inspire therapy can help. Inspire therapy is a breakthrough implantable treatment option for
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O115435A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0115435 A1 Wilkens (43) Pub. Date: (54) DENTAL TOOTHPASTE, SOLUTION, TABLET AND SYSTEM WITH PLAOUE COLOR INDICATOR
(19) United States US 2006O115435A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0115435 A1 Wilkens (43) Pub. Date: (54) DENTAL TOOTHPASTE, SOLUTION, TABLET AND SYSTEM WITH PLAOUE COLOR INDICATOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O184427A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0184427 A1 Singh (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING EXERCISE PROGRAMS, GOODS AND (52) U.S.
US 2006O184427A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0184427 A1 Singh (43) Pub. Date: (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR PROVIDING EXERCISE PROGRAMS, GOODS AND (52) U.S.
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
Inspire. therapy for sleep apnea. Giving you the freedom to sleep like everyone else
 Inspire therapy for sleep apnea Giving you the freedom to sleep like everyone else Take Comfort. Take Action. Inspire therapy can help. Here are some reasons people like you have chosen Inspire therapy
Inspire therapy for sleep apnea Giving you the freedom to sleep like everyone else Take Comfort. Take Action. Inspire therapy can help. Here are some reasons people like you have chosen Inspire therapy
(12) United States Patent Li et a].
![(12) United States Patent Li et a]. (12) United States Patent Li et a].](/thumbs/82/84922623.jpg) US008700126B2 (12) United States Patent Li et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2014 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR COMPUTER AIDED SEPTAL DEFECT DIAGNOSIS AND SURGERY FRAMEWORK (75) Inventors:
US008700126B2 (12) United States Patent Li et a]. (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 2014 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR COMPUTER AIDED SEPTAL DEFECT DIAGNOSIS AND SURGERY FRAMEWORK (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,359,123 B2
 USOO83591.23B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,359,123 B2 Tong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 22, 2013 (54) ROBOTIC SYSTEMANDTRAINING (56) References Cited METHOD FOR REHABILITATION USING
USOO83591.23B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,359,123 B2 Tong et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 22, 2013 (54) ROBOTIC SYSTEMANDTRAINING (56) References Cited METHOD FOR REHABILITATION USING
IHIH IIII. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,417, Date of Patent: May 23, Kawai et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
United States Patent (19) Szabo, deceased et al.
 United States Patent (19) Szabo, deceased et al. (54) 75 (73) 21 22 51 52 58) (56) REHABILITATION EXERCISE DEVICE Inventors: Assignee: Louis Szabo, deceased, late of Penticton, Edith Szabo, executrix;
United States Patent (19) Szabo, deceased et al. (54) 75 (73) 21 22 51 52 58) (56) REHABILITATION EXERCISE DEVICE Inventors: Assignee: Louis Szabo, deceased, late of Penticton, Edith Szabo, executrix;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 20010038703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0038703 A1 Paczkowski (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2001 (54) HEARING-AIDASSEMBLY USING FOLDED FLEX CIRCUITS (76)
(19) United States US 20010038703A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0038703 A1 Paczkowski (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 8, 2001 (54) HEARING-AIDASSEMBLY USING FOLDED FLEX CIRCUITS (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.0089051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0089051A1 Draudt et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2012 (54) BLOOD GLUCOSE METER HAVING INTEGRAL LANCET DEVICE
(19) United States US 2012.0089051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0089051A1 Draudt et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2012 (54) BLOOD GLUCOSE METER HAVING INTEGRAL LANCET DEVICE
United States Patent (19) Annoni
 United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100324626A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0324626 A1 Lefkovitz (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2010 (54) ELECTROTHERAPY STIMILATOR FOR OSTEOARTHRTIS (51) Int.
