Medication Administration
|
|
|
- Marianna Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Medication Administration
2 What is a medication? A medication is a drug or any other agent that is used to treat or prevent disease or injury or to restore or maintain normal functioning of body cells.
3 ADMINISTRATION Administration means assisting a person in the ingestion, application, or using universal precautions, rectal or vaginal insertion of medication, includes prescription and nonprescription medications, according to the written or printed directions of a licensed physician or other authorized practitioner, and making a written record thereof with regard to each medication administered, including the date, and time taken.
4 Monitoring Reminding a person to take medication at the time ordered by the physician or other authorized practitioner, handing a resident or assisting a resident with a container or package of medication that is prescribed for the consumer, visual observation of the consumer to ensure compliance; making a written record of the consumer s compliance with regard to each medication including the time taken, notification to the physician or other authorized practitioner if the consumer refuses to or is unable to comply with taking medications.
5 OTC-Over The Counter-Available without a prescription PRN or As Needed-Not taken on a regular basis, only when needed. Prescription-Only available when taken under the care of a physician. A written order from the physician is required before taking these medications and they must be obtained from the pharmacy.
6 Common Abbreviations Q OZ TSP q.d. b.i.d. t.i.d. q.i.d. mg. h.s. PRN tab Every Ounce Teaspoon Once a day/everyday Twice a day Three times a day Four times a day Milligrams Bedtime (hrs of sleep) As needed Tablet OTC Rx QTY P.O. A.M. P.M. d/c Over the counter Prescription Quantity By Mouth Morning Afternoon/Evening Discontinue
7 Types of Medications Liquids Emulsions-mixtures of oil and water that usually have a milky appearance, must be shaken prior to administration. Elixirs-Liquid preparations of medication with a sweetened alcohol base i.e. Nyquil Liniments- Aqueous preparations applied topically typically with massage. (similar to baby oil) Lotions-Aqueous preparations of suspended ingredients applied externally to treat skin conditions. Mixtures or Suspensions- Un-dissolved medications in a liquid. (must be shaken prior to administration) Syrups- Liquid preparation of medication in a sweetened base i.e. cough syrup. Sprays- Drugs prepared to be delivered by atomizers and used mainly in the treatment of nose and throat conditions.
8 Types of Medications Solids and Semi-Solids Capsules- Two part containers that contain powdered, oil, or liquid drugs. Creams- Usually an emulsion containing oil, water and medication. Generally they are opaque. Delayed Action Drugs- Drugs in a pill or capsule form that allow part of the granules to dissolve at once and part of the granules to dissolve later. Pills- Globe shaped forms, small enough to be easily swallowed. Tablets- Small discs containing medications and a cohesive substance. Tablets may be coated or uncoated. Lozenges- Large flat discs that are held in the mouth until dissolved. Ointments- Semi-solid preparations of medication that are applied locally to the skin or mucous membranes. Suppositories- Mixtures of drugs in a waxy base that melt at body temperature and are molded into shapes suitable for insertion into the vagina, rectum or urethra.
9 Routes of Administration Oral (by Mouth) G/NG/J tube Nasal Ear (Otic) Eye (Optic) Rectal Inhaled Topical (on the skin) SVN-breathing tx * IV-Intravenous * IM-Intramuscular * SQ-Subcutaneous * Sublingual-under the tongue Vaginal Our providers cannot do injections, administer oxygen, or start SVN treatments. We can assist with an Epi-pen, in a life threatening emergency.
10 Classifications of Drugs Analgesic-Relieves pain Anesthetic- Temporary loss of sensation Antibiotic- Kills living micro-organisms that cause infection Anticoagulants- Prevents blood from clotting. Anticonvulsants-Prevents or decreases seizures Antidepressants- Mood elevators used to treat depression. Antigens- Any substance that will lead to the development of antibodies Antihistamines- Drugs that neutralize histamines produced in the body. Antipsychotic- Drugs used to treat psychosis Antiseptics- Prevents or lessens the activity of infection by slowing the growth of micro-organisms Antitoxins-A serum used to lessen the effects of toxins or poisons produced by bacteria. Coagulants- Drugs that cause blood or fluids to clot Disinfectants- Agents that destroy disease producing substances or organisms. Diuretics- Drugs that increase the urine output
11 Classifications of Drugs Emetics- Substances that cause vomiting Expectorants-Medications used to increase secretions and aid in expelling mucous from the respiratory system. Laxatives- Drugs that aid in relieving constipation Narcotics- Drugs that produce sleep or stupor and relieve pain. Sedatives- Drugs that produce a quieting or calming effect. Stimulants- Drugs that increase activity, hastens action of the body. Vaccine- Drug derived from the growth of bacteria and used to confer immunity from certain diseases. Vasoconstrictors- Drugs that cause constriction or decrease the size of blood vessels. Vasodilators- Drugs that cause dilation or enlargement of the blood vessels.
12 The 5 Rights of Medication Administration Do I take pills??
13 Make sure you are administering the correct medication to the appropriate person. Ensure the person s name is correct on the medication bottle and the medication log. If you are giving medications to more than one person at a time make sure you finish administering medications to one person before proceeding to the next person.
14 The 5 Rights of Medication Administration
15 Factors that contribute to the wrong medication error include similar labeling and packaging of products, medications with very similar names, and storage of these very similar products together. In addition, poor communication is often a cause of medication errors. Always make sure you will not be distracted during medication administration Always repeat verbal orders Always check the label and dose against med log Never administer a med if you are unsure of labeling, orders, or dosage Never assume route of administration DO NOT ASSUME ANYTHING!!!!
16 The 5 Rights of Medication Administration
17 Always make sure the dosage on the medication label matches the dosage on the medication log. If the dosages don t match STOP and contact your supervisor, or if it is HCBS contact the Parent/Guardian/primary caregiver or doctor for further instructions. DO NOT just give the medication. Never assume the dosage will always stay the same!
