Stereochemistry. Dr. Sapna Gupta
|
|
|
- Audrey Cobb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stereochemistry Dr. Sapna Gupta
2 Introduction Stereo left and right handedness Any carbon that has four different groups will show chirality. hirality: the mirror image of the compound will not superimpose on the original molecule. Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 2
3 hirality When two mirror images are non imposable on each other. When the tetrahedral carbon has four different groups it is called a chiral center. The mirror image pair of the compounds are called enantiomers. The only thing different about the two molecules is how they rotate the plane polarized light. The rotation would be in equal and opposite direction. Drawing chiral molecules: draw dash (behind the plane) and wedges (coming out of paper) and plane line (in the plane) for bonds. ere are four representations of one compound. 3 O O O O (1) (2) (3) (4) ere are two representations for the enantiomer of (4). O O O (4) representations for th e enantiomer of (4) Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 3
4 Some Enantiomers 2-hlorobutane l l l 3-hlorocyclohexene l l Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 4
5 Another Example ow many chiral centers in the following compound? Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 5
6 Pasteur s Discovery of Enantiomers Louis Pasteur discovered that sodium ammonium salts of tartaric acid crystallize into right handed and left handed forms The optical rotations of equal concentrations of these forms have opposite optical rotations The solutions contain mirror image isomers, called enantiomers and they crystallized in mirror image shapes such an event is rare Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 6
7 Naming Enantiomers- The R,S System Also called the ahn-ingold-prelog system The four groups attached to the stereogenic/chiral carbon are assigned priorities from highest (a) to lowest (d) Priorities are assigned as follows Atoms directly attached to the chiral center are compared Atoms with higher atomic mass are given higher priority If priority cannot be assigned based on directly attached atoms, the next layer of atoms is examined Example Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 7
8 Naming Enantiomers- The R,S System, contd.. The molecule is rotated to put the lowest priority group back If the groups descend in priority (a,b then c) in clockwise direction the enantiomer is R If the groups descend in priority in counterclockwise direction the enantiomer is S Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 8
9 Assigning Priority 1. Look at the atom (not the group) directly attached to the carbon and arrange according to atomic weight (1) (6) (7) (8) 2. If priority cannot be assigned per the atoms bonded to the chiral center, look to the next set of atoms; priority is assigned at the first point of difference 3. Groups with double or -= triple 2 bonds are assigned -- priorities 2 as if their atoms were duplicated or triplicated -= 2 (16) Increasing priority (17) (35) (53) N 2 - O - S - l - Br - I (1) (6) - -= 2 O - (7) N 2 Increasing priority is treated as O is treated as is treated as is treated as is treated as is treated as (8) - 2 -O O O -- 2 O O O - is treated as is treated as is treated as Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry O O
10 Examples (S)-2-hlorobutane l S (R)-3-hlorocyclohexene 3 1 l 2 3 R (R)-Mevalonic acid 1 4 O R 3 O 2 O O Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 10
11 Identical or Not? Are A and B identical or enantiomers? Manipulate B to see if it will become superimposable with A Exchange 2 groups to try to convert B into A Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 11
12 Optical Activity Light restricted to pass through a plane is plane-polarized. Phenomenon discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot in the early 19 th century Plane-polarized light that passes through solutions of achiral compounds retains its original plane of polarization Solutions of chiral compounds rotate plane-polarized light and the molecules are said to be optically active The instrument is called a polarimeter Rotation is measured in degrees, is [ ] lockwise rotation is called dextrorotatory (d) Anti-clockwise is levorotatory (l) Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 12
13 The Polarimeter The source passes through a polarizer and then is detected at a second polarizer The angle between the entrance and exit planes is the optical rotation. Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 13
14 Specific Rotation To have a basis for comparison, define specific rotation, [ ] D for an optically active compound Specific rotation is that observed for 1 g/ml in solution in cell with a 10 cm path using light from sodium metal vapor (589 nm) OO OO 3 D O (S)-(+)-Lactic acid [ ] 21 = +2.6 O D 3 (R)-(-)-Lactic acid [ ] 21 = -2.6 Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 14
15 Specific Rotation and Molecules A compound must be chiral for it to be optically active. The specific rotation of the enantiomer pair is equal in magnitude but opposite in sign There is no correlation between the R,S designation of an enantiomer and the direction [(+) or (-)] in which it rotates plane polarized light ([+ = d] and [ = l]) Racemic mixture A 1:1 mixture of enantiomers No net optical rotation Often designated as (+) Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 15
16 Two hiral enters - Diastereomers Molecules that have two or more chiral centers. Each of the two chiral centers will have a pair of enantiomers. The other stereoisomers are called diastereomers. Enantiomers rotate plane polarized in opposite direction. Diastereomers have no optical relationship. The number of isomers are given by 2 n, where n is the number of chiral centers. It is important to understand the concept of symmetry. If a molecule has internal symmetry then it will not be optically active it will be achiral. Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 16
17 Two hiral enters There are two pairs of enantiomers (1, 2) and (3,4) Enantiomers are not easily separable so 1 and 2 cannot be separated from each other Diastereomers: stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other For instance 1 and 3 or 1 and 4 ave different physical properties and can be separated Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 17
18 Meso ompounds ompounds with two or more chiral centers but not the maximum number of stereoisomers (2n) This is because two enantiomers may be superimposable i.e. achiral (not optically active) This superimposability comes from the molecule having a plane of symmetry. as a plane of symmetry Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 18
19 Naming more than one hiral enter The molecule is manipulated to allow assignment of each stereogenic center separately This compound is (2R, 3R)-2,3-dibromobutane Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 19
20 More Examples 2-Methylcyclopentanol 1,2-yclopentanediol 3 O O 3 O O O O cis-2-methylcyclopentanol (a pair of enantiomers) diastereomers cis- 1,2-yclopentanediol (one meso compound) dia 3 3 O O O O trans- 2-Methylcyclopentanol (a pair of enantiomers) O O trans- 1,2-yclopentanediol (a pair of enantiomers) Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 20
