Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A Guide for the Recently Diagnosed Individual 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION
|
|
|
- Merryl Foster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A Guide for the Recently Diagnosed Individual 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION
2 DO YOU NEED ACCESS TO INFORMATION, RESOURCES AND PEACE OF MIND? THIS GUIDE IS YOUR KEY TO ALPHA-1 Do you understand Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency? Have you labored over a medical dictionary or struggled with the terms that doctors use? Or wondered what you can do to stay healthy? The Big Fat Reference Guide (BFRG) will help you unlock these answers. It s the most comprehensive resource for living with Alpha-1 available anywhere. With the BFRG, you can understand, manage, and live with Alpha-1. It has detailed information on genetics and on understanding lung disease, discussions on environmental risk factors, suggestions on diet, nutrition, activity and fitness, and much, much more. Plus there is practical information about insurance and disability, and explanations about key terms and the various diagnostic tests. This invaluable resource, available on-line at no cost, was developed by AlphaNet, a not-for-profit health management organization dedicated to improving the lives of patients with Alpha-1. Written by patients and healthcare professionals, it is part of AlphaNet's Disease Management and Prevention Program (ADMAPP), a key service staffed by Alphas to serve Alphas. Use the Big Fat Reference Guide, written in language that you can understand, to learn more and share the insight with your family. Register at to access the BFRG today. This ad courtesy of ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation acknowledges the significant contribution of AlphaNet in developing this comprehensive program for Alphas and for providing over $40 million to support our research mission.
3 A Guide for the Recently Diagnosed Individual The Diagnosis of Alpha-1 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency, also known as AAT Deficiency or Alpha-1, is a medical diagnosis that should lead to open discussions with your doctor and family. Many Alphas, as individuals diagnosed with Alpha-1 are known, live full and productive lives. The following information is designed to help you learn about this inherited disorder so that you and your family can take the necessary preventive measures to stay as healthy as possible. Share this information with your family and your healthcare professional. You may also want to seek professional genetic counseling and contact organizations listed at the end of this brochure to obtain more information. Understanding Alpha-1 Alpha-1 is an inherited disorder that it is present at birth. Alpha-1 may result in the development of serious lung and/or liver disease. Approximately 100,000 people in the United States are estimated to have Alpha-1. In typical individuals, large amounts of the alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) protein are made in the liver and released into the blood. The proteins are made from normal genes, which are an inherited component of every cell that direct specific biological functions. In affected individuals, altered genes make abnormally-shaped AAT proteins. The abnormal protein is retained in the liver and cannot be fully released into the blood, creating a deficiency in your body. Alpha-1 Is: n A genetic disorder inherited from one s parents. n Indicative of a reduced amount or lack of the AAT protein in the blood. n A cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, even in people who have never smoked. n A leading cause of genetic liver disease in infants and children. n Often misdiagnosed. Alpha-1 Can Cause: n Lung disorders, including asthma-like symptoms, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or bronchiectasis. These problems, usually seen in adults, are caused by the AAT protein deficiency and are commonly grouped under the term COPD, which means chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Normal AAT protein levels protect the lung tissue from the destructive effects of white blood cells circulating in that organ. When levels of the protein are low or absent, lung deterioration can occur. n Liver disorders, including elevated liver enzymes, neonatal hepatitis, chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. These problems are due to the accumulation of the abnormal protein in the liver cells. Although less common, Alpha-1 related liver disease can be seen at all ages beginning in infancy. Liver cancer is usually seen only in adults. n Panniculitis, a skin disease created by an excess of white blood cell products. Panniculitis frequently causes painful lumps under or on the surface of the skin. 1
4 Genetics of Alpha-1 In each of us, the normal AAT protein is made from a pair of genes obtained from one s parents. Each parent donates one alpha-1 gene. The normal protein is made from the M gene [See Testing for Alpha-1]. For unknown reasons, there are close to 100 altered or abnormal variants of the M gene, also called alleles, but only a few can cause serious lung, liver or skin disorders. Two important alleles are the S and Z gene variants. An individual with different gene variant pairs, such as the MZ genes, is called a heterozygote. Someone with similar gene variant pairs, such as the ZZ combination, is called a homozygote. Individuals with one normal and one variant alpha-1 gene are called carriers. Alphas can have parents who are both carriers, one parent who is a carrier and one who is severely deficient, or two parents who are severely deficient. Risks Associated With Common Genetic Variants Normal (MM): Does not have the disorder and does not carry any altered alpha-1 genes. Carrier (MS): It is unclear whether there is a risk for developing disease symptoms but this individual does have an altered alpha-1 gene. Most studies do not indicate an increased risk for disease. Carrier (MZ): An MZ carrier may have a mild AAT protein deficiency but rarely develops disease symptoms even though he/she does carry an altered gene. ALPHA-1 (SZ) or (ZZ) or (NULL NULL): Moderate (SZ) to severe (ZZ, Null Null) AAT deficiency. This individual could develop Alpha-1-related disease and has two altered alpha-1 genes. How Alpha-1 Is Inherited FIGURE 1 Affected by Alpha-1 Carrier of an Alpha-1 Gene No Alpha-1 *Spouses are indicated by a blue outline 2
5 Testing For Alpha-1 The diagnosis of Alpha-1 is usually determined by three rather sophisticated laboratory tests that require a small sample of blood. The tests: 1. Measure the level of the AAT protein in your blood 2. Characterize the phenotype of the protein in the blood, and 3. Determine the patient s alpha-1 genotype. Alpha-1 Blood Levels Most commercial medical laboratories can measure AAT protein blood levels. Clinically-significant deficiency exists when the blood levels are less than 80 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) or 11 micromolar (um). Patients with such low levels are called Alphas or are frequently noted to have Alpha-1. Alpha-1 Phenotype This test characterizes the type of alpha-1 gene (for example, MM, MZ, SZ, or ZZ) that circulates in your blood by visualizing the movement of the protein in a special electric field. Close to 100 types of alpha-1 gene variants producing AAT protein have been identified, yet each person has only one type of protein. The SZ and ZZ phenotypes are the most common genetic patterns associated with the lowest blood levels (the most serious deficiencies) of the AAT protein. Alpha-1 Genotype The genotype is determined through a test that identifies the actual genetic variants producing the AAT protein. This test detects the S and Z alleles with great accuracy. Most medical laboratories report AAT blood levels and phenotypes; special laboratories must determine genotypes. Your physician can suggest the best testing strategy for you and your family members. Lung Symptoms of AAT Deficiency If you have respiratory symptoms, you and your physician may observe: n Shortness of breath while at rest or with exercise n Wheezing, persistent cough n Recurrent lung infections n Persistent sputum (or phlegm) production n History of suspected allergies and/or asthma n Sinus infections Possible Liver Symptoms n Increased liver enzymes detected via a blood test ordered by a physician n Jaundice or yellowing of the eyes and skin n Enlarged liver and/or spleen, which may be noted by the patient, parent of child, or physician n Ascites or fluid collection in the abdomen n Cirrhosis, an excessive accumulation of scar tissue in the liver noted by a physician n Vomiting of blood n Persistent itching n Noticeable change in energy level or becoming easily fatigued n Blackish, purplish, dark or pale-colored stools n Poor appetite Even Alphas May Not Have Signs or Symptoms Even without symptoms, you should follow the recommendations in the next sections. If you practice a healthy lifestyle and obtain appropriate medical care, you may remain healthy. However, this does not mean that you will not have symptoms in the future, so monitoring of your medical condition by a healthcare provider is suggested. You may request a copy of the Alpha-1 Foundation s Healthcare Provider s Guide to give to your doctor. What Does Having Alpha-1 Mean to Me? The following sections deal with issues that are potentially major concerns for Alphas. The resources listed at the back of this brochure provide advice and support as does AlphaNet's Big Fat Reference Guide (see inside front cover). In addition, genetic counseling can provide the support and knowledge needed for informed decisions. 3
