SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Shavonne Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
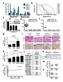
1 doi: /nature23291 Supplementary discussion part 1 Our model suggests that, in tumours that express Class 3 BRAF mutants and activated RAS, both BRAF MUT /RAF WT heterodimers and WT RAF dimers are expressed (Extended Data Figure 2b). RAF inhibitors will paradoxically activate the WT RAF dimers in these tumours. We found that RAF inhibitors can also inhibit the activity of class 3 BRAF MUT /CRAF WT heterodimers when they bind to CRAF, but have no effect when bound to the mutant BRAF protomer (Figure S1). This model is supported by Figure S2. When high levels of class 3 BRAF mutants were co-expressed in the CRAF knockout MEFs with low levels of CRAF WT or of the CRAF T421N gatekeeper mutant, vemurafenib only inhibited p-mek in the cells expressing CRAF WT without the gatekeeper mutation. It had no effect on ERK signaling driven by the Class 3 BRAF/CRAF T421N heterodimer. Thus binding of drug to the Class 3 mutant will not affect kinase activity of the heterodimer and binding of drug to wild type CRAF in the dimer will inhibit activity. In sum, the drugs cause 50% inhibition of class 3 BRAF MUT /CRAF heterodimers and paradoxically activate WT dimers, resulting in little effect on total ERK signaling. This model suggests that the degree of inhibition of ERK driven by Class 3 BRAF mutants will be a function of the ratio of expression of mutant BRAF to wild type RAF in the cell. At low levels of mutant expression, effect of RAF inhibitor on WT RAF heterodimers will predominate and ERK will be paradoxically activated by drug. As expression of the mutant increases, the proportion of mutant BRAF/WT RAF dimers increases. The activity of the heterodimers can be inhibited 50% by the drug, so at high levels of mutant expression, the drug can be moderately effective. In support of this idea, when we expressed low levels of class 3 BRAF mutants in NIH-3T3 cells, vemurafenib had almost no effect on pmek and perk (Figure 3b). This is also the case in the class 3 BRAF mutant tumour cell lines we tested (Figure 3c). However, when these mutants are expressed at higher levels, partial inhibition of pmek/perk by vemurafenib was observed (Figure S3). 1
2 Figure S1. Model shows that the binding of vemurafenib to different partners of the mutant BRAF dimer determines the biochemical consequences of drug treatment. Figure S2. V5-tagged WT or mutant BRAF were co-expressed with lower level V5- tagged WT (left panel) or T421N (right panel) CRAF in CRAF KO MEF cells, followed by treatment with or without vemurafenib (1 um, 1 hr). The ERK signaling of treated cells was assayed by Western blot. 2
3 Figure S3. NIH-3T3 cells inducibly expressing the indicated BRAF proteins were exposed to 1 ug/ml (high dose) doxycycline for 24 hrs, followed by vemurafenib treatment at the indicated concentrations for 1 hr. Cells were collected and cell lysates were examined by Western blot. Supplementary discussion part 2 A functional analysis of tumour-associated BRAF mutants was first reported in 2004 by Wan, Marais and colleagues 1, who made the seminal observation that whereas the catalytic activity of many tumour associated BRAF mutants is hyperactive, a subset are hypoactive or kinase dead. In Garnet et al. (2005) 2, Marais and colleagues examined the mechanism of activation of ERK by hypoactive RAF mutants. In that work, they showed that these hypoactive mutants bind to and directly activate CRAF in a RAS-independent manner in the cytosol, as opposed to WT BRAF which activates CRAF after binding to active RAS at the membrane. This view of activation of signaling by hypoactive mutants is not supported by our work. As shown in this paper, these mutants are RAS-dependent. They failed to activate CRAF in a RAS-less cells when they were expressed at a physiological level. This difference has extremely important mechanistic and translational consequences. 3
4 In Heidorn et al. (2010) 3, the mechanism of activation of ERK signaling by the kinase dead mutant BRAF D594A mutant was examined. First, they studied the mechanism whereby BRAF inhibitors paradoxically activate BRAF/CRAF dimers in tumours with NRAS mutation. They relied on their previous work showing that BRAF is not active in these tumours and on a presumption that the RAF inhibitors they used were BRAF selective, They posited that in these cells, WT BRAF is active enough to inhibit CRAF. The selective pharmacologic inhibition of BRAF therefore activates CRAF and stimulates signaling. To test this model they introduced the D594A kinase dead BRAF mutant into RAS mutant cells and found that it also induces ERK activation. Moreover, the kinase dead mutant synergized with mutant KRAS G12D to cause melanomas in GEMM models, whereas neither did by itself. The potential clinical importance of this finding was supported by their observation that D594 mutations in cancer coexisted with RAS mutations in 11.8% of the cases, suggesting a functional interaction. This paper reports several important observations, including the RAS dependence of activation of signaling by the kinase dead mutant and that kinase dead BRAF drives signaling by activating WT CRAF in mutant/wt CRAF heterodimers. However, the purported mechanism, inhibition of WT CRAF kinase by BRAF kinase and relief of this inhibition by selective BRAF inhibitors or by kinase dead BRAF, has been refuted by a variety of findings. First, the RAF inhibitors used in the paper are not selective BRAF inhibitors, they bind to and inhibit all 3 RAF family members in the proper context and they induce paradoxical activation of ERK in cell lacking BRAF 4 (in BRAF knockout cells). Second, RAF inhibitors paradoxically activate CRAF homodimers which are RASindependent 4. Third, selective inhibition of BRAF by most RAF inhibitors is not the proximal mechanism for paradoxical activation by these drugs, which is, instead, a result of three effects of binding of these cells to RAF: induction of dimerization of RAF monomers in a RAS-dependent fashion 5, allosteric activation of the second protomer in the RAF dimer after drug binds to the first 4 and, induction of negative cooperativity of binding to the second RAF protomer in the dimer by of drug to the first protomer. 6 Lastly, CRAF kinase dead mutants also activate signaling 7 and cause tumours (our unpublished data). 4
