Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System
|
|
|
- Bryan Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HOME TUBE FEEDING Home Tube Feeding Guide for Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Open Tube Feeding System Name: Dietitian: Telephone: Nurse: Telephone: Doctor: Telephone: Date:
2 Prepared and Revised by: Carmela Maloney, dietitian, 2011 Acknowledgements for contributors: MNH ALS Interdisciplinary Team Pamela Bager, speech language pathologist Lois Finch, physiotherapist Max Folkersma, physiotherapist Agi Fried, medical secretary Angela Genge, neurologist Sarog Gupta, social worker Philip Joudrey, chaplain Josée Lemoignon, occupational therapist Sharron Runions, nurse MNH-3 South nurses Clinical Dietetics Services Beth Armour, dietitian Donna Haddad, dietitian Sonia Miele, dietitian Illustrations by: Layout & Typesetting by: Funded by: French Translation by: Produced by: Timothy Maloney Neurophotography Friends of the Neuro and The Neuro-Patient Resource Centre McGill Translation Services The Neuro-Patient Resource Centre Cette brochure est aussi disponible en francais.
3 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION p.1 2. TUBE FEEDING PRESCRIBED FOR YOU p.2 a) Type of Tube Feeding b) Tube Feeding Formula c) Your Nutritional Requirements d) Method of Delivering Tube Feeding & Tube Feeding Protocol e) Equipment Needed 3. ADMINISTERING TUBE FEEDING p.4 a) Position of Body b) Verifying Gastric Residuals c) Starting Tube Feeding d) Stopping Tube Feeding 4. INFECTION CONTROL CONSIDERATIONS p.8 5. GIVING MEDICATIONS p.9 6. PERSONAL CARE TIPS p.9 7. PROBLEM SOLVING p.10 a) Feeling Sick (Nausea) b) Dry Mouth or Feeling Thirsty c) Constipation d) Diarrhea e) Clogged Feeding Tube
4 1. INTRODUCTION Good nutrition is important for overall health and well-being. For individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), maintaining adequate nutrient and fluid intake is a constant struggle when faced with increasing swallowing difficulties, fatigue, weakness, breathing problems and lack of appetite. Tube feeding thus provides a practical option for those individuals who are unable to meet their nutritional needs by mouth or unable to swallow safely. With a tube feeding, the source of food is in a liquid form. When given in the right amounts, tube feeding formulas provide all the nutrients found in a well-balanced diet. There are many individuals with ALS who are at home with their tube feedings and who maintain their lifestyles such as travelling, shopping, and participating in family activities. This booklet was prepared to help you manage your tube feeding at home. Your dietitian, nurse and doctor will assist you and your family in learning this feeding method. They will teach you how to prepare and administer your tube feeding, what equipment you need, infection control procedures, how to give your medications, how to prevent problems and what to do if problems should occur. Your tube feeding guide has been designed to meet your nutritional needs and lifestyle. Keep it close at hand and check it regularly. If you have any questions or would like more information, please contact your dietitian, nurse or doctor. The telephone numbers are on the front cover of this booklet
5 2. TUBE FEEDING PRESCRIBED FOR YOU a) Type of Tube Feeding: Your type of feeding is called a Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy or PEG tube feeding. This simply means that a feeding tube was placed directly into your stomach through the abdominal wall, to the outside of the body under the visual guidance of an endoscope (a lighted camera). Your tube extends cm from the skin with a cap on the end of it. To keep the tube in place, a bolster is placed near the skin surrounding your stoma (the opening to the stomach from the outside skin). Your nurse should mark your PEG tube exactly at the tube entry site with a non-toxic permanent marker. Any changes from this position will indicate that your PEG tube has moved. If so, do not start the feeding. Notify your nurse or doctor. Brand Name Size Date Inserted b) Type of Tube Feeding Formula: Jevity 1-2/Isosource 1.5 Nutren 2.0/Resource 2.0 Glucerna/ Diabetic Resource from Peptamen 1.2/Peptamen 1.5 Other: from If you need to make a substitution, check with your dietitian first as formulas vary in nutrient content. The above formulas can be purchased from your local pharmacy. Contact your pharmacist to make arrangements or for home delivery services: Dufort & Lavigne: (514) or Calea: (514) or Stoma Medical (450) c) Your Nutritional Requirements: calories per day. grams of protein per day. ml of water per day
6 d) Method of Delivering Tube Feeding & Tube Feeding Protocol: Intermittent: You need to deliver ml of formula within minutes, times per day. Schedule:,,,,,. You need to flush your feeding tube with ml of water after each feeding to prevent it from plugging. Continuous: You need to deliver ml per hour of formula from to for a total of hours. You need to flush your feeding tube with ml of water after each feeding to prevent it from plugging. Pump: You need to set your pump at ml per hour. Gravity Drip: You need to deliver your formula by gravity. Flush ml of water per day or ml 3 X per day. e) Equipment needed: pump to set rate of feeding. pole or for hanging tube feeding bag. administration set (feeding bag and tubing) syringe (60 ml or 2 oz catheter tip syringe) If covered by OPHQ, all equipment needed will be provided free of charge. Otherwise, the above may be purchased or rented from Dufort & Lavigne or Caremark or Stoma Medical. Refer to Tube Feeding Formula section for telephone numbers. Replacement of a PEG tube, cap or adapter can be obtained from GI department at the RVH. Tel: (514)