6 Having Alpha-1 May Require: Changes In Lifestyle If you or your child has Alpha-1, it may be necessary to make lifestyle changes to stay healthy, including: n Quitting smoking and keeping the Alpha adult or child away from second-hand smoke n Avoiding exposure to dust and fumes n Exercising regularly n Eating well n Drinking alcohol with caution, if at all. The consumption of alcoholic beverages can cause damage to the liver in normal people. Many authorities recommend low, infrequent or no alcohol consumption for ZZ patients, and patients with any indication of liver damage should avoid alcohol completely. n Review labels of over-the-counter medications, vitamins or herbal supplements carefully. Avoid products with acetaminophen and alcohol, both of which can injure the liver. n Advise your healthcare provider if you are taking vitamin supplements or herbal products. Environmental Awareness Environmental recommendations include avoiding pollutants that irritate the lungs, as well as avoiding liver toxins. Individuals should assess their home and work environments carefully, and consult with an occupational medicine specialist if indicated. Examples of such environmental irritants are: n Cigarette smoke, from personal smoking or second-hand tobacco smoke n Industrial and occupational pollutants such as dust, flower and tree pollen, ash, volatile compounds, fumes and other allergens n Air pollution n Wood-burning stoves n Fumes from cleaning solvents such as bleach, ammonia or household and industrial cleaners n Paints and/or toxic agents n Precautions should also be taken when handling chemicals and other materials, as those may be absorbed through the skin. The liver detoxifies poisonous chemicals that enter the body. If the liver is damaged, the detoxification process is altered. Increased Doctor Visits Alphas should seek expert medical treatment and may need to visit their healthcare provider more often. Various Treatments Alphas have various treatment options, depending upon their symptoms. The most common are: n Behavioral and lifestyle modification treatments n Medication therapy for lung problems n Surgical therapy for lung disease n Procedural treatments for the complications of liver disease n Organ transplantation What Do I Do Now? Individuals with Alpha-1 should NEVER smoke. Evidence shows that smoking tobacco products significantly increases the risk and severity of emphysema in Alphas and may decrease their lifespan by as much as ten years or more. Exercise and nutritional programs also contribute to maintaining a healthier body. You must aim to achieve and maintain a healthy lifestyle by adopting the following recommendations: 4
7 Smoking Cessation If you smoke, it is extremely important that you quit. This is necessary because smoking destroys the small amount of AAT protein in the lungs of those affected by the disorder and attracts white blood cells that have cell-damaging enzymes. These damaging enzymes speed the development of lung disease. If you are an Alpha, your lungs do not have the normal defenses against white blood cells. If your child has been diagnosed with Alpha-1, it is important to protect them from exposure to second-hand smoke. Educate your children on the dangers of smoking and the importance of avoiding second-hand smoke. Avoid Pollutants and Infection You should avoid occupational and environmental pollutants that can be inhaled, including pollen, dust, or organic fumes, and second-hand tobacco smoke. These substances can irritate your lungs, and cause or worsen lung problems. Chemicals can also be absorbed through the skin and thus damage the liver. Avoid air pollution and aerosolized sprays at all times. It is also important to realize that you may encounter pollutants and infections, both at home and at work. In The Workplace Avoid exposure to inorganic or organic dust, (coal, hay, etc.) or irritating gases (chlorine, isocyanates, etc.). Seek the healthiest possible work environment. Demand clean indoor air, with proper ventilation and filtration systems, and avoid second-hand tobacco smoke. Wear protective clothing such as rubber gloves when in contact with chemicals or other agents, many of which can be absorbed through the skin. Read labels closely. As previously suggested, consult with an occupational medicine specialist if you have any concerns about the specific effects of work-related exposures to your lungs and liver. In The Home You should avoid: n Household chemicals n Respiratory irritants from wood-burning stoves, dust and pollen, or second-hand smoke n Chlorine and ammonia, which are found in common household cleaning products n Pesticides n Pet dander Since bacterial and viral infections are harmful to the lungs, avoid contact with sick or infectious people whenever possible. Hand washing with soap is the single most effective way to avoid both contracting and spreading infectious diseases. Carry a hand disinfectant gel with you for times when hand washing is not possible. Develop An Exercise Program Routine exercise improves mental outlook, stamina and physical well-being. Exercise is essential to all Alphas. It is important to exercise muscles in the chest and upper body that are related to breathing as well as the large muscles of the legs. Walking Programs Walking programs (particularly in climate-controlled indoor shopping malls), strolling, swimming, and/or biking may improve your lung function and endurance. A Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercise Program A Pulmonary Rehabilitation Exercise Program (PREP) is highly recommended for Alphas with all stages of lung disease or pulmonary problems. A PREP that includes exercise, breathing retraining, education, smoking cessation, and nutritional counseling may help you achieve your fullest level of activity. As with all exercise programs, a PREP should be discussed with and recommended by your healthcare professional. Personal Exercise Plan You may want to have a personally tailored exercise program that is carefully monitored by your healthcare provider and/or exercise specialist. Start exercising slowly and build the intensity of your program over time as your tolerance increases. 5
8 Develop A Nutrition Program Proper eating habits may help to preserve lung and liver function; therefore you should establish or maintain good eating habits. Maintaining an ideal body weight, whether or not you have lung and/or liver disease, is important. Additionally, some scientific research indicates that people with lung disorders need to consume more calories than lung-healthy people. If you have lung and/ or liver problems, consider working with a nutritionist or registered dietician to set up an individualized nutrition program. The nutritional needs of patients with Alpha-1 related liver complications are highly individualized. Since fluid retention is common, sodium and protein intake may become a concern, and, good nutrition is advised. For instance, processed foods have high sodium content, so Alphas should read nutritional labels carefully. Vegetable sources of protein are better than those from animals. Vitamin A, B3 (Niacin), and iron supplements may stress an already compromised liver. In Alphas with signs of liver complications, fat absorption may be altered; therefore, your healthcare provider may recommend supplementing the diet with vitamins A, D, E and K. In the infant that is experiencing feeding difficulties, shows poor growth and a failure to thrive, a special formula is often recommended. Sometimes, total parenteral nutrition (TPN) may be necessary. Reduce Stressors Alphas report benefits with stress reduction techniques, including many relaxation exercises. These relaxation techniques may also contribute to a positive outlook on life and may prevent depression. Here are a few options to consider: n Yoga n Meditation n Breathing exercises n Muscle relaxation n Biofeedback n Visualization n Hypnotherapy n Positive thinking What Are the Current Treatments for Alpha-1? You may benefit from lifestyle modification. However, if you have lung and/or liver disease, seek expert medical care to treat your condition(s). There are specialized Clinical Resource Centers specializing in Alpha-1 throughout the United States. These centers are staffed with a healthcare team to provide medical treatment, and behavioral and lifestyle modification guidelines specifically for Alphas. To see if there is one in your area, please check the Foundation s website, Vaccinations n It is important for you to have annual flu shots. The use of these prophylactic or preventive vaccinations is of the utmost importance. n The Pneumovax vaccine may help prevent pneumonia. Consider repeating the pneumonia shot every six years. n Discuss the vaccines for Hepatitis A and B with your healthcare provider. Aggressive Treatment Of Lung Infections It is important to notify your healthcare provider immediately when you suspect a lung infection. Because the lungs contain more white blood cells when you have an infection (and hence, more destructive enzymes), it may be necessary to take antibiotics to fight the infection. These are some symptoms to watch for: n Fever (with or without chills) n Increased shortness of breath n Increased coughing n Changes in color or thickness of sputum (phlegm) Additional Preventive Measures Wash your hands frequently with soap to prevent the passage of viral or bacterial infections. 6
