Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method
|
|
|
- Tamsyn Tate
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the g ravity method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous endoscopic g astrostomy (PEG), g astrostomy tube (GT), or nasog astric tube (NGT). After you have your feeding tube placed, please call to schedule a follow-up appointment in the nutrition clinic. About Tube Feeding A feeding tube will give you nutrients if you aren t able to get enough through eating and drinking, or if you can t swallow safely. Nutrients provide energ y and help you heal. The g ravity method is a type of feeding where formula flows out from your feeding bag and into your feeding tube by g ravity. Tube Feeding Nutritional Guidelines Formula: Cans per day: (8 ounces each) Total calories per day: Calories Additional water to take per day: ml Total liquid volume per day: ml You can take additional clear liquids throug h your feeding tube. Clear liquids are anything you can see throug h, such as tea, black coffee, broth, clear sodas (such as 7-Up, Sprite, ginger ale, seltzer, or Gatorade ), or clear juices (such as white cranberry, white grape, or apple). You should take them at room temperature. These liquids shouldn t replace the amount of formula you need to take each day. Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 1/15
2 Tube Feeding Schedule You can choose the times of your feedings, as long as you reach your daily nutritional g oals. Write in the times you prefer or your doctor, nurse practitioner (NP), or dietitian recommends. Suggested times Amount of for mula Water flushes befor e and after feeding am can(s) or ml ml am pm can(s) or ml ml am pm can(s) or ml ml pm can(s) or ml ml pm can(s) or ml ml If you re admitted to the hospital and need tube feeding s, your NP will contact your dietitian so that there s no chang e in your feeding schedule. Bring your button adapter with you to the hospital, if you have one. Tube Feeding Position Sit up in a chair during your tube feeding. If you re getting your tube feeding while in bed, use a wedge pillow to prop yourself up to at least 45 degrees (see Figure 1). You can buy a wedge pillow through websites such as Amazon.com or at your local surg ical supply store. Fig ure 1. Sitting up at a 45-deg ree ang le Sit or stand in an uprig ht position for 1 hour after the feeding is finished. This will prevent the formula from entering your lung s if you vomit. You can also g et up and walk around, if you d like. Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 2/15
3 Tube Feeding Instructions 1. Clean your hands. If you re washing your hands with soap and water, wet your hands, apply soap, rub them tog ether thoroug hly for 15 seconds, then rinse. Dry your hands with a towel and use that same towel to turn off the faucet. If you re using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, be sure to cover all of your hands with it, rubbing them tog ether until they re dry. 2. Gather your supplies in a clean and comfortable place. Don t set up or do your tube feeding in the bathroom. You will need: The amount of formula prescribed by your doctor or NP A g ravity feeding bag A cup An IV pole or hook for hang ing the feeding bag A clean cloth or paper towel A container of water. You can use tap water as long as it s safe to drink. A 60 ml catheter tip syringe A clean cloth or paper towel Tape A button adapter, if you have a button (see Fig ure 2) instead of a tube (see Figure 3) Fig ure 2. Button Fig ure 3. Gastrostomy tube 3. Close the roller clamp on the feeding bag (see Figure 4). Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 3/15
4 Fig ure 4. Closing the roller clamp 4. Wipe the top of the formula can with a clean cloth or paper towel. Pour the prescribed amount of formula into the feeding bag (see Fig ure 5). This amount is listed in the Tube feeding schedule section of this resource. Fig ure 5. Filling the feeding bag 5. Hang the feeding bag 2 to 3 feet above you on either an IV pole or hook (see Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 4/15
5 Figure 6). It should be close to a comfortable chair or your bed. Fig ure 6. Hang ing the feeding bag 6. Hold the end of the feeding bag tube over a cup. Remove the cap at the end of the tube. Slowly open the roller clamp on the feeding bag tube (see Fig ure 7). Allow the formula to run through the tubing, then close the clamp. This gets the air out of the tubing. If your feeding bag tubing doesn t have a roller clamp, slowly open the cap and pinch the tubing until the liquid gets to the end. Fig ure 7. Opening roller clamp on feeding bag tube Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 5/15
6 7. Open the plug at the end of your feeding tube(see Figure 8). If you have a button, insert the adapter into it (see Figure 9). If you re using a tube without a clamp, such as one that was placed in Interventional Radiology, pinch the end of the tube to avoid leakage or put the tube in a cup. For the rest of this resource, when we use the words unclamp or reclamp, you should unpinch or repinch your feeding tube instead. Fig ure 8. Opening plug at end of feeding tube Fig ure 9. Inserting adapter into button 8. Fill the syringe with the amount of water recommended by your NP or dietitian into the catheter tip syring e. This amount of water to use is listed in the Tube feeding schedule section of this resource. Place the syring e into your feeding tube or button adapter. 9. Unclamp your feeding tube (see Figure 10). Flush your feeding tube (see Figure 11). Fig ure 10. Unclamping the feeding tube Fig ure 11. Flushing the feedin g tube Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 6/15