7 a) Position of Body: 3. ADMINISTERING TUBE FEEDING You can walk, sit upright in a chair or sit propped up in a bed while receiving your tube feeding. If lying down, make sure your head is elevated at an angle of at least 45 degrees from the bed. Stay in the above acceptable positions during and up to 30 to 60 minutes after your tube feeding is finished. DO NOT LIE FLAT UNTIL THEN. This will reduce the risk of aspiration (accidental entry of formula into the lungs). b) Verifying Gastric Residuals: (Only if asked for by the ALS Interdisciplinary team) 1. You will need to check the gastric residuals (presence of stomach contents) prior to each feeding. To do this, attach the syringe to the end of your gastrostomy tube (not the tubing on your feeding bag). 2. With the syringe in place, slowly pull back on the plunger until you meet resistance. This will cause the stomach contents to enter the syringe. 3. Note how much stomach contents or residuals can be withdrawn, then slowly push it back. Flush with 30 ml water. Any or all gastric residuals must be returned to the stomach. If the stomach is empty, nothing will be withdrawn. If the amount of residuals is greater than ml, wait 30 to 60 minutes. Recheck every hour. If it continues to be high, do not attempt the feeding and report the problem to your doctor, nurse or dietitian. N.B.: If you have just recently eaten by mouth, wait at least 30 minutes before checking for gastric residuals
8 c) Starting Tube Feeding: 1. Close the clamp on your feeding tube. 2. Pour ml of your formula into the feeding bag. 3. Hang the feeding bag on a pole or that is higher than your head. 4. Hold the end of your feeding tube to prevent spills. 5. Open the clamp. 6. Allow the formula to reach the end of your feeding tube to get rid of any air in the tube
9 7. Close the clamp. If you are using a pump, you now attach the feeding tube to the built-in receptacle on your pump. 8. Clamp or kink (if clamp is not available) your gastrostomy tube near the tip. 9. Open the cap on your gastrostomy tube and connect to the end of the feeding tube. 10. If you are using a pump, set the pump at ml per hour. Unclamp or unkink your gastrostomy tube and open the clamp of your feeding tube. Start the pump. If you are not using a pump, unclamp or unkink your gastros to my tube and slowly open the clamp on the feeding tube. If the feeding is too slow, open the clamp of the feeding tube more. If the feeding is too fast, close the clamp more
10 d) Stopping Tube Feeding: 1. When the formula in your feeding bag is finished, close the clamp of your feeding tube or stop the pump if applicable. 2. Disconnect the feeding tube from thegastrostomy tube. 3. Flush ml of water into your gastrostomy tube with a syringe. 4. Put the cap back on your gastrostomy tube. 5. Refer to your Tube Feeding Protocol to see if extra water is needed. 6. If you are refilling the feeding bag for continuous tube feeding, flush the gastrostomy tube with ml of water using a syringe. The feeding bag may be rinsed with warm water and then drained prior to refilling with the formula. See detailed instructions for cleaning under Infection Control Considerations section
11 4. INFECTION CONTROL CONSIDERATIONS Before you prepare your tube feeding, wash your hands with soap and water to reduce risk of infection. Use only clean equipment and administration set (tubing with feeding bag). Follow the manufacturer s instructions on how often it needs to be changed. Usually every 24 hours. If reusing the feeding bag with tubing, rinse with warm water and dish soap 3 times a day. Use a clean bottle brush to scrub inside the bag. Rinse again with warm water. Once a day, mix 60 ml (1/4 cup) of vinegar with 250 ml (1 cup) of water. Pour this vinegar and water mixture into the feeding bag and tubing. Sit the bag in the clean sink for 10 minutes. Empty bag out. Rinse the feeding bag and tubing again with cool water. Be sure to completely rinse it well. Keep your cleaned feeding bag and tubing in the refrigerator until used again. The syringe should be cleaned the same way. Discard the feeding bag with tubing if formula begins to adhere to the tubing and does not rinse clean or if any leaks should develop. Use only fresh formulas at every feeding time. Check the date of expiration prior to opening new formulas. For continuous tube feeding, hang fresh formula every 4 hours. Do not let formula hang longer than 4 hours at a time at room temperature especially during warm, humid weather as these are ideal conditions for bacteria to grow. Cover unused open formulas and refrigerate. Discard unused open formulas after 24 hours. PEG tube may need to be changed every 6 months to 1 year. Consult your doctor
12 5. GIVING MEDICATIONS Medications may be given through the gastrostomy tube if the doctor allows. Ask the doctor to order prescriptions in liquid form, if possible. You cannot crush just any medication. Consult your pharmacist about any possible interactions when taken in crushed form. Do not mix medications. Give separately. 1. If solid medication must be used, crush and dissolve the prescribed amount in 30-50ml of warm water in a small cup. If in liquid form, pour the prescribed amount of liquid into a small cup or dilute first with water if too viscous. 2. Open the cap of your gastrostomy tube. Flush with 30 ml of water. 3. Draw up the medication with a syringe. 4. Inject the medication into the gastrostomy tube. 5. Flush tube with ml of warm water and replace the cap. 6. Stay upright or at an angle of at least 30 degree from the bed for 30 minutes after administering the medication. If you are having trouble dissolving your medications, contact your nurse. 6. PERSONAL CARE TIPS WEIGHT Monitor your weight weekly, if possible. If you notice any weight change, please contact your clinical dietitian. Your tube feeding can be adjusted if needed. MOUTH CARE If possible, to keep your mouth clean, rinse 3 X a day. Use 5 ml (1 tsp) of baking soda in 500 ml (2 cups) of warm water to rinse. Clean your teeth carefully. An electric toothbrush, spongetipped toothettes and dental floss can be useful. You may also have your teeth cleaned by a dental hygienist. SKIN CARE AROUND STOMA Daily, using mild soap and warm water, gently clean and dry area around the gastrostomy tube as you bathe or shower. Always check for signs of redness, pain or soreness, or unusual leaking around the stoma. Report any signs of these symptoms to your nurse or doctor
