Use of percutaneous needle biopsy in the investigation
|
|
|
- Ethelbert Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thorax 1987;42: Use of percutaneous needle biopsy in the investigation of solitary pulmonary nodules A R L PENKETH, A A ROBINSON, V BARKER, C D R FLOWER From the East Anglian Regional Cardiothoracic Unit, Papworth Hospital, Cambridge ABSTRACT Percutaneous needle biopsies were performed on 683 patients with solitary pulmonary nodules during A cytological diagnosis of malignancy was made from the first biopsy in 473 patients (69%). A second biopsy was performed in 43 patients, a diagnosis of malignancy being made in a further 16 cases (37%). Histological material was available for comparison with cytological findings in 203 patients. Cytological examination was reliable in the diagnosis of malignancy with a high yield (75%) and low false positive rate (1-5%). Specific benign lesions were correctly diagnosed in 10 patients (1 5%). There was a false negative rate for the diagnosis of malignancy of 18% for the patients with a subsequent histological diagnosis. This compares with a false negative rate of 9% overall; the true rate probably lies between these figures. These results imply that a cytology report indicating no evidence of malignancy, but not diagnostic of a specific benign condition, does not reliably exclude a malignant lesion. In this series cytological typing was not accurate at predicting the cell type determined by histological examination (61% agreement) and was not able to discriminate between small cell and non-small cell lung cancer. Introduction Percutaneous needle biopsy is commonly used in the investigation of pulmonary nodules that are unlikely to be visualised bronchoscopically.' Most clinicians use some form of fine gauge needle to provide a sample, which is adequate for microbiological and cytological examination but rarely for histological examination. To assess the role of this technique in the management of patients with solitary pulmonary nodules, we have reviewed our experience retrospectively and determined the diagnostic yield and accuracy of cytology in our unit. Methods The records of all patients undergoing percutaneous needle biopsy at Papworth Hospital in the period I January December 1984 were examined and the results of cytological examination of needle biopsy specimens and, where available, subsequent his- Address for reprint requests: Dr C D R Flower, Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge. Accepted 3 August 1987 tological examination of surgical or necropsy specimens were noted. Biopsies were performed by a consultant radiologist or radiologists in training; they used a fine gauge (20 G or 22 G) aspirating needle or a 21 G Rotex screw biopsy needle (Ursus Konsult) and the material obtained was used to make a cytology smear preparation. One to three passes were made, the number depending on the appearance of the smear and the ease with which the lesion was sampled. All biopsies were of intrapulmonary masses that measured I cm or more in diameter on the chest radiograph. Fluoroscopic guidance was used as described previously.2 The material obtained was examined by the same cytopathologist (VB) and classified as being malignant, as showing a specific benign condition such as a hamartoma, or as showing "no evidence of malignancy." Tumours were subdivided into five groups: (I) squamous carcinoma; (2) adenocarcinoma; (3) undifferentiated tumour; (4) small cell tumours; (5) other tumours. Any tumour that could not be specifically typed was classified as an undifferentiated tumour. Results CLINICAL OUTCOME Percutaneous needle biopsies were performed on
2 968 Penketh, Robinson, Barker, Flower patients over a nine year period. Figure 1 s5ummarises performed on 10 patients with inoperable lesions, so the fate of all patients in this study. ) A positive that 150 cases diagnosed as malignant by needle diagnosis of malignancy was made fronn the first biopsy had histological material for comparison with biopsy in 473 patients (69%). Of these 47'3 patients, cytological specimens. There were three false positives: 140 had a thoracotomy. The remainder were con- patients with a pseudolymphoma and an eosinophilic sidered inoperable for reasons of age, lung fiunction, or granuloma were misdiagnosed as having undifferen- tiated carcinoma from the cytological specimens and a evidence of metastases. A necropsy was subsequently pulmonary infarct was misdiagnosed as squamous 683 carcinoma. Needle biopsy cytology result An inadequate specimen was obtained from two patients (0 3%), in whom the procedure was not Malignant /\ 473 Thoracotomy* Palliative 140 treatment 333 Fig 1 Diagnosis made by other investigations 19 Malignant Benign 12 7 Inadequate specimen Procedure not repeated 2 (0 3%) Specific benign diagnosis 10 (1 5%) 198 Cytology no evidence of malignancy Cytology 16 Thoracotomy Palliative 3 treatment 13 Thoracotomy 42 Malignant' Benign' malignant Thoracotomy 16) or necropsy 12) Malignant' Benign' 5 3 Cytolc eviden Repeat needle biopsy 1 malignant repeated as the original radiographic abnormalities resolved. A definite diagnosis of a benign condition was made by needle biopsy in 10 patients (I -5%). Five had tuberculosis diagnosed by culture of the organisms, one a mycetoma, one a rheumatoid nodule, and three hamartomas. Subsequent radiographic follow up of these patients for at least two years showed either No evi ence no change in appearance or resolution of the lesion. of malignancy A needle biopsy cytology report with "no evidence 198 (29%) of malignancy" but no specific diagnosis was obtained in 198 patients (29%). Figure 2 shows the further management of this group of patients. A diagnosis was obtained from other investigations in 19 patients (sputum cytology, bronchoscopy, culture of aspirated Necropsy* material, or radiographic follow up). Twelve of the 10 patients had inoperable malignant lesions while seven Outcome in 683 patients who had a needll e biopsy. had treatable infections or lesions that resolved on subsequent radiographs. Clinical suspicion of malignancy was sufficient to proceed directly to thoracotomy in 42 patients, 28 of whom did have a malignant lesion while 14 had benign conditions. In 94 patients (47%) the negative needle biopsy cytology No treatment Follow up report was compatible with the clinical features 43 > and radiographic appearances, and the result was accepted. Follow up of these patients is incomplete as some were discharged to the care of their general practitioner while others were followed up in hospital clinics, but none is known to have developed or died c no from lung cancer. A second needle biopsy was peric fmalignancy 27 formed in 43 patients, yielding a positive diagnosis of malignancy in 16 (37%), three of whom had operable lesions. Of the remaining 27 patients with two negative needle biopsy results, 18 were not investigated further and one had a positive third needle biopsy. Histological material was available from thoracotomy or necropsy for eight patients of this group of 27, five of No treatment Follow up 18 Fig 2 Management and outcome in the 198 patients whose first needle biopsy specimens were reported to show no evidence ofmalignancy. whom had a malignant lesion. VALUE OF NEEDLE BIOPSY In this series of 683 patients there were 1 12 patients in whom one or two needle biopsies provided no evidence of malignancy and who were assumed to have a benign lesion on the basis of radiographic and clinical
