Cognitive and neuroimaging findings in pathological gambling
|
|
|
- Marybeth Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cognitive and neuroimaging findings in pathological gambling TNU seminar on Pathological Gambling, Jakob Heinzle Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU), Institute for Biomedical Engineering (IBT), University and ETH Zürich
2 Overview General overview on cognitive and neuroimaging findings in PG (van Holst et al., 2010) Three studies that target cognitive distortions: Overconfidence (Goodie, 2005) Control vs. No-control (Goodie, 2005; Clark et al., 2009; Chase and Clark, 2010) Near-miss effect (Clark et al., 2009; Chase and Clark, 2010) 2
3 Van Holst et al, 2010 «Why gamblers fail to win: A review of cognitive and neuroimaging findings in pathological gambling» Reviews papers between 2003 and 2008 in 4 domains: Reward and punishment processing Attentional bias and cue reactivity Impulsivity Decision making and executive function 3
4 Reward and Punishment - Behavior Problem gambling characterized by increased reward seeking and/or increased insensitivity to loss in behavioral tasks (Cavedini et al., 2002; Petry, 2001b; Vitaro et al., 1999). PG do not stop playing (Card playing task) even if probabilities of getting reward worsen over time (Goudriaan, 2005). PG are more reward seeking. However, no reward seeking difference in a different study (Leiserson and Phil, 2007). 4
5 Reward and Punishment - fmri PG show smaller brain responses to reward in ventral striatum and VMPFC (Reuter et al, 2005). Another study showed less activation in VLPFC for PG compared to HC in both win and loss trials (de Ruiter et al, 2009). Reward sensitivity seems to be smaller in PG, i.e. similar amounts of reward result in smaller neuronal reward signals. 5
6 Attentional bias and cue reactivity - Behavior D-amphetamine increases the desire to gamble in PG (Zack and Poulos, 2004; same result with alcohol dependency). D-amphetamine increases reading spead on gambling related words, but decreases on others, compared to an overall increase in HC (Zack and Poulos, 2004). Haloperidol (D2 antagonist) in PG enhances desire to gamble during game, but not before (Zack and Poulos, 2007). Haloperidol increases reading spead on gambling related words (Zack and Poulos, 2007). DA function seems to play a role in pathological gambling. 6
7 Attentional bias and cue reactivity - fmri PG show less activity in ventral and dorsal ACC and right IPL when viewing gaming related scenes (Potenza et al, 2008). Less activation in PG (while watching gambling video) in CC, OFC, caudate, basal ganglia and thalamic areas (Potenza et al, 2003). Higher response (gambling video) in right DLPFC, right IFG, MFG, left parahippocampal region (Crockford et al, 2005). Inconclusive and highly uncontroled paradigms. 7
8 Impulsivitiy - Behavior How to measure impulsivity? Response inhibition as suppression of prepotent response (GO/NOGO, Stop Signal Task, Stroop task etc.) Delay discounting Measures of cognitive impulsivity (e.g. IGT, CGT, etc.) but this is also decision making, and will be treated there. 8
9 Impulsivitiy - Behavior PG make more errors in choice reaction tasks (Fuentes et al, 2006). Delay gratification and Stop Signal task are more strongly impaired in PG-ADHD patients compared to PG and HC. (Rodriguez-Jimenez et a, 2004). potential confounds of comorbidity PG perform below HC in a series of response inhibition tasks: GO task, circle tracing, Stroop (Goudriaan et al, 2006). Impairement in stop task predicts relapse in PG group (Goudriaan et al, 2008). Stroop task performance is worse in PG (Kertzman et al, 2006). 9
10 Impulsivitiy - Behavior PG respond slower (!) in CPT and GO/NOGO but make more commission errors. Problems in task switching (Kertzman et al, 2008). Delay discounting reliably differs between PG, PPG and HC. No difference in future time perspectives (MacKillop, 2006). PG consistently show signs of impulsivity in cognitive tasks. However, comorbidity factors are often not taken into account (ADHD example). 10
11 Impulsivitiy- fmri In color-word Stroop task PG show less activation in VLPFC (Potenza et al, 2003). However, behavior was inconsistent with other findings (PG=HC). Difficult to interpret because of conflicting behavioral results. 11
12 Decision making and executive function - Behavior The Iowa Gambling Task 4 decks with cards. 2 decks have higher wins and fewer, but even higher losses. On the long run it is favorable to go for the decks with the frequent but small losses. Normal people usually learn after about 50 trials. Other gambling tasks: Georgia Gambling Task (GGT), Cambridge Gambling Task (CGT). 12
13 Decision making and executive function - Behavior Performance of PG is worse on IGT (Goudriaan et al, 2006, Linnet et al., 2006, Lakey et al., 2007, Roca et al., 2008). Overconfidence and bet acceptance in GGT predict gambling severity (Lakey et al., 2007). No correlation between go/nogo and IGT results. (Roca et al., 2008). Cognitive flexibility is impaired in PG (Ruff Figural Fluency Test, Trail Making Task Part B) (Kalechstein et al., 2007) Large battery of tests (cognitive flexibility, working memory, inhibition) with PG results worse then HC (Forbush et al., 2008, Marazziti et al., 2008). 13
14 Decision making and executive function - Behavior Performance in a Game of Dice task correlates with executive function measures (Brand et al., 2005). No salivary cortisol or alpha-amylase difference compared to HC during Game of Dice task (Labodda et al., 2007) Working memory deficits (Leiserson and Pihl, 2007). Consistent deficits in decision making are observed. In many studies, effects of comorbidities can not be excluded. 14
15 Decision making and executive function - fmri Modified IGT in comorbid PG and SD: lowered VMPFC activity compared to HC (Tanabe et al, 2007). So far, inconclusive. Too few studies, non with PG without comorbidity. 15
16 Van Holst overall summary There are many differences in many cognitive aspects. However, only few are very consistent accross studies, e.g. stop signal, IGT performance. Except for 2 fmri studies that look at reward coding in PG, there is no conclusive neuroimaging study. 16
17 The effect of near misses and perceived control The role of perceived control and overconfidence in pathological gambling. (Goodie, Journal of Gambling Studies, 2005) Gambling near-misses enhance motivation to gamble and recruit win-related brain circuitry (Clark et al., Neuron, 2009) Gambling severity predicts midbrain responses to near-miss outcomes (Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 17
18 Role of perceived control and overconfidence Participants: University students that like to gamble. Scores: SOGS and a PG status directly derived from SOGS SOGS > 5 PG = 1 Probable PG SOGS = [3,4] PG = 0.5 problem gambling SOGS < 3 PG = 0, non-problem gambling Run 2 studies to compare SOGS with cognitive measures. Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
19 Task including knowledge - GGT Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
