Ultrasound Elastography Used for Preventive Non-Invasive Screening in Early Detection of Liver Fibrosis
|
|
|
- Alvin Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9): Ultrasound Elastography Used for Preventive Non-Invasive Screening in Early Detection of Liver Fibrosis Florian Bert a, c, Jona T. Stahmeyer b, Siegbert Rossol a Abstract Background: Early discovery of liver fibrosis is becoming more popular because of enhanced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ultrasound-based liver elastography is a method used to approve suspected liver fibrosis or cirrhosis. We assessed the clinical usefulness of acoustic radiation force impulse shear wave elasticity imaging (ARFI-SWEI) as a preventive screening method to uncover fibrosis. Methods: We screened 382 patients by native routine sonography for abnormal liver results and divided them into six groups: group 1: normal liver, groups 2-4: fatty liver grade I-III, group 5: liver cirrhosis, and group 6: inhomogenic liver tissue. Then ARFI-SWEI was performed and the results were compared with published shear wave velocity cut-off values that were predictive of each fibrosis stage (F0-4). A control group consisted of 20 healthy volunteers. Results: The part of liver fibrosis F2 was in groups 1-4: 20-32%, group 5: 100%, and group 6: 91%. Main causes for fibrosis stage F2 were (non)-alcoholic steatohepatitis, chronic viral or autoimmune hepatitis and chronic heart failure. Conclusions: Screening of the liver tissue in b-mode ultrasound can underestimate possible liver fibrosis; by using ARFI-SWEI, liver fibrosis can be uncovered early. It is a suitable preventive method comparable to colonoscopy for colon cancer. Keywords: Ultrasound; Liver fibrosis; Elastography; ARFI Introduction In recent years, the early discovery of progressive liver failure and liver fibrosis is becoming more popular because of enhanced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC Manuscript accepted for publication July 01, 2016 a Department of Internal Medicine, Krankenhaus Nordwest, Steinbacher Hohl 2-26, Frankfurt/Main, Germany b Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Health System Research, Hannover Medical School, Carl-Neuberg-Str. 1, Hannover, Germany c Corresponding Author: Florian Bert, Department of Internal Medicine, Krankenhaus Nordwest, Steinbacher Hohl 2-26, Frankfurt/Main, Germany. florianbert@freenet.de doi: is the third leading cause of cancer-related death and the fifth most common malignancy in men and the seventh in women worldwide [1, 2]. Nearly 95% of all HCCs are based on liver cirrhosis (LC) with an incidence up to 6% per year [3]. LC is the consequence of chronic liver disease (CLD). Non-alcoholic or alcoholic fatty liver disease ((N)AFLD) and chronic viral hepatitis B and C (HBV/HCV) are leading CLDs in the western world [4]. They induce an inflammatory response of the liver tissue with activation of immune cells, proliferation and transdifferentiation of mesenchymal cells and following progress to liver fibrosis up to LC [5]. Epidemiologic data from Germany estimate that nearly 4-5 million people suffer from CLD [6]. Mortality analysis shows that CLD as a cause of death ranges on place 5 in Germany and the risk to develop LC is up to 5% [5]. Data analysis from the US Department of Health and Human Services revealed that CLD ranges on place 12 of 15 leading causes of death in 2013 [7]. Often patients do not know about their possible liver failure because typical symptoms like fatigue or jaundice are missing until the late stage of the disease [8]. Today there exist successful therapeutic options for chronic HBV/HCV and the risk of following LC and/or HCC decreases. But steatosis hepatis and steatohepatitis are more and more problem for people of the industrialized countries. Less sporting activity, excess of calories and/or alcohol are the main reasons for developing overweight, fatty liver and/or steatohepatitis with elevated risk of LC and HCC. The obesity prevalence ranges from 2.3% to 12%, and overweight is 28.8%, mostly affecting females [9]. Nowadays (N)AFLD-associated LC is the second leading cause for liver transplant in the USA and will overtake the chronic HCV in the next years [10]. The life expectancy and prognosis of patients with LC are significantly lower with 1-year mortality of 40% [11]. Mortality and morbidity rates increase exponentially once cirrhosis develops; a systematic review of 118 studies involving 23,797 patients with LC by D Amico et al showed that the overall survival was only 64% over a median follow-up of 31 months [12]. To prevent LC, the aim is to uncover early stages of a liver fibrosis and corresponding CLD [13]. In the past, the diagnosis and follow-up of progressive liver fibrosis are based on histological examination using liver biopsy. Although biopsy is still considered the gold standard for histological evaluation, it is well known that this procedure has several limitations (i.e., sampling errors, bleeding complications) and poor tolerance as a stressful medical procedure for many patients [13, 14]. Thus, in recent years, interest increased in identifying and describing liver fibrosis by using non-invasive technical methods [14]. Acoustic radiation force impulse shear wave elastic- 650 Articles The authors Journal compilation J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited
2 Bert et al J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9): Figure 1. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) measurement, with the flexible metering box ( measurement box as size of region of interest (ROI), 10 mm long, 5 mm wide) is possible to localize a region of the liver for elastographic measurement at variable depths. ity imaging (ARFI-SWEI) is a novel ultrasound method for liver fibrosis assessment [15-17]. This dynamic method uses acoustic radiation force to produce an acoustic push pulse that generates shear waves, which propagate into the tissue; their speed reflects the underlying tissue stiffness and severity of liver fibrosis [18]. This method is comfortable for the patient and examiner. It can be used for assessing different degrees of liver stiffness (fibrosis stages) and correlated to the b-mode aspect of the liver in the same session [19]. Recent studies verified ARFI-SWEI as a powerful noninvasive method in predicting fibrosis F2 with high diagnostic accuracy and validity [18]. Because of its accuracy and easy handling, point of interest is to use this method for early discovering liver fibrosis independent of knowledge of a causal CLD. For this reason, the purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical usefulness of ARFI-SWEI screening to uncover possible liver fibrosis in patients of a large teaching hospital during routine ultrasound of the abdomen. Materials and Methods Patients In this cross-section study, over a period of 6 weeks, we screened 403 patients of nine departments (departments of surgery (visceral, thoracic, and orthopedic), gynecology, urology, neurology, oncology, radio-oncology, and internal medicine) of the Krankenhaus Nordwest in Frankfurt/Main for striking findings of liver by using routine ultrasound and additional liver elastography (ARFI-SWEI). The clinical cause for patient hospitalization was of no interest for the study. To avoid a bias, each patient taking part in the study should get any kind of ultrasound examination, independent of its indication and region to be investigated (e.g. thyroid gland, abdomen, vessels), and was screened with abdominal ultrasound and ARFI-SWEI. Additional blood samples of the participants were taken to determine the platelet count and the alanine aminotransferase (ALT) looking for signs of CLD in context of liver fibrosis. The correlation of severity of liver damage by histology was not the aim of this study, neither the estimation of the prognosis of the surveillance. The study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The institutional review board approved the study and the patients were informed of the study procedure. Twenty-one patients (4.5%) of 403 enrolled patients were not suitable for ARFI-SWEI measurement, because of low intercostal access (N = 4), high body mass index (BMI > 30 kg/ m 2, N = 10) or missing cooperation (N = 7) during the procedure. Thus, a total of 382 patients were included in the study. An additional control group consisted of 20 healthy volunteers (10 male and 10 female), with a median age of 50 ± 14 years without known history of liver damage. Native ultrasound scan and ARFI-SWEI Two physicians performed ultrasound scan and elastographic measurements independently with an ultrasound unit by Siemens AG (Germany), Acuson S 2000, which included the Vir- Articles The authors Journal compilation J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc 651