18 The 5 Rights of Medication Administration
19 Medications can be administered by a variety of routes, such as oral, rectal, topical, sublingual, intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, or nasally. The route prescribed depends on the type of medication (tablet/capsule, cream/ointment, suppository, injection, drops/liquid) the person s condition, and their ability to take medication. The correct route is indicated on the medication label.
20 The 5 Rights of Medication Administration
21 All medications are to be administered at the specific time they are ordered to be given. The most common staff error is when staff forget or fail to administer medication at the prescribed time. For this reason, medication times are often clustered to avoid the likelihood of forgetting to administer medications. For example medication times usually occur at 7:00 a.m., 12:00 noon, 3:00 p.m., & 7:00 p.m. for multiple people. There may be times that you might have to administer meds earlier or later due to labs, or medical testing. AT NO TIME WILL MEDICATIONS BE PREPARED EARLY!!!
22 The 5 Rights of Medication Administration Always check the 5 Rights 3 times when administering medications When verifying the medication against the medication log When measuring/placing meds in pill cup Before administering the medication
23 Right Client Right Medication Right Dose Right Route Right Time
24 Documentation Errors Documentation errors occur when staff administers the medication but fails to sign the medication log. This requires the next staff person to follow-up and ensure that the medication was actually administered prior to giving the next scheduled dose. Document the administration of medication IMMEDIATELY after the client takes the medication. If the client refuses to take the medication or there is some unavoidable reason the medication is going to be delayed document it on the medication log and write an incident report. IMMEDIATELY document and report all documentation errors on an incident report and follow incident report procedures.
25 Procedures for Administering Meds Gather all supplies- med log, pen, gloves, measuring devices, med cups, pill splitter/crusher, Q-tips, cotton balls, all of these things should be gathered up before starting to administer medications. Compare the medication label with the medication sheet and resolve any discrepancies before proceeding with the administration of medications. *Person is to be present at all times, do NOT prepare medications early!! Wash hands Put on gloves Administer medications one medication at a time Explain the procedure to the person Document the administration of the medication Return medication to storage area Dispose of used supplies Wash hands
26 Medication Errors Wrong time: Echoing Hope Ranch allows an hour window on either side of the prescribed time. For example if the prescribed time is 7:00 a.m., the medication can be given as early as 6:00 a.m. or as late as 8:00 a.m. An error occurs when the client has not received his/her medication within an hour of the usual prescribed time. Medication given at the wrong time or if it is missed completely is a med error and an incident report must be written. The on-call supervisor must be notified, and the staff must call poison control for further instructions on how to proceed.
27 Medication Errors Wrong Person Borrowing meds from one person to give them to another or giving meds to the wrong person. Giving medications to the wrong person is a serious threat to the client s health. Immediately call Poison Control for further instructions. Write an incident report Call On-Call Supervisor
28 Medication Errors Wrong Dose Overdosing may occur when too high a dose is administered. Underdosing is also an issue because the person is not receiving enough of the prescribed medication Write an incident report Call Poison Control Call On-Call Supervisor
29 Medication Errors Forgetting Meds Depending on how late the medications are Poison Control may have you go ahead and give them or have you hold them until the next dose, it is important to call and get direction. Contact Poison Control Call On-Call Supervisor Write an incident report
30 Medication Errors Refusal (If the person refuses or spits out medications) Med refusals may occur if a person is in a depressed or angry mood. Avoid power struggles and attempt to talk to them about alternate topics. Do not threaten them with loss of activities or privileges as it is their right to refuse medications. Call Poison Control Call On-Call Supervisor Write an Incident Report
31 Medication Errors Spilled/dropped meds If during the administration of medication the medication get spilled or medication is dropped on the ground you can just pour more meds and re-administer them to the client but you will need to write an incident report to document the wasted medication if there are medication counts that are going to be off.
32 Medication Errors Wrong Route Contact Poison Control Contact On-Call Supervisor Write Incident Report Get an anatomy doll and figure out what s what!!!
33 Charting Black or Blue ink only Never use white out or erase anything! Circle the box Chart the mistake on the back Date and initial Document meds only after the person has swallowed the medication Only document for medications you have administered. Your signature and initials should be at the bottom of the med log Staff is responsible for making sure the medication log matches the information on the medication labels.
34 Medication Disposal HCBS- This is the responsibility of the family or primary caregiver and DSP s will not be disposing of medications. Residential If it is a narcotic or controlled substance it must be returned to the pharmacy and be signed off on the EHR Medication Disposal Tracking Form. Non-narcotics can be placed into a plastic bag of cat litter or used coffee grounds and then disposed of in the trash can. Medication disposal will be documented with the medication name, date, time, and the amount of medication being disposed. Two staff must be present to witness the disposal
35 Echoing Hope Ranch - MONTHLY MEDICATION RECORD Setting: Person Month: Medication Dosage Route Time Medication Dosage Route Time Medication Dosage Route Time D= Day Program H= Home A = Absent R= Refused Staff name Staff signature Initials Staff name Staff signature Initals * Special Instructions: *C
36 Echoing Hope Ranch - MONTHLY MEDICATION RECORD Date Comment Staff Initials Staff Name Initials Staff Name Initials
37 OTC meds OTC- Over the counter medications can be administered to a person but we must have a OTC standing order on file for the person with a pre-approved list of medications that we are allowed to give. OTC meds are tracked on a separate medication log.
38 Standing Medical Order: Medications Administered Home: Client: Month: Year: Date Time Condition Dose Medication Route Initials Staff Name Staff Signature Staff Initials
39 Always learn about the individual served s meds so you know what to watch for. Desired effects- these are the effects that mean the drug is working the way that we expected it to work. Unwanted effects- also known as side effects, these may be expected and predictable such as drowsiness with some seizure meds. They may be harmless or they may be dangerous, therefore staff must know the possible side effects and watch for them. Drug interactions- whenever a person is taking more than one drug at a time there is a potential for drug interactions. It may increase the effects or decrease the effects of one or more of the medications or cause other unwanted effects.