9 Therapies For Alpha-1 Lung Disease Antibiotics Bacterial infections in the lung can lead to a dramatic influx of white blood cells into the organ s tissue and airways, which may be one of the major causes of lung destruction in Alpha-1. To minimize this risk, many physicians advocate aggressive antibiotic treatment at the first signs of a lung infection. Even though pulmonary exacerbations may not be caused by bacterial infection or may be due to a virus, which would not be expected to benefit from antibiotics, the benefits of this aggressive approach may, in some patients, outweigh the risks of antibiotic overuse. These risks include encouraging the growth of antibioticresistant bacteria, overgrowth of yeast and other agents that can lead to disease, and allergic reactions. Bronchodilators Some of the symptoms of Alpha-1 are similar to common lung diseases such as asthma and COPD. Medications called bronchodilators usually administered via inhalers, may be useful in relieving lung symptoms. Sometimes, different types of bronchodilators are combined, to achieve maximum benefit. These medications allow better airflow in and out of the lungs by relaxing smooth muscle that surround the airways. Corticosteroids Based on your healthcare provider s recommendation, the use of corticosteroids (or simply, steroids) can be an appropriate treatment for lung symptoms in some individuals. Steroids help reduce inflammation within and around the airways, and can be administered by inhalation, in pill form, or intravenously (into a vein). Steroids administered by mouth or vein are usually reserved to treat severe lung problems. Supplemental Oxygen Supplemental oxygen can be important and lifesaving therapy for individuals with low blood oxygen levels. Some people, however, need supplemental oxygen primarily during exercise or with sleep. For some, it is especially important when traveling by air or at high altitudes. Ask your healthcare provider about your need for this treatment. Augmentation Therapy Augmentation therapy, the process of receiving ATT protein that has been purified from the blood of human donors with normal alpha-1 genes, is appropriate for many Alphas with lung problems. As its name suggests, it increases, or augments, the protein levels in the blood. Augmentation therapy is usually given intravenously once per week. Augmentation therapy is not a cure; it will not reverse lung damage that has already occurred, nor treat or prevent liver problems related to Alpha-1. Currently, augmentation therapy can only be prescribed for individuals with Alpha-1-related emphysema under supervised professional care. Surgery Options Your healthcare provider may evaluate the need for one of the two types of surgery recommended for patients with severe Alpha-1: lung volume reduction and lung transplantation. Lung Volume Reduction Lung volume reduction may improve breathing by physically removing some of the most damaged lung tissue. The benefit is variable and may last only a few years. Lung Transplantation Lung transplantation for one or both lungs is an option for some Alphas with severe lung disease. Lifelong drugs to suppress the immune system are required afterward. As with all surgery, the outcomes and quality of life after such procedures depend on a number of issues specific to each person. Please consult with your healthcare professional about these options. 7
10 Therapies For Alpha-1 Liver Disease Augmentation Therapy There is no proven role for augmentation therapy to treat the liver manifestations of Alpha-1. General Treatment Of Liver Complications It is important for parents, caregivers, or significant others to be aware and advised of any indication of possible complications related to liver disease. Additional discussion and references concerning the diagnosis and treatment of severe liver disease can be found in the brochure entitled The Liver and Alpha-1. Once liver injury is identified in an Alpha, the first course of action is to evaluate your lifestyle for ingestion of potential liver toxins, such as alcohol, large doses of certain vitamins, and some medications. As with the pediatric population, careful follow-up of abnormal liver function is needed. Liver disease is treated symptomatically and preventatively. In adults, symptoms such as vomiting blood may occur suddenly with no prior indication of illness. Substances in some medications may be harmful to your liver. These include both prescription and over-thecounter formulas with acetaminophen or alcohol, and nutritional supplements such as vitamins, herbs, and protein drinks. Make a list of any medicines you use and review it with your healthcare provider. Often, the liver injury can prove to be mild and temporary. Medical/Surgical Procedures There are several treatment options that may become necessary to improve the symptoms of advanced liver disease. These include: n Large volume paracentesis (LVP), which is the removal of fluid from the abdomen. n Banding or sclerotherapy of veins in the esophagus to reduce bleeding from distended or swollen veins. Banding involves using rubber bands to stop blood flow. Sclerotherapy involves the injection of a chemical irritant which causes blood flow to shift to nearby healthy blood vessels from the diseased vein. n Portal vein decompression, which reduces the pressure in the blood vessels entering the liver from the digestive organs. This is a major surgery utilizing shunts to reroute blood flow to the liver and reduce the pressure in the blood vessel. The latter two options help control the increased risk for bleeding in those with advanced liver disease. Liver Transplantation Liver transplantation can dramatically improve the symptoms of advanced liver disease caused by Alpha-1. Because the organ recipient will begin to produce the protein of the donor liver, alpha-1 protein levels should be normal after the transplant. The option of livingdonor liver transplantation is available at some transplant facilities. If you decide to explore this option, check with the transplant center first to be certain that this choice is available to you. 8
11 Other Issues Of Concern For Alphas Listed below are some issues that you may face after diagnosis. These are merely a starting point for discussion with your physician, genetic counselor, or pastoral care advisor. Awareness Consider wearing a medical alert bracelet or necklace that lists important medical information. Psychosocial/Family Support Q: What do I tell family members? A: We recommend that you inform blood relatives of the test result because of the genetic nature of the disorder. Q: Should I urge family members to be tested? A: After consulting with your healthcare provider, it is reasonable to encourage your blood relatives to seek testing. Because of the genetic nature of Alpha-1, your blood relatives could be carriers or have the disorder themselves. Issues related to genetic discrimination in employment and insurance need to be considered, however. Confidential medical testing for Alpha-1 is available through a research study at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC); call for more information. Health Insurance Q: Will the Alpha-1 diagnosis affect my health insurance? A: It may. The answer to this question depends on your current insurance coverage. If you are insured, it is important that you educate yourself about your specific insurance policy and benefits related to coverage and reimbursement. Under the Affordable Care Act, insurers are no longer allowed to deny you coverage or charge you more based on a pre-existing medical condition. They also can t place annual limits on medical coverage of essential health benefits, which include prescription drugs and hospitalization. You are also likely to be eligible for some preventive services such as breast cancer screenings and cholesterol tests, with no out-of-pocket costs. Health plans can t cancel your coverage if you get sick a practice known as recission unless you committed fraud when you applied for coverage. The Affordable Care Act also requires many people to enroll in health insurance if they currently don t have any; offers insurance subsidies; and contains tax penalties for not having coverage. The requirement to have coverage can be waived for reasons including financial hardship or religious beliefs. For more information, see