3 ARFI for Non-Invasive Fibrosis Screening J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9): tual Touch TM Tissue Quantification Software for ARFI-SWEI technology. In the first step, we evaluated the liver tissue of the participants by b-mode native ultrasound. In case of fatty liver, the degree (grade 1-3) was defined according to the method by Saverymuttu (1986); the criterion for fatty liver was hyperechogenic liver tissue with fine, tightly packed echoes; as a reference for comparing normal liver tissue, we used the tissue of the kidney [20]. The ultrasound unit contains tissue harmonic imaging (THI), which resolves the problems related to ultrasound in technically difficult patients by providing a marked improvement in image quality. We used an Acuson S2000 4C1 curved transducer with a frequency of 4.5 MHz and mechanical index of ARFI-SWEI technique ARFI-SWEI technology is a real-time dual display imaging mode and allows a quantitative assessment of tissue stiffness, through measurement of shear wave velocity (SWV). Shear waves are generated by displacement of tissue and attenuate approximately 10,000 times more rapidly than conventional ultrasound waves. With a flexible metering box ( measurement box as size of region of interest (ROI), 10 mm long, 5 mm wide), it is possible to localize a region of the liver for elastographic measurement at variable depths. An acoustic push pulse transmitted by the transducer toward the tissue induces an elastic shear wave that propagates through the tissue. The propagation of the shear wave is followed by detection pulses that are used to measure the velocity of shear wave propagation, which is directly related to tissue stiffness, and is quantified in meters Table 1. Results of Native Ultrasound Scan of the Liver Native ultrasound (US) results Group (groups 1-6: N = 382) Normal native US Controls (N = 20); group 1 (N = 131) Fatty liver grade I Group 2 (N = 70) Fatty liver grade II Group 3 (N = 34) Fatty liver grade III Group 4 (N = 45) Cirrhotic tissue Group 5 (N = 43) Inhomogenic tissue Group 6 (N = 59) per second (m/s) [13, 16] (Fig. 1). To optimize the results, we standardized our ARFI-SWEI measurement. We did the examination in the morning and the patients were without food intake and fasting > 3 h. The patient was arranged in dorsal decubitus position, with the right arm under his head (maximum abduction). We made ARFI-SWEI measurement at the level of the right liver lobe segment VII/ VIII at a depth between 3.5 and 8.0 cm, while the patients were asked to stop breathing for a moment [17]. We performed 10 valid measurements in every patient, and the ratio between validated and total measurements as a median value was calculated. Only procedures with a success rate of at least 60%, and with the interquartile range of all validated measurements < 30% of the median value, were considered reliable [18]. We compared the results of ARFI-SWEI measurements with published SWV cut-off values that were predictive for each fibrosis stage correlated to the histological classification of METAVIR (F0-4): F0-1 < 1.24 m/s, F m/s, F m/s and F m/s [21, 22]. A distinguishing between F0 and F1 and conclusions about Figure 2. Fibrosis stages F1*-F4 in groups 1-6. (*Stage F1 includes although F0). 652 Articles The authors Journal compilation J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc
4 Bert et al J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9): Table 2. Characteristics of Patients Shown as Mean ± Standard Deviation and Patients Distribution in Different Groups Divided by Native Ultrasound Scan and Patients Separated in Two Groups (Cirrhosis (F4) Versus Non-Cirrhosis (F0-3)) P-value Groups 1-6 (non-cirrhosis) Groups 1-6 (cirrhosis) Controls Group 6 (inhomogenic tissue) Group 5 (cirrhosis) Groups 1-4 Total (without controls) Characteristics Total gender (male/female) 198/ /147 26/17 34/ /28 163/155 Age (years) 56 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 23 n.s. BMI (kg/m 2 ) 26 ± 6 29 ± 3 26 ± 4 25 ± 5 25 ± 3 26 ± 4 27 ± 3 n.s. ALT (< 35 U/L) 80 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 33 n.s. Thrombocytes ( /µl) 232 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 82 < F (19.90%) 199 ± 3 (70-79%) 0 (0%) 5 (9%) 20 (100%) 206 (19.90%) F2 78 (22.41%) 48 ± 16 (11-23%) 1 (3%) 22 (38%) 78 (22.41%) F3 34 (8.90%) 12 ± 7 (2-7%) 9 (22%) 11 (19%) 34 (8.90%) F4 64 (16.75%) 11 ± 10 (1-8%) 33 (75%) 20 (34%) 64 (16.75%) P-values were obtained by the unpaired t-test. the activity of (necro-)inflammation in the liver tissue is impossible for ARFI-SWEI and can be estimated by histology only. In case of elevated SWV with F2 (comparable to META- VIR: portal fibrosis with few septa), the patient history was scrutinized for further hints of CLD. Statistical analysis The results and measurements were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) or percentages, as appropriate. P-values were obtained by the unpaired t-test. For statistical analysis, we used Microsoft Excel. Results A total number of 382 patients were included in the study. According to the results of native ultrasound scan, the participants were divided into seven different groups (Table 1): controls, group 1: normal tissue, group 2: steatosis grade 1, group 3: steatosis grade 2, group 4: steatosis grade 3, group 5: cirrhotic tissue, and group 6: inhomogenic tissue. The ARFI results are shown in Figure 2. Groups 1-4 showed nearly the same distribution of fibrosis grading, independent of the steatosis grade: F %, F %, F3 2-7% and F4 0-8%. In contrast, the part of F4 exceeded over 75% in group 5 corresponding to the native b- mode. Group 6 showed no signs of fatty liver or cirrhosis. The liver tissue b-mode scan was described as inhomogenic and over 91% of the participants in this group had SWV values indicating F2. The additional control group (N = 20) had no signs of fatty liver and ARFI-SWEI SWVs were between 0.70 and 1.00 m/s (median: 0.85 m/s) in the normal range. The BMI was comparable in all other groups except controls, with highest values for groups 2-4, corresponding to fatty liver in the b-mode scan. The distribution of the participant gender in total and more obvious in subgroups 5 and 6 shows an overlap of male versus female. Analysis of ALT and thrombocyte count shows elevated values for ALT in all groups in context with elevated ARFI-SWEI SWV-values F2, but also in some patients with F0-1. In total there were no correlation found (no significance). Thrombocyte counts were significant reduced in patients with F4 only (Table 2). Looking for reasons of elevated SWV ( F2) in each group, we screened the history of those patients for possible liver failure; this added up to five different main causes: alcoholic (ASH, N = 43) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH, N = 47), viral hepatitis B/C (N = 12), chronic heart failure (CHF, N = 20), and autoimmune hepatitis (AIH)/primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)/primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) (N = 10) (Table 3). Discussion Liver fibrosis is a major public health problem with risk of developing LC and HCC. In CLD, the evaluation of liver fibrosis is essential. Recent studies show that ARFI-SWEI is a reli- Articles The authors Journal compilation J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc 653
