Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences Available online: Research Article
|
|
|
- Allen Wesley McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences Available online: Research Article ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION ULTRASOUND AND COLOR DOPPLER IN EVALUATION OF CERVICAL LYMPH NODES AND CORRELATION WITH HISTOPATHOLOGY Mohammed Atik Ahmed 1*, Hina Ahmed 2 1 Assistant Professor, Radiodiagnosis, Al-Ameen Medical College, Bijapur, India 2 Post Graduate Student, Radiodiagnosis, Al-Ameen Medical College, Bijapur, India Received: ; Revised: ; Accepted: *Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammed Atik Ahmed Assistant Professor Dept. of Radiodiagnosis Al-Ameen Medical College Athani Road, Bijapur, Karnataka, India, ABSTRACT Introduction and objective: Cervical lymphadenopathy is one of the most common causes of neck masses and to find out the cause is often a diagnostic challenge for proper treatment and follow up. The main objective of our study is to study the gray scale and Doppler characteristic of different causes of cervical lymphadenopathy and compare with the histopathology Methods: Gray scale Ultrasound and Doppler study was done on 100 patients with cervical lymph nodes enlargement, Gray scale ultrasound and Doppler features were compared with histopathology Results: Normal and reactive nodes were oval in shape with central echogenic hilum on gray scale ultrasound and showed hilar vascularity, low RI and PI values on color Doppler. Abnormal lymph nodes showed more round in shape (loss of normal oval shape), loss echogenic hilum and necrosis on gray scale ultrasound and peripheral and chaotic vascularity and sometime absent vascularity due to extensive necrosis on color Doppler. Infective nodes showed indeterminate doppler features. RI and PI of malignant nodes were significantly higher than benign nodes. Conclusion: High resolution Ultrasonography together with Color Doppler features are the primary modality of investigation in head and neck lymphadenopathy. Using clinical examination, ultrasonography and color Doppler criteria (S/L ratio, border sharpness, hilum, echogenicity, necrosis, matting and vascular pattern) it is possible to differentiate malignant and non malignant head and neck lymphadenopathy. Keywords: Lymph nodes, Gray scale ultrasound, Doppler, Resistive Index (RI), Pulsatility Index (PI). INTRODUCTION Cervical lymph nodes enlargement is common in various diseases of head and neck and non head and neck. Evaluation of cervical nodes is an important because it assesses the prognosis of the patients and helps to select appropriate treatment. Noninvasive imaging techniques such as CT and US be used for improved detection of metastasis in lymph nodes. Regardless of the primary tumor, the presence of a metastatic node reduces the 5-year survival rate by 50%, and the presence of another metastatic node on the contra lateral side further reduces the survival rate to 25% 1. Metastatic nodes are site-specific 2, and nodal metastasis of a particular head and neck cancer in an unexpected level indicates that the neoplasm is more aggressive 3. Sonography has proved highly effective for detection, localization and delineation of enlarged lymph nodes of the neck. Infiltration of adjacent structures, specifically the common, internal and external carotid arteries and the neck muscles are reliably demonstrated. Cervical lymph nodes are also common sites of involvement of lymphoma in the head and neck 4-6. Tuberculous lymphadenitis remains a diagnostic dilemma and lymph nodes in the head and neck regions are common sites of this infection 7,8. Tuberculous lymphadenitis is common in underdeveloped countries, and with the spread of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), tuberculous lymphadenitis is now frequently encountered in developed countries 9,10. Although the incidence of AIDS-related tuberculous lymphadenitis is increasing, it may also be found in patients without AIDS. The role of high-resolution ultrasound in assessment of cervical lymph nodes is well established, and grey-scale ultrasound is widely used to assess cervical nodes for their Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences 03 (01), Jan-March
2 number, site, size, nodal boundary, hilum, matting, adjacent soft tissue oedema and other internal nodal echo patterns 2, With the use of colour Doppler sonography (CDS), the amount of information that can be obtained during an ultrasound examination of cervical lymph nodes has increased. However, when CDS was initially applied in the assessment of cervical lymphadenopathy, its value in daily practice was often doubted because of inconsistent results and disagreement on methodology 17,18. With the development of technology assessment of the vascularity of lymph nodes by ultrasound has become more accurate Doppler sonography is more accurate in the assessment of small vessels, such as those found in lymph nodes The main objective of our study is to study the gray scale and Doppler characteristic of different causes of cervical lymphadenopathy and compare with the histopathology. The results obtained were correlated with histopathological findings and specificity and sensitivity of color Doppler parameters in differentiation of benign and malignant lymphadenopathy was determined. MATERIALS AND METHODS Prospective study of 100 with cervical lymph node enlargement referred from other department and high resolution ultrasonography and color Doppler study was performed in the Department of Radiodiognosis All studies were subjected for High resolution Ultrasonography and Color Doppler of cervical lymph nodes with SIEMENS ACUSON 300 PE Ultrasound Scanner with a linear probe with 7.5 MHz frequency with patient in supine position with neck extended. Doppler examination was preceded by grey scale sonography and we looked for size (L/S ratio), shape, echogenicity, nodal border and echogenicity of hilum. Calcification, intra nodal necrosis, matting and adjacent soft tissue edema if present were also noted. Colour Doppler parameters were adjusted for detection of low-velocity or low- volume flow and included: The color gain was first increased to a level which shows color noise, and then decreased to the level where the noise just disappeared. For measuring Doppler indices (RI and PI), the more prominent vessels were selected. For measuring Peak systolic velocity, (PSV) and end diastolic velocity (EDV), angle correction was made to an angle of 60 degree or less. Fine Needle Aspiration was done in all the cases and smears were sent for cytology and the results were compared with High resolution Ultrasound and Doppler findings. Chi- square test was used for overall efficacy of Doppler and spectral parameters in accurate differentiation of benign and malignant lymphadenopathy and student s t-test was used for determining significance of difference of means of roundness index, RI /PI in benign and malignant nodes. RESULTS The present study was undertaken in the department of Radiodiagnosis Al-Ameen medical college Bijapur-Karnataka state on 100 patients with lymph node masses in neck that were referred to our department for Doppler Ultrasonography. Malignant nodes outnumbered benign cases in our study as patients who were very sick and admitted on inpatient basis were usually referred to us. 58 of 100 cases in our study were malignant with metastatic nodes accounting for 38 cases. Grey scale features (Table 1) Solbiati Index (SI) or roundness index of lymph nodes is most important grey scale feature in differentiating benign from