Bronchial Adenoma. Clinical Material
|
|
|
- Camron Pope
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
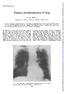
1 Robert E. Miller, Col, and Alan R. Hopeman, Col, both MC, USA (Ret) ABSTRACT Thirty-three patients with bronchial adenoma have been treated in U.S. Army hospitals. These included 27 with carcinoid, 3 with mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and 3 with adenoid cystic carcinoma. No deaths could be directly related to the adenomas during an average follow-up of 14.5 years. T he experience of the Memorial Cancer Center [ 11 portrays bronchial adenoma - including bronchial carcinoid, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and adenoid cystic carcinoma - as a rapidly developing lesion with a disc :ouraging 5-year survival rate. Others [2-4, 12,201 have characterized the lesions as showing slow growth, local extension, and. rare distant metastases and having a 5-year survival rate of 75 to 94%. The purpose of this report is to record an experience with bronchial adenoma in which no deaths could be directly related to the virulence of the malignancy. Clinical Material Thirty-three patients were treated for bronchial adenoma from 1945 to the present in five Army hospitals: 25 at Fitzsimons Army Medical Center, 4 at Letterman Army Medical Center, 2 at Tripler Army Medical Center, 1 at Walter Reed Army Medical Center, and 1 at Martin Army Hospital. Twenty-seven had carcinoid, 3 had mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and 3 had adenoid cystic carcinoma. The average age and sex distribution of the patients is shown in Table 1. There were 31 whites and 2 blacks. The symptoms when the patients were first seen included, in order of frequency, cough, recurrent pneumonia, hemoptysis, fever, and chest pain (Table 2). One patient was asymptomatic; the lesion was detected on routine chest roentgenogram. Four patients complained of hemoptysis as the only symptom. Four had had symptoms present for 1.5,4,5, and 10 years, respectively, while the remaining patients had had symptoms for less than 1 year. A diagnosis was made by bronchoscopy with biopsy in 8 patients. Biopsy of the mucosa overlying the tumor revealed chronic inflammatory bronchitis in 3 patients. In the remaining 22 patients the lesion was not visualized or biopsied. The sites of tumor (Figure) were almost equally distributed between the right and left lung with a slight predilection for the lower lobes. From the Department of Surgery, Fitzsimons Army Medical Center, Denver, Colo. We are grateful to Thomas G. Nelson, Col, Thomas J. Whelan, Jr., BG, and Arthur Cohen, Col, all MC, USA (Ret) for their assistance in collecting the material presented. We also wish to acknowledge the assistance of Mrs. Dell Benabese and Mrs. Doris Wiggins in the preparation of this paper. Accepted for publication Dec. 4, Address reprint requests to Dr. Miller, The Longmont Clinic, 1925 Mountain View Ave., Longmont, Colo THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
2 TABLE 1. AGE AND SEX DISTRIBUTION OF 33 PATIENTS WITH BRONCHIAL ADENOMA Average Age Sex Type of Adenoma No. of Patients (Range) Male Female Carcinoid (11-65) 22 5 Mucoepidermoid carcinoma 3 21 (12-30) 2 1 Adenoid cystic carcinoma 3 41 (37-51) 1 2 All 33 patients were treated by resection (Table 3). One patient had a wedge resection and another had segmental resection, leaving the superior segment of the left lower lobe. All patients with adenoid cystic carcinoma had central lesions requiring pneumonectomy. Postoperative irradiation was used in the treatment of 2 patients with positive nodes. Lymph node metastases were found in 3 patients with bronchial carcinoid and 2 with adenoid cystic carcinoma; none were found in patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma. No recurrences were observed in patients who had carcinoid adenoma or mucoepidermoid carcinoma, although 2 patients had recurrences of adenoid cystic carcinoma at 6 and 11 years, respectively. Survival statistics are shown in Table 4 and causes of death in Table 5. During the period of observation, 3 patients developed new malignancies (thyroid, breast, and kidney). Bronchial carcinoid syndrome was not observed in any of the 33 patients. Because of the perplexing problem of managing bronchial carcinoid with lymph node metastases, the following patients are discussed. CASE HISTORIES Patient 1. A 30-year-old man was admitted on December 10, 1945, for evaluation of an asymptomatic left pulmonary lesion detected on routine chest roentgenogram. Bronchoscopy revealed a left lower lobe lesion, but biopsy attempts were unsuccessful in establishing a preoperative diagnosis. A left lower lobectomy was performed and a diagnosis of bronchogenic adenocarcinoma with regional lymph node metastases was made. Radiation therapy, given in two courses, was completed in July and September, In January, 1947, chest roentgenograms revealed an increase in the density of the left lower lung field, and radiation therapy was again instituted. In September, 1947, the patient TABLE 2. SYMPTOMS IN 33 PATIENTS WITH BRONCHIAL ADENOMA Symptom Cough Recurrent pneumonia Hemoptysis Fever Chest pain No. of Patients VOL. 19. NO. 4, APRIL,
3 MILLER AND HOPEMAN Distribution of adenomas in 33 patients: Right side, 17 cases; left side, 16 cases. complained of a nonproductive cough and weight gain. Chest films revealed an increase in pleural fluid, and bronchoscopy revealed an extrinsic mass encroaching on the lumen of the left upper lobe bronchus. Radiation therapy was again instituted. Clinical signs of constrictive pericarditis precipitated operative intervention, which was unsuccessful. Postmortem examination revealed constrictive pericarditis secondary to radiation therapy; no tumor was present. Review of the original tissue by the Army Medical Museum revealed the lesion to be a bronchial adenoma, carcinoid ty Pe. When a regional lymph node contains metastatic bronchial carcinoid in a left lower lobectomy specimen, as in this patient, it would be uncertain whether or not there was tumor in the remaining portion of the left lung. Therefore, with a final diagnosis of bronchial adenoma at the time of operation, we would recommend a complete pneumonectomy and hilar lymphadenectomy to eradicate the lesion. Patient 2. A 19-year-old man was admitted on May 9, 1966, for evaluation of recurrent middle lobe pneumonia. Bronchoscopy revealed extrinsic pressure on the middle lobe bronchus. After evaluation, a middle lobectomy was performed. A bronchial carcinoid accounted for the extrinsic pressure, and regional lymph nodes contained metastatic tumor. A right lower lobectomy and lymphadenectomy of the right bronchus were performed; the lymph nodes again TABLE 3. TREATMENT IN 33 PATIENTS WITH BRONCHIAL ADENOMA Type of Adenoma Treatment No. of Patients Carcinoid (27 patients) Pneumonectomy Bilobectomy Lobectomy Segmental resection Wedge resection Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Bilobectomy (3 patients) Lobectomy Adenoid cystic carcinoma Pneumonectomy (3 patients) THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
