Macrophages and dendritic cells
|
|
|
- Margaret Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Primer on Tumor Immunology and Biological Therapy November 10, 2005 Hilton Alexandria Mark Center Alexandria, VA Macrophages and dendritic cells Giorgio Trinchieri NIH Fogarty Scholar and ORISE Senior Fellow Laboratory of Parasitic Diseases National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
2 Pro-inflammatory cytokines: Conventional Dendritic IL-1Cells (IL-12 IFN-γ) IL-6 TNF IL-23 IL-27 Antigen presentation Signal 1 Co-stimulation Signal 2 IL-18 Immunomodulatory Signal 3 Cytokines IL-12 Plasmacytoid precursor Dendritic Cells Type II immune IFN (IFN-γ) (Type I Interferon-producing cells) Type I Interferon (IFN-α/β/ω/κ)
3 Dendritic cells First identified in the epidermis (P. Langerhans, 1868) Characterized in lymphoid tissue (R. Steinman, 1973), and subsequently described in most organs; identified as the most efficient antigen-presenting cells. Methods to generate large numbers of dendritic cells in vitro (C. Caux, 1992; A. Lanzavecchia, 1994) Dendritic cells are «sentinels» controling the immune response through highly-efficient antigen capture, processing, and presentation to antigen-specific CD4 and CD8 T cells.
4 Dendritic cells have specialized mechanisms for antigen-uptake Phagocytosis Bacteria Zymozan Parasites Complement receptors(cr2) Fc receptors (FcRII) Mannose receptor Opsonized particles Apoptotic cells Clathrin-dependent endocytosis HIV virus Desialylated IgG Mannosylated compounds Lipoarabinomannan Hsp70/peptide Immune complexes Fc receptors (FcRII, FcRI) Mannose receptor HSP receptor? CD4 and chemokine receptors? ILT3? CD36, v 3, v 5? Macropinocytosis Soluble compounds
5 Pathways of antigen processing and presentation by DC Endogenous antigen Exogenous antigen protein peptide MHC-I MHC-I Cross-presentation MHC-II MHC-II
6
7 In situ localization of human DC populations Langerhans cells (Langerin + cells in skin epidermis) Dermal DCs (interstitial DCs) (CD1a + in skin dermis) skin Activated DCs (interdigitating DCs) (DC-LAMP + in T zone) Plasmacytoid DCs (CD123 + in T zone) tonsils
8 DC trafficking during pathogen invasion 1 Pathogens Immature DC DC Tissue Blood DC precursors DC 2 DC recruitment 3 Antigen uptake DC 4 DC Activation and Emigration DC DC Lymph Blood + CD34 Progenitors Bone marrow 5 T cell priming T DC T T T T T T DC DC Mature DC Lymphnode
9 Ex Vivo DENDRITIC CELL ADOPTIVE THERAPY (VACCINATION) Tumor-DC fusion DC Apoptotic tumor cells Apoptotic bodies Exosomes DC DC Protein/peptides Heat Shock Proteins cdna mrna Biragyn & Kwak: Nature Med. 6:966 (2000) (modified)
10 Variables in DC adoptive therapy Antigen loading Origin and type of DC Maturation/activation of DC Routes of injection
11 Dendritic cells are highly heterogeneous DC type Tissue location Langerhans cells epidermis, stratified epithelia Interstitial DC Interdigitating DC dermis / lamina propria, blood, lymphoid tissue, organs T-zone lymphoid tissue, thymus Veiled cells lymph Plasmacytoid DC (type-i IFN+++) blood, lymphoid tissue
12 Monocyte Precursor Plasmacytoid DC Monocyte-derived DC Plasmacytoid DC Modified from Shortman and Liu 2002 Nature Review Immunology
13 Sources of DC in Clinical Trials Purified from Peripheral Blood CD34+ cell-derived (GM-CSF + TNF) Monocyte-derived (GM-CSF + IL-4)