malignant nodes Mean Roundness index in benign nodes was 2 and in malignant nodes was Highest mean rounded index in benign node was 2.94 and lowest was Highest mean rounded index in malignant node was 1.75 and lowest was The difference was statistically significant with p value < 0.05 However, 7 out of 21 reactive nodes i.e 33% and 13 out of 26 tubercular nodes i.e 50% had SI < 2, whereas none of malignant nodes had SI > 2 in our study. So 19 of 27 nodes (70%) having SI < 2 were malignant. So there will be high false positive rate for predicting malignant nodes if roundness index is used as the only criteria. Necrosis and displaced hilum as a feature was seen more frequently in tubercular nodes and necrosis was not seen in any of the reactive lymph nodes. Vascular Distribution in Nodes (Table 2) Vascular distribution has been classified differently by different researchers. In our study, we have taken classification of Wu et al 23 who in addition to Avascular group classified vascularity into four types as Hilar type:a simple short feeding vessel, or a central longitudinal vessel, or a hilar vessel with regular and symmetric centrifugal branching; Spotted or multifocal type: scattered specks or segments of vessel signals distributed chaotically within the node; Peripheral type: vascular signals distributed only around the node or in a basket pattern with centripetal branching; Mixed type: a mixture of more than one of the foregoing types Hilar vascularity was common in reactive and Lymphomatous nodes and mixed pattern was frequently seen in metastatic nodes. (Figure 1, 2, 3) SPECTRAL INDICES OF NODAL VESSELS (Table 3 & Table 4) Resistive index of benign nodes was low with minimum value of 0.33 and maximum value of 0.7 while as Resistive index of malignant nodes was high with minimum value of 0.65 and maximum value of 1.15 Most of malignant nodes have RI value more than 0.7 and most of the benign nodes have RI value less than 0.7. Pulsatility index of benign nodes was low with minimum value of 0.42 and maximum value of 1.3 while as Pulsatility index of malignant nodes was high with minimum value of 1.1 and maximum value of 4.5 Most of malignant nodes have RI value more than 1.3 and most of the benign nodes have RI value less than 1.3. There was a significant difference in the mean RI and PI values of benign and malignant values with mean RI and PI of malignant nodes as 0.86(SD=0.11) and 1.76 (SD=0.72) respectively and mean RI and PI of benign nodes as 0.58(SD=0.1) and 0.85(SD=0.23) respectively. Difference of Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences 03 (01), Jan-March
3 means were found statistically significant using student s t-test with a p-value < Mean RI and PI of lymphoma and metastatic nodes was almost similar with no significant difference. Mean RI and PI of tubercular nodes is more than reactive nodes but less than malignant nodes. EDV of lymph nodes (Table 5) EDV of malignant nodes varied from -4.6 to 11.1 cm/s with mean of 2.8cm/s and EDV of benign nodes varied from 3.4 to 19.4 cm/s with mean value of 7.5cm/s. 23 of 28 vascular malignant nodes showed EDV < 5cm/s and vascular benign nodes showed EDV >/= 5cm/s. None of the benign node had EDV < 3.4 and none of the malignant node had EDV > 11.1cm/s. (figure 4, 5, 6, 7). PSV of lymph nodes PSV of malignant nodes varied from 7.79 to 43 cm/s with mean of 19.84cm/s and PSV of benign nodes varied from 8.4 to 29.4 cm/s with mean value of 17.37cm/s DISCUSSION Grey scale features most important in differentiation of benign and malignant lymphadenopathy were roundness index and hilum changes. Grey scale features had acceptable sensitivity for detecting a malignant node but had low specificity as half of tubercular nodes and 18% of reactive nodes had SI< 2. Hilar vascularity is commonly seen in reactive lymphadenopathy. 82% of cases in our study showed hilar vascularity. Ayata et al 24 noticed hilar vascularity in 88% of reactive lymph nodes. Ahuja et al 25 noticed hilar vascularity in 96% of reactive nodes Tubercular nodes usually have variable vascularity. In the present study, hilar (40%) and avascular (30%) forms were most common together accounting for 70% of cases. Multifocal and mixed vascularity was seen in 20% and 10% of cases respectively. In a study conducted by Wu et al 23 they found 72% of tuberculous lymphadenopathy lesions revealed either an avascular pattern or a hilar vascular pattern. Malignant nodes are characterized by extrahilar vessels which are induced by neovascularisation however incidence of extrahilar vessels in lymphoma is lower than metastatic nodes 26. In the present study, vascular distribution was variable with mixed vascularity being the most common form of vascularity in metastatic nodes and was found in 79% of cases. Wu et al 23 also found mixed vascularity the most common form and was seen in 53% of cases. Na et al 27 also noticed mixed vascularity in 82% of malignant nodes Spotted / Multifocal and Peripheral vascularity were the main vascular components present in the metastatic nodes with 15 of 19 nodes (79%) showing multifocal and 14 of 19 (74%) showing peripheral with both being together in mixed form usually. Only peripheral vascularity was only seen in 5.3% of cases. Na et al 27 also noticed similar findings with 47 of 52 nodes (90%) showing peripheral and 42 of 52(81%) showing multifocal with both forms being together usually in mixed form, they noticed pure peripheral vascularity in 6% of cases. Lymphomatous nodes usually showed hilar preponderance. In our study, 40% of nodes showed only hilar vascularity and 60% showed mixed vascularity with hilar component seen in all the cases showing mixed vascularity. Hilar vascularity in lymphoma was different from benign nodes in being more profuse and showing few large branches and it was also noticed by Giovagnorioet al 28 and they called it hilar activated or type 2 hilar vascularity. They also concluded that lymphoma and metastatic node can be differentiated by vascular pattern as hilar vascularity is more common in lymphoma and peripheral subcapsular vascularity is more a feature of metastasis. Wu 23 et al 1998 also found that hilar vascularity is the most common vascularity seen in lymphoma and is different from benign hilar vascularity as high vascular density is seen in lymphoma cases. Lymphadenopathy due to benign and malignant diseases can be distinguished with a high degree of accuracy by means of spectral waveform analysis. RI and PI of malignant nodes is significantly higher than benign nodes. In the present study, RI values ranged from 0.33 to 0.7 in benign nodes and 0.65 to 1.15 in malignant nodes and Mean RI of benign and malignant nodes in our study was 0.58 and 0.86 respectively. Choi et al 29 in their study noticed that RI ranged from 0.38 to 0.82 in benign nodes and 0.44 to 1.24 in malignant nodes with a mean RI of 0.59 in benign nodes and 0.92 in malignant nodes.. Ferrari et al 30 found mean RI of 0.58 and 0.84 in benign and malignant lymph nodes respectively almost in close agreement with the present study. PI values ranged from 0.42 to 1.3 in benign nodes and 1.1 to 4.5 in malignant nodes and mean PI of benign and malignant nodes in our study was 0.85 and 1.76 respectively.. Choi et al 29 in their study noticed that PI ranged from 0.46 to 1.43 in benign nodes and 0.59 to 6.16 in malignant nodes with a mean PI of 0.90 in benign nodes and 2.66 in malignant nodes. Ahuja et al 25 found a mean PI of 1.89 for malignant nodes and 1.07 for reactive nodes almost close to the values obtained in the present study. In the present study, mean RI and PI in