20 Example of measures Acurracy of confidence estimates Total win on gambles Bet acceptance Betting slope Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
21 Calculation of payoff for gambles and manipulations Study 1: Replication of earlier study. Win on gamble = 100/confidence equal payoff over many trials, if confidence estimates are correct. Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
22 Results Study 1 Gamblers are overconfident and thus earn less, because they get offered less favourable bets. The acceptance slope is flater in PPG. But, probable PG do not accept more gambles over all Study 2 Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
23 Calculation of payoff for gambles and manipulations Study 1: Replication of earlier study. Win on gamble = 100/confidence equal payoff over many trials, if confidence estimates are correct. Study 2: Win on gamble = 100 / accuracy, where accuracy is the average accuracy of all questions with the same confidence. equal payoff over many trials. Gamble can be either on the question (Control) or on a random gamble. (No-Control: Random number between 1 and 100, if smaller than e.g. 75%, you win.) Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
24 Role of perceived control PPG accept more bets Control increases the number of bets and decreases betting slope. Control has less impact on gamblers betting frequency. Slope is affected more strongly in PPG. Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
25 Summary Probable pathological gamblers are more overconfident. PG is associated with gamble acceptance if payoffs are equal. Control affects PG differently from non-pg. PPG weigh probabilities differently from non PPG (acceptance slope). Considerations : No payout (points only), real facts vs. random outcomes, Goodie et al., Journal of Gambling Studies,
26 The effect of near misses Participants: University students Subjective Ratings: Gambling Related Cognition Scale, 3 questions after each choice (every third choice in fmri). Second column is random 1/6 hits, 2/6 near misses, 3/6 misses First column: set by computer or set by participant «Influence on the game?» Clark et al., Neuron,
27 Subjective ratings for near misses (A)Chances of winning are estimated higher when participant chooses the object in the left column. (B) Subjects want to continue the game more strongly, at nearmisses, when they themselves choose the object. Clark et al., Neuron,
28 Win vs. miss and near-miss vs. fullmiss (A) p < 0.05 FWE corrected (B) p < 0.05 FWE corrected (masked with A). Map: p < unc. Clark et al., Neuron,
29 Differential effect of control in nearmisses vs. full-misses (A) p ~ 0.05 FWE corrected (masked with A). Map: p < unc. Clark et al., Neuron,
30 Gambling-related cognitions scale (GRCS) 23 questions that seem to display a high variance also in healthy controls (compared to SOGS). SOGS = South Oaks Gambling Screen Raylu and Oei, Addiction,
31 Neural correlates of subjective scores (A) p < 0.05 FWE corrected (masked with win > loss). Map: p < unc. (B) p < 0.05 FWE corrected (masked with win > loss). Map: p < unc. Clark et al., Neuron,
32 Near-misses in healthy controls - summary Wins activate the common reward network. Within this network: Near-misses activate ventral striatum more than full-misses. An interaction of control and near- vs. full-miss is found in the racc. Near-miss vs. Full-miss activation in anterior insula correlates with GRCS and desire to continue gambling. Clark et al., Neuron,
33 The discussion of the authors. «Near-misses were associated with significantly greater BOLD signal in the ventral striatum and anterior insula; areas that were also activated by unpredictable monetary wins on the task. Clark et al., Neuron,
34 Open question Are these findings relevant for pathological gambling or do they simply reflect normal behavior? Clark et al., Neuron,
35 Near-misses vs. Full-misses in regular gamblers Same paradigm as used in Clark et al (2009). 24 regular gamblers, 20 in Analysis (scored with DSM IV and SOGS). Analysis restricted to ROI defined in Clark et al. (2009) 4 contrasts (as in Clark et al) correlated with SOGS. Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 35
36 The game - reminder Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 36
37 Near-misses vs. Full-misses in regular gamblers Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 37
38 Gambling severity vs. midbrain activity (near - full miss) Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 38
39 Less smoothing (4 mm) to better detect midbrain nuclei p < 0.005, blue circles p < (unc.) Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 39
40 Comparison to non-gamblers from (Clark et al, 2009) p < (unc.) Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 40
41 Near-misses vs. Full-misses in regular gamblers - Summary Gambling severity is related to activity in the midbrain (SOGS) scores. However, no difference to healthy controls! Reward coding difference (confirm Reuter et al., 2005), but no difference in near-miss activity compared to controls. No single comorbidity scale had an influence on significance levels. Chase and Clark, Journal of Neuroscience, 2010) 41
42 Summary Cognitive functions are distorted in pathological gamblers fmri findings suggest a distorted reward coding (Reuter et al. 2005, Chase and Clark, 2010), but no evidence for distorted coding of near-misses. Cognitive functions have not been tested sufficiently using fmri. 42
Why gamblers fail to win: evidence from neuroscience
 Why gamblers fail to win: evidence from neuroscience Anna E. Goudriaan Principal Investigator Arkin Mental Health Academic Medical Center, Department of Psychiatry Universitty of Amsterdam Jellinek Gambling
Why gamblers fail to win: evidence from neuroscience Anna E. Goudriaan Principal Investigator Arkin Mental Health Academic Medical Center, Department of Psychiatry Universitty of Amsterdam Jellinek Gambling
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse. Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver
 Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
Gambling distortions and the brain reward system Dr Luke Clark
 Gambling distortions and the brain reward system Dr Luke Clark Department of Psychology University of Cambridge, U.K. Impulsive choice in PG as possible index of vmpfc dysfunction Functional imaging of
Gambling distortions and the brain reward system Dr Luke Clark Department of Psychology University of Cambridge, U.K. Impulsive choice in PG as possible index of vmpfc dysfunction Functional imaging of
Pathological Gambling: Neurobiological research and its relevance for treatment and relapse prevention: Recent research and future questions
 Pathological Gambling: Neurobiological research and its relevance for treatment and relapse prevention: Recent research and future questions Anneke. Goudriaan 1,2, Ph.D. Ruth van Holst 1,2, M.Sc. Dick
Pathological Gambling: Neurobiological research and its relevance for treatment and relapse prevention: Recent research and future questions Anneke. Goudriaan 1,2, Ph.D. Ruth van Holst 1,2, M.Sc. Dick
Connect with amygdala (emotional center) Compares expected with actual Compare expected reward/punishment with actual reward/punishment Intuitive