21 Six Membered Rings 1,4-dimethylcyclohexane (shown on the right) Neither the cis not trans isomers is optically active Each has a plane of symmetry 1,3-dimethylcyclohexane The trans and cis compounds each have two stereogenic centers The cis compound has a plane of symmetry and is meso The trans compound exists as a pair of enantiomers Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 21
22 Fisher Projections A 2-dimensional representation of chiral molecules Vertical lines represent bonds that project behind the plane of the paper orizontal lines represent bonds that project out of the plane of the paper Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 22
23 Stereoisomers With no hiral enters If the conformer is sterically hindered, it may exist as enantiomers. Examples given below and allenes. Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 23
24 Properties of Stereoisomers Enantiomers have identical physical and chemical properties in achiral environments. Diastereomers are different compounds and have different physical and chemical properties. meso tartaric acid, for example, has different physical and chemical properties from the R,R and S,S enantiomers Some properties of the stereoisomers of tartaric acid. OO OO OO O O O O O O specific rotation m elting point ( ) density at 20 (g/cm 3 ) solubility in water at 20 (g/100 ml) pk 1 (25 ) pk 2 (25 ) OO OO (R,R)-Tartaric acid (S,S)-Tartaric acid OO Meso tartaric acid Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 24
25 Resolution Racemic mixture: An equimolar mixture of two enantiomers. because a racemic mixture contains equal numbers of dextrorotatory and levorotatory molecules, its specific rotation is zero. Resolution: The separation of a racemic mixture into its enantiomers. One means of resolution is to convert the pair of enantiomers into two diastereomers. Diastereomers are different compounds and have different physical properties. A common reaction for chemical resolution is salt formation. ROO + : B ROO - B + (R + S)-arboxylic acid (R)-Base (R,R)-Salt + ( S,R)-Salt) After separation of the diastereomers, the enantiomerically pure acids are recovered by addition of an achiral acid. Racemic acids can be resolved using commercially available chiral bases such as 1- phenylethanamine. N 2 N 2 (S)-1-Ph enylethan amin e Racemic bases can be resolved using chiral acids such as (R)-1-Phenylethan amin e O O O 3 3 OO O O O O O O O O OO (2S,3S)-(+)-Tartaric acid (S)-(-)-Malic acid Dr. Sapna (1S,3R)-(+)-amphoric Gupta/Stereochemistry acid 25 3
26 Review of all Isomers ere is a flowchart of all isomers we have done so far. stereocenters but no chiral centers is,trans (E,Z) Isomers (can be called diastereomers) ompounds with the same molecular formula same connectivity Stereoisomers Meso ompounds with chiral centers different connectivity m ore than one chiral center achiral onstitutional Isomers chiral not mirror images rotation about single bonds one chiral center mirror images onformations rotation restricted onformational Isomers Atropisomers Enantiomers Diastereomers Enantiomers Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 26
27 Determining Stereochemistry Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 27
28 hemical Properties of Enantiomers Enantiomers have exactly the same chemical properties except for their reaction with chiral nonracemic reagents. Many drugs are chiral and often must react with a chiral receptor or chiral enzyme to be effective. One enantiomer of a drug may effectively treat a disease whereas its enatiomer may be ineffective or toxic. Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 28
29 Amino Acids and Proteins The 20 most common amino acids have a central carbon, called an -carbon, bonded to an N 2 group and a OO group. In 19 of the 20, the -carbon is a chiral center. 18 of the 19 -carbons have the R configuration, one has the S configuration. At neutral p, an amino acid exists as an internal salt. The symbol R = a side chain. Proteins: Long chains of amino acids connected by amide bonds (here shown in red) formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid Amide bond side chain 3 N O O - R Ionized or zw itterion form of an amino acid 3 N R O N R O N R O N n R O O - for most proteins, n= Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 29
30 hirality in the Biological World Except for inorganic salts and a few low-molecular-weight organic substances, the majority of molecules of living systems are chiral. Although these molecules can exist as a number of stereoisomers, generally only one is produced and used in a given biological system. onsider chymotrypsin, a protein-digesting enzyme in the digestive system of animals. chymotrypsin contains 251 chiral centers. the maximum number of stereoisomers possible is there are only 2 38 stars in our galaxy! Enzymes are like hands in a handshake. The substrate fits into a binding site on the enzyme surface. A left-handed molecule, like hands in gloves, will only fit into a lefthanded binding site and a right-handed molecule will only fit into a right-handed binding site. Because of the differences in their interactions with other chiral molecules in living systems, enantiomers have different physiological properties. Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 30
31 hirality in the Biological World.. A schematic diagram of an enzyme surface capable of binding with (R)- glyceraldehyde but not with (S)-glyceraldehyde. Dr. Sapna Gupta/Stereochemistry 31
32 Key Words/oncepts Stereoisomers hiral enter hirality Enantiomer Plane polarized light Dextrorotatory (d) Laevorotatory (l) Diastereomers Meso compounds ahn Ingold and Prelog nomenclature onfigurations (R and S) Racemic mixtures Fisher projections Enantiomeric excess Absolute configuration Resolution
Chirality. Chapter 5 Stereochemistry. Chiral Carbons. Stereoisomers. Mirror Planes of Symmetry. (R), (S) Nomenclature
 Organic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 5 Stereochemistry hirality andedness : right glove doesn t fit the left hand. Mirror-image object is different from the original object. Jo Blackburn
Organic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 5 Stereochemistry hirality andedness : right glove doesn t fit the left hand. Mirror-image object is different from the original object. Jo Blackburn
Stereochemistry - Chirality. Chapter 5 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John E. McMurry
 Stereochemistry - Chirality Chapter 5 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John E. McMurry Isomerism The two major classes of isomers are constitutional isomers and stereoisomers. Constitutional/structural isomers
Stereochemistry - Chirality Chapter 5 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John E. McMurry Isomerism The two major classes of isomers are constitutional isomers and stereoisomers. Constitutional/structural isomers
Chapter 5 Stereochemistry
 Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Chapter 5 Stereochemistry 1 Stereoisomers of 2,3-dibromobutane Figure 5.9 Pair of enantiomers: A and B Pairs of diastereomers:
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Chapter 5 Stereochemistry 1 Stereoisomers of 2,3-dibromobutane Figure 5.9 Pair of enantiomers: A and B Pairs of diastereomers:
CHEM 261 Feb. 16, stereogenic center H C C C
 77 EM 261 Feb. 16, 2017 eview of hiral enters 3 quinine - anti-malarial drug from the bark of the tree inchona officinalis malaria is cause by Plasmodium species transmitted by Anopheles mosquito example.