7 10. Reclamp your feeding tube. Disconnect the syring e. 11. Connect the end of the feeding bag tubing to your feeding tube or button adapter (see Figure 12). Make sure that the end of the tube is placed firmly. You can put a piece of tape over the connection to keep it from separating. Fig ure 12. Connecting feeding bag tubing to feedin g tube 12. Unclamp your feeding tube and slowly open the roller clamp on the feeding bag tubing (see Figure 13). Allow the formula to drip in over 30 to 45 minutes. Check the bag every 15 minutes. If the formula is flowing too fast or too slowly, adjust the roller clamp as needed (see Figure 13). You can also lower or raise the bag to change the flow of the formula. As you do this more and more, you will learn how high to hang the bag. Fig ure 13. Unclamping feeding tube and opening roller clamp on feeding bag tubing Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 7/15
8 13. When the feeding bag is empty, close the roller clamp on the feeding bag tubing and close the clamp on your feeding tube. Disconnect the feeding bag and set it aside. 14. Fill the syringe with the amount of water recommended by your NP or dietitian. This amount is listed in the Tube feeding schedule section of this resource. Insert the syring e into your feeding tube. Unclamp and flush your feeding tube. 15. Clamp your feeding tube, remove the button adapter (if you re using one), and cap your feeding tube. 16. Rinse the feeding bag and syringe with warm water after each feeding. Let your supplies air dry. Use a new feeding bag every 24 hours to prevent infection. 17. Repeat steps 1 to 16 with each feeding. 18. Repeat the full procedure times a day. If you feel too full or are having nausea and vomiting, tell your doctor, dietitian, or NP. Important points Always reclamp your feeding tube before removing your catheter tip syring e to avoid leakage. Move the clamp on your feeding tube to avoid permanent kinking of the tube. To avoid clogging, always flush your feeding tube with the amount of water recommended by your NP or dietitian (usually 30 to 60 ml) before and after: Each feeding. Taking each medication. Taking additional clear liquids. If you aren t using your feeding tube daily, flush it with 60 ml of water at least once a day. Taking Medications Through Your Feeding Tube Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 8/15
9 Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you can take your medications throug h your feeding tube. Most medications that you normally take by mouth can be taken throug h your feeding tube. Medications must be in liquid form or crushed into a powder to prevent your feeding tube from g etting clog g ed. Many medications come in a liquid form. Ask your doctor or pharmacist about liquid forms if you take pills, tablets, or capsules. Enteric-coated, extended-release (XR), or slow-release (SR) tablets or capsules cannot be g iven throug h your feeding tube. If you take any medications in that form, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you can g et the medication in a different form. Do not mix different medications tog ether unless instructed by your doctor or pharmacist. If you re taking more than 1 medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you can take any of them together. Some medications have to be taken on an empty stomach while others must be taken with food. Talk with your doctor about how to take your medications. Take esomeprazole (Nexium ), lansoprazole (Prevacid ), omeprazole (Prilosec ), and pantoprazole (Protonix ) at least 30 minutes before eating, with or without using a feeding tube. Write down your medication schedule and keep it readily available. Update it when anything chang es. That will make it easy for your family members or careg ivers to know your medication schedule. Bring a copy of the schedule to your doctor visits. Your doctor will want to review your medications at each visit. Always flush your feeding tube with 30 to 60 ml of water before and after you take each medication. This will prevent clogging. Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 9/15
10 Instructions for taking medications 1. Clean your hands. If you re washing your hands with soap and water, wet your hands, apply soap, rub them tog ether thoroug hly for 15 seconds, then rinse. Dry your hands with a towel, and use that same towel to turn off the faucet. If you re using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, be sure to cover all of your hands with it, rubbing them tog ether until they re dry. 2. Gather your supplies in a clean and comfortable place. Don t set up or do your tube feeding in the bathroom. You will need: A small cup or glass A 60 ml catheter tip syringe Medication in liquid or powder form Mortar and pestle or a pill crusher, if needed Water (You can use tap water as long as it s safe to drink) A spoon Button adapter, if you have a button 3. Flush your feeding tube with 30 to 60 ml of water. Clamp the feeding tube. 4. If your medication is in liquid form: Liquid medications may contain sorbitol. Sorbitol can cause bloating, cramping, diarrhea (loose or watery bowel movements), or all of these symptoms, if not taken as directed. Pour the medication into a small cup or measure the exact amount using a small measuring spoon. Unless you re g iven other instructions, take each liquid medication separately. Add 30 ml (1 ounce) of water to the medication. Draw up the solution using the catheter tip syring e. Go to step 5. If your medication is in tablet or pill form: Tablets and pills must be crushed to a fine powder using a mortar and Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 10/15