 Orbitofronal Notes Frontal lobe prefrontal cortex 1. Dorsolateral Last to myelinate Sleep deprivation 2. Orbitofrontal Like dorsolateral, involved in: Executive functions Working memory Cognitive flexibility
Orbitofronal Notes Frontal lobe prefrontal cortex 1. Dorsolateral Last to myelinate Sleep deprivation 2. Orbitofrontal Like dorsolateral, involved in: Executive functions Working memory Cognitive flexibility
Neuroscience of Gambling Addiction. Dr Luke Clark 28 th March 2015 Alberta Gambling Research Institute, Banff
 Neuroscience of Gambling Addiction Dr Luke Clark 28 th March 2015 Alberta Gambling Research Institute, Banff Overview Endogenous opioid function in pathological gamblers: understanding the mechanism of
Neuroscience of Gambling Addiction Dr Luke Clark 28 th March 2015 Alberta Gambling Research Institute, Banff Overview Endogenous opioid function in pathological gamblers: understanding the mechanism of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION In format provided by Goldstein and Volkow. (NOVEMBER 2011)
 Table S3. Functional neuroimaging studies (conducted during 2000-2010) comparing brain activity during cue exposure in addicted individuals (S) and healthy controls (C) Tool/ Nicotine Brody, Mandelkern
Table S3. Functional neuroimaging studies (conducted during 2000-2010) comparing brain activity during cue exposure in addicted individuals (S) and healthy controls (C) Tool/ Nicotine Brody, Mandelkern
Neuronal and Psychological Underpinnings of Pathological Gambling
 Neuronal and Psychological Underpinnings of Pathological Gambling Bryan Frederick Singer, Patrick Anselme, Mike James Ferrar Robinson and Paul Vezina Journal Name: Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience
Neuronal and Psychological Underpinnings of Pathological Gambling Bryan Frederick Singer, Patrick Anselme, Mike James Ferrar Robinson and Paul Vezina Journal Name: Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience
9/13/2018. Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria
 DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Neil P. Jones 7th Annual Conference on ADHD and Executive Function September 14, 218 Diagnosis Child
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria Neurobiological Aspects of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) Neil P. Jones 7th Annual Conference on ADHD and Executive Function September 14, 218 Diagnosis Child
Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk
 Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk... and corresponding risk prediction errors Peter Bossaerts 1 Contents 1. Reward Encoding And The Dopaminergic System 2. Reward Prediction Errors And TD (Temporal
Neurobiological Foundations of Reward and Risk... and corresponding risk prediction errors Peter Bossaerts 1 Contents 1. Reward Encoding And The Dopaminergic System 2. Reward Prediction Errors And TD (Temporal
The neurobiology of Pathological Gambling
 Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU) Institut für Biomedizinische Technik Universität Zürich & ETH Zürich The neurobiology of Pathological Gambling Gabor Stefanics Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU)
Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU) Institut für Biomedizinische Technik Universität Zürich & ETH Zürich The neurobiology of Pathological Gambling Gabor Stefanics Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU)
Opposing Effects of Acute Stress in a Rodent Model of Gambling Behaviour
 Opposing Effects of Acute Stress in a Rodent Model of Gambling Behaviour by Parisa Sadat Hedayatmofidi A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Institute
Opposing Effects of Acute Stress in a Rodent Model of Gambling Behaviour by Parisa Sadat Hedayatmofidi A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Institute
smokers) aged 37.3 ± 7.4 yrs (mean ± sd) and a group of twelve, age matched, healthy
 Methods Participants We examined a group of twelve male pathological gamblers (ten strictly right handed, all smokers) aged 37.3 ± 7.4 yrs (mean ± sd) and a group of twelve, age matched, healthy males,
Methods Participants We examined a group of twelve male pathological gamblers (ten strictly right handed, all smokers) aged 37.3 ± 7.4 yrs (mean ± sd) and a group of twelve, age matched, healthy males,
25 Things To Know. Pre- frontal
 25 Things To Know Pre- frontal Frontal lobes Cognition Touch Sound Phineas Gage First indication can survive major brain trauma Lost 1+ frontal lobe Gage Working on a railroad Gage (then 25) Foreman on
25 Things To Know Pre- frontal Frontal lobes Cognition Touch Sound Phineas Gage First indication can survive major brain trauma Lost 1+ frontal lobe Gage Working on a railroad Gage (then 25) Foreman on
Prefrontal dysfunction in drug addiction: Cause or consequence? Christa Nijnens
 Prefrontal dysfunction in drug addiction: Cause or consequence? Master Thesis Christa Nijnens September 16, 2009 University of Utrecht Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience Department of Neuroscience
Prefrontal dysfunction in drug addiction: Cause or consequence? Master Thesis Christa Nijnens September 16, 2009 University of Utrecht Rudolf Magnus Institute of Neuroscience Department of Neuroscience
Neural Basis of Decision Making. Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
Somatic Marker Hypothesis. Tasha Poppa Affective Computing Guest Lecture Fall 2017
 Somatic Marker Hypothesis Tasha Poppa Affective Computing Guest Lecture Fall 2017 Outline Historical context Some Useful Functional Neuroanatomy VMPFC patients: Clinical observations Somatic Marker Hypothesis
Somatic Marker Hypothesis Tasha Poppa Affective Computing Guest Lecture Fall 2017 Outline Historical context Some Useful Functional Neuroanatomy VMPFC patients: Clinical observations Somatic Marker Hypothesis
FMRI and Treatment Development for Addictions
 FMRI and Treatment Development for Addictions Marc N. Potenza, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Child Study, and Neurobiology Director, Yale Gambling Center of Research Excellence (CORE) Director,
FMRI and Treatment Development for Addictions Marc N. Potenza, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Psychiatry, Child Study, and Neurobiology Director, Yale Gambling Center of Research Excellence (CORE) Director,
Biological Risk Factors
 Biological Risk Factors Ms Angelina Crea Provisional Psychologist Academic Child Psychiatry Unit Royal Children s Hospital Professor Alasdair Vance Head Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics
Biological Risk Factors Ms Angelina Crea Provisional Psychologist Academic Child Psychiatry Unit Royal Children s Hospital Professor Alasdair Vance Head Academic Child Psychiatry Department of Paediatrics
Neural Basis of Decision Making. Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
Academic year Lecture 16 Emotions LECTURE 16 EMOTIONS
 Course Behavioral Economics Academic year 2013-2014 Lecture 16 Emotions Alessandro Innocenti LECTURE 16 EMOTIONS Aim: To explore the role of emotions in economic decisions. Outline: How emotions affect