5 This summarizes the state of our understanding of the mechanism of activation of signaling by these mutants prior to our current work. The previous work 2,3 states that hypoactive mutants and kinase dead RAS mutants activate signaling by different mechanisms, the former RAS independent, the latter RAS dependent, it does not adequately explain the mechanism of activation of either class of mutant, nor the reason that hypoactive mutants are found to coexist with RAS or NF1 mutations The previous work 1, 2, 3 was extremely important, but, unsurprisingly, did not answer all questions and came to some erroneous conclusions. The outlined in this paper reports the following advances in understanding these mutants and oncogenic RAF mutants in general. 1) It shows that both hypoactive and kinase dead RAF mutants signaled in a RASdependent manner. 2) It shows that ERK-dependent feedback is a powerful determinant of the types of RAF mutants found in cancer and is key for understanding how these mutants activate output. Activation of ERK potently feedback inhibits activation of WT RAS, therefore, in order to hyperactivate ERK output, oncogenic RAF mutants must be either RAS independent (Class 1 and 2 mutants) or coexist with mechanisms that maintain RAS activation despite induction of feedback (Class 3 mutants). 3) Consistent with this general model, we showed that activation of ERK output by Class 3 mutants depended on coexistent mutational or physiologic activation of RAS signaling to overcome feedback and that in melanoma, both hypoactive and kinase dead mutants coexist with mutants that served to activate RAS (NF1 inactivating or KRAS activating mutants). 4) We showed that both types of mutant activate signaling by the same proximal mechanism-increased binding to active RAS, which caused them to recruit and activate wild type CRAF. We further show that this is likely to be the proximate mechanism, since introducing a mutation that disables dimerization of these mutants with CRAF abolishes their activation of CRAF, but not their tighter binding to RAS. 5
6 5) Since hypoactive and kinase dead BRAF mutants have common properties ((a common mechanism of activating the ERK signaling (increased binding to active RAS), RAS dependence, sensitivity to ERK-dependent feedback inhibition of RAS, and requirement for co-existent mutational or physiologic activation of RAS)), we operationally define them as a single group of Class 3 BRAF mutants. 6) We recognize the biologic and translational implications of this model. Tumour cells with Class 3 mutants can be distinguished by the mechanism by which they activate RAS: RAS or NF1 mutation versus RTK activation. In the former, we have no current means of inhibiting RAS activation, in the latter, we do. This directly leads to a currently feasible means of effectively treating the latter tumours combining an inhibitor of the RTK that dominantly drives RAS with a MEK or an ERK inhibitor. There are a significant number of patients with such tumours. This method of treatment would be contraindicated if the Garnet model 2 is followed, since it asserts that hypoactive mutants are RAS-independent (and therefore likely to be insensitive to upstream inhibitors). The data in the Heidorn paper 3 is consistent with possibility that tumours with kinase dead BRAF mutations and WT RAS/NF1 would be sensitive to upstream inhibition, but this idea was not mentioned or subsequently pursued. To our knowledge, this paper is the first to suggest this mechanism based strategy for therapy and the first to demonstrate its efficacy in model systems and patients. 7) Mass sequencing of human tumours now reveals many different BRAF mutants, 16 of which we have characterized and identified as Class 3. They occur at significant frequency in cancer, and may constitute 3% of adenocarcinomas of the lungs. There is no published data on the great majority of these and those not in significant hotspots are often called passengers. There is no specific knowledge about their treatment. Previous work on these mutations has not been helpful in these regards. In this and in another paper 6 we present experimental algorithms which together allow classifying unknown BRAF mutations as belonging to Class 1, 2 or 3 or as potential passengers and testing class specific therapeutic strategies for each. 6
7 References: 1. Wan, P. T. et al. Mechanism of activation of the RAF-ERK signaling pathway by oncogenic mutations of B-RAF. Cell 116, (2004). 2. Garnett, M. J., Rana, S., Paterson, H., Barford, D. & Marais, R. Wild-type and mutant B-RAF activate C-RAF through distinct mechanisms involving heterodimerization. Mol Cell 20, , doi: /j.molcel (2005). 3. Heidorn, S. J. et al. Kinase-dead BRAF and oncogenic RAS cooperate to drive tumor progression through CRAF. Cell 140, , doi: /j.cell (2010). 4. Poulikakos, P. I., Zhang, C., Bollag, G., Shokat, K. M. & Rosen, N. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 464, , doi: /nature08902 (2010). 5. Hatzivassiliou, G. et al. RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth. Nature 464, , doi: /nature08833 (2010). 6. Yao, Z. et al. BRAF Mutants Evade ERK-Dependent Feedback by Different Mechanisms that Determine Their Sensitivity to Pharmacologic Inhibition. Cancer Cell 28, , doi: /j.ccell (2015). 7. Wu, X. et al. Increased BRAF heterodimerization is the common pathogenic mechanism for noonan syndrome-associated RAF1 mutants. Mol Cell Biol 32, , doi: /mcb (2012). 7
8 Oligos for mutagenesis of Class 3 BRAF mutants D287H-F: 5 - TATGACCAACTTCATTTGCTGTTTG-3 D287H-R: 5 - TTGGAGACAAACAGCAAATGAAGTTGGTC-3 V459L-F: 5 -AGATTACACTGGGACAAAGAATTGGA-3 V459L-R: 5 -CTTTGTCCCAGTGTAATCTGCCCATC-3 G466V-F: 5 -AGAATTGGATCTGTATCATTTGGA-3 G466V-R: 5 - TGTTCCAAATGATACAGATCCAAT -3 G466E-F: 5 -AGAATTGGATCTGAATCATTTGGA-3 G466E-R: 5 -TGTTCCAAATGATTCAGATCCAAT-3 G466A-F: 5 -AGAATTGGATCTGCATCATTTGGA-3 G466A-R: 5 - TGTTCCAAATGATGCAGATCCAAT -3 S467L-F: 5 -GGATCTGGATTATTTGGAACAGTCTA-3 S467L-R: 8
