Keeping Youth DRUG FREE
|
|
|
- Leslie McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Keeping Youth DRUG FREE
2
3 Keeping Youth DRUG FREE U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration Center for Substance Abuse Prevention
4 Acknowledgments This publication was prepared for the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) by the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) under contract number HHSS C, with SAMHSA, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). David Lamont Wilson served as the Government Project Officer. Disclaimer The views, opinions, and content of this publication are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views, opinions, or policies of SAMHSA or HHS. SAMHSA complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. SAMHSA cumple con las leyes federales de derechos civiles aplicables y no discrimina por motivos de raza, color, nacionalidad, edad, discapacidad o sexo. Electronic Access and Copies of Publication This publication may be downloaded or ordered at Or call SAMHSA s Store at SAMHSA-7 ( ) (English and Español). Recommended Citation Keeping Youth Drug Free. HHS Publication No. (SMA) Rockville, MD: Center for Substance Abuse Prevention, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Originating Office Center for Substance Abuse Prevention, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, 5600 Fishers Lane, Rockville, MD HHS Publication No. (SMA) First printed Revised Public Domain Notice All material appearing in this report is in the public domain and may be reproduced or copied without permission from SAMHSA. Citation of the source is appreciated. However, this publication may not be reproduced or distributed for a fee without the specific, written authorization of the Office of Communications, SAMHSA, HHS.
5 YOU HOLD THE KEY TO YOUR CHILD S FUTURE. Few things worry parents, grandparents, and other caregivers more than the prospect of children using alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drugs. They know youth under their charge spend many hours each day out of their sight and are subject to influences they can t control. Youth may be encouraged by their peers to try marijuana, try inhalants, or misuse prescription drugs. Media often link alcohol use with fun and excitement and with being popular and sophisticated. Dangers seem to lurk everywhere. 1
6 WHAT TO KNOW AND WHAT TO DO Your 16-year-old may be taller than you and faster than you at certain tasks, but his brain will still be developing when he s in his early twenties. From age 13 to 25, the young brain is intensively shaped and reshaped based on its experiences. Connections within the brain that are used a lot become stronger while those that are not used much get weaker. That s why it s vital for youth to get involved in challenging intellectual, athletic, and social activities it will do their brains good for the rest of their lives. The last region of the brain to develop is the pre-frontal cortex which governs judgment. Teens have a lot of energy and emotion, but without the ability to predict outcomes and plan accordingly, they can make choices such as using drugs and alcohol that will hurt them for life. 2
7 In 2015, 2.2 million youth ages reported using illicit drugs and 2.4 million used alcohol in the past month, with more than half of those youth reporting binge drinking. Each day, about 3,200 youth try marijuana for the first time and about 6,500 try alcohol for the first time. 1 The long-term effects of early alcohol and illicit drug use are even more alarming. Multiple studies have found associations between early initiation of alcohol or illicit drug use (for example, in adolescence) and an increased likelihood of developing substance use disorders. Recent years have brought heartening news with fewer youth using harmful substances. However, with many teens still using alcohol and illicit substances, our job in keeping youth alcohol-and drug-free, safe, and healthy is far from done. The good news is that you can influence whether or not your child uses alcohol or drugs. Taking a clear stand against substance use by talking with children early is a good place to start. The majority of adolescents who start drinking do so when they are in the 7th or 8th grade and are about years old. 2 That s why parents, caregivers, teachers, and others should start talking with children about alcohol use well before the teen years and should continue talking throughout adolescence. What s more, the sooner you talk to your children about alcohol, the greater chance you have of influencing their decisions about drinking. Studies have shown that parents have a significant influence on young people s decisions about alcohol, especially when parents create supportive and nurturing environments in which their children can make their own decisions. 1 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality. (2016). Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2015 national survey on drug use and health. (HHS Publication No. SMA , NSDUH Series H-51). Retrieved from NSDUH-FFR1-2015/NSDUH-FFR pdf 2 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of the Surgeon General. (2007). The Surgeon General s call to action to prevent and reduce underage drinking. Retrieved from 3
8 Watching and supporting a youth s emotional well-being is another important way for parents to reduce the odds of their child using harmful substances. Ties between substance use and mental health problems are strong. Youth who experience a major depressive episode are more likely to engage in illicit drug use and more likely to smoke cigarettes every day. They also are more likely to be dependent on or use illicit drugs or alcohol. Here are some steps you can take to help the child you love reject illicit drugs and alcohol. ESTABLISH AND MAINTAIN GOOD COMMUNICATION WITH YOUR CHILD. Talk with your child every day but most importantly, listen. We all need to be heard and understood. Listen especially for the feelings behind your child s words. Is the child in your care frightened, lonely, depressed or hurt? Suppose your 13-year-old daughter says flatly, Emily is having a party and Madison and Chloe are invited, but I m not. She doesn t look sad, so you don t think much of it and reply, That s good because we really need to get some errands done anyway. What if your daughter was in fact very hurt about not being invited to the party? She may be more upset than she realizes. After a series of conversations like this with you, she may start to keep more things to herself and seem to have less to say. With less of a connection with 4
9 you, she will need to seek gratification elsewhere and be more subject to peer pressures, as she searches for a place to belong and to have her emotional needs met. What if you had instead responded with Oh, honey, it must feel awful not to be invited when all your friends are going. I m so sorry. Your daughter may then open up and admit that she feels terrible and begin to cry. The tears will release her sadness, and she ll walk away feeling better and glad that she talked to you. Your relationship will become stronger and that strong relationship with you is her best protection against substance misuse. If you are successful in opening lines of communication with your child about routine matters, she will be more likely to talk to you about serious issues.