reactive nodes was 0.54 and 0.77, in tubercular nodes was 0.65 and 1.03, in Lymphomatous nodes was 0.86 and 1.83 and in metastatic nodes was 0.86 and 1.72 respectively. Na et al 27 found mean RI and PI of 0.57 and 0.85 in reactive nodes, 0.64 and 1.03 in tubercular nodes, 0.7 and 1.2 in lymphoma and 0.83 and 1.62 in metastatic nodes which.. In our study mean RI and PI of lymphoma cases was not much different from metastasis because most of our lymphoma cases were aggressive Non Hodgkin lymphoma as has been noticed by Picardi et al 31, that mean RI value of aggressive NHL was 0.85 and was significantly higher than the mean values of 0.74 in Hodgkin lymphoma. Different researchers have suggested different cut off for RI and PI for differentiating benign and malignant lymphadenopathy. Wu et al 23 suggested cut off of 0.7 for RI and 1.1 for PI and found that accuracy was 73% and 76%, respectively. Chang et al 32 suggested a cut off of 0.6 for RI and 1.2 for PI and found sensitivity and specificity of 81% each. However, they had selected the lowest indices from each node. Shirakawa et al 26 suggested cut off of 0.72 for RI and 1.3 for PI and found it appropriate for acceptable sensitivity, specificity and Ahuja et al 33 suggested the cut off of 0.7 for RI and 1.4 for PI. Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences 03 (01), Jan-March
4 In the present study sensitivity and specificity was seen at three different values of RI and PI and it was noticed that at RI of 0.7 and PI of 1.3 high sensitivity (93%,89%) and specificity (94%,94%) was obtained with a p-value < ( using Chi Square test) while increasing the cut off to 0.8 for RI increased the specificity to 100% but reduced sensitivity to 68% and by decreasing cut off to 0.6 sensitivity increased to 100% but specificity was reduced to 45. Na et al 27 also looked for sensitivity and specificity at different cut off values and found sensitivity for labeling a node malignant at RI of 0.6 was >90% but specificity was 50%, at RI of 0.8 sensitivity reduced to around 50% but specificity was 100%. Likewise, for a cut off PI value of 1.1, sensitivity was > 80% but specificity was around 70% but at a cut off value of 1.5 sensitivity reduced to 55% but specificity reached 100% Mean Peak systolic velocity in the present study was similar in benign and malignant lymph nodes with malignant nodes showing mean PSV of 19.84cm/s and benign nodes showing mean PSV of 17.37cm/s and mean End diastolic velocity in malignant nodes was 2.8cm/s which was significantly lower than mean EDV of benign nodes which was 7.5 cm/s. EDV in malignant nodes varied from -4.6 to 11.1cm/s and EDV in benign nodes ranged from 3.4 to 19.4 cm/s. So in our study EDV> 11.1 cm/s has 100% negative predictive value for nodal metastasis, and EDV<3.4 cm/s has 100% specificity and PPV for metastasis. Choi et al 29 also found mean PSV similar in two groups with mean PSV of 25cm/s in malignant and 24cm/s in benign nodes. Mean EDV of malignant and benign nodes was 2cm/s and 10cm/s respectively. EDV in benign nodes varied from - 10cm/s to 14cm/s and EDV in benign nodes ranged from 3cm/s to 51 cm/s Brnic and Hebrang 34 also noticed that EDV>9 cm/s has 100% negative predictive value for nodal metastasis, and EDV<1 cm/s has 100% specificity and PPV for metastasis. Most important marker for differentiation of benign and malignant node in our study was RI with a sensitivity of 93%, specificity of 94% and accuracy of 93.5% at a cut off value of 0.7 with a p-value of < Issing et al 35 also concluded that most valuable parameter was Pourcelot index (RI) with a specificity of 92% for detecting malignant node. Ayata et al 24 also suggested RI as the most important marker with a sensitivity of 84.6, specificity of 100% and accuracy of 95.7% at a cut off value of 0.7 for differentiating benign from neoplastic lymphadenopathy. CONCLUSION 1. Ultrasound with Color Doppler is the primary modality of investigation in head and neck lymphadenopathy 2. Using clinical examination, ultrasonography and color Doppler criteria (S/L ratio, border sharpness, hilum, echogenicity, necrosis, matting and vascular pattern) it is possible to differentiate malignant and non malignant head and neck lymphadenopathy 3. Ultrasonography being a bedside and outpatient procedure can be used by radiologists as well as surgeons and physicians for the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy. 4. Though histopathological examination is the gold standard for detection of lymphnode metastasis, ultrasonography with color doppler can be used alternatively. REFERENCES 1. Som PM. Detection of metastasis in cervical lymph nodes: CT and MR criteria and differential diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1992; 158: Ahuja A, Ying M, King W, Metreweli C. A practical approach to ultrasound of cervical lymph nodes. J Laryngol Otol, 1997; 111: Som PM. Lymph nodes of the neck. Radiology, 1987; 165: Bragg DG. Radiology of the lymphomas. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol, 1987; 16: Swartz JD, Yussen PS, Popky GL. Imaging of the neck: nodal disease.crit Rev Diagn Imaging, 1991; 31: Lee YY, Van Tassel P, Nauert C, et al. Lymphomas of head and neck: CT findings at initial presentation. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1987; 49: Ishikawa H, Hyo Y, Ono T. Tuberculous submandibular lymphadenitis.j Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1982;40: Qizilbash AH, Young JEM. Lymph nodes. In Guides to clinical aspiration biopsy: head and neck. New- York: Igaku-Shoin, 1988; Radin DR. Intraabdominal Mycobacterium tuberculosis vs Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infections in patients with AIDS: distinction based on CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1991; 156: Shapiro AL, Pincus RL. Fine-needle aspiration of diffuse cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1991; 105: Ahuja A, Ying M, Evans R, et al. The application of ultrasound criteria for malignancy in differentiating tuberculous cervical adenitis from metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Radiol, 1995;50: Ahuja AT, Ying M, Yuen HY, Metreweli C. Pseudocystic appearance of non-hodgkin s lymphomatous nodes: an infrequent finding with high-resolution transducers. Clin Radiol, 2001;56: Ying M, Ahuja AT, Evans R, et al. Cervical lymphadenopathy: sonographic differentiation between tuberculous nodes and nodal metastases from non-head and neck carcinomas. J Clin Ultrasound, 1998; 26: van den Brekel MW, Stel HV, Castelijns JA, et al. Cervical lymph node metastasis: assessment of radiologic criteria. Radiology, 1990; 177: Bruneton JN, Normand F, Balu-Maestro C, et al. Lymphomatous superficial lymph nodes: US detection. Radiology, 987; 165: Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences 03 (01), Jan-March