14 Two pathways of dendritic cell development from CD34 hematopoietic progenitors M-CSF TISSUE MACROPHAGES CD14+, CD1a -, CD83 -, CD86 - PROGENITOR CELLS GM-CSF + TNF CD14 + GM-CSF + TNF DENDROCYTES: INTERSTITIAL TYPE DENDRITIC CELLS CD14-, CD1a +, CD83 +, CD86 + CD34 + BG-, Lag-, Langerin -, E-Cad -, CD68+, Fact. XIIIa + GM-CSF + TNF GM-CSF + TNF LANGERHANS CELLS: EPITHELIAL TYPE DENDRITIC CELLS CD1a + DAY 0 DAY 5 DAY 14 CD14-, CD1a +, CD83 +, CD86 + BG+, Lag+, Langerin +, E-Cad +, CD68-, Fact. XIIIa -
15 In vitro development of dendritic cells from CD34 hematopoietic progenitors or from monocytes BLOOD MONOCYTES GM-CSF + IL-4 M-CSF TISSUE MACROPHAGES CD14 + PROGENITOR CELLS GM-CSF + TNF CD14 + GM-CSF + TNF DENDROCYTES: INTERSTITIAL TYPE DENDRITIC CELLS CD34 + GM-CSF + TNF CD1a + GM-CSF + TNF LANGERHANS CELLS: EPITHELIAL TYPE DENDRITIC CELLS DAY 0 DAY 5 DAY 14
16 In vitro development of Langerhans cells BLOOD MONOCYTES GM-CSF + IL-4 CD14 + PROGENITOR CELLS GM-CSF + TNF CD14 + GM-CSF + TNF DENDROCYTES: INTERSTITIAL TYPE DENDRITIC CELLS CD34 + GM-CSF + TNF CD1a + GM-CSF + TNF LANGERHANS CELLS: EPITHELIAL TYPE DENDRITIC CELLS BLOOD MONOCYTES CD14 + GM-CSF + IL-4 + TGFß or GM-CSF + IL15
17 Langherans-like DC Interstitial-like DC Modified from: Bancherau and Palucka, 2005
18 Variables in DC adoptive therapy Antigen loading Origin and type of DC Maturation/activation of DC Routes of injection
19 IMMUNITY TOLERANCE Modified from Shortman and Liu 2002 Nature Review Immunology
20 Toll-like receptors Other receptors Autocrine cytokines Activated NK cells Activated NKT cells Activated T cells Cytokines (e.g. IFN-g) Cell-surface molecules (e.g. CD40L) Modified from Mellman I et al, Trends in Cell Biology 1998
21 Immature DC Intermediate DC Mature/activated DC Modified from Mellman I et al, Trends in Cell Biology 1998
22 Signal 1 Antigen uptake Migration Signal 2 Timmerman JM, Levy R. Signal 3 Dendritic cell vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Annu Rev Med. 1999;50:507
23 Maturation/Activation of DC in Clinical Trials Monocyte-conditioned medium TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, PGE2 Trance/RANKL, CD40L
24 Variables in DC adoptive therapy Antigen loading Origin and type of DC Maturation/activation of DC Routes of injection
25 Routes of injection of Dendritic Cells Pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine cascade Modified from Randolph et al. Nature Review Immunology 2005
26 DC adoptive therapy / vaccination in cancer patients is safe, often induces an immune response against tumor-associated antigens, and in a proportion of cases induces a lasting partial or rarely complete remission that has been correlated with the extent of the immune response generated. Clinical outcome of cancer vaccines in patients with melanoma (Rosenberg et al, Nature Medicine, 2004) From: Bancherau and Palucka, Nature Review Immunology, 2005
27 Ex Vivo Chemokine-Ag Mannose-Ag Fc-Ag Antibody-Ag In Vivo Tumor-DC fusion Cell Surface receptor Apoptotic tumor cells Apoptotic bodies Exosomes DC Receptor-mediated internalization Immature DC Mileau of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines with recruitment of other cells Migration to lymphoid organs and maturation DC Mature DC DC MHCI MHCII Protein/peptides Heat Shock Proteins CD8+ T-cell cdna or mrna Proinflammatory Cytokines and Factors CD4+ T-cell Biragyn & Kwak: Nature Med. 6:966 (2000) (modified)