77 EM 261 Feb. 16, 2017 eview of hiral enters 3 quinine - anti-malarial drug from the bark of the tree inchona officinalis malaria is cause by Plasmodium species transmitted by Anopheles mosquito example.
Stereochemistry 1.1 INTRODUCTION
 1 Stereochemistry 1.1 INTRODUTION The isomers which have same arrangement of atoms but differ only due to different orientation of atoms in space within the molecule are called Stereoisomers and the phenomenon
1 Stereochemistry 1.1 INTRODUTION The isomers which have same arrangement of atoms but differ only due to different orientation of atoms in space within the molecule are called Stereoisomers and the phenomenon
As a result, IV and V are chiral molecules and are enantiomers.
 5.1 lassify each of the following objects as to whether it is chiral or achiral: (a) A screwdriver achiral (d) A tennis shoe chiral (g) A car chiral (b) A baseball bat achiral (e) An ear chiral (h) A hammer
5.1 lassify each of the following objects as to whether it is chiral or achiral: (a) A screwdriver achiral (d) A tennis shoe chiral (g) A car chiral (b) A baseball bat achiral (e) An ear chiral (h) A hammer
CHAPTER 5 HW: STEREOISOMERS
 CAPTER 5 W: STEREISMERS CIRALITY AND ENANTIMERS 1. Define the following terms: a. Chiral A chiral substance has the possibility of having right and left handed versions (or it can have an enantiomer).
CAPTER 5 W: STEREISMERS CIRALITY AND ENANTIMERS 1. Define the following terms: a. Chiral A chiral substance has the possibility of having right and left handed versions (or it can have an enantiomer).
CHEM 109A Organic Chemistry
 CEM 09A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter Isomers The arrangement of atoms in space MIDTERM Wednesday Feb. Chapter Sections.8.6 melting, boiling points, conformations
CEM 09A Organic Chemistry https://labs.chem.ucsb.edu/zakarian/armen/courses.html Chapter Isomers The arrangement of atoms in space MIDTERM Wednesday Feb. Chapter Sections.8.6 melting, boiling points, conformations
Practice Problems for Video CH 5-1:
 CEM 243 Organic Chemistry C-5: Stereochemistry - Chiral Molecules Study Guide: Key Concepts and Practice Problems Key concepts you need to understand: Chirality and chiral centers; stereoisomers; (R,S)
CEM 243 Organic Chemistry C-5: Stereochemistry - Chiral Molecules Study Guide: Key Concepts and Practice Problems Key concepts you need to understand: Chirality and chiral centers; stereoisomers; (R,S)
Chemistry I (Organic) Stereochemistry LECTURE 2 Stereogenic elements & enantiomers
 1 Chemistry I (Organic) Stereochemistry LECTURE 2 Stereogenic elements & enantiomers Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk Oct 2011 2 Format & scope of lecture Isomers & stereoisomers some definitions
1 Chemistry I (Organic) Stereochemistry LECTURE 2 Stereogenic elements & enantiomers Alan C. Spivey a.c.spivey@imperial.ac.uk Oct 2011 2 Format & scope of lecture Isomers & stereoisomers some definitions
Stereochemistry: 3-D Chemistry. 3-D Chemistry. Enantiomers
 Stereochemistry: 3-D Chemistry 3-D Chemistry Enantiomers If a molecule and its mirror image are not superimposable these molecules are isomers; in particular, these mirror image isomers are called enantiomers
Stereochemistry: 3-D Chemistry 3-D Chemistry Enantiomers If a molecule and its mirror image are not superimposable these molecules are isomers; in particular, these mirror image isomers are called enantiomers
CHAPTER 26 STEREOISOMERISM SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 C26 09/17/2013 10:52:31 Page 379 CHAPTER 26 STEREOISOMERISM SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. A chiral carbon atom is one to which four different atoms or groups are attached and is a center of asymmetry
C26 09/17/2013 10:52:31 Page 379 CHAPTER 26 STEREOISOMERISM SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. A chiral carbon atom is one to which four different atoms or groups are attached and is a center of asymmetry
Stereo-Isomers in Pesticides. Martin Rodler, CropLife International
 Stereo-Isomers in Pesticides Martin Rodler, CropLife International Outline Relevance of Stereo-Isomers for Pesticides Regulatory Evaluation of Pesticides Introduction to Stereo-Isomerism Enantiomers Diastereomers
Stereo-Isomers in Pesticides Martin Rodler, CropLife International Outline Relevance of Stereo-Isomers for Pesticides Regulatory Evaluation of Pesticides Introduction to Stereo-Isomerism Enantiomers Diastereomers
3.7A: Compounds with multiple stereocenters
 Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki BioWiki GeoWiki StatWiki
Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki BioWiki GeoWiki StatWiki
CHAPTER 5 HW: STEREOISOMERS
 CAPTER 5 W: STEREISMERS CIRALITY AND ENANTIMERS 1. Define the following terms: a. Chiral b. Enantiomers (and give an example) 2. Put an asterisk (*) on all chiral centers in these compounds. Some may have
CAPTER 5 W: STEREISMERS CIRALITY AND ENANTIMERS 1. Define the following terms: a. Chiral b. Enantiomers (and give an example) 2. Put an asterisk (*) on all chiral centers in these compounds. Some may have
Chemistry 261 Homework 3: Chapters 5, 6 Out: 11/20/17 Due: 11/30/17 Point Value: 9 points (7 EC points possible when combined with part I)
 Chemistry 261 omework 3: Chapters 5, 6 ut: 11/20/17 Due: 11/30/17 Point Value: 9 points (7 EC points possible when combined with part I) The following homework assignment contains 28 questions valued at