10 GET INVOLVED IN YOUR CHILD S LIFE. Young people are much less likely to use drugs when they have caring adults in their lives and interesting activities to keep them busy, happy, and productive. Spend at least 15 minutes a day doing an age-appropriate activity that your child enjoys, such as reading a book, watching a TV program together, riding bikes, going to the library, or playing a game. Do something special together each week, such as going for a walk or searching on the Internet for information about a topic you both find interesting. Recognize good behavior consistently and immediately. Make the extra effort to catch your child being good. Use meal times as an opportunity to share news of the day or to discuss current affairs. By being involved, you will notice when your child is under stress or needs extra attention. 6
11 MAKE CLEAR RULES AND ENFORCE THEM CONSISTENTLY. If you let your child know that you don t approve of him using alcohol, tobacco, or drugs, he is less likely to do it. You can: Discuss why tobacco, illicit drugs, and underage drinking are not acceptable. Make sure your child is clear about your rules. Lay out what the consequences will be if your rules are broken, and follow through if they are. Acknowledge and praise your child when he obeys your rules. Rules and consequences are important so your child knows exactly where you stand on the issue of substance misuse. Rules also provide structure that is needed for emotional well-being. BE A POSITIVE ROLE MODEL. Children learn by watching you. If you make yourself a drink to deal with disappointment or anger, they notice. If you tell your son not to smoke, but then ask him to get you an ashtray from the cupboard, he notices that, too. Children can understand that adults have privileges they don t have, because adults assume responsibilities that children don t. But if your kids see you misusing substances, you are setting an example that speaks much louder than words. Do as I say, not as I do has never been a very compelling argument. If you use illicit drugs or misuse prescription drugs, your children may conclude: The best way to cope with stress and worry is to use drugs. Happiness comes from being high on drugs, not from good relationships. It s easier to take drugs to escape from your problems than to deal with them. 7
12 How to be a good role model to your child: Do not misuse alcohol or use tobacco or illicit drugs. Even young children imitate and are influenced by adult behaviors. If you can t quit, then at least make sure you do not involve your child in your use of alcohol, tobacco, or illicit drugs. When possible, point out examples of bad behavior and negative consequences as a result of substance misuse. The fact is, if you use alcohol, tobacco, or drugs, your children are more likely to use them too. If you used illicit drugs in the past, this topic may make you uneasy. Should you tell your child that you used drugs? That depends on a variety of factors, such as your relationship and the child s age and maturity. Some children may not want or need to know about it. Others may benefit from the lessons you learned. Remember, your child needs your guidance. Don t let your past drug use stop you from warning your child about the dangers of alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drugs. Some messages to share with your child are: Using drugs and alcohol won t solve your problems. Using drugs and alcohol won t make you popular. Drugs and alcohol won t help you build a strong body or mind. In fact, they can harm your physical and mental growth and prevent you from participating in sports and other activities. I stopped doing drugs (or smoking cigarettes or drinking alcohol), and I m much happier because of it. I find joy in life from my accomplishments, and from doing fun things with family and friends, not from getting stoned. 8
13 I don t want you to make the same mistakes I did. Your brain is still developing into your mid-twenties and doing drugs and alcohol may harm your brain in ways that can t be corrected later. MONITOR YOUR CHILD S ACTIVITIES. Many young people say they started smoking marijuana or using drugs out of boredom. Children with lots of unsupervised time on their hands are at greater risk of substance misuse. Establish relationships with your child s friends. Get to know other parents and reinforce each other s efforts. Ask for phone numbers and addresses of friends houses and other places your child goes, and let him know you might drop by. Start doing this when he is 8 or 9, and it will seem normal when he is 14. Have your child check in at regular times. Many children have cell phones or can be taught to use a phone card. If your child s cell phone has texting capability, use this feature to check in with them periodically. Make sure she has both your cell and work numbers so she can reach you. Set up a system (a code word or phrase) so your child can let you know if he needs to be picked up from a party or other social event where alcohol and drugs are being used. Know where your child is going, with whom, and what the activity will be. 9
14 TEACH YOUR CHILD TO CHOOSE FRIENDS WISELY. The power of peer pressure can be seen any time one person stands alone against a group, because we all want to fit in and belong. As an adult, you can probably remember times when everyone in a group seemed to be in agreement on a certain topic except you. Was it hard to speak up, knowing you d have the whole group against you? Maybe everyone wants to go to the all-you-can-eat buffet, but you know you will overeat if you do. You might feel torn between your desire to lose weight and your desire to be part of the group. Children have this same need to belong, but usually don t have the strength to stand alone against the group. Therefore it s important that your child not become part of a group that will collectively decide to use drugs, tobacco, or alcohol, for he will then be in the uncomfortable position of having to choose between his friends and his better instincts. Help your child make friends with kids who are involved in fun, healthy, wholesome activities, not kids with lots of time on their hands and no positive activities, hobbies or sports to focus on. The friendships formed in a swim team, newspaper club, theater group, choir, or pottery class are based on mutual aspirations and interests, and the children in those groups are usually too busy pursuing their goals to bother with substance use. Some specific action steps include: Encourage your child to get involved with groups doing the things that interest her. Whether it s dog training, amateur astronomy, soccer, dance, yearbook, or music lessons, help your child pursue her interests with peers who are doing the same. Help your child practice resisting peer pressure. Help her feel comfortable saying No thanks or even Bye, I m out of here. 10
15 Help your child feel comfortable in social situations by teaching her how to ask questions and be a good listener. Let her also know that it s okay to feel awkward at times; we all do. Loneliness, boredom and isolation are risk factors for mental and substance use disorders. Help your child develop healthy, wholesome relationships with other happy kids and you will make it less likely that she will turn to drugs or alcohol for comfort. 11
16 DRUG FACTS YOU NEED TO KNOW Would you know what to say if your son asked you what roofies are? Or if your daughter told you that one of her friends has started smoking blunts? Here are some basics about commonly misused drugs, their symptoms, and their consequences. For the latest list of drug slang code words, visit Alcohol Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Liquor, beer, and wine (bourbon, champagne, gin, tequila, vodka, whiskey, and wine coolers). Booze, juice, sauce, brew. Slurred speech, confusion, impaired judgment and motor skills, drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, emotional volatility, loss of coordination, visual distortions, impaired memory, sexual dysfunction and depression. Impaired judgment can result in inappropriate sexual behavior, sexually transmitted diseases, injuries, and auto crashes. Habitual use can lead to an inability to control drinking, high tolerance level, blackouts and memory loss, interference with personal relationships, cirrhosis of the liver, vitamin deficiencies, damage to the heart and central nervous system, sexual impotence, and weight gain. Excessive consumption can result in death due to alcohol poisoning or asphyxiation. Overdoses can result in death. Ingested by drinking. For appetite stimulation and mild sedation. Legal status Illegal for purchase or use by those under