9 5 - TGTTCCAAATAATCCAGATCCAATTCT-3 G469E-F: 5 -GGATCTGGATCATTTGAAACAGTCTAC-3 G469E-R: 5 -CCTTGTAGACTGTTTCAAATGATCC-3 N581S-F: 5 -GACCTCAAGAGTAATAGTATATTTCTT-3 N581S-R: 5 - TTCATGAAGAAATATACTATTACTCTT-3 N581I-F: 5 -GACCTCAAGAGTAATATTATATTTCTT-3 N581I-R: 5 - TTCATGAAGAAATATAATATTACTCTT-3 D594N-F: 5 -ATAGGTAATTTTGGTCTAGCTACAGTG-3 D594N-R: 5 -TAGACCAAAATTACCTATTTTTACTGTGA-3 D594G-F: 5 -CTCACAGTAAAAATAGGTGGTTTTGGTCTAGC-3 D594G-R: 5 -CACTGTAGCTAGACCAAAACCACCTATTTTTAC-3 D594A-F: 5 -ATAGGTGCTTTTGGTCTAGCTACAGTG-3 D594A-R: 5 -TAGACCAAAAGCACCTATTTTTACTGTGA-3 D594H-F: 5 -ATAGGTCATTTGGTCTAGCTACAGTG-3 9
10 D594H-R: 5 -TAGACCAAAATGACCTATTTTTACTGTGA-3 F595L-F: 5 -AATAGGTGATTTAGGTCTAGCTACA-3 F595L-R: 5 - TAGACCTAAATCACCTATTTTTACTGTGA-3 G596D-F: 5 -ATAGGTGATTTTGATCTAGCTACAGTGA-3 G596D-R: 5 -GTAGCTAGATCAAAATCACCTATTTTTACTGTGAGGT-3 G596R-F: 5 -ATAGGTGATTTTCGTCTAGCTACAGTGA-3 G596R-R: 5 -GTAGCTAGACGAAAATCACCTATTTTTACTGTGAGGT
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nature. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 22.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2010 March 18; 464(7287): 427 430. doi:10.1038/nature08902. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signaling in cells
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2010 March 18; 464(7287): 427 430. doi:10.1038/nature08902. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signaling in cells
RAS and RAF Signalling in Melanoma: Biology and Therapies Professor Richard Marais
 RAS and RAF Signalling in Melanoma: Molecular Oncology, The Institute of Cancer Research, UK 1 Melanoma Melanocytes are specialised pigment cells - Skin, eyes, ear, brain, heart - Skin/hair tone - Protection
RAS and RAF Signalling in Melanoma: Molecular Oncology, The Institute of Cancer Research, UK 1 Melanoma Melanocytes are specialised pigment cells - Skin, eyes, ear, brain, heart - Skin/hair tone - Protection
Nilotinib and MEK Inhibitors Induce Synthetic Lethality through Paradoxical Activation of RAF in Drug-Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Article Nilotinib and MEK Inhibitors Induce Synthetic Lethality through Paradoxical Activation of RAF in Drug-Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Leisl M. Packer, 1 Sareena Rana, 1 Robert Hayward, 1 Thomas
Article Nilotinib and MEK Inhibitors Induce Synthetic Lethality through Paradoxical Activation of RAF in Drug-Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Leisl M. Packer, 1 Sareena Rana, 1 Robert Hayward, 1 Thomas
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma
 Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Disruption of CRAF-Mediated MEK Activation Is Required for Effective MEK Inhibition in KRAS Mutant Tumors
 Article Disruption of CRAF-Mediated MEK Activation Is Required for Effective MEK Inhibition in KRAS Mutant Tumors Piro Lito, 1,2,8 Anna Saborowski, 3,8 Jingyin Yue, 2 Martha Solomon, 2 Eric Joseph, 2 Sunyana
Article Disruption of CRAF-Mediated MEK Activation Is Required for Effective MEK Inhibition in KRAS Mutant Tumors Piro Lito, 1,2,8 Anna Saborowski, 3,8 Jingyin Yue, 2 Martha Solomon, 2 Eric Joseph, 2 Sunyana
GENETIC ANALYSIS OF RAS SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN CELL PROLIFERATION, MIGRATION AND SURVIVAL
 Manuscript EMBO-2009-72496 GENETIC ANALYSIS OF RAS SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN CELL PROLIFERATION, MIGRATION AND SURVIVAL Matthias Drosten, Alma Dhawahir, Eleanor Sum, Jelena Urosevic, Carmen Lechuga, Luis Esteban,
Manuscript EMBO-2009-72496 GENETIC ANALYSIS OF RAS SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN CELL PROLIFERATION, MIGRATION AND SURVIVAL Matthias Drosten, Alma Dhawahir, Eleanor Sum, Jelena Urosevic, Carmen Lechuga, Luis Esteban,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH TITLE: An in Vivo shrna-drug Screen to Identify Novel Targeted Therapy Combinations for KRAS Mutant Cancers
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in Vivo shrna-drug Screen to Identify Novel Targeted Therapy Combinations for KRAS Mutant Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in Vivo shrna-drug Screen to Identify Novel Targeted Therapy Combinations for KRAS Mutant Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING
1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance. 13/10/2017 Sara Redaelli
 Dott.ssa Sara Redaelli 13/10/2017 1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance Tumor Heterogeneity: Oncogenic Drivers in NSCLC The Promise of Genotype-Directed Therapy
Dott.ssa Sara Redaelli 13/10/2017 1.Basis of resistance 2.Mechanisms of resistance 3.How to overcome resistance Tumor Heterogeneity: Oncogenic Drivers in NSCLC The Promise of Genotype-Directed Therapy
AACR 101st Annual Meeting 2010, Washington D.C. Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics Section 29; Abstract #3855
 Investigation of the Growth Inhibitory Activity of the MEK Inhibitor ARRY-162 in Combination with Everolimus in a Variety of KRas and PI3K Pathway Mutant Cancers Brian Tunquist, Tyler Risom, Debbie Anderson,
Investigation of the Growth Inhibitory Activity of the MEK Inhibitor ARRY-162 in Combination with Everolimus in a Variety of KRas and PI3K Pathway Mutant Cancers Brian Tunquist, Tyler Risom, Debbie Anderson,
K-Ras EGFR pegfr Tubulin. pplcγ 1. Mock EGF
 shcttl shkras EGF + + 15 17 17 KRas EGFR pegfr 13 pplcγ 1 Level of pegfr (A.U.) 1 8 6 4 2 shkras Mock EGF Supplementary Figure S1. KRasdeficient pancreatic cancer cells retain normal RTK signalling. (a)
shcttl shkras EGF + + 15 17 17 KRas EGFR pegfr 13 pplcγ 1 Level of pegfr (A.U.) 1 8 6 4 2 shkras Mock EGF Supplementary Figure S1. KRasdeficient pancreatic cancer cells retain normal RTK signalling. (a)
Normal RAS-RAF (MAPK) pathway signaling
 BRAF-Mutations in Melanomas L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia, Locarno 77. Annual Meeting Swiss Society of Pathology, Lucerne 2011 Sponsored by Roche Pharma Switzerland Melanoma has increased
BRAF-Mutations in Melanomas L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia, Locarno 77. Annual Meeting Swiss Society of Pathology, Lucerne 2011 Sponsored by Roche Pharma Switzerland Melanoma has increased
Wild-Type and Mutant B-RAF Activate C-RAF through Distinct Mechanisms Involving Heterodimerization. Short Article
 Molecular Cell, Vol. 20, 963 969, December 22, 2005, Copyright ª2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.022 Wild-Type and Mutant B-RAF Activate C-RAF through Distinct Mechanisms Involving Heterodimerization
Molecular Cell, Vol. 20, 963 969, December 22, 2005, Copyright ª2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.022 Wild-Type and Mutant B-RAF Activate C-RAF through Distinct Mechanisms Involving Heterodimerization
