Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases
|
|
|
- Erin Carter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine Ed e seguenti
2 Chronic hepatitis classification by cause Type of Hepatitis Diagnostic Test(s) Autoantibodies Therapy Chronic hepatitis B HBsAg, IgG anti-hbc, HBeAg, HBV DNA Uncommon IFN-, PEG IFN-, lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir,tenofovir, telbivudine Chronic hepatitis C Anti-HCV, HCV RNA Anti-LKM1 a PEG IFN- plus ribavirin, telaprevir boceprevir Chronic hepatitis D Anti-HDV, HDV RNA, HBsAg, IgG anti-hbc Anti-LKM3 IFN-, PEG IFN- b Autoimmune hepatitis ANA c (homogeneous), anti-lkm1(±), Hyperglobulinemia ANA, anti-lkm1, anti- SLA d Prednisone, azathioprine Drug-associated Uncommon Withdraw drug Cryptogenic All negative None Prednisone (?), azathioprine (?)
3 Autoimmune liver diseases AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis (cirrhosis) PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis AIC: Autoimmune cholangitis
4 Autoimmune hepatitis Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disorder characterized by continuing hepatocellular necrosis and inflammation, usually with fibrosis, which can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure. Based on contemporary estimates of the natural history of treated autoimmune hepatitis, the 10-year survival is 80 90%. The prominence of extrahepatic features of autoimmunity as well as seroimmunologic abnormalities in this disorder supports an autoimmune process in its pathogenesis; Autoantibodies and other typical features of autoimmunity, however, do not occur in all cases;
5 Autoimmune hepatitis Evidence to support an autoimmune pathogenesis in this type of hepatitis includes the following: (1) In the liver, the histopathologic lesions are composed predominantly of cytotoxic T cells and plasma cells; (2) circulating autoantibodies (nuclear, smooth muscle, thyroid, etc.; see below), rheumatoid factor, and hyperglobulinemia are common; (3) other autoimmune disorders such as thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, ulcerative colitis, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, juvenile diabetes mellitus, celiac disease, and Sjögren's syndrome occur with increased frequency in patients who have autoimmune hepatitis and in their relatives; (4) histocompatibility haplotypes associated with autoimmune diseases, such as HLA-B1, -B8, -DR3, and -DR4 as well as extended haplotype DRB1 alleles, are common in patients with autoimmune hepatitis; (5) this type of chronic hepatitis is responsive to glucocorticoid/immunosuppressive therapy, effective in a variety of autoimmune disorders.
6 Autoimmune attack to the hepatocyte Mieli-Vergani, G. & Vergani, D. (2011) Autoimmune hepatitis Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. doi: /nrgastro
7 Autoimmune hepatitis: drugs
8 Autoimmune hepatitis Clinical features of autoimmune hepatitis are similar to those described for chronic viral hepatitis. The onset of disease may be insidious or abrupt; the disease may present initially like an acute viral hepatitis; A subset of patients with autoimmune hepatitis has distinct features. This is the group with positive lupus erythematosus (LE) antibodies (initially labeled "lupoid" hepatitis) in whom other autoimmune features are common. Such patients are predominantly young to middle-aged women with marked hyperglobulinemia and high-titer circulating ANAs. Fatigue, malaise, anorexia, amenorrhea, acne, arthralgias, and jaundice are common. Occasionally arthritis, maculopapular eruptions (including cutaneous vasculitis), erythema nodosum, colitis, pleurisy, pericarditis, anemia, azotemia, and sicca syndrome (keratoconjunctivitis, xerostomia) occur.
9 Autoimmune hepatitis: laboratory findings Laboratory features of autoimmune hepatitis are similar to those seen in chronic viral hepatitis. Liver biochemical tests are invariably abnormal but may not correlate with the clinical severity or histopathologic features in individual cases. Serum AST and ALT levels are increased and fluctuate in the range of units. In severe cases, the serum bilirubin level is moderately elevated (3 10 mg/dl)]. Hypoalbuminemia occurs in patients with very active or advanced disease. Serum alkaline phosphatase levels may be moderately elevated or near normal. In a small proportion of patients, marked elevations of alkaline phosphatase activity occur; in such patients, clinical and laboratory features overlap with those of primary biliary cirrhosis. The prothrombin time is often prolonged, particularly late in the disease or during active phases.
10 Autoimmune hepatitis: laboratory findings Hypergammaglobulinemia (>2.5 g/dl) is common in autoimmune hepatitis. Rheumatoid factor is common as well. As noted above, circulating autoantibodies are also prevalent. The most characteristic are ANAs in a homogeneous staining pattern. Smoothmuscle antibodies are less specific, seen just as frequently in chronic viral hepatitis. Because of the high levels of globulins achieved in the circulation of some patients with autoimmune hepatitis, occasionally the globulins may bind nonspecifically in solid-phase binding immunoassays for viral antibodies. This has been recognized most commonly in tests for antibodies to hepatitis C virus, as noted above. In fact, studies of autoantibodies in autoimmune hepatitis have led to the recognition of new categories of autoimmune hepatitis.