4 TABLE 4. LENGTH OF SURVIVAL IN 33 PATIENTS WITH BRONCHIAL ADENOMA Type of Adenoma Average Survival (Yr) Range Carcinoid (27 patients) yr Mucoepidermoid carcinoma yr (3 patients) Adenoid cystic carcinoma hr- 15 yr (3 patients) contained metastatic bronchial carcinoid. A complete pneumonectomy and mediastinal lymph node dissection were accomplished at a later date, at which time no tumor was found in the resected nodes or specimens. The patient was thereafter medically retired and was performing normal activities as an aircraft mechanic as of July 10, This patient underwent staged operations to remove the tumor, while we simultaneously attempted to preserve maximal pulmonary function. In retrospect, we believe that the second operation eradicated the tumor, although the complete pneumonectomy and lymphadenectomy were the only means of assuring total extirpation of the disease. Patient 3. A 23-year-old woman was admitted on October 19, 1970, for evaluation of hemoptysis of 4 months duration. A chest roentgenogram revealed a solitary lesion in the right lower lobe, and bronchography demonstrated occlusion of the posterior basilar segmental bronchus. During the course of a right lower lobectomy, a lymph node in the minor fissure was found 2 cm from the tumor. Pathological examination by frozen section revealed reactive hyperplasia in the lymph node and bronchial carcinoid in the pulmonary tumor. Permanent histological sections showed a focus of metastatic bronchial carcinoid in the lymph node. The patient had a benign postoperative course and was performing normal activities as of April, 1974, with no roentgenographic abnormalities. TABLE 5. CAUSE OF DEATH AFTER OPERATION IN 6 PATIENTS WITH BRONCHIAL ADENOMA Time after Operation Cause of Death CARClNOlD 16 yr Renal failure 16 yr Acute hemorrhagic pneumonitis 12 yr Subarachnoid hemorrhage 1.5 yr Constrictive pericarditis secondary to irradiation ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA 12 hr 13 yr Pulmonary edema Pulmonary insufficiency 8c pneumonitis VOL. 19, NO. 4, APRIL,
5 MILLER AND HOPEMAN The involvement of adjacent pulmonary tissue and other lymph nodes with metastatic bronchial carcinoid is unknown. To assure complete local resection, a middle lobectomy and lymphadenectomy of the right bronchus would be recommended. If metastatic foci were found, further resection would be indicated, as in Patient 2, since despite careful follow-up, roentgenographic changes might not fully document growth of the carcinoid before it became unresectable. Comment Bronchial adenoma has been a useful term for identifying those pulmonary lesions having a malignant potential but a less aggressive nature than bronchogenic carcinoma. The terms bronchial carcinoid, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and adenoid cystic carcinoma must be used for any meaningful discussion of these tumors. BRONCHIAL CARCINOID The first clinically diagnosed bronchial carcinoid was described by Kramer 171 in 1930, although Laennec [8] recognized the lesion in Carcinoid tumors have a slight predilection for the lower lobes. Most lesions are visible by bronchoscopy, but peripheral as well as multiple lesions occur. Distant metastases or regional lymph node involvement occurs in approximately 12% of cases [lo]. Most reports [2-4, 12, 201 indicate that bronchial carcinoid grows slowly, has a low potential for malignancy, and allows long-term survival. A recent report [ 191, however, revealed a dismal 5-year survival rate of 59%. To explain the different results, specific factors will be analyzed: namely, age of the patient, stage of disease, and type of treatment. Since most reports on bronchial adenoma do not evaluate the specific types but present the data collectively, exact evaluations are impossible. The average age range in five series [2-4, 12, 201 was 40 to 49 years for all patients with bronchial adenoma. The average age for patients with bronchial carcinoid in the series reported by Turnbull and associates [ 191 was 49 years. In our 27 patients the average age was 30 years. Age seems to play a minor role in survival with carcinoid adenomas. In Turnbull and associates series [ 191 the span of treatment encompassed the years from 1926 to Of the 44 patients with carcinoid, only 27 had thoracotomies. There were 24 resections, 7 pneumonectomies, 14 lobectomies, and 3 wedge or segmental resections. The 5-year survival was 59%. In the series of Wilkins and co-workers [20], the span of treatment encompassed the years from 1909 to Only 67 of 82 lesions were resected. All 57 patients with carcinoid adenoma who were explored underwent resection. There were 14 pneumonectomies, 16 bilobectomies, 23 lobectomies, and 4 lesser resections. The 5-year survival was 75%. In our series all patients underwent resection, and only 3 required pneumonectomy. Patients in Turnbull s [19] and Wilkins [20] series were treated with fulguration and radiation for tumors that would now be considered for resection. Not all 382 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
6 patients in their series who had exploratory operations underwent resection, and greater parenchymal resections probably indicated more advanced disease. McBurney, Kirklin, and Woolner [ 101 reviewed 700 patients with bronchial adenoma up to 1952 and found 87 with metastatic disease. In thirteen articles since that time 79 metastasizing lesions were found in 645 patients. Again the type of adenoma was not always identified; however, approximately one-third of the metastatic lesions in patients reported up through 1952 were adenoid cystic carcinomas. If we realize that approximately 12% of the lesions will metastasize, we must perform adequate resection and carefully examine the resected specimen to insure complete removal of the tumor. If there is any metastatic disease, further resection should be done. ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA Hamper1 [6] described adenoid cystic carcinoma (cylindroma) in This tumor is more aggressive and has a greater propensity for recurrence. Adenoid cystic carcinoma occurs more centrally than carcinoid and more frequently spreads to regional lymph nodes. There is a general consensus that the malignant potential of the tumor is formidable [9, 12, MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA Mucoepidermoid carcinoma was described in 1952 by Smetana [161 as the third variety of endobronchial neoplasm. A patient in this series, 1 of 2 initially described by Dr. Smetana, is alive and well as of April, 1974, 23 years after operation. Payne and colleagues [ 141 and Meckstroth and co-workers 1111 considered these tumors almost benign. In 1966, Reichle and Rosemond [ 151 reviewed 29 patients and reported no recurrence when the tumor had been completely resected. Ozlu [IS] and Dowling [5] and their co-workers discussed the first patients dying from metastatic mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the lung. Twelve patients presented by Turnbull and associates [ 191 constitute the largest series of patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma reported. All these patients died from their disease within 18 months. Axelsson, Burcharth, and Johansen [ 11 concluded that this is a malignant lesion that grows rapidly, and they recommend radical resection. Approximately 50 patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma have been reported in the English literature. Any conclusions drawn from this small number of cases are tentative, although some generalizations do seem apparent. The inconsistency in the degree of malignancy can best be explained by noting the age of the patient and the stage of the disease when treated. In the Turnbull and Axelsson series the average age was 59 and 61 years, respectively. In Reichle s review the average age was 45 years, and among our 3 patients it was 2 1. In Turnbull s series of 12 patients, 7 had exploratory operations; 3 had a pneumonectomy, 1 a lobectomy, and 3 were unresectable. Six patients who had preoperative localized disease survived operation but later died of widespread metastatic disease. Five patients had metastatic disease on admission and were treated symptomatically. Of the 4 patients in Axelsson s series who had exploratory operations, 2 had a pneumonectomy and 1 a lobectomy. Two patients were free of disease in a short VOL. 19, NO. 4, APRIL