11 pestle or a pill crusher. You can buy these at your local pharmacy. Crush each medication separately. Add 30 ml (1 ounce) of warm water to each medication. Mix it well with the spoon until the medication dissolves. Draw the prepared medication into the catheter tip syring e. Remember to draw up each medication separately unless directed otherwise. Go to step 5. If your medication is a capsule: Capsules must be opened so that the powder inside can dissolve. Open the prescribed number of capsule(s). Add 30 ml (1 ounce) of warm water to the medication. Mix it well with the spoon until the medication dissolves. Draw the prepared medication into the catheter tip syring e. Go to step Attach the syring e to the feeding tube or button adapter, if you re using one. Unclamp the tube and g ently push in the medication. Reclamp the tube. 6. Attach the syringe filled with 30 to 60 ml of water to your feeding tube. Unclamp the tube and flush it thoroug hly. Reclamp it before removing the syring e. Repeat the flushing if the water moves too slowly throug h the tube. 7. Close the plug or reattach the cap at the end of your feeding tube. Remove the button adapter, if you re using one. 8. After taking the medication(s), pull the syringe apart and wash all of the equipment with warm water. Let your supplies air dry. Tracking Symptoms Keep a diary Keeping a diary can help you keep track of any problems or questions you may have. It will also help you remember what has been going on at home if you need to come to the hospital. In your diary: Write down your weight twice a week. Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 11/15
12 If you re allowed to eat or drink by mouth, keep track of the amount. This will tell you your total nutritional intake. Write down any swelling of your face, hands, or feet. Write down any chang es in your bowel movement, such as in the color, consistency, frequency, or amount. Write down any chang es in your urine, such as in the color, frequency, or amount. Write down any abdominal (belly) discomfort, nausea, vomiting, or other problem that may relate to your feeding. If you re not sure, write it down and talk with your doctor, NP, or dietitian about it. Monitoring your fluid balance Weigh yourself 2 times a week at the same time of day and in the same type of clothing. Write it down in your diary. Call your doctor, dietitian, or NP if you: Gain more than 5 pounds (2.3 kilograms) in 1 week Lose more than 2 pounds (.90 kilog rams) in 1 week Have swelling in your feet, legs, hands, or face Feel very thirsty Feel dizzy Have difficulty breathing Managing Side Effects Constipation Your bowel movements may chang e while you re on tube feeding s. They may also chang e if you re on pain medication. The leng th of time between bowel movements (passing stool) varies from person to person, but if you re having fewer bowel movements than what s normal for you, you may be constipated (having fewer bowel movements than what is normal for you). To avoid constipation, talk with your doctor or NP about taking a stool softener such as docusate sodium (Colace ), a mild laxative such as senna (Senokot ), Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 12/15
13 or a fiber supplement such as Metamucil. If you re constipated, discuss the following options with your doctor, NP, or dietician: Drink liquids if you re allowed, or take additional liquids throug h your feeding tube Take 1 cup of liquid 3 times a day between your feeding s throug h your feeding tube. Take 4 ounces of prune juice every day. If you re taking the prune juice through your feeding tube, flush your feeding tube with 30 to 60 ml of water after taking the juice. Call your doctor, NP, or dietitian if: Your bowel movements are hard and dry. You don t have a bowel movement after 2 days. You have nausea or vomiting. Bloating, nausea, stomach cramps, or diarrhea If you have bloating, nausea, stomach cramps, or diarrhea: Replace the formula in your next feeding with an equal amount of clear liquid, such as tea, coffee, broth, or clear juices (white cranberry, white g rape, or apple). For example, if you take 240 ml of formula per feeding, take 240 ml of clear liquid diluted with 240 ml of water instead of formula. Then, for your next feeding, take half as much formula as you usually take and double the amount of water you usually use for your water flushes. Allow it to drip slowly. When your symptoms g o away, take the full amount of formula and your usual water flushes before and after each feeding. If the bloating, nausea, stomach cramps, or diarrhea last long er than 24 hours or you vomit, call your doctor or NP. Ordering Supplies Your case manag er will check with your insurance company about your insurance coverage. If your insurance covers tube feedings, we will refer you to a Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 13/15