17 Cannabinoids Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status Marijuana, hashish, cannabis sativa, and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Sativex). Marijuana: Weed, pot, grass, reefer, joint, ganga (pronounced GAHN-juh), herb, bud, Mary Jane, green, trees, smoke, sinsemilla, skunk, and blunt. Hashish: Boom, gangster, hash, and hemp. Mood swings, relaxation, distorted sensory perception, euphoria, slow thinking and reflexes, dilated pupils, increased appetite, impaired balance and coordination, dry mouth, increased pulse rate, impaired learning, impaired attention and memory, sleepiness, anxiety, panic attacks, delusions, and hallucinations. Addiction; breathing problems, including inflammation of the airways and symptoms of chronic bronchitis, such as daily cough and phlegm; short-term declines in memory, attention, and learning; increased risk of poisoning among children; increased risk for low birth weight in babies when a mother uses during her pregnancy; increased risk for psychosis or schizophrenia. Ingested, smoked, and vaporized. Amelioration of nausea and vomiting, stimulation of hunger in chemotherapy and patients living with HIV/AIDS, lowered intraocular eye pressure, treatment of spasticity from multiple sclerosis, as well as general analgesic effects (pain reliever). Marinol, the active ingredient found in the marijuana plant, can be prescribed for the control of nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapeutic agents used for cancer treatment. Marijuana is also illegal federally. 13
18 Club Drugs Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status GHB (gammahydroxybutyric acid), MDMA (methylenedioxymethamphetamine), and flunitrazepam (Rohypnol). GHB: Liquid ecstasy, liquid X, G, grievous bodily harm, soap, scoop, goop, and Georgia home boy. MDMA: Ecstasy, E, X, XTC, Adam, clarity, Eve, lover s speed, peace and uppers, Molly. Flunitrazepam: R-2, roofies, roach, forget-me pill, Mexican Valium, Roche, roofinol, rope, rophies and the date rape drug. GHB: Drowsiness, nausea, headache, disorientation, loss of coordination and memory loss. MDMA: Mild hallucinogenic effects, dilated pupils, increased tactile sensitivity, empathic feelings, lowered inhibition, anxiety, chills, sweating, teeth clenching and muscle cramping. Flunitrazepam: Sedation, muscle relaxation, confusion, memory loss, dizziness and impaired coordination. Impaired judgment and coordination can result in greater risk for injury, self-inflicted injury, violent behavior, paranoia, depression, anxiety, and unpredictable flashbacks. In addition, consequences for MDMA use include sleep disturbances, depression, impaired memory, hypothermia and addiction; Flunitrazepam use can result in addiction; and GHB can result in unconsciousness, seizures and comas. Ingested and sniffed. None. Illegal. 14
19 Dissociative Drugs Products include Ketamine, PCP and analogs, Salvia divinorum, and DXM (dextromethorphan). Street Names Ketamine: cat Valium, K, Special K, and vitamin K. PCP and analogs: Angel dust, angel mist, animal tranquilizer, boat, hog, love boat and peace pill. Salvia divinorum: Salvia, Shepherdess s Herb, Maria Pastora, magic mint, and Sally-D. DXM: Robotripping, robo, and triple C. Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status All dissociative drugs: Feelings of being separate from one s body and environment and impaired motor function. Ketamine: Analgesia, impaired memory, delirium, and respiratory depression. PCP and analogs: Analgesia, psychosis, aggression, violence, slurred speech, loss of coordination, and hallucinations. DXM: Euphoria, slurred speech, confusion, dizziness and distorted visual perceptions. Anxiety, tremors, numbness, memory loss, nausea, and death. Injected, ingested, sniffed, chewed, and smoked. Ketamine: Used as an injectable, short-acting anesthetic in humans and animals. DXM: Market cough suppressant. Ketamine: Legal by prescription. PCP and analogs: Illegal. DXM: Not a controlled substance. 15
20 Hallucinogens Products include LSD, mescaline, psilocybin, DMT (dimethyltryptamine), MDA (methylenedioxyamphetamine), and STP (dimethoxymethamphetamine). Street Names LSD: Acid, blotted, cubes, microdot, yellow sunshine, blue heaven, A, and windowpane. Mescaline: Buttons, cactus, mesc, and peyote. Psilocybin: Magic mushrooms, purple passion, shrooms, little smoke, and mushrooms. Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status All hallucinogens: Altered states of perception and feeling, hallucinations, and nausea. LSD and mescaline: Increased body temperature, heart rate and blood pressure; loss of appetite; sweating; sleeplessness; impulsive behavior; weakness; rapid shifts in emotion; and tremors. Psilocybin: Nervousness, paranoia, and panic. Flashbacks or replays of the drug experience, and prolonged depression. Ingested, smoked, and absorbed through mouth tissues. None. Illegal. 16
21 Nonprescription Opioids Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status Heroin and opium. Heroin: Smack, horse, brown sugar, dope, H, junk, skag, skunk, white horse, and China white. Opium: Big O, black stuff, block, gum, and hop. Euphoria, drowsiness, impaired coordination, dizziness, confusion, nausea, sedation, feeling of heaviness in the body, and slowed or arrested breathing. Constipation, endocarditis, hepatitis, HIV, addiction and fatal overdose. Ingested, smoked, and injected intravenously. None. Illegal. 17
22 Other Compounds Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status Anabolic steroids: Anadrol, Oxandrin, Depo-Testosterone, and Equipoise. Inhalants: Solvents (paint thinners, gasoline, glues, organic solvents, nail polish remover); gases (butane, propane, aerosol propellants, nitrous oxide, hair spray; and nitrites (isoamyl, isobutyl, and cyclohexyl). Anabolic steroids: Roids, juice, gym candy, and pumpers. Inhalants: Laughing gas, poppers, snappers, glue, bang, huff, kick, sniff, Texas shoeshine, and whippets. Anabolic steroids: No immediate intoxication effects. Inhalants: While symptoms vary by chemical, potential symptoms include loss of inhibition, stimulation, headache, nausea or vomiting, slurred speech, loss of motor coordination, and wheezing. Anabolic steroids: Hypertension; blood clotting and cholesterol changes; liver cysts; hostility and aggression; acne; premature growth stoppage in adolescents; prostate cancer, reduced sperm production, shrunken testicles and breast enlargement in males; and menstrual irregularities, as well as development of beard and other masculine characteristics in females. Inhalants: Cramps, muscle weakness, depression, memory impairment, damage to cardiovascular and nervous systems, unconsciousness, and sudden death. Anabolic steroids: Injected, ingested and applied to skin. Inhalants: Inhaled through nose or mouth. Anabolic steroids: used to help people with certain kinds of anemia and men who don t produce enough testosterone. Nitrous oxide (inhalant): used for anesthesia. Most inhalants are available in retail stores. Anabolic steroids are illegal, except by prescription. 18
23 Prescription Medications Products include Street Names CNS depressants: Barbiturates (Amytal, Nembutal, Seconal and Phenobarbital); benzodiazepines (Ativan, Halcion, Librium, Valium and Xanax); and sleep medications (Ambien, Sonata and Lunesta). Opioids and morphine derivatives: Codeine (Empirin with Codeine, Fiorinal with Codeine, Robitussin A-C, and Tylenol with Codeine); morphine (Roxanol and Duramorph); methadone (Methadose and Dolophine); fentanyl and analogs (Actiq, Duragesic, and Sublimaze); tramadol products; and other opioid pain relievers such as oxycodone HCL, hydrocodone, bitartrate, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, meperidine and propoxyphene (Tylox, OxyContin, Percodan, Percocet, Vicodin, Lortab, Lorcet, Dilaudid, Opana, Numporphan, Numorphone, Demerol, Meperidine Hydrochloride, Darvon and Darvocet). Stimulants: Amphetamines (Biphetamine, Dexedrine and Adderall); and methylphenidate (Concerta and Ritalin). Other: Dextromethorphan (DXM). Barbiturates: Barbs, reds, red birds, phennies, tooies, yellows, and yellow jackets. Benzodiazepines: Canday, downers, sleeping pills and tranks. Sleep medications: Forget-me pill, Mexican Valium, R2, Roche, roofies, roofinol, rophies. Codeine: Captain cody, cody, schoolboy, and (when mixed with glutethimide) doors and fours, loads, and pancakes and syrup. Morphine: M, Miss Emma, monkey, white stuff, mojo, mud, Mary, Murphy, and Mister Black. Methadone: Fizzies, amidone, dollies, and (with MDMA) chocolate chip cookies. Fentanyl and analogs: Apache, China girl, China white, dance fever, friend, goodfella, jackpot, murder 8, TNT, and tango and cash. 19
24 Street Names Continued Symptoms of use Potential consequences Other opioid pain relievers: Oxy, O.C., oxycotton, oxycet, hillbilly heroin, percs, vike, Watson-387, juice, smack, D, footballs, dillies, biscuits, blue heaven, blues, Mrs. O, octagons, stop signs, O bomb, demmies, and pain killer. Amphetamines: Bennies, black beauties, crosses, hearts, LA turnaround, speed, truck drivers, and uppers. Methylphenidate: JIF, MPH, R-ball, skippy, the smart drug, and vitamin R. Dextromethorphan (DXM): Robotripping, robo, and triple C. Depressants: Sedation/drowsiness, reduced anxiety, feelings of well-being, lowered inhibitions, slurred speech, poor concentration, confusion, dizziness, and impaired coordination and memory. (For barbiturates specifically: euphoria, unusual excitement, fever, and irritability.) Opioids and morphine derivatives: Pain relief, euphoria, drowsiness, dizziness, sedation, weakness, nausea, impaired coordination, confusion, dry mouth, itching, sweating, clammy skin, and constipation. Stimulants: Feelings of exhilaration; increased energy; and mental alertness. DXM: Euphoria and slurred speech. Depressants: Lowered blood pressure, slowed breathing, withdrawal, addiction, increased risk of respiratory distress, and death when combined with alcohol. (For barbiturates specifically: Life threatening withdrawal in chronic users.) Opioids and morphine derivatives: Slowed or arrested breathing, lowered pulse and blood pressure, high potential for addiction, heart or respiratory problems, mood swings, chronic constipation, tremors, toxic psychosis, HIV infection, unconsciousness, coma and death. Risk of death is increased when combined with alcohol or other CNS depressants. (For oxycodone specifically: Muscle relaxation that is twice as potent as analgesic or morphine, and high abuse potential.) (For methadone specifically: Significant overdose risk when used improperly.) 20
