Arielle Bokhour, class of 2017
|
|
|
- Tamsyn Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Arielle Bokhour, class of 2017
2 Objectives 1. Understand the actions and innervation of the extrinsic and intrinsic eye muscles 2. Describe the pathways for pupillary constriction and dilation 3. Understand the Accommodation reflex and its pathway 4. Describe Horner s Syndrome 5. Describe the pathway for conjugate lateral and vertical gaze 6. Understand Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia 7. Understand how lesions may affect visual reflexes
3 Visual Reflexes and Gaze Visual reflexes provide automatic control of 1. the amount of light entering the eye 2. the curvature of the lens They depend upon autonomic control of the intrinsic smooth muscles of the eye. Gaze: Neural pathways automatically move both eyes simultaneously for conjugate gaze.
4 Visual Reflexes Testing visual reflexes has great clinical significance because these reflexes depend upon brainstem centers. Abnormal responses can be a key to recognizing CNS pathology
5 Clinical Examples 1. Your neighbor became unconscious after a fall earlier in the day. On exam, his right eye is dilated compared to the left. When you shine a light into the right eye, there is no change, but the left eye constricts. When you shine the light into the left eye, the left eye constricts, but the right eye is unchanged. 2. A 25-year old woman complained that she sees double when she looks at objects on her left. On exam, her eyes move together normally as they follow your finger up, down, and to her right. When you move your finger to her left, her left eye moves left, but her right looks straight ahead.
6 Overview How does the brain control movement of the eye direction of eye size of pupil we have 2 eyes! voluntary vs reflexive actions
7 Eye Muscles Superior rectus Inferior rectus Medial rectus Inferior oblique Levator palpebrae superior CN III Pupillary constrictor Ciliary muscle
8 Eye Muscles Lateral rectus Superior oblique Pupillary dilator Superior tarsal muscle Cutaneous arteries Sweat glands of face CN VI CN IV Sympathetic
9 Eye Movement
10 Effects of Lesions CN III, IV, VI can be damaged by: head trauma (shearing forces) aneurysms and masses vascular disease, diabetes infections R L If an eye muscle loses its nerve supply, the resting position of the eye will be determined by the remaining active muscles.
11 Check out this web site for a cool demo on how eye muscles work Additional information and animations are found here:
12 Pupil Size Pupillary Constriction and Dilation sphincter contraction makes pupil smaller Radial muscles contraction makes pupil larger
13 Pupillary Constriction Controls the pupillary sphincter to decrease the amount of light entering the eye via parasympathetic fibers. Light shined in one eye causes both eyes to constrict - direct and consensual responses.
14 Pupillary Constriction Reflex: light in one eye causes motor response (contraction) in both eyes. Occulomotor nuc Midbrain contains the reflex center that controls this response: pretectal area and Edinger Westfal nucleus This is a brainstem reflex that can be used in clinical testing.
15 level of pretectal area
16 Pupillary Constriction Brachium of superior colliculus
17 Pupillary Constriction Retina (nasal/temp) Optic N/Chiasm/Tract Brachium Sup Colliculus Pretectal Area (Posterior Commissure) Edinger-Westphal Nuc CN III Ciliary Ganglion Pupillary Constrictor 4-neuron reflex
18 Pupillary Constriction Pretectal Area Axons from pretectal area project bilaterally to the EW Nucleus (cross in posterior commissure). Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers from EW travel in CN III to Ciliary Gang. Postganglionic fibers travel in short ciliary nerves to the pupillary constrictor.