28 Mahnke K, Qian Y, Fondel S, Brueck J, Becker C, Enk AH. Targeting of antigens to activated dendritic cells in vivo cures metastatic melanoma in mice. Cancer Res : Ag DC surface molecules DEC205 (interdigitating DC In T cell area of LN) DC-SIGN (dermal DC). The antigen-coupled antibodies reach DC in all tissues, including LN, and are internalized, inducing Ag-presentation to T cells + anti-cd40 +TLR-ligands s.c. s.c. Immature DC TOLERANCE Mature DC IMMUNITY, TUMOR REJECTION Bonifaz L, Bonnyay D, Mahnke K, Rivera M, Nussenzweig MC, Steinman RM. Efficient targeting of protein antigen to the dendritic cell receptor DEC-205 in the steady state leads to antigen presentation on major histocompatibility complex class I products and peripheral CD8+ T cell tolerance. J Exp Med :
29 Plasmacytoid precursor dendritic cells or type I Interferon producing cells. Type I IFN-producing cells (IPC) (Plasmacytoid pre-dc) IPC are the only cell type in human blood able to produce type IFN in response to viruses VIRUS IFN-α/β NK cell Cytotoxicity IPC represent 1/500 to 1/200 of PBMC IPC are MHC class II positive but distinct in functions and morphology from Dendritic Cells IPC are very poor APC but are required for NK cell-mediated killing of virus-infected cells ( ) DC HuIPC
30 Characteristics of human myeloid DC and plasmacytoid precursor DC (YJ. Liu et al.) IL-3 CD40L Conventional dendritic cells IL-12 in response to Gram + and - bacteria, intracellular parasites IFN-α/β secretion in response to polyi:c but not to most viruses TLR 2± 3+ 4± 7± Plasmacytoid precursor dendritic cells (Liu, Briere, Colonna, 1999) Type I IFN producing cells (70-80s) High titer of IFN-α in response to viruses and certain CpG Low IL-12 secretion ` TLR (10+)
31 Lipid ligands Sequence variants in TLR4 and TLR1/6/10 have been associated with prostate cancer risk.? TLR2 TLR10 MyD88 Humans, diacyl lipopeptides TLR1 TIRAP MyD88 TLR6 Rat, Toll-like Not Mouse receptors Toll-likepH receptors NOD1, 2 TLR2 triacyl lipopeptides TIRAP MyD88 TLR2 TLR8 TLR7 CD14 MD-2 TIRAP MyD88 MyD88 TRAM ssrna? Imiquimod ssrna R848 ssrna Imiquimod R848 LPS TLR4 TRIF MyD88 (ph Nucleic ) acid ligands CpG DNA Protein ligands flagellin TLR5 MyD88 dsrna TLR3 TLR3 Uropathog. Bacteria Apicomplexan profilins TLR11 TLR5 Mouse, Mouse, Not humans Not humans dsrna IL-1, IL-18 MyD88 RIG-I IL-1R family Rick/Rip2 MyD88 MyD88 Humans, Not Mouse?, MyD88 TLR7 TLR8 MyD88 TLR9 TLR9 TRIF IKKε TBK1 The Toll-like (TLR) / IL-1 Receptor Family
32 Human dendritic cell subsets Plasmacytoid DC ILT3 + ILT1 - BDCA-2 Myeloid DC ILT3 + ILT1 + BDCA-1=CD1c FSC CD4-PE Cy5 Coktail Fitc: CD1a, 3, 14, 16, 19 CD11c PE
33 Afferent lymphacytic vessels Plasmacytoid Dentritic Cells Infected or inflammed tissues Steinman, R. M. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 2002;109: High endothelial venules, Central artery Copyright 2002 American Society for Clinical Investigation
34 Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells pdc are very efficient producers of type I Interferon (IFN-a/b) and, in the Mouse but not in Humans, also produce IL-12. pdc are the main but not the only producer of type I IFN in most virus infections. By producing IFN and other cytokines, pdc are important players in the activation of innate resistance and inflammation and in the interface between innate and adaptive resistance. pdc are poor antigen presenting cells for T cells and are able to induce proliferation of pre-activated rather than naïve T cells. There are several reports that in vitro pdc may be tolerogenic and pdc have been shown to play an important role in regulating the response against harmless antigens in lung, liver, and gut (oral tolerance). By producing IFN and IL-6, pdc enhance B cell differentiation into plasma cells and may be involved in autoimmune diseases such as SLE and psoriasis.