25 Potential consequences Continued How used Medical uses Legal status Stimulants: Increased heart rate, blood pressure and metabolism; chronic sleep problems; anxiety or nervousness; decreased emotional control; severe depression; reduced appetite; weight loss; nutritional deficiency; insomnia; seizures; heart attack; stroke; and death from heart failure or suicide. (For amphetamines specifically: Delirium, panic, paranoia, hallucinations, impulsive behavior, aggressiveness, and addiction.) (For methylphenidate specifically: Increase or decrease in blood pressure, digestive problems, loss of appetite, and weight loss.) DXM: Increased heart rate and blood pressure, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, confusion, paranoia, distorted visual perceptions, and impaired motor function. Depressants: Injected, ingested and sniffed. Opioids and morphine derivatives: Injected, ingested, smoked, sniffed, chewed, and via suppositories. Stimulants: Injected, ingested, smoked and sniffed. DXM: Ingested. CNS depressants: Used to treat anxiety and sleep problems. Opioids: Used to treat pain. Stimulants: Used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. DXM: Used in some cough and cold medicines. Select CNS depressants and opioids are legal by prescription only. DXM is not a controlled substance. 21
26 Stimulants Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status Cocaine, amphetamine, methamphetamine, Desoxyn, Dexedrine, Ionamin, methcathinone, biphetamine, and Tenuate. Cocaine: Coke, snow, blow, toot, C, candy, flake, bump, Charlie, crack, rock, and dust. Crack cocaine: Crack, rock, base, sugar block, and Rox/Roxanne. Amphetamines: Bennies, black beauties, crosses, hearts, LA turnaround, speed, truck, drivers, and uppers. Methamphetamines: Meth, ice, crank, chalk, crystal, fire, grass, go fast, and speed. Anxiety, excitability, euphoria, insomnia, sweating, tremors, dry mouth and lips, bad breath, weight loss, talkativeness, increased pulse rate, dilated pupils, paranoia, agitation, and hallucinations. High risk for addiction, violent or erratic behavior, hallucinations, high blood pressure, anxiety or nervousness, decreased emotional control, severe depression, cocaine psychosis, eating or sleeping disorders, impaired sexual performance, respiratory problems, collapse of the nasal septum, and death from cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest or suicide. Sniffed, injected, ingested and smoked. For narcolepsy, obesity, and hyperkinesis. Cocaine: Rarely used in hospital settings. Amphetamines: Pharmaceutical products are available only through a prescription that cannot be refilled. Methamphetamine: Desoxyn is the only legal meth product and is available only through a prescription that cannot be refilled. 22
27 Synthetic Drugs Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status Synthetic cannabinoids or marijuana: K2/Spice. Synthetic stimulants: MDPV and mephedrone. K2/Spice: Bliss, black momba, Bombay blue, fake week, genie, Spice, and zohai. MDPV and mephedrone: Meow meow, MCAT, drone, plant feeder, bubbles, bliss, blue silk, cloud nine, energy-1, ivory wave, lunar wave, ocean burst, pure ivory, purple wave, red dove, snow leopard, stardust, vanilla sky, white dove, white night, and white lightning. K2/Spice: Euphoria, sociability, and relaxation. MDPV and mephedrone: Increased alertness, sexual arousal, anxiety, agitation, diminished desire for food and sleep, euphoria, sociability, stimulation, and hallucinations. K2/Spice: Anxiety, paranoia, headache, vomiting, psychosis, diaphoresis, increased blood pressure and heart rate, and seizures. MDPV and mephedrone: Tachycardia, hypertension, vasoconstriction, diaphoresis, seizures, panic attacks, inability to open mouth, loss of appetite, increase in body temperature and sweating, increased blood pressure and heart rate, dehydration, insomnia, hallucinations, delusions, psychosis, depression, suicidal ideation, abstinence syndrome, and psychosis with high doses or frequent use. K2/Spice: Smoked and ingested. MDPV and mephedrone: Sniffed, ingested, smoked, injected and via suppositories. K2/Spice: None. MDPV and mephedrone: Found in retail products including bath salts, and has no approved medical use. K2/Spice: Available in convenience stores, at gas stations and on the internet; five synthetic cannabinoids are currently placed into Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act. MDPV and mephedrone: Found in retail products including bath salts. 23
28 Tobacco Products include Street Names Symptoms of use Potential consequences How used Medical uses Legal status Nicotine (cigarettes, cigars, bidis, smokeless tobacco, e-cigarettes, vaporizers, and hookah). Cigarettes: Smokes, cancer sticks, butts, and squares. Chewing tobacco: Dip, chew, snuff, and spit tobacco. Smelly hair, clothes, and breath; yellowing of teeth; coughs; increased asthma attacks; shortness of breath; increased blood pressure and heart rate; and poorer athletic performance. Addiction; respiratory problems such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis; heart and cardiovascular disease; stroke; acute myeloid leukemia; adverse pregnancy outcomes; and cancer of the lung, larynx, pharynx, stomach, cervix, esophagus, bladder, pancreas, kidney, and mouth. After only a few weeks, users of spit tobacco can develop cracked lips, white spots, sores, and bleeding in the mouth. Smoked (traditional, vaping, e-cigarette, or hookah), sniffed, and absorbed through mouth tissues. None. Illegal for youth under 19 in Alabama, Alaska, and Utah. Illegal for youth under 18 in all remaining States. 24
29 For more information, visit Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, MD SAMHSA s Store 877-SAMHSA-7 or (English and Español) (TTY) (FAX) 25
30 Additional Resources Talk. They Hear You. App KnowBullying App Stop Underage Drinking Too SMART To START Sound of Your Voice Guide: About-Alcohol/SMA Video: 26
31 27
32 HHS Publication No. (SMA) First printed Revised 2017
Street Drugs and Effects
 Street Drugs and Effects Substances: Category and Name Examples of Commercial and Street Names DEA Schedule*/ How Administered** ntoxication Side Effects/Principles of Drug Addiction Treatment Cannabinoids
Street Drugs and Effects Substances: Category and Name Examples of Commercial and Street Names DEA Schedule*/ How Administered** ntoxication Side Effects/Principles of Drug Addiction Treatment Cannabinoids
CARD TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff
 CARD 1 1. TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff 2. ALCOHOL: Beer, Wine, Liquor 3. MARIJUANA: Grass, Pot, Hashish, Hash, Hash Oil, Weed, Ganja, Marijuana Edibles
CARD 1 1. TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff 2. ALCOHOL: Beer, Wine, Liquor 3. MARIJUANA: Grass, Pot, Hashish, Hash, Hash Oil, Weed, Ganja, Marijuana Edibles
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Prescription Drug Abuse and Teens
 Prescription Drug Abuse and Teens 2 Abuse Facts The fourth most commonly misused type of addictive substance among teens in the United States is controlled prescription drugs The likelihood of misusing
Prescription Drug Abuse and Teens 2 Abuse Facts The fourth most commonly misused type of addictive substance among teens in the United States is controlled prescription drugs The likelihood of misusing
Many drugs of abuse are illegal drugs. Possessing, using, buying, or selling these drugs is illegal for people of any age.
 1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
Live A Life Above The Influence!
 Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
4 CATEGORIES. Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs
 DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
Week 15: Neurochemical Addiction. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology
 Week 15: Neurochemical Addiction Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology 1 Week 15 Topics Lecture 1: What is addiction? Factors mediating addiction Lecture 2: Commonly abused Drugs Mechanisms of addiction
Week 15: Neurochemical Addiction Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology 1 Week 15 Topics Lecture 1: What is addiction? Factors mediating addiction Lecture 2: Commonly abused Drugs Mechanisms of addiction
What Are Hallucinogens? (National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services)
 What Are Hallucinogens? (National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services) Hallucinogens are a diverse group of drugs that alter perception
What Are Hallucinogens? (National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services) Hallucinogens are a diverse group of drugs that alter perception
Non-prescription Drugs. Wasted Youth
 Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE
 DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
Substance Misuse and Abuse
 CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
QUESTION 1. What is a drug? ANSWER: A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel.