40 Know your resources Pill Book-Medication inserts On-Call Supervisor Poison Control Always make sure you are familiar with the medications you administer Always follow the FIVE RIGHTS!
Section 5: Appendices
 MEDICATION ASSISTANCE IN ASSISTED LIVING Section 5: Appendices Medication Terminology Definitions Abbreviations 60 Appendix A: Medication Terminology There are many terms associated with medications and
MEDICATION ASSISTANCE IN ASSISTED LIVING Section 5: Appendices Medication Terminology Definitions Abbreviations 60 Appendix A: Medication Terminology There are many terms associated with medications and
Module II Medication Basics
 Module II Medication Basics Kinds of Medications People make different choices about medications and remedies. Today, there are more than 11,000 medications available to the consumer. There are also hundreds
Module II Medication Basics Kinds of Medications People make different choices about medications and remedies. Today, there are more than 11,000 medications available to the consumer. There are also hundreds
Medication Administration Curriculum INSTRUCTOR S MANUAL. Name State Date
 Instructions: Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. If select modules were presented, only fill out the questions related to those modules. MODULE 1
Instructions: Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. If select modules were presented, only fill out the questions related to those modules. MODULE 1
Medication Administration and Documentation. A NC Approved CE Class offered by
 Medication Administration and Documentation A NC Approved CE Class offered by Common Medical Abbreviations - Doses gm = gram gtt = drop mg = milligram ss = 1/2 mcg = microgram oz = ounce cc = cubic centimeter
Medication Administration and Documentation A NC Approved CE Class offered by Common Medical Abbreviations - Doses gm = gram gtt = drop mg = milligram ss = 1/2 mcg = microgram oz = ounce cc = cubic centimeter
INFORMATION TOPIC: II-5 OR DEMONSTRATION: II-5. DOSAGE, MEASUREMENTS, AND DRUG FORMS (Lesson Title) OBJECTIVES THE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO:
 LESSON PLAN: 5 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: II MEDICATION TECHNICIAN GENERAL PRINCIPLES SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes medication terminology, dosage, measurements, drug forms, transcribing physician s orders,
LESSON PLAN: 5 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: II MEDICATION TECHNICIAN GENERAL PRINCIPLES SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes medication terminology, dosage, measurements, drug forms, transcribing physician s orders,
Medication Administration. By: Carolyn McCune RN, BSN, MSN, CRNP
 Medication Administration By: Carolyn McCune RN, BSN, MSN, CRNP Percutaneous Administration Medications application to the skin or mucus membranes Ointments, creams, powders, lotions, solutions into the
Medication Administration By: Carolyn McCune RN, BSN, MSN, CRNP Percutaneous Administration Medications application to the skin or mucus membranes Ointments, creams, powders, lotions, solutions into the
Routes of drug administration
 Routes of drug administration Definition:- A route of administration in pharmacy is the path by which a drug is taken into the body. Classification:- The various routes of administrations are classified
Routes of drug administration Definition:- A route of administration in pharmacy is the path by which a drug is taken into the body. Classification:- The various routes of administrations are classified
INFORMATION TOPIC: II-5 OR DEMONSTRATION: II-5. DOSAGE, MEASUREMENTS, AND DRUG FORMS (Lesson Title) OBJECTIVES THE STUDENT WILL BE ABLE TO:
 LESSON PLAN: 5 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: II MEDICATION TECHNICIAN GENERAL PRINCIPLES SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes medication terminology, dosage, measurements, drug forms, transcribing physician s orders,
LESSON PLAN: 5 COURSE TITLE: UNIT: II MEDICATION TECHNICIAN GENERAL PRINCIPLES SCOPE OF UNIT: This unit includes medication terminology, dosage, measurements, drug forms, transcribing physician s orders,
Lesson 5: Recording and Storage of Medication
 Lesson 5: Recording and Storage of Medication Transcript Title Slide (no narration) Narrator Slide Hello. My name is Jill Morrow and I am the Medical Director for the Office of Developmental Programs.
Lesson 5: Recording and Storage of Medication Transcript Title Slide (no narration) Narrator Slide Hello. My name is Jill Morrow and I am the Medical Director for the Office of Developmental Programs.
Medications. Managing and Administering Medication
 Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
MOD 4: Medication Administration
 NSE22 Page 1 1. MOD 4: Medication Administration October1310 8:12 PM The CNO identifies eight rights of medication administration. Identify the eight rights and the rationale for each Right Client give
NSE22 Page 1 1. MOD 4: Medication Administration October1310 8:12 PM The CNO identifies eight rights of medication administration. Identify the eight rights and the rationale for each Right Client give
MODULE 3 How to Administer Medication
 MODULE 3 How to Administer Medication Introduction: top common errors 5 Rights Identifying as needed conditions Universal/standard precautions Preparing to administer medication Medication administration
MODULE 3 How to Administer Medication Introduction: top common errors 5 Rights Identifying as needed conditions Universal/standard precautions Preparing to administer medication Medication administration
Do Not Reproduce. Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider
 Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. 2 Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider Before medicine is prescribed, tell him or her: Medicines on your health plan s preferred drug list (formulary).
Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. 2 Things to Tell Your Health Care Provider Before medicine is prescribed, tell him or her: Medicines on your health plan s preferred drug list (formulary).
Medication Safety Presentation
 Appendix E Aid 1: Sample Event Poster Medication Safety Presentation Do YOU know your role on the healthcare team? Do YOU know the questions to ask your pharmacist? Do YOU know safe medication practices?
Appendix E Aid 1: Sample Event Poster Medication Safety Presentation Do YOU know your role on the healthcare team? Do YOU know the questions to ask your pharmacist? Do YOU know safe medication practices?