11 Autoimmune hepatitis
12 Autoimmune hepatitis Type I autoimmune hepatitis is the classic syndrome occurring in young women, associated with marked hyperglobulinemia, lupoid features, circulating ANAs, and HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4. Also associated with type I autoimmune hepatitis are autoantibodies against actin (anti-sma) as well as atypical perinuclear antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies (panca).
13 Autoimmune hepatitis Type II autoimmune hepatitis, often seen in children, more common in Mediterranean populations, and linked to HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 haplotypes, is associated not with ANA but with anti-lkm. Actually, anti-lkm represent a heterogeneous group of antibodies. In type II autoimmune hepatitis, the antibody is anti-lkm1, directed against cytochrome P450 2D6. This is the same anti-lkm seen in some patients with chronic hepatitis C. Anti-LKM2 is seen in drug-induced hepatitis, and anti-lkm3 is seen in patients with chronic hepatitis D. Anti-liver kidney microsomal
14 Autoimmune hepatitis Liver biopsy abnormalities are similar to those described for chronic viral hepatitis. Expanding portal tracts and extending beyond the plate of periportal hepatocytes into the parenchyma (designated interface hepatitis or piecemeal necrosis) is a mononuclear cell infiltrate that, in autoimmune hepatitis, may include the presence of plasma cells. Necroinflammatory activity characterizes the lobular parenchyma, and evidence of hepatocellular regeneration is reflected by "rosette" formation, the occurrence of thickened liver cell plates, and regenerative "pseudolobules." Septal fibrosis, bridging fibrosis, and cirrhosis are frequent. Bile duct injury and granulomas are uncommon; however, a subgroup of patients with autoimmune hepatitis have histologic, biochemical, and serologic features overlapping those of primary biliary cirrhosis
15 Autoimmune hepatitis Exclusion of liver disease caused by genetic disorders, viral hepatitis, drug hepatotoxicity, and alcohol are linked with such inclusive diagnostic criteria as hyperglobulinemia, autoantibodies, and characteristic histologic features. Factors in favor of the diagnosis include female gender; predominant aminotransferase elevation; presence and level of globulin elevation; presence of nuclear, smooth muscle, LKM1, and other autoantibodies; concurrent other autoimmune diseases; characteristic histologic features (interface hepatitis, plasma cells, rosettes); HLA DR3 or DR4 markers; and response to treatment (see below). Weighing against the diagnosis are predominant alkaline phosphatase elevation, mitochondrial antibodies, markers of viral hepatitis, history of hepatotoxic drugs or excessive alcohol, histologic evidence of bile duct injury, or such atypical histologic features as fatty infiltration, iron overload, and viral inclusions.
16 Autoimmune hepatitis Differential Diagnosis Early during the course of chronic hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis may resemble typical acute viral hepatitis. In adolescence, Wilson's disease may present with features of chronic hepatitis long before neurologic manifestations become apparent and before the formation of Kayser- Fleischer rings. In this age group, serum ceruloplasmin and serum and urinary copper determinations plus measurement of liver copper levels will establish the correct diagnosis. Primary biliary cirrhosis share clinical features with autoimmune hepatitis, and both alcoholic hepatitis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis may present with many features common to autoimmune hepatitis; historic, biochemical, serologic, and histologic assessments are usually sufficient to allow these entities to be distinguished from autoimmune hepatitis. Of course, the distinction between autoimmune and chronic viral hepatitis is not always straightforward, especially when viral antibodies occur in patients with autoimmune disease or when autoantibodies occur in patients with viral disease. Finally, occasionally, features of autoimmune hepatitis overlap with features of autoimmune biliary disorders such as primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, or, even more rarely, mitochondrial antibody-negative autoimmune cholangitis. Such overlap syndromes are difficult to categorize, and often response to therapy may be the distinguishing factor that establishes the diagnosis.
17 Autoimmune hepatitis: aggressive clinical feature The course of autoimmune hepatitis may be variable. In those with mild disease or limited histologic lesions (e.g., piecemeal necrosis without bridging), progression to cirrhosis is limited. In those with severe symptomatic autoimmune hepatitis (aminotransferase levels >10 times normal, marked hyperglobulinemia, "aggressive" histologic lesions bridging necrosis or multilobular collapse, cirrhosis), the 6-month mortality without therapy may be as high as 40%. Such severe disease accounts for only 20% of cases; the natural history of milder disease is variable, often accentuated by spontaneous remissions and exacerbations. Especially poor prognostic signs include the presence histologically of multilobular collapse at the time of initial presentation and failure of the bilirubin to improve after 2 weeks of therapy. Death may result from complications of cirrhosis
18 Autoimmune hepatitis Autoimmune Hepatitis: Treatment The mainstay of management in autoimmune hepatitis is glucocorticoid therapy. Therapy may be initiated at 20 mg/d, but a popular regimen relies on an initiation dose of 60 mg/d. This high dose is tapered successively over the course of a month down to a maintenance level of 20 mg/d. An alternative but equally effective approach is to begin with half the prednisone dose (30 mg/d) along with azathioprine (50 mg/d). With azathioprine maintained at 50 mg/d, the prednisone dose is tapered over the course of a month down to a maintenance level of 10 mg/d. The advantage of the combination approach is a reduction, over the span of an 18-month course of therapy, in serious, life-threatening complications of steroid therapy from 66% down to under 20%.