 What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1
 Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1 The Importance of Total Abstinence Abstinence from all substances that affect the brain even alcohol greatly increases the chances of a successful recovery. Matrix
Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1 The Importance of Total Abstinence Abstinence from all substances that affect the brain even alcohol greatly increases the chances of a successful recovery. Matrix
ALCOHOL, SMOKING AND ILLICIT DRUGS: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW IF YOU HAVE DIABETES
 LIFESTYLE ALCOHOL, SMOKING AND ILLICIT DRUGS: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW IF YOU HAVE DIABETES WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? The purpose of this leaflet is to inform you about the effects that alcohol, nicotine
LIFESTYLE ALCOHOL, SMOKING AND ILLICIT DRUGS: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW IF YOU HAVE DIABETES WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? The purpose of this leaflet is to inform you about the effects that alcohol, nicotine
Tobacco Notes. An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums)
 Tobacco Notes What is Tobacco? An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums) What Products have Tobacco in them? Cigarettes,
Tobacco Notes What is Tobacco? An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums) What Products have Tobacco in them? Cigarettes,
The Parents Back to School Kit Part 2 Kids and the misuse of Medications
 The Parents Back to School Kit Part 2 Kids and the misuse of Medications Prescription drugs and over the counter medications are the third most commonly misused substances (after alcohol and cannabis)
The Parents Back to School Kit Part 2 Kids and the misuse of Medications Prescription drugs and over the counter medications are the third most commonly misused substances (after alcohol and cannabis)
Using your Take Home Naloxone Kit
 Your kit contains naloxone, a medication that can restore breathing to someone having an overdose from opioid drugs. Inside the kit What is Naloxone? Naloxone is a medication that can reverse an overdose
Your kit contains naloxone, a medication that can restore breathing to someone having an overdose from opioid drugs. Inside the kit What is Naloxone? Naloxone is a medication that can reverse an overdose
Baseline Questions for Personal Feedback Report
 1. How old are you? years old (Q1) A. Marijuana Use We begin the Teen Marijuana Check-Up by asking about your experiences with marijuana. When we ask about marijuana, we are referring to marijuana or hashish
1. How old are you? years old (Q1) A. Marijuana Use We begin the Teen Marijuana Check-Up by asking about your experiences with marijuana. When we ask about marijuana, we are referring to marijuana or hashish
Substance Abuse. Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances.
 Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances. Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the overuse, or multiple use of a drug, use of
Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances. Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the overuse, or multiple use of a drug, use of
NIDA Quick Screen V1.0F1
 NIDA Quick Screen V1.0F1 Name:... Sex ( ) F ( ) M Age... Interviewer... Date.../.../... Introduction (Please read to patient) Hi, I m, nice to meet you. If it s okay with you, I d like to ask you a few
NIDA Quick Screen V1.0F1 Name:... Sex ( ) F ( ) M Age... Interviewer... Date.../.../... Introduction (Please read to patient) Hi, I m, nice to meet you. If it s okay with you, I d like to ask you a few
Drug Abuse in America. the United States in Now days there is a lot of help to prevent drug use, like anti drug
 1 Karla Campos Prof. Camille Pack English 2010 January 28, 2015 Drug Abuse in America Drugs are a major problem in American life, but not a new problem. Drugs have been a part of American history, humans
1 Karla Campos Prof. Camille Pack English 2010 January 28, 2015 Drug Abuse in America Drugs are a major problem in American life, but not a new problem. Drugs have been a part of American history, humans
Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
DRUNK DRIVING AND DRUGGED PREVENTION MONTH
 DRUNK DRIVING AND DRUGGED PREVENTION MONTH There are approximately 79,000 deaths from excessive alcohol use each year in the United States. Excessive alcohol use is the 3 rd leading lifestyle-related cause
DRUNK DRIVING AND DRUGGED PREVENTION MONTH There are approximately 79,000 deaths from excessive alcohol use each year in the United States. Excessive alcohol use is the 3 rd leading lifestyle-related cause
NIDA-Modified ASSIST Prescreen V1.0 1
 NIDA-Modified ASSIST Prescreen V1.0 1 F Name:... Sex ( ) F ( ) M Age... Interviewer... Date.../.../... Introduction (Please read to patient) Hi, I m, nice to meet you. If it s okay with you, I d like to
NIDA-Modified ASSIST Prescreen V1.0 1 F Name:... Sex ( ) F ( ) M Age... Interviewer... Date.../.../... Introduction (Please read to patient) Hi, I m, nice to meet you. If it s okay with you, I d like to
LEARN THE FACTS TO KEEP YOUR KIDS SAFE. Drug Free Kids Canada Where families come for help
 DRUG GUIDE FOR PARENTS: LEARN THE FACTS TO KEEP YOUR KIDS SAFE Drug Free Kids Canada Where families come for help It s important to know as much as possible about the drugs and other substances your pre-teens
DRUG GUIDE FOR PARENTS: LEARN THE FACTS TO KEEP YOUR KIDS SAFE Drug Free Kids Canada Where families come for help It s important to know as much as possible about the drugs and other substances your pre-teens
ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT
 ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT CLICKER SURVEY WHAT ARE DRUGS? A drug is an often illegal and sometimes addictive substance that causes changes in behavior and perception and is taken for it s effects. CATEGORIES
ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT CLICKER SURVEY WHAT ARE DRUGS? A drug is an often illegal and sometimes addictive substance that causes changes in behavior and perception and is taken for it s effects. CATEGORIES
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER:
 NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
SMS 32312
 0800 12 13 14 SMS 32312 Building a Caring Society. Together. THE SIGNS OF USING TIK... Building a Caring Society. Together. social development Department: Social Development REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA www.dsd.gov.za
0800 12 13 14 SMS 32312 Building a Caring Society. Together. THE SIGNS OF USING TIK... Building a Caring Society. Together. social development Department: Social Development REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA www.dsd.gov.za
Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996)
 APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
Chapter 23. Medicines and Drugs
 Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
Prescription Drugs MODULE 5 ALLIED TRADES ASSISTANCE PROGRAM. Preventative Education: Substance Use Disorder
 Prescription Drugs MODULE 5 ALLIED TRADES ASSISTANCE PROGRAM Preventative Education: Substance Use Disorder Misuse of prescription pain relievers is, after marijuana use, the second most common form of
Prescription Drugs MODULE 5 ALLIED TRADES ASSISTANCE PROGRAM Preventative Education: Substance Use Disorder Misuse of prescription pain relievers is, after marijuana use, the second most common form of
Pharming, the new way to party. Presented by: Carrie Terrill, LCDC
 Pharming, the new way to party Presented by: Carrie Terrill, LCDC The contents of your medicine cabinet may seem harmless, but have the potential to be dangerous, addictive, and even deadly. What is Pharming
Pharming, the new way to party Presented by: Carrie Terrill, LCDC The contents of your medicine cabinet may seem harmless, but have the potential to be dangerous, addictive, and even deadly. What is Pharming
NIDA-Modified ASSIST - Prescreen V1.0*
 NIDA-Modified ASSIST Assessment Instrument [1] NIDA-Modified ASSIST - Prescreen V1.0* *This screening tool was adapted from the WHO Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) Version
NIDA-Modified ASSIST Assessment Instrument [1] NIDA-Modified ASSIST - Prescreen V1.0* *This screening tool was adapted from the WHO Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test (ASSIST) Version
7th grade HEALTH- Chapter 11 9/15/2015
 Drugs and Alcohol Using Medicines Safely In this chapter, you will learn about Different types of medicines and their proper use. How alcohol affects the body. In this lesson, you will learn about Different
Drugs and Alcohol Using Medicines Safely In this chapter, you will learn about Different types of medicines and their proper use. How alcohol affects the body. In this lesson, you will learn about Different
Opioids and Heroin in Snohomish County. Marijuana and Opioid Prevention Training May 2018
 Opioids and Heroin in Snohomish County Marijuana and Opioid Prevention Training May 2018 OPIOIDS 101 What are Opioids? Opioids 101 Opium Poppy Plant Opiates: A type of pain medication that is naturally
Opioids and Heroin in Snohomish County Marijuana and Opioid Prevention Training May 2018 OPIOIDS 101 What are Opioids? Opioids 101 Opium Poppy Plant Opiates: A type of pain medication that is naturally
BELL WORK. Write how your life would change if you were addicted to drugs.
 BELL WORK Write how your life would change if you were addicted to drugs. REVIEW What are the two types of medicines? Prescription and over the counter Any effect of a medicine other than the one intended
BELL WORK Write how your life would change if you were addicted to drugs. REVIEW What are the two types of medicines? Prescription and over the counter Any effect of a medicine other than the one intended
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Please review the following slides prior to class. Information from these slides will be used to answer patient cases. Come prepared!