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care
 Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Division 1 Introduction to Advanced Prehospital Care Chapter 7 Intravenous Access and Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Topics Aseptic Technique Medication
Chapter 7. Principles of Pharmacology
 Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology Introduction Administering medications is a serious business. Medications may alleviate pain and improve patient s well-being. Used inappropriately, may cause harm
Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology Introduction Administering medications is a serious business. Medications may alleviate pain and improve patient s well-being. Used inappropriately, may cause harm
CHAPTER 3 Medicines 35
 P CHA TER 3 Medicines 35 Learning About Medicines Medicines medicines Medicines are something you use when you are sick and want to get better. You can also use medicines to stay healthy. Medicines are
P CHA TER 3 Medicines 35 Learning About Medicines Medicines medicines Medicines are something you use when you are sick and want to get better. You can also use medicines to stay healthy. Medicines are
PHOLCODINE. Please follow the instructions on the packaging of the medicine you purchased and in this leaflet before you start using pholcodine.
 PHOLCODINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains pholcodine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
PHOLCODINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains pholcodine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
How to Manage Medications Caregiving Series
 How to Manage Medications Caregiving Series Objectives Upon completion of this training, the participant will: Learn the warning signs of improper medication use Have an understanding of how aging changes
How to Manage Medications Caregiving Series Objectives Upon completion of this training, the participant will: Learn the warning signs of improper medication use Have an understanding of how aging changes
Transcribing Rules & Tips:
 Transcribing Rules & Tips: Using blue or black ink only: Line1 = Medication ne & Strength only Lines 2 & 3= Dose, Route, Frequency AM medications on top 2 rows PM medications on bottom rows No Medical
Transcribing Rules & Tips: Using blue or black ink only: Line1 = Medication ne & Strength only Lines 2 & 3= Dose, Route, Frequency AM medications on top 2 rows PM medications on bottom rows No Medical
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Medication Administration 2 Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes
 EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
EduCare Knowledge & Skill Assessment Medication I Routes Employee Name Date Demonstration/Skill Assessment Oral (O) Pass Fail 1. Wash your hands; apply gloves. 2. Perform the 3 safety checks on the Simple
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
 PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib )
 Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
For External Use Only. Should neither be swallowed. Nor injected
 For External Use Only Should neither be swallowed Nor injected Preparations which are applied to the skin. (Topical preparations) Preparations which are applied to the mucus membranes. Local effect Systemic
For External Use Only Should neither be swallowed Nor injected Preparations which are applied to the skin. (Topical preparations) Preparations which are applied to the mucus membranes. Local effect Systemic
Family Self-Care and Over the Counter Medications Program. Sponsored by: FAHC Department of Pharmacy
 Family Self-Care and Over the Counter Medications Program Sponsored by: FAHC Department of Pharmacy What are Over the Counter Medications? Nonprescription medications and products Often referred to as
Family Self-Care and Over the Counter Medications Program Sponsored by: FAHC Department of Pharmacy What are Over the Counter Medications? Nonprescription medications and products Often referred to as
SANDOMIGRAN. 0.5mg tablet Pizotifen malate
 SANDOMIGRAN 0.5mg tablet Pizotifen malate What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Sandomigran. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place
SANDOMIGRAN 0.5mg tablet Pizotifen malate What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Sandomigran. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place
Oral Systemic Therapy
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Oral Systemic Therapy www.nscancercare.ca Patient s Name: Type of Treatment: Cancer Doctor: Cancer Clinic: Phone Number: Emergency Department Phone Number: Who do I call if
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Oral Systemic Therapy www.nscancercare.ca Patient s Name: Type of Treatment: Cancer Doctor: Cancer Clinic: Phone Number: Emergency Department Phone Number: Who do I call if
Safe Use, Storage, and Disposal of Opioid Drugs Safe Use, Storage, and Disposal of Opioid Drugs
 Return to Web version Safe Use, Storage, and Disposal of Opioid Drugs Safe Use, Storage, and Disposal of Opioid Drugs What are opioids? Opioids (say: "oh-pee-oyds") are powerful pain relievers your doctor
Return to Web version Safe Use, Storage, and Disposal of Opioid Drugs Safe Use, Storage, and Disposal of Opioid Drugs What are opioids? Opioids (say: "oh-pee-oyds") are powerful pain relievers your doctor
Oral Systemic Therapy
 Oral Systemic Therapy This information does not take the place of the care and advice of your Cancer Care Team. Talk to your Cancer Care Team about your health concerns, treatment options and any questions
Oral Systemic Therapy This information does not take the place of the care and advice of your Cancer Care Team. Talk to your Cancer Care Team about your health concerns, treatment options and any questions
Chemists Own Strong Pain Extra Paracetamol and Codeine Phosphate
 Chemists Own Strong Pain Extra Paracetamol and Codeine Phosphate Consumer Medicine Information(CMI) Please read this information before you start taking this medicine. What is in this CMI? This CMI answers
Chemists Own Strong Pain Extra Paracetamol and Codeine Phosphate Consumer Medicine Information(CMI) Please read this information before you start taking this medicine. What is in this CMI? This CMI answers
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica )
 Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib )
 Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
TRIPROLIDINE. Please read this leaflet and the packaging of the medicine you purchased, carefully before you start using triprolidine.
 TRIPROLIDINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains triprolidine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
TRIPROLIDINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet The medicine you have purchased contains triprolidine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
Medication Administration in School
 Medication Administration in School Southington Public Schools Southington, Connecticut Click each page to proceed. Objectives Understand the definition of qualified personnel. Understand and adhere to
Medication Administration in School Southington Public Schools Southington, Connecticut Click each page to proceed. Objectives Understand the definition of qualified personnel. Understand and adhere to
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name tamoxifen citrate (tuh-mok-sih-fen SIH-trayt) Brand name Soltamox (SOL-ta-mox) Approved uses Tamoxifen is used to treat certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer
Name of your medication Generic name tamoxifen citrate (tuh-mok-sih-fen SIH-trayt) Brand name Soltamox (SOL-ta-mox) Approved uses Tamoxifen is used to treat certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer
CHAPTER 4 Medication Preparation & Supplies
 CHAPTER 4 Medication Preparation & Supplies drug form (drug preparation) type of preparation in which the drug is supplied most pharmaceutical companies prepare a drug in a form most suitable for route
CHAPTER 4 Medication Preparation & Supplies drug form (drug preparation) type of preparation in which the drug is supplied most pharmaceutical companies prepare a drug in a form most suitable for route
Chapter 1 Pharmacists discussing Medicines
 Chapter 1 Pharmacists discussing Medicines What is medicine? Medicines are substances that can influence the (1) physiology, (2) psychology, (3) function, (4) structure of your body. What can the pharmacist
Chapter 1 Pharmacists discussing Medicines What is medicine? Medicines are substances that can influence the (1) physiology, (2) psychology, (3) function, (4) structure of your body. What can the pharmacist
Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration
 1 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration 2 Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures to reduce your
1 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration 2 Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures to reduce your
Eltrombopag (Promacta )
 Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Unit6. Prescriptions. Speaking:Giving A Prescription. Vocabulary: Common Latin Rx Terms. Articles: A Prescription: Understanding.
 Unit6 Prescriptions Grammar: The Future: Will\ Going to Expressing the Future in Time Clauses Using the Present Progressive and Simple Present to Express Future Time Future Progressive Speaking:Giving
Unit6 Prescriptions Grammar: The Future: Will\ Going to Expressing the Future in Time Clauses Using the Present Progressive and Simple Present to Express Future Time Future Progressive Speaking:Giving
Consumer Medicine Information TOPICIL. Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Topicil Capsules.
 Clindamycin hydrochloride Capsules 150 mg What is in this leaflet Consumer Medicine Information TOPICIL Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Topicil Capsules. This leaflet answers
Clindamycin hydrochloride Capsules 150 mg What is in this leaflet Consumer Medicine Information TOPICIL Please read this leaflet carefully before you start using Topicil Capsules. This leaflet answers
THE FACTS ABOUT PRESCRIPTION MEDICINE MISUSE
 JUNE This month, Health is Primary is focusing on safe use of prescription medicines. We are sharing the facts about the risks of medicine misuse and the importance of using medicines as prescribed along
JUNE This month, Health is Primary is focusing on safe use of prescription medicines. We are sharing the facts about the risks of medicine misuse and the importance of using medicines as prescribed along
Chloroform Codeine Ether
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Chapter 6, Part 1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF PHARMACOLOGY Part 1 Basic Pharmacology Drugs are chemicals used to diagnose, treat, and disease. Pharmacology is the study of drugs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Chapter 6, Part 1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF PHARMACOLOGY Part 1 Basic Pharmacology Drugs are chemicals used to diagnose, treat, and disease. Pharmacology is the study of drugs
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers
 Medication Information for Parents and Teachers General Information About Medication Melatonin Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination of medical and psychological
Medication Information for Parents and Teachers General Information About Medication Melatonin Each child and adolescent is different. No one has exactly the same combination of medical and psychological
MODULE 1: BASIC DRUG KNOWLEDGE
 MODULE 1: BASIC DRUG KNOWLEDGE 1.1 How Drugs Work A drug is a medicine or substance (but not food or water) which when ingested (or otherwise introduced into the body) alters the way the body works physically
MODULE 1: BASIC DRUG KNOWLEDGE 1.1 How Drugs Work A drug is a medicine or substance (but not food or water) which when ingested (or otherwise introduced into the body) alters the way the body works physically
Administering Medicines to Students Asthma Inhaler Exemption
 Administering Medicines to Students Asthma Inhaler Exemption Any school employee authorized in writing by the district administrator or school principal: 1. May assist in the self-administration of any
Administering Medicines to Students Asthma Inhaler Exemption Any school employee authorized in writing by the district administrator or school principal: 1. May assist in the self-administration of any
Chapter 7. National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) National EMS Education Standard Competencies (2 of 5) Principles of Pharmacology
 Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Pharmacology Applies fundamental knowledge of the medications that the EMT may assist/administer to a patient
Chapter 7 Principles of Pharmacology National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Pharmacology Applies fundamental knowledge of the medications that the EMT may assist/administer to a patient
health care quality Your Medicine: Play It Safe Medicine Record Form at the Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the
 Your Medicine: Play It Safe Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the Medicine Record Form at the back of this booklet to keep track of your medicines. Logo Here health care quality Have you
Your Medicine: Play It Safe Learn more about how to take medicines safely. Use the Medicine Record Form at the back of this booklet to keep track of your medicines. Logo Here health care quality Have you
Information Sheet 10. Medication Hints and Tips (Updated August 2014)
 An information sheet on Medication problems and how to prevent them. Memory Loss... People who suffer from dementia or Alzheimer s disease may simply forget to take their medications, causing them to skip
An information sheet on Medication problems and how to prevent them. Memory Loss... People who suffer from dementia or Alzheimer s disease may simply forget to take their medications, causing them to skip
MOST Operations Manual page 1 MEDICATION INVENTORY TABLE OF CONTENTS
 MOST Operations Manual page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS MEDICATION INVENTORY 1. Background and rationale...2 2. Equipment and supplies...2 3. Detailed measurement procedures...2 3.1 Targeted medications...2 3.2
MOST Operations Manual page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS MEDICATION INVENTORY 1. Background and rationale...2 2. Equipment and supplies...2 3. Detailed measurement procedures...2 3.1 Targeted medications...2 3.2
Tacrolimus. Information for Parents/Carers
 Tacrolimus Information for Parents/Carers St Michael s C Ward 01 878 4258 01 878 4431 Main Hospital Number 01 878 4200 What is tacrolimus and what is it used for? Tacrolimus is an immunosuppressant drug,
Tacrolimus Information for Parents/Carers St Michael s C Ward 01 878 4258 01 878 4431 Main Hospital Number 01 878 4200 What is tacrolimus and what is it used for? Tacrolimus is an immunosuppressant drug,
Chapter 11 - Principles of Pharmacology
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Chapter 11 Principles of Pharmacology National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Pharmacology Applies fundamental knowledge of the medications that the EMT may assist/administer
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Chapter 11 Principles of Pharmacology National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Pharmacology Applies fundamental knowledge of the medications that the EMT may assist/administer
Medications What You Need To Know
 1. Things to Tell Your Doctor Before medicine is prescribed for you, let your doctor know the names and doses of all of the medicines and dietary supplements you take. Medications What You Need To Know
1. Things to Tell Your Doctor Before medicine is prescribed for you, let your doctor know the names and doses of all of the medicines and dietary supplements you take. Medications What You Need To Know
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar )
 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
PHARMACY TECHNICIAN TRAINING COURSE Week #1
 PHARMACY TECHNICIAN TRAINING COURSE Week #1 What we want to do this week: - Welcome! and complete some information on students - make sure we know how to use our calculators - learn about units and how
PHARMACY TECHNICIAN TRAINING COURSE Week #1 What we want to do this week: - Welcome! and complete some information on students - make sure we know how to use our calculators - learn about units and how
Within the proportion the two outside numbers are referred to as the extremes. The two inside numbers are referred to as the means.