3 Use ofpercutaneous needle biopsy in the investigation ofsolitary pulmonary nodules Table I Accuracy of cytological diagnosis ofmalignant and benign lesions from percutaneous needle biopsy specimens compared with histological diagnosis in 203 patients who underwent the two procedures No (%) of Cytology No of patients with report patients histological confirmation Malignant (98) No evidence of malignancy (32) Total (81) condition at follow up. Three hundred and thirty three patients who had a cytological diagnosis of malignancy were considered inoperable and had no necropsy. It is against this background that the overall estimates of false positive rate (three patients, 0 4%) and false negative rate (62 patients, 9%) must be viewed. Cytology results from the needle biopsies were compared with the histological diagnosis made in the 203 cases where surgical or necropsy material was available (tables 1 and 2). A cytological report of malignancy was made in 150 cases and was correct in all but three, giving a false positive rate in these 150 cases of 1[5%. Of the 53 patients who had no cytological evidence of malignancy, 36 had histological evidence of malignancy, giving a false negative rate of 36 in 203 (18%). The overall agreement of cytology with histology in the diagnosis of malignancy was 81%. ACCURACY OF CELL TYPING OF TUMOURS Table 2 compares the cell type reports on cytological specimens from the first needle biopsy of malignant lesions compared with the subsequent histological diagnosis based on thoracotomy or necropsy material Table 2 Cell type reportsfrom needle biopsy specimens in 150 patients with malignant lesions diagnosed cytologically compared with histological diagnosis No (%) ofpatients Cytology No of with this cell type report* patients diagnosed histologically Squamous cell carcinoma (67) Adenocarcinoma (85) Undifferentiated carcinoma 19 1 (5) Small cell 4 1 (25) Other malignancies 10 9 (90) Total (61) *First needle biopsy. 969 There was agreement in 91 of the 150 cases (61 %) overall. Cytology was most accurate in the diagnosis of adenocarcinoma, 17 out of 20 patients being diagnosed correctly (85%); the other patients had a squamous cell carcinoma (1) or rare tumours (2). Sixty seven per cent of those reported as having squamous cell carcinomas were diagnosed correctly from cytology specimens, the other 32 patients having adenocarcinoma (24), undifferentiated tumours (2), anaplastic tumours (2), clear cell tumours (2), transitional cell carcinoma (1), and a pulmonary infarct. Nineteen tumours were classified cytologically as undifferentiated but only one (5%) was confirmed as such from histological appearances. The other 18 patients had squamous cell carcinoma (7), adenocarcinoma (6), benign lesions (2), and rare tumours (3). Cytology was poor for diagnosing small cell carcinoma of the bronchus; of four cases with this cytological diagnosis, only one had the diagnosis confirmed histologically and a further histologically proved case had been diagnosed as lymphosarcoma by cytology. Nine out of 10 other specific tumours were correctly diagnosed by cytology. REPEAT NEEDLE BIOPSIES A second needle biopsy was performed in 43 of the 198 patients with no evidence of malignancy from the first biopsy. The yield of malignancy at the second biopsy was 37% (16 cases, three confirmed at thoracotomy). There was no evidence of malignancy in 27 patients, six ofwhom were subsequently found to have cancer at thoracotomy, necropsy, or further lung biopsy (fig 2). The false negative rate for the second biopsy was 14%. Discussion Percutaneous aspiration needle biopsy of the lung has become more widely used with the advent of fluoroscopy and image intensification.3 A limited amount of material is obtained, which is usually adequate only for microbiological or cytological examination. The latter may be technically difficult if the sample is distorted in the process of biopsy or during the preparation of the specimen, so that appearances may differ from those seen in exfoliative cytological preparations.4 The usefulness of this technique in the investigation of pulmonary nodules depends on the ability to differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, thereby obviating the need for an exploratory thoracotomy. In this series a specific benign diagnosis was made in only 10 patients (1-5%). This figure may be artificially low as most patients with infections, many of whom are immunosuppressed, are inves-
4 970 Table 3 Distribution ofcell types oflung cancer reported for needle biopsy cytology specimensfrom 473 patients compared with results in the subgroup of 150 casesfor whom histological diagnosis was later available % ofneedle % with this cell biopsy specimens type diagnosed with this cytologically who diagnosis later had thoracotomy Cell type (n = 473) or necropsy (n = ISO) Squamous cell carcinoma Undifferentiated carcinoma Adenocarcinoma Small cell or other tumours 6 7 tigated by needle biopsy at another site in our district and have not been included in this series. Most negative cytological samples in this series were simply described as showing "no evidence of malignancy." The estimated false negative rate overall was 9%, but in the group for whom histological material was available for comparison (203 of the 683 patients) the false negative rate was 18%. The former figure may therefore be an underestimate as the diagnosis of a benign lesion was presumptive in 112 patients. The figure of 18% may be too high, however, since all patients in whom there was a suspicion of malignancy despite a negative cytology report were sent for thoracotomy, while those with a low index of suspicion were not investigated further. The true false negative rate probably lies between the two figures; this would compare with figures quoted by other authors-that is, from 5% to 16%."' If cytological specimens could have been prepared and examined immediately at the time of biopsy the yield would probably have been improved and the need for repeated biopsies reduced. Unfortunately this facility is not available in our unit. None of the false negative results were due to inadequacy of the specimens for cytological purposes, although this had been a common cause of false negatives in other series. The false positive rate in this series was low, from 0 4% to 1-5%, although other authors have had no false positives."79 Forty two of our patients had a second needle biopsy, with a 37% yield of malignancy. Sargent et ar performed second biopsies in 44 cases with a yield of 45% and third biopsies in 16 cases with a yield of 56%. These authors and others'" have suggested that at least three attempts should be made before a lesion is considered to be benign, although no details of their false negative rates from repeat attempts were given. In our series the false negative rate of first and second attempts was fairly similar and we would suggest that, if adequate material has been obtained, other forms of investigation should be considered if there is clinical suspicion of malignancy Penketh, Robinson, Barker, Flower in the presence of a negative needle biopsy result. In summary, our results suggest that, if a positive diagnosis of malignancy or of a specific benign condition is made cytologically from a percutaneous needle biopsy specimen of a pulmonary nodule, the result is reliable. A non-specific negative result, however, cannot be relied on. The second role for needle biopsy in the investigation of pulmonary nodules is to provide a histological diagnosis on the basis of which a decision can be made about palliative treatment in those patients with cancer for whom surgery is not an option. Payne et ap showed that needle biopsy material is not as accurate at predicting cell type as other biopsy material. In their large study there was agreement of needle biopsy cytology with histology in 62%, similar to the 61% in the present series (the patients in the present