13 A) FEELING SICK (NAUSEA) 7. PROBLEM SOLVING Take your feeding more slowly. Adjust the clamp or reduce your tube feeding rate to ml/hour. Sit up during your feeding. Do not lie down during and up to 60 minutes after your feeding is finished. Walk if you can after your feeding has finished. Carefully open the cap on your tube to let gas out of your stomach. Protect your clothing as stomach contents may come out as well. B) DRY MOUTH OR FEELING THIRSTY Always follow your schedule for water. If you are still thirsty or have a dry mouth, call your dietitian to reevaluate your water requirement. For immediate relief, swab your mouth with moistened sponge-tipped toothettes. C) CONSTIPATION Flush ml more water into your gastrostomy tube after feedings. Add ml of prune juice into your gastrostomy tube times a day. Rinse your tube well with 30 ml of water after the prune juice. Ask your dietitian for a formula containing fiber if you are not already on it. If the problem persists, you may need to ask your doctor to prescribe bulk-forming agents, stool softener or laxative
14 D) DIARRHEA Always use formula that is at room temperature. Always use clean equipment. Take your feedings more slowly. Adjust the clamp or reduce your tube feeding rate to ml/hour. Increase the amount of water taken to ml with each feeding. Add 30 ml of liquid pectin into your gastrostomy tube times per day: Mix pectin well in a small cup with ml warm water. Draw up the pectin solution with a syringe and inject into the tube. Flush with at least 30 ml warm water. Check your temperature. If your temperature is above normal value, inform your nurse or doctor. E) CLOGGED FEEDING TUBE If completely blocked: DO NOT attempt to unblock with liquids or insert any foreign object into tube. Contact your doctor. If partially clogged: Flush your feeding tube with 60 ml of warm water. Then aspirate by pulling back on the plunger. Repeat several times. If it continues to be partially blocked,contact your doctor or nurse. A pancreatic enzyme may be prescribed. To prevent a clogged feeding tube: Do not mix your medications together. Take each one separately. Do not mix medications with formula. Rinse your feeding tube with at least 30 ml of warm water before and after your medications. Make sure you always flush your feeding tube with the amount of water prescribed in your guide every 4 hours with continuous feedings and before and after intermittent feedings. Flush feeding tube after checking residuals. Flush feeding tube after any beverages taken N.B.: If you are experiencing vomiting, unusual distention in the abdomen area, severe cramps, or significant weight change, contact your doctor
15 Notes
16 HOME TUBE FEEDING
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults. Clinical Nutrition Services
 Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Tube Feed Management at Home for Adults Clinical Nutrition Services CEAC 0078 April 2017 Table of Contents To Obtain Tube Feeding Formula...2 To Obtain Tube Feeding Supplies... 3 Tube Feeding....4 Types
Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the gravity method to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous
Tube Feeding With a Pump
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATON Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will help teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications through your percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy
Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version)
 The Patient was given access to the following documents on Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version) Before you leave the hospital,
The Patient was given access to the following documents on Your Home Tube Feeding: PEG Tubes, G Tubes, and J Tubes (TJUH) General Information, English (SaveNote version) Before you leave the hospital,
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding
 Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Gastrostomy Tube Feeding A gastrostomy tube (g-tube) is a tube that enters through your abdomen and rests in your stomach. This tube is used for tube feeding formula, water, and medicine (instead of taking
Enteral Nutrition. Introduction. Brooks Health Care, Inc. Patient Instruction 1
 Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
Introduction Receiving Nutrition through a feeding tube will take some time to get used to, but it s important to remember that you can still enjoy many of the things you ve always enjoyed. With time and
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal tube
 Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
Tube feeding with a nasogastric or nasojejunal This factsheet tells you how to care for your feeding and how to take your feed and medications via your. Your dietitian needs to fill in parts of this factsheet.