19 Autoimmune hepatitis: therapy EASL Guidelines 2015
20 Primary biliary cholangitis (cirrhosis) The major causes of intrahepatic cholestatic syndromes are primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), autoimmune cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and idiopathic adulthood ductopenia. These syndromes are usually clinically distinguished from each other by antibody testing, cholangiographic findings, and clinical presentation. However, they all share the histopathologic features of chronic cholestasis, such as cholate stasis, copper deposition, xanthomatous transformation of hepatocytes, and irregular so-called biliary fibrosis. In addition, there may be chronic portal inflammation, interface activity, and chronic lobular inflammation. Ductopenia is a result of this progressive disease as patients develop cirrhosis
21 Autoimmune liver diseases AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis (cirrhosis) PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis AIC: Autoimmune cholangitis
22 Primary biliary cirrhosis PBC is seen in about individuals per million, with a strong female preponderance and a median age of around 50 years at the time of diagnosis. The cause of PBC is unknown; it is characterized by portal inflammation and necrosis of cholangiocytes in small and medium-sized bile ducts. Cholestatic features prevail, and biliary cirrhosis is characterized by an elevated bilirubin level and progressive liver failure. Liver transplantation is the treatment of choice for patients with decompensated cirrhosis due to PBC. A variety of therapies have been proposed, but ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is the only approved treatment that has some degree of efficacy by slowing the rate of progression of the disease. Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) are present in about 90% of patients with PBC. These autoantibodies recognize intermitochondrial membrane proteins that are enzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), the branched chain 2-oxoacid dehydrogenase complex, and the 2-oxogluterate dehydrogenase complex. Novel nomeclature since September 2015: Primary Biliary Cholangitis
23 Primary biliary cirrhosis Histopathologic analyses of liver biopsies of patients with PBC have resulted in identifying four distinct stages of the disease as it progresses. The earliest lesion is termed chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis and is a necrotizing inflammatory process of the portal tracts. Medium and small bile ducts are infiltrated with lymphocytes and undergo duct destruction. Mild fibrosis and sometimes bile stasis can occur. With progression, the inflammatory infiltrate becomes less prominent, but the number of bile ducts is reduced and there is proliferation of smaller bile ductules. Increased fibrosis ensues with the expansion of periportal fibrosis to bridging fibrosis. Finally, cirrhosis, which may be micronodular or macronodular, develops.
24 Primary biliary cirrhosis
25 Primary biliary cirrhosis Currently most patients with PBC are asymptomatic. When symptoms are present, they most prominently include a significant degree of fatigue out of proportion to what would be expected for either the severity of the liver disease or the age of the patient. Pruritus is seen in approximately 50% of patients at the time of diagnosis and can be debilitating. Physical examination can show jaundice and other complications of chronic liver disease including hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, ascites, and edema. Other features that are unique to PBC include hyperpigmentation, xanthelasma, and xanthomata, which are related to the altered cholesterol metabolism seen in this disease. Hyperpigmentation is evident on the trunk and the
26 Primary biliary crirrhosis Laboratory findings in PBC show cholestatic liver enzyme abnormalities with an elevation in γ-glutamyl transpeptidase and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) along with mild elevations in aminotransferases (ALT and AST). Immunoglobulins, particularly IgM, are typically increased. PBC patients are AMA positive (90%) Hyperbilirubinemia usually is seen once cirrhosis has developed. Thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and anemia may be seen in patients with portal hypertension and hypersplenism.
27 Primary biliary cirrhosis
28 Primary biliary cirrhosis
29 Primary biliary crirrhosis Liver biopsy shows characteristic features Up to 10% of patients with characteristic PBC will have features of AIH as well and are defined as having "overlap" syndrome. These patients are treated as PBC patients and may progress to cirrhosis with the same frequency as typical PBC patients. As many as 10% of patients with PBC may be AMA-negative. Liver biopsy is most important in this setting of AMA-negative PBC. In patients who are AMA-negative with cholestatic liver enzymes, PSC should be ruled out by way of cholangiography.