series seen during are included in the series of Payne et al). Only 150 of the 473 cases with a needle biopsy cytology report of malignancy, however, had histological material available for comparison in the present series, 32% of the group. There is obviously room for error if the distribution of cell type in this subgroup is not representative of the group as a whole. Table 3 shows the distribution of the cell type of tumour diagnosed at cytology in the whole group of 473 patients and the subgroup of 150 who later had surgery or necropsy. In the latter group there is a higher percentage of squamous cell carcinoma and a lower percentage of adenocarcinoma than in the group as a whole. One major error of cytology compared with histology was the misdiagnosis of adenocarcinoma as squamous cell carcinoma. The other error was in misdiagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma as undifferentiated tumour. The proportion of undifferentiated tumours and small cell tumours diagnosed cytologically was relatively constant in the two groups. Rudd et all'0 compared the accuracy of diagnosis of small cell tumours by needle and bronchial biopsy techniques and found that it was reliable by both methods. We have found, however, that needle biopsy cytology is not accurate in the diagnosis of small cell carcinoma, although our group with this cell type was extremely small. We are grateful to Dr JE Stark, Dr JM Shneerson, and Dr TW Higenbottam for allowing us to report on their patients and for their advice. We also thank Dr PGI Stovin for his advice and Mrs Karin Frans for typing the manuscript. References 1 MacFarlane J. Lung Biopsy [editorial]. Br Med J 1985;290: Flower CDR, Verney GI. Percutaneous needle biopsy of
5 Use ofpercutaneous needle biopsy in the investigation ofsolitary pulmonary nodules thoracic lesions-an evaluation of 300 biopsies. Clin Radiol 1979;30: Dahlgren S, Nordstrom B. Transthoracic needle biopsy. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers, Payne CR, Hadfield JW, Stovin PGI, Barker V, Heard B, Stark JE. Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in primary bronchial carcinoma. J Clin Pathol 198 1;34: Winning AJ, Mclvor J, Seed WA, Husain OAN, Metaxas N. Interpretation of negative results in fine needle aspiration of discrete pulmonary lesions. Thorax 1986; 41: Nordstrom B. Technical aspects of obtaining cellular 971 material from lesions deep in the lung. Acta Cytol 1984;28: Sargent EN, Turner AF, Gordonson J, Schwinn CP, Pashky 0. Percutaneous pulmonary needle biopsy. Am J Roenigenol 1974;122: Allison DJ, Hemingway P. Percutaneous needle biopsy of the lung. Br Med J 198 1;282: Dick R, Heard BE, Huson KFW, Kerr IH, Pearson MC. Aspiration needle biopsy of thoracic lesions: an assessment of 227 biopsies. Br J Dis Chest 1974;68: Rudd RM, Gellert AR, Boldy DAR, etal. Bronchoscopic and percutaneous aspiration biopsy in the diagnosis of bronchial carcinoma cell type. Thorax 1982;37: Thorax: first published as /thx on 1 December Downloaded from on 8 March 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 294-299 Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in primary bronchial carcinoma C R PAYNE, P G I STOVIN, V BARKER, S McVITTIE, AND J E STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard,
Thorax, 1979, 34, 294-299 Diagnostic accuracy of cytology and biopsy in primary bronchial carcinoma C R PAYNE, P G I STOVIN, V BARKER, S McVITTIE, AND J E STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard,
came from a carcinoma and in 12 from a sarcoma. Ninety lesions were intrapulmonary and the as the chest wall and pleura. Details of the primary
 Thorax 1982;37:366-370 Thoracic metastases MARY P SHEPHERD From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Harefield ABSTRACI One hundred and four patients are reviewed who were found to have thoracic
Thorax 1982;37:366-370 Thoracic metastases MARY P SHEPHERD From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Harefield ABSTRACI One hundred and four patients are reviewed who were found to have thoracic
Electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules
 Original article Electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules Samuel Copeland MD, Shrinivas Kambali MD, Gilbert Berdine MD, Raed Alalawi MD Abstract Background:
Original article Electromagnetic navigational bronchoscopy in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules Samuel Copeland MD, Shrinivas Kambali MD, Gilbert Berdine MD, Raed Alalawi MD Abstract Background:
Carcinoma of the Lung
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
MATERIALS AND METHODS. We retrospectively reviewed a consecutive series
 Huanqi Li1 Phillip M. Boiselle1 2 Jo-Anne 0. Shepard1 Beatrice Trotman-Dickenson1 Theresa C. McLoud1 Received January 2, 1996; accepted after revision Febru ary 19, 1996. tchest Division, Department of
Huanqi Li1 Phillip M. Boiselle1 2 Jo-Anne 0. Shepard1 Beatrice Trotman-Dickenson1 Theresa C. McLoud1 Received January 2, 1996; accepted after revision Febru ary 19, 1996. tchest Division, Department of
Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit
 Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
Page1 Original Article NJR 2011;1(1):1 7;Available online at www.nranepal.org Diagnostic and Complication Rate of Image-guided Lung Biopsies in Raigmore Hospital, Inverness: A Retrospective Re-audit S
Improved Diagnostic Efficacy by Rapid Cytology Test in Fluoroscopy-Guided Bronchoscopy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Diagnostic Efficacy by Rapid Cytology Test in Fluoroscopy-Guided Bronchoscopy Junji Uchida, MD, Fumio Imamura, MD, Akemi Takenaka, CT, Mana Yoshimura, MD, Kiyonobu Ueno, MD, Kazuyuki
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Diagnostic Efficacy by Rapid Cytology Test in Fluoroscopy-Guided Bronchoscopy Junji Uchida, MD, Fumio Imamura, MD, Akemi Takenaka, CT, Mana Yoshimura, MD, Kiyonobu Ueno, MD, Kazuyuki
Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center
 Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center Ala Qayet MD*, Laith Obaidat MD**, Mazin Al-Omari MD*, Ashraf Al-Tamimi MD^, Ahmad
Pneumothorax Post CT-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy for Lung Nodules: Our Experience in King Hussein Medical Center Ala Qayet MD*, Laith Obaidat MD**, Mazin Al-Omari MD*, Ashraf Al-Tamimi MD^, Ahmad
VOLUME 19 NUMBER 2 * FEBRUARY 1975
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 9 NUMBER 2 * FEBRUARY 975 Medias tinoscopy Its Application in Central Versus
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 9 NUMBER 2 * FEBRUARY 975 Medias tinoscopy Its Application in Central Versus
May-Lin Wilgus. A. Study Purpose and Rationale
 Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
Utility of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis Program in the Evaluation of Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Detected on Computed Tomography Scans: A Prospective Observational Study May-Lin Wilgus A. Study Purpose and
Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions
 Original article: Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions *Dr.Prasanthi cherukuri 1, Dr.B.V.Madhavi 2 1Assitant Proferssor, Gitam institute of Medical sciences and research,visakhapatnam,
Original article: Concordance of cytology and histopathology of intra-thoracic lesions *Dr.Prasanthi cherukuri 1, Dr.B.V.Madhavi 2 1Assitant Proferssor, Gitam institute of Medical sciences and research,visakhapatnam,
Transbronchial fine needle aspiration
 Thorax 1982;37 :270-274 Transbronchial fine needle aspiration J LEMER, E MALBERGER, R KONIG-NATIV From the Departments of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and Cytology, Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel ABSTRACT