5 16. Bruneton JN, Roux P, Caramella E, et al. Ear, nose, and throat cancer: ultrasound diagnosis of metastasis to cervical lymph nodes. Radiology, 1984; 152: Chang DB, Yuan A, Yu CJ, et al. Differentiation of benign and malignant cervical lymph nodes with color Doppler sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1994; 162: Choi MY, Lee JW, Jang KJ. Distinction between benign and malignant causes of cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymphadenopathy: value of Doppler spectral waveform analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1995; 165: Ariji Y, Kimura Y, Hayashi N, et al. Power Doppler sonography of cervical lymph nodes in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 1998; 19: Na DG, Lim HK, Byun HS, et al. Differential diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopathy: usefulness of color Doppler sonography. AJR Am JRoentgenol, 1997; 168: Steinkamp HJ, Mueffelmann M, Bock JC, et al. Differential diagnosis of lymph node lesions: a semiquantitative approach with colour Doppler ultrasound. Br J Radiol, 1998; 71: Wu CH, Hsu MM, Chang YL, Hsieh FJ. Vascular pathology of malignant cervical lymphadenopathy: qualitative and quantitative assessment with power Doppler ultrasound. Cancer, 1998 ;83: Wu CH, Chang YL, Hsu WC, et al. Usefulness of Doppler spectral analysis and power Doppler sonography in the differentiation of cervical lymphadenopathies. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1998;171: Ayata Z, Apaydin M, Varer M et al. Differential diagnosis in cervical lymphadenopathies : efficacy of B-mode, color and power Doppler Ultrasonography. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg, 2009; 19(4): Ahuja A, Ying M, Phil M et al. Lymph Node Hilus : Gray Scale & Power Doppler Sonography of Cervical Nodes. J Ultrasound Med 2001; 20: Shirakawa T, Miyamoto Y, Yamagishi J et al. Color/power Doppler sonographic differential diagnosis of superficial lymphadenopathy: metastasis, malignant lymphoma, and benign process. J Ultrasound Med. 2001; 20(5): Na DG, Lim HK, Byun HS et al. Differential Diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopayhy: Usefulness of Color Doppler Sonography. AJR 1997; 168: Giovagnorio F, Galluzo M, Andreoli C et al. Color Doppler Sonography in the evaluation of superficial Lymphomatous lymph nodes. J Ultrasound Med 2002; 21: Choi MY, Lee JW and Jang KJ. Distinction between Benign and Malignant causes of cervical, axillary and inguinal Lymphadenopathy: value of Doppler spectral waveform Analysis. AJR1995; 165: Ferrari FS, Cozza S, Guazzi G et al. Role of Doppler color in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant adenopathies. Radiol Med. 1997; 93(3): Picardi M, Gennarelli N, Ciancia R et al. Randomized Comparison of Power Doppler-Directed Excisional Biopsy with Standard Excisional Biopsy for the characterization of lymphadenopathies in patients with suspected Lymphoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2004; 22: Chang DB, Yuan A, Yu CJ et al. Differentiation of benign and malignant cervical lymph nodes with Color Doppler Sonography. AJR1994; 162: Ahuja AT, Ying M, Ho SY et al. Ultrasound of malignant cervical lymph nodes. Cancer Imaging 2008; 8(1): Brnic Z and Hebrang A. Usefulness of Doppler waveform analysis in differential diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopathy. Eur Radiol, 2003; 13(1): Issing PR, Kettling T, Kempf HG et al. Ultrasound evaluation of characteristics of cervical lymph nodes with special reference to color Doppler ultrasound. A contribution to differentiating reactive from metastatic lymph node involvement in the neck. Laryngorhinootologie ; 78(10): Table 1: Grey scale feature Diagnosis mean Roundness index Hilar features (L/S) Normal Absent Displaced Necrosis Reactive Tuberculosis Lymphoma Metastatic TYPE OF VASCULARITY Table 2: Vascular Distribution in Nodes Patients with Patients with reactive tuberculosis ( n =22) ( n =20) Patients with metastasis ( n =38) Patients with lymphoma ( n =20) Hilar (5.26%) 8 Multifocal 2 4 2(5.26%) 0 Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences 03 (01), Jan-March
6 Peripheral 0 0 2(5.26%) 0 Avascular 0 6 2(5.26%) 0 Hilar, peripheral and multifocal 0 0 4(10.52%) 0 Peripheral and multifocal (52.6%) 0 Hilar and peripheral 2 2 2(5.26%) 10 Hilar and multifocal 0 0 4(10.52%) 2 SPECTRAL INDICES OF NODAL VESSELS (Table 3 & Table 4) Table 3 DIAGNOSIS MEAN RI MEAN PI BENIGN MALIGNANT Table 4 DIAGNOSIS MEAN RI MEAN PI METASTASIS LYMPHOMA REACTIVE TUBERCULOSIS Table 5: EDV of lymph nodes EDV(cm/s) BENIGN MALIGNANT < >= Figure 1: Colour Doppler of a reactive node showing single hilar vessel Figure 3: Power Doppler of a Metastatic node with multicentric and peripheral vascularity Figure 2: Power Doppler of a lymphomatous node with activated hilar vascularity Figure 4: Spectral trace of a reactive node showing low RI, PI Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences 03 (01), Jan-March
7 Figure 5: spectral Doppler of lymphomatous node seen in Figure 2 shows high RI and PI Figure 6: spectral doppler of Metastatic node (Figure 3) shows high RI, PI and low EDV Figure 7: Doppler of a tubercular node with necrosis and multifocal vascularity and spectral trace also being indeterminate Source of support: Nil, Conflict of interest: None Declared Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences 03 (01), Jan-March
Role of spectral doppler in the differentiation of benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy
 Al Am een J Med Sci 2014; 7(4):291-298 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Role of spectral doppler in the differentiation of benign
Al Am een J Med Sci 2014; 7(4):291-298 US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal ISSN 0974-1143 ORIGI NAL ARTICLE C O D E N : A A J MB G Role of spectral doppler in the differentiation of benign
Lymph Node Hilus. Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography of Cervical Nodes. Article
 Article Lymph Node Hilus Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography of Cervical Nodes Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Michael Ying, MPhil, Ann King, FRCR, Hok Yuen Yuen, FRCR Objective. To investigate the difference in
Article Lymph Node Hilus Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography of Cervical Nodes Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Michael Ying, MPhil, Ann King, FRCR, Hok Yuen Yuen, FRCR Objective. To investigate the difference in
Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/74 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation Suresh Kumar 1, Sonjjay Pande
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/74 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Cytological Correlation Suresh Kumar 1, Sonjjay Pande
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 17; 5(11D):11-1 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 17; 5(11D):11-1 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
ÖZERK ÖMÜR ÖKTEN 1, NERM N TUNÇB LEK 1, HAKKI MUAMMER KARAKAfi 2 ABSTRACT KEY WORDS:
 156 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.4, 2004 The value of qualitative and semiquantitative ultrasonographic findings in the differential diagnosis of lymphomatous superficial lymph node enlargements
156 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.4, 2004 The value of qualitative and semiquantitative ultrasonographic findings in the differential diagnosis of lymphomatous superficial lymph node enlargements
Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler in Evaluation of Neck Nodes And Differentiating Benign from Malignant Nodes
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IX (November. 2016), PP 71-80 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 11 Ver. IX (November. 2016), PP 71-80 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Ultrasonography And Doppler
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 09/Jan 29, 2015 Page 1533
 EVALUATION OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES BY ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN CORRELATION WITH FNAC Aaditya Kumar Singh 1, Purnima Hegde 2, Anil Kumar Sakalecha 3, T. N. Suresh 4, P. N. Sreeramulu 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