 Basic Formulas Speaker: Jana Ogden This lecture will demonstrate the expectations for performing a variety of the more complex calculations. You are expected to refer to your text and complete the designated
Basic Formulas Speaker: Jana Ogden This lecture will demonstrate the expectations for performing a variety of the more complex calculations. You are expected to refer to your text and complete the designated
Medication Education Module 2. Disposal. Company LOGO
 Medication Education Module 2 Disposal Company Objectives 1. What does med disposal mean? 2. When would I dispose of meds? 3. How are meds disposed of? 4. How many staff are needed? Medication Disposal
Medication Education Module 2 Disposal Company Objectives 1. What does med disposal mean? 2. When would I dispose of meds? 3. How are meds disposed of? 4. How many staff are needed? Medication Disposal
Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always
 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures
1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 7, Medication Administration Part 1 Principles and Routes of Medication Administration Caution: Administering medications is business Always take appropriate Standard measures
FAIRFIELD SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM. PROCEDURE: Administration of Oral, Topical or Inhalant Medications by Principals and Teachers
 FAIRFIELD SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM PROCEDURE: Administration of Oral, Topical or Inhalant Medications by Principals and Teachers 1. Obtain key Access to all stored medications is limited to persons authorized
FAIRFIELD SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM PROCEDURE: Administration of Oral, Topical or Inhalant Medications by Principals and Teachers 1. Obtain key Access to all stored medications is limited to persons authorized
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults
 Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Medicines and You: A Guide for Older Adults Council on Family Health Provided in cooperation with U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration and the Administration on Aging
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Clinical Calculation 5 th Edition
 Clinical Calculation 5 th Edition Chapter 6 Calculation of Oral Medications Pages 40-54 Oral Medications Medications that are administered by mouth and absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract are known
Clinical Calculation 5 th Edition Chapter 6 Calculation of Oral Medications Pages 40-54 Oral Medications Medications that are administered by mouth and absorbed via the gastrointestinal tract are known
Cold, Flu, or Allergy?
 Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Introduction: A cold, the flu, and allergies all affect the respiratory system and have many similar symptoms. It can be difficult to tell whether someone has a cold, the flu, or
Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Introduction: A cold, the flu, and allergies all affect the respiratory system and have many similar symptoms. It can be difficult to tell whether someone has a cold, the flu, or
Ceclor CD cefaclor monohydrate sustained release tablets
 Ceclor CD cefaclor monohydrate sustained release tablets Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Ceclor CD. It does not contain all
Ceclor CD cefaclor monohydrate sustained release tablets Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about Ceclor CD. It does not contain all
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name letrozole (LEH-truh-zole) Brand name Femara (FEH-muh-ruh) Approved uses Letrozole is used in the treatment of certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal
Name of your medication Generic name letrozole (LEH-truh-zole) Brand name Femara (FEH-muh-ruh) Approved uses Letrozole is used in the treatment of certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal
PHAR 7632 Chapter 7. Table Market and Share of Pharmaceuticals by ROA Data from Viswanathan, 2004
 Student Objectives for this Chapter After completing the material in this chapter each student should:- be able to describe various routes of drug administration including the concentration versus time
Student Objectives for this Chapter After completing the material in this chapter each student should:- be able to describe various routes of drug administration including the concentration versus time
CRINONE 8% Progesterone 90 mg, Prolonged Release Vaginal gel with Polyethylene applicator
 CRINONE 8% Progesterone 90 mg, Prolonged Release Vaginal gel with Polyethylene applicator Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about CRINONE.
CRINONE 8% Progesterone 90 mg, Prolonged Release Vaginal gel with Polyethylene applicator Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about CRINONE.