Thorax 1982;37 :270-274 Transbronchial fine needle aspiration J LEMER, E MALBERGER, R KONIG-NATIV From the Departments of Cardio-thoracic Surgery and Cytology, Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel ABSTRACT
Review of Literatures
 Review of Literatures Fine needle biopsy was popular in the Scandinavian countries some four decades ago. Though FNAC for any palpable tumor was first introduced in America in the 1920s by Martin, Ellis
Review of Literatures Fine needle biopsy was popular in the Scandinavian countries some four decades ago. Though FNAC for any palpable tumor was first introduced in America in the 1920s by Martin, Ellis
PERCUTANEOUS CT GUIDED CUTTING NEEDLE BIOPSY OF LUNG LESIONS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE PERCUTANEOUS CT GUIDED CUTTING NEEDLE BIOPSY OF LUNG LESIONS Abdur Rehman Khan, Arshad Javed, Mohammad Ejaz Department of Radiology and Department of Pulmonology, Postgraduate Medical
ORIGINAL ARTICLE PERCUTANEOUS CT GUIDED CUTTING NEEDLE BIOPSY OF LUNG LESIONS Abdur Rehman Khan, Arshad Javed, Mohammad Ejaz Department of Radiology and Department of Pulmonology, Postgraduate Medical
Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions
 Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Walter J. McCarthy, M.D., Miriam L. Christ, M.D., and Willard A. Fry, M.D. ABSTRACT Forty-one intraoperative fine needle aspiration biopsies
Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Walter J. McCarthy, M.D., Miriam L. Christ, M.D., and Willard A. Fry, M.D. ABSTRACT Forty-one intraoperative fine needle aspiration biopsies
Percutaneous Needle Aspiration Biopsy (PCNA) of Pulmonary Lesions: Evaluation of a Reaspiration or a Rebiopsy (second PCNA) 1
 Percutaneous Needle Aspiration Biopsy (PCNA) of Pulmonary Lesions: Evaluation of a Reaspiration or a Rebiopsy (second PCNA) 1 In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Ki-Suck Jung, M.D. 2, Hyoung June Im,
Percutaneous Needle Aspiration Biopsy (PCNA) of Pulmonary Lesions: Evaluation of a Reaspiration or a Rebiopsy (second PCNA) 1 In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Ki-Suck Jung, M.D. 2, Hyoung June Im,
Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis)
 Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
Diagnostic Value of EBUS-TBNA in Various Lung Diseases (Lymphoma, Tuberculosis, Sarcoidosis) Sevda Sener Cömert, MD, FCCP. SBU, Kartal Dr.Lütfi Kırdar Training and Research Hospital Department of Pulmonary
bronchopleural fistula
 Role of automatic staplers in the aetiology of bronchopleural fistula MOHSIN HAKIM, BB MILSTEIN From the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Papworth Hospital, Cambridge Thorax 1985;40:27-31 ABSTRACT
Role of automatic staplers in the aetiology of bronchopleural fistula MOHSIN HAKIM, BB MILSTEIN From the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Papworth Hospital, Cambridge Thorax 1985;40:27-31 ABSTRACT
Diagnosing Non-small Cell Carcinoma In Small Biopsy And Cytology READ ONLINE
 Diagnosing Non-small Cell Carcinoma In Small Biopsy And Cytology READ ONLINE Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [Staging of non-small cell lung cancer. Diagnosis efficacy of structural (CT) and functional
Diagnosing Non-small Cell Carcinoma In Small Biopsy And Cytology READ ONLINE Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [Staging of non-small cell lung cancer. Diagnosis efficacy of structural (CT) and functional
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ARM Fauzi, MRCP*, L Balakrishnan MRCP**, MY Rathor MD* Introduction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Usefulness of Cytological Specimens from Bronchial Brushings and Bronchial Washings in Addition to Endobronchial Biopsies During Bronchoscopy for Lung Cancer: 3 Years Data from a Chest
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Usefulness of Cytological Specimens from Bronchial Brushings and Bronchial Washings in Addition to Endobronchial Biopsies During Bronchoscopy for Lung Cancer: 3 Years Data from a Chest
Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy: Correlation of Cytology and Biopsy Results
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tanaffos (2007) 6(2), 46-50 2007 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy: Correlation of Cytology and Biopsy Results Zohreh Mohammad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tanaffos (2007) 6(2), 46-50 2007 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran Fiberoptic Bronchoscopy: Correlation of Cytology and Biopsy Results Zohreh Mohammad
Diagnostic Correlation of Findings of Multidetector Computed Tomography and Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Lung Masses
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Diagnostic Correlation of Findings 10.5005/jp-journals-10057-0004 of MDCT and FNAC in Lung Masses Diagnostic Correlation of Findings of Multidetector Computed Tomography and Fine Needle
RESEARCH ARTICLE Diagnostic Correlation of Findings 10.5005/jp-journals-10057-0004 of MDCT and FNAC in Lung Masses Diagnostic Correlation of Findings of Multidetector Computed Tomography and Fine Needle
The solitary pulmonary nodule: Assessing the success of predicting malignancy
 The solitary pulmonary nodule: Assessing the success of predicting malignancy Poster No.: C-0829 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: R. W. K. Lindsay, J. Foster, K. McManus;
The solitary pulmonary nodule: Assessing the success of predicting malignancy Poster No.: C-0829 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: R. W. K. Lindsay, J. Foster, K. McManus;
Aspiration biopsy of thoracic lesions
 Aspiration biopsy of thoracic lesions Anthony F. Lalli, M.D. Department of Diagnostic Radiology Fluoroscopically guided aspiration biopsies of thoracic lesions have been executed for several years and
Aspiration biopsy of thoracic lesions Anthony F. Lalli, M.D. Department of Diagnostic Radiology Fluoroscopically guided aspiration biopsies of thoracic lesions have been executed for several years and
Abstract. Introduction. Salah Abobaker Ali
 Sensitivity and specificity of combined fine needle aspiration cytology and cell block biopsy versus needle core biopsy in the diagnosis of sonographically detected abdominal masses Salah Abobaker Ali
Sensitivity and specificity of combined fine needle aspiration cytology and cell block biopsy versus needle core biopsy in the diagnosis of sonographically detected abdominal masses Salah Abobaker Ali
Repeat Thyroid Nodule Fine-Needle Aspiration in Patients With Initial Benign Cytologic Results
 Anatomic Pathology / REPEAT THYROID FINE-NEEDLE ASPIRATION Repeat Thyroid Nodule Fine-Needle Aspiration in Patients With Initial Benign Cytologic Results Melina B. Flanagan, MD, MSPH, 1 N. Paul Ohori,
Anatomic Pathology / REPEAT THYROID FINE-NEEDLE ASPIRATION Repeat Thyroid Nodule Fine-Needle Aspiration in Patients With Initial Benign Cytologic Results Melina B. Flanagan, MD, MSPH, 1 N. Paul Ohori,
Lung scanning in carcinoma of the bronchus
 Thorax (1971), 26, 23. Lung scanning in carcinoma of the bronchus R. H. SECKER WALKER, J. L. PROVAN1, J. A. JACKSON, and J. GOODWIN The Medical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, University
Thorax (1971), 26, 23. Lung scanning in carcinoma of the bronchus R. H. SECKER WALKER, J. L. PROVAN1, J. A. JACKSON, and J. GOODWIN The Medical Unit, University College Hospital Medical School, University
A Study of Thyroid Swellings and Correlation between FNAC and Histopathology Results
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 265-269 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.030