7 MILLER AND HOPEMAN follow-up and 1 died in the postoperative period with no residual disease. One patient had unresectable disease and died 5 months postoperatively. In Reichle's review of 29 patients, 6 had a pneumonectomy and 13 had either lobectomy, bilobectomy, or segmental resection. Two patients had endoscopic resection and 6 received irradiation or conservative treatment. In 2 the treatment was not recorded. Of the latter 6, the average age was 55. The 3 patients in our series had no nodal involvement and underwent lobectomy or bilobectomy. All patients are now living and well. Conclusion Symptoms of persistent cough, hemoptysis, fever, chest pain, and recurrent pneumonia should stimulate aggressive diagnostic investigation. If lesions are found during bronchoscopy, biopsy should be performed. The vascularity of these lesions should not deter biopsy, but rather incite the endoscopist to careful observation and management. From the material presented, it is evident that the survival rate is higher in younger patients and less parenchymal resection is required to eradicate the tumor. Long-term follow-up is essential, not only to better understand the disease entities, but to aid early detection of unrelated malignancies 19, 19, 201. Bronchial carcinoid, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and adenoid cystic carcinoma must be considered as separate entities. Ref rences 1. Axelsson, C., Burcharth, F., and Johansen, A. Mucoepidermoid lung tumors. J Thorac Cardwvasc Surg 65:902, Batson, J. F., Gale, J. W., and Hickey, R. C. Bronchial adenomata: A clinical resume. Arch Surg 92:623, Bower, G. Bronchial adenoma: A review of 28 cases. Am Rev Resp Dis 92:558, Donahue, J. K., Weichert, R. F., and Ochsner, J. L. Bronchial adenoma. Ann Surg 167:873, Dowling, E. A., Miller, R. E., Johnson, I. M., and Collier, S. C. D. Mucoepidermoid tumors of bronchus. Surgery 52:600, Hamperl, W. Uber gutartige bronchial Tumoren (Cylindroma und Carcinoide). Virchows Arch Pathol Anat 300:46, Kramer, R. Adenoma of bronchus. Am Otol39:689, Laennec, R. T. H. Trait6 de l'auscultation mediate et des maladies des poumons et du coeur (3d ed). Paris: Chaud, Vol 1, p Logan, W. D., Jr., Sehdena, J., Hatcher, C. R., and Abbott, 0. A. Tracheobronchial adenomas. Am Surg 36:359, McBurney, R. P., Kirklin, W., and Woolner, L. B. Metastasizing bronchial adenomas. Surg Gynecol Obstet 96:482, Meckstroth, C. V., Davidson, H. B., and Kress, G. 0. Mucoepidermoid tumor of the bronchus. Chest 40:652, OGrady, W. P., McDivitt, R. W., Holman, C. W., and Moore, S. W. Bronchial adenoma. Arch Surg 101:558, Ozlu, C., Christopherson, W. M., and Allen, J. D., Jr. Mucoepidermoid tuiiiorsof the bronchus. J Thorac Cardiouasc Surg 42:24, Payne, W. S., Ellis, F. H., Jr., Woolner, L. B., and Moersch, H. J. The surgical treatment of cylindroma (adenoid cystic carcinoma) and mucoepidermoid tumors of the bronchus. J Thorac Cardiouasc Surg 38:709, I 384 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY
8 15. Rkchle, F. A., and Rosemond, G. P. Mucoepidermoid tumors of the bronchus. J Thorac Cardwvasc Surg 51:443, Smetana, H. F. Quoted by A. A. Liebow in Tumors of the Lower Respiratory Tract. In Atlas of Tumor Pathology, Sect V, Fasc Washington, D.C.: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Takita, H., Vincent, D. G., and Adler, R. H. Bronchial adenoma. NJ State J Med 71:563, Toole, A. L., and Stern, H. Carcinoid and adenoid cystic carcinoma of the bronchus. Ann Thorac Surg 13:63, Turnbull, A. D., Huvos, A. G., Goodner, J. T., and Beattie, E. J., Jr. The malignant potential of bronchial adenoma. Ann Thorac Surg 14:453, Wilkins, E. W., Darling, R. C., Soulter, L., and Sniffen, R. C. A continuing clinical survey of adenomas of the trachea and bronchus in a general hospital. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 46:279, NOTICE FROM THE SOUTHERN THORACIC SURGICAL ASSOCIATION The Twenty-second Annual Meeting of the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association will be held at the Fairmont-Roosevelt Hotel, New Orleans, La., on November 6-8, Reservations may be made by writing to the Reservations Manager, Fairmont-Roosevelt Hotel, New Orleans, La. Members wishing to participate in the scientific program should submit abstracts - typed double-spaced and in triplicate - to David C. Sabiston, Jr., M.D. [Chairman of the Program Committee], Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C The deadline for submission of abstracts is June 1, The Council of the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association has ruled that all slides used during presentation of papers and discussions must be of 35-mm size. If additional information is required, inquiries should be directed to Dr. Sabiston. Application for membership in the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association, on forms provided by the Association, should be sent directly to J. Alex Hailer, Jr., M.D. [Chairman of the Membership Committee], The Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Md The deadline for application to membership is September 1, Papers that are accepted for the program will be considered for publication in The Annals and must be submitted to the Editor by October 15, JAMES W. BROOKS, M.D. Secretary-Treasurer VOL. 19, NO. 4, APRIL,
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Trachea ORIGINAL ARTICLES
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Trachea and Bronchus: The Case for Conservative Resection Robert H. Breyer, M.D., John R. Dainauskas, M.D., Robert J. Jensik, M.D., and L. Penfield Faber,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Trachea and Bronchus: The Case for Conservative Resection Robert H. Breyer, M.D., John R. Dainauskas, M.D., Robert J. Jensik, M.D., and L. Penfield Faber,
Carcinoma of the Lung
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 1 I - NUMBER 3 0 MARCH 1971 Carcinoma of the Lung M. L. Dillon, M.D., and
Muco-Epidermoid Tumor of the Bronchus
 Muco-Epidermoid Tumor of the Bronchus CHARLES V. MECKSTROTH, MD., F.C.C.P., HORACE B. DAVIDSON, M.D. and GEORGE O. KRESS, MD., F.C.C.P. Columbus, ome- As the techniques of pulmonary resection became known
Muco-Epidermoid Tumor of the Bronchus CHARLES V. MECKSTROTH, MD., F.C.C.P., HORACE B. DAVIDSON, M.D. and GEORGE O. KRESS, MD., F.C.C.P. Columbus, ome- As the techniques of pulmonary resection became known
The Role of Radiation Therapy
 The Role of Radiation Therapy and Surgery in the Treatment of Bronchogenic Carcinoma R Adams Cowley, M.D., Morris J. Wizenberg, M.D., and Eugene J. Linberg, M.D. A study of the combined use of preoperative
The Role of Radiation Therapy and Surgery in the Treatment of Bronchogenic Carcinoma R Adams Cowley, M.D., Morris J. Wizenberg, M.D., and Eugene J. Linberg, M.D. A study of the combined use of preoperative
Carcinoma of the Lung in Women
 Carcinoma of the Lung in Marvin M. Kirsh, M.D., Jeanne Tashian, M.A., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT The 5-year survival of 293 men and of 78 women undergoing pulmonary resection and mediastinal lymph
Carcinoma of the Lung in Marvin M. Kirsh, M.D., Jeanne Tashian, M.A., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT The 5-year survival of 293 men and of 78 women undergoing pulmonary resection and mediastinal lymph
came from a carcinoma and in 12 from a sarcoma. Ninety lesions were intrapulmonary and the as the chest wall and pleura. Details of the primary
 Thorax 1982;37:366-370 Thoracic metastases MARY P SHEPHERD From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Harefield ABSTRACI One hundred and four patients are reviewed who were found to have thoracic
Thorax 1982;37:366-370 Thoracic metastases MARY P SHEPHERD From the Thoracic Surgical Unit, Harefield Hospital, Harefield ABSTRACI One hundred and four patients are reviewed who were found to have thoracic
Despite their reputation of benignity, carcinoid tumors
 Operative Risk and Prognostic Factors of Typical Bronchial Carcinoid Tumors Xavier Ducrocq, MD, Pascal Thomas, MD, Gilbert Massard, MD, Pierre Barsotti, MD, Roger Giudicelli, MD, Pierre Fuentes, MD, and
Operative Risk and Prognostic Factors of Typical Bronchial Carcinoid Tumors Xavier Ducrocq, MD, Pascal Thomas, MD, Gilbert Massard, MD, Pierre Barsotti, MD, Roger Giudicelli, MD, Pierre Fuentes, MD, and
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER
 MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
MEDIASTINAL LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN PATIENTS WITH CLINICAL STAGE I PERIPHERAL NON-SMALL-CELL LUNG CANCER Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Hideki Akamatsu, MD a Yuzo
Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
Surgical Treatment for Pulmonary Me. Tsunehisa; Kugimiya, Toshiyasu. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1983, 28