14 home care provider. They will supply you with formula and equipment. If your insurance doesn t cover your formula or supplies, you can buy that brand or a generic substitute at a local pharmacy, grocery store, or online. Always reorder formula and equipment when you have only 10 days of supplies at home. If you re no long er having tube feeding s, your leftover supplies can often be donated. Please contact the Oley Foundation by calling or g oing to their website at Storing Formula Check the expiration date of your formula. Unopened cans of formula can be stored at room temperature for long periods of time. Cover open cans of formula and store them in the refrig erator between feeding s. Throw away any open, unused cans of formula after 24 hours. Call Your Doctor or NP if You: See any of the following at your insertion site: Bleeding that soaks a small gauze pad Pus or drainage with a foul smell Redness Swelling Increased pain that doesn t g o away with medication Feel too full after feedings Have swelling in your abdomen Have nausea or vomiting for more than 24 hours Have bloating, stomach cramps, or diarrhea for more than 24 hours Haven t had a bowel movement in 2 days Have hard and dry bowel movements Have any chang es in your bowel movement, such as in the color, consistency, frequency, or amount. Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 14/15
15 Have any chang es in your urine, such as in the color, frequency, or amount. Have a temperature of 101 F (38.3 C) or hig her Have chills Gain more than 5 pounds (2.3 kilog rams) per week Lose more than 2 pounds (.90 kilog rams) per week Have swelling of your feet, legs, hands, or face Are dizzy Have difficulty breathing Contact Information If you have any questions or concerns, call the Nutrition Service office at and ask for the outpatient NP. You can reach the office Monday through Friday from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM. After 5:00 PM, during weekend, and on holidays, please call and ask for the g astrointestinal (GI) fellow on call. Doctor: Telephone: Home care agency: Telephone: Home care agency contact person: Telephone: Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 2018 Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center - Generated on Aug ust 17, 2018 Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method 15/15
Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method This information will help teach you how to use the bolus method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method This information will help teach you how to use the bolus method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
Tube Feeding With a Pump
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your feeding tube. This includes percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your feeding tube. This includes percutaneous
Tube Feeding With a Pump
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding
 Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version)
 The Patient was given access to the following documents on Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version) Before you leave the hospital,
The Patient was given access to the following documents on Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version) Before you leave the hospital,
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS
 YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults. Clinical Nutrition Services
 Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Self-Catheterization for Females
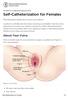 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
About Your PleurX Drainage Catheter
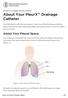 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your PleurX Drainage Catheter This information will help you prepare to have your PleurX drainag e catheter placed at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) and teach you how
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your PleurX Drainage Catheter This information will help you prepare to have your PleurX drainag e catheter placed at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK) and teach you how
Enteral Nutrition. Introduction. Brooks Health Care, Inc. Patient Instruction 1
 Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home.
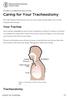 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Home Total Parenteral Nutrition This information will help teach you and your caregiver how to give total parenteral nutrition (TPN) at home. You will also receive a copy
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Home Total Parenteral Nutrition This information will help teach you and your caregiver how to give total parenteral nutrition (TPN) at home. You will also receive a copy
Sperm Collection by Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE)
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Sperm Collection by Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) This information will help you prepare for your sperm collection by testicular sperm extraction (TESE) procedure at
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Sperm Collection by Testicular Sperm Extraction (TESE) This information will help you prepare for your sperm collection by testicular sperm extraction (TESE) procedure at
Tube Feeding At Home. A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers
 A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
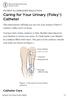 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Diagnostic Laparoscopy This information describes your diag nostic laparoscopy. About Your Diagnostic Laparoscopy A diag nostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure.
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Diagnostic Laparoscopy This information describes your diag nostic laparoscopy. About Your Diagnostic Laparoscopy A diag nostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure.
Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression
 Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression What is a Gastrostomy? A gastrostomy (g-tube) is a procedure that creates a small opening in your outer abdomen into the stomach. A thin tube is placed through this hole.
Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression What is a Gastrostomy? A gastrostomy (g-tube) is a procedure that creates a small opening in your outer abdomen into the stomach. A thin tube is placed through this hole.
Going home after breast surgery without drains
 Going home after breast surgery without drains Princess Margaret Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn: How to care for yourself when you go home What activities you can do
Going home after breast surgery without drains Princess Margaret Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn: How to care for yourself when you go home What activities you can do
About Intravesical Therapy
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Intravesical Therapy This information explains intravesical (in-tra-ves-i-cal) therapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). It also describes what to expect before and
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Intravesical Therapy This information explains intravesical (in-tra-ves-i-cal) therapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). It also describes what to expect before and
Tube Feeding at Home. Your Nutrition Partner. Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit
 Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
Giving Yourself an Emergency Injection Using Solu-Cortef Act-O-Vial 1/8
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Giving Yourself an Emergency Injection Using Solu-Cortef Act- O-Vial This information explains how to g ive yourself an emerg ency injection (shot) of Solu-Cortef About Cortisol.
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Giving Yourself an Emergency Injection Using Solu-Cortef Act- O-Vial This information explains how to g ive yourself an emerg ency injection (shot) of Solu-Cortef About Cortisol.
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
After Your Bariatric Surgery
 After Your Bariatric Surgery Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment who to
After Your Bariatric Surgery Information for patients and families Read this information to learn: what problems to look out for how to care for yourself at home about your follow-up appointment who to
What is a catheter? What do I need to learn about catheter care?
 Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar )
 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Urinary Catheter Care
 Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Nephrostomy Tube Care
 Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Help Your Body Heal. Clinic Visits. After weight loss surgery
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Follow-up After weight loss surgery This section of the Guide to Your Weight Loss Surgery explains clinic visits and medical and other concerns in the weeks after surgery.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Follow-up After weight loss surgery This section of the Guide to Your Weight Loss Surgery explains clinic visits and medical and other concerns in the weeks after surgery.
Changing Your Two-Piece Disposable Urostomy Appliance
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Changing Your Two-Piece Disposable Urostomy Appliance This information will help you care for your 2-piece disposable urostomy appliance. Changing Your Appliance You will
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Changing Your Two-Piece Disposable Urostomy Appliance This information will help you care for your 2-piece disposable urostomy appliance. Changing Your Appliance You will
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica )
 Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Early Stage Oral Cavity Cancer
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Early Stage Oral Cavity Cancer This information will help you understand early stag e cancer of the oral cavity (mouth), including symptoms, diag nosis, and treatment. About
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Early Stage Oral Cavity Cancer This information will help you understand early stag e cancer of the oral cavity (mouth), including symptoms, diag nosis, and treatment. About
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib )
 Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System
 HOME TUBE FEEDING Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System Name: Dietitian: Telephone: Nurse: Telephone: Doctor: Telephone: Date: Prepared and Revised
HOME TUBE FEEDING Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System Name: Dietitian: Telephone: Nurse: Telephone: Doctor: Telephone: Date: Prepared and Revised
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
Exercises After Breast Surgery
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Exercises After Breast Surgery This information describes how to do arm and shoulder exercises, a breathing exercise, and scar massag e after your breast surg ery. Starting
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Exercises After Breast Surgery This information describes how to do arm and shoulder exercises, a breathing exercise, and scar massag e after your breast surg ery. Starting
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~
 TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
About Implanted Ports
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Implanted Port This information will teach you about the placement and care of your implanted port. An implanted port is a type of central venous catheter (CVC).
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Implanted Port This information will teach you about the placement and care of your implanted port. An implanted port is a type of central venous catheter (CVC).