5 ARFI for Non-Invasive Fibrosis Screening J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9): Table 3. Distribution of Patients With Elevated SWV (F2-4): Main Causes Group 1 (N = 33) Group 2 (N = 22) Group 3 (N = 9) Group 4 (N = 13) Group 5 (N = 43) Group 6 (N = 53) ASH Hepatitis B/C Heart failure NASH AIH/PBC/PSC Unknown able method to evaluate liver stiffness. In our study, we proved ultrasonography-based ARFI-SWEI elastography for its clinical usefulness as a screening method to uncover liver fibrosis. The accuracy of ARFI-SWEI is well tested and it is reliable in prediction of fibrosis in early stages ( F2) [13, 19]. The sensitivity and specificity of the ARFI-SWEI method is ascertained of 83-88% and 89-90% and its accuracy, expressed as area under the curve receiver-operating characteristic (AU- ROC), is near 1 [13, 19, 23]. Because of its reliability, we supported that elevated SWV values indicate a possible liver failure. Our procedure of ARFI-SWEI was standardized to ensure that the results of the patients were comparable. ARFI-SWEI measurement failed in 4.96% (21 of 403 patients) because of low intercostal access, heightened BMI or uncooperative patient cooperation. This is comparable to literature data ( %) [24]. Ultrasound is the most sufficient technique to detect steatosis of the liver and allows morphologic description of the liver tissue with its potential content of fat. In our study, we separated the participants with the native ultrasound in three different groups (groups 2-4) according to the steatosis degree. Nearly 15-22% of these patients had steatosis and elevated SWV corresponding to F2; the grade of steatosis was independent of liver fibrosis stage because the percentage of F2-4 was more elevated in group 2 than in groups 3 and 4 (32% vs. 23% vs. 30). Motosugi et al (2011) found out in 200 individuals that steatosis alone without histology assured inflammation shows normal SWV values: the SWV results of the fatty liver group were similar to those of the normal liver group (1.03 ± 0.12 vs ± 0.12 m/s (P < )) and the authors concluded that steatosis alone does not affect the liver stiffness measurement [25]. Fibrosis F2 in context with steatosis is a possible hint for steatohepatitis which can lead to liver cirrhosis. In groups 2-4, the leading cause for steatosis seemed to be (N)ASH. Whereas patients of group 1 (33/131) show elevated SWV ( F2) caused by heart failure, viral hepatitis or autoimmune hepatitis, but in nearly 60% (20/33) of the cases, the cause of SWV elevation was unclear and further diagnostic was recommended. For group 5, the main reasons for liver cirrhosis were ASH and NASH (> 50%). Even though the b- mode scan gave no hints of fatty liver, the fibrotic/cirrhotic transformation was based on (N)ASH in the past. This was also supposed for group 6. ARFI-SWEI is a reliable tool to determine the degree of liver fibrosis in context of liver failure and CLD. Serological marker and b-mode ultrasound alone can underestimate the progressive liver failure with fibrosis. Only the thrombocyte count in patients with LC showed significant correlation. (N) ASH seemed to be the main causes for liver fibrosis in our study. Both are frequent CLDs in the industrialized world. Their incidences will raise in the future, especially NASH. ARFI-SWEI is useful and comfortable for detecting early fibrotic alterations of the liver tissue. Consecutively protective action can be implemented. Conclusion The results of our study show that in cases of normal native ultrasound scan, liver damage can be underestimated; by using ARFI-SWEI as an additional method, a tissue damage of the liver can be uncovered for further diagnostic evaluation. The method is comfortable for the physician and the patient; it is further useful in cases of known liver damage for a longitudinal follow-up. Liver biopsy with its complications (i.e. pain, bleeding) can be avoided. The ARFI-SWEI system integrated in an ultrasound device has a good accuracy and the reproducibility is high. The evaluation of liver stiffness corresponding to native ultrasound scan is fast. This procedure is suitable for preventive measure to uncover CLD comparable to preventive colonoscopy for colon cancer. Further socioeconomic studies in view of the preventive effect and costs were necessary. Our results show that ARFI-SWEI is an adequate method in terms of fast examination of the liver in routine ultrasound. In particular fibrosis stage F2 and higher are of interest and for this ARFI-SWEI has high sensitivity and specificity. Competing Interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Grant Support None. Financial Disclosure All authors have no financial disclosure to report. 654 Articles The authors Journal compilation J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc
6 Bert et al J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(9): References 1. Aghemo A, Colombo M. Hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C: from bench to bedside. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(1): Paradis V. Histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2013;190: Lencioni R, Kudo M, Ye SL, Bronowicki JP, Chen XP, Dagher L, Furuse J, et al. First interim analysis of the GIDEON (Global Investigation of therapeutic decisions in hepatocellular carcinoma and of its treatment with sorafenib) non-interventional study. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66(7): Schutte K, Kipper M, Kahl S, Bornschein J, Gotze T, Adolf D, Arend J, et al. Clinical characteristics and time trends in etiology of hepatocellular cancer in Germany. Digestion. 2013;87(3): Tacke F, Weiskirchen R. [Liver fibrosis - pathogenesis and novel therapeutic approaches]. Internist (Berl). 2010;51(1): Gesundheitsbericht fur Deutschland 1998: Kapitel Accessed June 5, Xu J, Murphy SL, Kochanek KD, Bastian BA. Deaths: Final Data for Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2016;64(2): Lencioni R, Kudo M, Ye SL, Bronowicki JP, Chen XP, Dagher L, Furuse J, et al. GIDEON (Global Investigation of therapeutic DEcisions in hepatocellular carcinoma and Of its treatment with sorafenib): second interim analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2014;68(5): Poobalan A, Aucott L. Obesity Among Young Adults in Developing Countries: A Systematic Overview. Curr Obes Rep. 2016;5(1): Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, Ahmed A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(3): Gines P, Quintero E, Arroyo V, Teres J, Bruguera M, Rimola A, Caballeria J, et al. Compensated cirrhosis: natural history and prognostic factors. Hepatology. 1987;7(1): D'Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol. 2006;44(1): Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A, Danila M. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI)-a new modality for the evaluation of liver fibrosis. Med Ultrason. 2010;12(1): Martinez SM, Crespo G, Navasa M, Forns X. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 2011;53(1): Gallotti A, D'Onofrio M, Pozzi Mucelli R. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) technique in ultrasound with Virtual Touch tissue quantification of the upper abdomen. Radiol Med. 2010;115(6): Palmeri ML, Wang MH, Rouze NC, Abdelmalek MF, Guy CD, Moser B, Diehl AM, et al. Noninvasive evaluation of hepatic fibrosis using acoustic radiation forcebased shear stiffness in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2011;55(3): Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF, Fromageau J, Bojunga J, Calliada F, Cantisani V, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: Basic principles and technology. Ultraschall Med. 2013;34(2): Sporea I, Bota S, Gradinaru-Tascau O, Sirli R, Popescu A. Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic techniques: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography and ElastPQ. Med Ultrason. 2014;16(4): Friedrich-Rust M, Nierhoff J, Lupsor M, Sporea I, Fierbinteanu-Braticevici C, Strobel D, Takahashi H, et al. Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse imaging for the staging of liver fibrosis: a pooled meta-analysis. J Viral Hepat. 2012;19(2):e Saverymuttu SH, Joseph AE, Maxwell JD. Ultrasound scanning in the detection of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;292(6512): Jaffer OS, Lung PF, Bosanac D, Patel VM, Ryan SM, Heneghan MA, Quaglia A, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse quantification: repeatability of measurements in selected liver segments and influence of age, body mass index and liver capsule-to-box distance. Br J Radiol. 2012;85(1018):e Goertz RS, Egger C, Neurath MF, Strobel D. Impact of food intake, ultrasound transducer, breathing maneuvers and body position on acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastometry of the liver. Ultraschall Med. 2012;33(4): Tsochatzis EA, Gurusamy KS, Ntaoula S, Cholongitas E, Davidson BR, Burroughs AK. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: a meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J Hepatol. 2011;54(4): Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A, Danila M, Sendroiu M. Factors that influence the correlation of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI), elastography with liver fibrosis. Med Ultrason. 2011;13(2): Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Niitsuma Y, Araki T. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography of the liver: can fat deposition in the liver affect the measurement of liver stiffness? Jpn J Radiol. 2011;29(9): Articles The authors Journal compilation J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc 655
The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases
 RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
 The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 4, 309-314 DOI: Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic techniques: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography and ElastPQ
Original papers Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 4, 309-314 DOI: Comparative study between two point Shear Wave Elastographic techniques: Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography and ElastPQ
How useful are ARFI elastography cut-off values proposed by metaanalysis for predicting the significant fibrosis and compensated liver cirrhosis?
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 2, 200-205 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.172.arfi How useful are ARFI elastography cut-off values proposed by metaanalysis for predicting the significant fibrosis
Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 2, 200-205 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.172.arfi How useful are ARFI elastography cut-off values proposed by metaanalysis for predicting the significant fibrosis
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4,
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 268-272 DOI: How many measurements are needed for liver stiffness assessment by 2D-Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE) and which value should be used: the
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 268-272 DOI: How many measurements are needed for liver stiffness assessment by 2D-Shear Wave Elastography (2D-SWE) and which value should be used: the
Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases
 4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO
 PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
Ultrasound elastography of liver: How Radiologist can help.
 116 Review Article Ultrasound elastography of liver: How Radiologist can help. Maharjan S 1, Panta OB 2, Lohani B 1, Pathak YR 2, Ansari MA 1 1 Department of radiology and Imaging, Tribhuvan University
116 Review Article Ultrasound elastography of liver: How Radiologist can help. Maharjan S 1, Panta OB 2, Lohani B 1, Pathak YR 2, Ansari MA 1 1 Department of radiology and Imaging, Tribhuvan University
Preliminary clinical experience with Shear Wave Dispersion Imaging for liver viscosity
 Preliminary clinical experience with Shear Wave Dispersion Imaging for liver viscosity Dr. Katsutoshi Sugimoto Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical University, Japan Introduction
Preliminary clinical experience with Shear Wave Dispersion Imaging for liver viscosity Dr. Katsutoshi Sugimoto Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical University, Japan Introduction
Research Elastography: Liver
 Research Elastography: Liver Giovanna Ferraioli EFSUMB Ultrasound Learning Center Ultrasound Unit - Infectious Diseases Dept. Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico S. Matteo Medical School University of Pavia,
Research Elastography: Liver Giovanna Ferraioli EFSUMB Ultrasound Learning Center Ultrasound Unit - Infectious Diseases Dept. Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico S. Matteo Medical School University of Pavia,
ULTRASOUND IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE
 ULTRASOUND IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE Prof. Ioan Sporea, MD, PhD Head of Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timişoara, Romania WFUMB Center of Education (COE),
ULTRASOUND IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE Prof. Ioan Sporea, MD, PhD Head of Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timişoara, Romania WFUMB Center of Education (COE),
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI
 Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients
 Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
RSNA-QIBA SWS Profile What the Clinical Workflow Would look like and a Review of Biological Confounders. Manish Dhyani, MD Anthony Samir, MD MPH
 RSNA-QIBA SWS Profile What the Clinical Workflow Would look like and a Review of Biological Confounders Manish Dhyani, MD Anthony Samir, MD MPH Background Liver fibrosis is the final common pathway for
RSNA-QIBA SWS Profile What the Clinical Workflow Would look like and a Review of Biological Confounders Manish Dhyani, MD Anthony Samir, MD MPH Background Liver fibrosis is the final common pathway for
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients
 Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging(ARFI) and Transient Elastography(TE) for liver fibrosis assessment in chronic viral hepatitis
 Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging(ARFI) and Transient Elastography(TE) for liver fibrosis assessment in chronic viral hepatitis Poster No.: C-2115 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Acoustic Radiation Force Imaging(ARFI) and Transient Elastography(TE) for liver fibrosis assessment in chronic viral hepatitis Poster No.: C-2115 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A.