19 Consensual response: Pupillary Constriction 1. Light in 1 eye goes to both sides of midbrain 2. Each pretectal area connects to both EWN Loss of the pup light reflex: 1. Optic nerve lesions 2. CN III lesions
20 Uncal Herniation uncus tentorium CNIII
21 Clinical Importance of Brainstem Reflexes CASE: On returning home from shopping, a wife finds her 59 year-old husband unconscious on the floor. He has no pulse. After calling 911, she begins CPR. When Mr. T arrives in the ED, he is in ventricular fibrillation. Spontaneous circulation is eventually restored, but he remains comatose. After 3 days in coma, his wife asks about her husband s condition and the probability of a good outcome. How assess extent of CNS damage/function in unconscious patient 1. Somatosensory Evoked Potential 2. Corneal reflex 3. Pupillary Light Reflex
22 Accommodation Begins as voluntary action (decision to track an approaching object), but is followed by automatic responses. Voluntary part uses Visual Pathway and cortex to track object. Automatic part uses Midbrain Oculomotor Reflex Center
23 Accommodation Cortical reflex that allows eyes to focus on near objects. Involves 3 actions: 1. Convergence- eyes turn medially 2. Pupillary constriction 3. Lens rounding Reflex parasym control parasympathetic signals in CN III cause contraction of the ciliary muscle which produces an inward, squeezing force. This relaxes tension on the suspensory ligaments, causing the lens to become rounder, with greater ability to focus near objects. retina cortex Midbrain reflex center supraoculomotor nuc near the pretectal area eye
24 Accommodation Information from the retina travels to visual cortex via the optic radiations (geniculocalcarine fibers). Fibers from visual cortex travel back through the optic radiations and enter the midbrain through the brachium of superior colliculus.
25 Brachium fibers synapse in supraoculomotor nuc then bilaterally to oculomotor nuc + Edinger Westfal Accommodation CN III CN III medial rectus pupil constrictor ciliary muscle
26 Argyll-Robertson Pupil pupil Small, irregular pupils that constrict in accommodation but not to direct light. Causes: syphilis, diabetes Probable lesion location pretectal area, but supraoculomotor nuc is intact for accommodation.
27 Pupillary Dilation The pupillary dilator muscle is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system. Sympathetics also control: Superior tarsal muscle Cutaneous arteries Sweat glands of face
28 Sympathetic tone sets the resting tension in the dilator muscle. 1. Reduced ambient light levels relax the constrictor and allow the dilator to be more effective. light, pain, fear, anger 2. Emotional situations cause dilation via the hypothalamus.
29 Pupillary Dilation Hypothalamus Hypothalamospinal fibers [Spinal cord Intermediolateral cell column] Thoracic roots Sympathetic chain to Superior Cervical Gang Carotid plexus/artery Pupillary dilator
30 Pupillary Dilation Brainstem Hypothalamospinal fibers travel near ALS Lesions in lateral areas of brainstem or spinal cord cause Horner s Syn Neighbors with ALS!! ALS
31 Spinal Cord Pupillary Dilation Hypothalamospinal fibers terminate on preganglionic sympathetic neurons in Intermediolateral cell column. Axons enter the sympathetic chain. Intermediolateral cell column T1-L3
32 Pupillary Dilation
33 Horner s Syndrome Results from loss of sympathetic innervation to eye/face Caused by a lesion anywhere along the pathway for pupillary dilation: lateral brainstem, spinal cord, thoracic roots, sympathetic chain, carotid plexus, cavernous sinus, orbit May indicate stroke, tumor or mass in thoracic cavity/neck, trauma to neck, carotid dissection, or cluster headache.