K-Ras signalling in NSCLC
 Targeting the Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk pathway Egbert F. Smit MD PhD Dept. Pulmonary Diseases Vrije Universiteit VU Medical Centre Amsterdam, The Netherlands K-Ras signalling in NSCLC Sun et al. Nature Rev. Cancer
Targeting the Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk pathway Egbert F. Smit MD PhD Dept. Pulmonary Diseases Vrije Universiteit VU Medical Centre Amsterdam, The Netherlands K-Ras signalling in NSCLC Sun et al. Nature Rev. Cancer
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Rationale and results from. BRAFi and immunotherapy
 Rationale and results from emerging combinations of BRAFi and immunotherapy Antoni Ribas, M.D. rofessor of Medicine rofessor of Surgery rofessor of Molecular and Medical harmacology Director, Tumor Immunology
Rationale and results from emerging combinations of BRAFi and immunotherapy Antoni Ribas, M.D. rofessor of Medicine rofessor of Surgery rofessor of Molecular and Medical harmacology Director, Tumor Immunology
Progression of RAS-Mutant Leukemia during RAF Inhibitor Treatment
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e brief report Progression of RAS-Mutant Leukemia during RAF Inhibitor Treatment Margaret K. Callahan, M.D., Ph.D., Raajit Rampal, M.D., Ph.D., James
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e brief report Progression of RAS-Mutant Leukemia during RAF Inhibitor Treatment Margaret K. Callahan, M.D., Ph.D., Raajit Rampal, M.D., Ph.D., James
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature13898 Supplementary Information Table 1 Kras mutation status of carcinogen-induced mouse lung adenomas Tumour Treatment Strain Grade Genotype Kras status (WES)* Kras status (Sanger) 32T1
doi:10.1038/nature13898 Supplementary Information Table 1 Kras mutation status of carcinogen-induced mouse lung adenomas Tumour Treatment Strain Grade Genotype Kras status (WES)* Kras status (Sanger) 32T1
Discrete cytosolic macromolecular BRAF complexes exhibit distinct activities and composition
 Article Discrete cytosolic macromolecular BRAF complexes exhibit distinct activities and composition Britta Diedrich 1,2,, Kristoffer TG Rigbolt 1,2,,, Michael Röring 3,, Ricarda Herr 3, Stephanie Kaeser-Pebernard
Article Discrete cytosolic macromolecular BRAF complexes exhibit distinct activities and composition Britta Diedrich 1,2,, Kristoffer TG Rigbolt 1,2,,, Michael Röring 3,, Ricarda Herr 3, Stephanie Kaeser-Pebernard
Identification of BRAF mutations in melanoma lesions with the Roche z480 instrument
 Identification of BRAF mutations in melanoma lesions with the Roche z480 instrument Márta Széll IAP, Siófok May 14, 2012 Multifactorial skin diseses: much more frequent then genodermatoses exhibit familial
Identification of BRAF mutations in melanoma lesions with the Roche z480 instrument Márta Széll IAP, Siófok May 14, 2012 Multifactorial skin diseses: much more frequent then genodermatoses exhibit familial
BRAF: dal melanoma alla HCL
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE PER LO STUDIO E LA CURA DEI TUMORI FONDAZIONE G. Pascale NAPOLI SC Biologia Cellulare e Bioterapie CENTRO RICERCHE ONCOLOGICHE MERCOGLIANO (AV) Laboratorio di Farmacogenomica BRAF: dal
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE PER LO STUDIO E LA CURA DEI TUMORI FONDAZIONE G. Pascale NAPOLI SC Biologia Cellulare e Bioterapie CENTRO RICERCHE ONCOLOGICHE MERCOGLIANO (AV) Laboratorio di Farmacogenomica BRAF: dal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway
 Cell. Mol. Life Sci. DOI 10.1007/s00018-016-2297-8 Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences REVIEW Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway David Lake 1 Sonia A. L. Corrêa 2,3 Jürgen Müller
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. DOI 10.1007/s00018-016-2297-8 Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences REVIEW Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway David Lake 1 Sonia A. L. Corrêa 2,3 Jürgen Müller
Complexity of intra- and inter-pathway loops in colon cancer and melanoma: implications for targeted therapies
 Complexity of intra- and inter-pathway loops in colon cancer and melanoma: implications for targeted therapies René Bernards The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam The Netherlands Molecular versus
Complexity of intra- and inter-pathway loops in colon cancer and melanoma: implications for targeted therapies René Bernards The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam The Netherlands Molecular versus
Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma
 Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma Muska Hassan NCI-ICBP Summer Fellow Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cancer Program Mentor: Cory Johannessen,
Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma Muska Hassan NCI-ICBP Summer Fellow Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cancer Program Mentor: Cory Johannessen,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Cancer Discov. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 March 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cancer Discov. 2012 March ; 2(3): 227 235. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-11-0341. EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Cancer Discov. 2012 March ; 2(3): 227 235. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-11-0341. EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
KRAS: ONE ACTOR, MANY POTENTIAL ROLES IN DIAGNOSIS
 UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PALERMO Scuola di Specializzazione in Biochimica Clinica Direttore Prof. Marcello Ciaccio KRAS: ONE ACTOR, MANY POTENTIAL ROLES IN DIAGNOSIS Loredana Bruno KRAS gene Proto-oncogene
UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DI PALERMO Scuola di Specializzazione in Biochimica Clinica Direttore Prof. Marcello Ciaccio KRAS: ONE ACTOR, MANY POTENTIAL ROLES IN DIAGNOSIS Loredana Bruno KRAS gene Proto-oncogene
w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz
 w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz {w Æ Æ wyw{ x w Germ-line mutations in BRCA1 are associated
w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz {w Æ Æ wyw{ x w Germ-line mutations in BRCA1 are associated