Xiao-Ping Ye, MM, Hai-Tao Ran, MD, Juan Cheng, MM, Ye-Feng Zhu, MM, Da-Zhi Zhang, MD, Ping Zhang, MD, Yuan-Yi Zheng, MD
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Liver and Spleen Stiffness Measured by Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis and Esophageal Varices in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Liver and Spleen Stiffness Measured by Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography for Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis and Esophageal Varices in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 2, Ioan Sporea, Iulia Raţiu, Simona Bota, Roxana Şirli, Ana Jurchiş
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 2, 111-115 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.152.is1ir2 Are different cut-off values of liver stiffness assessed by Transient Elastography according to the etiology
Original papers Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 2, 111-115 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.152.is1ir2 Are different cut-off values of liver stiffness assessed by Transient Elastography according to the etiology
Research Article Utility of Shear Wave Elastography for Diagnosing Chronic Autoimmune Thyroiditis
 yroid Research Volume 2015, Article ID 164548, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/164548 Research Article Utility of Shear Wave Elastography for Diagnosing Chronic Autoimmune Thyroiditis Takahiro Fukuhara,
yroid Research Volume 2015, Article ID 164548, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/164548 Research Article Utility of Shear Wave Elastography for Diagnosing Chronic Autoimmune Thyroiditis Takahiro Fukuhara,
MR Elastography of Liver
 MR Elastography of Liver Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, MD, FRCR Professor of Radiology Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Consultant, Abdominal Division Radiology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA 19 th May 2018 2018
MR Elastography of Liver Sudhakar K. Venkatesh, MD, FRCR Professor of Radiology Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Consultant, Abdominal Division Radiology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA 19 th May 2018 2018
Original Article Gastrointestinal Imaging
 Original Article Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.750 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(5):750-757 Prospective Comparison of Liver Stiffness Measurements
Original Article Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.750 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(5):750-757 Prospective Comparison of Liver Stiffness Measurements
Clinical Medicine Review
 Dighe M. et al. Clinical Medicine Review, 2018 Page 1 of 15 Clinical Medicine Review Published: July 09, 2018 Citation: Dighe M. et al. (2018) Review of ultrasound elastography techniques in the liver.
Dighe M. et al. Clinical Medicine Review, 2018 Page 1 of 15 Clinical Medicine Review Published: July 09, 2018 Citation: Dighe M. et al. (2018) Review of ultrasound elastography techniques in the liver.
Ultrasound elastography in abdominal imaging
 Ultrasound elastography in abdominal imaging Olivier ucidarme Pitié Salpêtrière - UPMC Paris France Ultraschall Med. 013 Apr;34():169-84 Ultraschall Med. 013 Jun;34(3):38-53. US elastography Ultraschall
Ultrasound elastography in abdominal imaging Olivier ucidarme Pitié Salpêtrière - UPMC Paris France Ultraschall Med. 013 Apr;34():169-84 Ultraschall Med. 013 Jun;34(3):38-53. US elastography Ultraschall
Liver Shear-Wave Velocity and Serum Fibrosis Markers to Diagnose Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Viral Hepatitis B
 Original Article Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.396 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(3):396-404 Liver Shear-Wave Velocity and Serum Fibrosis Markers
Original Article Gastrointestinal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.3.396 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(3):396-404 Liver Shear-Wave Velocity and Serum Fibrosis Markers
Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine
 Ultrasound Customer story Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine Philips Affiniti ultrasound for elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) Where Sonography Institute, Uster, Switzerland
Ultrasound Customer story Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine Philips Affiniti ultrasound for elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) Where Sonography Institute, Uster, Switzerland
Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis
 NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
NONINVASIVE TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATION AND MONITORING OF CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE
 LIVER DISEASE Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
LIVER DISEASE Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
CONFOUNDING FACTORS affecting the performance of US elastography
 Clinical Ultrasound in Hepatology: Training for Hepatologists UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, Royal Free Hospital, London, UK June 2018 CONFOUNDING FACTORS affecting the performance of US
Clinical Ultrasound in Hepatology: Training for Hepatologists UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health, Royal Free Hospital, London, UK June 2018 CONFOUNDING FACTORS affecting the performance of US
NONINVASIVE IMAGING METHODS FOR ASSESSMENT OF LIVER DAMAGE IN NASH
 NONINVASIVE IMAGING METHODS FOR ASSESSMENT OF LIVER DAMAGE IN NASH Bachir Taouli, MD Director of Body MRI and Cancer Imaging Program Department of Radiology / Translational and Molecular Imaging Institute
NONINVASIVE IMAGING METHODS FOR ASSESSMENT OF LIVER DAMAGE IN NASH Bachir Taouli, MD Director of Body MRI and Cancer Imaging Program Department of Radiology / Translational and Molecular Imaging Institute
Elastography in the. technically difficult patient. EPIQ ultrasound system. Ultrasound
 Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Motion effects on the measurement of stiffness on ultrasound shear wave elastography: a moving liver fibrosis phantom study
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2018, Vol. 20, no. 1, 14-20 DOI: 10.11152/mu-1138 Motion effects on the measurement of stiffness on ultrasound shear wave elastography: a moving liver fibrosis phantom study
Original papers Med Ultrason 2018, Vol. 20, no. 1, 14-20 DOI: 10.11152/mu-1138 Motion effects on the measurement of stiffness on ultrasound shear wave elastography: a moving liver fibrosis phantom study
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning
 Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
Liver elastography ultrasound cpt code
 Liver elastography ultrasound cpt code In a multi-center study, Barbero-Villares et al (2012) evaluated the presence of significant liver fibrosis by transient elastography (FibroScan) in inflammatory.
Liver elastography ultrasound cpt code In a multi-center study, Barbero-Villares et al (2012) evaluated the presence of significant liver fibrosis by transient elastography (FibroScan) in inflammatory.