35 Physical, mechanical cause Auto-immunity Infection Endogenous factors TUMOR INFLAMMATION: Very LOW Very HIGH Deficiency in pro-inflammatory genes results in resistance to carcinogenesis: IL-1, MIF, CSF-1, TNF, STAT3 Anti-inflammatory cytokines prevent carcinogenesis: IL-10 T regulatory cells may prevent H. hepaticus induced colon carcinogenesis by producing IL-10 Pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g. IL-12, IL-18, IFN-γ, IFN-α, TNF, IL-2, IL-15) and ELR(-) interferon-inducible chemokines (IP-10, Mig, I-TAC) have anti-tumor and anti-angiogenis effects. TLR-ligands have anti-tumor activity that is enhanced by antagonism of IL-10. Mice deficient for IFN-γ, IL 12, or IFN-α have increased incidence of spontaneous or carcinogenesis induced tumors. Modified from Coussens L.M. and Werb Z. Nature 2002, 420: The inflammatory and immune responses select tumors that have escape mechanisms and resist these responses.
36 CD1a + DC in breast cancer are in direct contact with tumor cells DC-LAMP+ and CD40+ DC in breast cancer are clustered in peri-tumoral lymphoid-like structures DC-Lamp + CD40 + (~30% positive tumors) 255 patients with invasive non-metastatic breast cancer treated at Centre Leon Berard, Lyon, in (~50% positive tumors) Treilleux I et al. Dendritic cell infiltration and prognosis of early stage breast cancer Clin Cancer Res. 10:
37 Tumor-infiltrating Dendritic Cells: Friends or Foes? CD123 + DC (and BDCA-2+) plasmacytoid DC) infiltrate human breast tumors in 13% of the patients The presence of pdc in the primary tumor strongly correlates with poor prognosis 1,0,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 0,0 0 Overall survival pdc- pdc+ 80 X20 1,0,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1 0,0 0 Disease-free survival Months 60 pdc- pdc+ 80
38 Mouse TIDC are anergic but respond to select TLR ligands when IL-10 is inhibited IL-12p40 IL-12p IFNγ none 1668 R848 LPS+γ+aCD40 poly IC TNFα IFNγ (pg/ml/10 6 cells) TNFα (pg/ml/10 6 cells) IL12p40 (pg/ml/10 6 cells) IL12p70 (pg/ml/10 6 cells) 0 none 1668 R848 LPS+g+aCD40 poly IC none anti-il10r 0 0 none 1668 R848 LPS+g+aCD40 poly IC none 1668 R848 LPS+g+aCD40 poly IC None 1668 CpG R848 LPS + IFN-γ + acd40 Poly I:C None 1668 CpG R848 LPS + IFN-γ + acd40 Poly I:C
39 Interleukin-10 plays an important role in the immunosuppressive tumor environment. TLR ITAM-R (e.g. FcR) Lectin (e.g. Dectin) Other R? MyD88 ERK, p38, IRAK1 STAT3, Sp1 IL-10 STAT3 DC (anergic) STAT3 STAT3 Tumor Macrophages (M2)
40 Alternative Macrophage Activation Tumor Associated Macrophages (TAM) [Tumor Infiltrating Dendritic Cells (TIDC)] IFN-γ TLR agonists IL- 4 IL-13 IL-10 M1 M2 IL-12 inos NO (IDO) TNF IL-10 TGF-β (IL-12) (IL-10) No IL-12 Low Class II Arginases IL-1ra Mantovani et al, 2002
41 Is it possible to induce an immune response to the tumor own antigens by removing immuno-suppression and providing an inflammatory stimulus? TSA tumors (>5mm) treated with adenovirus vector expressing LEC/CCL16, intratumoral CpG, and systemic anti-il-10r. AdCCL16+CpG+aIL10R (similar results for TSA, 4T1,MC38 and for inhibition of spontaneous metastases of 4T1)
42 TSA WT TNF KO >WT MCA38 CCL16/CpG/aIL10R 16-h p.t. CCL16 + CpG + anti-il-10r treatment induces a rapid hemorrhagic tumor necrosis that is dependent on TNF, IL-12, and CD40.