30 Primary biliary cirrhosis Treatment of the typical manifestations of cirrhosis are no different for PBC than for other forms of cirrhosis. UDCA has been shown to improve both biochemical and histologic features of the disease. Improvement is greatest when therapy is initiated early; the likelihood of significant improvement with UDCA is low in patients with PBC who present with manifestations of cirrhosis. UDCA is given in doses of mg/kg per day In UDCA-non responsive patients the obeticholic acid could be started (might have severe side effects) Patients with PBC require long-term follow-up by a physician experienced with the disease. Certain patients may need to be considered for liver transplantation should their liver disease decompensate. Pruritus is treated with antihistamines, narcotic receptor antagonists (naltrexone), and rifampin. Cholestyramine, a bile salt sequestering agent, has been helpful in some patients but is somewhat tedious and difficult to take.
31 Autoimmune liver diseases AIH: Autoimmune hepatitis PBC: Primary biliary cholangitis (cirrhosis) PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis AIC: Autoimmune cholangitis
32 Primary sclerosing cholangitis PSC is a chronic cholestatic syndrome that is characterized by diffuse inflammation and fibrosis involving the entire biliary tree, resulting in chronic cholestasis. This pathologic process ultimately results in obliteration of both the intra- and extrahepatic biliary tree, leading to biliary cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and liver failure. The cause of PSC remains unknown despite extensive investigation into various mechanisms related to bacterial and viral infections, toxins, genetic predisposition, and immunologic mechanisms, all of which have been postulated to contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of this syndrome.
33 Primary sclerosing cholangitis Pathologic changes that can occur in PSC show bile duct proliferation as well as ductopenia and fibrous cholangitis (pericholangitis). Liver biopsy changes in PSC are not pathognomonic, and establishing the diagnosis of PSC must involve imaging of the biliary tree. Periductal fibrosis is occasionally seen on biopsy specimens and can be quite helpful in making the diagnosis. As the disease progresses, biliary cirrhosis is the final end-stage manifestation of PSC.
34 PSC- histology and ERCP
35 Primary sclerosing cholangitis Clinical Features The usual clinical features of PSC are those found in cholestatic liver disease, with fatigue, pruritus, steatorrhea, deficiencies of fat-soluble vitamins, and the associated consequences. As in PBC, the fatigue is profound and nonspecific. Pruritus can often be debilitating and is related to the cholestasis. The severity of pruritus does not correlate with the severity of the disease. Metabolic bone disease, as seen in PBC, can occur with PSC
36 Primary sclerosing cholangitis Laboratory Findings Patients with PSC typically are identified in the course of an evaluation of abnormal liver enzymes. Most patients have at least a twofold increase in ALP and may have elevated aminotransferases as well. Albumin levels may be decreased, and prothrombin times are prolonged in a substantial proportion of patients at the time of diagnosis. Some degree of correction of a prolonged prothrombin time may occur with parenteral vitamin K.
37 Primary sclerosing cholangitis Laboratory Findings A small subset of patients have aminotransferase elevations greater than five times the upper limit of normal and may have features of AIH on biopsy. These individuals are thought to have an overlap syndrome between PSC and AIH. Autoantibodies are frequently positive in patients with the overlap syndrome but are typically negative in patients who only have PSC. One autoantibody, the perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (P-ANCA) is positive in about 65% of patients with PSC. Over 50% of patients with PSC also have ulcerative colitis.
38 Primary sclerosing cholangitis The definitive diagnosis of PSC requires cholangiographic imaging. Over the last several years, MRI with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) has been utilized as the imaging technique of choice for initial evaluation. Some investigators feel that endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) should also be performed to be certain whether or not a dominant stricture is present.
39 Primary sclerosing cholangitis ERCP and MR
40 Primary sclerosing cholangitis Treatment There is no specific proven treatment for PSC, although studies are currently ongoing using high-dose (20 mg/kg per day) UDCA to determine its benefit. Endoscopic dilatation of dominant strictures can be helpful, but the ultimate treatment is liver transplantation. A complication of PSC is the development of cholangiocarcinoma, which is a relative contraindication to liver transplantation. Symptoms of pruritus are common, and the approach is as mentioned previously for this problem in patients with PBC (see above).
41 Overlapping syndromes
42 Overlapping syndromes Overlap syndrome AIH-PBC AIH-PSC laboratory features Serology features Histology features Mild forms may have AP =2 ULN AST/ALT>ULN g-globulin and IgG >ULN AP or GGT>ULN Interface hepatitis Interface hepatitis Ductopenia Portal edema AMA + AMA - Cholangiography Normal Stricture AIH cholestatic syndrome AST/ALT>ULN (2) g-globulin and IgG >ULN AP or GGT >ULN Interface hepatitis Destructive cholangitis AMA- Normal
43 Primary sclerosing cholangitis
44
45
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
ACCME/Disclosures. The Overlap Syndromes: Do They Exist? Key Points and Questions 4/6/2016. Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Hépatopathies auto-immunes
 16 ème Journée d'automne Lausanne, le 19 octobre 2017 Hépatopathies auto-immunes Nurullah Aslan et Darius Moradpour Service de Gastroentérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois
16 ème Journée d'automne Lausanne, le 19 octobre 2017 Hépatopathies auto-immunes Nurullah Aslan et Darius Moradpour Service de Gastroentérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Sarah Landes October 23, 2014
 Sarah Landes October 23, 2014 A T-cell mediated inflammatory destruction of intralobular bile ducts progressively leading to cholestasis and cirrhosis 9:1 F to M ratio Mostly diagnosed between 30-60 years
Sarah Landes October 23, 2014 A T-cell mediated inflammatory destruction of intralobular bile ducts progressively leading to cholestasis and cirrhosis 9:1 F to M ratio Mostly diagnosed between 30-60 years
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
 Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features?