Mycophenolate. Information for Parents/Carers
 Mycophenolate Information for Parents/Carers St Michael s C Ward 01 878 4258 01 878 4431 Main Hospital Number 01 878 4200 What is mycophenolate and what is it used for? Mycophenolate is an immunosuppressant
Mycophenolate Information for Parents/Carers St Michael s C Ward 01 878 4258 01 878 4431 Main Hospital Number 01 878 4200 What is mycophenolate and what is it used for? Mycophenolate is an immunosuppressant
More about using medicines safely. Quick info. Doctor s phone number: Pharmacy phone number: 24 hour Poison Control Center
 More about using medicines safely Medicines in My Home: FDA Consumer Medicine Education: www.fda.gov/usemedicinesafely National Council on Patient Information and Education: www.bemedwise.org Medline Plus,
More about using medicines safely Medicines in My Home: FDA Consumer Medicine Education: www.fda.gov/usemedicinesafely National Council on Patient Information and Education: www.bemedwise.org Medline Plus,
Shopping List for Knee Arthroscopy
 inserts 8-08.qxp 9/16/2008 3:41 PM Page 1 Shopping List for Knee Arthroscopy The following is a list of supplies which you should have at home following your surgery: Adhesive bandages (Band-Aids ) Helpful
inserts 8-08.qxp 9/16/2008 3:41 PM Page 1 Shopping List for Knee Arthroscopy The following is a list of supplies which you should have at home following your surgery: Adhesive bandages (Band-Aids ) Helpful
The expiration date. If you have any doubts, check with your pharmacist.
 including your medicine cabinet Spring is the ideal time to perform a major cleanup. Clearing out your medicine cabinet should be an integral part of your spring cleaning routine. Over time, a multitude
including your medicine cabinet Spring is the ideal time to perform a major cleanup. Clearing out your medicine cabinet should be an integral part of your spring cleaning routine. Over time, a multitude
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
APPENDIX 1 PROCEDURES FOR ADMINISTERING MEDICATION
 APPENDIX 1 PROCEDURES FOR ADMINISTERING MEDICATION 1. Wash and thoroughly dry hands and any utensil that may be required e.g. medicine spoon, measure, glass, tablet cutter 2. Where a clinical tasks protocol
APPENDIX 1 PROCEDURES FOR ADMINISTERING MEDICATION 1. Wash and thoroughly dry hands and any utensil that may be required e.g. medicine spoon, measure, glass, tablet cutter 2. Where a clinical tasks protocol
NANO 243/CENG 207 Course Use Only
 L6. Drug Administration & Transport by Fluid Motion April 19, 2018 Part I: Drug Administration Routes of Drug Administration Topical: local effect, substance is applied directly where its action is desired.
L6. Drug Administration & Transport by Fluid Motion April 19, 2018 Part I: Drug Administration Routes of Drug Administration Topical: local effect, substance is applied directly where its action is desired.
CRINONE 8% Progesterone 90 mg, Prolonged Release Vaginal gel with Polyethylene applicator
 CRINONE 8% Progesterone 90 mg, Prolonged Release Vaginal gel with Polyethylene applicator Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about CRINONE.
CRINONE 8% Progesterone 90 mg, Prolonged Release Vaginal gel with Polyethylene applicator Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about CRINONE.
IMPORTANT POINTS ABOUT MEDICATIONS
 IMPORTANT POINTS ABOUT MEDICATIONS The U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) advises that there are significant health benefits to quitting smoking. The health benefits of quitting smoking include a reduction
IMPORTANT POINTS ABOUT MEDICATIONS The U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) advises that there are significant health benefits to quitting smoking. The health benefits of quitting smoking include a reduction
Page 1 of 41. Reviewed/Revised 5/11/18
 A prescription is needed for all meds, including over the counter. No borrowing medications between clients. All medications are kept in a locked, secure location in AFC homes Internal and external medications
A prescription is needed for all meds, including over the counter. No borrowing medications between clients. All medications are kept in a locked, secure location in AFC homes Internal and external medications
Chapter 11 How to state your conditions clearly to the doctor
 Chapter 11 How to state your conditions clearly to the doctor Chapter 11 How to state your conditions clearly to the doctor While seeing doctor, details of your statement should include the following:
Chapter 11 How to state your conditions clearly to the doctor Chapter 11 How to state your conditions clearly to the doctor While seeing doctor, details of your statement should include the following:
WELCOME TO VIROQUA AREA SCHOOLS. Health Information Packet
 WELCOME TO VIROQUA AREA SCHOOLS Health Information Packet Viroqua Area Schools HEALTH SERVICES 100 Blackhawk Drive Viroqua, WI 54665 Phone: (608) 637-1509 MS/HS, (608) 637-1103 Elementary Fax: (608) 637-8034
WELCOME TO VIROQUA AREA SCHOOLS Health Information Packet Viroqua Area Schools HEALTH SERVICES 100 Blackhawk Drive Viroqua, WI 54665 Phone: (608) 637-1509 MS/HS, (608) 637-1103 Elementary Fax: (608) 637-8034
Fever Management and Medication Dosing
 Fever Management and Medication Dosing What is a fever? A fever is when your child s temperature is higher than the normal body temperature and is measured to be 100.4 F or higher Fever is often the body
Fever Management and Medication Dosing What is a fever? A fever is when your child s temperature is higher than the normal body temperature and is measured to be 100.4 F or higher Fever is often the body
MEDICINES AND PRESCRIPTIONS
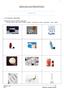 1 MEDICINES AND PRESCRIPTIONS MEDICINES I VOCABULARY: MEDICINES 1. Match the picture and the medication. capsule - cream - drip - drops - inhaler - injection - ointment - pill - spray - suppository - syrup
1 MEDICINES AND PRESCRIPTIONS MEDICINES I VOCABULARY: MEDICINES 1. Match the picture and the medication. capsule - cream - drip - drops - inhaler - injection - ointment - pill - spray - suppository - syrup
PHENYLEPHRINE. Please read this leaflet and the label of the medicine you purchased, carefully before you start using Phenylephrine.
 What is in this leaflet PHENYLEPHRINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information The medicine you have purchased contains Phenylephrine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
What is in this leaflet PHENYLEPHRINE New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information The medicine you have purchased contains Phenylephrine. This leaflet is intended to provide information on the active ingredient
paracetamol Please read this leaflet carefully before you are given Paracetamol BNM.