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS
 YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
YOUR HOME ENTERAL NUTRITION SURVIVAL GUIDE FOR JEJUNOSTOMY FEEDINGS INTRODUCTION: Your health care team may prescribe a program of home Enteral nutrition (or home tube feeding) designed to meet your nutritional
Tube Feeding at Home. Your Nutrition Partner. Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit
 Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
Your Nutrition Partner Use under medical supervision. For more information on Abbott Products, visit www.abbottnutrition.com. Tube Feeding at Home 2013 Abbott Laboratories LITHO IN USA 60715-017/March
Tube Feeding At Home. A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers
 A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
A Guidebook for Patients, Families & Caregivers Tube Feeding at Home This guidebook is for Date RD 2 Table of Contents What is Tube Feeding?... 4 Your Feeding Tube... 4 Checking and Maintaining Your Feeding
Nasogastric Tube Patient Passport
 Nutrition and Dietetics Department Nasogastric Tube Patient Passport Please bring this booklet with you for all tube changes Patient Information If you need this information in another format or language
Nutrition and Dietetics Department Nasogastric Tube Patient Passport Please bring this booklet with you for all tube changes Patient Information If you need this information in another format or language
Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method This information will help teach you how to use the bolus method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Bolus Method This information will help teach you how to use the bolus method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the g ravity method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding Using the Gravity Method This information will help teach you how to use the g ravity method to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your percutaneous
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY
 Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Grey Bruce Health Network EVIDENCE-BASED CARE PROGRAM PATIENT EDUCATION BOOKLET TURP (TRANS URETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE) PATHWAY Introduction: Prostate or bladder surgery requires special care.
Freka Balloon Gastrostomy Feeding. CARE GUIDELINES For Patients & Carers
 Freka Balloon Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES For Patients & Carers Useful Contacts GP Hospital Dietitian Community Dietitian Nutrition Nurse District Nurse Nutrition Feed Company/Nurse Advisor Hospital
Freka Balloon Gastrostomy Feeding CARE GUIDELINES For Patients & Carers Useful Contacts GP Hospital Dietitian Community Dietitian Nutrition Nurse District Nurse Nutrition Feed Company/Nurse Advisor Hospital
Information about Feeding Tubes
 Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Information about Feeding Tubes By Theresa Imperato, RN and Lorraine Danowski, RD What is a feeding tube? It is a small, flexible tube, about ¼ in diameter that is an alternative route for nourishment
Midostaurin (Rydapt )
 Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Midostaurin (Rydapt ) ( mye doe STAW rin ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and other cancers. How to take this drug 1. Take this
Tube Feeding With a Pump
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your feeding tube. This includes percutaneous
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Tube Feeding With a Pump This information will teach you how to use a pump to feed yourself and take your medications throug h your feeding tube. This includes percutaneous
Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Drainage Gastrostomy Tube This information will help you care for your drainag e g astrostomy tube (g-tube). About Your Drainage G-Tube A drainage g-tube is
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide This guide provides detailed instruction on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of Veletri (epoprostenol) for Injection. It is intended to be used after your healthcare
A step-by-step preparation guide This guide provides detailed instruction on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of Veletri (epoprostenol) for Injection. It is intended to be used after your healthcare
Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE. Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage. Physician Contact Information. Dr. Phone:
 Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage Physician Contact Information Dr. Phone: CHEST DRAINAGE Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter Valve Connector
Drainage Frequency: PATIENT GUIDE Dressing Frequency: Every Drainage Weekly Drainage Physician Contact Information Dr. Phone: CHEST DRAINAGE Pleural Space Insertion Site Cuff Exit Site Catheter Valve Connector
Gastrostomy Tube Management
 Gastrostomy Tube Management Information for School Nurse Services and School Health Services Disclaimer: The information in this pamphlet is for information purposes only. Please follow individual school
Gastrostomy Tube Management Information for School Nurse Services and School Health Services Disclaimer: The information in this pamphlet is for information purposes only. Please follow individual school
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Peritoneal Dialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. There are 2 types of PD: continuous ambulatory
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib )
 Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Lenvatinib (Lenvima ) ( len-va-ti-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To treat thyroid cancer or other cancers How to take this drug This medicine can be taken with or without food. Take each dose
Having a PEG tube inserted
 Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Having a PEG tube inserted This information leaflet is for patients who are having a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube inserted. It explains what is involved, what to expect and what significant
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib )
 Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
Imatinib (Gleevec ) ( eye-mat-eh-nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: stops growth of cancer cells in leukemia, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST), and other cancers How to take the drug by mouth
MICAFUNGIN MIXING
 1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
1 1-800-862-2731 MICAFUNGIN MIXING Drug Name: MICAFUNGIN Volume and Rate: over 1 hour Schedule: KEY POINTS: FLUSHING: Saline Micafungin Saline Heparin 1. Always wash your hands with an antibacterial soap
Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation Side effects are problems caused by radiation therapy. These problems are different for each person and
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Short-Term Side Effects from Head and Neck Radiation Side effects are problems caused by radiation therapy. These problems are different for each person and
PATIENT INFORMATION What is VITRAKVI? and and
 PATIENT INFORMATION VITRAKVI (vi trak vee) (larotrectinib) capsules and oral solution What is VITRAKVI? VITRAKVI is a prescription medicine that is used to treat adults and children with solid tumors (cancer)
PATIENT INFORMATION VITRAKVI (vi trak vee) (larotrectinib) capsules and oral solution What is VITRAKVI? VITRAKVI is a prescription medicine that is used to treat adults and children with solid tumors (cancer)