the Foundation website, Employment Q: Can I continue to work? A: The answer to this question usually depends upon two conditions: n The present state of your health, and n The possibility of unwanted airborne exposures such as dust and fumes at work, or other hazardous chemicals that might be in contact with your skin. Work is good for your mental and emotional wellbeing. If, after discussion with your doctor, you are physically able to do so and can avoid occupational hazards, you should continue to work. Otherwise, your healthcare provider may suggest changing jobs to reduce these exposures. Please note that your eligibility to continue health insurance coverage may vary from state to state. If you change jobs after diagnosis, the issue of disclosure of your disorder may also affect your future coverage. Q: What is the role of disability insurance? A: If your physical condition does not allow you to work, discuss your eligibility for disability insurance payments with your healthcare provider and other professionals familiar with these benefits. Confidentiality Q: Who will know that I have Alpha-1? A: The results of your test will be included in your medical record. Although generally treated as confidential, insurance companies, healthcare facilities and other professionals may access this information, which may affect future employment and insurance benefits. You may obtain confidential Alpha-1 testing through the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC). Q: To whom should (or must) I disclose my diagnosis? A: You must make your own decisions about releasing this information. However, it is highly recommended that you tell blood relatives about their inherited risk of Alpha-1 and urge them to be tested. You should also inform future healthcare providers. You may be required to inform insurance companies if you change insurance policies. Finding out about an Alpha-1 diagnosis can be an overwhelming and potentially upsetting experience. It is important to share this information with family and seek professional counseling, if necessary. We recommend calling the Alpha-1 Foundation Genetic Counseling Program at This is a free and confidential service. 9
12 Glossary Of Terms Allele: Another general name for the altered form of a gene. For example, the Z allele is an altered form of the M gene. There are many different alpha-1 gene alleles. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Protein: The alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) protein is primarily made in the liver, which releases it into the bloodstream in typical individuals. The alpha-1 protein has many functions, one of which is to protect delicate tissue in the body from being destroyed by neutrophil elastase, a tissue-digesting enzyme most commonly found in circulating white blood cells. These enzymes are released into tissue when the white blood cells fight infection. Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1): A genetic condition caused by the inability to pass the AAT protein out of the liver, which creates a deficiency throughout the body. People with Alpha-1 might develop liver problems or lung diseases such as emphysema, or a skin disorder known as panniculitis. Others do not have any symptoms or illness. Ascites: Fluid collection in the abdomen. Antibiotics: Antibiotics are drugs that can kill or stop the growth of bacteria. Sometimes the term is used to describe drugs that can treat any infections such as those caused by bacteria, fungus, tuberculosis, and even viruses. Asthma: A condition of the lungs characterized by widespread narrowing of the airways due to spasm of the smooth muscle, swelling of the mucous membrane lining the respiratory tract, and the presence of mucus in the inner spaces of the airway branches leading to the lungs. Augmentation Therapy: Intravenous administration of the alpha-1 antitrypsin protein purified from human blood. Bilirubin: Bilirubin is a by-product of red blood cell breakdown that is normally formed in the liver. It creates the yellow tinge of normal serum, the yellow-green hue of bile, the brown color in stools, and the yellow color of urine. When the liver is not functioning normally, the bilirubin level can rise, which causes jaundice, a yellowing of the eyes and skin. Biopsy: The term biopsy is used to describe both a procedure to remove tissue from an organ or a piece of tissue that is being examined under a microscope. There are three basic types of biopsies: a fine needle biopsy, a core needle biopsy, and a wedge biopsy. Bronchiectasis: Chronic dilation or widening of the bronchial tubes within the lung signals bronchiectasis. It is often caused by inflammatory diseases or obstruction and leads to chronic lung infection. Cholestasis: A backup of bile in the liver; may result in jaundice, dark urine, pale stools, and itching. Chronic Bronchitis: A lung disease characterized by inability to move air in and out of the lung combined with the production of sputum on most days of the year. This is one of the diseases caused by cigarette smoking. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): COPD is a broad category of lung problems including emphysema, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, and chronic asthma in adults. A main component of all these diseases is the obstruction of inhalation and exhalation. COPD is responsible for more than 100,000 deaths each year and is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is extensive scarring and hardening of the liver. This condition is most often associated with advanced liver disease. 10
13 Corticosteroids (Steroids, Prednisone): A class of drugs modeled after hormones released by the body s adrenal glands. They are the most potent anti-inflammation drugs currently available and can be lifesaving to people with severe COPD and asthma, but they re also known for having serious side effects. Emphysema: A lung disease that involves damage to the alveoli or air sacs in the lungs. In emphysema, the damaged air sacs do not deflate normally so breathing is harder. Lungs with emphysema may be slow to expel used-up air and unable to fill with enough fresh air to ensure an adequate oxygen supply to the body. In Alphas, the lungs actually become hyper inflated or enlarged, and the emphysema occurs mainly in the lower lungs since that is where most of the AAT-deficient blood flows. Smoking related emphysema is usually in the upper lungs. An Alpha who smokes or has smoked may have emphysema throughout their lungs. Esophageal Varices: Enlarged veins in the esophagus resulting from the increased pressure in the portal vein through which blood flows into the liver. This commonly occurs in cirrhosis. Fibrosis Of The Liver: The presence of scar tissue made of collagen within the framework of the liver tissue. When the liver is badly scarred, the organ will not function properly. Genes: Genes are sections of DNA that determine specific human characteristics; 25,000 genes exist. Each parent gives you one gene that can alone, or in combination, result in certain characteristics. Genes also hold the instructions for making proteins, each of which has a different function in the body. Genotype: The human genome is a very long complex combination of gene sequences. The genotype is a description of the variation of the sequence of a particular gene. The specific change in an individual s alpha-1 gene sequence, known as a genotype, determines their specific characteristics, which is their phenotype. Hepatitis: Inflammation of the liver which can be caused by viruses, abnormalities of the immune system, and medications, as well as Alpha-1. Hepatomegaly: Enlargement of the liver. In some cases, the liver can be felt below the rib cage. Hepatosplenomegaly: Enlargement of the liver and the spleen. Heterozygote/Homozygote: Every cell of the body is composed of genes and every gene is actually a pair of alleles, one from the father and one from the mother. If your mother and father each give you the same allele, this gene is called a homozygote. If your mother and father each give you a different allele, this gene is called a heterozygote. Heterozygotes most often have one normal allele (M) and one abnormal allele (Z), a combination known as MZ. Alphas that are homozygotes have two abnormal genes, such as ZZ. Icteric: Yellowing of the whites of the eyes associated with jaundice. Influenza: Commonly known as the flu, influenza is an acute, contagious viral infection, commonly occurring in epidemics. It is characterized by inflammation of the respiratory tract and by the sudden onset of fever, chills, muscular pain, headache and severe fatigue. Jaundice: A condition characterized by a yellowish tint of the skin, white portion of the eye, tissue lining of the mouth, and body fluids due to excess bilirubin in the blood. Liver Enzymes: Proteins (specifically enzymes) found in high concentration in the liver and lower amounts in the blood and body tissue. The enzymes are released into the blood when liver cells are injured. Doctors can measure the amount of enzyme released from cells and estimate the extent of liver damage using the AST (or SGOT), ALT (or SGPT), alkaline phosphatase, and GGT-P tests. There are other blood tests to monitor liver function that are commonly performed as well. 11