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 265-269 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.030
Value of imprint cytology for ultrasound-guided transthoracic core biopsy
 Eur Respir J 2004; 24: 905 909 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.04.00030404 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2004 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 CLINICAL FORUM Value of imprint
Eur Respir J 2004; 24: 905 909 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.04.00030404 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2004 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 CLINICAL FORUM Value of imprint
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Carcinoma of unknown primary origin (CUP) Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Carcinoma of
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Carcinoma of unknown primary origin (CUP) Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Carcinoma of
Aspiration Needle Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions
 Aspiration Needle Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions T. R. J. Todd, F.R.C.S.(C), G. Weisbrod, F.R.C.P.(C), L. C. Tao, F.R.C.P.(C), D. E. Sanders, F.R.C.P.(C), N. C. Delarue, F.R.C.S.(C), D. W. Chamberlain, F.R.C.P.(C),
Aspiration Needle Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions T. R. J. Todd, F.R.C.S.(C), G. Weisbrod, F.R.C.P.(C), L. C. Tao, F.R.C.P.(C), D. E. Sanders, F.R.C.P.(C), N. C. Delarue, F.R.C.S.(C), D. W. Chamberlain, F.R.C.P.(C),
Endobronchial metastasis in breast cancer
 Endobronchial metastasis in breast cancer ROBERT E ALBERTINI AND NORMAN L EKBERG Thorax, 198, 35, 435-44 From the Department of Thoracic Medicine, Geisinger Medical Center, Danville, Pennsylvania, USA
Endobronchial metastasis in breast cancer ROBERT E ALBERTINI AND NORMAN L EKBERG Thorax, 198, 35, 435-44 From the Department of Thoracic Medicine, Geisinger Medical Center, Danville, Pennsylvania, USA
Computed Tomography (CT) Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Mediastinal and Pulmonary Masses-using A Team Approach
 ProceedingS.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 9(3-1) 1995, pp. 78-82. Computed Tomography (CT) Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Mediastinal and Pulmonary Masses-using A Team Approach M.A. Rahim Khan, Bilquees A. Suleman,
ProceedingS.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 9(3-1) 1995, pp. 78-82. Computed Tomography (CT) Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Mediastinal and Pulmonary Masses-using A Team Approach M.A. Rahim Khan, Bilquees A. Suleman,
Validation of death certificates in asbestos workers
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1969, 26, 302-307 Validation of death certificates in asbestos workers M. L. NEWHOUSE AND J. C. WAGNER London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine TUC Centenary Institute of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1969, 26, 302-307 Validation of death certificates in asbestos workers M. L. NEWHOUSE AND J. C. WAGNER London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine TUC Centenary Institute of
Accuracy of morphological diagnosis of lung cancer
 J Clin Pathol 1982;35:414-419 Accuracy of morphological diagnosis of lung cancer in a department of respiratory medicine MARTIN D CLEE, HELEN LD DUGUID,* DAVID JM SINCLAIRt From the Department oj Respiratory
J Clin Pathol 1982;35:414-419 Accuracy of morphological diagnosis of lung cancer in a department of respiratory medicine MARTIN D CLEE, HELEN LD DUGUID,* DAVID JM SINCLAIRt From the Department oj Respiratory
Percutaneous Transthoracic Aspiration Needle Biopsy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Percutaneous Transthoracic Aspiration Needle Biopsy Stuart S. Sagel, M.D., Thomas B. Ferguson, M.D., John V. Forrest, M.D., Charles L. Roper, M.D., Clarence S. Weldon, M.D., and Richard
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Percutaneous Transthoracic Aspiration Needle Biopsy Stuart S. Sagel, M.D., Thomas B. Ferguson, M.D., John V. Forrest, M.D., Charles L. Roper, M.D., Clarence S. Weldon, M.D., and Richard
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER
 MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
Lung Cancer: A review of 589 Malaysian patients
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 43 No. 4 December 1988 Lung Cancer: A review of 589 Malaysian patients Prathap Gopal, MBBS(Mal), FRCP(Lond), AM(Mal), FCCP(USA) Kuppusamy Iyawoo, MBBS(Mal), MRCP(I) Hooi Lai Ngoh,
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 43 No. 4 December 1988 Lung Cancer: A review of 589 Malaysian patients Prathap Gopal, MBBS(Mal), FRCP(Lond), AM(Mal), FCCP(USA) Kuppusamy Iyawoo, MBBS(Mal), MRCP(I) Hooi Lai Ngoh,
squamous-cell carcinoma1
 Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
GROUP 1: Peripheral tumour with normal hilar and mediastinum on staging CT with no disant metastases. Including: Excluding:
 GROUP 1: Including: Excluding: Peripheral tumour with normal hilar and mediastinum on staging CT with no disant metastases Solid pulmonary nodules 8mm diameter / 300mm3 volume and BROCK risk of malignancy
GROUP 1: Including: Excluding: Peripheral tumour with normal hilar and mediastinum on staging CT with no disant metastases Solid pulmonary nodules 8mm diameter / 300mm3 volume and BROCK risk of malignancy
Fine-Needle Aspiration and Cytologic Findings of Surgical Scar Lesions in Women With Breast Cancer
 148 Fine-Needle Aspiration and Cytologic Findings of Surgical Scar Lesions in Women With Breast Cancer Ehud Malberger, DMD, FIAC,* Yeouda Edoute, MD, PhD,t Osnaf Toledano, MD,* and Dov Sapir, MDS Benign
148 Fine-Needle Aspiration and Cytologic Findings of Surgical Scar Lesions in Women With Breast Cancer Ehud Malberger, DMD, FIAC,* Yeouda Edoute, MD, PhD,t Osnaf Toledano, MD,* and Dov Sapir, MDS Benign
Percutaneous Lung Biopsy in the Molecular Profiling Era: A Survey of Current Practices
 Percutaneous Lung Biopsy in the Molecular Profiling Era: A Survey of Current Practices PHILLIP GUICHET, B.A. 1, FEREIDOUN ABTIN, M.D. 2, CHRISTOPHER LEE, M.D. 1 1 KECK SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OF USC, DEPT OF
Percutaneous Lung Biopsy in the Molecular Profiling Era: A Survey of Current Practices PHILLIP GUICHET, B.A. 1, FEREIDOUN ABTIN, M.D. 2, CHRISTOPHER LEE, M.D. 1 1 KECK SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OF USC, DEPT OF
Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule
 Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Choi et al. Outcomes of Biopsies of Small Pulmonary Nodules Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Sang Hyun Choi 1 Eun Jin Chae Ji-Eun Kim Eun Young Kim Sang
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Choi et al. Outcomes of Biopsies of Small Pulmonary Nodules Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Sang Hyun Choi 1 Eun Jin Chae Ji-Eun Kim Eun Young Kim Sang
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma
 Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions
 ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions Guy s Hospital, London, 16 April 2018 Laxmi Batav Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College NHS Trust Cytology Workload Cervical Cytology 57,500 (decreases
ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions Guy s Hospital, London, 16 April 2018 Laxmi Batav Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College NHS Trust Cytology Workload Cervical Cytology 57,500 (decreases
CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience
 CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience Poster No.: C-0097 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Casarin, G. Rech, C. Cicero, A.