Chemistry 261 omework 3: Chapters 5, 6 ut: 11/20/17 Due: 11/30/17 Point Value: 9 points (7 EC points possible when combined with part I) The following homework assignment contains 28 questions valued at
CHEM J-6 June 2014
 CEM1611 2014-J-6 June 2014 rlistat (shown below) is a drug for obesity management which acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats. Indicate all stereogenic centres on the structure below. 6 rlistat
CEM1611 2014-J-6 June 2014 rlistat (shown below) is a drug for obesity management which acts by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats. Indicate all stereogenic centres on the structure below. 6 rlistat
Two chiral centres (diastereoisomers)
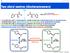 1 Two chiral centres (diastereoisomers) Mirror N S N Two enantiomers differ by absolute configuration N N 2 N 2 N A molecule with 1 stereogenic centre exists as 2 stereoisomers or enantiomers Enantiomers
1 Two chiral centres (diastereoisomers) Mirror N S N Two enantiomers differ by absolute configuration N N 2 N 2 N A molecule with 1 stereogenic centre exists as 2 stereoisomers or enantiomers Enantiomers
CHM 220 Stereochemistry
 CM 220 Stereochemistry Stereocenters 1. ow many stereocenters are there in 2,2,4-tribromo-3-methyl-1-pentanol? (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 2. ow many stereocenters are there in 2,3-dibromo-4-methylpentane?
CM 220 Stereochemistry Stereocenters 1. ow many stereocenters are there in 2,2,4-tribromo-3-methyl-1-pentanol? (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 2. ow many stereocenters are there in 2,3-dibromo-4-methylpentane?
A. CONFORMATIONAL ISOMERS
 EMISTRY 104 elp Sheet #3 Organic (Part II): ISOMERS hapters 2.9 (structural isomers), 6.5 (geometric isomers), 6.11 (constitutional isomers), 7.2f (optical isomers) Do the topics appropriate for your lecture
EMISTRY 104 elp Sheet #3 Organic (Part II): ISOMERS hapters 2.9 (structural isomers), 6.5 (geometric isomers), 6.11 (constitutional isomers), 7.2f (optical isomers) Do the topics appropriate for your lecture
Carbohydrates. Chapter 18
 Carbohydrates Chapter 18 Biochemistry an overview Biochemistry is the study of chemical substances in living organisms and the chemical interactions of these substances with each other. Biochemical substances
Carbohydrates Chapter 18 Biochemistry an overview Biochemistry is the study of chemical substances in living organisms and the chemical interactions of these substances with each other. Biochemical substances
MEDCHEM 562. Physicochemical Properties of Drugs: Lecture 2; Kent Kunze. Stereochemistry (Double the trouble. or double the fun?)
 1 MEDCHEM 562 Physicochemical Properties of Drugs: Lecture 2; Kent Kunze Stereochemistry (Double the trouble. or double the fun?) The vast majority of drugs contain at least one stereo-center or site of
1 MEDCHEM 562 Physicochemical Properties of Drugs: Lecture 2; Kent Kunze Stereochemistry (Double the trouble. or double the fun?) The vast majority of drugs contain at least one stereo-center or site of
Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) peptides and proteins (Chapter 25) nucleic acids (Chapter 26)
 Chapter 23: Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n Plants: photosynthesis 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O hν C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units
Chapter 23: Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n Plants: photosynthesis 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O hν C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units
CH 3 H C 2 H 5. C Cl C H. H 3 C Cl H H 5 C 2. H Cl. Cl H. C Cl H. H Cl. Problem Set 7: Stereochemistry-2
 Problem Set 7: Stereochemistry-2 hemistry 260 Organic hemistry 1. ow many constitutional isomers of 7 16 have stereogenic centres? (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 (4) 4 (5) none 2. Indicate which of the following compounds
Problem Set 7: Stereochemistry-2 hemistry 260 Organic hemistry 1. ow many constitutional isomers of 7 16 have stereogenic centres? (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 (4) 4 (5) none 2. Indicate which of the following compounds
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22
 Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Level 3 Chemistry, 2007
 Level 3 hemistry, 2007 Annotated answers to this organic paper. Q1 QUESTIN NE Give the proper name that gives the structure a unique name (a) Give the systematic IUPA names for the following molecules
Level 3 hemistry, 2007 Annotated answers to this organic paper. Q1 QUESTIN NE Give the proper name that gives the structure a unique name (a) Give the systematic IUPA names for the following molecules
These rules give the absolute configuration, R- and S- for each chiral center within a compound. The chiral centers are names either R- or S-.
 The ahn-ingold-prelog rules These rules give the absolute configuration, R- and S- for each chiral center within a compound. The chiral centers are names either R- or S-. To name a chiral center using
The ahn-ingold-prelog rules These rules give the absolute configuration, R- and S- for each chiral center within a compound. The chiral centers are names either R- or S-. To name a chiral center using
Organic/Biochem Test #2 Takehome Name: Spring 2012 Page 1 of 6. Multiple choice: Circle the best answer for each of the following questions.