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Series
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Series This information will help you g et ready for your upper g astrointestinal (GI) series at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). About Your GI
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Series This information will help you g et ready for your upper g astrointestinal (GI) series at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). About Your GI
Lower Anterior Resection (LAR) with Ileostomy
 Lower Anterior Resection (LAR) with Ileostomy Information for patients and families UHN Read this information to learn: what an LAR with ileostomy is how to care for yourself when you get home what problems
Lower Anterior Resection (LAR) with Ileostomy Information for patients and families UHN Read this information to learn: what an LAR with ileostomy is how to care for yourself when you get home what problems
Steps for Giving an Enema
 Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Table of Contents. Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings
 Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
Table of Contents Dialysis Port Care Chemotherapy Port Care G-Tube Care Colostomy Bags Wound Dressings Dialysis Port Care Know What Type of Vascular Access You Have. Fistula: An artery in your forearm
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
It is used to prevent or treat soft, brittle bones (osteoporosis). It may be g iven to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Alendronate Brand Names: US Binosto; Fosamax Brand Names: Canada Fosamax What is this drug used for? It is used to prevent or treat soft, brittle bones (osteoporosis). It
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Alendronate Brand Names: US Binosto; Fosamax Brand Names: Canada Fosamax What is this drug used for? It is used to prevent or treat soft, brittle bones (osteoporosis). It
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib )
 Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Sorafenib (Nexavar ) ( sor-af-e-nib ) How the drug is given: by mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer, liver cancer, and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth Take on
Discharge Instructions for Duodenal Switch and Distal Gastric Bypass Surgeries
 Col Columbia University Center for Metabolic and Weight Loss Surgery Columbia University Medical Center The Herbert Irving Pavilion 161 Fort Washington Ave, 5 th floor, Room 524 New York, New York 10032
Col Columbia University Center for Metabolic and Weight Loss Surgery Columbia University Medical Center The Herbert Irving Pavilion 161 Fort Washington Ave, 5 th floor, Room 524 New York, New York 10032
Gastric Bypass, Banded Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy Surgery Discharge Instructions
 Columbia University Center for Metabolic and Weight Loss Surgery Columbia University Medical Center The Herbert Irving Pavilion 161 Fort Washington Ave, 5 th floor, Room 524 New York, New York 10032 Health
Columbia University Center for Metabolic and Weight Loss Surgery Columbia University Medical Center The Herbert Irving Pavilion 161 Fort Washington Ave, 5 th floor, Room 524 New York, New York 10032 Health
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery
 Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal tube
 Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
Bowel Resection Surgery (Open Method)
 Bowel Resection Surgery (Open Method) What is a bowel resection? A bowel resection is surgery to remove a part of the large or small intestine. These parts are shown on this diagram. small intestine large
Bowel Resection Surgery (Open Method) What is a bowel resection? A bowel resection is surgery to remove a part of the large or small intestine. These parts are shown on this diagram. small intestine large
MICAFUNGIN MIXING
 1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
It is used to lower blood sugar in patients with high blood sugar (diabetes). What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Semaglutide Brand Names: US Ozempic Brand Names: Canada Ozempic Warning This drug has been shown to cause thyroid cancer in some animals. It is not known if this happens in
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Semaglutide Brand Names: US Ozempic Brand Names: Canada Ozempic Warning This drug has been shown to cause thyroid cancer in some animals. It is not known if this happens in
Apical Bullectomy Surgery
 Apical Bullectomy Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: how to prepare for your surgery what to expect while in hospital what to expect after you return home who
Apical Bullectomy Surgery UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: how to prepare for your surgery what to expect while in hospital what to expect after you return home who
Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit.
 Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit. You are about to undergo a major operation. The healing process takes time and we would like for you to observe the following
Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit. You are about to undergo a major operation. The healing process takes time and we would like for you to observe the following
Using a leg bag. drainage tube. leg bag. spout
 Using a leg bag A leg bag collects the urine that drains from your catheter. It can be worn under clothes where no one else can see it. A leg bag attaches to your thigh or calf so you can move around while
Using a leg bag A leg bag collects the urine that drains from your catheter. It can be worn under clothes where no one else can see it. A leg bag attaches to your thigh or calf so you can move around while
Frequently Asked Questions About Ommaya Reservoirs and Ommaya Taps for Pediatric
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Frequently Asked Questions About Ommaya Reservoirs and Ommaya Taps for Pediatric Patients This information answers some commonly asked questions about Ommaya reservoirs and
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Frequently Asked Questions About Ommaya Reservoirs and Ommaya Taps for Pediatric Patients This information answers some commonly asked questions about Ommaya reservoirs and
Appendix Surgery. (Appendectomy) Your surgery and recovery at home. This booklet belongs to: Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital
 Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
Appendix Surgery (Appendectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. PCV Treatment Chemotherapy for brain tumors DRAFT. PCV is a type of chemotherapy (chemo) treatment for brain
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION PCV Treatment for brain tumors This handout explains PCV treatment for brain tumors. It includes how to take each of the drugs and how to handle common side effects. What
You can only get this drug through the Natpara REMS Program.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Parathyroid Hormone Brand Names: US Natpara Warning This drug has been shown to raise the chance of bone tumors in lab animals. It is not known if there is a higher chance
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Parathyroid Hormone Brand Names: US Natpara Warning This drug has been shown to raise the chance of bone tumors in lab animals. It is not known if there is a higher chance
DEPARTMENT NAME GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT
 GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
GASTROSTOMY CARE AND MANAGEMENT Texas Children s Hospital Advanced Practice Provider Conference Pediatric Surgery April 4 th, 2019 Madison Fitzgerald PA-C, Celia Flores PA-C OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the
SAMPLE. Check your child s skin with each pouch change. Size the stoma and cut the barrier to fit the stoma.