34 Sympathetics control: superior tarsal muscle, dilator muscle, sweat glands, cutaneous arteries. Symptoms: ptosis- drooping eyelid (loss of superior tarsal muscle innervation) miosis- constricted pupil anhidrosis- dryness (loss of sweat gland innervation) affected half of face is warm, flushed (loss of vasoconstrictors) Horner s Syndrome
35 Control of Eye Movements Frontal Eye Fields FEF motor areas Brainstem control centers Brainstem control centers: pons (paramedian pontine reticular formation/horizontal gaze center) superior colliculus Nuclei of CN III, IV, VI Involve voluntary (cortical) and automatic (brainstem) features
36 Sup rectus Inf rectus Sup rectus Inf rectus Conjugate Vertical Gaze Muscles acts in pairs: Sup/Sup; Inf/Inf Requires bilateral coordination via posterior commissure pineal Lesions of Sup Coll/post comm cause paralysis of upward gaze - pinealomas Frontal Eye Field Vertical Gaze Center (midbrain) CN III nuc Superior Colliculus
37 Conjugate Lateral Gaze Horizontal gaze of the 2 eyes requires coordination of medial rectus in 1 eye with lateral rectus in other eye medial rectus lateral rectus III MLF VI PPRF - paramedian pontine reticular formation PPRF MLF - medial longitudinal fasciculus
38 Conjugate Lateral Gaze medial rectus lateral rectus Frontal Eye Field is center for voluntary lateral gaze. It sends axons to the contralateral PPRF. MLF VI III PPRF
39 Conjugate Lateral Gaze FEF to medial rectus MLF III IV VI PPRF to lateral rectus
40 Conjugate Lateral Gaze Activation of FEF in the left hemisphere causes eyes to move to the right. Clinical Implications: Central eye position results from balanced activity in FEF of each side. Seizures (abnormal excitatory activity) involving FEF on one side cause gaze to opposite side. Loss of activity in FEF on one side (eg infarct) causes gaze toward that side. R The eyes look towards a hemisphere lesion (inactivity) L
41 Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia Results from a lesion in the MLF MS, diabetes Disconnects activation of medial rectus from lateral rectus gaze normal INO Cannot turn past mid-position Cannot turn past mid-position
42 Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia medial rectus lateral rectus III MLF VI PPRF
43 Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia But, convergence is normal! Accommodation uses a pathway different from lateral conj gaze, although both ultimately activate CN III/medial rectus. R L lateral rectus CN III CN VI VI accommodation
44 Effects of CN Lesions CN III- Ptosis External Strabismus (eye turned laterally) Dilated Pupil CN IV- CN VI- Difficulty depressing eye when adducted Internal Strabismus (eye turned medially) Diplopia- Double Vision - results from any condition that causes misalignment of eyes (dysconjugate gaze)
VISUAL REFLEXES. B. The oculomotor nucleus, Edinger-Westphal nucleus, and oculomotor nerve at level of the superior colliculus.
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15 HyperBrain: Ch 7 with quizzes and or Lab 7 videotape http://www-medlib.med.utah.edu/kw/hyperbrain/anim/reflex.html
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15 HyperBrain: Ch 7 with quizzes and or Lab 7 videotape http://www-medlib.med.utah.edu/kw/hyperbrain/anim/reflex.html
Oculomotor System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Oculomotor System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Define different types of eye movement and their underlying neural
Oculomotor System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Define different types of eye movement and their underlying neural
GNK485 The eye and related structures. Prof MC Bosman 2012
 GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE
 REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
Lecture 10 Orbit and control of eye movements
 Lecture 10 Orbit and control of eye movements Overview of structures in the orbit (Moore pp 899, Netter Plate 1) The orbit contains the eye, from which the optic nerve exits into the cranial cavity optic
Lecture 10 Orbit and control of eye movements Overview of structures in the orbit (Moore pp 899, Netter Plate 1) The orbit contains the eye, from which the optic nerve exits into the cranial cavity optic
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Eye Movements. Geometry of the Orbit. Extraocular Muscles
 Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
Extraocular Muscles and Ocular Motor Control of Eye Movements
 Extraocular Muscles and Ocular Motor Control of Eye Movements Linda K. McLoon PhD mcloo001@umn.edu Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Neurosciences Your Eyes Are Constantly Moving. Yarbus, 1967 Eye
Extraocular Muscles and Ocular Motor Control of Eye Movements Linda K. McLoon PhD mcloo001@umn.edu Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Neurosciences Your Eyes Are Constantly Moving. Yarbus, 1967 Eye
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
mistake ;slides in bold but you still have to go back to our slides to see the figure, tables and some scheme
 Khozama jehad : I am doing my best and I am sorry for any unintended mistake ;slides in bold but you still have to go back to our slides to see the figure, tables and some scheme The Orbit, Orbital Contents
Khozama jehad : I am doing my best and I am sorry for any unintended mistake ;slides in bold but you still have to go back to our slides to see the figure, tables and some scheme The Orbit, Orbital Contents
V1-ophthalmic. V2-maxillary. V3-mandibular. motor
 4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
4. Trigeminal Nerve I. Objectives:. Understand the types of sensory information transmitted by the trigeminal system.. Describe the major peripheral divisions of the trigeminal nerve and how they innervate
THE BRAINSTEM. Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania
 THE BRAINSTEM Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania Overview of Brainstem Functions The brainstem serves numerous crucial neurologic functions. The most clinically relevant functions include:
THE BRAINSTEM Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania Overview of Brainstem Functions The brainstem serves numerous crucial neurologic functions. The most clinically relevant functions include:
Normal Pupil. The normal pupil is 2 mm to 6 mm in diameter. In ordinary ambient light the pupils are usually 3 mm to 4 mm in diameter.