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ADMINISTRATION OF A FEEDING (CONTINUOUS OR INTERMITTENT) OR MEDICATION VIA A GASTROSTOMY TUBE-ADULT Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 07/82
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: ADMINISTRATION OF A FEEDING (CONTINUOUS OR INTERMITTENT) OR MEDICATION VIA A GASTROSTOMY TUBE-ADULT Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 07/82
My patient has a feeding tube
 My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG tube) Naso jejunal
My patient has a feeding tube What does that mean? Martha Kliebenstein, MSN, RN Clinical Educator Types of tubes Gastrostomy (G-tube) Gastrostomy jejunostomy (G-J tube) Naso gastric (NG tube) Naso jejunal
UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO HOSPITAL
 UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO HOSPITAL Information for Patients and their Families RADIATION ONCOLOGY INSTRUCTIONS DURING HEAD & NECK RADIOTHERAPY Skin Care Radiation treatments to the neck can make the treated
UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO HOSPITAL Information for Patients and their Families RADIATION ONCOLOGY INSTRUCTIONS DURING HEAD & NECK RADIOTHERAPY Skin Care Radiation treatments to the neck can make the treated
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica )
 Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ) ( eye BROO ti nib ) How drug is given: by mouth Purpose: to stop the growth of cancer cells in lymphoma and other cancers How to take the drug Take each dose at the same time every
A practical guide to tube feeding
 A practical guide to tube feeding FOR ADULTS The aim of this guide is to provide information and easy-tofollow guidance on the day-to-day aspects of tube feeding, as well as handy tips from other people
A practical guide to tube feeding FOR ADULTS The aim of this guide is to provide information and easy-tofollow guidance on the day-to-day aspects of tube feeding, as well as handy tips from other people
Purcutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Purcutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) An information guide Purcutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) Introduction This booklet aims
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Purcutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) An information guide Purcutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) Introduction This booklet aims
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients
 Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
Urinary Catheter Passport for patients Nursing A guide for patients and visitors Contents Why people need a urinary catheter...1 How your bladder and kidneys work...1 What is a catheter?...3 Drainage bags...3
GASTRECTOMY. Date of Surgery. Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34
 GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
GASTRECTOMY Date of Surgery Please bring this booklet the day of your surgery. QHC#34 What is a Gastrectomy? A Gastrectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the stomach. The stomach is the digestion
What is a catheter? What do I need to learn about catheter care?
 Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Catheter care What is a catheter? A catheter is a tube that drains urine from your child s body. The catheter is connected to tubing and a bag to collect the urine. Catheters come in different sizes and
Date Issued Planned Review PGN No: Part of NTW(C)29 - Trust Standard for Assessment and Management of Physical Health Author/Designation
 Trust Standard for Assessment and Management of Physical Health Policy Practice Guidance Note Enteral Tube Care, Management and Feeding (Gastrostomy and Jejunostomy) V01 Date Issued Planned Review PGN
Trust Standard for Assessment and Management of Physical Health Policy Practice Guidance Note Enteral Tube Care, Management and Feeding (Gastrostomy and Jejunostomy) V01 Date Issued Planned Review PGN
To you who will receive a T-Port PATIENT INFORMATION
 To you who will receive a T-Port PATIENT INFORMATION T-Port Patient information What is a T-Port? Why this booklet The purpose of this handout is to help you understand how it is to receive and live with
To you who will receive a T-Port PATIENT INFORMATION T-Port Patient information What is a T-Port? Why this booklet The purpose of this handout is to help you understand how it is to receive and live with
How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN
 Page 1 of 10 How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN Important: Do not change any of the supplies listed here. Keep supplies away from children. Only your home care nurse or persons trained by Fairview Home
Page 1 of 10 How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN Important: Do not change any of the supplies listed here. Keep supplies away from children. Only your home care nurse or persons trained by Fairview Home
Nephrostomy Tube Care
 Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Nephrostomy Tube Care CEAC 0585 January 2012 Problems to report to the doctor If your nephrostomy tube falls out, call your urologist or go to a hospital Emergency Department immediately to have the tube
Rhino Clear Sprint Atomizer
 Visit us online to view our wide range of sinus therapy medications for use with the Rhino Clear Sprint atomizer. www.woodlandhillspharmacy.com 20631 Ventura Blvd, Ste 305 Woodland Hills, CA 91364 Phone:
Visit us online to view our wide range of sinus therapy medications for use with the Rhino Clear Sprint atomizer. www.woodlandhillspharmacy.com 20631 Ventura Blvd, Ste 305 Woodland Hills, CA 91364 Phone:
Steps for Giving an Enema
 Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Patient and Family Education Steps for Giving an Enema 1 of 6 Step 1: Gather supplies Fun activities for your child Enema bag 26 fr. Silicone Catheter with 30ml balloon 30ml syringe (slip tip) to inflate
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Peritoneal Dialysis. Choosing your logo. V2.0 logos. information. you can trust. Certified Member. The Information Standard
 Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name abiraterone acetate (A-bih-RA-the-rone A-seh-tayt) Brand name Zytiga (zye-tee-ga) Approved uses Abiraterone acetate is used in combination with prednisone to treat
Name of your medication Generic name abiraterone acetate (A-bih-RA-the-rone A-seh-tayt) Brand name Zytiga (zye-tee-ga) Approved uses Abiraterone acetate is used in combination with prednisone to treat
Urinary Catheter Care
 Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Nikki Hardness, DO Aashish Kabra, MD John Logan, MD Jeremy Weiss, DO Elizabeth Kelly McKnight, PA Phone: (303) 388-9321 What is a urinary catheter? Urinary Catheter Care A urinary catheter is a long, hollow,
Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass Information
 1441 Constitution Boulevard, Salinas, CA 93906 (831) 783-2556 www.natividad.com/weight-loss (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass) What is gastric bypass surgery? Gastric bypass surgery, a type of bariatric surgery
1441 Constitution Boulevard, Salinas, CA 93906 (831) 783-2556 www.natividad.com/weight-loss (Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass) What is gastric bypass surgery? Gastric bypass surgery, a type of bariatric surgery
Everolimus (Afinitor )
 Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Everolimus (Afinitor ) ( e-ver-oh-li-mus ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: to slow the growth of cancer cells in kidney cancer and other cancers How to take the drug Take with or without food and
Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit.
 Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit. You are about to undergo a major operation. The healing process takes time and we would like for you to observe the following
Expectations and Post Op Instructions: Robotic Cystectomy / Ileal Conduit. You are about to undergo a major operation. The healing process takes time and we would like for you to observe the following
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar )
 Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Dabrafenib (Tafinlar ) ( da-braf-e-nib ) How drug is given: By mouth Purpose: To stop the growth of cancer cells in melanoma and other cancers. How to take this drug Take this medication on an empty stomach
Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow IV Push
 Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow IV Push CEAC 0818 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow Intravenous Push Always record the time you administer your flushes and medication
Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow IV Push CEAC 0818 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Slow Intravenous Push Always record the time you administer your flushes and medication
How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery
 Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Form: D-3251 How to Care for a Foley Catheter After Surgery For patients going home from the Day Surgery Unit at Toronto Western Hospital Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of the Foley
Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump
 Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump CEAC 0820 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump You must change the tubing every day around the same time each day. Always
Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump CEAC 0820 February 2015 Administering Intravenous Medication By Syringe Pump You must change the tubing every day around the same time each day. Always
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name tamoxifen citrate (tuh-mok-sih-fen SIH-trayt) Brand name Soltamox (SOL-ta-mox) Approved uses Tamoxifen is used to treat certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer
Name of your medication Generic name tamoxifen citrate (tuh-mok-sih-fen SIH-trayt) Brand name Soltamox (SOL-ta-mox) Approved uses Tamoxifen is used to treat certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer
HOME TUBE FEEDING BASICS
 HOME TUBE FEEDING BASICS UBC DIETETICS PROGRAM Module 1 of 2 SCOPE OF THESE MODULES Modules 1 & 2 address the following Nutrition Care Process steps Intervention Monitoring and Evaluation Assessment and
HOME TUBE FEEDING BASICS UBC DIETETICS PROGRAM Module 1 of 2 SCOPE OF THESE MODULES Modules 1 & 2 address the following Nutrition Care Process steps Intervention Monitoring and Evaluation Assessment and
Produced by La Direction des communications du ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux
 Produced by La Direction des communications du ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux This document is available online and can be ordered at msss.gouv.qc.ca by clicking Documentation and then Publications.
Produced by La Direction des communications du ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux This document is available online and can be ordered at msss.gouv.qc.ca by clicking Documentation and then Publications.
For the Patient: CAP. Capecitabine. Uses:
 For the Patient: CAP Other names: BRAVCAP CAP Capecitabine Uses: BRAVCAP is an oral chemotherapy drug treatment plan, given as therapy for metastatic breast cancer, in the hope of destroying breast cancer
For the Patient: CAP Other names: BRAVCAP CAP Capecitabine Uses: BRAVCAP is an oral chemotherapy drug treatment plan, given as therapy for metastatic breast cancer, in the hope of destroying breast cancer
Enteral Nutrition (Continuing Care)
 Approved by: Enteral Nutrition (Continuing Care) Senior Operating Officer, Addiction & Mental Health and Continuing Care, Edmonton; and Senior Operating Officer, Rural Services Corporate Policy & Procedures
Approved by: Enteral Nutrition (Continuing Care) Senior Operating Officer, Addiction & Mental Health and Continuing Care, Edmonton; and Senior Operating Officer, Rural Services Corporate Policy & Procedures
IDPN. A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition. Toll Free: Toll Free:
 IDPN A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Executive Infusion is pleased to announce our nutritional services which include Intradialytic
IDPN A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Executive Infusion is pleased to announce our nutritional services which include Intradialytic
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
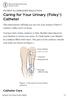 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
Medications. Managing and Administering Medication
 Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Medications Managing and Administering Medication The Medication Administration Checklist Administering medications is an important and vital responsibility. It is important to make sure that no errors
Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression
 Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression What is a Gastrostomy? A gastrostomy (g-tube) is a procedure that creates a small opening in your outer abdomen into the stomach. A thin tube is placed through this hole.
Gastrostomy Tube for Decompression What is a Gastrostomy? A gastrostomy (g-tube) is a procedure that creates a small opening in your outer abdomen into the stomach. A thin tube is placed through this hole.