EVALUATION OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES BY ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN CORRELATION WITH FNAC Aaditya Kumar Singh 1, Purnima Hegde 2, Anil Kumar Sakalecha 3, T. N. Suresh 4, P. N. Sreeramulu 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 39/ May 14, 2015 Page 6787
 ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography in Cases of Kimura Disease
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :51 51, March 1 Case Report Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography in Cases of Kimura Disease Anil Ahuja, Michael Ying, J.S.W. Mok, and Constantine Metreweli Anil Summary: Kimura
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :51 51, March 1 Case Report Gray Scale and Power Doppler Sonography in Cases of Kimura Disease Anil Ahuja, Michael Ying, J.S.W. Mok, and Constantine Metreweli Anil Summary: Kimura
Cervical Lymph Nodes
 Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
ULTRASOUND DIFFERENTIATION OF BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 Original Article ULTRASOUND DIFFERENTIATION OF BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CERVICAL LYMPH NODES Md. Mizanur Rahman 1, ASQM Sadeque 2, Eliza Omar 3 and Sonjoy Kumar Bhakta 4 1 Department of Radiology and Imaging,
Original Article ULTRASOUND DIFFERENTIATION OF BENIGN AND MALIGNANT CERVICAL LYMPH NODES Md. Mizanur Rahman 1, ASQM Sadeque 2, Eliza Omar 3 and Sonjoy Kumar Bhakta 4 1 Department of Radiology and Imaging,
B-330 Cervical lymph node ultrasonography in HIV infected children
 B-330 Cervical lymph node ultrasonography in HIV infected children Scientific Paper B-330 Cervical lymph node ultrasonography in HIV infected children A. Butnaru (Cluj Napoca/RO) S. D. Bolboaca (Cluj Napoca/RO)
B-330 Cervical lymph node ultrasonography in HIV infected children Scientific Paper B-330 Cervical lymph node ultrasonography in HIV infected children A. Butnaru (Cluj Napoca/RO) S. D. Bolboaca (Cluj Napoca/RO)
Evaluation of supplementary diagnostic value of contrastenhanced ultrasound for lymph node puncture biopsy
 Original Article on Quantitative Imaging of Thoracic Diseases Evaluation of supplementary diagnostic value of contrastenhanced ultrasound for lymph node puncture biopsy Jie Zhang 1 *, Xin Hao 2 *, Yang
Original Article on Quantitative Imaging of Thoracic Diseases Evaluation of supplementary diagnostic value of contrastenhanced ultrasound for lymph node puncture biopsy Jie Zhang 1 *, Xin Hao 2 *, Yang
Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary Lymph Node Involvement In Breast Carcinoma
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. II. (Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Study on Efficacy of Preoperative Ultrasonography for Axillary
Role of high-resolution colored-doppler ultrasound in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy
 Role of high-resolution colored-doppler ultrasound in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy Shahad D. Ali (1) *, Taghreed F. Zaidan (2), Fadhil Al-Janabi (3) 1 Department
Role of high-resolution colored-doppler ultrasound in the differentiation between benign and malignant cervical lymphadenopathy Shahad D. Ali (1) *, Taghreed F. Zaidan (2), Fadhil Al-Janabi (3) 1 Department
Ultrasonographic Differentiation Between Metastatic and Benign Lymph Nodes in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
 Article Ultrasonographic Differentiation Between Metastatic and Benign Lymph Nodes in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Pedro Weslley Souza Rosário, PhD, Sérgio de Faria, MD, Luciano Bicalho, MD,
Article Ultrasonographic Differentiation Between Metastatic and Benign Lymph Nodes in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Pedro Weslley Souza Rosário, PhD, Sérgio de Faria, MD, Luciano Bicalho, MD,
Differentiating Benign from Malignant Cervical Lymph Nodes with Sonoelastography
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(4): 42-46 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170504.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Differentiating
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2017; 5(4): 42-46 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20170504.11 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN: 2330-832X (Online) Differentiating
REVIEW. Ultrasound of malignant cervical lymph nodes
 Cancer Imaging (2008) 8, 48 56 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2008.0006 REVIEW Ultrasound of malignant cervical lymph nodes A.T. Ahuja a, M. Ying b, S.Y. Ho a, G. Antonio a, Y.P. Lee a, A.D. King a and K.T. Wong
Cancer Imaging (2008) 8, 48 56 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2008.0006 REVIEW Ultrasound of malignant cervical lymph nodes A.T. Ahuja a, M. Ying b, S.Y. Ho a, G. Antonio a, Y.P. Lee a, A.D. King a and K.T. Wong
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes
 ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 37/Aug 21, 2014 Page 9580
 THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
 C A S E R E P O R T Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Yi-Lun Tseng, Li-Jen Liao* We present a case with an initial presentation of smooth nasopharyngeal mucosa
C A S E R E P O R T Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Yi-Lun Tseng, Li-Jen Liao* We present a case with an initial presentation of smooth nasopharyngeal mucosa
Sonographic Appearance and Distribution of Normal Cervical Lymph Nodes in a Chinese Population
 Sonographic Appearance and Distribution of Normal Cervical Lymph Nodes in a Chinese Population Michael Ying, POOR, Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Fiona Brook, DCR, RDMS~ Brian Brown, PhD, Constantine Metreweli, FRCR
Sonographic Appearance and Distribution of Normal Cervical Lymph Nodes in a Chinese Population Michael Ying, POOR, Anil Ahuja, FRCR, Fiona Brook, DCR, RDMS~ Brian Brown, PhD, Constantine Metreweli, FRCR
Preoperative Evaluation
 Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Toru Chikui, Koichi Yonetsu, and Takashi Nakamura. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21: , March 2000
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:561 567, March 2000 Multivariate Feature Analysis of Sonographic Findings of Metastatic Cervical Lymph Nodes: Contribution of Blood Flow Features Revealed by Power Doppler Sonography
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:561 567, March 2000 Multivariate Feature Analysis of Sonographic Findings of Metastatic Cervical Lymph Nodes: Contribution of Blood Flow Features Revealed by Power Doppler Sonography
The place of CEUS in distinguishing benign from malignant cervical lymph nodes: a prospective study
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 1, 7-14 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2014.2066.161.lp1os2 The place of CEUS in distinguishing benign from malignant cervical lymph nodes: a prospective study Laura Poanta
Original papers Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 1, 7-14 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2014.2066.161.lp1os2 The place of CEUS in distinguishing benign from malignant cervical lymph nodes: a prospective study Laura Poanta
Malignant Breast Masses Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 4-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad
 ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
ACCURACY OF THE DOPPLER RESISTIVE INDEX IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT BREAST MASSES Sadaf Aziz, Arfan-ul-Haq*, Asad Maqbool Ahmad Combined Military Hospital Khuzdar, *AFIRI Rawalpindi ABSTRACT Objective:
Lymphadenopathy: Differentiation of Benign from Malignant Disease by Color Doppler Ultrasonography Assessment of Intranodal Angioarchitecture.