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Surgical Treatment for Pulmonary Me Ayabe, Hiroyoshi; Tomita, Masao; Na Katsunobu; Nakao, Susumu; Eguchi, M Tsunehisa; Kugimiya, Toshiyasu Citation Acta
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Surgical Treatment for Pulmonary Me Ayabe, Hiroyoshi; Tomita, Masao; Na Katsunobu; Nakao, Susumu; Eguchi, M Tsunehisa; Kugimiya, Toshiyasu Citation Acta
The Value of Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Pulmonary and Chest Wall Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 The Value of Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Pulmonary and Chest Wall Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma G. A. Patterson, M.D., R. Ilves, M.D., R. J. Ginsberg, M.D., J. D. Cooper, M.D., T. R. J. Todd, M.D.,
The Value of Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Pulmonary and Chest Wall Resection for Bronchogenic Carcinoma G. A. Patterson, M.D., R. Ilves, M.D., R. J. Ginsberg, M.D., J. D. Cooper, M.D., T. R. J. Todd, M.D.,
Bronchial Carcinoma and the Lymphatic Sump: The Importance of Bronchoscopic Findings
 Bronchial Carcinoma and the Lymphatic Sump: The Importance of Bronchoscopic Findings Gordon F. Murray, M.D., Ormond C. Mendes, M.D., and Benson R. Wilcox, M.D. ABSTRACT The lymphatic sump of Borrie is
Bronchial Carcinoma and the Lymphatic Sump: The Importance of Bronchoscopic Findings Gordon F. Murray, M.D., Ormond C. Mendes, M.D., and Benson R. Wilcox, M.D. ABSTRACT The lymphatic sump of Borrie is
Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
ORIGINAL ARTICLES: Superior and Basal Segment Lung Cancers in the Lower Lobe Have Different Lymph Node Metastatic Pathways and Prognosis Shun-ichi Watanabe, MD, Kenji Suzuki, MD, and Hisao Asamura, MD
Mediastinal Spread of Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Bronchogenic Carcinoma*
 Mediastinal Spread of Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Bronchogenic Carcinoma* Mediastinal Nodal Metastases in Lung Cancer Yoh Watanabe, M.D., F.C.C.P.; ]unzo Shimizu, M.D.; Makoto Tsubota, M.D.; and Takashi
Mediastinal Spread of Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Bronchogenic Carcinoma* Mediastinal Nodal Metastases in Lung Cancer Yoh Watanabe, M.D., F.C.C.P.; ]unzo Shimizu, M.D.; Makoto Tsubota, M.D.; and Takashi
The right middle lobe is the smallest lobe in the lung, and
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Superior Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastases on Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Located in the Right Middle Lobe Yukinori Sakao, MD, PhD,* Sakae Okumura, MD,* Mun Mingyon,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Superior Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastases on Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Located in the Right Middle Lobe Yukinori Sakao, MD, PhD,* Sakae Okumura, MD,* Mun Mingyon,
Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma
 CASE REPORTS Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Bronchus Graham Fallon, M.D., Medad Schiller, M.D., and James W. Kilman, M.D. ABSTRACT A 6-year-old child with an unresectable rhabdomyosarcoma of the right
CASE REPORTS Primary Rhabdomyosarcoma of the Bronchus Graham Fallon, M.D., Medad Schiller, M.D., and James W. Kilman, M.D. ABSTRACT A 6-year-old child with an unresectable rhabdomyosarcoma of the right
VOLUME 19 NUMBER 2 * FEBRUARY 1975
 THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 9 NUMBER 2 * FEBRUARY 975 Medias tinoscopy Its Application in Central Versus
THE ANNALS OF THORACIC SURGERY Journal of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Southern Thoracic Surgical Association VOLUME 9 NUMBER 2 * FEBRUARY 975 Medias tinoscopy Its Application in Central Versus
Preferred Surgical Treatment for Alveolar Cell Caranoma
 Preferred Surgical Treatment for Alveolar Cell Caranoma Edwin C. James, LTC, George F. Schuchmann, LTC, Roger V. Hall, MAJ, James R. Patterson, MAJ, James T. Gillespie, COL, and Alphonse C. Gomez, COL,
Preferred Surgical Treatment for Alveolar Cell Caranoma Edwin C. James, LTC, George F. Schuchmann, LTC, Roger V. Hall, MAJ, James R. Patterson, MAJ, James T. Gillespie, COL, and Alphonse C. Gomez, COL,
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital Muhammad Rizwan Khan,Sulaiman B. Hasan,Shahid A. Sami ( Department of Surgery, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Disease Spectrum and Management in a Tertiary Care Hospital Muhammad Rizwan Khan,Sulaiman B. Hasan,Shahid A. Sami ( Department of Surgery, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/23566
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/23566
Aggressive Slurgical Management of Testicular Carcinoma Metastatic to Lungs and Mediastinurn
 Aggressive Slurgical Management of Testicular Carcinoma Metastatic to Lungs and Mediastinurn Isadore Mandelbaum, M.D., Stephen D. Williams, M.D., and Lawrence H. Einhorn, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past
Aggressive Slurgical Management of Testicular Carcinoma Metastatic to Lungs and Mediastinurn Isadore Mandelbaum, M.D., Stephen D. Williams, M.D., and Lawrence H. Einhorn, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past
LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN SMALL PERIPHERAL ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE LUNG
 LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN SMALL PERIPHERAL ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE LUNG Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Takehiro Watanabe, MD a Yuzo Kurita, MD b Akira Yokoyama, MD b Keiichi
LYMPH NODE METASTASIS IN SMALL PERIPHERAL ADENOCARCINOMA OF THE LUNG Tsuneyo Takizawa, MD a Masanori Terashima, MD a Teruaki Koike, MD a Takehiro Watanabe, MD a Yuzo Kurita, MD b Akira Yokoyama, MD b Keiichi
Lung Cancer-a primer. Sai Yendamuri, MD Professor and Chair, Dept of Thoracic Surgery,RPCI,Buffalo
 Lung Cancer-a primer Sai Yendamuri, MD Professor and Chair, Dept of Thoracic Surgery,RPCI,Buffalo CLINICAL CATEGORIES THE SOLITARY PULMONARY NODULE MULTIPLE PULMONARY NODULES Differential Diagnosis Malignant
Lung Cancer-a primer Sai Yendamuri, MD Professor and Chair, Dept of Thoracic Surgery,RPCI,Buffalo CLINICAL CATEGORIES THE SOLITARY PULMONARY NODULE MULTIPLE PULMONARY NODULES Differential Diagnosis Malignant
Inflammatory Pseudotumor Suspected of Lung Cancer Treated by Thoracoscopic Resection
 Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011; 17: 48 52 Case Report Inflammatory Pseudotumor Suspected of Lung Cancer Treated by Thoracoscopic Resection Shinji Hirai, MD, 1 Tatsuya Katayama, MD, 1 Naru Chatani, MD,
Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011; 17: 48 52 Case Report Inflammatory Pseudotumor Suspected of Lung Cancer Treated by Thoracoscopic Resection Shinji Hirai, MD, 1 Tatsuya Katayama, MD, 1 Naru Chatani, MD,
Treatment of Clinical Stage I Lung Cancer: Thoracoscopic Lobectomy is the Standard
 Treatment of Clinical Stage I Lung Cancer: Thoracoscopic Lobectomy is the Standard AATS General Thoracic Surgery Symposium May 5, 2010 Thomas A. D Amico MD Professor of Surgery, Duke University Medical
Treatment of Clinical Stage I Lung Cancer: Thoracoscopic Lobectomy is the Standard AATS General Thoracic Surgery Symposium May 5, 2010 Thomas A. D Amico MD Professor of Surgery, Duke University Medical
24 Ann Thorac Surg 46:24-28, July Copyright by The Society of Thoracic Surgeons
 Surgical Management of Lung Cancer with Solitary Cerebral Metastasis John R. Hankins, M.D., John E. Miller, M.D., Michael Salcman, M.D., Frank Ferraro, M.D., David C. Green, M.D., Safuh Attar, M.D., and
Surgical Management of Lung Cancer with Solitary Cerebral Metastasis John R. Hankins, M.D., John E. Miller, M.D., Michael Salcman, M.D., Frank Ferraro, M.D., David C. Green, M.D., Safuh Attar, M.D., and
The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) Lung Cancer Staging Project, Data Elements
 Page 1 Contents 1.1. Registration... 2 1.2. Patient Characteristics... 3 1.3. Laboratory Values at Diagnosis... 5 1.4. Lung Cancers with Multiple Lesions... 6 1.5. Primary Tumour Description... 10 1.6.