 22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
22 November 2018 BD-IAP UK-LPG Liver Update PBC/AIH variant/ overlap syndrome vs PBC with hepatitic features? in a UDCA non-responder Dina G. Tiniakos Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical
Autoimmune hepatitis
 Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Autoimmune hepatitis: Autoimmune hepatitis a spectrum within a spectrum Alastair Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine Newcastle University Spectrum of autoimmune liver disease Autoimmune
Pediatric PSC A children s tale
 Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Keith D. Lindor, MD, FACG 1, Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FACG 2, and M. Edwyn Harrison, MD 3 1 College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University, Phoenix,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Keith D. Lindor, MD, FACG 1, Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FACG 2, and M. Edwyn Harrison, MD 3 1 College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University, Phoenix,
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
Primary Biliary Cholangitis PBC Foundation (UK) Ltd 6 Hill Street Edinburgh EH2 3JZ Tel: +44 (0) 131 556 6811 info@pbcfoundation.org.uk www.pbcfoundation.org.uk PBC for Healthcare Practitioners Introduction
Chronic Biliary Disease. Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths
 Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Chronic Biliary Disease Dr Susan Davies & Dr Bill Griffiths Chronic Biliary Disease Terminology is confusing with pathologists and hepatologists using the same language BUT with different meanings. Chronic
Key Points: Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective. Jenny Heathcote, MD. University of Toronto
 Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Serologic Markers CONVENTIONAL ANTIBODIES ANTIBODIES UNCONVENTIONAL. AIH Type I
 Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Hangzhou, 15 March Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam
 Clinical Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hangzhou, 15 March 2008 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam Epidemiology of Primary
Clinical Aspects of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Hangzhou, 15 March 2008 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Academic Medical Center University of Amsterdam Epidemiology of Primary
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease
 CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
CASE 1 Plasma Cell Infiltrates: Significance in post liver transplantation and in chronic liver disease Maria Isabel Fiel, M.D. The Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York Case A 57 yo man, 7 months
Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark
 Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark Study of Prognosis of PSC Difficulties: Disease is rare The duration of the course of disease may be very
Prognosis of untreated Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Erik Christensen Copenhagen, Denmark Study of Prognosis of PSC Difficulties: Disease is rare The duration of the course of disease may be very
Autoimmune Hepatitis. Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern. November 14th, 2018
 Autoimmune Hepatitis Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern November 14th, 2018 AIH - Definition Manns MP J Hepatol 2015, vol 62, P 100-111 AIH - Definition Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is
Autoimmune Hepatitis Dr. Stefania Casu Hepatology, UVCM, Inselspital Bern November 14th, 2018 AIH - Definition Manns MP J Hepatol 2015, vol 62, P 100-111 AIH - Definition Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis
 Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC
 Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London A family affair? Central vein Hepatocytes
Current Concepts in the Management and Treatment of PBC & PSC Michael A Heneghan, MD, MMedSc, FRCPI. Institute of Liver Studies, King s College Hospital, London A family affair? Central vein Hepatocytes
Morning Report Presentation. Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005
 Morning Report Presentation Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis! PBC is a chronic, progressive, cholestatic liver disease of unknown cause that usually affects middle-aged women
Morning Report Presentation Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis! PBC is a chronic, progressive, cholestatic liver disease of unknown cause that usually affects middle-aged women
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA
 LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children: Is the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Scoring System Useful?