 Research Article International Journal of advances in health sciences (IJHS) ISSN 2349-7033 Vol2, Issue1, 2015, pp82-88 http://www.ijhsonline.com Lymphadenopathy: Differentiation of Benign from Malignant
Research Article International Journal of advances in health sciences (IJHS) ISSN 2349-7033 Vol2, Issue1, 2015, pp82-88 http://www.ijhsonline.com Lymphadenopathy: Differentiation of Benign from Malignant
The Reliability of Ultrasonography in Neck Masses Evaluation.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. XII (Oct. 2017), PP 33-40 www.iosrjournals.org The Reliability of Ultrasonography in
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. XII (Oct. 2017), PP 33-40 www.iosrjournals.org The Reliability of Ultrasonography in
Value of Gray-Scale and Color Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 79, No. 2, March: 59-65, 2011 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Value of Gray-Scale and Color Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy AHMED M. KADDAH,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 79, No. 2, March: 59-65, 2011 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Value of Gray-Scale and Color Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Cervical Lymphadenopathy AHMED M. KADDAH,
Role of High Resolution UltrasonogramandElastographyIn Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.9 March. (2018), PP 05-10 www.iosrjournals.org Role of High Resolution UltrasonogramandElastographyIn
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 3 Ver.9 March. (2018), PP 05-10 www.iosrjournals.org Role of High Resolution UltrasonogramandElastographyIn
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonographic features for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma: a singlecenter retrospective study
 Liu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:32 DOI 10.1186/s12957-017-1099-2 RESEARCH Open Access Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonographic features for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid
Liu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2017) 15:32 DOI 10.1186/s12957-017-1099-2 RESEARCH Open Access Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonographic features for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1
 The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
Endocrine University, 2016 AACE-ACE-MAYO CLINIC
 Endocrine University, 2016 AACE-ACE-MAYO CLINIC Dev Abraham MD, MRCP (UK), ECNU Professor of Medicine (clinical), Division of Endocrinology Adjunct Professor of Surgery and Pathology Medical Director,
Endocrine University, 2016 AACE-ACE-MAYO CLINIC Dev Abraham MD, MRCP (UK), ECNU Professor of Medicine (clinical), Division of Endocrinology Adjunct Professor of Surgery and Pathology Medical Director,
Clinical Study B-Mode and Elastosonographic Evaluation to Determine the Reference Elastosonography Values for Cervical Lymph Nodes
 ISRN Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 895287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.5402/2013/895287 Clinical Study B-Mode and Elastosonographic Evaluation to Determine the Reference Elastosonography Values for
ISRN Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 895287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.5402/2013/895287 Clinical Study B-Mode and Elastosonographic Evaluation to Determine the Reference Elastosonography Values for
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Three-Dimensional Doppler Ultrasonography in Assessing Nodal Metastases and Staging Head and Neck Cancer
 The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Three-Dimensional Doppler Ultrasonography in Assessing Nodal Metastases and Staging Head and Neck Cancer
The Laryngoscope VC 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Three-Dimensional Doppler Ultrasonography in Assessing Nodal Metastases and Staging Head and Neck Cancer
Combination of Helical CT and Doppler Sonography in the Follow-up of Patients with Clinical N0 Stage Neck Disease and Oral Cancer
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:312 318, March 2003 Combination of Helical CT and Doppler Sonography in the Follow-up of Patients with Clinical N0 Stage Neck Disease and Oral Cancer Sato Eida, Misa Sumi, Koichi
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:312 318, March 2003 Combination of Helical CT and Doppler Sonography in the Follow-up of Patients with Clinical N0 Stage Neck Disease and Oral Cancer Sato Eida, Misa Sumi, Koichi
Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis
 Original article: Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis *Dr Rajvi Matalia, ** Dr Y.P.Sachdev, ***Dr D.S.Kulkarni *Junior Resident,
Original article: Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis *Dr Rajvi Matalia, ** Dr Y.P.Sachdev, ***Dr D.S.Kulkarni *Junior Resident,
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3
 PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
Kimura s Disease in the Lower Extremity: A Case Report Mimicking the Malignant Soft Tissue Mass
 Kimura s Disease in the Lower Extremity: A Case Report Mimicking the Malignant Soft Tissue Mass Jee Young Lee, M.D. 1, Kyung Jin Suh, M.D. 2, Hong-Geun Jung, M.D. 3 We present a case of a 37-year-old woman
Kimura s Disease in the Lower Extremity: A Case Report Mimicking the Malignant Soft Tissue Mass Jee Young Lee, M.D. 1, Kyung Jin Suh, M.D. 2, Hong-Geun Jung, M.D. 3 We present a case of a 37-year-old woman
Evaluation of thyroid nodules by Gray scale and Doppler sonography and correlation with fine needle aspiration cytology
 International Surgery Journal Singh D et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jul;4(7):2197-2204 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172766
International Surgery Journal Singh D et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jul;4(7):2197-2204 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172766
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012. Lymph Nodes. John McGrath
 Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Assessment of Cervical Metastasis in Patients Undergoing Elective Neck Dissection
 Iran J Radiol. 2014 August; 11(3): e7928. Published online 2014 August 1. HEAD & NECK IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.7928 Research Article Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Assessment
Iran J Radiol. 2014 August; 11(3): e7928. Published online 2014 August 1. HEAD & NECK IMAGING DOI: 10.5812/iranjradiol.7928 Research Article Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Assessment
Imaging superficial lymph nodes: Is there a clue for malignancy?
 Imaging superficial lymph nodes: Is there a clue for malignancy? Poster No.: C-2477 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Zaghouani Ben Alaya, N. Benzina, Z. Kmira, W. Kermani, 1 1 1
Imaging superficial lymph nodes: Is there a clue for malignancy? Poster No.: C-2477 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Zaghouani Ben Alaya, N. Benzina, Z. Kmira, W. Kermani, 1 1 1
Laly Jose, Sara Ammu Chacko, Simi.
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 9, September-2014 512 Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology with Evaluation of Pathological Distribution of Thyroid
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 9, September-2014 512 Ultrasound Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology with Evaluation of Pathological Distribution of Thyroid
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
Clinical Value of Real Time Elastography in Patients with Unexplained Cervical Lymphadenopathy: Quantitative Evaluation
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.13.5487 Clinical Value of Real Time Elastography in Patients with Unexplained Cervical Lymphadenopathy RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Value of Real Time Elastography
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.13.5487 Clinical Value of Real Time Elastography in Patients with Unexplained Cervical Lymphadenopathy RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinical Value of Real Time Elastography
Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for retrojugular lymph nodes in the neck
 Kim World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:121 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for retrojugular lymph nodes in the neck Dong Wook Kim
Kim World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:121 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for retrojugular lymph nodes in the neck Dong Wook Kim
Prospective Study of Computed Tomography and Ultrasound Imaging for Palpable Neck Lesions at a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital
 Original article Prospective Study of Computed Tomography and Ultrasound Imaging for Palpable Neck Lesions at a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital Dr. Sunil Kumar Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article Prospective Study of Computed Tomography and Ultrasound Imaging for Palpable Neck Lesions at a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital Dr. Sunil Kumar Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI. Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals
 Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals Applications Both maternal uterine and fetal circulations can be studied with doppler sonography Uterine arteries
Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals Applications Both maternal uterine and fetal circulations can be studied with doppler sonography Uterine arteries
ISPUB.COM. A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar INTRODUCTION MATERIAL AND METHOD
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC LYMPHADENOPATHY.
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY: A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN LYMPHADENOPTHY
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Mahesh S Patil and Anand A S, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Mahesh S Patil and Anand A S, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION
The role of CEUS in characterization of superficial lymph nodes: a single center prospective study RETRACTED
 /, Vol. 7, No. 32 The role of CEUS in characterization of superficial lymph nodes: a single center prospective study Giorgio de Stefano 1, Umberto Scognamiglio 1, Filomena Di Martino 2, Roberto Parrella
/, Vol. 7, No. 32 The role of CEUS in characterization of superficial lymph nodes: a single center prospective study Giorgio de Stefano 1, Umberto Scognamiglio 1, Filomena Di Martino 2, Roberto Parrella
To date, open cervical lymph node (LN) biopsy
 Ultrasound Elastography: Its Potential Role in Assessment of Cervical Lymphadenopathy Rong Tan, MM, Ying Xiao, MD, PhD, Qun He, MD Rationale and Objectives: The aims of this study were to investigate the
Ultrasound Elastography: Its Potential Role in Assessment of Cervical Lymphadenopathy Rong Tan, MM, Ying Xiao, MD, PhD, Qun He, MD Rationale and Objectives: The aims of this study were to investigate the
Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.767 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(4):767-775 Comparison of Ultrasonographic Findings of Biopsy-Proven
Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.4.767 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(4):767-775 Comparison of Ultrasonographic Findings of Biopsy-Proven
A Clinicopathological study on Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Original Research Article A Clinicopathological study on Cervical Lymphadenopathy R. Maheshwari 1*, Rakesh Fernando 2 1 Professor, 2 Assistant Professor Department of General Surgery, Tirunelveli Medical
Original Research Article A Clinicopathological study on Cervical Lymphadenopathy R. Maheshwari 1*, Rakesh Fernando 2 1 Professor, 2 Assistant Professor Department of General Surgery, Tirunelveli Medical