 1 Consumer Medicine Information paracetamol 1000 mg/100 ml solution for injection What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you are given. This leaflet answers some common questions
1 Consumer Medicine Information paracetamol 1000 mg/100 ml solution for injection What is in this leaflet Please read this leaflet carefully before you are given. This leaflet answers some common questions
Healthy Aging MEDICATIONS & ALCOHOL
 Healthy Aging MEDICATIONS & ALCOHOL Family, work, hobbies, travel... ALL this can keep you busy! Don t let problems with medications or alcohol slow you down. Take a few simple steps to get the most out
Healthy Aging MEDICATIONS & ALCOHOL Family, work, hobbies, travel... ALL this can keep you busy! Don t let problems with medications or alcohol slow you down. Take a few simple steps to get the most out
MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION
 Washtenaw County Community Mental Health MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION Revised 2017 This comprehensive training will provide the employee with knowledge and practical skills to safely select, prepare and give
Washtenaw County Community Mental Health MEDICATION ADMINISTRATION Revised 2017 This comprehensive training will provide the employee with knowledge and practical skills to safely select, prepare and give
Dilaudid, a narcotic analgesic, is prescribed for the relief of moderate to severe pain such as that due to:
 DrugFAQs Dilaudid Generic name: Hydromorphone hydrochloride Brand names: Dilaudid Why is Dilaudid prescribed? Dilaudid, a narcotic analgesic, is prescribed for the relief of moderate to severe pain such
DrugFAQs Dilaudid Generic name: Hydromorphone hydrochloride Brand names: Dilaudid Why is Dilaudid prescribed? Dilaudid, a narcotic analgesic, is prescribed for the relief of moderate to severe pain such
2. Important Pharmacy Abbreviations A. Routes (p 8) B. Forms (p 8) C. Times (p 9) D. Measurements (p 9) E. Other (p 10) F. Sample Questions (p 11)
 Module Three Pharmacology, Medical and Pharmacy Abbreviations Table of Contents 1. Basic Pharmacology A. Pharmacology i. The Object of Drug Delivery (p 3) ii. Drug Receptors (p 3) iii. Concentration to
Module Three Pharmacology, Medical and Pharmacy Abbreviations Table of Contents 1. Basic Pharmacology A. Pharmacology i. The Object of Drug Delivery (p 3) ii. Drug Receptors (p 3) iii. Concentration to
MOST Operations Manual page 1 MEDICATION INVENTORY
 MOST Operations Manual page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS MEDICATION INVENTORY 1. Background and rationale... 2 2. Equipment and supplies... 2 3. Detailed measurement procedures... 2 3.1 Drug definition guidelines...
MOST Operations Manual page 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS MEDICATION INVENTORY 1. Background and rationale... 2 2. Equipment and supplies... 2 3. Detailed measurement procedures... 2 3.1 Drug definition guidelines...
MANAGING POST-OP PAIN AT HOME
 MANAGING POST-OP PAIN AT HOME Medicines and Self-Care After Surgery Managing Pain at Home Pain is expected after surgery. Know that you have a right to have this pain controlled. Managing pain helps you
MANAGING POST-OP PAIN AT HOME Medicines and Self-Care After Surgery Managing Pain at Home Pain is expected after surgery. Know that you have a right to have this pain controlled. Managing pain helps you
Principals and dosage forms of pharmaceutics
 Principals and dosage forms of pharmaceutics Part II. Semisolid dosage forms: ointments, creams, gels, pastes, suppositories, pessaries 2017 Dr. Farkas, Gyula Pharmaceutical Propedeutics Institute of Pharmaceutical
Principals and dosage forms of pharmaceutics Part II. Semisolid dosage forms: ointments, creams, gels, pastes, suppositories, pessaries 2017 Dr. Farkas, Gyula Pharmaceutical Propedeutics Institute of Pharmaceutical
UNIT 2 SOLID AND LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS
 UNIT 2 SOLID AND LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS Solid and Liquid Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Solid Tablets Capsules 2.3 Liquid Advantages of Liquid Disadvantages of Liquid Classification of Liquid Monophasic
UNIT 2 SOLID AND LIQUID DOSAGE FORMS Solid and Liquid Structure 2.1 Introduction Objectives 2.2 Solid Tablets Capsules 2.3 Liquid Advantages of Liquid Disadvantages of Liquid Classification of Liquid Monophasic
6. SR, XR, CR, and TR are examples of formulations. A) oral B) modified release C) repeat action D) soft gels
 1. Which is a parenteral route of administration? A) oral B) vaginal C) sublingual D) rectal 2. A local effect occurs A) at the site of administration. B) throughout the body. C) only after intravenous
1. Which is a parenteral route of administration? A) oral B) vaginal C) sublingual D) rectal 2. A local effect occurs A) at the site of administration. B) throughout the body. C) only after intravenous
How can I benefit most from my COPD medications?
 Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
6. Never give SUBSYS to anyone else, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them or even cause death.
 Medication Guide SUBSYS (sub sis) CII (fentanyl) sublingual spray 100 mcg, 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg IMPORTANT: Do not use SUBSYS unless you are regularly using another opioid pain medicine around-the-clock
Medication Guide SUBSYS (sub sis) CII (fentanyl) sublingual spray 100 mcg, 200 mcg, 400 mcg, 600 mcg, 800 mcg IMPORTANT: Do not use SUBSYS unless you are regularly using another opioid pain medicine around-the-clock
Drug Classifications
 CLASSIFICATIONS: QUIZ 2 Drug Classifications 1. Which category of drugs is used to relieve minor to severe pain? a. Alkylates b. Analgesics c. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors d. Androgens e. Anesthetics
CLASSIFICATIONS: QUIZ 2 Drug Classifications 1. Which category of drugs is used to relieve minor to severe pain? a. Alkylates b. Analgesics c. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors d. Androgens e. Anesthetics
What causes abnormal secretions?
 Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department
 Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
This leaflet answers some common questions about TIBERAL tablets.
 Consumer Medicine Information Tiberal Ornidazole 500mg film-coated tablets What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about TIBEAL tablets. It does not contain all the available
Consumer Medicine Information Tiberal Ornidazole 500mg film-coated tablets What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about TIBEAL tablets. It does not contain all the available