Page 1 Contents 1.1. Registration... 2 1.2. Patient Characteristics... 3 1.3. Laboratory Values at Diagnosis... 5 1.4. Lung Cancers with Multiple Lesions... 6 1.5. Primary Tumour Description... 10 1.6.
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma
 Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
Tumour size as a prognostic factor after resection of lung carcinoma A. S. SOORAE AND R. ABBEY SMITH Thorax, 1977, 32, 19-25 From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Walsgrave Hospital, Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery
 Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Complex Thoracoscopic Resections for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer
 Complex Thoracoscopic Resections for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Duke Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Workshop March 21, 2018 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery Section Chief, Thoracic Surgery,
Complex Thoracoscopic Resections for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Duke Thoracoscopic Lobectomy Workshop March 21, 2018 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery Section Chief, Thoracic Surgery,
Carcinoma of the Lung: A Clinical Review
 Carcinoma of the Lung: A Clinical Review R. Samuel Cromartie, 111, M.D., Edward F. Parker, M.D., James E. May, M.D., John S. Metcalf, M.D., and David M. Bartles, M.S. ABSTRACT Records of 702 patients with
Carcinoma of the Lung: A Clinical Review R. Samuel Cromartie, 111, M.D., Edward F. Parker, M.D., James E. May, M.D., John S. Metcalf, M.D., and David M. Bartles, M.S. ABSTRACT Records of 702 patients with
Chemotherapy for Adenocarcinoma and Alveolar Cell Carcinoma
 Chemotherapy for Adenocarcinoma and Alveolar Cell Carcinoma of the Lung Scott L. Faulkner, M.D., R. Benton Adkins, Jr., M.D., and Vernon H. Reynolds, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with inoperable or recurrent
Chemotherapy for Adenocarcinoma and Alveolar Cell Carcinoma of the Lung Scott L. Faulkner, M.D., R. Benton Adkins, Jr., M.D., and Vernon H. Reynolds, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with inoperable or recurrent
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
Site of Recurrence in Patients. of the Lung Resected for Cure. with Stages I and I1 Carcinoma
 Site of Recurrence in Patients with Stages I and I1 Carcinoma of the Lung Resected for Cure Steven C. Immerman, M.D., Robert M. Vanecko, M.D., Willard A. Fry, M.D., Louis R. Head, M.D., and Thomas W. Shields,
Site of Recurrence in Patients with Stages I and I1 Carcinoma of the Lung Resected for Cure Steven C. Immerman, M.D., Robert M. Vanecko, M.D., Willard A. Fry, M.D., Louis R. Head, M.D., and Thomas W. Shields,
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul. Epidemiology. Risk factors/aetiology
 Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Lymph node dissection for lung cancer is both an old
 LOBE-SPECIFIC EXTENT OF SYSTEMATIC LYMPH NODE DISSECTION FOR NON SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMAS ACCORDING TO A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF METASTASIS AND PROGNOSIS Hisao Asamura, MD Haruhiko Nakayama, MD Haruhiko
LOBE-SPECIFIC EXTENT OF SYSTEMATIC LYMPH NODE DISSECTION FOR NON SMALL CELL LUNG CARCINOMAS ACCORDING TO A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY OF METASTASIS AND PROGNOSIS Hisao Asamura, MD Haruhiko Nakayama, MD Haruhiko
Video-Mediastinoscopy Thoracoscopy (VATS)
 Surgical techniques Video-Mediastinoscopy Thoracoscopy (VATS) Gunda Leschber Department of Thoracic Surgery ELK Berlin Chest Hospital, Berlin, Germany Teaching Hospital of Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Surgical techniques Video-Mediastinoscopy Thoracoscopy (VATS) Gunda Leschber Department of Thoracic Surgery ELK Berlin Chest Hospital, Berlin, Germany Teaching Hospital of Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Primary Tumors of Ribs
 Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
Primary Tumors of Ribs Frank E. Schmidt, M.D., and Max J. Trummer, Capt, MC, USN ABSTRACT An analysis of 50 consecutive patients with primary rib tumors operated on at the U.S. Naval Hospital, San Diego,
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Radical treatment for left upper-lobe cancer via complete VATS. Jun Liu, Fei Cui, Shu-Ben Li. Introduction
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Radical treatment for left upper-lobe cancer via complete VATS Jun Liu, Fei Cui, Shu-Ben Li The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical College, Guangzhou, China ABSTRACT KEYWORDS
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Radical treatment for left upper-lobe cancer via complete VATS Jun Liu, Fei Cui, Shu-Ben Li The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical College, Guangzhou, China ABSTRACT KEYWORDS
Pulmonary Blas toma. A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Jimmy L. Cox, M.D., Robert L. Fuson, M.D., and John T. Daly, M.D.
 Pulmonary Blas toma A Case Report and Review of the Literature Jimmy L. Cox, M.D., Robert L. Fuson, M.D., and John T. Daly, M.D. P rimary pulmonary blastoma was first recognized as a distinct pathological
Pulmonary Blas toma A Case Report and Review of the Literature Jimmy L. Cox, M.D., Robert L. Fuson, M.D., and John T. Daly, M.D. P rimary pulmonary blastoma was first recognized as a distinct pathological
and Strength of Recommendations
 ASTRO with ASCO Qualifying Statements in Bold Italics s patients with T1-2, N0 non-small cell lung cancer who are medically operable? 1A: Patients with stage I NSCLC should be evaluated by a thoracic surgeon,
ASTRO with ASCO Qualifying Statements in Bold Italics s patients with T1-2, N0 non-small cell lung cancer who are medically operable? 1A: Patients with stage I NSCLC should be evaluated by a thoracic surgeon,
Although the international TNM classification system
 Prognostic Significance of Perioperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of 1,000 Consecutive Resections for Clinical Stage I Disease Morihito Okada, MD, PhD, Wataru
Prognostic Significance of Perioperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of 1,000 Consecutive Resections for Clinical Stage I Disease Morihito Okada, MD, PhD, Wataru
Treatment of Inoperable Lung Carcinoma: A Combined Modality Approach
 Treatment of Inoperable ung Carcinoma: A Combined Modality Approach Hiroshi Takita, M.D., Ariel C. Hollinshead, h.d., Donna J. Rizzo, R.N., Christine M. Kramer, M.S., Tah Y. Chen, M.D., Joginder N. Bhayana,
Treatment of Inoperable ung Carcinoma: A Combined Modality Approach Hiroshi Takita, M.D., Ariel C. Hollinshead, h.d., Donna J. Rizzo, R.N., Christine M. Kramer, M.S., Tah Y. Chen, M.D., Joginder N. Bhayana,
The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review
 Case Report The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review Jian Tang 1, Min Cao 1, Liqiang Qian 2, Yujie Fu 1,
Case Report The pure distal left main bronchial sleeve resection with total lung parenchymal preservation: report of two cases and literature review Jian Tang 1, Min Cao 1, Liqiang Qian 2, Yujie Fu 1,
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Thoracoscopic Lobectomy for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer. Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando September 19, 2014
 for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando September 19, 2014 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Endowed Professor and Vice Chair of Surgery Chief Thoracic Surgery
for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando September 19, 2014 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Endowed Professor and Vice Chair of Surgery Chief Thoracic Surgery
The Spectrum of Management of Pulmonary Ground Glass Nodules
 The Spectrum of Management of Pulmonary Ground Glass Nodules Stanley S Siegelman CT Society 10/26/2011 No financial disclosures. Noguchi M et al. Cancer 75: 2844-2852, 1995. 236 surgically resected peripheral
The Spectrum of Management of Pulmonary Ground Glass Nodules Stanley S Siegelman CT Society 10/26/2011 No financial disclosures. Noguchi M et al. Cancer 75: 2844-2852, 1995. 236 surgically resected peripheral
Lung. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density in the inferior lingular segment worrisome for neoplasm. Malignancy cannot be excluded.
 Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
Lung Case Scenario 1 A 54 year white male presents with a recent abnormal CT of the chest. The patient has a history of melanoma, kidney, and prostate cancers. 10/24/13 Chest X-ray: 2.9 cm mass like density
Thirty years of surgery for carcinoma of the bronchus
 Thorax 1983;38:428-432 Thirty years of surgery for carcinoma of the bronchus JR BELCHER From the London Chest and Middlesex Hospitals, London ABSTRACr A study has been made of 8781 patients with bronchial
Thorax 1983;38:428-432 Thirty years of surgery for carcinoma of the bronchus JR BELCHER From the London Chest and Middlesex Hospitals, London ABSTRACr A study has been made of 8781 patients with bronchial
Mediastinal Staging. Samer Kanaan, M.D.
 Mediastinal Staging Samer Kanaan, M.D. Overview Importance of accurate nodal staging Accuracy of radiographic staging Mediastinoscopy EUS EBUS Staging TNM Definitions T Stage Size of the Primary Tumor
Mediastinal Staging Samer Kanaan, M.D. Overview Importance of accurate nodal staging Accuracy of radiographic staging Mediastinoscopy EUS EBUS Staging TNM Definitions T Stage Size of the Primary Tumor
Thoracic Surgery; An Overview
 Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
Thoracic Surgery What we see Thoracic Surgery; An Overview James P. Locher, Jr, MD Methodist Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery Lung cancer Mets Fungus and TB Lung abcess and empyema Pleural based disease
squamous-cell carcinoma1
 Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
Thorax (1975), 30, 152. Local ablative procedures designed to destroy squamous-cell carcinoma1 J. M. LEE, FREDERICK P. STITIK, DARRYL CARTER, and R. ROBINSON BAKER Departments of Surgery, Pathology, and
VATS Metastasectomy. Inderpal (Netu) S. Sarkaria, MD, FACS
 VATS Metastasectomy Inderpal (Netu) S. Sarkaria, MD, FACS Vice Chairman, Clinical Affairs Director, Robotic Thoracic Surgery Co-Director, Esophageal and Lung Surgery Institute Disclosures Speaking & Education:
VATS Metastasectomy Inderpal (Netu) S. Sarkaria, MD, FACS Vice Chairman, Clinical Affairs Director, Robotic Thoracic Surgery Co-Director, Esophageal and Lung Surgery Institute Disclosures Speaking & Education:
Treatment Strategy for Patients With Surgically Discovered N2 Stage IIIA Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Treatment Strategy for Patients With Surgically Discovered N2 Stage IIIA Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Ryoichi Nakanishi, MD, Toshihiro Osaki, MD, Kozo Nakanishi, MD, Ichiro Yoshino, MD, Takashi Yoshimatsu,
Treatment Strategy for Patients With Surgically Discovered N2 Stage IIIA Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Ryoichi Nakanishi, MD, Toshihiro Osaki, MD, Kozo Nakanishi, MD, Ichiro Yoshino, MD, Takashi Yoshimatsu,
Accomplishes fundamental surgical tenets of R0 resection with systematic nodal staging for NSCLC Equivalent survival for Stage 1A disease
 Segmentectomy Made Simple Matthew J. Schuchert and Rodney J. Landreneau Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Financial Disclosures none Why Consider Anatomic Segmentectomy?
Segmentectomy Made Simple Matthew J. Schuchert and Rodney J. Landreneau Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Financial Disclosures none Why Consider Anatomic Segmentectomy?
Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015
 Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015 Review lung cancer statistics Review the risk factors Discuss presentation and staging Discuss treatment options and outcomes Discuss the status of screening
Charles Mulligan, MD, FACS, FCCP 26 March 2015 Review lung cancer statistics Review the risk factors Discuss presentation and staging Discuss treatment options and outcomes Discuss the status of screening
Quality of Life (QOL) versus Curability for Lung Cancer Surgery
 Quality of Life (QOL) versus Curability for Lung Cancer Surgery Hirokuni Yoshimura, MD Standard operations for lung cancer patients are generally accepted as performing lobectomy or pneumonectomy on the
Quality of Life (QOL) versus Curability for Lung Cancer Surgery Hirokuni Yoshimura, MD Standard operations for lung cancer patients are generally accepted as performing lobectomy or pneumonectomy on the
Bronchial carcinosarcoma
 Bronchial carcinosarcoma Carolina Carcano 1*, Edward Savage 2, Maria Julia Diacovo 3, Jacobo Kirsch 1 1. Division of Radiology, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Fl, USA 2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
Bronchial carcinosarcoma Carolina Carcano 1*, Edward Savage 2, Maria Julia Diacovo 3, Jacobo Kirsch 1 1. Division of Radiology, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Fl, USA 2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular
SURVIVAL AFTER LUNG RESECTION FOR BRONCHIAL CARCINOMA
 Thorax (1955), 10, 183. SURVIVAL AFTER LUNG RESECTION FOR BRONCHIAL CARCINOMA BY J. R. BIGNALL AND A. J. MOON From the Brompton Hospital, the London Chest Hospital, and the Institute of Diseases of the
Thorax (1955), 10, 183. SURVIVAL AFTER LUNG RESECTION FOR BRONCHIAL CARCINOMA BY J. R. BIGNALL AND A. J. MOON From the Brompton Hospital, the London Chest Hospital, and the Institute of Diseases of the
T3 NSCLC: Chest Wall, Diaphragm, Mediastinum
 for T3 NSCLC: Chest Wall, Diaphragm, Mediastinum AATS Postgraduate Course April 29, 2012 Thomas A. D Amico MD Professor of Surgery, Chief of Thoracic Surgery Duke University Health System Disclosure No
for T3 NSCLC: Chest Wall, Diaphragm, Mediastinum AATS Postgraduate Course April 29, 2012 Thomas A. D Amico MD Professor of Surgery, Chief of Thoracic Surgery Duke University Health System Disclosure No
The roles of adjuvant chemotherapy and thoracic irradiation
 Factors Predicting Patterns of Recurrence After Resection of N1 Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Timothy E. Sawyer, MD, James A. Bonner, MD, Perry M. Gould, MD, Robert L. Foote, MD, Claude Deschamps, MD,
Factors Predicting Patterns of Recurrence After Resection of N1 Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Timothy E. Sawyer, MD, James A. Bonner, MD, Perry M. Gould, MD, Robert L. Foote, MD, Claude Deschamps, MD,
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
Surgical Approaches to Pulmonary Metastases
 Surgical Approaches to Pulmonary Metastases Raja M Flores MD Professor and Chief Thoracic Surgery Mount Sinai School of Medicine New York, New York History of Lung Metastasectomy 1882 Weinlechner +CW 1926
Surgical Approaches to Pulmonary Metastases Raja M Flores MD Professor and Chief Thoracic Surgery Mount Sinai School of Medicine New York, New York History of Lung Metastasectomy 1882 Weinlechner +CW 1926
OBJECTIVES. Solitary Solid Spiculated Nodule. What would you do next? Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules.
 Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
Organ Imaging : September 25 2015 OBJECTIVES Case Based Discussion: State of the Art Management of Lung Nodules Dr. Elsie T. Nguyen Dr. Kazuhiro Yasufuku 1. To review guidelines for follow up and management
EXTENDED SLEEVE LOBECTOMY FOR LUNG CANCER: THE AVOIDANCE OF PNEUMONECTOMY
 EXTENDED SLEEVE LOBECTOMY FOR LUNG CANCER: THE AVOIDANCE OF PNEUMONECTOMY Morihito Okada, MD Noriaki Tsubota, MD Masahiro Yoshimura, MD Yoshifumi Miyamoto, MD Hidehito Matsuoka, MD, Shinsuke Satake, MD
EXTENDED SLEEVE LOBECTOMY FOR LUNG CANCER: THE AVOIDANCE OF PNEUMONECTOMY Morihito Okada, MD Noriaki Tsubota, MD Masahiro Yoshimura, MD Yoshifumi Miyamoto, MD Hidehito Matsuoka, MD, Shinsuke Satake, MD
P sumed to have early lung disease with a favorable
 Survival After Resection of Stage I1 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Nael Martini, MD, Michael E. Burt, MD, PhD, Manjit S. Bains, MD, Patricia M. McCormack, MD, Valerie W. Rusch, MD, and Robert J. Ginsberg,
Survival After Resection of Stage I1 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Nael Martini, MD, Michael E. Burt, MD, PhD, Manjit S. Bains, MD, Patricia M. McCormack, MD, Valerie W. Rusch, MD, and Robert J. Ginsberg,
Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice
 Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice Robert D. Ambrosini, MD, PhD, Christopher Gange, MD, Katherine Kaproth-Joslin, MD, PhD, Susan Hobbs, MD, PhD Department of Imaging
Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice Robert D. Ambrosini, MD, PhD, Christopher Gange, MD, Katherine Kaproth-Joslin, MD, PhD, Susan Hobbs, MD, PhD Department of Imaging
Thoracoscopic Lobectomy: Technical Aspects in Years of Progress
 Thoracoscopic Lobectomy: Technical Aspects in 2015 16 Years of Progress 8 th Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando September 25, 2015 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery
Thoracoscopic Lobectomy: Technical Aspects in 2015 16 Years of Progress 8 th Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando September 25, 2015 Thomas A. D Amico MD Gary Hock Professor of Surgery
Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions
 Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Walter J. McCarthy, M.D., Miriam L. Christ, M.D., and Willard A. Fry, M.D. ABSTRACT Forty-one intraoperative fine needle aspiration biopsies
Intraoperative Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy of Thoracic Lesions Walter J. McCarthy, M.D., Miriam L. Christ, M.D., and Willard A. Fry, M.D. ABSTRACT Forty-one intraoperative fine needle aspiration biopsies
Case Scenario 1. The patient agreed to a CT guided biopsy of the left upper lobe mass. This was performed and confirmed non-small cell carcinoma.
 Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Case Scenario 1 An 89 year old male patient presented with a progressive cough for approximately six weeks for which he received approximately three rounds of antibiotic therapy without response. A chest
Primary mediastinal tumours
 Primary mediastinal tumours Thorax (1974), 29, 475. YOUSF D. AL-NAAMAN, MOHAMAD S. AL-AN, and MUAYYAD M. AL-OMER Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad,
Primary mediastinal tumours Thorax (1974), 29, 475. YOUSF D. AL-NAAMAN, MOHAMAD S. AL-AN, and MUAYYAD M. AL-OMER Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Significance of Metastatic Disease
 Significance of Metastatic Disease in Subaortic Lymph Nodes G. A. Patterson, M.D., D. Piazza, M.D., F. G. Pearson, M.D., T. R. J. Todd, M.D., R. J. Ginsberg, M.D., M. Goldberg, M.D., P. Waters, M.D., D.
Significance of Metastatic Disease in Subaortic Lymph Nodes G. A. Patterson, M.D., D. Piazza, M.D., F. G. Pearson, M.D., T. R. J. Todd, M.D., R. J. Ginsberg, M.D., M. Goldberg, M.D., P. Waters, M.D., D.
141 Ann Thorac Surg , Aug Copyright by The Society of Thoracic Surgeons
 Completion Pneumonectomy: Indications, Complications, and Results Eilis M. McGovern, M.B.B.Ch., Victor F. Trastek, M.D., Peter C. Pairolero, M.D., and W. Spencer Payne, M.D. ABSTRACT From 958 through 985,
Completion Pneumonectomy: Indications, Complications, and Results Eilis M. McGovern, M.B.B.Ch., Victor F. Trastek, M.D., Peter C. Pairolero, M.D., and W. Spencer Payne, M.D. ABSTRACT From 958 through 985,
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Predicting Postoperative Pulmonary Function in Patients Undergoing Lung Resection*
 Predicting Postoperative Pulmonary Function in Patients Undergoing Lung Resection* Bernhardt G. Zeiher, MD; Thomas ]. Gross, MD; Jeffery A. Kern, MD, FCCP; Louis A. Lanza, MD, FCCP; and Michael W. Peterson,
Predicting Postoperative Pulmonary Function in Patients Undergoing Lung Resection* Bernhardt G. Zeiher, MD; Thomas ]. Gross, MD; Jeffery A. Kern, MD, FCCP; Louis A. Lanza, MD, FCCP; and Michael W. Peterson,
Therapeutic Bronchoscopy Etiology - Benign Stenosis Post - intubation Trauma Post - operative Inflammatory Idiopathic
 Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Tracheobronchopulmonary Carcinoid Tumors: Analysis of 40 Patients
 Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011; 17: 7 12 Original Article Tracheobronchopulmonary Carcinoid Tumors: Analysis of 40 Patients Reza Bagheri, MD, 1 Mohammad taghi Rajabi Mashhadi, MD, 1 S.Ziaallah Haghi,
Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011; 17: 7 12 Original Article Tracheobronchopulmonary Carcinoid Tumors: Analysis of 40 Patients Reza Bagheri, MD, 1 Mohammad taghi Rajabi Mashhadi, MD, 1 S.Ziaallah Haghi,
CASE REPORT. Introduction. Case series reports. J Thorac Dis 2012;4(S1): DOI: /j.issn s003
 CASE REPORT Lost in time pulmonary metastases of renal cell carcinoma: complete surgical resection of metachronous metastases, 18 and 15 years after nephrectomy Kosmas Tsakiridis 1, Aikaterini N Visouli
CASE REPORT Lost in time pulmonary metastases of renal cell carcinoma: complete surgical resection of metachronous metastases, 18 and 15 years after nephrectomy Kosmas Tsakiridis 1, Aikaterini N Visouli
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai, China
 www.springerlink.com Chin J Cancer Res 23(4):265 270, 2011 265 Original Article Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai,
www.springerlink.com Chin J Cancer Res 23(4):265 270, 2011 265 Original Article Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai,
PET/CT in lung cancer
 PET/CT in lung cancer Andrei Šamarin North Estonia Medical Centre 3 rd Baltic Congress of Radiology 08.10.2010 Imaging in lung cancer Why do we need PET/CT? CT is routine imaging modality for staging of
PET/CT in lung cancer Andrei Šamarin North Estonia Medical Centre 3 rd Baltic Congress of Radiology 08.10.2010 Imaging in lung cancer Why do we need PET/CT? CT is routine imaging modality for staging of
Use of a Lung Stapler in Pulmonary Resection
 Use of a Lung Stapler in Pulmonary Resection Reeve H. Betts, M.D., and Timothy Takaro, M.D. A lthough the results of pulmonary resection by standard techniques are good, there is a continuing need for,