Course Behavioral Economics Academic year 2013-2014 Lecture 16 Emotions Alessandro Innocenti LECTURE 16 EMOTIONS Aim: To explore the role of emotions in economic decisions. Outline: How emotions affect
Imaging studies in pathological gambling: similarities and differences with alcohol dependence van Holst, R.J.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Imaging studies in pathological gambling: similarities and differences with alcohol dependence van Holst, R.J. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Imaging studies in pathological gambling: similarities and differences with alcohol dependence van Holst, R.J. Link to publication Citation for published version
Medical Treatment of Problem Gambling. Donald W. Black, M.D. Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine Department of Psychiatry
 Medical Treatment of Problem Gambling Donald W. Black, M.D. Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Disclosures Research Support: Forest Labs Nellie Ball Trust Fund National
Medical Treatment of Problem Gambling Donald W. Black, M.D. Roy J. and Lucille A. Carver College of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Disclosures Research Support: Forest Labs Nellie Ball Trust Fund National
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
BIOMED 509. Executive Control UNM SOM. Primate Research Inst. Kyoto,Japan. Cambridge University. JL Brigman
 BIOMED 509 Executive Control Cambridge University Primate Research Inst. Kyoto,Japan UNM SOM JL Brigman 4-7-17 Symptoms and Assays of Cognitive Disorders Symptoms of Cognitive Disorders Learning & Memory
BIOMED 509 Executive Control Cambridge University Primate Research Inst. Kyoto,Japan UNM SOM JL Brigman 4-7-17 Symptoms and Assays of Cognitive Disorders Symptoms of Cognitive Disorders Learning & Memory
590,000 deaths can be attributed to an addictive substance in some way
 Mortality and morbidity attributable to use of addictive substances in the United States. The Association of American Physicians from 1999 60 million tobacco smokers in the U.S. 14 million dependent on
Mortality and morbidity attributable to use of addictive substances in the United States. The Association of American Physicians from 1999 60 million tobacco smokers in the U.S. 14 million dependent on
Knowing How Gamblers Think: Improving Treatment Outcomes
 Knowing How Gamblers Think: Improving Treatment Outcomes Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Minnesota School of Medicine Minneapolis, MN Disclosure Information I have the following financial
Knowing How Gamblers Think: Improving Treatment Outcomes Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Minnesota School of Medicine Minneapolis, MN Disclosure Information I have the following financial
The National Methamphetamine Symposium
 The National Methamphetamine Symposium Making Research Work in Practice 12 May 2015 Arts Centre, Melbourne Neural and cognitive effects of methamphetamine and implications for treatment Rob Hester National
The National Methamphetamine Symposium Making Research Work in Practice 12 May 2015 Arts Centre, Melbourne Neural and cognitive effects of methamphetamine and implications for treatment Rob Hester National
Constructions of Cravings in Disordered Gambling Research: Theory and Evidence
 Constructions of Cravings in Disordered Gambling Research: Theory and Evidence Glenn W. Harrison (1, 2, 3), Morten I. Lau (4), Don Ross (2, 3, 5), J. Todd Swarthout (6) 1 Department of Risk Management
Constructions of Cravings in Disordered Gambling Research: Theory and Evidence Glenn W. Harrison (1, 2, 3), Morten I. Lau (4), Don Ross (2, 3, 5), J. Todd Swarthout (6) 1 Department of Risk Management
Basic definition and Classification of Anhedonia. Preclinical and Clinical assessment of anhedonia.
 Basic definition and Classification of Anhedonia. Preclinical and Clinical assessment of anhedonia. Neurobiological basis and pathways involved in anhedonia. Objective characterization and computational
Basic definition and Classification of Anhedonia. Preclinical and Clinical assessment of anhedonia. Neurobiological basis and pathways involved in anhedonia. Objective characterization and computational
Mapping Neural circuitry of Risk and Resilience for Suicidal Behavior and Mood Disorders
 Mapping Neural circuitry of Risk and Resilience for Suicidal Behavior and Mood Disorders J. John Mann, MD Paul Janssen Professor of Translational Neuroscience in Psychiatry and Radiology Columbia University
Mapping Neural circuitry of Risk and Resilience for Suicidal Behavior and Mood Disorders J. John Mann, MD Paul Janssen Professor of Translational Neuroscience in Psychiatry and Radiology Columbia University
Characterization of the decision-making deficit of patients with ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions
 Brain (2000), 123, 2189 2202 Characterization of the decision-making deficit of patients with ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions Antoine Bechara, Daniel Tranel and Hanna Damasio Department of Neurology,
Brain (2000), 123, 2189 2202 Characterization of the decision-making deficit of patients with ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions Antoine Bechara, Daniel Tranel and Hanna Damasio Department of Neurology,
The Effect of Regular Naltrexone Dosing on Disordered Gamblers: An Examination of Neural Activation, Gambling Urges, and Gambling Behaviour
 The Effect of Regular Naltrexone Dosing on Disordered Gamblers: An Examination of Neural Activation, Gambling Urges, and Gambling Behaviour Darren R. Christensen, PhD Chair in Gambling, Alberta Gambling
The Effect of Regular Naltrexone Dosing on Disordered Gamblers: An Examination of Neural Activation, Gambling Urges, and Gambling Behaviour Darren R. Christensen, PhD Chair in Gambling, Alberta Gambling
Talk 2. Neurocognitive differences in children with or without CU- traits 05/12/2013. Psychological. Behavioural
 Neurocognitive differences in children with or without CU- traits Prof Essi Viding Developmental Risk and Resilience Unit, Psychology and Language Sciences, UCL e.viding@ucl.ac.uk Talk 2. Environment Psychological
Neurocognitive differences in children with or without CU- traits Prof Essi Viding Developmental Risk and Resilience Unit, Psychology and Language Sciences, UCL e.viding@ucl.ac.uk Talk 2. Environment Psychological
Risky Behavior in Gambling Tasks in Individuals with ADHD Groen, Yvonne; Gaastra, Geraldina; Lewis-Evans, Ben; Tucha, Oliver
 University of Groningen Risky Behavior in Gambling Tasks in Individuals with ADHD Groen, Yvonne; Gaastra, Geraldina; Lewis-Evans, Ben; Tucha, Oliver Published in: PLoS ONE DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074909
University of Groningen Risky Behavior in Gambling Tasks in Individuals with ADHD Groen, Yvonne; Gaastra, Geraldina; Lewis-Evans, Ben; Tucha, Oliver Published in: PLoS ONE DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074909
Proactive and reactive control during emotional interference and its relationship to trait anxiety
 brain research 1481 (2012) 13 36 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Proactive and reactive control during emotional interference and its relationship