 Please review the following slides prior to class Information from these slides will be used to answer patient cases. Come prepared! Alcohol and Opiate Dependence Reference Slides Substances of Abuse A
Please review the following slides prior to class Information from these slides will be used to answer patient cases. Come prepared! Alcohol and Opiate Dependence Reference Slides Substances of Abuse A
The Affects of Drugs & Alcohol on the Nervous System
 The Affects of Drugs & Alcohol on the Nervous System How do drugs work? Drugs are chemicals or substances that change the way our bodies work. Enter the body through swallowing, inhaling or injecting)
The Affects of Drugs & Alcohol on the Nervous System How do drugs work? Drugs are chemicals or substances that change the way our bodies work. Enter the body through swallowing, inhaling or injecting)
Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Drug and Alcohol Impairment. Alabama DRE / SFST Program
 Drug and Alcohol Impairment Alabama DRE / SFST Program WHAT IS A DRUG? Working Definition of Drug : Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a
Drug and Alcohol Impairment Alabama DRE / SFST Program WHAT IS A DRUG? Working Definition of Drug : Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a
Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern. Chapter 12
 Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern Chapter 12 Introduction Use, misuse, and abuse of mind-altering substances predates recorded history Chronic alcohol and other drug abuse or dependence
Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern Chapter 12 Introduction Use, misuse, and abuse of mind-altering substances predates recorded history Chronic alcohol and other drug abuse or dependence
Guide to common drugs
 Guide to common drugs www.cambsdaat.org 1 This guide will help you to identify common drugs that you might come into contact with. It will show you what they look like It will tell you how they are usually
Guide to common drugs www.cambsdaat.org 1 This guide will help you to identify common drugs that you might come into contact with. It will show you what they look like It will tell you how they are usually
Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes.
 Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes. Illegal drugs- chemical substances that people of any age may not lawfully manufacture, possess, buy,
Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes. Illegal drugs- chemical substances that people of any age may not lawfully manufacture, possess, buy,
XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs. Alcohol
 XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs Alcohol Alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse in America. Use of alcohol may affect judgment and decision-making
XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs Alcohol Alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse in America. Use of alcohol may affect judgment and decision-making
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information
 Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
Defining Drugs. Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions
 Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
H NDS-ONHealth. Prescription Drug Abuse. Drug overdose death rates in the United States have more than tripled since 1990 and have never been higher.
 H NDS-ONHealth Health Wave Newsletter, October 2013 Visit us on our website at www.healthwaveinc.com Drug overdose death rates in the United States have more than tripled since 1990 and have never been
H NDS-ONHealth Health Wave Newsletter, October 2013 Visit us on our website at www.healthwaveinc.com Drug overdose death rates in the United States have more than tripled since 1990 and have never been
Drugs and the School Aged Child. Objectives. Substance Abuse. Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN. n List signs of drug use in children
 Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Club Drugs. Club Drugs na'unin4. Alan I. Leshner*
 CI 14 1 ill119111 2543 Club Drugs )L-0 03/474, 59 Club Drugs na'unin4 Alan I. Leshner* Abstract : Alan I. Leshner. 2000. Club drugs. Thai J Hlth Resch 14(1): 59-63. There are detecting alarming increases
CI 14 1 ill119111 2543 Club Drugs )L-0 03/474, 59 Club Drugs na'unin4 Alan I. Leshner* Abstract : Alan I. Leshner. 2000. Club drugs. Thai J Hlth Resch 14(1): 59-63. There are detecting alarming increases
CHARLOTTE-MECKLENBURG SCHOOLS 2017 STUDENT SURVEY
 Dear Student: Thank you for taking the 2017 CMS Student survey! This survey collects information about what students think about alcohol, drugs, and their school. It will only take about 20-25 minutes
Dear Student: Thank you for taking the 2017 CMS Student survey! This survey collects information about what students think about alcohol, drugs, and their school. It will only take about 20-25 minutes
teen drug use Percent of 12th-graders Who Used A Substance in the Past Month (Type of Drug & Prevalence): 13% 33% 11% 23%
 teen drug use As kids get older, they often start to question the life lessons they hear from parents and teachers. They become more heavily influenced by the things they see on TV, the Internet and social
teen drug use As kids get older, they often start to question the life lessons they hear from parents and teachers. They become more heavily influenced by the things they see on TV, the Internet and social
Role of Medicines. Chapter 19 Lesson 1
 Role of Medicines Chapter 19 Lesson 1 Types of Medicine Medicines drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions Drugs substances other than food that change the structure or function
Role of Medicines Chapter 19 Lesson 1 Types of Medicine Medicines drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions Drugs substances other than food that change the structure or function
Substance Abuse Awareness. What every parent needs to know
 Substance Abuse Awareness What every parent needs to know Introduction Frisco Independent School District continues to take a proactive stance on alcohol and drug prevention and intervention. The following
Substance Abuse Awareness What every parent needs to know Introduction Frisco Independent School District continues to take a proactive stance on alcohol and drug prevention and intervention. The following
Alcohol. Fits Hallucinations. Hallucinations Brain damage. Cirrhosis Gastritis. Diabetes Vomiting blood
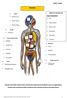 Alcohol. Brain Hallucinations Brain damage. Lungs Coughing Effects of Alcohol use Fits Hallucinations Headaches. Liver and pancreas Hepatitis 4 Numbness Vomiting Swollen liver 5 5. Stomach Ulcers Cirrhosis
Alcohol. Brain Hallucinations Brain damage. Lungs Coughing Effects of Alcohol use Fits Hallucinations Headaches. Liver and pancreas Hepatitis 4 Numbness Vomiting Swollen liver 5 5. Stomach Ulcers Cirrhosis
Lisa Booze, PharmD, CSPI
 Lisa Booze, PharmD, CSPI Psychoactive drugs created to avoid existing laws Modify existing drugs or new drugs with different chemical structures >200 new drugs and 8 classes of drugs since 2009 80 new
Lisa Booze, PharmD, CSPI Psychoactive drugs created to avoid existing laws Modify existing drugs or new drugs with different chemical structures >200 new drugs and 8 classes of drugs since 2009 80 new
Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs Unit Lesson One Indirect Sticky Sort
 Topic ATOD Vocabulary Duration 1-52 minute class period Purpose To activate prior knowledge of vocabulary used when discussing alcohol, tobacco and other drugs. Materials Large sheet of paper or poster
Topic ATOD Vocabulary Duration 1-52 minute class period Purpose To activate prior knowledge of vocabulary used when discussing alcohol, tobacco and other drugs. Materials Large sheet of paper or poster
National Council on Patient Information and Education
 National Council on Patient Information and Education You are not alone The type of pain that caused your doctor to prescribe a pain medicine for you can make you feel that you are different from everyone
National Council on Patient Information and Education You are not alone The type of pain that caused your doctor to prescribe a pain medicine for you can make you feel that you are different from everyone
Pinkston Psychology, LLC Ph. (318) Fx. (318) Completed this form Patient Spouse Parent Other
 Pinkston Psychology, LLC Ph. (318) 553-5099 paula@pinkstonpsychology.com Fx. (318) 553-5338 ADULT HISTORY FORM Date Completed this form Patient Spouse Parent Other Patient s Name Date of Birth Age Sex
Pinkston Psychology, LLC Ph. (318) 553-5099 paula@pinkstonpsychology.com Fx. (318) 553-5338 ADULT HISTORY FORM Date Completed this form Patient Spouse Parent Other Patient s Name Date of Birth Age Sex
Developed by Michelle Pasichnyk. Substance Abuse Prevention Health Promoter, Haldimand-Norfolk Health Unit 2008.
 1 2 Developed by Michelle Pasichnyk. Substance Abuse Prevention Health Promoter, Haldimand-Norfolk Health Unit 2008. Drug Categories... 4 Tobacco... 6 Alcohol... 10 Marijuana... 14 Other Drugs... 18 Addiction...
1 2 Developed by Michelle Pasichnyk. Substance Abuse Prevention Health Promoter, Haldimand-Norfolk Health Unit 2008. Drug Categories... 4 Tobacco... 6 Alcohol... 10 Marijuana... 14 Other Drugs... 18 Addiction...