14 Micromolar: Abbreviated as µm, it is used to designate the amounts of alpha-1 antitrypsin protein when serum levels are tested. A person is considered deficient in AAT protein when their serum level is 11 µm or below. Milk Thistle: This is an herb with an active ingredient called silymarin. Milk thistle is thought to be helpful for individuals with liver disease due to silymarin s cleansing and protective properties. It is extremely important that your healthcare provider be informed if you take, intend to take or intend to give this herb to your child. The National Institute of Health's National Advisory Council for Complementary and Alternative Medicine is currently studying this herb extensively. Panniculitis: Panniculitis is an inflammation within the layers of fat beneath the skin which causes the skin to may harden and form extremely painful lumps, patches, or lesions. It is likely that the damage is initiated by destructive action of unrestrained neutrophils. In some patients, damage from panniculitis occur after an incident of trauma to the affected area. It occurs in children as well as adults, and has been linked to the ZZ and MZ phenotypes and possibly other alleles as well. Phenotype: The specific characteristic or type of ATT protein circulating in your blood; it is genetically determined by the alpha-1 genes received from your mother and father at birth. Other environmental factors may affect these characteristics. Phlegm: Thick, sticky, stringy mucus secreted by the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, as during a cold or other respiratory infection. Pneumonia: An acute or chronic disease marked by inflammation of the lungs and caused by viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms and sometimes by physical and chemical irritants. Portal Hypertension: Blood flows from veins in the stomach, intestines, spleen and pancreas and goes into the liver through the portal vein. When the liver is diseased and unable to function properly, this blood flow is impaired, and pressure builds in the portal vein, which can cause a number of problems. This condition is known as portal hypertension. Pruritus: Medical term for itching. Sclerotherapy: A procedure that may be used in the treatment of bleeding from varices in the esophagus. Intravenous medication is injected directly into the enlarged veins to stop the bleeding. Spleen: An organ that is a part of the lymphatic system in the human body. It functions as the body s defense mechanism, is involved in the formation and destruction of certain blood cells, and acts as a blood reservoir. Blood from the spleen goes into the liver. Splenomegaly: Splenomegaly, an enlarged spleen, occurs when the spleen has a disease or when portal hypertension develops due to liver disease. Sputum: Matter coughed up and usually expelled from the mouth, especially mucus or pus that is expectorated (ejected or spit) in diseases of the air passages. TPN: Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) is the administration of nutritionally-adequate solution intravenously; TPN may become necessary to provide nutrition to individuals with severe liver damage. Vitamins A, D, E, K: Fat-soluble vitamins that are necessary for proper nutrition and are frequently prescribed as dietary supplements when severe liver disease prevents their absorption into the blood stream. 12
15 Where Do I Get More Information? Below are a number of organizations that help and support people with Alpha-1. Each of these organizations works with Alphas in unique ways. Alpha-1 Foundation Toll Free: (877) The not-for-profit Foundation provides resources, education, and information on testing and diagnosis for healthcare providers and people affected by Alpha-1. It funds cutting edge research to find treatments and a cure and supports worldwide detection of Alpha-1. AlphaNet Toll Free: (800) AlphaNet assists patients and families with support, education and strategies to manage their health. It also sponsors clinical trials for Alpha-1 therapies and produces The Big Fat Reference Guide to Alpha-1, a complete guide to understanding, managing and living with Alpha-1, and includes key terms, testing, genetics, and treatment options. It is available through the website or number listed above. The Alpha-1 Research Registry Toll Free: (877) The Research Registry is a confidential database of Alphas and carriers. The Registry gives patients the opportunity to provide information to help advance research on the disorder through questionnaires and clinical trials. It also provides access to experts on Alpha-1 care. Individuals enrolled in the Registry have the ongoing opportunity to participate directly in clinical trials of new therapeutic approaches, in addition to other research opportunities. Alpha-1 Foundation Patient Information Line Toll Free: (800) The Patient Information Line is available free of charge to anyone affected by Alpha-1 and provides support to newly diagnosed Alphas, Alphas seeking basic information, or help such as requesting a peer guide, physician referral, requests for literature, etc. Alpha-1 Foundation Genetic Counseling Program Toll Free: (800) The Genetic Counseling Program offers free phone-based confidential information and resources to Alphas, family members and medical professionals. It provides information on the genetics of Alpha-1 and testing options. Alpha-1 Foundation Support Network Toll Free: (855) The Support Network is a collective of more than 80 Support Groups including four Virtual Support Groups. These groups are committed to improving the quality of life of individuals and their families affected by Alpha-1 and to extending the mission of the Alpha-1 Foundation. Alpha-1 Kids (877) Alpha-1 Kids provides support and information for parents and children with Alpha-1. American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (703) This is the leading organization of scientists and healthcare professionals committed to preventing and curing liver disease. American Liver Foundation Toll Free: (800) The Foundation provides information on prevention, treatment and potential cures for liver diseases. American Lung Association (ALA) Toll Free: (800) The ALA focuses on the prevention of lung disease through educational programs, research and advocacy. Children s Liver Association for Support Services Toll Free: (877) This group serves the emotional, educational and financial needs of families and children with liver disease. Cholestatic Liver Disease Consortium (720) The Consortium provides support and information for children and families with rare cholestatic liver diseases. For information on liver issues related to AAT, visit this website and click on the Alpha-1 link.
16 1 The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people affected by Alpha-1 worldwide. The Foundation has invested more than $50 million to support Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency research at 97 institutions in North America, Europe, the Middle East and Australia. The Foundation also offers an array of programs for people diagnosed with Alpha-1, their families, caregivers and healthcare providers. For more information about the Alpha-1 Foundation, visit (877) 2 CURE A1 1 (877) PONCE DE LEON BLVD. CORAL GABLES, FL Unrestricted educational grants provided by: Grifols Dohmen Life Science Services AlphaNet 2006 Alpha-1 Foundation, Version 1.7 (07/14) PR e
1 ALPHA-1. Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? FOUNDATION FOUNDATION. Learn how being an Alpha-1 carrier can affect you and your family
 Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people affected by Alpha-1 worldwide.
Am I an Alpha-1 Carrier? 1 ALPHA-1 FOUNDATION The Alpha-1 Foundation is committed to finding a cure for Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and to improving the lives of people affected by Alpha-1 worldwide.
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A Guide for the Recently Diagnosed Individual
 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A Guide for the Recently Diagnosed Individual DO YOU NEED ACCESS TO INFORMATION, RESOURCES AND PEACE OF MIND? THIS GUIDE IS YOUR KEY TO ALPHA-1 Do you understand Alpha-1
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency A Guide for the Recently Diagnosed Individual DO YOU NEED ACCESS TO INFORMATION, RESOURCES AND PEACE OF MIND? THIS GUIDE IS YOUR KEY TO ALPHA-1 Do you understand Alpha-1
A GUIDE TO ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY
 A GUIDE TO ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY DO YOU OR YOUR FAMILY MEMBERS SUFFER ANY OF THESE CONDITIONS? Asthma Jaundice Early onset emphysema Abnormal liver function Chronic bronchitis Recurrent chest
A GUIDE TO ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY DO YOU OR YOUR FAMILY MEMBERS SUFFER ANY OF THESE CONDITIONS? Asthma Jaundice Early onset emphysema Abnormal liver function Chronic bronchitis Recurrent chest
LIVER CIRRHOSIS. The liver extracts nutrients from the blood and processes them for later use.
 LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
LIVER CIRRHOSIS William Sanchez, M.D. & Jayant A. Talwalkar, M.D., M.P.H. Advanced Liver Disease Study Group Miles and Shirley Fiterman Center for Digestive Diseases Mayo College of Medicine Rochester,
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
 Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency This information is for people in the UK who have been diagnosed with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, their families, friends and carers. It explains what alpha-1-antitrypsin
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency This information is for people in the UK who have been diagnosed with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, their families, friends and carers. It explains what alpha-1-antitrypsin
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Alpha-1 Lung Disease
 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Alpha-1 Lung Disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) affects millions of people each year. Chronic means long term, obstructive means it is hard to get air in
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Alpha-1 Lung Disease Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) affects millions of people each year. Chronic means long term, obstructive means it is hard to get air in
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency: Liver Disease
 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency: Liver Disease Who is at risk to develop Alpha-1 liver disease? Alpha-1 liver disease may affect children and adults who have abnormal Alpha-1 antitrypsin genes. Keys to
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency: Liver Disease Who is at risk to develop Alpha-1 liver disease? Alpha-1 liver disease may affect children and adults who have abnormal Alpha-1 antitrypsin genes. Keys to
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Cough Associated with Bronchitis
 Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
Cough Associated with Bronchitis Bronchitis (bron-ki-tis) is a condition in which the bronchial tubes, the tubes that carry air to your lungs, become inflamed. People who have bronchitis often have a cough
COPD. The goals of COPD. about. you quit. If you. efforts to quit. Heart
 How Is COPD Treated? COPD has no cure yet. However, lifestyle changes and treatments can help you feel better, stay more active, and slow the progress of the disease. The goals of COPD treatment include:
How Is COPD Treated? COPD has no cure yet. However, lifestyle changes and treatments can help you feel better, stay more active, and slow the progress of the disease. The goals of COPD treatment include:
RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 RESPIRATORY DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Respiratory disorders refers to the medical term that include different pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues of respiratory system which make gas
RESPIRATORY DISORDERS INTRODUCTION Respiratory disorders refers to the medical term that include different pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues of respiratory system which make gas
Emphysema. Lungs The lungs help us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Everyone is born with 2 lungs: a right lung and a left lung.
 Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects millions of people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This makes
Emphysema Introduction Emphysema is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD. COPD affects millions of people worldwide. Emphysema involves damage to the air sacs in the lungs. This makes
COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes. Chapter 7
 COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes Chapter 7 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD 4 th leading cause of death in the U.S. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Any chronic conditions
COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes Chapter 7 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD 4 th leading cause of death in the U.S. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Any chronic conditions
Could Your Asthma or COPD be Hereditary?
 Could Your Asthma or COPD be Hereditary? A Guide to Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Registered Charity England & Wales 1146330 : Scotland SC043177 Could your asthma or COPD be caused by an hereditary condition
Could Your Asthma or COPD be Hereditary? A Guide to Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Registered Charity England & Wales 1146330 : Scotland SC043177 Could your asthma or COPD be caused by an hereditary condition
What Is Cirrhosis? CIRRHOSIS. Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is. by chronic conditions and diseases. permanently scarred or injured
 What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
Self-study course. Pneumonia
 Self-study course Pneumonia This brochure is available in alternate formats. Call 1-800-282-8096 (V/TTY) 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1) Identify a series of steps
Self-study course Pneumonia This brochure is available in alternate formats. Call 1-800-282-8096 (V/TTY) 2 Course objectives: At the end of this course you will be able to: 1) Identify a series of steps
ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER S GUIDE
 ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER S GUIDE Foreword Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) is one of the most common serious hereditary disorders. Alpha-1 has been identified in virtually
ALPHA-1 ANTITRYPSIN DEFICIENCY A HEALTHCARE PROVIDER S GUIDE Foreword Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) is one of the most common serious hereditary disorders. Alpha-1 has been identified in virtually
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION
 Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
What Is This Module About? What Will You Learn From This Module?
 What Is This Module About? Breathing is very important and natural to man. Every breath means life. Do you know what system of the human body helps us breathe? What elements in air does man need to live?
What Is This Module About? Breathing is very important and natural to man. Every breath means life. Do you know what system of the human body helps us breathe? What elements in air does man need to live?
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. Healthcare Provider s Guide
 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Healthcare Provider s Guide FOREWORD Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) is one of the most common serious hereditary disorders. Alpha-1 has been identified in virtually
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Healthcare Provider s Guide FOREWORD Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (Alpha-1) is one of the most common serious hereditary disorders. Alpha-1 has been identified in virtually
People with asthma who smoke. The combination of asthma, a chronic airway disease, and smoking increases the risk of COPD even more.
 COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
Welcome to the Hepatitis C Education Class
 Welcome to the Hepatitis C Education Class Topics of the Class Your liver Types of hepatitis How hepatitis C is spread How to protect your liver Treatment for hepatitis C What is the Liver? Makes chemicals
Welcome to the Hepatitis C Education Class Topics of the Class Your liver Types of hepatitis How hepatitis C is spread How to protect your liver Treatment for hepatitis C What is the Liver? Makes chemicals
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
Living well with COPD
 This factsheet aims to show people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and their friends and family how they can live a full life with this disease. What is COPD? COPD is a condition that
This factsheet aims to show people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and their friends and family how they can live a full life with this disease. What is COPD? COPD is a condition that
What is Hepatitis? Hepatitis A
 What is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is inflammation and swelling of the liver that can be caused by certain drugs, alcohol, toxins, autoimmune disorders or viral infections. Viral hepatitis will be the topic
What is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is inflammation and swelling of the liver that can be caused by certain drugs, alcohol, toxins, autoimmune disorders or viral infections. Viral hepatitis will be the topic
COPD COPD. C - Chronic O - Obstructive P - Pulmonary D - Disease OBJECTIVES
 COPD C - Chronic O - Obstructive P - Pulmonary D - Disease 1 OBJECTIVES Following this presentation the participant should be able to demonstrate understanding of chronic lung disease by successful completion
COPD C - Chronic O - Obstructive P - Pulmonary D - Disease 1 OBJECTIVES Following this presentation the participant should be able to demonstrate understanding of chronic lung disease by successful completion
COPD. Helen Suen & Lexi Smith
 COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
Cirrhosis. A Chronic Liver Problem
 Cirrhosis A Chronic Liver Problem What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a chronic (long-lasting) liver problem. It results from damaged and scarred liver tissue. Cirrhosis can t be cured, but it can be treated.
Cirrhosis A Chronic Liver Problem What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis is a chronic (long-lasting) liver problem. It results from damaged and scarred liver tissue. Cirrhosis can t be cured, but it can be treated.
Pi ZZ Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
 Pi ZZ Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency An information leaflet for patients and families Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please
Pi ZZ Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency An information leaflet for patients and families Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Chronic obstructive lung disease. Dr/Rehab F.Gwada
 Chronic obstructive lung disease Dr/Rehab F.Gwada Obstructive lung diseases Problem is in the expiratory phase Lung disease Restrictive lung disease Restriction may be with, or within the chest wall Problem
Chronic obstructive lung disease Dr/Rehab F.Gwada Obstructive lung diseases Problem is in the expiratory phase Lung disease Restrictive lung disease Restriction may be with, or within the chest wall Problem
COPD and other lung conditions
 COPD and other lung conditions COPD COPD is an umbrella term used to describe a collection of lung diseases including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. C Chronic - long term condition O Obstructive - difficulty
COPD and other lung conditions COPD COPD is an umbrella term used to describe a collection of lung diseases including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. C Chronic - long term condition O Obstructive - difficulty
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING
 UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail
 Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
A patient educational resource provided by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
 Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) 1 Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It filters out harmful substances
Alcohol-Related Liver Disease Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) 1 Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It filters out harmful substances
H1N1 and Flu Shots During Pregnancy
 H1N1 and Flu Shots During Pregnancy HEALTH EDUCATION HEALTH EDUCATION The H1N1 flu and seasonal vaccines are safe and recommended for pregnant women. Be sure to: Get the H1N1 flu vaccine for yourself and
H1N1 and Flu Shots During Pregnancy HEALTH EDUCATION HEALTH EDUCATION The H1N1 flu and seasonal vaccines are safe and recommended for pregnant women. Be sure to: Get the H1N1 flu vaccine for yourself and
Bronchiectasis. What is bronchiectasis? What causes bronchiectasis?