 Problem Solving Irritated and Red Skin The skin around your child s stoma can become irritated and red. This is the most common problem for new ostomy patients. It is most often due to stool or urine on
Problem Solving Irritated and Red Skin The skin around your child s stoma can become irritated and red. This is the most common problem for new ostomy patients. It is most often due to stool or urine on
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~
 Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Orthotopic Bladder Reconstruction Surgery ~ Neobladder Surgery ~ Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Small bowel An organ in the body that
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation Side effects are problems caused by radiation therapy. These problems are different for each person and
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation Side effects are problems caused by radiation therapy. These problems are different for each person and
Emergency Care for Patients of The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Emergency Care for Patients of The James Emergency Care During and After Treatment Here are guidelines about when and how to report problems that you may have
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Information about Feeding Tubes
 Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Exercises After Your Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Exercises After Your Axillary Lymph Node Dissection This information describes how to do exercises to help you reg ain your rang e of motion after your axillary lymph node
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Exercises After Your Axillary Lymph Node Dissection This information describes how to do exercises to help you reg ain your rang e of motion after your axillary lymph node
Preparing for your Laparoscopic Myotomy
 Preparing for your Laparoscopic Myotomy Pre and post-operative information Department of Table of Contents: What is a Laparoscopic Myotomy...3 Planning for surgery...3 Preparing for surgery/bowel prep.4
Preparing for your Laparoscopic Myotomy Pre and post-operative information Department of Table of Contents: What is a Laparoscopic Myotomy...3 Planning for surgery...3 Preparing for surgery/bowel prep.4
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters
 Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Orbital Fractures UHN. For patients going home after surgery
 Orbital Fractures UHN For patients going home after surgery Read this resource to learn about: How to care for your wound How to cope with pain What to do in case of emergency Do not drive a car or drink
Orbital Fractures UHN For patients going home after surgery Read this resource to learn about: How to care for your wound How to cope with pain What to do in case of emergency Do not drive a car or drink
It may be g iven to your child for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Gabapentin Brand Names: US Gralise; Gralise Starter; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada Neurontin What is this drug used for? It is used to treat seizures. It may be g iven to
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Gabapentin Brand Names: US Gralise; Gralise Starter; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada Neurontin What is this drug used for? It is used to treat seizures. It may be g iven to
Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level
 If you have multiple myeloma and have already tried at least 2 other types of treatment Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level What is
If you have multiple myeloma and have already tried at least 2 other types of treatment Open to the possibility of a multiple myeloma treatment that works in cells in your body at the DNA level What is
PATIENT INFORMATION What is VITRAKVI? and and
 PATIENT INFORMATION VITRAKVI (vi trak vee) (larotrectinib) capsules and oral solution What is VITRAKVI? VITRAKVI is a prescription medicine that is used to treat adults and children with solid tumors (cancer)
PATIENT INFORMATION VITRAKVI (vi trak vee) (larotrectinib) capsules and oral solution What is VITRAKVI? VITRAKVI is a prescription medicine that is used to treat adults and children with solid tumors (cancer)
What are some things I need to know or do while I take
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Cyclophosphamide Brand Names: Canada Procytox What is this drug used for? It is used to treat cancer. It is used to treat nephrotic syndrome. It may be g iven to you for other
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Cyclophosphamide Brand Names: Canada Procytox What is this drug used for? It is used to treat cancer. It is used to treat nephrotic syndrome. It may be g iven to you for other
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ADMINISTRATION OF A FEEDING (CONTINUOUS OR INTERMITTENT) OR MEDICATION VIA A GASTROSTOMY TUBE-ADULT Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 07/82
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ADMINISTRATION OF A FEEDING (CONTINUOUS OR INTERMITTENT) OR MEDICATION VIA A GASTROSTOMY TUBE-ADULT Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 07/82
Acetylcysteine Injection; Acetylcysteine Solution; Mucomyst; Parvolex. It is used to thin mucus so it can be taken from the body by coughing.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Acetylcysteine Brand Names: US Acetadote; Cetylev Brand Names: Canada Acetylcysteine Injection; Acetylcysteine Solution; Mucomyst; Parvolex What is this drug used for? It