43 TUMOR M2 M2 M2 IL-10 Arginase I. Inflammatory Hemorragic Necrosis 6-16 h p.t. CpG-OGN Anti-IL-10R (anti-cd25) CD4+ CD8+ M1 M1 M1 Nitric Oxide TNF IL-12 IFN-γ CD40/CD40L DC migration to draining LN 0-6 h p.t. TNF CCR7/CCR7L CD25+ CD4+ T REG Draining LN Tumor Ag-specific regulatory CD8+ T cells II. Tumor Ag-specific Effector CD8+ T cells
44 Alain Vicari Christophe Dercamp Christophe Caux Francine Brière Serge Lebecque LIR, Schering-Plough Research Institute Dardilly, France Cristiana Guiducci Mario Colombo National Tumor Institute Milano, Italy Jean-Yves Blay Isabelle Treilleux Centre Leon Berard, LYON
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Dendritic cells and their role in immunity
 PART I Dendritic cells and their role in immunity CHAPTER 1 Subpopulations and differentiation of mouse dendritic cells Carlos Ardavín Universidad Autónoma 1.1 DENDRITIC CELL SUBPOPULATIONS Dendritic cells
PART I Dendritic cells and their role in immunity CHAPTER 1 Subpopulations and differentiation of mouse dendritic cells Carlos Ardavín Universidad Autónoma 1.1 DENDRITIC CELL SUBPOPULATIONS Dendritic cells
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Dendritic Cell Based Immunotherapy for Cancer. Edgar G. Engleman, M.D.
 Dendritic Cell Based Immunotherapy for Cancer Edgar G. Engleman, M.D. Two main DC subsets Myeloid (mydc) Derived from monocytes Capture/process/present Ag to T cells Activate NK cells and B cells Plasmacytoid
Dendritic Cell Based Immunotherapy for Cancer Edgar G. Engleman, M.D. Two main DC subsets Myeloid (mydc) Derived from monocytes Capture/process/present Ag to T cells Activate NK cells and B cells Plasmacytoid
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F Lyon
 Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
Basis of Immunology and
 Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
The Use of Human Dendritic Cell
 The Use of Human Dendritic Cell Subsets in Cancer Vaccines Jolien Sweere Student #: 3145298 Master Thesis Infection and Immunity Supervisor: Dr. Jeanette Leusen Immunotherapy University Medical Centre
The Use of Human Dendritic Cell Subsets in Cancer Vaccines Jolien Sweere Student #: 3145298 Master Thesis Infection and Immunity Supervisor: Dr. Jeanette Leusen Immunotherapy University Medical Centre
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang
 Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
Dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy Aimin Jiang Feb. 11, 2014 Dendritic cells at the interface of innate and adaptive immune responses Dendritic cells: initiators of adaptive immune responses Dendritic
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON. Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR CANCER A NEW HORIZON Ekaterini Boleti MD, PhD, FRCP Consultant in Medical Oncology Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust ASCO Names Advance of the Year: Cancer Immunotherapy No recent
Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity
 MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
MICR2209 Adaptive immune responses: T cell-mediated immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will discuss the T-cell mediated immune response, how it is activated,
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Tumor Immunology. Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant
 Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Tumor Immunology Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncology Consultant 1) Immune responses that develop to cancer cells 2) Escape of cancer cells 3) Therapies: clinical and experimental Cancer cells can be
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals. Taniawati Supali. Department of Parasitology
 Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy
 Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies. Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018
 Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018 Macrophages: Professional phagocytes of the myeloid lineage APC,
Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018 Macrophages: Professional phagocytes of the myeloid lineage APC,
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription (-) TLR2 PGN MDP. MyD88 IRAK ECSIT TRAF6 NIK. Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IKK.