brain research 1481 (2012) 13 36 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/brainres Research Report Proactive and reactive control during emotional interference and its relationship
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Task timeline for Solo and Info trials.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Task timeline for Solo and Info trials. Each trial started with a New Round screen. Participants made a series of choices between two gambles, one of which was objectively riskier
Supplementary Figure 1 Task timeline for Solo and Info trials. Each trial started with a New Round screen. Participants made a series of choices between two gambles, one of which was objectively riskier
Neuro-cognitive systems underpinning antisocial behavior and the impact of maltreatment and substance abuse on their development
 Neuro-cognitive systems underpinning antisocial behavior and the impact of maltreatment and substance abuse on their development R.J.R. Blair Center for Neurobehavioral Research 1 Talk plan Boys Town and
Neuro-cognitive systems underpinning antisocial behavior and the impact of maltreatment and substance abuse on their development R.J.R. Blair Center for Neurobehavioral Research 1 Talk plan Boys Town and
Biopsychosocial model of Adolescent Gambling
 Biopsychosocial model of Adolescent Gambling We begin a discussion of specific risk taking domains: Adolescent gambling. Unlike other risk domains as there is an index or level of risk taking Non-gamblers,
Biopsychosocial model of Adolescent Gambling We begin a discussion of specific risk taking domains: Adolescent gambling. Unlike other risk domains as there is an index or level of risk taking Non-gamblers,
Pathological Gambling: An Impulse Control Disorder? Measurement of impulsivity Using Neurocognitive Tests
 IMAJ VOL 12 april 2010 REVIEWS Pathological Gambling: An Impulse Control Disorder? Measurement of impulsivity Using Neurocognitive Tests Pinhas N. Dannon MD, Netta Shoenfeld BA, Oded Rosenberg MD, Semion
IMAJ VOL 12 april 2010 REVIEWS Pathological Gambling: An Impulse Control Disorder? Measurement of impulsivity Using Neurocognitive Tests Pinhas N. Dannon MD, Netta Shoenfeld BA, Oded Rosenberg MD, Semion
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is characterized
 REVIEW Cool Inferior Frontostriatal Dysfunction in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Versus Hot Ventromedial Orbitofrontal-Limbic Dysfunction in Conduct Disorder: A Review Katya Rubia Attention-deficit/hyperactivity
REVIEW Cool Inferior Frontostriatal Dysfunction in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Versus Hot Ventromedial Orbitofrontal-Limbic Dysfunction in Conduct Disorder: A Review Katya Rubia Attention-deficit/hyperactivity
FUNCTIONAL MRI IMPULSIVENESS IMPULSIVENESS IMPULSIVENESS. Tests of cognitive control. Rubia. Katya Rubia. Mapping abnormal brain function.
 IMPULSIVENESS Mapping abnormal brain function in the effects of MPH and specificity of abnormality Rubia Dep. Child Psychiatry Institute of Psychiatry : Hyperactivity, Inattention, Impulsiveness (DSM IV)
IMPULSIVENESS Mapping abnormal brain function in the effects of MPH and specificity of abnormality Rubia Dep. Child Psychiatry Institute of Psychiatry : Hyperactivity, Inattention, Impulsiveness (DSM IV)
Supporting Information. Demonstration of effort-discounting in dlpfc
 Supporting Information Demonstration of effort-discounting in dlpfc In the fmri study on effort discounting by Botvinick, Huffstettler, and McGuire [1], described in detail in the original publication,
Supporting Information Demonstration of effort-discounting in dlpfc In the fmri study on effort discounting by Botvinick, Huffstettler, and McGuire [1], described in detail in the original publication,
Role of the ventral striatum in developing anorexia nervosa
 Role of the ventral striatum in developing anorexia nervosa Anne-Katharina Fladung 1 PhD, Ulrike M. E.Schulze 2 MD, Friederike Schöll 1, Kathrin Bauer 1, Georg Grön 1 PhD 1 University of Ulm, Department
Role of the ventral striatum in developing anorexia nervosa Anne-Katharina Fladung 1 PhD, Ulrike M. E.Schulze 2 MD, Friederike Schöll 1, Kathrin Bauer 1, Georg Grön 1 PhD 1 University of Ulm, Department
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Adolescent risk-taking
 Adolescent risk-taking OVERVIEW This document provides an overview of the scientific community s current understanding of why adolescents are more likely than children or adults to engage in risk-taking
Adolescent risk-taking OVERVIEW This document provides an overview of the scientific community s current understanding of why adolescents are more likely than children or adults to engage in risk-taking
Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain. Circuitry
 Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain Circuitry Luke Clark 1, Andrew J Lawrence 1, Frances Astley-Jones 1, Nicola Gray 1 1 Behavioural and Clinical Neuroscience
Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain Circuitry Luke Clark 1, Andrew J Lawrence 1, Frances Astley-Jones 1, Nicola Gray 1 1 Behavioural and Clinical Neuroscience
Interactions between Affective and Cognitive Processing Systems in Problematic Gamblers: A Functional Connectivity Study
 Interactions between Affective and Cognitive Processing Systems in Problematic Gamblers: A Functional Connectivity Study The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
Interactions between Affective and Cognitive Processing Systems in Problematic Gamblers: A Functional Connectivity Study The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
Neurobiology of Addiction. Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago
 Neurobiology of Addiction Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Disclosure Information I have the following financial relationships to disclose: My research is supported by NIDA, AFSP,
Neurobiology of Addiction Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Disclosure Information I have the following financial relationships to disclose: My research is supported by NIDA, AFSP,
Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain Circuitry
 Article Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain Circuitry Luke Clark, 1, * Andrew J. Lawrence, 1 Frances Astley-Jones, 1 and Nicola Gray 1 1 Behavioural and Clinical
Article Gambling Near-Misses Enhance Motivation to Gamble and Recruit Win-Related Brain Circuitry Luke Clark, 1, * Andrew J. Lawrence, 1 Frances Astley-Jones, 1 and Nicola Gray 1 1 Behavioural and Clinical
Behavioral addictions among adolescents: Do the predictors of pathological behaviors differ across gambling and video-gaming?
 11th European Conference on Gambling Studies and Policy Issues, Lisbon 2016 Behavioral addictions among adolescents: Do the predictors of pathological behaviors differ across gambling and video-gaming?
11th European Conference on Gambling Studies and Policy Issues, Lisbon 2016 Behavioral addictions among adolescents: Do the predictors of pathological behaviors differ across gambling and video-gaming?