Medical Review Approaches to the Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis
 Medical Review Approaches to the Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis Hiroko Iijima Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Ultrasound Imaging Center, Hyogo College of Medicine Hiroko Iijima Department
Medical Review Approaches to the Diagnosis of Liver Fibrosis Hiroko Iijima Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disease Ultrasound Imaging Center, Hyogo College of Medicine Hiroko Iijima Department
Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI): a review of an useful technique to assess liver stiffness
 Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI): a review of an useful technique to assess liver stiffness Poster No.: C-2166 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Elorz, A. Benito, L. Garcia
Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI): a review of an useful technique to assess liver stiffness Poster No.: C-2166 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Elorz, A. Benito, L. Garcia
M30 Apoptosense ELISA. A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH
 M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
Ultrasound Transient Elastography for Liver Fibrosis
 Ultrasound Transient Elastography for Liver Fibrosis Protocol: RAD042 Effective Date: June 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 DESCRIPTION OF SERVICES...
Ultrasound Transient Elastography for Liver Fibrosis Protocol: RAD042 Effective Date: June 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 DESCRIPTION OF SERVICES...
Normal ALT for men 30 IU/L 36% US males abnormal. Abnl ALT. Assess alcohol use/meds. Recheck in 6-8 weeks. still pos
 Fatty liver disease Its not just for big boys anymore Ken Flora, MD, FAASLD, FACG, AGAF No disclosures Common situation Normal ALT for men 30 IU/L 36% US males abnormal Normal ALT for women 20 IU/L 28%
Fatty liver disease Its not just for big boys anymore Ken Flora, MD, FAASLD, FACG, AGAF No disclosures Common situation Normal ALT for men 30 IU/L 36% US males abnormal Normal ALT for women 20 IU/L 28%
Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis using ARFI with pathological correlation, a prospective study
 440 Yap WW, et al., 2013; 12 (4): 440-447 ORIGINAL ARTICLE July-August, Vol. 12 No.4, 2013: 440-447 Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis using ARFI with pathological correlation, a prospective study
440 Yap WW, et al., 2013; 12 (4): 440-447 ORIGINAL ARTICLE July-August, Vol. 12 No.4, 2013: 440-447 Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis using ARFI with pathological correlation, a prospective study
Tissue Strain Analytics Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification
 Whitepaper Tissue Strain Analytics Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification ACUSON S2000 Ultrasound System Answers for life. Page 1 Tissue Strain Analytics: Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification
Whitepaper Tissue Strain Analytics Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification ACUSON S2000 Ultrasound System Answers for life. Page 1 Tissue Strain Analytics: Virtual Touch Tissue Imaging and Quantification
Liver Stiffness Measurements Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in Recipients of Living-Donor and Deceased- Donor Orthotopic Liver Transplant
 ArtIcle Liver Stiffness Measurements Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in Recipients of Living-Donor and Deceased- Donor Orthotopic Liver Transplant Kemal Murat Haberal, 1 Hale Turnaoğlu, 1 Adnan
ArtIcle Liver Stiffness Measurements Using Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse in Recipients of Living-Donor and Deceased- Donor Orthotopic Liver Transplant Kemal Murat Haberal, 1 Hale Turnaoğlu, 1 Adnan
Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital
 Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital CEUS & US Elastography : Contents CEUS Introduction Contrast agents & imaging Clinical application US Video WS Summary US
Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Department of Radiology Seoul National University Hospital CEUS & US Elastography : Contents CEUS Introduction Contrast agents & imaging Clinical application US Video WS Summary US
Medical technologies guidance Published: 23 September 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg27
 Virtual Touch Quantification to diagnose and monitor liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C Medical technologies guidance Published: 23 September 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg27 NICE 2017. All rights
Virtual Touch Quantification to diagnose and monitor liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C Medical technologies guidance Published: 23 September 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg27 NICE 2017. All rights
Performance of 2D-SWE.GE for predicting different stages of liver fibrosis, using Transient Elastography as the reference method
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2017, Vol. 19, no. 2, 143-149 DOI: 10.11152/mu-910 Performance of 2D-SWE.GE for predicting different stages of liver fibrosis, using Transient Elastography as the reference
Original papers Med Ultrason 2017, Vol. 19, no. 2, 143-149 DOI: 10.11152/mu-910 Performance of 2D-SWE.GE for predicting different stages of liver fibrosis, using Transient Elastography as the reference
In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
DISCLOSURES. This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea
 DISCLOSURES This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea Cardea Services is approved as a provider of continuing nursing education by Montana Nurses Association,
DISCLOSURES This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea Cardea Services is approved as a provider of continuing nursing education by Montana Nurses Association,
iu22 Liver Shear Wave ElastPQ
 iu22 Liver Shear Wave ElastPQ Clinical Case Study Lucy Wang Clinical Application Specialist ASEAN Case Study: History: 58-year-old male patient, hepatitis B virus (HBV) carrier, with non clinical symptoms
iu22 Liver Shear Wave ElastPQ Clinical Case Study Lucy Wang Clinical Application Specialist ASEAN Case Study: History: 58-year-old male patient, hepatitis B virus (HBV) carrier, with non clinical symptoms
Invasive. Sampling error. Interobserver variability. Nondynamic evaluation of
 How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
Hepatology For The Nonhepatologist
 Hepatology For The Nonhepatologist Andrew Aronsohn, MD Associate Professor of Medicine University of Chicago Chicago, Illinois Learning Objectives After attending this presentation, learners will be able
Hepatology For The Nonhepatologist Andrew Aronsohn, MD Associate Professor of Medicine University of Chicago Chicago, Illinois Learning Objectives After attending this presentation, learners will be able
Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient Elastography in Diabetics with Fatty Liver A Single Center Cross Sectional observational Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
POWERED BY. Innovation in liver disease management
 POWERED BY VCTE Innovation in liver disease management An intelligent solution to aid clinical diagnosis, FibroScan uses state of the art fibrosis and steatosis quantification with the most advanced non-invasive
POWERED BY VCTE Innovation in liver disease management An intelligent solution to aid clinical diagnosis, FibroScan uses state of the art fibrosis and steatosis quantification with the most advanced non-invasive
shear wave elastography
 Ultrasound ElastQ Imaging Introducing next-generation shear wave elastography Philips ElastQ Imaging Vijay Shamdasani, PhD and Hua Xie, PhD, Philips Ultrasound Tissue stiffness has long provided important
Ultrasound ElastQ Imaging Introducing next-generation shear wave elastography Philips ElastQ Imaging Vijay Shamdasani, PhD and Hua Xie, PhD, Philips Ultrasound Tissue stiffness has long provided important
ACOUSTIC RADIATION FORCE IMAGING (ARFI) in assessment of renal stiffness in patients with chronic kidney disease
 ACOUSTIC RADIATION FORCE IMAGING (ARFI) in assessment of renal stiffness in patients with chronic kidney disease Poster No.: C-2134 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Januszewicz 1,
ACOUSTIC RADIATION FORCE IMAGING (ARFI) in assessment of renal stiffness in patients with chronic kidney disease Poster No.: C-2134 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Januszewicz 1,
Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the liver Reasons for imaging Focal lesions Diffuse disease Can we do more? The Liver The Liver The Liver
Liver Ultrasound - Beyond the Basics Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the liver Reasons for imaging Focal lesions Diffuse disease Can we do more? The Liver The Liver The Liver
Original Article. Abstract. Background
 E2 Original Article THIEME Evaluation of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging (ARFI) for the Determination of Liver Stiffness Using Transient Elastography as a Reference in Children Authors A. Sagir
E2 Original Article THIEME Evaluation of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging (ARFI) for the Determination of Liver Stiffness Using Transient Elastography as a Reference in Children Authors A. Sagir
LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography
 LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography Introduction Tissue stiffness is often related to underlying disease. For millennia, physicians have used palpation as a diagnostic tool to detect various ailments such
LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography Introduction Tissue stiffness is often related to underlying disease. For millennia, physicians have used palpation as a diagnostic tool to detect various ailments such
Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease. Naveen Gara, MD
 Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease Naveen Gara, MD Outline Brief overview of the anatomy of liver Liver-related lab tests Chronic liver disease progression Estimation of liver fibrosis
Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease Naveen Gara, MD Outline Brief overview of the anatomy of liver Liver-related lab tests Chronic liver disease progression Estimation of liver fibrosis
Ultrasound Committee Activities
 Ultrasound Committee Activities Anthony E. Samir MD MPH Clinical Director MGH/MIT Center for Ultrasound Research & Translation PINTAD 2014 Disclosures Grant Support Harvard Catalyst: Pilot Grant (NIBIB
Ultrasound Committee Activities Anthony E. Samir MD MPH Clinical Director MGH/MIT Center for Ultrasound Research & Translation PINTAD 2014 Disclosures Grant Support Harvard Catalyst: Pilot Grant (NIBIB
Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography
 Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1118 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 7, 2018 Next Review Date: August
Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1118 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 7, 2018 Next Review Date: August
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology
 Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography
 LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography Introduction Tissue stiffness is often related to underlying disease. For millennia, physicians have used palpation as a diagnostic tool to detect various ailments such
LOGIQ E9 Shear Wave Elastography Introduction Tissue stiffness is often related to underlying disease. For millennia, physicians have used palpation as a diagnostic tool to detect various ailments such
Abstract. Introduction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, September: 185-194, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Staging Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, September: 185-194, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Staging Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in
UMHS-PUHSC JOINT INSTITUTE
 Role of Visceral Adiposity in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean versus Obese Patients: A Comparative Study between Patients at UMHS versus PUHSC Lai WEI and Anna LOK W Zhang,
Role of Visceral Adiposity in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean versus Obese Patients: A Comparative Study between Patients at UMHS versus PUHSC Lai WEI and Anna LOK W Zhang,
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr PREVALENCE OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC POPULATION
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr PREVALENCE OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC POPULATION
Transient elastography the state of the art
 Transient elastography the state of the art Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris-7, France White Nights of Hepatology, St Petersburg, Russia, june
Transient elastography the state of the art Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris-7, France White Nights of Hepatology, St Petersburg, Russia, june
Non-invasive diagnosis of hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ bpgoffice@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.445 World J Gastroenterol 2014 January 14; 20(2): 445-459 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2014
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ bpgoffice@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.445 World J Gastroenterol 2014 January 14; 20(2): 445-459 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2014
Pretreatment Evaluation
 Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
 HEPATO-PANCREATO-BILIARY STOMACH CANCER PROGRAM Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Steatosis and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Management Recommendations UCSF Fresno Department of Surgery
HEPATO-PANCREATO-BILIARY STOMACH CANCER PROGRAM Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Steatosis and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Management Recommendations UCSF Fresno Department of Surgery
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
Diagnostic Accuracy of SuperSonic Shear Imaging for Staging of Liver Fibrosis
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Accuracy of SuperSonic Shear Imaging for Staging of Liver Fibrosis A Meta-analysis Jin-Chun Feng, MD, Jun Li, MD, Xiang-Wei Wu, MD, PhD, Xin-Yu Peng, MD, PhD Received March
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Accuracy of SuperSonic Shear Imaging for Staging of Liver Fibrosis A Meta-analysis Jin-Chun Feng, MD, Jun Li, MD, Xiang-Wei Wu, MD, PhD, Xin-Yu Peng, MD, PhD Received March
NAFLD/NASH. Definitions. Pathology NASH. Vicki Shah PA-C, MMS Rush University Hepatology
 NAFLD/NASH Vicki Shah PA-C, MMS Rush University Hepatology Definitions NAFLD Evidence of hepatic steatosis by histology (5%) or imaging No causes for secondary fat accumulation EtOH, Drugs, hereditary
NAFLD/NASH Vicki Shah PA-C, MMS Rush University Hepatology Definitions NAFLD Evidence of hepatic steatosis by histology (5%) or imaging No causes for secondary fat accumulation EtOH, Drugs, hereditary
Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in distinguishing hepatic haemangiomata from metastases: preliminary observations
 The British Journal of Radiology, 84 (2011), 939 943 SHORT COMMUNICATION Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in distinguishing hepatic haemangiomata from metastases: preliminary observations
The British Journal of Radiology, 84 (2011), 939 943 SHORT COMMUNICATION Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in distinguishing hepatic haemangiomata from metastases: preliminary observations
Liver Fat Quantification
 Liver Fat Quantification Jie Deng, PhD, DABMP Department of Medical Imaging May 18 th, 2017 Disclosure Research agreement with Siemens Medical Solutions 2 Background Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Liver Fat Quantification Jie Deng, PhD, DABMP Department of Medical Imaging May 18 th, 2017 Disclosure Research agreement with Siemens Medical Solutions 2 Background Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Liver Pathology and the Clinician in 2015: At the Crossroads. Thomas D. Schiano, M.D. Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York
 Liver Pathology and the Clinician in 2015: At the Crossroads Thomas D. Schiano, M.D. Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York DISCLOSURES Consultant for: Salix Merck Gilead BMS Synageva Research funding:
Liver Pathology and the Clinician in 2015: At the Crossroads Thomas D. Schiano, M.D. Mount Sinai Medical Center New York, New York DISCLOSURES Consultant for: Salix Merck Gilead BMS Synageva Research funding:
Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease
 HKASLD 30 th ASM and International Symposium on Hepatology 2017 Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease 5 Nov 2017 Dr. Lau Yue Leung Joulen Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital NAFLD