CT Fluoroscopy-Guided vs Multislice CT Biopsy ModeGuided Lung Biopies:a preliminary experience Poster No.: C-0097 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Casarin, G. Rech, C. Cicero, A.
Single Plane Fluoroscopic Guided Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions
 Single Plane Fluoroscopic Guided Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 73 To 77 Sarwat Hussain ( The Aga Khan University Medical Center, Karachi. ) Single plane fluoroscoyic
Single Plane Fluoroscopic Guided Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 73 To 77 Sarwat Hussain ( The Aga Khan University Medical Center, Karachi. ) Single plane fluoroscoyic
ULTRASOUND GUIDED THYROID FINE- NEEDLE ASPIRATION, SAMPLE ADEQUACY WITH AND WITHOUT IMMEDIATE CYTOPATHOLOGY ANALYSIS
 ULTRASOUND GUIDED THYROID FINE- NEEDLE ASPIRATION, SAMPLE ADEQUACY WITH AND WITHOUT IMMEDIATE CYTOPATHOLOGY ANALYSIS Richard Grinstead, DO Chief Radiology Resident, PGY-4, R-3 Arnot Ogden Medical Center
ULTRASOUND GUIDED THYROID FINE- NEEDLE ASPIRATION, SAMPLE ADEQUACY WITH AND WITHOUT IMMEDIATE CYTOPATHOLOGY ANALYSIS Richard Grinstead, DO Chief Radiology Resident, PGY-4, R-3 Arnot Ogden Medical Center
Summary CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 Summary This thesis aims to evaluate the diagnostic work-up in postmenopausal women presenting with abnormal vaginal bleeding. The Society of Dutch Obstetrics and Gynaecology composed a guideline, which
Summary This thesis aims to evaluate the diagnostic work-up in postmenopausal women presenting with abnormal vaginal bleeding. The Society of Dutch Obstetrics and Gynaecology composed a guideline, which
Lung cancer in women
 Thorax (1969), 24, 446. Lung cancer in women DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From Morristoll Hospital, Swantsea Eighty-three instances of lung cancer in women are presented. The frequency of the
Thorax (1969), 24, 446. Lung cancer in women DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From Morristoll Hospital, Swantsea Eighty-three instances of lung cancer in women are presented. The frequency of the
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC LYMPHADENOPATHY.
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
Mixed glandular and squamous-cell carcinoma
 Thorax (1967), 22, 431. Mixed glandular and squamous-cell carcinoma of the bronchus DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From the Pathology Department, Morriston Hospital, Swansea A group of 26 examples
Thorax (1967), 22, 431. Mixed glandular and squamous-cell carcinoma of the bronchus DAVID J. B. ASHLEY AND H. DUNCAN DAVIES From the Pathology Department, Morriston Hospital, Swansea A group of 26 examples
Diagnosis of Cancer of the Lung by the Cytologic Method*
 Diagnosis of Cancer of the Lung by the Cytologic Method* GEORGE N. PAPANICOLAOU, M.D., Ph.D. and HENRY A. CROMWELL, M.D.-- New York, New York The application of the fixation and staining technique developed
Diagnosis of Cancer of the Lung by the Cytologic Method* GEORGE N. PAPANICOLAOU, M.D., Ph.D. and HENRY A. CROMWELL, M.D.-- New York, New York The application of the fixation and staining technique developed
Can Color Doppler Sonography Aid in the Prediction of Malignancy of Thyroid Nodules?
 Article Can Color Doppler Sonography Aid in the Prediction of Malignancy of Thyroid Nodules? Mary C. Frates, MD, Carol B. Benson, MD, Peter M. Doubilet, MD, PhD, Edmund S. Cibas, MD, Ellen Marqusee, MD
Article Can Color Doppler Sonography Aid in the Prediction of Malignancy of Thyroid Nodules? Mary C. Frates, MD, Carol B. Benson, MD, Peter M. Doubilet, MD, PhD, Edmund S. Cibas, MD, Ellen Marqusee, MD
The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy in Evaluating The causes of Undiagnosed Pleural Effusion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-083, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VI (January. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-083, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VI (January. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Fiberoptic bronchoscopy
Percutaneous CT-guided biopsy of hilar lesions: Diagnostic accuracy and complication rate
 Percutaneous CT-guided biopsy of hilar lesions: Diagnostic accuracy and complication rate Poster No.: C-1878 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Interventional Radiology Authors: M. C. Freund
Percutaneous CT-guided biopsy of hilar lesions: Diagnostic accuracy and complication rate Poster No.: C-1878 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Interventional Radiology Authors: M. C. Freund
The Frequency and Significance of Small (15 mm) Hepatic Lesions Detected by CT
 535 Elizabeth C. Jones1 Judith L. Chezmar Rendon C. Nelson Michael E. Bernardino Received July 22, 1991 ; accepted after revision October 16, 1991. Presented atthe annual meeting ofthe American Aoentgen
535 Elizabeth C. Jones1 Judith L. Chezmar Rendon C. Nelson Michael E. Bernardino Received July 22, 1991 ; accepted after revision October 16, 1991. Presented atthe annual meeting ofthe American Aoentgen
Study of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast Lump: Correlation of Cytologically Malignant Cases with Their Histological Findings
 Study of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast Lump: Correlation of Cytologically Malignant Cases with Their Histological Findings Touhid Uddin Rupom 1, Tamanna Choudhury 2, Sultana Gulshana Banu 3
Study of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast Lump: Correlation of Cytologically Malignant Cases with Their Histological Findings Touhid Uddin Rupom 1, Tamanna Choudhury 2, Sultana Gulshana Banu 3
A Chronology of Advancements in the Diagnosing of Lung Nodules
 November 17, 2017 A Chronology of Advancements in the Diagnosing of Lung Nodules Presenter: Daniel P. Harley, MD, MSB, FACS Surgical Director of the Angelos Center for Lung Diseases 1 Pulmonary Nodules
November 17, 2017 A Chronology of Advancements in the Diagnosing of Lung Nodules Presenter: Daniel P. Harley, MD, MSB, FACS Surgical Director of the Angelos Center for Lung Diseases 1 Pulmonary Nodules
To evaluate the role of sputum in the diagnosis of lung cancer in south Indian population
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Muniyappa M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2014 May;2(2):545-550 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20140534
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Muniyappa M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2014 May;2(2):545-550 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20140534
providers in these settings face in adhering to guidelines for evaluating patients for TB. We identified diagnostic guideline adherence and
 Summary 87 Summary The studies presented in this thesis were focused on the quality of diagnostic care provided to suspected tuberculosis (TB) patients and centre on four principle investigations. The
Summary 87 Summary The studies presented in this thesis were focused on the quality of diagnostic care provided to suspected tuberculosis (TB) patients and centre on four principle investigations. The
Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
 Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 450 454, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh088 Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