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder
 Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago, IL 6/8/2016 Disclosure Information My research is
Evidence-Based Treatment Approaches for Gambling Disorder Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor University of Chicago Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago, IL 6/8/2016 Disclosure Information My research is
Gambling and Problem Gambling among Nordic Adolescents
 Gambling and Problem Gambling among Nordic Adolescents Daníel Þór Ólason D.Phil Department of Psychology University of Iceland 6th Nordic Conference Copenhagen, Denmark, Mai 2007 Part I: Gambling among
Gambling and Problem Gambling among Nordic Adolescents Daníel Þór Ólason D.Phil Department of Psychology University of Iceland 6th Nordic Conference Copenhagen, Denmark, Mai 2007 Part I: Gambling among
Structural and Functional Neuroimaging of Restricted and Repetitive Behavior in Autism Spectrum Disorder
 Journal of Intellectual Disability - Diagnosis and Treatment, 2015, 3, 21-34 21 Structural and Functional Neuroimaging of Restricted and Repetitive Behavior in Autism Spectrum Disorder Jenna M. Traynor
Journal of Intellectual Disability - Diagnosis and Treatment, 2015, 3, 21-34 21 Structural and Functional Neuroimaging of Restricted and Repetitive Behavior in Autism Spectrum Disorder Jenna M. Traynor
Heightened aversion to risk and loss in depressed patients with a suicide attempt history
 www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 1 December 2016 Accepted: 10 August 2017 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Heightened aversion to risk and loss in depressed patients with a suicide attempt history
www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 1 December 2016 Accepted: 10 August 2017 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Heightened aversion to risk and loss in depressed patients with a suicide attempt history
Gambling and the Brain: Why Neuroscience Research is Vital to Gambling Research
 INCREASING THE ODDS A Series Dedicated to Understanding Gambling Disorders VOLUME 6 Gambling and the Brain: Why Neuroscience Research is Vital to Gambling Research 2011 National Center for Responsible
INCREASING THE ODDS A Series Dedicated to Understanding Gambling Disorders VOLUME 6 Gambling and the Brain: Why Neuroscience Research is Vital to Gambling Research 2011 National Center for Responsible
Characteristics 9/26/2014. Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Treatment Targets in Gambling
 Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Treatment Targets in Gambling Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor, University of Chicago Source: Look Magazine, March, 1963 Characteristics Age: usually begins in early adulthood
Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Treatment Targets in Gambling Jon E. Grant, JD, MD, MPH Professor, University of Chicago Source: Look Magazine, March, 1963 Characteristics Age: usually begins in early adulthood
Distinct valuation subsystems in the human brain for effort and delay
 Supplemental material for Distinct valuation subsystems in the human brain for effort and delay Charlotte Prévost, Mathias Pessiglione, Elise Météreau, Marie-Laure Cléry-Melin and Jean-Claude Dreher This
Supplemental material for Distinct valuation subsystems in the human brain for effort and delay Charlotte Prévost, Mathias Pessiglione, Elise Météreau, Marie-Laure Cléry-Melin and Jean-Claude Dreher This
Decision-making deficit in chronic migraine patients with medication overuse
 DOI 10.1007/s10072-012-1071-4 ORAL COMMUNICATIONS Decision-making deficit in chronic migraine patients with medication overuse B. Biagianti L. Grazzi O. Gambini S. Usai R. Muffatti S. Scarone G. Bussone
DOI 10.1007/s10072-012-1071-4 ORAL COMMUNICATIONS Decision-making deficit in chronic migraine patients with medication overuse B. Biagianti L. Grazzi O. Gambini S. Usai R. Muffatti S. Scarone G. Bussone
Addressing Co-occurring Disorders among Problem Gambling Clients David M. Ledgerwood, Ph.D.
 Addressing Co-occurring Disorders among Problem Gambling Clients David M. Ledgerwood, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Neurosciences Wayne State School of Medicine dledgerw@med.wayne.edu Outline
Addressing Co-occurring Disorders among Problem Gambling Clients David M. Ledgerwood, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Neurosciences Wayne State School of Medicine dledgerw@med.wayne.edu Outline
Experienced poker players differ from inexperienced poker players in estimation bias and decision bias
 86 Estimation bias and decision bias among poker players Experienced poker players differ from inexperienced poker players in estimation bias and decision bias Jakob Linnet, 1,2 Line Gebauer, 1,2 Howard
86 Estimation bias and decision bias among poker players Experienced poker players differ from inexperienced poker players in estimation bias and decision bias Jakob Linnet, 1,2 Line Gebauer, 1,2 Howard
A possible mechanism for impaired joint attention in autism
 A possible mechanism for impaired joint attention in autism Justin H G Williams Morven McWhirr Gordon D Waiter Cambridge Sept 10 th 2010 Joint attention in autism Declarative and receptive aspects initiating
A possible mechanism for impaired joint attention in autism Justin H G Williams Morven McWhirr Gordon D Waiter Cambridge Sept 10 th 2010 Joint attention in autism Declarative and receptive aspects initiating
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH Volume 7, Number 1 Submitted: March 11, 2011 Revisions: April 2, 2011 Accepted: April 4, 2011 Published: April 6, 2011 The Effects of Explicit and Implicit Cognitive
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH Volume 7, Number 1 Submitted: March 11, 2011 Revisions: April 2, 2011 Accepted: April 4, 2011 Published: April 6, 2011 The Effects of Explicit and Implicit Cognitive
Proposal for a cognitive model to the treatment of pathological gambling
 Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 33 (2012) 742 746 PSIWORLD 2011 Proposal for a cognitive model to the treatment of pathological gambling Steliana Rizeanu a, b * a University of Bucharest, Faculty
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 33 (2012) 742 746 PSIWORLD 2011 Proposal for a cognitive model to the treatment of pathological gambling Steliana Rizeanu a, b * a University of Bucharest, Faculty
The neural mechanisms of inter-temporal decision-making: understanding variability
 Review Feature Review The neural mechanisms of inter-temporal decision-making: understanding variability Jan Peters and Christian Büchel Department of Systems Neuroscience, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf,
Review Feature Review The neural mechanisms of inter-temporal decision-making: understanding variability Jan Peters and Christian Büchel Department of Systems Neuroscience, University Medical Centre Hamburg-Eppendorf,
Gambling Decision making Assessment Validity
 J Gambl Stud (2010) 26:639 644 DOI 10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x ORIGINAL PAPER Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview for Gambling Severity (DIGS) with the South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS)
J Gambl Stud (2010) 26:639 644 DOI 10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x ORIGINAL PAPER Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview for Gambling Severity (DIGS) with the South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS)
Neuroplasticity: functional MRI techniques M.A. Rocca