HKASLD 30 th ASM and International Symposium on Hepatology 2017 Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease 5 Nov 2017 Dr. Lau Yue Leung Joulen Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital NAFLD
Liver Pathology in the 0bese
 Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Liver Pathology in the 0bese Rob Goldin Centre for Pathology, Imperial College r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Ludwig et al. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic
 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic Amir Shlomai MD,PhD Head, Department of Medicine D The Liver Institute Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Hospital The IASLD semi-annual meeting-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic Amir Shlomai MD,PhD Head, Department of Medicine D The Liver Institute Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Hospital The IASLD semi-annual meeting-
NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES
 NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES Preface Zobair M. Younossi xiii Epidemiology and Natural History of NAFLD and NASH 1 Janus P. Ong and Zobair M. Younossi Understanding
NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES Preface Zobair M. Younossi xiii Epidemiology and Natural History of NAFLD and NASH 1 Janus P. Ong and Zobair M. Younossi Understanding
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist
 Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Liver Elastography An Update
 Review Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 304-314 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.154.isp23 Liver Elastography An Update Ioan Sporea 1, Odd Helge Gilja 2, Simona Bota 1, Roxana Șirli 1, Alina Popescu 1 1 Department
Review Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 4, 304-314 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.154.isp23 Liver Elastography An Update Ioan Sporea 1, Odd Helge Gilja 2, Simona Bota 1, Roxana Șirli 1, Alina Popescu 1 1 Department
Clinical Policy Title: Noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis
 Clinical Policy Title: Noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis Clinical Policy Number: 08.01.03 Effective Date: Oct. 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 17, 2017
Clinical Policy Title: Noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis Clinical Policy Number: 08.01.03 Effective Date: Oct. 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 17, 2017
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis. Pierre BEDOSSA
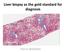 Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
Abstract. Flaviu Bob 1, Simona Bota 2 *, Ioan Sporea 2, Roxana Sirli 2, Ligia Petrica 1, Adalbert Schiller 1 RESEARCH ARTICLE
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Kidney Shear Wave Speed Values in Subjects with and without Renal Pathology and Inter-Operator Reproducibility of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography (ARFI) - Preliminary Results
RESEARCH ARTICLE Kidney Shear Wave Speed Values in Subjects with and without Renal Pathology and Inter-Operator Reproducibility of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Elastography (ARFI) - Preliminary Results
CDHNF & NASPGHAN A Partnership for Research and Education for Children s Digestive and Nutritional Health
 CDHNF & NASPGHAN A Partnership for Research and Education for Children s Digestive and Nutritional Health Obesity and NAFLD Definitions: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver
CDHNF & NASPGHAN A Partnership for Research and Education for Children s Digestive and Nutritional Health Obesity and NAFLD Definitions: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) of the pancreas.
 Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) of the pancreas. Poster No.: C-0686 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Crosara, M. D'Onofrio, R. De Robertis, S. Canestrini, E. Demozzi, R.
Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) of the pancreas. Poster No.: C-0686 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Crosara, M. D'Onofrio, R. De Robertis, S. Canestrini, E. Demozzi, R.
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
As a result of the growing obesity epidemic,
 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 63, NO. 6, 2016 STEATOHEPATITIS/METABOLIC LIVER DISEASE Liver Stiffness in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Comparison of Supersonic
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 63, NO. 6, 2016 STEATOHEPATITIS/METABOLIC LIVER DISEASE Liver Stiffness in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Comparison of Supersonic
DISCLOSURES. This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea
 DISCLOSURES This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea Cardea Services is approved as a provider of continuing nursing education by Montana Nurses Association,
DISCLOSURES This activity is jointly provided by Northwest Portland Area Indian Health Board and Cardea Cardea Services is approved as a provider of continuing nursing education by Montana Nurses Association,
Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using ShearWave Elastography on Aixplorer
 Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using ShearWave Elastography on Aixplorer SSID02892-01 November 2012 Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using SWE on Aixplorer Introduction From a clinical standpoint, staging liver
Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using ShearWave Elastography on Aixplorer SSID02892-01 November 2012 Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis using SWE on Aixplorer Introduction From a clinical standpoint, staging liver
Evaluation of liver fibrosis index calculated by strain elastography for assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic viral hepatitis
 Journal of Scientific Research and Studies Vol. 4(11), pp. 340-344, November, 2017 ISSN 2375-8791 Copyright 2017 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.modernrespub.org/jsrs/index.htm
Journal of Scientific Research and Studies Vol. 4(11), pp. 340-344, November, 2017 ISSN 2375-8791 Copyright 2017 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.modernrespub.org/jsrs/index.htm
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing?
 Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing? Stephen D Ryder Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust and Biomedical research Unit What are we currently
Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing? Stephen D Ryder Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust and Biomedical research Unit What are we currently
Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies
 4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant. Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
Bio Predictive. FibroTest Scientific Publications. Ratziu 2016 FibroMax NASH. Friedman 2016 FibroTest NASH EASL Key Publications for 2017
 EASL 2017 Scientific Publications Ratziu 2016 NASH Friedman 2016 NASH SteatoTest and sensitive markers of improvement in NASH trial using Elafibranor Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator
EASL 2017 Scientific Publications Ratziu 2016 NASH Friedman 2016 NASH SteatoTest and sensitive markers of improvement in NASH trial using Elafibranor Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Typical and Atypical
 Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Typical and Atypical Disclosure Naim Alkhouri, MD discloses the following relationships with commercial companies: Membership in the Speakers Bureau for Alexion
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children: Typical and Atypical Disclosure Naim Alkhouri, MD discloses the following relationships with commercial companies: Membership in the Speakers Bureau for Alexion
Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence Risk by Ultrasound Elastography
 2235-1795/14/0031-0001$39.50/0 1 Editorial Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence Risk by Ultrasound Elastography Prof. M. Kudo Editor Liver Cancer In patients with chronic hepatitis and continuous
2235-1795/14/0031-0001$39.50/0 1 Editorial Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence Risk by Ultrasound Elastography Prof. M. Kudo Editor Liver Cancer In patients with chronic hepatitis and continuous