 This factsheet explains what bronchiectasis is, what causes it, and how it is diagnosed and managed. More detailed information is available on the Bronchiectasis Patient Priorities website: www.europeanlunginfo.org/bronchiectasis
This factsheet explains what bronchiectasis is, what causes it, and how it is diagnosed and managed. More detailed information is available on the Bronchiectasis Patient Priorities website: www.europeanlunginfo.org/bronchiectasis
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
PROGRESSIVE FAMILIAL INTRAHEPATIC CHOLESTASIS (PFIC)
 The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. PROGRESSIVE FAMILIAL INTRAHEPATIC
The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. PROGRESSIVE FAMILIAL INTRAHEPATIC
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease
 Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and Augmentation Therapy-Prolastin-C Post Test
 Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and Augmentation Therapy-Prolastin-C Post Test 1. Persons with Alpha-1 are at high risk for developing life-threatening liver disease for which of the following reasons?
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and Augmentation Therapy-Prolastin-C Post Test 1. Persons with Alpha-1 are at high risk for developing life-threatening liver disease for which of the following reasons?
Understanding Lung Problems Make Each Breath Healthy
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Understanding Lung Problems Make Each Breath Healthy Lupe has smoked for over 45 years. This year she started having trouble keeping up with her 3-year-old grandson
National Institute on Aging AgePage Understanding Lung Problems Make Each Breath Healthy Lupe has smoked for over 45 years. This year she started having trouble keeping up with her 3-year-old grandson
A cough can be acute, subacute, or chronic, depending on how long it lasts.
 What Is? A cough is a natural reflex that protects your lungs. ing helps clear your airways of lung irritants, such as smoke and mucus (a slimy substance). This helps prevent infections. A cough also can
What Is? A cough is a natural reflex that protects your lungs. ing helps clear your airways of lung irritants, such as smoke and mucus (a slimy substance). This helps prevent infections. A cough also can
The facts you need to know
 Hepatitis B The facts you need to know Patient information booklet Know it. Test it. Treat it. Table of contents About this booklet 3 What is hepatitis? 3 What is chronic hepatitis B? 3 Can someone be
Hepatitis B The facts you need to know Patient information booklet Know it. Test it. Treat it. Table of contents About this booklet 3 What is hepatitis? 3 What is chronic hepatitis B? 3 Can someone be
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
SEPSIS INFORMATION BOOKLET. A life-threatening condition triggered by infection
 SEPSIS INFORMATION BOOKLET SEPSIS is A life-threatening condition triggered by infection It affects the function of the organs and is most effectively treated if recognised early If you have infection
SEPSIS INFORMATION BOOKLET SEPSIS is A life-threatening condition triggered by infection It affects the function of the organs and is most effectively treated if recognised early If you have infection
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
 Primary Biliary Cholangitis What is primary biliary cholangitis? Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease. When a person has PBC, the immune
Primary Biliary Cholangitis What is primary biliary cholangitis? Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is a chronic liver disease. When a person has PBC, the immune
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease A breathtaking condition
 1. Jan Crouch JC 2. Diane Cruikshank DC 3. Jillian Millar Drysdale JMD 4. Medical Editor 5. Robert Clarke Article: COPD & smoking.doc Section: Growing Older Family Health: Fall 2008 Chronic Obstructive
1. Jan Crouch JC 2. Diane Cruikshank DC 3. Jillian Millar Drysdale JMD 4. Medical Editor 5. Robert Clarke Article: COPD & smoking.doc Section: Growing Older Family Health: Fall 2008 Chronic Obstructive
Because we care about your health
 Contact us For information on Trust services see www.awp.nhs.uk PALS To make a comment, raise a concern or make a complaint, please contact the Trust s Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS). Smoking
Contact us For information on Trust services see www.awp.nhs.uk PALS To make a comment, raise a concern or make a complaint, please contact the Trust s Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS). Smoking
Supported by an educational grant from
 IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS: PATIENT INFORMATION BROCHURE Supported by an educational grant from 08232-106 CONTENTS What is Pulmonary Fibrosis?.......................................................
IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS: PATIENT INFORMATION BROCHURE Supported by an educational grant from 08232-106 CONTENTS What is Pulmonary Fibrosis?.......................................................
Patient Education Kidney Early Education Program (KEEP) Chapter 2 bjectives: Overview 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms
 Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
What Your Kidneys Do
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away
 written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
written by Harvard Medical School COPD It Can Take Your Breath Away www.patientedu.org What Is COPD? COPD stands for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. There are 2 major diseases included in COPD:
Biochemistry of Lungs. Lecture # 35 Lecturer: Alexander Koval
 Biochemistry of Lungs Lecture # 35 Lecturer: Alexander Koval Introduction Biochemistry of lungs Overview of substances produced (surfactant, mucus, collagen), inactivated (ROS, kinins, serotonin, catecholamines)
Biochemistry of Lungs Lecture # 35 Lecturer: Alexander Koval Introduction Biochemistry of lungs Overview of substances produced (surfactant, mucus, collagen), inactivated (ROS, kinins, serotonin, catecholamines)
What You Must Know about Hepatitis C. Facts, Symptoms, Treatment and Cures
 What You Must Know about Hepatitis C Facts, Symptoms, Treatment and Cures Hepatitis C can be life threatening. Today the hepatitis C virus kills more Americans than HIV. And it has become alarmingly widespread,
What You Must Know about Hepatitis C Facts, Symptoms, Treatment and Cures Hepatitis C can be life threatening. Today the hepatitis C virus kills more Americans than HIV. And it has become alarmingly widespread,
Wildfire Smoke and Your Health
 Wildfire Smoke and Your Health Frequently Asked Questions about Wildfire Smoke and Public Health Q: Why is wildfire smoke bad for my health? A: Wildfire smoke is a mixture of gases and fine particles from
Wildfire Smoke and Your Health Frequently Asked Questions about Wildfire Smoke and Public Health Q: Why is wildfire smoke bad for my health? A: Wildfire smoke is a mixture of gases and fine particles from
Hepatitis B. What Is Hepatitis? What Are The Two Stages Of Hepatitis? Published on: 5 Oct 2010
 Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu
 INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
INFLUENZA (FLU) Cleaning to Prevent the Flu Cleaning to Prevent the Flu 24 hours How long can the flu virus live on objects, such as doorknobs and tables? The flu virus can live on some surfaces for up
Frequently asked questions about wildfire smoke and public health
 PUBLIC HEALTH DIVISION http://public.health.oregon.gov Frequently asked questions about wildfire smoke and public health Wildfire smoke Q: Why is wildfire smoke bad for my health? A: Wildfire smoke is
PUBLIC HEALTH DIVISION http://public.health.oregon.gov Frequently asked questions about wildfire smoke and public health Wildfire smoke Q: Why is wildfire smoke bad for my health? A: Wildfire smoke is
Table of Contents. What is COPD? 1. Slowing the Progression of COPD 2. Treatment for COPD 3. Proper Inhaler Technique 5. Breathing Exercises 6
 1 Table of Contents What is COPD? 1 Slowing the Progression of COPD 2 Treatment for COPD 3 Proper Inhaler Technique 5 Breathing Exercises 6 Exercise 7 Nutrition 7 Avoiding Infection 8 Managing Daily Life
1 Table of Contents What is COPD? 1 Slowing the Progression of COPD 2 Treatment for COPD 3 Proper Inhaler Technique 5 Breathing Exercises 6 Exercise 7 Nutrition 7 Avoiding Infection 8 Managing Daily Life
Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu)
 Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu) For additional information go to: http://www.cdc.gov/ swineflu/general_info.htm Note: The information in this document is based on information from the CDC. The CDC site
Hot Topic: H1N1 Flu (Swine Flu) For additional information go to: http://www.cdc.gov/ swineflu/general_info.htm Note: The information in this document is based on information from the CDC. The CDC site
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather
 Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
A Patient s Guide to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 A Patient s Guide to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Table of Contents What is COPD? 2 How the Lungs Work 2 Lungs with Chronic Bronchitis 3 Lungs with Emphysema 4 Causes of COPD 4 COPD Symptoms