Use of a Lung Stapler in Pulmonary Resection Reeve H. Betts, M.D., and Timothy Takaro, M.D. A lthough the results of pulmonary resection by standard techniques are good, there is a continuing need for,
and Cardiac Presentations of Histoplasmosis
 Pulmonary, Mediastinal, and Cardiac Presentations of Histoplasmosis Richard L. Prager, M.D., D. Patrick Burney, M.D., George Waterhouse, M.D., and Harvey W. Bender, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Sixty-one patients
Pulmonary, Mediastinal, and Cardiac Presentations of Histoplasmosis Richard L. Prager, M.D., D. Patrick Burney, M.D., George Waterhouse, M.D., and Harvey W. Bender, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Sixty-one patients
Thoracoscopic left upper lobectomy with systematic lymph nodes dissection under left pulmonary artery clamping
 GCTAB Column Thoracoscopic left upper lobectomy with systematic lymph nodes dissection under left pulmonary artery clamping Yi-Nan Dong, Nan Sun, Yi Ren, Liang Zhang, Ji-Jia Li, Yong-Yu Liu Department
GCTAB Column Thoracoscopic left upper lobectomy with systematic lymph nodes dissection under left pulmonary artery clamping Yi-Nan Dong, Nan Sun, Yi Ren, Liang Zhang, Ji-Jia Li, Yong-Yu Liu Department
Reasons for conversion during VATS lobectomy: what happens with increased experience
 Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Page 1 of 5 Reasons for conversion during VATS lobectomy: what happens with increased experience Dario Amore, Davide Di Natale, Roberto Scaramuzzi, Carlo Curcio Division
Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Page 1 of 5 Reasons for conversion during VATS lobectomy: what happens with increased experience Dario Amore, Davide Di Natale, Roberto Scaramuzzi, Carlo Curcio Division
Uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery segmentectomy
 Case Report on Thoracic Surgery Page 1 of 5 Uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery segmentectomy John K. C. Tam 1,2 1 Division of Thoracic Surgery, National University Heart Centre, Singapore;
Case Report on Thoracic Surgery Page 1 of 5 Uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery segmentectomy John K. C. Tam 1,2 1 Division of Thoracic Surgery, National University Heart Centre, Singapore;
Surgical Management of Pulmonary Metastases. Dr AG Jacobs Principal Specialist Dept Cardiothoracic Surgery Steve Biko Academic Hospital
 Surgical Management of Pulmonary Metastases Dr AG Jacobs Principal Specialist Dept Cardiothoracic Surgery Steve Biko Academic Hospital Introduction Lungs 2 nd most common site of metastatic deposition
Surgical Management of Pulmonary Metastases Dr AG Jacobs Principal Specialist Dept Cardiothoracic Surgery Steve Biko Academic Hospital Introduction Lungs 2 nd most common site of metastatic deposition
The Importance of Histo-pathological Factors in Setting the Long Term Prognosis for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Importance of Histo-pathological Factors in Setting the Long Term Prognosis for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Suciu B 1, Bud V 1, Copotoiu C 1, Brânzaniuc Klara 2, Copotoiu Ruxandra 3,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Importance of Histo-pathological Factors in Setting the Long Term Prognosis for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Suciu B 1, Bud V 1, Copotoiu C 1, Brânzaniuc Klara 2, Copotoiu Ruxandra 3,
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
THORACIK RICK. Lungs. Outline and objectives Richard A. Malthaner MD MSc FRCSC FACS
 THORACIK RICK Outline and objectives Lungs Management of a solitary lung nodule Mediastinum Management of a mediastinal mass Pleura Management of a pleural fluid & pneumothorax Esophagus & Stomach Management
THORACIK RICK Outline and objectives Lungs Management of a solitary lung nodule Mediastinum Management of a mediastinal mass Pleura Management of a pleural fluid & pneumothorax Esophagus & Stomach Management
Pleomorphic carcinoma is a rare epithelial malignant. Personal Experience in Surgical Management of Pulmonary Pleomorphic Carcinoma
 Personal Experience in Surgical Management of Pulmonary Pleomorphic Carcinoma Federico Raveglia, MD, Maurizio Mezzetti, MD, Tiziana Panigalli, MD, Simone Furia, MD, Luigi Giuliani, MD, Serena Conforti,
Personal Experience in Surgical Management of Pulmonary Pleomorphic Carcinoma Federico Raveglia, MD, Maurizio Mezzetti, MD, Tiziana Panigalli, MD, Simone Furia, MD, Luigi Giuliani, MD, Serena Conforti,
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules
 Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Standard treatment for pulmonary metastasis of non-small
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resection of Pulmonary Metastasis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Kenichi Okubo, MD,* Toru Bando, MD,* Ryo Miyahara, MD,* Hiroaki Sakai, MD,* Tsuyoshi Shoji, MD,* Makoto Sonobe, MD,* Takuji
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resection of Pulmonary Metastasis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Kenichi Okubo, MD,* Toru Bando, MD,* Ryo Miyahara, MD,* Hiroaki Sakai, MD,* Tsuyoshi Shoji, MD,* Makoto Sonobe, MD,* Takuji
Congenital Tracheoesophageal Fistula in the Adult
 CASE REPORT Congenital Tracheoesophageal Fistula in the Adult Jerry L. Acosta, M.D., and J. Stanley Battersby, M.D. ABSTRACT Congenital tracheoesophageal fistula can persist and remain undetected until
CASE REPORT Congenital Tracheoesophageal Fistula in the Adult Jerry L. Acosta, M.D., and J. Stanley Battersby, M.D. ABSTRACT Congenital tracheoesophageal fistula can persist and remain undetected until
Carcinoid Tumors of the Lung: Do Atypical Features Require Aggressive Management?
 Carcinoid Tumors of the Lung: Do Atypical Features Require Aggressive Management? Charles-Henri Marty-An6, MD, Val6rie Costes, MD, Jean-Louis Pujol, MD, Michel Alauzen, MD, Pierre Baldet, MD, and Henri
Carcinoid Tumors of the Lung: Do Atypical Features Require Aggressive Management? Charles-Henri Marty-An6, MD, Val6rie Costes, MD, Jean-Louis Pujol, MD, Michel Alauzen, MD, Pierre Baldet, MD, and Henri
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1989, 34
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Histological evaluation of cancer e cancer. Ayabe, Hiroyoshi; Tomita, Masao; Ka Hsieh, Chia-Ming; Oka, Tadayuki; Ts Taniguchi, Hideki; Touchika, Hirono
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Histological evaluation of cancer e cancer. Ayabe, Hiroyoshi; Tomita, Masao; Ka Hsieh, Chia-Ming; Oka, Tadayuki; Ts Taniguchi, Hideki; Touchika, Hirono
Lung cancer is a major cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Factors in 3315 Completely Resected Cases of Clinical Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Teruaki Koike, MD,* Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, Yasunori Sohara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Factors in 3315 Completely Resected Cases of Clinical Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Teruaki Koike, MD,* Ryosuke Tsuchiya, MD, Tomoyuki Goya, MD, Yasunori Sohara,