Diagnostic Screening Tool
 Name: Section I: Mood Diagnostic Screening Tool than a 1. Little interest or pleasure in doing things? 2. Feeling down, depressed, or hopeless? If either of your answers to items 1 or 2 is greater than
Name: Section I: Mood Diagnostic Screening Tool than a 1. Little interest or pleasure in doing things? 2. Feeling down, depressed, or hopeless? If either of your answers to items 1 or 2 is greater than
Diagnostic Screening Tool
 Name: Section I: Mood Diagnostic Screening Tool than a half the 1. Little interest or pleasure in doing things? 2. Feeling down, depressed, or hopeless? If your answer to item 1 or 2 is greater than 1,
Name: Section I: Mood Diagnostic Screening Tool than a half the 1. Little interest or pleasure in doing things? 2. Feeling down, depressed, or hopeless? If your answer to item 1 or 2 is greater than 1,
What is the difference between Vicoden, OxyContin, Percocet and Percodan
 CHAPTER 5 DRUGS NARCOTICS Narcotics are drugs that induce sleep and relieve pain. The term narcotic is used incorrectly today for example the cocaine is labeled as a narcotic but is actually a stimulant
CHAPTER 5 DRUGS NARCOTICS Narcotics are drugs that induce sleep and relieve pain. The term narcotic is used incorrectly today for example the cocaine is labeled as a narcotic but is actually a stimulant
Research Paper 21/08/
 Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
national institute on drug abuse national institutes of health Revised
 national institute on drug abuse national institutes of health Revised Contents... What is marijuana? Are there different kinds? 2 How is marijuana used? 4 How long does marijuana stay in the user s body?
national institute on drug abuse national institutes of health Revised Contents... What is marijuana? Are there different kinds? 2 How is marijuana used? 4 How long does marijuana stay in the user s body?
Glencoe Health. Lesson 2 Marijuana, Inhalants, and Steroids
 Glencoe Health Lesson 2 Marijuana, Inhalants, and Steroids Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Three often-abused drugs that can have serious physical and mental side effects are marijuana, inhalants, and
Glencoe Health Lesson 2 Marijuana, Inhalants, and Steroids Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Three often-abused drugs that can have serious physical and mental side effects are marijuana, inhalants, and
The Art of being Human
 Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Drugs and the Brain. Sooren Moosavy and Vanessa Travieso
 Drugs and the Brain Sooren Moosavy and Vanessa Travieso What are drugs? DRUG: any substance which, when ingested in relatively small amounts, induces a physiological change LD50 lethal dose 50% = dose
Drugs and the Brain Sooren Moosavy and Vanessa Travieso What are drugs? DRUG: any substance which, when ingested in relatively small amounts, induces a physiological change LD50 lethal dose 50% = dose
STATS, FACTS & TALKING POINTS ABOUT ALCOHOL AND OTHER DRUGS PARENT ACTION PACK
 ARE YOU PREPARED TO HELP YOUR TEEN MAKE GOOD DECISIONS? STATS, FACTS & TALKING POINTS ABOUT ALCOHOL AND OTHER DRUGS PARENT ACTION PACK facebook.com/parentactionondrugs @PAD_Ontario YOU ARE YOUR TEEN S
ARE YOU PREPARED TO HELP YOUR TEEN MAKE GOOD DECISIONS? STATS, FACTS & TALKING POINTS ABOUT ALCOHOL AND OTHER DRUGS PARENT ACTION PACK facebook.com/parentactionondrugs @PAD_Ontario YOU ARE YOUR TEEN S
VANCOUVER POLICE DEPARTMENT BACKGROUND INVESTIGATION PROCESS: AUTOMATIC DISQUALIFIERS
 VANCOUVER POLICE DEPARTMENT BACKGROUND INVESTIGATION PROCESS: AUTOMATIC DISQUALIFIERS For All Non-Sworn Applicants (Excluding Police Service Technician (PST), Evidence Technician, Digital Evidence Cybercrime
VANCOUVER POLICE DEPARTMENT BACKGROUND INVESTIGATION PROCESS: AUTOMATIC DISQUALIFIERS For All Non-Sworn Applicants (Excluding Police Service Technician (PST), Evidence Technician, Digital Evidence Cybercrime
A. Definition and Categories of Drugs Instructor Led Presentations B. Incidence and Characteristics of Reading Assignments
 Briefly review the objectives, content and activities of this session. Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: Define the term drug in the context of this course. Name the seven
Briefly review the objectives, content and activities of this session. Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: Define the term drug in the context of this course. Name the seven
Current Drug Trends Among Youth. Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol
 Current Drug Trends Among Youth Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Inv. J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Troop C, Grand Island Investigative Services Drug Division BA 2006, C.J., UNL Joined
Current Drug Trends Among Youth Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Inv. J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Troop C, Grand Island Investigative Services Drug Division BA 2006, C.J., UNL Joined
Chapter 7. Depressants and Inhalants. Depressants & Inhalants. History: Before Barbiturates 10/1/2012
 Chapter 7 Depressants and Inhalants Depressants & Inhalants Depressants = drugs that slow activity in the central nervous system Include prescription drugs that treat anxiety (sedatives) and insomnia (hypnotics)
Chapter 7 Depressants and Inhalants Depressants & Inhalants Depressants = drugs that slow activity in the central nervous system Include prescription drugs that treat anxiety (sedatives) and insomnia (hypnotics)
CLUB DRUGS DESIGNER DRUGS
 Club drugs are being used by young adults at all-night dance parties such as "raves" or "trances," dance clubs, and bars. MDMA (Ecstasy), GHB, Rohypnol, Ketamine, Methamphetamine, and LSD are some Of the
Club drugs are being used by young adults at all-night dance parties such as "raves" or "trances," dance clubs, and bars. MDMA (Ecstasy), GHB, Rohypnol, Ketamine, Methamphetamine, and LSD are some Of the
CARD 1 ALASKAN NATIVE/ESKIMO/ALEUT AMERICAN INDIAN... 20
 CARD 1 ALASKAN NATIVE/ESKIMO/ALEUT... 10 AMERICAN INDIAN... 20 ASIAN OR ASIAN-AMERICAN Chinese... 30 (East) Indian... 31 Filipino... 32 Japanese... 33 Other (Specify):... 34 BLACK African American... 40
CARD 1 ALASKAN NATIVE/ESKIMO/ALEUT... 10 AMERICAN INDIAN... 20 ASIAN OR ASIAN-AMERICAN Chinese... 30 (East) Indian... 31 Filipino... 32 Japanese... 33 Other (Specify):... 34 BLACK African American... 40
DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES
 DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES In compliance the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for the illegal possession or distribution
DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES In compliance the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for the illegal possession or distribution
Sometimes the hardest thing and the right thing are the same Unknown
 National Substance Abuse Month Although we talk about substance abuse in other months, in May we address the problem from a more national, social, and systematic view. May is Trivia Month, you and your
National Substance Abuse Month Although we talk about substance abuse in other months, in May we address the problem from a more national, social, and systematic view. May is Trivia Month, you and your
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS. RG 5c
 PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
CANAM INTERVENTIONS. Addiction
 CANAM INTERVENTIONS Addiction PREVENTION RESEARCH FACTS The principles listed below are the result of long-term research studies on the origins of drug abuse behaviors and the common elements of effective
CANAM INTERVENTIONS Addiction PREVENTION RESEARCH FACTS The principles listed below are the result of long-term research studies on the origins of drug abuse behaviors and the common elements of effective
Drug Presentations. Biology Honors - Per. 1
 Drug Presentations Biology Honors - Per. 1 Alcohol-Classification What is it? Depressant Natural Drug Produced by fermentation of yeast, sugars, and starches Street names: booze, juice How it works: Consumed
Drug Presentations Biology Honors - Per. 1 Alcohol-Classification What is it? Depressant Natural Drug Produced by fermentation of yeast, sugars, and starches Street names: booze, juice How it works: Consumed
Tobacco can lead to harder drugs. Tobacco is often the first drug used by kids who use alcohol and illegal drugs like marijuana.