 Spring 2012 Page 1 of 6 Multiple choice: Circle the best answer for each of the following questions. 1. The general formula for a carboxylic acid is: a) RCHO b) RCOR c) R-OH d) R-COOH 2. In which of the
Spring 2012 Page 1 of 6 Multiple choice: Circle the best answer for each of the following questions. 1. The general formula for a carboxylic acid is: a) RCHO b) RCOR c) R-OH d) R-COOH 2. In which of the
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Stereoisomerism There are two types of stereoisomerism, E-Z Isomerism and Optical Isomerism.
 Stereoisomerism There are two types of stereoisomerism, E-Z Isomerism and Optical Isomerism. E Z Isomerism This type tells us about the positions of substituent's either side of the carbon carbon double
Stereoisomerism There are two types of stereoisomerism, E-Z Isomerism and Optical Isomerism. E Z Isomerism This type tells us about the positions of substituent's either side of the carbon carbon double
Lecture 3: 8/24. CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids
 Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Anomeric carbon Erythritol is achiral because of a mirror plane in the molecule and therefore, the product is optically inactive.
 APTER 22 Practice Exercises 22.1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 D-Ribulose L-Ribulose D-Xyulose L-Xyulose (one pair of enantiomers) (a second pair of enantiomers) 22.3 2 Anomeric carbon Glycosidic bond 3 () Methyl -D-mannopyranoside
APTER 22 Practice Exercises 22.1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 D-Ribulose L-Ribulose D-Xyulose L-Xyulose (one pair of enantiomers) (a second pair of enantiomers) 22.3 2 Anomeric carbon Glycosidic bond 3 () Methyl -D-mannopyranoside
Student Handout. This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have
 Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
Student Handout This experiment allows you to explore the properties of chiral molecules. You have learned that some compounds exist as enantiomers non-identical mirror images, such as your left and right
Stereochemistry: biological significance of isomerism
 S Stereochemistry: biological significance of isomerism Craig Wheelock October 17 th, 2008 craig.wheelock@ki.se http://www.metabolomics.se/ (copies of slides can be downloaded from my homepage) Learning
S Stereochemistry: biological significance of isomerism Craig Wheelock October 17 th, 2008 craig.wheelock@ki.se http://www.metabolomics.se/ (copies of slides can be downloaded from my homepage) Learning
6.1 Cis Trans Isomers
 6.1 CIS TRANS ISMERS 179 two dimensions on the pages of a book. The use of models is an invaluable aid in understanding the material presented in this chapter. You are strongly encouraged to build models
6.1 CIS TRANS ISMERS 179 two dimensions on the pages of a book. The use of models is an invaluable aid in understanding the material presented in this chapter. You are strongly encouraged to build models
O H 2 N. α H. Chapter 4 - Amino Acids
 hapter 4 - Amino Acids Introduction Several amino acids were produced in the electrical discharge in the reducing, primordial atmosphere that gave rise to the first biomolecules (see chapter 1). The importance
hapter 4 - Amino Acids Introduction Several amino acids were produced in the electrical discharge in the reducing, primordial atmosphere that gave rise to the first biomolecules (see chapter 1). The importance
Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS!
 Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS! Monosaccharaides Q. Can hydrolysis occur at anytime
Long time ago, people who sacrifice their sleep, family, food, laughter, and other joys of life were called SAINTS. But now, they are called STUDENTS! Monosaccharaides Q. Can hydrolysis occur at anytime
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush. Tarek Khrisat
 1 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 18 th 2013 Tarek Khrisat 1 Lecture Outline: Aldoses and Ketoses Optical isomers -Fischer projection -Enantiomers, Diastereomers, and Epimers Isomers: Compounds with the same
1 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 18 th 2013 Tarek Khrisat 1 Lecture Outline: Aldoses and Ketoses Optical isomers -Fischer projection -Enantiomers, Diastereomers, and Epimers Isomers: Compounds with the same
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
CHAPTER 27 CARBOHYDRATES SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 27 09/17/2013 11:12:35 Page 397 APTER 27 ARBYDRATES SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. In general, the carbohydrate carbon oxidation state determines the carbon s metabolic energy content. The more oxidized
27 09/17/2013 11:12:35 Page 397 APTER 27 ARBYDRATES SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. In general, the carbohydrate carbon oxidation state determines the carbon s metabolic energy content. The more oxidized
AMINO ACIDS. Qualitative Tests
 AMINO ACIDS Qualitative Tests AMINO ACIDS Amino acid play A central role as building block of proteins. Amino acids also converted to specialized products. More than 300 different amino acids have been
AMINO ACIDS Qualitative Tests AMINO ACIDS Amino acid play A central role as building block of proteins. Amino acids also converted to specialized products. More than 300 different amino acids have been
Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n. Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer)
 Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν 6 C + 6 C 6 6 + 6 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: carbohydrates
Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν 6 C + 6 C 6 6 + 6 Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: carbohydrates
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Problem Set 2 Out: November 5, 1999 Due Back: November 12, 1999 Chemistry 221, 1999
 Problem Set ut: November 5, 1999 Due Back: November 1, 1999 hemistry 1, 1999 Answers to the following problems should be written, in order and labeled, on 8 1/ x 11 inch paper. Answers written on the problem
Problem Set ut: November 5, 1999 Due Back: November 1, 1999 hemistry 1, 1999 Answers to the following problems should be written, in order and labeled, on 8 1/ x 11 inch paper. Answers written on the problem
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates
 Chapter 7 Carbohydrates Definition of Carbohydrates carbohydrate: hydrate of carbon ; C n ( 2 ) m Examples: glucose (C 6 12 6 or C 6 ( 2 ) 6 ), sucrose (C 12 22 11 or C 12 ( 2 ) 11 ) saccharide: simple
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates Definition of Carbohydrates carbohydrate: hydrate of carbon ; C n ( 2 ) m Examples: glucose (C 6 12 6 or C 6 ( 2 ) 6 ), sucrose (C 12 22 11 or C 12 ( 2 ) 11 ) saccharide: simple
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry. CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 6: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates CHAPTER SUMMARY
 14 2 cellulose 2 2 arbohydrates 2 amylose APTER SUMMARY 14.1 hemical Nature of arbohydrates - Polyhydroxy Aldehydes and Ketones arbohydrates are a class of organic biopolymers which consist of polyhydroxy
14 2 cellulose 2 2 arbohydrates 2 amylose APTER SUMMARY 14.1 hemical Nature of arbohydrates - Polyhydroxy Aldehydes and Ketones arbohydrates are a class of organic biopolymers which consist of polyhydroxy
Model 2: Aldohexoses, aldopentoses, ketohexoses and ketopentoses
 Model 1: D and L Sugars CHEM1405 Worksheet 13: Sugars and Amino Acids The simplest sugar is glyceraldehyde. This is a chiral molecule and the two enantiomers are shown opposite with wedges and dashes and
Model 1: D and L Sugars CHEM1405 Worksheet 13: Sugars and Amino Acids The simplest sugar is glyceraldehyde. This is a chiral molecule and the two enantiomers are shown opposite with wedges and dashes and
Sheet #8 Dr. Nafeth Abu-Tarboush
 1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
1 arbohydrates There are two topic goals in our study of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: to recognize their structure, properties, & their stereochemistry. The nature of di-, oligo- & polysaccharides.