Original article Annals of Oncology 14: 450 454, 2003 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh088 Mammographic features and correlation with biopsy findings using 11-gauge stereotactic vacuum-assisted breast biopsy (SVABB)
Atypical And Suspicious Categories In Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology Of The Breast
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (October. 216), PP 57-61 www.iosrjournals.org Atypical And Suspicious Categories in
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-853, p-issn: 2279-861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. III (October. 216), PP 57-61 www.iosrjournals.org Atypical And Suspicious Categories in
Lara Kujtan, MD; Abdulraheem Qasem, MD
 The Treatment of Lung Cancer Between 2013-2014 at Truman Medical Center: A Retrospective Review in Fulfillment of the Requirements of Standard 4.6 (Monitoring Compliance with Evidence- Based Guidelines)
The Treatment of Lung Cancer Between 2013-2014 at Truman Medical Center: A Retrospective Review in Fulfillment of the Requirements of Standard 4.6 (Monitoring Compliance with Evidence- Based Guidelines)
Lung cancer is one of the most common and most. Delays in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer*
 Delays in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer* Eija-Riitta Salomaa, MD, PhD; Susanna Sällinen, BM; Heikki Hiekkanen, MSc; and Kari Liippo, MD, PhD Study objectives: This study was undertaken to
Delays in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer* Eija-Riitta Salomaa, MD, PhD; Susanna Sällinen, BM; Heikki Hiekkanen, MSc; and Kari Liippo, MD, PhD Study objectives: This study was undertaken to
PET/CT in lung cancer
 PET/CT in lung cancer Andrei Šamarin North Estonia Medical Centre 3 rd Baltic Congress of Radiology 08.10.2010 Imaging in lung cancer Why do we need PET/CT? CT is routine imaging modality for staging of
PET/CT in lung cancer Andrei Šamarin North Estonia Medical Centre 3 rd Baltic Congress of Radiology 08.10.2010 Imaging in lung cancer Why do we need PET/CT? CT is routine imaging modality for staging of
Gold Anchor enables safe reach to inner organs
 Gold Anchor enables safe reach to inner organs Fine needles for cytology have been used >50 years in all parts of the human body with no to very little harm Gold Anchor comes pre-loaded in needles of the
Gold Anchor enables safe reach to inner organs Fine needles for cytology have been used >50 years in all parts of the human body with no to very little harm Gold Anchor comes pre-loaded in needles of the
Learning Objectives. 1. Identify which patients meet criteria for annual lung cancer screening
 Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital Muhammad Rizwan Khan,Sulaiman B. Hasan,Shahid A. Sami ( Department of Surgery, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital Muhammad Rizwan Khan,Sulaiman B. Hasan,Shahid A. Sami ( Department of Surgery, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
A pitfall in the cytodiagnosis of sputum of asthmatics
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 84 A pitfall in the cytodiagnosis of sputum of asthmatics BERNARD NAYLOR AND CONSTANTINE RAILEY' From the Department ofpathology, the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan,
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 84 A pitfall in the cytodiagnosis of sputum of asthmatics BERNARD NAYLOR AND CONSTANTINE RAILEY' From the Department ofpathology, the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan,
A Comparison Of Fine-Needle Aspiration Versus Non- Aspiration Cytology Of Thyroid Nodules
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 2 A Comparison Of Fine-Needle Aspiration Versus Non- Aspiration Cytology Of Thyroid Nodules K McElvanna, P Pyper, K Miller Citation K McElvanna,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 2 A Comparison Of Fine-Needle Aspiration Versus Non- Aspiration Cytology Of Thyroid Nodules K McElvanna, P Pyper, K Miller Citation K McElvanna,
Risk of Pneumothorax in Post Lung Biopsy Patients: Is Short-Term Monitoring Necessary?
 Risk of Pneumothorax in Post Lung Biopsy Patients: Is Short-Term Monitoring Necessary? Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Hayter, T. Berkmen; New
Risk of Pneumothorax in Post Lung Biopsy Patients: Is Short-Term Monitoring Necessary? Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit R. Hayter, T. Berkmen; New
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP)
 Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Pathways and Guidelines V1.0 London Cancer September 2013 The following pathways and guidelines document has been compiled by the London Cancer CUP technical subgroup and
Cancer of Unknown Primary (CUP) Pathways and Guidelines V1.0 London Cancer September 2013 The following pathways and guidelines document has been compiled by the London Cancer CUP technical subgroup and
Case # year old man with a 2 cm right kidney mass
 Case # 4. 52 year old man with a 2 cm right kidney mass Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 4 Diagnosis: Negative/Non-diagnostic Normal kidney tissue Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the kidney is performed
Case # 4. 52 year old man with a 2 cm right kidney mass Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 4 Diagnosis: Negative/Non-diagnostic Normal kidney tissue Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the kidney is performed
Computerized tomography guided percutaneous transthoracic fine needle aspiration of lung lesions
 Original Research Article Computerized tomography guided percutaneous transthoracic fine needle aspiration of lung lesions Sunita Bajaj 1*, Sandeep R Saboo 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
Original Research Article Computerized tomography guided percutaneous transthoracic fine needle aspiration of lung lesions Sunita Bajaj 1*, Sandeep R Saboo 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiology,
T hese guidelines have been developed at the
 920 BTS GUIDELINES Guidelines for radiologically guided lung biopsy A Manhire, Chairman, M Charig, C Clelland, F Gleeson, R Miller, H Moss, K Pointon, C Richardson, E Sawicka... See end of article for
920 BTS GUIDELINES Guidelines for radiologically guided lung biopsy A Manhire, Chairman, M Charig, C Clelland, F Gleeson, R Miller, H Moss, K Pointon, C Richardson, E Sawicka... See end of article for
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
5/1/2009. Squamous Dysplasia/CIS AAH DIPNECH. Adenocarcinoma
 Pathological Assessment of Diagnostic Specimens Keith Kerr Department of Pathology Aberdeen University Medical School Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Foresterhill, Aberdeen, Scotland, UK Tumours of the Lung:
Pathological Assessment of Diagnostic Specimens Keith Kerr Department of Pathology Aberdeen University Medical School Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Foresterhill, Aberdeen, Scotland, UK Tumours of the Lung:
SURVIVAL AFTER LUNG RESECTION FOR BRONCHIAL CARCINOMA
 Thorax (1955), 10, 183. SURVIVAL AFTER LUNG RESECTION FOR BRONCHIAL CARCINOMA BY J. R. BIGNALL AND A. J. MOON From the Brompton Hospital, the London Chest Hospital, and the Institute of Diseases of the
Thorax (1955), 10, 183. SURVIVAL AFTER LUNG RESECTION FOR BRONCHIAL CARCINOMA BY J. R. BIGNALL AND A. J. MOON From the Brompton Hospital, the London Chest Hospital, and the Institute of Diseases of the
Keywords: papillary carcinoma, Hurthle, FNAC, follicular pattern.