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:935 940 Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children: Is the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Scoring System Useful? REGAN L. EBBESON* and RICHARD
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:935 940 Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children: Is the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Scoring System Useful? REGAN L. EBBESON* and RICHARD
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases
 Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases
 Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
Chronic Cholestatic Liver Diseases - EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines - Rome, 8 October 2010 Ulrich Beuers Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Tytgat Institute of Liver and Intestinal Research
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male
 Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Prototypes of autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis in childhood
 RIUNIONE MONOTEMATICA AISF 2013 Personalizzazione della Cura in Epatologia 17-19 ottobre 2013, PISA Prototypes of autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis in childhood La sottoscritta dichiara di
RIUNIONE MONOTEMATICA AISF 2013 Personalizzazione della Cura in Epatologia 17-19 ottobre 2013, PISA Prototypes of autoimmune hepatitis and sclerosing cholangitis in childhood La sottoscritta dichiara di
Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice
 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
Pediatric Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Potential Therapies
 Pediatric Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Potential Therapies Philip Rosenthal, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Surgery University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE I have the following financial
Pediatric Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Potential Therapies Philip Rosenthal, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Surgery University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE I have the following financial
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
PBC and PSC: Back to Basics
 Disclosure No financial interest or other relationship with the manufacturer(s) of the product(s) or provider(s) of the service(s) that will be discussed in this presentation. PBC and PSC: Back to Basics
Disclosure No financial interest or other relationship with the manufacturer(s) of the product(s) or provider(s) of the service(s) that will be discussed in this presentation. PBC and PSC: Back to Basics
HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM
 EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
A Case of Autoimmune Hepatitis with Antimitochondrial Antibody and No Detectable Antinuclear Antibody
 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF St. Marianna Med. J. Case Report Vol. 32, pp. 33 38, 2004 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF A Case
FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF St. Marianna Med. J. Case Report Vol. 32, pp. 33 38, 2004 FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF A Case
Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis: Current Status and Future Directions
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 2, March 2016, pp. 177-203 Review Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis: Current Status and Future Directions Albert J. Czaja Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 2, March 2016, pp. 177-203 Review Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis: Current Status and Future Directions Albert J. Czaja Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Page 1 of 6 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Ocaliva (obeticholic acid) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Disclosure. Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes
 Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Diagnosis and Management of PBC
 Diagnosis and Management of PBC Cynthia Levy, MD, FAASLD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida 1 Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Chronic cholestatic liver disease Autoimmune in
Diagnosis and Management of PBC Cynthia Levy, MD, FAASLD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Miami, Florida 1 Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Chronic cholestatic liver disease Autoimmune in
Domenico ALVARO, MD Sapienza, University of Rome, Italy. Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di GastroReumatologia, Roma, 25 Giugno 2015.
 Epatite autoimmune e sindrome da "overlap Domenico ALVARO, MD Sapienza, University of Rome, Italy Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di GastroReumatologia, Roma, 25 Giugno 2015. AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS
Epatite autoimmune e sindrome da "overlap Domenico ALVARO, MD Sapienza, University of Rome, Italy Congresso Nazionale della Società Italiana di GastroReumatologia, Roma, 25 Giugno 2015. AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS
Evaluation of the revised versus the simplified scoring system in patients with autoimmune hepatitis
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 131-136, 2014 Evaluation of the revised versus the simplified scoring system in patients with autoimmune hepatitis YI LI, MILIN PENG and GUOZHONG GONG Institute
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 131-136, 2014 Evaluation of the revised versus the simplified scoring system in patients with autoimmune hepatitis YI LI, MILIN PENG and GUOZHONG GONG Institute
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology
 REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
REVIEW Autoimmune Hepatitis: Histopathology Stephen A. Geller M.D.*, Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), a chronic hepatic necroinflammatory disorder, occurs mostly in women. AIH is characterized by prominent
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease. Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC
 Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Update on Autoimmune Liver Disease Role of Liver Biopsy in Autoimmune Hepatitis, PBC and PSC Stefan Hübscher, School of Cancer Sciences, University of Birmingham Dept of Cellular Pathology, Queen Elizabeth
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
Hepatitis. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 5/2/2019. Mob:
 Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
Cholestatic Liver Diseases: Update on Diagnosis and Management. Cholestatic Liver Diseases: Location of Injury Determines Phenotype