Hydrolytic transformations involving amide-, ester bonds are the easiest to perform
 Hydrolytic reactions Hydrolytic transformations involving amide-, ester bonds are the easiest to perform Proteins used for these reactions are proteases, esterases or lipases. A favourite class of enzymes
Hydrolytic reactions Hydrolytic transformations involving amide-, ester bonds are the easiest to perform Proteins used for these reactions are proteases, esterases or lipases. A favourite class of enzymes
DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY SCHOOL OF PHARMACY
 KEY DEPARTMET F MEDIIAL EMISTRY SL F PARMAY BASI PARMAEUTIAL SIEE FR TE PRATIIG PARMAIST MED 527, Fall 2008 Quiz #4, Dr. Desai, 100 points; ovember 4, 2008 AME (In APITAL Letters LY) I affirm that I have
KEY DEPARTMET F MEDIIAL EMISTRY SL F PARMAY BASI PARMAEUTIAL SIEE FR TE PRATIIG PARMAIST MED 527, Fall 2008 Quiz #4, Dr. Desai, 100 points; ovember 4, 2008 AME (In APITAL Letters LY) I affirm that I have
Chapter 24: Carbohydrates
 Chapter 24: Carbohydrates [Sections: 24.1 24.10] 1. Carbohydrates definition naturally occuring compounds derived from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen the net molecular formula comes from each carbon having
Chapter 24: Carbohydrates [Sections: 24.1 24.10] 1. Carbohydrates definition naturally occuring compounds derived from carbon, oxygen and hydrogen the net molecular formula comes from each carbon having
Chapter 18. Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry. Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1
 Chapter 18 Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1 Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Bioenergetics Metabolism and
Chapter 18 Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry Carbohydrates with an Introduction to Biochemistry page 1 Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids, and Bioenergetics Metabolism and
CHM 2200C April 28, (Please Print)
 M 2200 April 28, 2005 Final Exam Name KEY (Please Print) Points The test consists of six pages. Print your name legibly on each page now. A seventh page contains approximate pk values for some acids. You
M 2200 April 28, 2005 Final Exam Name KEY (Please Print) Points The test consists of six pages. Print your name legibly on each page now. A seventh page contains approximate pk values for some acids. You
Final Exam, Page 1 of 15. Your full signature
 Final Exam, Page 1 of 15 Your full signature Print your full name Your SID If you are making up an I grade Indicate the semester you took the course Name of the instructor for that course: This exam has
Final Exam, Page 1 of 15 Your full signature Print your full name Your SID If you are making up an I grade Indicate the semester you took the course Name of the instructor for that course: This exam has
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates
 24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.). The polymer
24.1 Introduction to Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) are abundant in nature: They are high energy biomolecules. They provide structural rigidity for organisms (plants, crustaceans, etc.). The polymer
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Org/Biochem Final Lec Form, Spring 2012 Page 1 of 6
 Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Chem 1120 Final 210 points Dr. Luther Giddings
 Chem 1120 Final 210 points Dr. Luther Giddings Name Phone or E-Mail Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notebook test. You may not discuss this exam with anyone, either during or after the exam,
Chem 1120 Final 210 points Dr. Luther Giddings Name Phone or E-Mail Instructions: This is a closed book, closed notebook test. You may not discuss this exam with anyone, either during or after the exam,
Part I => CARBS and LIPIDS. 1.2 Monosaccharides 1.2a Stereochemistry 1.2b Derivatives
 Part I => CARBS and LIPIDS 1.2 Monosaccharides 1.2a Stereochemistry 1.2b Derivatives Section 1.2a: Stereochemistry Synopsis 1.2a monosaccharide (greek) sugar - Monosaccharides are carbonyl polyols (or
Part I => CARBS and LIPIDS 1.2 Monosaccharides 1.2a Stereochemistry 1.2b Derivatives Section 1.2a: Stereochemistry Synopsis 1.2a monosaccharide (greek) sugar - Monosaccharides are carbonyl polyols (or
CHEM 203 HOMEWORK 4 Chemistry of Alkenes - II. Answer the above questions by writing a detailed mechanism for the conversion of A into lanosterol.