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Acetylcysteine Brand Names: US Acetadote; Cetylev Brand Names: Canada Acetylcysteine Injection; Acetylcysteine Solution; Mucomyst; Parvolex What is this drug used for? It
Esophagectomy Surgery
 Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
The Johns Hopkins Hospital Patient Information Home Instructions After REVERSE Total Shoulder Replacement Surgery
 Shoulder Replacement Edward G. McFarland, M.D. Johns Hopkins Division of Shoulder Department of Orthopaedic 10753 Falls Road/Suite 215 Lutherville, MD 21093 The following instructions are a guide for the
Shoulder Replacement Edward G. McFarland, M.D. Johns Hopkins Division of Shoulder Department of Orthopaedic 10753 Falls Road/Suite 215 Lutherville, MD 21093 The following instructions are a guide for the
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION. Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID
 STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID This handy guide will help you manage your subcutaneous administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID. If you have questions on
STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO SELF-INFUSION Subcutaneous Administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID This handy guide will help you manage your subcutaneous administration of GAMMAGARD LIQUID. If you have questions on
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Women 1986 2016 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon, Noah Fallis,
Managing your Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) with tube feeds
 Managing your Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) with tube feeds (Enteral nutrition) This is Nicholas. During this part of his treatment for IBD, he gets all his daily nutrition with tube feeds. Your health
Managing your Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) with tube feeds (Enteral nutrition) This is Nicholas. During this part of his treatment for IBD, he gets all his daily nutrition with tube feeds. Your health
Eltrombopag (Promacta )
 Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Eltrombopag (Promacta ) ( el TROM boe pag ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to treat aplastic anemia and increase low platelet counts in some conditions How to take this drug 1. Take this medication
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment
 Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
Managing bowel problems after cancer treatment Information for cancer survivors Read this pamphlet to learn: What bowel problems are What causes bowel problems What you can do to manage your bowel problems
Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE. Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage. Physician Contact Information. Dr. Phone:
 Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage Physician Contact Information Dr. Phone: CHEST DRAINAGE Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter Valve Connector
Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage Physician Contact Information Dr. Phone: CHEST DRAINAGE Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter Valve Connector
Gallbladder Surgery. (Cholecystectomy) Your surgery and recovery at home. This booklet belongs to: Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital
 Gallbladder Surgery (Cholecystectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read
Gallbladder Surgery (Cholecystectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Eagle Ridge Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA
 For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
It is used to treat or prevent upset stomach and throwing up. What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug?
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ondansetron Brand Names: US Zofran; Zofran ODT [DSC]; Zuplenz Brand Names: Canada Ondissolve ODF; Zofran ODT What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent upset
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Ondansetron Brand Names: US Zofran; Zofran ODT [DSC]; Zuplenz Brand Names: Canada Ondissolve ODF; Zofran ODT What is this drug used for? It is used to treat or prevent upset
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Men and Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
About Your Surgery to Treat Bile Duct Tumors
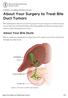 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Surgery to Treat Bile Duct Tumors This information will tell you how to prepare for your surg ery to remove tumors in your bile duct at Memorial Sloan Kettering
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Surgery to Treat Bile Duct Tumors This information will tell you how to prepare for your surg ery to remove tumors in your bile duct at Memorial Sloan Kettering
Royal Columbian Hospital. We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets carefully.
 Adrenal Surgery (Adrenalectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets carefully. Bring
Adrenal Surgery (Adrenalectomy) Royal Columbian Hospital Your surgery and recovery at home This booklet belongs to: We also give you Preparing for Your Surgery booklet. Read both booklets carefully. Bring
Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop.
 Dexamethasone Other Names: Decadron About This Drug Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Increased
Dexamethasone Other Names: Decadron About This Drug Dexamethasone is used to treat cancer. This drug can be given in the vein (IV), by mouth, or as an eye drop. Possible Side Effects (More Common) Increased
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients
 Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