Yanping Li, Maho Takahashi, and Philip J. S. Stork 1 From the Vollum Institute, Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon 97239
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 288, NO. 38, pp. 27646 27657, September 20, 2013 2013 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in the U.S.A. Ras-mutant Cancer
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 288, NO. 38, pp. 27646 27657, September 20, 2013 2013 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in the U.S.A. Ras-mutant Cancer
Sustained ERK inhibition maximizes responses of Braf V600E thyroid cancers to radioiodine
 Sustained ERK inhibition maximizes responses of Braf V600E thyroid cancers to radioiodine James Nagarajah, 1,2 Mina Le, 1,3 Jeffrey A. Knauf, 1 Giuseppe Ferrandino, 4 Cristina Montero-Conde, 1 Nagavarakishore
Sustained ERK inhibition maximizes responses of Braf V600E thyroid cancers to radioiodine James Nagarajah, 1,2 Mina Le, 1,3 Jeffrey A. Knauf, 1 Giuseppe Ferrandino, 4 Cristina Montero-Conde, 1 Nagavarakishore
Bersagli molecolari nel melanoma
 Bersagli molecolari nel melanoma Giuseppe Palmieri - Unit of Cancer Genetics Institute of Biomolecular Chemistry, CNR, Sassari Essential alterations in malignant cells Hanahan & Weinberg, Cell 2000 Essential
Bersagli molecolari nel melanoma Giuseppe Palmieri - Unit of Cancer Genetics Institute of Biomolecular Chemistry, CNR, Sassari Essential alterations in malignant cells Hanahan & Weinberg, Cell 2000 Essential
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
The selective ERK inhibitor BVD-523 is active in models of MAPK pathway-dependent cancers, including those with intrinsic and acquired drug resistance
 The selective ERK inhibitor BVD-523 is active in models of MAPK pathway-dependent cancers, including those with intrinsic and acquired drug resistance Ursula Germann 1, Brinley Furey 2, Jeff Roix 3, William
The selective ERK inhibitor BVD-523 is active in models of MAPK pathway-dependent cancers, including those with intrinsic and acquired drug resistance Ursula Germann 1, Brinley Furey 2, Jeff Roix 3, William
MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: the long and winding road
 MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: the long and winding road Christopher J. Caunt 1, Matthew J. Sale 2, Paul D. Smith 3 and Simon J. Cook 2 Abstract The role of the ERK signalling pathway in
MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: the long and winding road Christopher J. Caunt 1, Matthew J. Sale 2, Paul D. Smith 3 and Simon J. Cook 2 Abstract The role of the ERK signalling pathway in
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
Update on Targeted Therapy in Melanoma
 Update on Targeted Therapy in Melanoma Seville June 2013 James Larkin FRCP PhD London UK Overview What are the targets in melanoma? BRAF / KIT / NRAS / GNAQ / MEK DNA / microtubules CTLA4 / PD1 / PDL1
Update on Targeted Therapy in Melanoma Seville June 2013 James Larkin FRCP PhD London UK Overview What are the targets in melanoma? BRAF / KIT / NRAS / GNAQ / MEK DNA / microtubules CTLA4 / PD1 / PDL1
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. Relative cell viability. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng SCR shyap1-1 shyap
 Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Pre-clinical PK/PD modelling of combination therapies in oncology: abemaciclib and vemurafenib
 Pre-clinical PK/PD modelling of combination therapies in oncology: abemaciclib and vemurafenib Combination Therapies in Oncology Combination therapies in oncology have been explored and used for many decades
Pre-clinical PK/PD modelling of combination therapies in oncology: abemaciclib and vemurafenib Combination Therapies in Oncology Combination therapies in oncology have been explored and used for many decades
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San
 Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Partner exchange: protein protein interactions in the Raf pathway
 Review Partner exchange: protein protein interactions in the Raf pathway Reiner Wimmer and Manuela Baccarini University of Vienna, Center for Molecular Biology, Max F. Perutz Laboratories, Doktor-Bohr-Gasse
Review Partner exchange: protein protein interactions in the Raf pathway Reiner Wimmer and Manuela Baccarini University of Vienna, Center for Molecular Biology, Max F. Perutz Laboratories, Doktor-Bohr-Gasse
Final published version:
 Paradoxical activation of MEK/ERK signaling induced by B-Raf inhibition enhances DR5 expression and DR5 activation-induced apoptosis in Ras-mutant cancer cells Youtake Oh, Emory University Jiusheng Deng,
Paradoxical activation of MEK/ERK signaling induced by B-Raf inhibition enhances DR5 expression and DR5 activation-induced apoptosis in Ras-mutant cancer cells Youtake Oh, Emory University Jiusheng Deng,
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy
 Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring a BRAF mutation: a multicentre study exploring clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes in a real-life setting: EXPLORE GFPC
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring a BRAF mutation: a multicentre study exploring clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes in a real-life setting: EXPLORE GFPC
a study of 754 cases highlighting potential pitfalls and guidelines for
 Histopathology 2016 DOI: 10.1111/his.12992 BRAF V600E and NRAS Q61L/Q61R mutation analysis in metastatic melanoma using immunohistochemistry: a study of 754 cases highlighting potential pitfalls and guidelines
Histopathology 2016 DOI: 10.1111/his.12992 BRAF V600E and NRAS Q61L/Q61R mutation analysis in metastatic melanoma using immunohistochemistry: a study of 754 cases highlighting potential pitfalls and guidelines
Personalized Healthcare Update
 Dr. Kai - Oliver Wesche Market Development Manager, Personalized Healthcare QIAGEN Personalized Healthcare Update Pioneering Personalized Medicine through Partnering TOMTOVOK BKM120 Zelboraf QIAGEN partners:
Dr. Kai - Oliver Wesche Market Development Manager, Personalized Healthcare QIAGEN Personalized Healthcare Update Pioneering Personalized Medicine through Partnering TOMTOVOK BKM120 Zelboraf QIAGEN partners:
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description:
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of Ras biochemical coupled assay.