 bü z ÇtÄ TÜà väx Efficacy of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Swellings in Red Sea State, Sudan 1 Abstract Background: Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a safe, easy
bü z ÇtÄ TÜà väx Efficacy of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Diagnosis of Thyroid Swellings in Red Sea State, Sudan 1 Abstract Background: Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a safe, easy
Atypical Presentations of lung cancers
 8 Original Article Atypical Presentations of lung cancers PVV Bharadwaj, VV Ramana Reddy, Ganeswar Behera, JV Praveen, DSS Sowjanya, B Krishna Prithvi Abstract: Aim: The aim of this study was to examine
8 Original Article Atypical Presentations of lung cancers PVV Bharadwaj, VV Ramana Reddy, Ganeswar Behera, JV Praveen, DSS Sowjanya, B Krishna Prithvi Abstract: Aim: The aim of this study was to examine
The Rotex Screw Needle Biopsy Instrument
 The Rotex Screw Needle Biopsy Instrument The original Rotex Screw Needle Biopsy instrument for sampling of cellular material was first introduced on the market by URSUS in 1975. It consists of a thin screw
The Rotex Screw Needle Biopsy Instrument The original Rotex Screw Needle Biopsy instrument for sampling of cellular material was first introduced on the market by URSUS in 1975. It consists of a thin screw
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Transbronchial fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of mediastinal/hilar sarcoidosis
 DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2303.2006.00336.x Transbronchial fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of mediastinal/hilar sarcoidosis S. Smojver-Ježek*, T. Peroš-Golubičić, J. Tekavec-Trkanjec, I. Mažuranić
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2303.2006.00336.x Transbronchial fine needle aspiration cytology in the diagnosis of mediastinal/hilar sarcoidosis S. Smojver-Ježek*, T. Peroš-Golubičić, J. Tekavec-Trkanjec, I. Mažuranić
THORACIK RICK. Lungs. Outline and objectives Richard A. Malthaner MD MSc FRCSC FACS
 THORACIK RICK Outline and objectives Lungs Management of a solitary lung nodule Mediastinum Management of a mediastinal mass Pleura Management of a pleural fluid & pneumothorax Esophagus & Stomach Management
THORACIK RICK Outline and objectives Lungs Management of a solitary lung nodule Mediastinum Management of a mediastinal mass Pleura Management of a pleural fluid & pneumothorax Esophagus & Stomach Management
Accuracy and safety of CT guided transthoracic needle biopsy
 Original Article Accuracy and safety of CT guided transthoracic needle biopsy * Atheer A. Fadhil** FICMS-CABMS-FICMS (Pulm.), DMRD, FIBMS (Rad.), Fac Med Baghdad 2012; Vol. 54, No. 1 Received Dec.2011
Original Article Accuracy and safety of CT guided transthoracic needle biopsy * Atheer A. Fadhil** FICMS-CABMS-FICMS (Pulm.), DMRD, FIBMS (Rad.), Fac Med Baghdad 2012; Vol. 54, No. 1 Received Dec.2011
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL
 The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
Owing to the recent attention given to lung cancer
 Electromagnetic : A Surgeon s Perspective Todd S. Weiser, MD, Kevin Hyman, MD, Jaime Yun, MD, Virginia Litle, MD, Cythinia Chin, MD, and Scott J. Swanson, MD Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Mount
Electromagnetic : A Surgeon s Perspective Todd S. Weiser, MD, Kevin Hyman, MD, Jaime Yun, MD, Virginia Litle, MD, Cythinia Chin, MD, and Scott J. Swanson, MD Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Mount
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
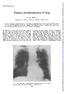 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
 THIS DOCUMENT IS North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer [Based on WOSCAN NSCLC CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN] UNCONTROLLED
THIS DOCUMENT IS North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Non Small Cell Lung Cancer [Based on WOSCAN NSCLC CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN] UNCONTROLLED
ISPUB.COM. Coccidioidomycosis In A Cancer Hospital. A Huaringa INTRODUCTION
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 11 Number 2 Coccidioidomycosis In A Cancer Hospital A Huaringa Citation A Huaringa. Coccidioidomycosis In A Cancer Hospital. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 11 Number 2 Coccidioidomycosis In A Cancer Hospital A Huaringa Citation A Huaringa. Coccidioidomycosis In A Cancer Hospital. The Internet Journal
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Clinical Study Needle Gauge and Cytological Yield in CT-Guided Lung Biopsy
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pulmonology Volume 2011, Article ID 970813, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/970813 Clinical Study Needle Gauge and Cytological Yield in CT-Guided Lung Biopsy William
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pulmonology Volume 2011, Article ID 970813, 4 pages doi:10.5402/2011/970813 Clinical Study Needle Gauge and Cytological Yield in CT-Guided Lung Biopsy William
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION. Occult Micrometastasis to Bone Marrow in Early Lung Cancer: A Clinicopathologic Study from West Bengal, India
 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Occult Micrometastasis to Bone Marrow in Early Lung Cancer: A Clinicopathologic Study from West Bengal, India Saumitra Biswas 1*, Supriya Sarkar 2, Jayati Chakraborty 1, Sudipta
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Occult Micrometastasis to Bone Marrow in Early Lung Cancer: A Clinicopathologic Study from West Bengal, India Saumitra Biswas 1*, Supriya Sarkar 2, Jayati Chakraborty 1, Sudipta
Localised airway narrowing in sarcoidosis
 Thorax 1982;37:443-447 JW HADFIELD, RL PAGE, CDR FLOWER, JE STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge, and Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge ABSTRACr Four patients developed multiple narrowings
Thorax 1982;37:443-447 JW HADFIELD, RL PAGE, CDR FLOWER, JE STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge, and Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge ABSTRACr Four patients developed multiple narrowings
Audit of reporting of thyroid cytology specimens and their correlation with thyroid histology. A Bartlett, TS Bracey, T Malik
 Audit of reporting of thyroid cytology specimens and their correlation with thyroid histology A Bartlett, TS Bracey, T Malik Background Royal College of Pathology 2009 guidelines for the reporting of thyroid
Audit of reporting of thyroid cytology specimens and their correlation with thyroid histology A Bartlett, TS Bracey, T Malik Background Royal College of Pathology 2009 guidelines for the reporting of thyroid
Approach to Pulmonary Nodules
 Approach to Pulmonary Nodules Edwin Jackson, Jr., DO Assistant Professor-Clinical Director, James Early Detection Clinic Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and
Approach to Pulmonary Nodules Edwin Jackson, Jr., DO Assistant Professor-Clinical Director, James Early Detection Clinic Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and