 Cigarettes (Smokes, Cigs, Butts. Smokeless Tobacco: Chew, Dip, Spit Tobacco, Snuff) Tobacco damages your health. Smoking is the most common cause of lung cancer. Smoking is also a leading cause of cancer
Cigarettes (Smokes, Cigs, Butts. Smokeless Tobacco: Chew, Dip, Spit Tobacco, Snuff) Tobacco damages your health. Smoking is the most common cause of lung cancer. Smoking is also a leading cause of cancer
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29
 PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
States of Consciousness Day 2
 States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
ONS/REC: 1 = WITHIN LAST 2 WEEKS 2 = 2 WEEKS TO < 1 MONTH 3 = 1 MONTH TO < 6 MONTHS 4 = 6 MONTHS TO < 1 YEAR 5 = 1 YEAR OR LONGER
 ONS/REC: 1 = WITHIN LAST 2 WEEKS 2 = 2 WEEKS TO < 1 MONTH 3 = 1 MONTH TO < 6 MONTHS 4 = 6 MONTHS TO < 1 YEAR 5 = 1 YEAR OR LONGER CARD_ONS.WPD: 05/01/2001 CARD A LIFE EVENTS Record these events on the
ONS/REC: 1 = WITHIN LAST 2 WEEKS 2 = 2 WEEKS TO < 1 MONTH 3 = 1 MONTH TO < 6 MONTHS 4 = 6 MONTHS TO < 1 YEAR 5 = 1 YEAR OR LONGER CARD_ONS.WPD: 05/01/2001 CARD A LIFE EVENTS Record these events on the
Suboxone Program FORMS PACKET
 51 Locust Street, Northampton, Massachusetts 01060 Suboxone Program FORMS PACKET 413 584 SICK Please fill this out and drop it off at 51 Locust Street in Northampton. It will be reviewed by our Suboxone
51 Locust Street, Northampton, Massachusetts 01060 Suboxone Program FORMS PACKET 413 584 SICK Please fill this out and drop it off at 51 Locust Street in Northampton. It will be reviewed by our Suboxone
Table 1: Middlesex League s High School Responses with Comparisons to Commonwealth and Nation Middlesex League MA U.S.
 Table 1: Middlesex League s High School Responses with Comparisons to Commonwealth and Nation Middlesex League MA U.S. n % % % UNINTENTIONAL INJURY AND VIOLENCE Rode with a driver who had been drinking
Table 1: Middlesex League s High School Responses with Comparisons to Commonwealth and Nation Middlesex League MA U.S. n % % % UNINTENTIONAL INJURY AND VIOLENCE Rode with a driver who had been drinking
Hallucinogens Marijuana
 Introduction A drug is defined as a natural or synthetic substance that is used to produce physiological or psychological effects in humans or other higher order animals. Narcotic drugs are analgesics,
Introduction A drug is defined as a natural or synthetic substance that is used to produce physiological or psychological effects in humans or other higher order animals. Narcotic drugs are analgesics,
Alcohol and Drug Abuse Prevention Handbook
 2016 Alcohol and Drug Abuse Prevention Handbook OHIO CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY OFFICE OF STUDENT DEVELOPMENT 1 Table of Contents Substance Abuse Policies... 2 Employee Policy... 2 Drug Testing... 2 Undergraduate
2016 Alcohol and Drug Abuse Prevention Handbook OHIO CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY OFFICE OF STUDENT DEVELOPMENT 1 Table of Contents Substance Abuse Policies... 2 Employee Policy... 2 Drug Testing... 2 Undergraduate
What are they? Why do people take these drugs?
 What are they? Legal or illegal highs, head shop or herbal highs are names given to psychoactive substances (drugs) that may be on sale in Ireland through shops that sell drug-related products (head shops,
What are they? Legal or illegal highs, head shop or herbal highs are names given to psychoactive substances (drugs) that may be on sale in Ireland through shops that sell drug-related products (head shops,
What is a DRE. Introduction to Drugged Driving
 Introduction to Drugged Driving What is a DRE DRE Training & Certification For a list of classes scheduled in 2016, click here. The DEC Program trains police officers and other approved public safety officials
Introduction to Drugged Driving What is a DRE DRE Training & Certification For a list of classes scheduled in 2016, click here. The DEC Program trains police officers and other approved public safety officials
3. What is the most common form in which tobacco is used? Name three other tobacco products.
 Chapter 13 lesson 1: 1. What is nicotine? 2. Identify and describe the risks associated with three harmful substances found in all forms of tobacco. 3. What is the most common form in which tobacco is
Chapter 13 lesson 1: 1. What is nicotine? 2. Identify and describe the risks associated with three harmful substances found in all forms of tobacco. 3. What is the most common form in which tobacco is
THE OPIATE EPIDEMIC AND LIBRARIES. Presented by Dr. Steve Albrecht, PHR, CPP, BCC, CTM
 THE OPIATE EPIDEMIC AND LIBRARIES Presented by Dr. Steve Albrecht, PHR, CPP, BCC, CTM DrSteve@DrSteveAlbrecht.com 866-261-5150 @DrSteveAlbrecht REALITY IS NOT A RIVER IN EGYPT... Some Caveats... I m not
THE OPIATE EPIDEMIC AND LIBRARIES Presented by Dr. Steve Albrecht, PHR, CPP, BCC, CTM DrSteve@DrSteveAlbrecht.com 866-261-5150 @DrSteveAlbrecht REALITY IS NOT A RIVER IN EGYPT... Some Caveats... I m not
Main Questions. Why study addiction? Substance Use Disorders, Part 1 Alecia Schweinsburg, MA Abnromal Psychology, Fall Substance Use Disorders
 Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Teens Living with Epilepsy
 Teens Living with Epilepsy If you are a kid, please see the other side of this brochure. www.keppra.com 2005, UCB Pharma, Inc., Smyrna, GA 30080 All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. K1599-0505 Introduction
Teens Living with Epilepsy If you are a kid, please see the other side of this brochure. www.keppra.com 2005, UCB Pharma, Inc., Smyrna, GA 30080 All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. K1599-0505 Introduction
Identifying the Drug Impaired Person Sgt. Jeff Chapman
 Identifying the Drug Impaired Person Sgt. Jeff Chapman 9/13/2017 1 About Officer Chapman Phoenix Police Department National Association of Field Training Officers 9/13/2017 2 Course Overview Drug categories
Identifying the Drug Impaired Person Sgt. Jeff Chapman 9/13/2017 1 About Officer Chapman Phoenix Police Department National Association of Field Training Officers 9/13/2017 2 Course Overview Drug categories
Alcohol WE ASK EVERYONE. Did you know? Something to try: Mixing prescriptions with alcohol or over-the-counter drugs can be dangerous!
 Did you know? Mixing prescriptions with alcohol or over-the-counter drugs can be dangerous! It can cause a drop in heart rate and breathing It can increase risk of overdose and death Something to try:
Did you know? Mixing prescriptions with alcohol or over-the-counter drugs can be dangerous! It can cause a drop in heart rate and breathing It can increase risk of overdose and death Something to try:
10 Questions to Ask. Before You Use Marijuana
 10 Questions to Ask Before You Use Marijuana 1 You ve probably heard conflicting opinions about marijuana and its risks. The health information included here is based on recent studies done by researchers
10 Questions to Ask Before You Use Marijuana 1 You ve probably heard conflicting opinions about marijuana and its risks. The health information included here is based on recent studies done by researchers
Club Drugs. Key Messages. D. Deitch, PhD Emeritus Professor of Psychiatry UCSD - CCARTA
 Club Drugs D. Deitch, PhD Emeritus Professor of Psychiatry UCSD - CCARTA Key Messages 1. Our concern is for health and safety. 2. Not using is safest. 3. If you do use, there are ways to reduce harm. 4.
Club Drugs D. Deitch, PhD Emeritus Professor of Psychiatry UCSD - CCARTA Key Messages 1. Our concern is for health and safety. 2. Not using is safest. 3. If you do use, there are ways to reduce harm. 4.