 EM 203 MEWK 4 hemistry of Alkenes - II 1. The following questions may have occurred to you: (i) do carbocations occur in living systems? (ii) an an olefin (a Lewis base) react with a carbocation (a Lewis
EM 203 MEWK 4 hemistry of Alkenes - II 1. The following questions may have occurred to you: (i) do carbocations occur in living systems? (ii) an an olefin (a Lewis base) react with a carbocation (a Lewis
Chem 60 Takehome Test 2 Student Section
 Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Carbohydrate Structure and Nomenclature. Essentials of Glycobiology 1 April 2004
 1 Carbohydrate Structure and Nomenclature Essentials of Glycobiology 1 April 2004 Nathaniel Finney Dept. of Chemistry and Biochemistry UCSD nfinney@chem.ucsd.edu 2 Lecture utline 1. Carbohydrates - definition
1 Carbohydrate Structure and Nomenclature Essentials of Glycobiology 1 April 2004 Nathaniel Finney Dept. of Chemistry and Biochemistry UCSD nfinney@chem.ucsd.edu 2 Lecture utline 1. Carbohydrates - definition
Organic Chemistry III
 rganic Chemistry III (Yuki Goto, Bioorganic Chemistry Lab.) rganic chemistry of biomolecules rganic chemistry of radicals 6/6 (Wed) 6/13 (Wed) 6/20 (Wed) 6/27 (Wed) 7/4 (Wed) Examples of biomolecules?
rganic Chemistry III (Yuki Goto, Bioorganic Chemistry Lab.) rganic chemistry of biomolecules rganic chemistry of radicals 6/6 (Wed) 6/13 (Wed) 6/20 (Wed) 6/27 (Wed) 7/4 (Wed) Examples of biomolecules?
Additional problems: 1. Match and label the conjugate acid and base pairs in the following reactions. Which one of these systems is a good buffer?
 1 ESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry Sections to review: 10.2,.3,.4,.6.9,.12,.13 omplete the following sentences 1. 2 3 is a acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid
1 ESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry Sections to review: 10.2,.3,.4,.6.9,.12,.13 omplete the following sentences 1. 2 3 is a acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
For more info visit
 Carbohydrates Classification of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: Polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to give simpler carbohydrates.examples: Glucose, Fructose,
Carbohydrates Classification of carbohydrates: Monosaccharides: Polyhydroxy aldehydes or polyhydroxy ketones which cannot be decomposed by hydrolysis to give simpler carbohydrates.examples: Glucose, Fructose,
Carbohydrates. Chapter 12
 Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
Carbohydrates Chapter 12 Educational Goals 1. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it as either aldoses or ketoses. 2. Given a Fischer projection of a monosaccharide, classify it by
3150:112 SAMPLE TEST 2. Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck!
 SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
Oregon State University
 H 223 Worksheet 9 Notes Oregon State University 1. Draw a primary alcohol and name it. OH 1-propanol Note: A primary alcohol has the form RH 2 OH; a secondary alcohol has the form R 2 H OH; and a tertiary
H 223 Worksheet 9 Notes Oregon State University 1. Draw a primary alcohol and name it. OH 1-propanol Note: A primary alcohol has the form RH 2 OH; a secondary alcohol has the form R 2 H OH; and a tertiary
Carbohydrates. Learning Objective
 , one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
, one of the four major classes of biomolecules, are aldehyde or ketone compounds with multiple hydroxyl groups. They function as energy stores, metabolic intermediates and important fuels for the body.
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush. Rana N. Talj
 2 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 19 th 2013 Rana N. Talj Review: Fischer suggested a projection in which the horizontal bonds are projecting towards the viewer and the vertical ones project away from the
2 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 19 th 2013 Rana N. Talj Review: Fischer suggested a projection in which the horizontal bonds are projecting towards the viewer and the vertical ones project away from the
BCH302 [Practical] 1
![BCH302 [Practical] 1 BCH302 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/78/76808179.jpg) BCH302 [Practical] 1 Amino acids play a central role: i. As building blocks of proteins. ii. As intermediates in metabolism, converted to specialized products. There are 20 natural amino acids that are
BCH302 [Practical] 1 Amino acids play a central role: i. As building blocks of proteins. ii. As intermediates in metabolism, converted to specialized products. There are 20 natural amino acids that are
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates
 Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Introduction Classification of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have the general formula C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances that
Chapter 22 Carbohydrates Introduction Classification of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have the general formula C x (H 2 O) y Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances that
Amino acids. (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi
 Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
1. Draw a standard line bond structure for compounds of the following molecular formulas:
 TF ame: LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #1 Due Friday 9/29 at noon in your TF s drop box on the 2 nd floor of Science Center all questions including extra ones should be turned in 1. Draw a standard line bond
TF ame: LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #1 Due Friday 9/29 at noon in your TF s drop box on the 2 nd floor of Science Center all questions including extra ones should be turned in 1. Draw a standard line bond
Chapter 23: Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n (H 2 O) n. Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer)
 Chapter : Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν C + C + Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: Monomer units:
Chapter : Carbohydrates hydrates of carbon: general formula C n ( ) n Plants: photosynthesis hν C + C + Polymers: large molecules made up of repeating smaller units (monomer) Biopolymers: Monomer units:
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
AS Describe aspects of organic chemistry. COLLATED POLYMER QUESTIONS - polyesters, polyamides and peptides
 o Brain Too Small EMISTRY AS 90698 Describe aspects of organic chemistry LLATED PLYMER QUESTIS - polyesters, polyamides and peptides (2011:2) ylon 6,6 is a polymer with the following structure: (a) (b)
o Brain Too Small EMISTRY AS 90698 Describe aspects of organic chemistry LLATED PLYMER QUESTIS - polyesters, polyamides and peptides (2011:2) ylon 6,6 is a polymer with the following structure: (a) (b)
Structure of Alkenes In ethene (ethylene) each carbon is bonded to 3 other atoms, with zero nonbonding electrons => sp 2 hybridization.