 Neuroplasticity: functional MRI techniques M.A. Rocca Neuroimaging Research Unit, Institute of Experimental Neurology, Division of Neuroscience, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Vita-Salute San Raffaele
Neuroplasticity: functional MRI techniques M.A. Rocca Neuroimaging Research Unit, Institute of Experimental Neurology, Division of Neuroscience, San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Vita-Salute San Raffaele
Reinforcement learning and the brain: the problems we face all day. Reinforcement Learning in the brain
 Reinforcement learning and the brain: the problems we face all day Reinforcement Learning in the brain Reading: Y Niv, Reinforcement learning in the brain, 2009. Decision making at all levels Reinforcement
Reinforcement learning and the brain: the problems we face all day Reinforcement Learning in the brain Reading: Y Niv, Reinforcement learning in the brain, 2009. Decision making at all levels Reinforcement
Imaging studies in pathological gambling: similarities and differences with alcohol dependence van Holst, R.J.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Imaging studies in pathological gambling: similarities and differences with alcohol dependence van Holst, R.J. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Imaging studies in pathological gambling: similarities and differences with alcohol dependence van Holst, R.J. Link to publication Citation for published version
Supplemental Information. Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion
 Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion Luke J. Chang, Alec Smith, Martin Dufwenberg, and Alan G. Sanfey Supplemental Information
Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion Luke J. Chang, Alec Smith, Martin Dufwenberg, and Alan G. Sanfey Supplemental Information
An Overview of Gambling Disorder. Timothy Fong MD UCLA Gambling Studies Program IDAA Annual Meeting August 2018
 An Overview of Gambling Disorder Timothy Fong MD UCLA Gambling Studies Program IDAA Annual Meeting August 2018 Financial Disclosures Speaker Bureau Indivior Research Support Constellation Connections in
An Overview of Gambling Disorder Timothy Fong MD UCLA Gambling Studies Program IDAA Annual Meeting August 2018 Financial Disclosures Speaker Bureau Indivior Research Support Constellation Connections in
Gambling Disorder A Lens Through Which to Understand the Rest of the Process Addictions
 Gambling Disorder A Lens Through Which to Understand the Rest of the Process Addictions Kirk Moberg, MD, PhD, FASAM Executive Medical Director, UnityPoint Illinois Institute for Addiction Recovery Clinical
Gambling Disorder A Lens Through Which to Understand the Rest of the Process Addictions Kirk Moberg, MD, PhD, FASAM Executive Medical Director, UnityPoint Illinois Institute for Addiction Recovery Clinical
Neuroimaging vs. other methods
 BASIC LOGIC OF NEUROIMAGING fmri (functional magnetic resonance imaging) Bottom line on how it works: Adapts MRI to register the magnetic properties of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin, allowing
BASIC LOGIC OF NEUROIMAGING fmri (functional magnetic resonance imaging) Bottom line on how it works: Adapts MRI to register the magnetic properties of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin, allowing
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review
 The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
Reward Systems: Human
 Reward Systems: Human 345 Reward Systems: Human M R Delgado, Rutgers University, Newark, NJ, USA ã 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Introduction Rewards can be broadly defined as stimuli of positive
Reward Systems: Human 345 Reward Systems: Human M R Delgado, Rutgers University, Newark, NJ, USA ã 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Introduction Rewards can be broadly defined as stimuli of positive
Gambling Severity Predicted by Midbrain Response to Near-Miss Outcomes. Henry W. Chase 1, Luke Clark 2
 This version is the Authors Pre-Print (i.e. pre-peer review refereeing and journal page-setting), submitted to the Journal of Neuroscience on 16/7/09, and which we are able to distribute freely in accordance
This version is the Authors Pre-Print (i.e. pre-peer review refereeing and journal page-setting), submitted to the Journal of Neuroscience on 16/7/09, and which we are able to distribute freely in accordance
A Functional Neuroimaging Study of Self- Regulatory Control in Adults with Gambling and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects Graduate Center 9-2018 A Functional Neuroimaging Study of Self- Regulatory Control in Adults with Gambling
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Dissertations, Theses, and Capstone Projects Graduate Center 9-2018 A Functional Neuroimaging Study of Self- Regulatory Control in Adults with Gambling
The Nature of the Potential
 Lawrence May 2017 The Nature of the Potential Bita Moghaddam Professor and Chair Department of Behavioral Neuroscience Oregon Health and Science University Research Support: NIH/NIMH Andrew Mellon Foundation
Lawrence May 2017 The Nature of the Potential Bita Moghaddam Professor and Chair Department of Behavioral Neuroscience Oregon Health and Science University Research Support: NIH/NIMH Andrew Mellon Foundation
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lingnau et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902262106 Fig. S1. Material presented during motor act observation (A) and execution (B). Each row shows one of the 8 different motor acts. Columns in
Supporting Information Lingnau et al. 10.1073/pnas.0902262106 Fig. S1. Material presented during motor act observation (A) and execution (B). Each row shows one of the 8 different motor acts. Columns in
The Somatic Marker Hypothesis: Human Emotions in Decision-Making
 The Somatic Marker Hypothesis: Human Emotions in Decision-Making Presented by Lin Xiao Brain and Creativity Institute University of Southern California Most of us are taught from early on that : -logical,
The Somatic Marker Hypothesis: Human Emotions in Decision-Making Presented by Lin Xiao Brain and Creativity Institute University of Southern California Most of us are taught from early on that : -logical,
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION
 BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics
 How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics Hecke CNS Seminar WS 2006/07 Motivation Motivation Ferdinand Porsche "Wir wollen Autos bauen, die keiner braucht aber jeder haben will." Outline 1 Introduction
How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics Hecke CNS Seminar WS 2006/07 Motivation Motivation Ferdinand Porsche "Wir wollen Autos bauen, die keiner braucht aber jeder haben will." Outline 1 Introduction
Serotonin and Dopamine Interactions. Atanas Stankov Computational Psychiatry Seminar Translational Neuromodeling Unit
 Serotonin and Dopamine Interactions Atanas Stankov Computational Psychiatry Seminar Translational Neuromodeling Unit 02.05.2014 Outline NT Review Opponent/complement Interactions DA-5HT opponency L-Dopa
Serotonin and Dopamine Interactions Atanas Stankov Computational Psychiatry Seminar Translational Neuromodeling Unit 02.05.2014 Outline NT Review Opponent/complement Interactions DA-5HT opponency L-Dopa
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Gambl Stud. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 December 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Gambl Stud. 2010 December ; 26(4): 639 644. doi:10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x. Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Gambl Stud. 2010 December ; 26(4): 639 644. doi:10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x. Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Linking thought and movement simultaneously! Forebrain Basal ganglia Midbrain and