 D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
Manipulating the Tumor Environment
 Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer - TLR9 as a therapeutic target -
 Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer - TLR9 as a therapeutic target - Wilfried Eberhardt,, MD Head of Outpatient Unit, Dept. of Internal Medicine (Cancer Research) West German Cancer Centre Essen University Hospital
Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer - TLR9 as a therapeutic target - Wilfried Eberhardt,, MD Head of Outpatient Unit, Dept. of Internal Medicine (Cancer Research) West German Cancer Centre Essen University Hospital
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION. 1 hour between 8:30 a.m. - 10:00 a.m. McIntyre Medical Rm 504 (Martin Amphitheatre)
 GROUP (Version) 1 Annotated version April 8, 2011, RGEP DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION Course Coordinator: Dr. Roger Palfree Date: Thursday, March
GROUP (Version) 1 Annotated version April 8, 2011, RGEP DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Immunology MIMM-314 MID-TERM II EXAMINATION Course Coordinator: Dr. Roger Palfree Date: Thursday, March
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
Innate Immunity II. Integration. Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2
 Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
The Adaptive Immune Responses
 The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
The Adaptive Immune Responses The two arms of the immune responses are; 1) the cell mediated, and 2) the humoral responses. In this chapter we will discuss the two responses in detail and we will start
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Dendritic Cells: A Lesser known Part of the Immune System
 Dendritic Cells: A Lesser known Part of the Immune System Mei Mei Tian Immunology has long focused on the relationship between lymphocytes and antigens, however their presence in a system does not always
Dendritic Cells: A Lesser known Part of the Immune System Mei Mei Tian Immunology has long focused on the relationship between lymphocytes and antigens, however their presence in a system does not always
Immunology. T-Lymphocytes. 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters,
 Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
Immunology T-Lymphocytes 16. Oktober 2014, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Karin Peters, karin.peters@rub.de The role of T-effector cells in the immune response against microbes cellular immunity humoral immunity
DENDRITIC CELLS AS THERAPEUTIC VACCINES AGAINST CANCER
 DENDRITIC CELLS AS THERAPEUTIC VACCINES AGAINST CANCER Jacques Banchereau and A. Karolina Palucka Abstract Mouse studies have shown that the immune system can reject tumours, and the identification of
DENDRITIC CELLS AS THERAPEUTIC VACCINES AGAINST CANCER Jacques Banchereau and A. Karolina Palucka Abstract Mouse studies have shown that the immune system can reject tumours, and the identification of
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007
 Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007 TheComponents Of The Immune System and Innate Immunity: Ref: Immunobiology-5 th edition. Janeway et al. Chapters-1 & 2.
Introduction to Immunology Lectures 1-3 by Bellur S. Prabhakar. March 13-14, 2007 TheComponents Of The Immune System and Innate Immunity: Ref: Immunobiology-5 th edition. Janeway et al. Chapters-1 & 2.
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Vaccines. Prof. Lana E. Kandalaft. Director Centre of Experimental Therapeutics, Deparment of Oncology, UNIL CHUV
 Vaccines Prof. Lana E. Kandalaft Director Centre of Experimental Therapeutics, Deparment of Oncology, UNIL CHUV Assisant Professor, Ludwig Cancer Reaserch Branch Adjunct Assistant Professor, University
Vaccines Prof. Lana E. Kandalaft Director Centre of Experimental Therapeutics, Deparment of Oncology, UNIL CHUV Assisant Professor, Ludwig Cancer Reaserch Branch Adjunct Assistant Professor, University
Adaptive Immunity. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 16 Adaptive Immunity The Body s Third Line of Defense Adaptive Immunity Adaptive immunity
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 16 Adaptive Immunity The Body s Third Line of Defense Adaptive Immunity Adaptive immunity
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel:
 Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
The Adaptive Immune Response. T-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
The Adaptive Immune Response T-cells T Lymphocytes T lymphocytes develop from precursors in the thymus. Mature T cells are found in the blood, where they constitute 60% to 70% of lymphocytes, and in T-cell
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
5/1/13. The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age. The cellular organization of the thymus
 T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
T cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow via the blood to the thymus to mature 1 2 The cellular organization of the thymus The proportion of thymus that produces T cells decreases with age 3 4 1
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
CYTOKINES. Based on: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 4 th ed.,abbas A.K., Lichtman A.H. and Pober J.S. Sounders company; Philadelphia, 2010.