 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Alkenes (olefins) are hydrocarbons which have carbon carbon double bonds. A double bond is a bond and a bond. Double bond B.D.E. bond B.D.E. = 146 kcal/mol = 83 kcal/mol
Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Alkenes (olefins) are hydrocarbons which have carbon carbon double bonds. A double bond is a bond and a bond. Double bond B.D.E. bond B.D.E. = 146 kcal/mol = 83 kcal/mol
CHAPTER 5: STEREOISOMERS
 APTER 5: STEREISMERS SIMPLE STEREISMERS NSTITUTINAL ISMERS VERSUS STEREISMERS A constitutional isomer A stereoisomer Page 1 IRALITY (ANDEDNESS) hiral object: Achiral object: Are these objects chiral or
APTER 5: STEREISMERS SIMPLE STEREISMERS NSTITUTINAL ISMERS VERSUS STEREISMERS A constitutional isomer A stereoisomer Page 1 IRALITY (ANDEDNESS) hiral object: Achiral object: Are these objects chiral or
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins No. 1 of 10 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? (A) Serine (B) Proline (C) Alanine (D) Phenylalanine (E) Glycine
rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins No. 1 of 10 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? (A) Serine (B) Proline (C) Alanine (D) Phenylalanine (E) Glycine
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES
 3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
Protiens and Amino Acids 2
 Protiens and Amino Acids 2 By Alaa J. Mahrath, Biochemistry Department / College of Medicine/ Babylon University 2 Amino Acid Stereoisomers Protiens and Amino Acids All the a-amino acids except for glycine
Protiens and Amino Acids 2 By Alaa J. Mahrath, Biochemistry Department / College of Medicine/ Babylon University 2 Amino Acid Stereoisomers Protiens and Amino Acids All the a-amino acids except for glycine
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay
 Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Acid/Base chemistry. NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 Review problems for the first exam. Complete the following sentences
 1 NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry 1. 2 3 is a weak acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid is a weak base 3. p is the measure of a solutions acidity. 4. 3 and
1 NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry 1. 2 3 is a weak acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid is a weak base 3. p is the measure of a solutions acidity. 4. 3 and
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Review of literature Previously there is lot of work done on Sertraline hydrochloride a psychotic drugs undesired isomer recycling
 Review of literature Previously there is lot of work done on Sertraline hydrochloride a psychotic drugs undesired isomer recycling In the above mentioned scheme sertraline have four different isomers possible.
Review of literature Previously there is lot of work done on Sertraline hydrochloride a psychotic drugs undesired isomer recycling In the above mentioned scheme sertraline have four different isomers possible.
Cahn - Ingold - Prelog system. Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009. The Fischer Convention (1) G (2) (3)
 Chapter 4 (1) G Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009 A V L I M P F W Chapter 4 (2) S (3) T N Q Y C K R H D E The Fischer Convention Absolute configuration about an asymmetric carbon related
Chapter 4 (1) G Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009 A V L I M P F W Chapter 4 (2) S (3) T N Q Y C K R H D E The Fischer Convention Absolute configuration about an asymmetric carbon related
Chemistry 2030 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2012 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 Chemistry 2030 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2012 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5: The Final Lipids, Carbohydrates, Nucleobases & DNA. Monday, December 10, 2012, 3 5 pm. Name: Question
Chemistry 2030 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2012 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5: The Final Lipids, Carbohydrates, Nucleobases & DNA. Monday, December 10, 2012, 3 5 pm. Name: Question
Chapter 05 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions part 01
 hapter 05 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions part 01 EM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg ook 2012 Gregory R ook Alkenes ompounds that contain double bonds. Ethylene (Ethene) 2 2012
hapter 05 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions part 01 EM 341: Spring 2012 Prof. Greg ook 2012 Gregory R ook Alkenes ompounds that contain double bonds. Ethylene (Ethene) 2 2012
Alkenes and Alkynes: Structure and Nomenclature
 hapter 3 3 : Structure and Nomenclature APTER SUMMARY 3.1 Introduction to Alkenes are hydrocarbons in which there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond; alkynes have at least one carbon-carbon triple
hapter 3 3 : Structure and Nomenclature APTER SUMMARY 3.1 Introduction to Alkenes are hydrocarbons in which there is at least one carbon-carbon double bond; alkynes have at least one carbon-carbon triple
Isolation and Purification of Organic Compounds Steam Distillation of Essential Oils
 Isolation and Purification of Organic Compounds Steam Distillation of Essential Oils Distillation relies on the fact that the substance with the greatest vapor pressure will be enriched in the vapor phase
Isolation and Purification of Organic Compounds Steam Distillation of Essential Oils Distillation relies on the fact that the substance with the greatest vapor pressure will be enriched in the vapor phase
Chem 263 Nov 22, Carbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See Handout
 hem 263 Nov 22, 2016 arbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See andout Approximately 0.02% of the sun s energy is used on this planet for photosynthesis in which organisms convert carbon dioxide
hem 263 Nov 22, 2016 arbohydrates (also known as sugars or saccharides) See andout Approximately 0.02% of the sun s energy is used on this planet for photosynthesis in which organisms convert carbon dioxide
Chapter 7- Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity. Ashley Piekarski, Ph.D. Alkene
 Chapter 7- Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity Ashley Piekarski, Ph.D. Alkene What is an alkene func
Chapter 7- Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity Ashley Piekarski, Ph.D. Alkene What is an alkene func
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Functional Group. Chapter 7 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes. Bond Lengths and Angles. Orbital Description. Pi Bond. Elements of Unsaturation
 Organic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 7 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Jo Blackburn Richland ollege, Dallas, TX Dallas ounty ommunity ollege District 2003, Prentice all Functional Group
Organic hemistry, 5 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. hapter 7 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes Jo Blackburn Richland ollege, Dallas, TX Dallas ounty ommunity ollege District 2003, Prentice all Functional Group