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name letrozole (LEH-truh-zole) Brand name Femara (FEH-muh-ruh) Approved uses Letrozole is used in the treatment of certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal
Name of your medication Generic name letrozole (LEH-truh-zole) Brand name Femara (FEH-muh-ruh) Approved uses Letrozole is used in the treatment of certain types of hormone-dependent breast cancer in postmenopausal
For the Patient: Ponatinib Other names: ICLUSIG
 For the Patient: Other names: ICLUSIG (poe na' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose. Tell your doctor if you
For the Patient: Other names: ICLUSIG (poe na' ti nib) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. The tablet contains lactose. Tell your doctor if you
TUBES R US. Enteral Access & Management
 TUBES R US SHEILA BELL, MS, RN, CPNP PC Christine Gangi, RN, CPN Center for Gastrointestinal Motility and Functional Disorders Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition Enteral Access & Management
TUBES R US SHEILA BELL, MS, RN, CPNP PC Christine Gangi, RN, CPN Center for Gastrointestinal Motility and Functional Disorders Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition Enteral Access & Management
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Booklet
 Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
(pack li TAX ell) For treating breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma or other cancers
 Medication Information Sheet (pack li TAX ell) This document provides general information about your medication. It does not replace the advice of your health care professional. Always discuss your therapy
Medication Information Sheet (pack li TAX ell) This document provides general information about your medication. It does not replace the advice of your health care professional. Always discuss your therapy
Western General Hospital Tubefeeding Group Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Protocol, October 2008
 Lothian University Hospitals Division Western General Hospital Protocol for the Care of Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Tube 14 FG Medicina G Tube CARE OF PATIENT FOLLOWING TUBE INSERTION OBSERVATIONS
Lothian University Hospitals Division Western General Hospital Protocol for the Care of Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy Tube 14 FG Medicina G Tube CARE OF PATIENT FOLLOWING TUBE INSERTION OBSERVATIONS
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name vismodegib (VIS-moh-DEH-gib) Brand name Erivedge (AYR-ih-vej) Approved uses Vismodegib is used to treat advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma. Dose and schedule
Name of your medication Generic name vismodegib (VIS-moh-DEH-gib) Brand name Erivedge (AYR-ih-vej) Approved uses Vismodegib is used to treat advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma. Dose and schedule
MYALEPT (MAI-uh-lept) (metreleptin) for injection for subcutaneous use
 .3 mg per vial _ A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for the first time. A healthcare provider should also watch you inject your MYALEPT dose the first time you
.3 mg per vial _ A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for the first time. A healthcare provider should also watch you inject your MYALEPT dose the first time you
Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems
 If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
PRODUCED BY La Direction des communications du ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux
 OPIOIDS: PRODUCED BY La Direction des communications du ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux This document is available online and can be ordered at msss.gouv.qc.ca by clicking Documentation and
OPIOIDS: PRODUCED BY La Direction des communications du ministère de la Santé et des Services sociaux This document is available online and can be ordered at msss.gouv.qc.ca by clicking Documentation and
Module 10 Troubleshooting Guide
 Module 10 Troubleshooting Guide Your safety and wellbeing are our priority. Issues can occur during your treatment and it is important that you recognize the symptoms. This guide will teach you how to
Module 10 Troubleshooting Guide Your safety and wellbeing are our priority. Issues can occur during your treatment and it is important that you recognize the symptoms. This guide will teach you how to
This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home.
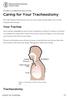 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Tracheostomy This information will help you care for your tracheostomy while you re in the hospital and at home. Your Trachea Your trachea (windpipe) is part
Vial. A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for
 MYALEPT (metreleptin) for injection Instructions for Use MYALEPT (MAI-uh-lept) (metreleptin) for injection Vial A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for 8 Do not
MYALEPT (metreleptin) for injection Instructions for Use MYALEPT (MAI-uh-lept) (metreleptin) for injection Vial A healthcare provider should show you how to inject MYALEPT before you use it for 8 Do not
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name procarbazine (proh-kar-buh-zeen) Brand name Matulane (MA-choo-layn) Approved uses Procarbazine is used to treat Hodgkin s disease. Dose and schedule Taking procarbazine
Name of your medication Generic name procarbazine (proh-kar-buh-zeen) Brand name Matulane (MA-choo-layn) Approved uses Procarbazine is used to treat Hodgkin s disease. Dose and schedule Taking procarbazine
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name niraparib (nih-ra-puh-rib) Brand name Zejula (zeh-joo-luh) Approved uses Niraparib is used to treat adult patients with recurrent fallopian tube cancer, ovarian cancer,
Name of your medication Generic name niraparib (nih-ra-puh-rib) Brand name Zejula (zeh-joo-luh) Approved uses Niraparib is used to treat adult patients with recurrent fallopian tube cancer, ovarian cancer,
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name etoposide (ee-toh-poh-side) Brand name VePesid (ve-pe-sid) Approved uses Etoposide is used to treat adults with small cell lung cancer and testicular cancer. Dose and
Name of your medication Generic name etoposide (ee-toh-poh-side) Brand name VePesid (ve-pe-sid) Approved uses Etoposide is used to treat adults with small cell lung cancer and testicular cancer. Dose and
HOMES AND SENIORS SERVICES. APPROVAL DATE: February 2011 REVISION DATE: January 2015; July 2018
 POLICY: Page 1 of 6 A resident requiring enteral (tube) feeding as a sole source or adjunctive nutrition support have access to a comprehensive enteral feeding program and receive appropriate support from
POLICY: Page 1 of 6 A resident requiring enteral (tube) feeding as a sole source or adjunctive nutrition support have access to a comprehensive enteral feeding program and receive appropriate support from
and how I would respond.