 Normal Pupil The normal pupil is 2 mm to 6 mm in diameter. In ordinary ambient light the pupils are usually 3 mm to 4 mm in diameter. Normal Pupil The pupils are small and poorly reactive at birth and
Normal Pupil The normal pupil is 2 mm to 6 mm in diameter. In ordinary ambient light the pupils are usually 3 mm to 4 mm in diameter. Normal Pupil The pupils are small and poorly reactive at birth and
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
BRAINSTEM SYNDROMES OF NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGICAL INTEREST
 BRAINSTEM SYNDROMES OF NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGICAL INTEREST Steven L. Galetta, MD NYU Langone Medical Center New York, NY I. Anatomical Considerations The brain stem is about the size of a fat forefinger and
BRAINSTEM SYNDROMES OF NEURO-OPHTHALMOLOGICAL INTEREST Steven L. Galetta, MD NYU Langone Medical Center New York, NY I. Anatomical Considerations The brain stem is about the size of a fat forefinger and
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The NIHSS score is 4 (considering 2 pts for the ataxia involving upper and lower limbs.
 Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
let's continue talking about the eye,
 Eye is mainly composed of 3 layers: External layer, which called The Sclera which is a hard connective tissue that gives the eye its round shape. Extension of the sclera into the front is the cornea, which
Eye is mainly composed of 3 layers: External layer, which called The Sclera which is a hard connective tissue that gives the eye its round shape. Extension of the sclera into the front is the cornea, which
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs. János Hanics M.D.
 Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
4/22/16. Eye. External Anatomy of Eye. Accessory Structures. Bio 40B Dr. Kandula
 Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Vestibular System. Dian Yu, class of 2016
 Vestibular System Dian Yu, class of 2016 Objectives 1. Describe the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? 2. Describe the vestibular
Vestibular System Dian Yu, class of 2016 Objectives 1. Describe the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? 2. Describe the vestibular
ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
Lecture Content. Disorders of optic nerve and retina Chiasmal and retrochiasmal disorders Pupil disorders Motility disorders
 Neuro-Ophthalmology Celia H. Chang MD Department of Neurology MIND Institute University of California, Davis, Health System celia.chang@ucdmc.ucdavis.edu Lecture Content Disorders of optic nerve and retina
Neuro-Ophthalmology Celia H. Chang MD Department of Neurology MIND Institute University of California, Davis, Health System celia.chang@ucdmc.ucdavis.edu Lecture Content Disorders of optic nerve and retina
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app.
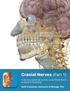 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors We've split our Cranial Nerves lab activity into two parts. Part 1 is pre-lab exercises
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors We've split our Cranial Nerves lab activity into two parts. Part 1 is pre-lab exercises
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
The orbit-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions
 Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D.
 Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Vision II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat. Mohd.Khatatbeh
 10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
10 Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Ahmad Rabei & Hamad Mrayat Mohd.Khatatbeh Before you start: Important terminology: 1 Ganglion: Nerve cell cluster, where neurons are typically linked by synapses. Also, it`s
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
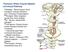 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day)
 Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
Pupil Exams and Visual Fields
 Pupil Exams and Visual Fields A Closer Look at Cranial Nerves No Financial Interests Amy Jost does not have any financial interests related to this presentation AMY JOST, BS, COMT, CCRC, OSC CINCINNATI
Pupil Exams and Visual Fields A Closer Look at Cranial Nerves No Financial Interests Amy Jost does not have any financial interests related to this presentation AMY JOST, BS, COMT, CCRC, OSC CINCINNATI
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5
 NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
Autonomic Division of NS
 Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM. Deficits cause: Vertigo. Falling Tilting Nystagmus Nausea, vomiting
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM Objectives: Understand the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? Describe the vestibular apparatus, the 2
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM Objectives: Understand the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? Describe the vestibular apparatus, the 2
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Sheet lab 3. Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation:
 Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses
 Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Pain and Temperature Objectives
 Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Review or skim Ch 12 on the vascular supply of the brain. Just look at pictures and legends for the clinical part at the end.
 Dental Neuroanatomy January 20 and 27, 10-12, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. Dear Students: Please print these notes and bring them with you. My style is to use a Tablet PC and I draw on either a Word
Dental Neuroanatomy January 20 and 27, 10-12, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. Dear Students: Please print these notes and bring them with you. My style is to use a Tablet PC and I draw on either a Word
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Neuroradiology in the Ocular Motility Disorders :
 Neuroradiology in the Ocular Motility Disorders : I. Supranuclear Pathway 1 H y u ng-jin Kim, M.D. 1, 2, Byung Hoon Lim, M.D. 3, Jae Bum Na, M.D. Jae Hyoung Kim, M.D., Sung Hoon Chung, M.D. The supranuclear
Neuroradiology in the Ocular Motility Disorders : I. Supranuclear Pathway 1 H y u ng-jin Kim, M.D. 1, 2, Byung Hoon Lim, M.D. 3, Jae Bum Na, M.D. Jae Hyoung Kim, M.D., Sung Hoon Chung, M.D. The supranuclear
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball
 Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
THE VESTIBULAR APPRATUS AND PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy February 23, 2012 Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. Reading: Waxman Chapter 17 Also pp 105-108 on control of eye movments Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch. 8 Vestibulospinal Pathway Quiz http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/animations/hyperbrain/pathways/
Dental Neuroanatomy February 23, 2012 Suzanne Stensaas, Ph.D. Reading: Waxman Chapter 17 Also pp 105-108 on control of eye movments Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch. 8 Vestibulospinal Pathway Quiz http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/animations/hyperbrain/pathways/
The Special Senses: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 15 The Special Senses: Part A Warm Up What is the function of the eyeball? List any structures of the eyeball that you
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 15 The Special Senses: Part A Warm Up What is the function of the eyeball? List any structures of the eyeball that you
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
3/16/2018. Optic Nerve Examination. Hassan Eisa Swify FRCS Ed (Ophthalmology) Air Force Hospital
 Optic Nerve Examination Hassan Eisa Swify FRCS Ed (Ophthalmology) Air Force Hospital 1 Examination Structure ( optic disc) Function Examination of the optic disc The only cranial nerve (brain tract) which
Optic Nerve Examination Hassan Eisa Swify FRCS Ed (Ophthalmology) Air Force Hospital 1 Examination Structure ( optic disc) Function Examination of the optic disc The only cranial nerve (brain tract) which
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
The Nervous System. Autonomic Division. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
4/8/2015. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS. Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Neuroanatomy, Text and Atlas (J. H. Martin), 3 rd Edition Chapter 7, The Visual System, pp ,
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: RETINA and CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Friday, 20
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: RETINA and CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Friday, 20
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY
 Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
4/9/2019. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Rashed Al-Jomard. Alanood Bostanji
 Anatomy #2 The Orbit & Cranial Nerve III, IV, VI Rashed AlJomard Alanood Bostanji 1 P a g e The Orbit & Cranial nerves III,IV&VI ** Some notes about the last lec & first MM : Lens :: "just clarify for
Anatomy #2 The Orbit & Cranial Nerve III, IV, VI Rashed AlJomard Alanood Bostanji 1 P a g e The Orbit & Cranial nerves III,IV&VI ** Some notes about the last lec & first MM : Lens :: "just clarify for
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