 Cholestatic Liver Diseases: Update on Diagnosis and Management R. Todd Stravitz, M.D. Hume-Lee Transplant Center Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Cholestatic Liver Diseases: Location
Cholestatic Liver Diseases: Update on Diagnosis and Management R. Todd Stravitz, M.D. Hume-Lee Transplant Center Section of Hepatology Virginia Commonwealth University Cholestatic Liver Diseases: Location
Autoimmune Hepatitis/Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome in Childhood: A 16-Year Prospective Study
 Autoimmune Hepatitis/Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome in Childhood: A 16-Year Prospective Study GERMANA V. GREGORIO, 1 BERNARD PORTMANN, 2 JOHN KARANI, 3 PHIL HARRISON, 2 PETER T. DONALDSON, 2 DIEGO
Autoimmune Hepatitis/Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlap Syndrome in Childhood: A 16-Year Prospective Study GERMANA V. GREGORIO, 1 BERNARD PORTMANN, 2 JOHN KARANI, 3 PHIL HARRISON, 2 PETER T. DONALDSON, 2 DIEGO
In 1993, the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:417 421 Validation and Modification of Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children ELIZABETH MILETI,* PHILIP ROSENTHAL,*, and MARION
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:417 421 Validation and Modification of Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis in Children ELIZABETH MILETI,* PHILIP ROSENTHAL,*, and MARION
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management Kapil Chopra M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Transplant Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona PSC Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Medical Management Kapil Chopra M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Transplant Medicine Mayo Clinic Arizona PSC Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive
21/07/2017. Update on Autoimmune Biliary Disease. Changing Role of Liver Biopsy in PBC and PSC. Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cholangitis Update on Autoimmune Biliary Disease Changing Change in Nomenclature for PBC : From Cirrhosis to Cholangitis (EASL Panel, Beuers et al J Hepatol Nov 2015, Gut Nov
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cholangitis Update on Autoimmune Biliary Disease Changing Change in Nomenclature for PBC : From Cirrhosis to Cholangitis (EASL Panel, Beuers et al J Hepatol Nov 2015, Gut Nov
Introduction. Kaoru Omori 1 Masahiro Kan 1. Kanako Yoshida
 Clin J Gastroenterol (2016) 9:312 318 DOI 10.1007/s28-016-0676-1 CASE REPORT Familial occurrence of autoimmune liver disease with overlapping features of primary biliary cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis
Clin J Gastroenterol (2016) 9:312 318 DOI 10.1007/s28-016-0676-1 CASE REPORT Familial occurrence of autoimmune liver disease with overlapping features of primary biliary cholangitis and autoimmune hepatitis
ACCME/Disclosures. PBC and PSC Revisited 4/6/2016. Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cholangitis (PBC)
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION FOR OVERLAP SYNDROMES OF AUTOIMMUNE LIVER DISEASES No conflict of interest Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions Objectives Introduction Methods Results Conclusions
Histology. The pathology of the. bile ducts. pancreas. liver. The lecture in summary. Vt-2006
 Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
Hwajeong Lee, MD, Robert T. Stapp, DO, Adrian H. Ormsby, MD, and Veena V. Shah, MD
 Anatomic Pathology / Overlap Syndrome The Usefulness of IgG and IgM Immunostaining of Periportal Inflammatory Cells (Plasma Cells and Lymphocytes) for the Distinction of Autoimmune Hepatitis and Primary
Anatomic Pathology / Overlap Syndrome The Usefulness of IgG and IgM Immunostaining of Periportal Inflammatory Cells (Plasma Cells and Lymphocytes) for the Distinction of Autoimmune Hepatitis and Primary
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets)
 Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets) Policy Number: 5.01.619 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2016 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Ocaliva (obeticholic acid tablets) Policy Number: 5.01.619 Last Review: 11/2018 Origination: 11/2016 Next Review: 11/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage
Novel Therapies in Autoimmune Hepatitis
 Novel Therapies in Autoimmune Hepatitis Paul W. Rassam,MD Ass. Clinical Professor of Medicine Div. of Gastroenterology and Hepatology St George Hospital University Medical Center University of Balamand
Novel Therapies in Autoimmune Hepatitis Paul W. Rassam,MD Ass. Clinical Professor of Medicine Div. of Gastroenterology and Hepatology St George Hospital University Medical Center University of Balamand
Abnormal liver enzymes with selected common liver diseases
 Abnormal liver enzymes with selected common liver diseases SAAD ALKHOWAITER, MD, DABIM, FRCP(C) CONSULTANT OF GASTROENTEROLOGY, HEPATOLOGY AND MOTILITY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DIVISION OF GASTROENTEROLOGY
Abnormal liver enzymes with selected common liver diseases SAAD ALKHOWAITER, MD, DABIM, FRCP(C) CONSULTANT OF GASTROENTEROLOGY, HEPATOLOGY AND MOTILITY ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DIVISION OF GASTROENTEROLOGY
Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings
 6 Jan 2018 Vol 11 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings Simpal Gill, MD* Pathology Laboratory services, Houston Medical
6 Jan 2018 Vol 11 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Overview and Pathological Findings Simpal Gill, MD* Pathology Laboratory services, Houston Medical
Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator
 Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:98 103 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Serologic Markers Do Not Predict Histologic Severity or Response to Treatment in Patients With
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:98 103 ORIGINAL ARTICLES LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Serologic Markers Do Not Predict Histologic Severity or Response to Treatment in Patients With
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland
 Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Two Cases of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlapping with Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults
 CASE REPORT Two Cases of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlapping with Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults Go Igarashi 1, Tetsu Endo 1, Kenichiro Mikami 1, Naoya Sawada 1,RyuSatake 1, Rie Ohta 1, Juichi Sakamoto
CASE REPORT Two Cases of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Overlapping with Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults Go Igarashi 1, Tetsu Endo 1, Kenichiro Mikami 1, Naoya Sawada 1,RyuSatake 1, Rie Ohta 1, Juichi Sakamoto