 CYTOKINES Based on: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 4 th ed.,abbas A.K., Lichtman A.H. and Pober J.S. Sounders company; Philadelphia, 2010. 1 What are cytokines? Glycoproteins (15 25 kda): Interleukins
CYTOKINES Based on: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 4 th ed.,abbas A.K., Lichtman A.H. and Pober J.S. Sounders company; Philadelphia, 2010. 1 What are cytokines? Glycoproteins (15 25 kda): Interleukins
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology
 Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Immunity to Viruses. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly September 25, 2008
 Immunity to Viruses Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly September 25, 2008 The Immune System Deals with a Huge Range of Pathogens Roitt, 2003 Immune Responses to Viruses Viruses are dependent on the host cell
Immunity to Viruses Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly September 25, 2008 The Immune System Deals with a Huge Range of Pathogens Roitt, 2003 Immune Responses to Viruses Viruses are dependent on the host cell
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Immune Checkpoints. PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich
 Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Measles virus vaccine induces oncolysis of tumor cells and activates immune responses.
 Measles virus vaccine induces oncolysis of tumor cells and activates immune responses. Marc Grégoire*, J.-F. Fonteneau, N. Boisgerault, J.-B. Guillerme and F. Tangy. * INSERM, Nantes, F-44, France. Pasteur
Measles virus vaccine induces oncolysis of tumor cells and activates immune responses. Marc Grégoire*, J.-F. Fonteneau, N. Boisgerault, J.-B. Guillerme and F. Tangy. * INSERM, Nantes, F-44, France. Pasteur
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 19: Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Autoinflammation Prepared
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 19 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 19: Tolerance, Autoimmunity, and Autoinflammation Prepared
Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses
 MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
MICR2209 Adaptive Immunity: Humoral Immune Responses Dr Allison Imrie 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which constitute the humoral immune response, and examine the antibody
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Adaptive Immunity. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R
 CSLO7. Describe functions of host defenses and the immune system in combating infectious diseases and explain how immunizations protect against specific diseases. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared
CSLO7. Describe functions of host defenses and the immune system in combating infectious diseases and explain how immunizations protect against specific diseases. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared
Prepared by Cyrus H. Nozad, MD, University of Tennessee and John Seyerle, MD, Ohio State University
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 21 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, Seventh Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 21: Antigen-Presenting Dendritic Cells (Pages
Chapter 13: Cytokines
 Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Relative sizes of infectious agents
 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance. Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco
 Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
Determinants of Immunogenicity and Tolerance Abul K. Abbas, MD Department of Pathology University of California San Francisco EIP Symposium Feb 2016 Why do some people respond to therapeutic proteins?
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany
 How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
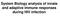 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
Diseases of Immunity CL Davis General Pathology. Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc
 Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 6 th Ed Veterinary Immunology,
Diseases of Immunity 2017 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Inc Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 6 th Ed Veterinary Immunology,
Felix Yarovinsky. Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii
 Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
The Immune System. A macrophage. ! Functions of the Immune System. ! Types of Immune Responses. ! Organization of the Immune System
 The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
Immune Regulation and Tolerance
 Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
Immune Regulation and Tolerance Immunoregulation: A balance between activation and suppression of effector cells to achieve an efficient immune response without damaging the host. Activation (immunity)
CD40L TCR IL-12 TLR-L
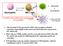 CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Microbiology 204: Cellular and Molecular Immunology
 Microbiology 204: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Class meets MWF 1:00-2:30PM (*exceptions: no class Fri Sept 23, Fri Oct 14, Nov 11, or Wed Nov 23) Lectures are open to auditors and will be live-streamed
Microbiology 204: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Class meets MWF 1:00-2:30PM (*exceptions: no class Fri Sept 23, Fri Oct 14, Nov 11, or Wed Nov 23) Lectures are open to auditors and will be live-streamed