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of Ras biochemical coupled assay.
Molecularly Targeted Therapies: Mechanisms of Resistance
 An AACR Special Conference on Molecularly Targeted Therapies: Mechanisms of Resistance May 9-12, 2012 Westin San Diego San Diego, CA Wednesday, May 9 7:00 p.m.-8:00 p.m. Opening Keynote Session BRAF and
An AACR Special Conference on Molecularly Targeted Therapies: Mechanisms of Resistance May 9-12, 2012 Westin San Diego San Diego, CA Wednesday, May 9 7:00 p.m.-8:00 p.m. Opening Keynote Session BRAF and
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME- ASSOCIATED BRAF MUTANTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND CANCER
 CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME- ASSOCIATED BRAF MUTANTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND CANCER by Erica Tiberia A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Department of
CARDIOFACIOCUTANEOUS SYNDROME- ASSOCIATED BRAF MUTANTS IN DEVELOPMENT AND CANCER by Erica Tiberia A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Department of
Targeted Therapy for Cutaneous Melanoma: Beyond BRAF...
 Journal of Patient-Centered Research and Volume 1 Issue 1 -- Melanoma Research Article 4 2-28-2014 Targeted Therapy for Cutaneous Melanoma: Beyond BRAF... Michael A. Davies Follow this and additional works
Journal of Patient-Centered Research and Volume 1 Issue 1 -- Melanoma Research Article 4 2-28-2014 Targeted Therapy for Cutaneous Melanoma: Beyond BRAF... Michael A. Davies Follow this and additional works
BRAF pathway. Sun Young Kim. Division of Medical Oncology Center for Colorectal Cancer National Cancer Center
 BRAF pathway Sun Young Kim Division of Medical Oncology Center for Colorectal Cancer National Cancer Center Contents BRAF inhibitor in advanced melanoma Paradoxical MAPK pathway activation by BRAF inhibitor
BRAF pathway Sun Young Kim Division of Medical Oncology Center for Colorectal Cancer National Cancer Center Contents BRAF inhibitor in advanced melanoma Paradoxical MAPK pathway activation by BRAF inhibitor
Antitumor activity of the ERK inhibitor SCH against BRAF mutant, NRAS mutant and wild-type melanoma
 Wong et al. Molecular Cancer 2014, 13:194 RESEARCH Open Access Antitumor activity of the ERK inhibitor SCH722984 against BRAF mutant, NRAS mutant and wild-type melanoma Deborah JL Wong 1, Lidia Robert
Wong et al. Molecular Cancer 2014, 13:194 RESEARCH Open Access Antitumor activity of the ERK inhibitor SCH722984 against BRAF mutant, NRAS mutant and wild-type melanoma Deborah JL Wong 1, Lidia Robert
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
RESISTANCE TO TARGETED THERAPIES IN MELANOMA: NEW INSIGHTS
 RESISTANCE TO TARGETED THERAPIES IN MELANOMA: NEW INSIGHTS Giuseppe Palmieri, 1 Maria Colombino, 1 Maria Cristina Sini, 1 Antonella Manca, 1 Paolo Antonio Ascierto, 2 Antonio Cossu 3 1. Institute of Biomolecular
RESISTANCE TO TARGETED THERAPIES IN MELANOMA: NEW INSIGHTS Giuseppe Palmieri, 1 Maria Colombino, 1 Maria Cristina Sini, 1 Antonella Manca, 1 Paolo Antonio Ascierto, 2 Antonio Cossu 3 1. Institute of Biomolecular
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
Normal Skin. Tissue Samples and Melanoma Cell Lines. BRAF Mut. RAS Mut RAS WT /BRAF WT
 Supplemental Figure 1. MERTK gene expression in melanoma cell line panel from Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. A. Microarray analysis of melanoma cell lines from UNC collection grouped by oncogenic mutation.
Supplemental Figure 1. MERTK gene expression in melanoma cell line panel from Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. A. Microarray analysis of melanoma cell lines from UNC collection grouped by oncogenic mutation.
Fig S1. ZNF697-NOTCH2 rearrangement: Diagram of the ZNF697-NOTCH2 fusion and
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES: Fig S1. ZNF697-NOTCH2 rearrangement: Diagram of the ZNF697-NOTCH2 fusion and breakpoint. The 5 untranslated region of ZNF697 is joined out of frame with exon 26 of NOTCH2, with the
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES: Fig S1. ZNF697-NOTCH2 rearrangement: Diagram of the ZNF697-NOTCH2 fusion and breakpoint. The 5 untranslated region of ZNF697 is joined out of frame with exon 26 of NOTCH2, with the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
Corporate Medical Policy Molecular Analysis for Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: molecular_analysis_for_targeted_therapy_for_non_small_cell_lung_cancer
Clinical significance of genetic analysis in glioblastoma treatment
 Clinical significance of genetic analysis in glioblastoma treatment Department of Neurosurgery, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan Koji Yoshimoto Can we get prognostic
Clinical significance of genetic analysis in glioblastoma treatment Department of Neurosurgery, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan Koji Yoshimoto Can we get prognostic
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
Quantification of early stage lesions for loss of p53 should be shown in the main figures.
 Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
Black is the New Black or How I learned to stop worrying and love melanoma (with apologies to Dr. Strangelove)
 Black is the New Black or How I learned to stop worrying and love melanoma (with apologies to Dr. Strangelove) Provincial Cancer Care Conference 2018 Ralph P.W. Wong MD FRCPC St Boniface Site Director
Black is the New Black or How I learned to stop worrying and love melanoma (with apologies to Dr. Strangelove) Provincial Cancer Care Conference 2018 Ralph P.W. Wong MD FRCPC St Boniface Site Director
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Kris MG, Johnson BE, Berry LD, et al. Using Multiplexed Assays of Oncogenic Drivers in Lung Cancers to Select Targeted Drugs. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3741 etable 1. Trials
Supplementary Online Content Kris MG, Johnson BE, Berry LD, et al. Using Multiplexed Assays of Oncogenic Drivers in Lung Cancers to Select Targeted Drugs. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3741 etable 1. Trials
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S5. ROS regulated the signaling responses of A. gambiae 4a3B cells to human insulin. (A) 4a3B cells were stimulated with 6000
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Exogenous H 2 O 2 induced rapid activation of ERK in Anopheles stephensi cells. ASE cells were treated with PBS or with 500 mmh 2 O 2 for 5, 30, 60, and 180 min.
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Exogenous H 2 O 2 induced rapid activation of ERK in Anopheles stephensi cells. ASE cells were treated with PBS or with 500 mmh 2 O 2 for 5, 30, 60, and 180 min.
Tunable-Combinatorial Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance Limit the Efficacy of BRAF/MEK Cotargeting but Result in Melanoma Drug Addiction
 Article Tunable-Combinatorial Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance Limit the Efficacy of BRAF/MEK Cotargeting but Result in Melanoma Drug Addiction Highlights d BRAFi+MEKi-resistant melanomas augment mutational
Article Tunable-Combinatorial Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance Limit the Efficacy of BRAF/MEK Cotargeting but Result in Melanoma Drug Addiction Highlights d BRAFi+MEKi-resistant melanomas augment mutational
Frequency(%) KRAS G12 KRAS G13 KRAS A146 KRAS Q61 KRAS K117N PIK3CA H1047 PIK3CA E545 PIK3CA E542K PIK3CA Q546. EGFR exon19 NFS-indel EGFR L858R
 Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
Frequency(%) 1 a b ALK FS-indel ALK R1Q HRAS Q61R HRAS G13R IDH R17K IDH R14Q MET exon14 SS-indel KIT D8Y KIT L76P KIT exon11 NFS-indel SMAD4 R361 IDH1 R13 CTNNB1 S37 CTNNB1 S4 AKT1 E17K ERBB D769H ERBB
The Role of Next Generation Sequencing in Solid Tumor Mutation Testing
 The Role of Next Generation Sequencing in Solid Tumor Mutation Testing Allie H. Grossmann MD PhD Department of Pathology, University of Utah Division of Anatomic Pathology & Oncology, ARUP Laboratories
The Role of Next Generation Sequencing in Solid Tumor Mutation Testing Allie H. Grossmann MD PhD Department of Pathology, University of Utah Division of Anatomic Pathology & Oncology, ARUP Laboratories
Melanoma Mutagenesis and Aberrant Cell Signaling
 Expanding knowledge of the molecular alterations in melanoma is making additional targeted therapies possible. Tenzin Norbu Lama. Yaks (detail). Melanoma Mutagenesis and Aberrant Cell Signaling Danielle
Expanding knowledge of the molecular alterations in melanoma is making additional targeted therapies possible. Tenzin Norbu Lama. Yaks (detail). Melanoma Mutagenesis and Aberrant Cell Signaling Danielle
BRAF inhibitors Anti-angiogenic therapy Other molecular targets Discussion
 If you experience any technical difficulties call 8-274-939 or e-mail informed@commpartners.com Slides will advance automatically. You can also advance/ review the presentation using the control buttons
If you experience any technical difficulties call 8-274-939 or e-mail informed@commpartners.com Slides will advance automatically. You can also advance/ review the presentation using the control buttons
Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers
 Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers from genomics to clinical application Aldo Scarpa ARC-NET Applied Research on Cancer Department of Pathology and Diagnostics
Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers from genomics to clinical application Aldo Scarpa ARC-NET Applied Research on Cancer Department of Pathology and Diagnostics
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Kinome Profiling: The Potential in ER-Negative Patients. Charles M. Perou, Ph.D. Departments of Genetics and Pathology
 Kinome Profiling: The Potential in ER-Negative Patients Charles M. Perou, Ph.D. Departments of Genetics and Pathology Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, North
Kinome Profiling: The Potential in ER-Negative Patients Charles M. Perou, Ph.D. Departments of Genetics and Pathology Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, North
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SAM library or vector. Introduce AKT reporter
 Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SM library or vector Introduce reporter Grow cells in presence of puromycin for 5 days Vector control SM library fewer surviving cells More surviving
Infect MCF-7 cells carrying dcas9-vp64 + psm2-p65-hsf1 with SM library or vector Introduce reporter Grow cells in presence of puromycin for 5 days Vector control SM library fewer surviving cells More surviving
BRAF inhibitors in advanced BRAF-positive non-small cell lung cancer
 Editorial BRAF inhibitors in advanced BRAF-positive non-small cell lung cancer Tiziana Vavalà Department of Oncology, ASL CN1, Hospital of Saluzzo, 58 Spielberg street, 12037 Saluzzo (CN), Italy Correspondence
Editorial BRAF inhibitors in advanced BRAF-positive non-small cell lung cancer Tiziana Vavalà Department of Oncology, ASL CN1, Hospital of Saluzzo, 58 Spielberg street, 12037 Saluzzo (CN), Italy Correspondence
METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: TUMOR MUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND ITS IMPACT ON CHEMOTHERAPY SUMA SATTI, MD
 METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: TUMOR MUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND ITS IMPACT ON CHEMOTHERAPY SUMA SATTI, MD INTRODUCTION Second leading cause of cancer related death in the United States. 136,830 cases in 2014
METASTATIC COLORECTAL CANCER: TUMOR MUTATIONAL ANALYSIS AND ITS IMPACT ON CHEMOTHERAPY SUMA SATTI, MD INTRODUCTION Second leading cause of cancer related death in the United States. 136,830 cases in 2014
LY , a panraf inhibitor, has significant anti-tumor activity in BRAF and KRAS mutant preclinical models of colorectal cancer