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Bibleclass Felix Brunner
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Bibleclass 29.04.2015 Felix Brunner Overview Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical Features, Genetics, Immunology Diagnosing PSC Treatment Medications, Transplantation Cancer-Risk
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Bibleclass 29.04.2015 Felix Brunner Overview Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical Features, Genetics, Immunology Diagnosing PSC Treatment Medications, Transplantation Cancer-Risk
PBC features and management in the era of UDCA and Budesonide
 PBC features and management in the era of UDCA and Budesonide Raoul Poupon, MD Université P&M Curie, AP-Hôpitaux de Paris, Inserm, Paris, France The changing pattern of PBC Over the last 2 decades: More
PBC features and management in the era of UDCA and Budesonide Raoul Poupon, MD Université P&M Curie, AP-Hôpitaux de Paris, Inserm, Paris, France The changing pattern of PBC Over the last 2 decades: More
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas
 Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
WEEK. MPharm Programme. Liver Biochemistry. Slide 1 of 49 MPHM14 Liver Biochemistry
 MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September Leeds cases
 British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
British Liver Transplant Group Pathology meeting September 2014 Leeds cases Leeds Case 1 Male 61 years Liver transplant for HCV cirrhosis with HCC in January 2014. Now raised ALT and bilirubin,? acute
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013
 Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
Resident, PGY1 David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles Society of Pathology Resident and Fellow Symposium 2013 85 year old female with past medical history including paroxysmal atrial fibrillation,
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
Abnormal liver enzymes
 Abnormal liver enzymes Objectives: Approach to liver enzymes Selected disease Team Members: Ameera Niazi, Jawaher Abanumy, Atheer alrasheed, Laila mathkour Doctor: Dr. Saad alkohwaiter Team Leader: Nawaf
Abnormal liver enzymes Objectives: Approach to liver enzymes Selected disease Team Members: Ameera Niazi, Jawaher Abanumy, Atheer alrasheed, Laila mathkour Doctor: Dr. Saad alkohwaiter Team Leader: Nawaf
DILI PATHOLOGY. PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting
 DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
DILI PATHOLOGY PHILIP KAYE November 2017 BSG Pathology Winter Meeting General Mechanisms Role of Liver Biopsy Outline Kleiner Categories Pathology! Differentials Severity Finally Drugs/Toxins may cause
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES. Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis. 1. Preamble. 2. Introduction
 AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis Michael P. Manns, 1 Albert J. Czaja, 2 James D. Gorham, 3 Edward L. Krawitt, 4 Giorgina Mieli-Vergani, 5 Diego Vergani, 6 and
AASLD PRACTICE GUIDELINES Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis Michael P. Manns, 1 Albert J. Czaja, 2 James D. Gorham, 3 Edward L. Krawitt, 4 Giorgina Mieli-Vergani, 5 Diego Vergani, 6 and
ABIM Review Hepatobiliary
 ABIM Review Hepatobiliary Danielle Brandman, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco ABIM Certification Exam ABIM Certification Exam Hepatobiliary Review Diagnostic
ABIM Review Hepatobiliary Danielle Brandman, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco ABIM Certification Exam ABIM Certification Exam Hepatobiliary Review Diagnostic
Interpreting Your Tests
 Interpreting Your Tests Lisa M. Forman, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Section Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver Outline Bile Duct Anatomy Lab Tests LFTs Tumor
Interpreting Your Tests Lisa M. Forman, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Section Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver Outline Bile Duct Anatomy Lab Tests LFTs Tumor
Management of autoimmune hepatitis. Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France
 Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD
 Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
doi: /s
 doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2734-6 Harada - 1 - Clinicopathological significance of serum fractalkine in primary biliary cirrhosis Kenichi Harada 1), Yuko Kakuda 1), Minoru Nakamura 2), Shinji Shimoda 3),
doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2734-6 Harada - 1 - Clinicopathological significance of serum fractalkine in primary biliary cirrhosis Kenichi Harada 1), Yuko Kakuda 1), Minoru Nakamura 2), Shinji Shimoda 3),
TREATMENT OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS (PBC)
 TREATMENT OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS (PBC) URSO not indicated Therapy for PBC Difficulties Etiology is uncertain Therapies are based on ideas regarding pathogenesis Present medical therapies have a limited
TREATMENT OF PRIMARY BILIARY CIRRHOSIS (PBC) URSO not indicated Therapy for PBC Difficulties Etiology is uncertain Therapies are based on ideas regarding pathogenesis Present medical therapies have a limited
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 primary sclerosing cholangitis primary sclerosing cholangitis pdf primary sclerosing cholangitis Diagnosis and Management
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 primary sclerosing cholangitis primary sclerosing cholangitis pdf primary sclerosing cholangitis Diagnosis and Management
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
A Retrospective Single-Center Review of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Children
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:239 245 A Retrospective Single-Center Review of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Children TAMIR MILOH,* RONEN ARNON,* BENJAMIN SHNEIDER, FREDERICK SUCHY,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:239 245 A Retrospective Single-Center Review of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Children TAMIR MILOH,* RONEN ARNON,* BENJAMIN SHNEIDER, FREDERICK SUCHY,*
Steatosis/Steatohepatitis
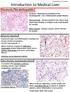 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Waldenström first described the disease entity now
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:1502 1517 Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Challenges MICHAEL P. MANNS and CHRISTIAN P. STRASSBURG Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:1502 1517 Autoimmune Hepatitis: Clinical Challenges MICHAEL P. MANNS and CHRISTIAN P. STRASSBURG Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover,