THE BRAIN HABIT BRIDGING THE CONSCIOUS AND UNCONSCIOUS MIND Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Linking thought and movement simultaneously! Forebrain Basal ganglia Midbrain and
Orbitofrontal cortex. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Approximate location of the OFC shown on a sagittal MRI
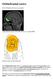 Orbitofrontal cortex From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Approximate location of the OFC shown on a sagittal MRI Orbital surface of left frontal lobe. The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex
Orbitofrontal cortex From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Approximate location of the OFC shown on a sagittal MRI Orbital surface of left frontal lobe. The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex
The Adolescent Developmental Stage
 The Adolescent Developmental Stage o Physical maturation o Drive for independence o Increased salience of social and peer interactions o Brain development o Inflection in risky behaviors including experimentation
The Adolescent Developmental Stage o Physical maturation o Drive for independence o Increased salience of social and peer interactions o Brain development o Inflection in risky behaviors including experimentation
Animal models of gambling. Catharine A. Winstanley University of British Columbia, Canada
 Animal models of gambling Catharine A. Winstanley University of British Columbia, Canada Disclosures Advisory Board: Shire What questions can preclinical research help to answer? Which brain areas are
Animal models of gambling Catharine A. Winstanley University of British Columbia, Canada Disclosures Advisory Board: Shire What questions can preclinical research help to answer? Which brain areas are
DOES THE D 3 DOPAMINE RECEPTOR (D 3 r)play A ROLE IN ADDICTION? Isabelle Boileau, PhD
 DOES THE D 3 DOPAMINE RECEPTOR (D 3 r)play A ROLE IN ADDICTION? Isabelle Boileau, PhD Acknowledgments Human Neurochemical Pathology Lab Stephen J. Kish, PhD Jun Chao Tong, PhD Centre for Movement Disorders
DOES THE D 3 DOPAMINE RECEPTOR (D 3 r)play A ROLE IN ADDICTION? Isabelle Boileau, PhD Acknowledgments Human Neurochemical Pathology Lab Stephen J. Kish, PhD Jun Chao Tong, PhD Centre for Movement Disorders
Damage to Insula Abolishes Cognitive Distortions during Simulated Gambling. Department of Psychology, University of Iowa
 Damage to Insula Abolishes Cognitive Distortions during Simulated Gambling Luke Clark 1, Bettina Studer 1,2, Joel Bruss 3, Daniel Tranel 3,4, Antoine Bechara 5 1 Department of Psychology, University of
Damage to Insula Abolishes Cognitive Distortions during Simulated Gambling Luke Clark 1, Bettina Studer 1,2, Joel Bruss 3, Daniel Tranel 3,4, Antoine Bechara 5 1 Department of Psychology, University of
Neuroanatomy of Emotion, Fear, and Anxiety
 Neuroanatomy of Emotion, Fear, and Anxiety Outline Neuroanatomy of emotion Critical conceptual, experimental design, and interpretation issues in neuroimaging research Fear and anxiety Neuroimaging research
Neuroanatomy of Emotion, Fear, and Anxiety Outline Neuroanatomy of emotion Critical conceptual, experimental design, and interpretation issues in neuroimaging research Fear and anxiety Neuroimaging research
Altruistic Behavior: Lessons from Neuroeconomics. Kei Yoshida Postdoctoral Research Fellow University of Tokyo Center for Philosophy (UTCP)
 Altruistic Behavior: Lessons from Neuroeconomics Kei Yoshida Postdoctoral Research Fellow University of Tokyo Center for Philosophy (UTCP) Table of Contents 1. The Emergence of Neuroeconomics, or the Decline
Altruistic Behavior: Lessons from Neuroeconomics Kei Yoshida Postdoctoral Research Fellow University of Tokyo Center for Philosophy (UTCP) Table of Contents 1. The Emergence of Neuroeconomics, or the Decline
BINGES, BLUNTS AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT
 BINGES, BLUNTS AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Why delaying the onset of alcohol and other drug use during adolescence is so important Aaron White, PhD Division of Epidemiology and Prevention Research National Institute
BINGES, BLUNTS AND BRAIN DEVELOPMENT Why delaying the onset of alcohol and other drug use during adolescence is so important Aaron White, PhD Division of Epidemiology and Prevention Research National Institute
From Habit to Addiction: A Study in Online Gambling Behavior
 From Habit to Addiction: A Study in Online Gambling Behavior European Association for the Study of Gambling 8 th European Conference 14-17 September 2010 Bill Jolley, Ph.D. Norwich University Deborah Black,
From Habit to Addiction: A Study in Online Gambling Behavior European Association for the Study of Gambling 8 th European Conference 14-17 September 2010 Bill Jolley, Ph.D. Norwich University Deborah Black,
Mindfulness and compassion as the foundations of well-being Saturday 7 October am
 Mindfulness and compassion as the foundations of well-being Saturday 7 October 2017 9am Felicia A. Huppert Emeritus Professor of Psychology and Director of the Well-being Institute, University of Cambridge,
Mindfulness and compassion as the foundations of well-being Saturday 7 October 2017 9am Felicia A. Huppert Emeritus Professor of Psychology and Director of the Well-being Institute, University of Cambridge,
Decision making, cognitive distortions and emotional distress: A comparison between pathological gamblers and healthy controls
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306941573 Decision making, cognitive distortions and emotional distress: A comparison between
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/306941573 Decision making, cognitive distortions and emotional distress: A comparison between
MON 542 Post-Prandial Brain Response to High-Calorie Visual Food Cues is Greater in Obese vs. Lean Children
 MON 542 Post-Prandial Brain Response to High-Calorie Visual Food Cues is Greater in Obese vs. Lean Children Ellen A Schur 1, Susan J Melhorn 1, Kelley Scholz 2,3, Mary Rosalynn De Leon 1, Maya Rowland
MON 542 Post-Prandial Brain Response to High-Calorie Visual Food Cues is Greater in Obese vs. Lean Children Ellen A Schur 1, Susan J Melhorn 1, Kelley Scholz 2,3, Mary Rosalynn De Leon 1, Maya Rowland
The physiology of the BOLD signal What do we measure with fmri?
 The physiology of the BOLD signal What do we measure with fmri? Methods and Models in fmri, 10.11.2012 Jakob Heinzle Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU) Institute for Biomedical Engineering (IBT) University
The physiology of the BOLD signal What do we measure with fmri? Methods and Models in fmri, 10.11.2012 Jakob Heinzle Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU) Institute for Biomedical Engineering (IBT) University
The roles of valuation and reward processing in cognitive function and psychiatric disorders
 Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences The final publication is available from the New York Academy of Sciences via http://dx.doi.org/xx The roles of valuation and reward processing in cognitive function
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences The final publication is available from the New York Academy of Sciences via http://dx.doi.org/xx The roles of valuation and reward processing in cognitive function
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