(19) United States US 20100324626A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0324626 A1 Lefkovitz (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2010 (54) ELECTROTHERAPY STIMILATOR FOR OSTEOARTHRTIS (51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. Shennib (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 22, 2015
 (19) United States US 2015 0023512A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0023512 A1 Shennib (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 22, 2015 (54) ONLINE HEARING AID FITTING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. AND
(19) United States US 2015 0023512A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0023512 A1 Shennib (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 22, 2015 (54) ONLINE HEARING AID FITTING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl. AND
CPC... 46th Au (2013 on 46th 44 Brett P. Belden. Foley & Lardner LLP
 US009301731B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,301,731 B2 Henderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 5, 2016 (54) ULTRASOUND SYSTEMANDTRANSDUCER 2: E: ck 358. ihal. 1 361,679.41 mith et
US009301731B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,301,731 B2 Henderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 5, 2016 (54) ULTRASOUND SYSTEMANDTRANSDUCER 2: E: ck 358. ihal. 1 361,679.41 mith et
U.S. Cl /14. 58) Field of Search /14, / / /14 - ATRAL RATE - VENTRICULAR RATE FLYWHEEL
 United States Patent (19) Stoop IIII USOO5792.193A 11 Patent Number: 5,792,193 45) Date of Patent: Aug. 11, 1998 54 PACEMAKER SYSTEM AND METHOD WTH VENTRICULAR RATE SMOOTHING DURING HGH RATE ATRAL ARRHYTHMA
United States Patent (19) Stoop IIII USOO5792.193A 11 Patent Number: 5,792,193 45) Date of Patent: Aug. 11, 1998 54 PACEMAKER SYSTEM AND METHOD WTH VENTRICULAR RATE SMOOTHING DURING HGH RATE ATRAL ARRHYTHMA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Truax (54) DENTAL UNDERCUT APPLICATION DEVICE AND METHOD OF USE 75) Inventor: Lloyd H. Truax, Rochester, Minn. 73) Assignee: Tru-Tain, Inc., Rochester, Minn. (21) Appl. No.: 782,159
United States Patent (19) Truax (54) DENTAL UNDERCUT APPLICATION DEVICE AND METHOD OF USE 75) Inventor: Lloyd H. Truax, Rochester, Minn. 73) Assignee: Tru-Tain, Inc., Rochester, Minn. (21) Appl. No.: 782,159
...d. EEEEEEE/EE/EE. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 200802684.85A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0268485 A1 Guarino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) ICONIC DISPLAY OF MARKERS FOR A METER (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 200802684.85A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0268485 A1 Guarino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 30, 2008 (54) ICONIC DISPLAY OF MARKERS FOR A METER (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,224,174 B1
 USOO6224174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,224,174 B1 Mu (45) Date of Patent: *May 1, 2001 (54) POSTER DISPLAY APPARATUS 3.817,393 6/1974 Neilsen... 211/50 4,164,309 8/1979 Staats...
USOO6224174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,224,174 B1 Mu (45) Date of Patent: *May 1, 2001 (54) POSTER DISPLAY APPARATUS 3.817,393 6/1974 Neilsen... 211/50 4,164,309 8/1979 Staats...
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7672702B2 (12) United States Patent Hwang et al. (54) NONINVASIVE IN VIVO MEASURING SYSTEMAND NONINVASIVE IN VIVO MEASURING METHOD BY CORRECTING INFLUENCE OF HEMOGLOBIN (75) Inventors: In Duk Hwang,
USOO7672702B2 (12) United States Patent Hwang et al. (54) NONINVASIVE IN VIVO MEASURING SYSTEMAND NONINVASIVE IN VIVO MEASURING METHOD BY CORRECTING INFLUENCE OF HEMOGLOBIN (75) Inventors: In Duk Hwang,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160135916A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135916 A1 RAKC et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ARTICULATING ARM LIMITER FOR FI6M I3/02 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20160135916A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135916 A1 RAKC et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) ARTICULATING ARM LIMITER FOR FI6M I3/02 (2006.01)
US 8,287,508 B1. Oct. 16, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: VACUUM PUMP URINE RESERVOIR. Sanchez
 US008287508B1 (12) United States Patent Sanchez () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2012 (54) USING MOISTURE-WICKING ARTICLE WRAPPED OVER OPENINGS IN AN ELONGATED URINE COLLECTING CONTAINER FOR
US008287508B1 (12) United States Patent Sanchez () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 16, 2012 (54) USING MOISTURE-WICKING ARTICLE WRAPPED OVER OPENINGS IN AN ELONGATED URINE COLLECTING CONTAINER FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) James
 United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4,821,355 Burkhardt (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 1989
 United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4,821,5 Burkhardt () Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 1989 (54) SELF-ADJUSTING ORTHOPEDIC 4,447,922 5/1984 Brochu... 5/434 CERVICAL PLLOW 4,528,705 7/1985 Greenawalt...
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4,821,5 Burkhardt () Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 1989 (54) SELF-ADJUSTING ORTHOPEDIC 4,447,922 5/1984 Brochu... 5/434 CERVICAL PLLOW 4,528,705 7/1985 Greenawalt...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0171675A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0171675 A1 Tsukamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MEASURING DEVICE AND MEASURING (52) U.S. Cl. METHOD CPC...