A Patient s Guide to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Table of Contents What is COPD? 2 How the Lungs Work 2 Lungs with Chronic Bronchitis 3 Lungs with Emphysema 4 Causes of COPD 4 COPD Symptoms
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Sepsis what you need to know. Adult information leaflet
 Sepsis what you need to know Adult information leaflet Sepsis is a life-threatening condition. It can happen when the body develops an which then affects the organs. If it is not treated quickly, sepsis
Sepsis what you need to know Adult information leaflet Sepsis is a life-threatening condition. It can happen when the body develops an which then affects the organs. If it is not treated quickly, sepsis
Cirrhosis of the Liver
 What I need to know about Cirrhosis of the Liver NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about
What I need to know about Cirrhosis of the Liver NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services What I need to know about
Cystic Fibrosis. Information for Caregivers
 Cystic Fibrosis Information for Caregivers Arkansas Children s Hospital is an accredited Cystic Fibrosis Care Center by the National Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Cystic Fibrosis: Information for Caregivers
Cystic Fibrosis Information for Caregivers Arkansas Children s Hospital is an accredited Cystic Fibrosis Care Center by the National Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Cystic Fibrosis: Information for Caregivers
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Bronchiectasis. Issued by Respiratory Medicine
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Bronchiectasis Issued by Respiratory Medicine The aim of this booklet is to help you manage your bronchiectasis. It contains information which you should find
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Bronchiectasis Issued by Respiratory Medicine The aim of this booklet is to help you manage your bronchiectasis. It contains information which you should find
Living Healthy , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. hp Last reviewed: 03/30/2017 1
 Living Healthy Introduction Most diseases that cause disability and death among Americans can be prevented or delayed. Practicing healthy living habits and having regular medical screenings can help you
Living Healthy Introduction Most diseases that cause disability and death among Americans can be prevented or delayed. Practicing healthy living habits and having regular medical screenings can help you
Use of abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis - patient information
 Practical management of patients receiving abatacept 1 Use of abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis - patient information Evidence-based Medicine Official Recommendations Expert opinion Key points 1. Abatacept
Practical management of patients receiving abatacept 1 Use of abatacept in rheumatoid arthritis - patient information Evidence-based Medicine Official Recommendations Expert opinion Key points 1. Abatacept
FACT SHEET. H1N1 Influenza phone
 www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
www.cookcountypublichealth.org 708-492-2000 phone H1N1 Influenza FACT SHEET What is novel H1N1? Novel H1N1 (referred to as swine flu early on) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This new
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple)
 Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Vaccine Information Statement: PEDIATRIC VACCINES (Multiple) 1. Your Baby s First Vaccines: What You Need to Know Babies get six vaccines between birth and 6 months of age. These vaccines protect your
Living with COPD: 5 steps to better lung health
 Living with COPD: 5 steps to better lung health Breathe better Feel good Do more Name: Date: COPD or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease mainly affects your lungs and how well you can breathe, but it
Living with COPD: 5 steps to better lung health Breathe better Feel good Do more Name: Date: COPD or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease mainly affects your lungs and how well you can breathe, but it
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-200-01-021914-E
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Health Promotion and Education Program Rev. 2014 2014, MMM Healthcare, Inc. - PMC Medicare Choice, Inc. Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-200-01-021914-E
Chapter 13. Preventing Infectious Diseases. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Reference Guide for Group Education
 A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 1 Introduction to Living Well with COPD Education Program Participants Expectations Towards the Program Health in COPD
A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 1 Introduction to Living Well with COPD Education Program Participants Expectations Towards the Program Health in COPD
BILIARY ATRESIA. What is biliary atresia?
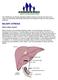 The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Food Allergy , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. imf10101 Last reviewed: 10/15/2017 1
 Food Allergy Introduction A food allergy is an abnormal response to a food. It is triggered by your body's immune system. An allergic reaction to a food can sometimes cause severe illness or death. Tree
Food Allergy Introduction A food allergy is an abnormal response to a food. It is triggered by your body's immune system. An allergic reaction to a food can sometimes cause severe illness or death. Tree
What You Need to Know About ARZERRA (ofatumumab)
 Starting your treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) What You Need to Know About ARZERRA (ofatumumab) Approved Use ARZERRA is a prescription medication used: With a chemotherapy drug called chlorambucil
Starting your treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) What You Need to Know About ARZERRA (ofatumumab) Approved Use ARZERRA is a prescription medication used: With a chemotherapy drug called chlorambucil
How can I benefit most from my COPD medications?
 Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
Pandemic H1N1 Frequently Asked Questions
 Pandemic H1N1 Frequently Asked Questions What is pandemic H1N1 flu? Pandemic H1N1 influenza (once referred to as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that causes respiratory illness in people. The Centers for
Pandemic H1N1 Frequently Asked Questions What is pandemic H1N1 flu? Pandemic H1N1 influenza (once referred to as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that causes respiratory illness in people. The Centers for
information Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease - COPD (1 of 5) What is COPD? What is going on in my lungs? What are the symptoms of COPD?
 information If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) on 0800 374 208 email: pal.service@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
information If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) on 0800 374 208 email: pal.service@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses
 Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
Understanding Respiratory Illnesses Respiratory illnesses can make you very sick. Some respiratory illnesses are not serious. A cold may make you feel sick for a few days, but you will get better. Other
Pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis
 Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Reference Guide for Group Education
 A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 5 Plan of Action: Part I Overview of the Plan of Action and Management of Respiratory Infections Plan of Action: Objectives
A p l a n o f a c t i o n f o r l i f e Reference Guide for Group Education Session 5 Plan of Action: Part I Overview of the Plan of Action and Management of Respiratory Infections Plan of Action: Objectives
Asthma. & Healthy Living FOR PATIENTS & CARERS. A guide to healthy habits and lifestyle choices for people with asthma
 Asthma & Healthy Living A guide to healthy habits and lifestyle choices for people with asthma FOR PATIENTS & CARERS what is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the airways, the small tubes which carry air
Asthma & Healthy Living A guide to healthy habits and lifestyle choices for people with asthma FOR PATIENTS & CARERS what is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the airways, the small tubes which carry air
Heart Failure. Symptoms and Treatments. FloridaHospital.com
 Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
X-Plain Hepatitis B Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hepatitis B Reference Summary Introduction Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks the liver. The virus is transmitted through
X-Plain Hepatitis B Reference Summary Introduction Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks the liver. The virus is transmitted through
PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
Cold, Flu, or Allergy?
 Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Introduction: A cold, the flu, and allergies all affect the respiratory system and have many similar symptoms. It can be difficult to tell whether someone has a cold, the flu, or
Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Introduction: A cold, the flu, and allergies all affect the respiratory system and have many similar symptoms. It can be difficult to tell whether someone has a cold, the flu, or