1. Resident Doctor, 2. Professor, Geetanjali Medical College & Hospital, Udaipur, Rajasthan.
 International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) www.ijmse.com Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) www.ijmse.com Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ROLE OF ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION OF RIGHT ILIAC FOSSA MASS
 ROLE OF ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION OF RIGHT ILIAC FOSSA MASS Madhushankar L 1, Satish Kumar R 2, Sanjay S.C 3, Laxmikanta. L 4, Hemanth V 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Madhushankar L, Satish
ROLE OF ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN PRE-OPERATIVE EVALUATION OF RIGHT ILIAC FOSSA MASS Madhushankar L 1, Satish Kumar R 2, Sanjay S.C 3, Laxmikanta. L 4, Hemanth V 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Madhushankar L, Satish
GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL
 GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Carotid Duplex Ultrasound SECTION: Vascular Ultrasound ORIGINATOR: Deborah L. Richert, BSVT, RDMS, RVT DATE: October 15, 2015
GUNDERSEN/LUTHERAN ULTRASOUND DEPARTMENT POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SUBJECT: Carotid Duplex Ultrasound SECTION: Vascular Ultrasound ORIGINATOR: Deborah L. Richert, BSVT, RDMS, RVT DATE: October 15, 2015
Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition
 Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition Nodular thyroid is a common clinical entity. All patients were evaluated by grey
Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition Nodular thyroid is a common clinical entity. All patients were evaluated by grey
Original Article. J Fac Med Baghdad 193. Introduction:
 Original Article The value of Gray scale, color doppler and ultrasound guided- FNA in detection metastasis to the axillary lymph node in patient with primary breast cancer. * Qusay A. Fahad* Enam A.Al
Original Article The value of Gray scale, color doppler and ultrasound guided- FNA in detection metastasis to the axillary lymph node in patient with primary breast cancer. * Qusay A. Fahad* Enam A.Al
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report
 Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
106 Korean J Radiol 10(2), April 2009
 Diagnostic Benefit of Thyroglobulin Measurement in Fine-Needle Aspiration for Diagnosing Metastatic Cervical Lymph Nodes from Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Correlations with US Features Se Jeong Jeon, MD 1,
Diagnostic Benefit of Thyroglobulin Measurement in Fine-Needle Aspiration for Diagnosing Metastatic Cervical Lymph Nodes from Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Correlations with US Features Se Jeong Jeon, MD 1,
Original Article Feasibility of fine-needle aspiration biopsy and its applications in superficial cervical lesion biopsies
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(8):5165-5170 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000929 Original Article Feasibility of fine-needle aspiration biopsy and its applications in superficial cervical lesion biopsies
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(8):5165-5170 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000929 Original Article Feasibility of fine-needle aspiration biopsy and its applications in superficial cervical lesion biopsies
Radiological imaging in primary parotid malignancy q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 637 643 Radiological imaging in primary parotid malignancy q C. Raine a, *, K. Saliba b, A.J. Chippindale b, N.R. McLean a a Department of Plastic
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 637 643 Radiological imaging in primary parotid malignancy q C. Raine a, *, K. Saliba b, A.J. Chippindale b, N.R. McLean a a Department of Plastic
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat Page 1
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Tongue: A Case Report Authors: Nanayakkara PR*, Arudchelvam JD** Ariyaratne JC*, Mendis K*, Jayasekera
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Primary Malignant Melanoma of the Tongue: A Case Report Authors: Nanayakkara PR*, Arudchelvam JD** Ariyaratne JC*, Mendis K*, Jayasekera
BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND. Deep Vein Thrombosis. Probe used
 BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND Part 2 Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis Kishore Kumar Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, CMC, Vellore Summary: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a problem encountered in
BEDSIDE ULTRASOUND Part 2 Diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis Kishore Kumar Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, CMC, Vellore Summary: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a problem encountered in
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
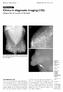 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Ultrasound Physics & Doppler
 Ultrasound Physics & Doppler Endocrine University 2018 Mark Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Objectives Review the essential components of ultrasound physics in neck sonography Demonstrate the importance of ultrasound
Ultrasound Physics & Doppler Endocrine University 2018 Mark Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Objectives Review the essential components of ultrasound physics in neck sonography Demonstrate the importance of ultrasound
Kenji Yuasa, Toshiyuki Kawazu, Naonobu Kunitake, Satoru Uehara, Junichi Omagari, Kazunori Yoshiura, Eiji Nakayama, and Shigenobu Kanda
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1127 1132, June/July 2000 Sonography for the Detection of Cervical Lymph Node Metastases among Patients with Tongue Cancer: Criteria for Early Detection and Assessment of Follow-up
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1127 1132, June/July 2000 Sonography for the Detection of Cervical Lymph Node Metastases among Patients with Tongue Cancer: Criteria for Early Detection and Assessment of Follow-up
The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes
 Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
High thyroglobulin (Tg) in a lymph node indicates metastatic
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Optimized Cutoff Value and Indication for Washout Thyroglobulin Level According to Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer J.Y. Jung, J.H.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK Optimized Cutoff Value and Indication for Washout Thyroglobulin Level According to Ultrasound Findings in Patients with Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer J.Y. Jung, J.H.
MAIN ARTICLE S-T TOH 1, H-W YUEN 3, K-H LIM 2, Y-H GOH 1, H-K C GOH 1
 The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2011), 125, 70 77. JLO (1984) Limited, 2010 doi:10.1017/s0022215110001933 MAIN ARTICLE Residual cervical lymphadenopathy after definitive treatment of nasopharyngeal
The Journal of Laryngology & Otology (2011), 125, 70 77. JLO (1984) Limited, 2010 doi:10.1017/s0022215110001933 MAIN ARTICLE Residual cervical lymphadenopathy after definitive treatment of nasopharyngeal
Ultrasonography of the Neck as an Adjunct to FNA. Nicole Massoll M.D.
 Ultrasonography of the Neck as an Adjunct to FNA Nicole Massoll M.D. Basic Features of Head and Neck Ultrasound and Anatomy Nicole Massoll M.D. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock
Ultrasonography of the Neck as an Adjunct to FNA Nicole Massoll M.D. Basic Features of Head and Neck Ultrasound and Anatomy Nicole Massoll M.D. University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock
4/22/2010. Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey.
 Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Head Neck Surgeon Perspective Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey Thyroid gland Small endocrine gland:
Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Head Neck Surgeon Perspective Hakan Korkmaz, MD Assoc. Prof. of Otolaryngology Ankara Dıșkapı Training Hospital-Turkey Thyroid gland Small endocrine gland:
Diagnosis of lymph node metastases of head and neck cancer and evaluation of effects of chemoradiotherapy using ultrasonography
 Int J Clin Oncol (2010) 15:23 32 DOI 10.1007/s10147-009-0017-1 REVIEW ARTICLE Diagnosis of lymph node metastases of head and neck cancer and evaluation of effects of chemoradiotherapy using ultrasonography
Int J Clin Oncol (2010) 15:23 32 DOI 10.1007/s10147-009-0017-1 REVIEW ARTICLE Diagnosis of lymph node metastases of head and neck cancer and evaluation of effects of chemoradiotherapy using ultrasonography
challenge is to distinguish the few clinically significant malignant nodules from many benign ones (Table 1).
 Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2015, pp- 71-76 IndianJournals.com A product of Diva Enterprises Pvt. Ltd. DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2015.00018.7 Original Research Ultrasound
Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2015, pp- 71-76 IndianJournals.com A product of Diva Enterprises Pvt. Ltd. DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2015.00018.7 Original Research Ultrasound
Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/24 Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study K Florence, K Suresh, K Lavanya Department
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/24 Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study K Florence, K Suresh, K Lavanya Department
JMSCR Vol 3 Issue 10 Page October 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i10.37 Spectrum of Cytological Findings In Patients with Superficial Lymphadenopathy:
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i10.37 Spectrum of Cytological Findings In Patients with Superficial Lymphadenopathy:
A Standard Endobronchial Ultrasound Image Classification System
 CHEST Original Research INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY The Utility of Sonographic Features During Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration for Lymph Node Staging in Patients With Lung
CHEST Original Research INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY The Utility of Sonographic Features During Endobronchial Ultrasound-Guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration for Lymph Node Staging in Patients With Lung
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological Findings in Patients with Breast Cancer
 DOI:10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3615 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:06/09/2018 Acceptance:10/13/2018 Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological
DOI:10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.12.3615 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:06/09/2018 Acceptance:10/13/2018 Diagnostic Accuracy of Axillary Ultrasonography Compared with Intra-operative Pathological
Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorder Unit Regina Apostolorum Hospital
 Enrico Papini Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorder Unit Regina Apostolorum Hospital Albano Laziale, Italy The Following Faculty have provide no information regarding significant relationship with commercial
Enrico Papini Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorder Unit Regina Apostolorum Hospital Albano Laziale, Italy The Following Faculty have provide no information regarding significant relationship with commercial
Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of breast lesions with USG and colour Doppler Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler Falguni Shah 1, Hemangi Patel 2*, Nila Gandhi 3, Sudhir Singh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of breast lesions with USG and colour Doppler Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler Falguni Shah 1, Hemangi Patel 2*, Nila Gandhi 3, Sudhir Singh
Correlation CEUS & Sono Elastography for Malignant Thyroid Nodule Evaluation
 Correlation CEUS & Sono Elastography for Malignant Thyroid Nodule Evaluation N Kumaran MD, Md Ameen MD ULTRASOUND Department Of Radiodiagnosis, Velammal Teaching Hospital, MaduralTuticorin Ring Road, Anupandi,
Correlation CEUS & Sono Elastography for Malignant Thyroid Nodule Evaluation N Kumaran MD, Md Ameen MD ULTRASOUND Department Of Radiodiagnosis, Velammal Teaching Hospital, MaduralTuticorin Ring Road, Anupandi,
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
COMPARISON OF ULTRASOUND FINDINGS WITH CYTOLOGIC RESULTS IN THYROID NODULES
 COMPARISON OF ULTRASOUND FINDINGS WITH CYTOLOGIC RESULTS IN THYROID NODULES E. Razmpa 1, H. Ghanaati 2, B. Naghibzadeh 3, P. Mazloom 1 and A. Kashfi 1 1) Department of Otolaryngology, School of Medicine,
COMPARISON OF ULTRASOUND FINDINGS WITH CYTOLOGIC RESULTS IN THYROID NODULES E. Razmpa 1, H. Ghanaati 2, B. Naghibzadeh 3, P. Mazloom 1 and A. Kashfi 1 1) Department of Otolaryngology, School of Medicine,
KYAMC Journal Vol. 4, No.-2, January 2014
 Orginal Artical Detection of Cervical Lymphnode Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Ultrasonogram Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) and Comparison with Computed Tomographic (CT) Findings
Orginal Artical Detection of Cervical Lymphnode Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Ultrasonogram Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) and Comparison with Computed Tomographic (CT) Findings
Evaluation of Neck Lymph Node Metastasis on Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound: An Animal Study
 Original rticle Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 10, No. 1: 109-114, March 2017 https://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2015.01284 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Evaluation of Neck Lymph Node Metastasis
Original rticle Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 10, No. 1: 109-114, March 2017 https://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2015.01284 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Evaluation of Neck Lymph Node Metastasis
Radiologic Importance of a High- Resistive Vertebral Artery Doppler Waveform on Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography
 CME Article Radiologic Importance of a High- Resistive Vertebral Artery Doppler Waveform on Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography Esther S. H. Kim, MD, MPH, Megan Thompson, Kristine M. Nacion, BA, Carmel Celestin,
CME Article Radiologic Importance of a High- Resistive Vertebral Artery Doppler Waveform on Carotid Duplex Ultrasonography Esther S. H. Kim, MD, MPH, Megan Thompson, Kristine M. Nacion, BA, Carmel Celestin,
Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management
 Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University,
Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 02 Pages February 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i2.95 Evaluation of Doppler Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i2.95 Evaluation of Doppler Spectral Indices
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Sonographically Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Cervical Lymphadenopathy in Patients Without Known Malignancy
 Article Sonographically Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Cervical Lymphadenopathy in Patients Without Known Malignancy Byung Moon Kim, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Min Jung Kim, MD, Woo-Ik Yang, MD, Cheong Soo Park,
Article Sonographically Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Cervical Lymphadenopathy in Patients Without Known Malignancy Byung Moon Kim, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Min Jung Kim, MD, Woo-Ik Yang, MD, Cheong Soo Park,
Sonographic assessment of thyroid diseases with histopathological correlation
 Original article Sonographic assessment of thyroid diseases with histopathological correlation Vijaykanth reddy* 1, Shivaprasad V.R 2, Nimisha E.K 3 *1 Resident, Department of Radiology, Sri Venkateshwaraa
Original article Sonographic assessment of thyroid diseases with histopathological correlation Vijaykanth reddy* 1, Shivaprasad V.R 2, Nimisha E.K 3 *1 Resident, Department of Radiology, Sri Venkateshwaraa
CONSENSUS ULTRASOUND SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL AFTER POSITIVE SENTINEL LYMPH NODE BIOPSY FOR MELANOMA
 CONSENSUS ULTRASOUND SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL AFTER POSITIVE SENTINEL LYMPH NODE BIOPSY FOR MELANOMA Created by Drs P. Robins, Z. Al-Ogaili and B. Adler in collaboration with the WA Kirkbride Melanoma Advisory
CONSENSUS ULTRASOUND SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL AFTER POSITIVE SENTINEL LYMPH NODE BIOPSY FOR MELANOMA Created by Drs P. Robins, Z. Al-Ogaili and B. Adler in collaboration with the WA Kirkbride Melanoma Advisory