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 6), pp: 9251-9266 LY3009120, a panraf inhibitor, has significant anti-tumor activity in BRAF and KRAS mutant preclinical models of colorectal cancer Eliza Vakana 1,*, Susan Pratt
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 6), pp: 9251-9266 LY3009120, a panraf inhibitor, has significant anti-tumor activity in BRAF and KRAS mutant preclinical models of colorectal cancer Eliza Vakana 1,*, Susan Pratt
Insights from Sequencing the Melanoma Exome
 Insights from Sequencing the Melanoma Exome Michael Krauthammer, MD PhD, December 2 2015 Yale University School Yof Medicine 1 2012 Exome Screens and Results Exome Sequencing of 108 sun-exposed melanomas
Insights from Sequencing the Melanoma Exome Michael Krauthammer, MD PhD, December 2 2015 Yale University School Yof Medicine 1 2012 Exome Screens and Results Exome Sequencing of 108 sun-exposed melanomas
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in vivo shrna-drug screen to identify novel targeted therapy combinations for KRAS mutant cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, MD PhD CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in vivo shrna-drug screen to identify novel targeted therapy combinations for KRAS mutant cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, MD PhD CONTRACTING
Melanoma: From Chemotherapy to Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy. What every patient needs to know. James Larkin
 Melanoma: From Chemotherapy to Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy What every patient needs to know James Larkin Melanoma Therapy 1846-2017 Surgery 1846 Cytotoxic Chemotherapy 1946 Checkpoint Inhibitors
Melanoma: From Chemotherapy to Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy What every patient needs to know James Larkin Melanoma Therapy 1846-2017 Surgery 1846 Cytotoxic Chemotherapy 1946 Checkpoint Inhibitors
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2
 ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
BRAF Inhibition in Melanoma
 BRAF Inhibition in Melanoma New York City, Mar 22-23, 2013 Bartosz Chmielowski, MD, PhD Assistant Clinical Professor University of California Los Angeles Disclosures Speaker Bureau: BMS, Genentech, Prometheus
BRAF Inhibition in Melanoma New York City, Mar 22-23, 2013 Bartosz Chmielowski, MD, PhD Assistant Clinical Professor University of California Los Angeles Disclosures Speaker Bureau: BMS, Genentech, Prometheus
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
Results and Discussion of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Activation
 Results and Discussion of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation To demonstrate the contribution which RCytoscape s molecular maps can make to biological understanding via exploratory data analysis, we here
Results and Discussion of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation To demonstrate the contribution which RCytoscape s molecular maps can make to biological understanding via exploratory data analysis, we here
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11905 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of integrated chorda tympani nerve responses. Quantification
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11905 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of integrated chorda tympani nerve responses. Quantification
Development of Rational Drug Combinations for Oncology Indications - An Industry Perspective
 Development of Rational Drug Combinations for Oncology Indications An Industry Perspective Stuart Lutzker, MDPhD Vice President Oncology Early Development Genentech Inc 1 Conventional Oncology Drug Development
Development of Rational Drug Combinations for Oncology Indications An Industry Perspective Stuart Lutzker, MDPhD Vice President Oncology Early Development Genentech Inc 1 Conventional Oncology Drug Development
RAS and BRAF in metastatic colorectal cancer management
 Review Article RAS and BRAF in metastatic colorectal cancer management Jun Gong 1, May Cho 1, Marwan Fakih 2 1 Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA, USA; 2 Medical
Review Article RAS and BRAF in metastatic colorectal cancer management Jun Gong 1, May Cho 1, Marwan Fakih 2 1 Department of Medical Oncology, City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, CA, USA; 2 Medical
Targets & therapies for colorectal cancer
 Targets & therapies for colorectal cancer Jan Schellens Werkgroep "MOLECULAIRE DIAGNOSTIEK IN DE PATHOLOGIE 31-01-2014 Current treatment options for advanced colorectal cancer (CRC) First line: - CAPOX
Targets & therapies for colorectal cancer Jan Schellens Werkgroep "MOLECULAIRE DIAGNOSTIEK IN DE PATHOLOGIE 31-01-2014 Current treatment options for advanced colorectal cancer (CRC) First line: - CAPOX
Κίκα Πλοιαρχοπούλου. Παθολόγος Ογκολόγος Ευρωκλινική Αθηνών
 Κίκα Πλοιαρχοπούλου Παθολόγος Ογκολόγος Ευρωκλινική Αθηνών Time (months) Survival outcomes in mcrc have progressively improved over the past two decades Treatment options for many patients Multidisciplinary
Κίκα Πλοιαρχοπούλου Παθολόγος Ογκολόγος Ευρωκλινική Αθηνών Time (months) Survival outcomes in mcrc have progressively improved over the past two decades Treatment options for many patients Multidisciplinary
BRAF inhibitors: two edged sword Research Article
 Gene Therapy and Molecular Biology Vol 16, page 195 Gene Ther Mol Biol Vol 16, 195-200, 2014 BRAF inhibitors: two edged sword Research Article Yasir Y Elamin 1, Shereen Rafee 2, Sinead Toomey 1, Bryan
Gene Therapy and Molecular Biology Vol 16, page 195 Gene Ther Mol Biol Vol 16, 195-200, 2014 BRAF inhibitors: two edged sword Research Article Yasir Y Elamin 1, Shereen Rafee 2, Sinead Toomey 1, Bryan
DIRECT TARGETING OF KRAS MUTANT CANCERS WITH A KRAS G12C MUTATION-SELECTIVE INHIBITOR
 DIRECT TARGETING OF KRAS MUTANT CANCERS WITH A KRAS G12C MUTATION-SELECTIVE INHIBITOR THE KRAS REVIVAL KRAS is the single most frequently mutated oncogene and as the first of more than 700 genes to be
DIRECT TARGETING OF KRAS MUTANT CANCERS WITH A KRAS G12C MUTATION-SELECTIVE INHIBITOR THE KRAS REVIVAL KRAS is the single most frequently mutated oncogene and as the first of more than 700 genes to be
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
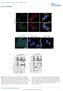 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
Qualifying Examination (Part I)
 Student Edition Qualifying Exam December 2015 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15, 2015 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Time Student Name
Student Edition Qualifying Exam December 2015 Department of Pharmacology Qualifying Examination (Part I) December 15, 2015 ALL EXAMS TAKE PLACE IN THE BASS CONFERENCE ROOM, 436 RRB Date Time Student Name
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