 Our Journey with Tube Feeding (G-Tube or J-Tube) Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. I can tell you what problems may occur with tube feedings 1. Sore
Our Journey with Tube Feeding (G-Tube or J-Tube) Si usted desea esta información en español, por favor pídasela a su enfermero o doctor. I can tell you what problems may occur with tube feedings 1. Sore
How to Change a. Foley catheter. Patient Education Rehabilitation Nursing. Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
SymlinPen (SĬM-lĭnPen) 120 (pramlintide acetate) Pen-Injector
 SYMLIN (pramlintide acetate) injection for subcutaneous use 4 SymlinPen (SĬM-lĭnPen) 120 (pramlintide acetate) Pen-Injector Read the Medication Guide and these Instructions for Use before you start using
SYMLIN (pramlintide acetate) injection for subcutaneous use 4 SymlinPen (SĬM-lĭnPen) 120 (pramlintide acetate) Pen-Injector Read the Medication Guide and these Instructions for Use before you start using
Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
Methotrexate Injections
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Methotrexate Injections Steps to follow Your provider has prescribed that you receive methotrexate by injection. This handout explains the drug, its side effects, drug interactions,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Methotrexate Injections Steps to follow Your provider has prescribed that you receive methotrexate by injection. This handout explains the drug, its side effects, drug interactions,
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name palbociclib (PAL-boh-SY-klib) Brand name Ibrance (I-brans) Approved uses Palbociclib is used to treat hormone receptor positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor
Name of your medication Generic name palbociclib (PAL-boh-SY-klib) Brand name Ibrance (I-brans) Approved uses Palbociclib is used to treat hormone receptor positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor
ORAL CHEMOTHERAPY EDUCATION
 Name of your medication Generic name thioguanine (THY-oh-GWAH-neen) Brand name Tabloid (TAB-loyd) Approved uses Thioguanine is used to treat adult and pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Name of your medication Generic name thioguanine (THY-oh-GWAH-neen) Brand name Tabloid (TAB-loyd) Approved uses Thioguanine is used to treat adult and pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
POST OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS ARTHROSCOPIC MENISCECTOMY / CHONDROPLASTY / DEBRIDEMENT
 POST OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS ARTHROSCOPIC MENISCECTOMY / CHONDROPLASTY / DEBRIDEMENT DIET Start with clear liquids (jello, soup broth, Gatorade, etc.), crackers, white bread and other light foods Progress
POST OPERATIVE INSTRUCTIONS ARTHROSCOPIC MENISCECTOMY / CHONDROPLASTY / DEBRIDEMENT DIET Start with clear liquids (jello, soup broth, Gatorade, etc.), crackers, white bread and other light foods Progress
In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer. Cancer Services Information for patients
 In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet provides information about brachytherapy (a type of internal radiotherapy). We hope
In-patient brachytherapy for gynaecological cancer Cancer Services Information for patients i Introduction This booklet provides information about brachytherapy (a type of internal radiotherapy). We hope
Patient Information. EGRIFTA (eh-grif-tuh) (tesamorelin for injection) for subcutaneous use
 Patient Information EGRIFTA (eh-grif-tuh) (tesamorelin for injection) for subcutaneous use Read the Patient Information that comes with EGRIFTA before you start to take it and each time you get a refill.
Patient Information EGRIFTA (eh-grif-tuh) (tesamorelin for injection) for subcutaneous use Read the Patient Information that comes with EGRIFTA before you start to take it and each time you get a refill.
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Men and Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Going Home with Your Peripheral Nerve Catheter and Pain Relief Pump
 Northwestern Memorial Hospital Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT If you have any questions about the pain relief pump, please call the Anesthesia Pain Service. Going Home with Your Peripheral Nerve
Northwestern Memorial Hospital Patient Education CARE AND TREATMENT If you have any questions about the pain relief pump, please call the Anesthesia Pain Service. Going Home with Your Peripheral Nerve
Chapter 19. Assisting With Bowel Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Chapter 19 Assisting With Bowel Elimination Normal Bowel Elimination Time and frequency of bowel movements (BMs) vary. To assist with bowel elimination, you need to know these terms: Defecation is the
Instructions for Use NITYR (ni-tir) (nitisinone) tablets
 Instructions for Use NITYR (ni-tir) (nitisinone) tablets Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking NITYR tablets using an oral syringe or mixed in applesauce, and each time you get a refill.
Instructions for Use NITYR (ni-tir) (nitisinone) tablets Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking NITYR tablets using an oral syringe or mixed in applesauce, and each time you get a refill.
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR
 For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
For the Patient: Everolimus tablets Other names: AFINITOR Everolimus (e'' ver oh' li mus) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. It is a tablet that you take by mouth. Tell your doctor if