(19) United States US 2013 0171675A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0171675 A1 Tsukamoto et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) MEASURING DEVICE AND MEASURING (52) U.S. Cl. METHOD CPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100140264A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0140264 A1 Hernandez (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 10, 2010 (54) CONTROLLING THE RATED BURST PRESSURE OF A RUPTURE
(19) United States US 20100140264A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0140264 A1 Hernandez (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 10, 2010 (54) CONTROLLING THE RATED BURST PRESSURE OF A RUPTURE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060264.751A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0264751A1 Wendelken et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 23, 2006 (54) PROTECTIVE THIN FILM DRESSING FOR Publication
US 20060264.751A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0264751A1 Wendelken et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 23, 2006 (54) PROTECTIVE THIN FILM DRESSING FOR Publication
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2
 US0090395.74B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2 Wilson (45) Date of Patent: May 26, 2015 (54) EXERCISE RING USPC... 482/24, 44 50, 79, 91, 92, 121-128, 482/131, 139 (76) Inventor:
US0090395.74B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2 Wilson (45) Date of Patent: May 26, 2015 (54) EXERCISE RING USPC... 482/24, 44 50, 79, 91, 92, 121-128, 482/131, 139 (76) Inventor:
Balboa Island Dentistry (949)
 Do You Snore? Are you always tired? Snoring is no laughing matter! It may be more than an annoying habit. It may be a sign of. How well do you sleep? Just about everyone snores occasionally. Even a baby
Do You Snore? Are you always tired? Snoring is no laughing matter! It may be more than an annoying habit. It may be a sign of. How well do you sleep? Just about everyone snores occasionally. Even a baby
(12) United States Patent
 US009 138575B2 (12) United States Patent Osypka (54) (71) BALLOON CATHETER Applicant: Peter Osypka Stiftung, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (72) Inventor: Peter Osypka, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (73) Assignee: Peter
US009 138575B2 (12) United States Patent Osypka (54) (71) BALLOON CATHETER Applicant: Peter Osypka Stiftung, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (72) Inventor: Peter Osypka, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (73) Assignee: Peter
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007 O185493A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0185493 A1 Feibel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 9, 2007 (54) CLAVICULAR BONE PLATE (30) Foreign Application
US 2007 O185493A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0185493 A1 Feibel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 9, 2007 (54) CLAVICULAR BONE PLATE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,351,671 B1
 USOO6351671B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Myklebust et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AND WO WO OO/27464 + 5/2000 ANALYZING CARDIO-PULMONARY RESUSCITATION
USOO6351671B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Myklebust et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AND WO WO OO/27464 + 5/2000 ANALYZING CARDIO-PULMONARY RESUSCITATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,334,451 B1
 USOO6334451B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 6,334,451 B1 Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH WITH FILLIG OF 1,340,043 A 5/1920 Grace... 132/311 TOOTHPASTE 1,451,941. A
USOO6334451B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 6,334,451 B1 Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH WITH FILLIG OF 1,340,043 A 5/1920 Grace... 132/311 TOOTHPASTE 1,451,941. A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0287886 A1 Patti US 20140287886A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PROTECTOR FOR EXERCISE BAR Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0287886 A1 Patti US 20140287886A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PROTECTOR FOR EXERCISE BAR Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1 DISPLAY VOCODER 122 TEXT CONVERSION ENGINE 126 PERSONALEZED CONTROLLER 144
 (19) United States US 20100030557A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0030557 A1 Molloy et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) VOICE AND TEXT COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, METHOD AND
(19) United States US 20100030557A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0030557 A1 Molloy et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 4, 2010 (54) VOICE AND TEXT COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, METHOD AND
What is a sleep center? Mercy Sleep Centers Staff Mercy Sleep Center Clive What is a sleep evaluation? Mercy Sleep Center Ames
 Mercy Sleep Center What is a sleep center? A sleep center is a medical facility dedicated to diagnosing and treating patients with sleep-related problems. Mercy Sleep Center is staffed by board certified/eligible
Mercy Sleep Center What is a sleep center? A sleep center is a medical facility dedicated to diagnosing and treating patients with sleep-related problems. Mercy Sleep Center is staffed by board certified/eligible
III. United States Patent (19) Hess et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,584,802 (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 17, 1996
 United States Patent (19) Hess et al. (54) ELASTIC KNEE-JOINT BANDAGE (75) Inventors: Heinrich Hess, Saarlouis; Wolfgang Krause, Kassel; Hans B. Bauerfeind, Kempen, all of Germany 73) Assignee: Bauerfeind
United States Patent (19) Hess et al. (54) ELASTIC KNEE-JOINT BANDAGE (75) Inventors: Heinrich Hess, Saarlouis; Wolfgang Krause, Kassel; Hans B. Bauerfeind, Kempen, all of Germany 73) Assignee: Bauerfeind
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060264767A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0264767 A1 Shennib (43) Pub. Date: (54) PROGRAMMABLE ECG SENSOR PATCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 6OO/SO9 (75) Inventor:
US 20060264767A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0264767 A1 Shennib (43) Pub. Date: (54) PROGRAMMABLE ECG SENSOR PATCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 6OO/SO9 (75) Inventor:
