Innate Immunity & Inflammation
|
|
|
- Conrad Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited set of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that recognize specific pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) commonly present in microbes but not in host. Upon detection of PAMPs, some PRRs trigger an inflammatory response leading to efficient destruction of the invading pathogens. Three main families of PRRs have been shown to initiate proinflammatory signaling pathways: the Toll-like receptors (TLRs), the NOD-like receptors (NLRs) and RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs). Toll Like Receptors (TLRs) TLRs are the first identified and best characterized receptors among the signaling PRRs. They initiate key inflammatory responses and also shape adaptative immunity. They recognize a variety of PAMPs from bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), flagellin, and CpG DNA. TLRs initiate shared and distinct signaling pathways leading to the activation of various transcription factors, such as NF- -1, and the subsequent production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Nod-Like Receptors (NLRs) NLRs (also known as CATERPILLERs) constitute a recently identified family of intracellular PRRs, which contains more than 20 members in mammals. Although the ligands and functions of many of these receptors are not known, their primary role is to recognize cytoplasmic PAMPs and/or endogenous danger signal, inducing immune responses. NLRs have been grouped into several subfamilies on the basis of their effector domains: NODs, NALPs, CIITA, IPAF, and NAIPs. RIG-I-Like Receptors (RLRs) RLRs constitute a family of cytoplasmic RNA helicases that are critical for host antiviral responses. RIG-I (retinoic-acid-inducible protein 1) and MDA-5 (melanoma-differentiation-associated gene 5) sense double-stranded RNA (dsrna), a replication intermediate for RNA viruses, leading to production of type I interferons (IFNs) in infected cells. A third RLR has been described: laboratory of genetics and physiology 2 (LGP2), that acts as a negative feedback regulator of RIG-I and MDA-5. Inflammasomes The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor (NLR) family of proteins is involved in the regulation of innate immunity responses. Certain members of the NLR family sense pathogenassociated molecular patterns (PAMPs) in the cytosol and induce the assembly of large caspase-1-activating complexes called inflammasomes. Other Pathogen Sensors Besides TLRs, NLRs and RLRs, other receptors can also recognize molecules present on pathogenic organisms. Those receptors include members of the PGRP (peptidoglycan recognition proteins) and C-type lectin families. C-type lectins, also called C-type lectin receptors (CLRs), encompass a large family of proteins that act as phagocytic receptors that bind carbohydrate moieties of various pathogens. This family comprises MBL, Dectin1, DC-SIGN and the structurally related receptors SIGNRs. Danger Signal - DAMPS PRRs detect not only PAMPs, but also molecules released by stressed cells undergoing necrosis called damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) or alarmins. These DAMPs act as endogenous danger signals to alert and activate innate immune cells. The major DAMPs are HMGB1 (high mobility group box protein-1), S100A8/A9, heat-shock proteins, uric acid and DNA.
2 Toll-Like Receptors InvivoGen offers a large set of tools to study Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) pathways: TLR and related genes, TLR expressing cell lines, TLR Detection products, antibodies against TLR, TLR inhibitors, a large choice of TLR ligands and antagonist. Introduction Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) play a critical role in the early innate immune response to invading pathogens by sensing microorganisms. These evolutionarily conserved receptors, homologues of the Drosophila Toll gene, recognize highly conserved structural motifs only expressed by microbial pathogens, called pathogen-associated microbial patterns (PAMPs). TLR & TLR-Related Genes InvivoGen offers the largest collection of human and mouse genes involved in the TLR pathways. The entire open reading frames (ORFs) of these genes are provided in an expression plasmid and are fully sequenced. The genes are available native, tagged or modified to act as dominant negative mutants. TLR Expressing Cell lines TLR Detection TLR Antibodies InvivoGen provides an expanding collection of TLR expressing cells. These cells enable efficient monitoring of TLR activity using ELISA analysis such as IL-8 titration or reporter-based systems that monitor the activation of NF- InvivoGen offers a comprehensive set of tools designed for the detection of Toll-like receptors. These tools include primers to detect the expression of the TLRs at the mrna or protein level, fusions between the TLRs and a fluorescent protein to study their localization and a family of inducible plasmids to monitor TLR activation. - TLR antibodies include a selection of IgA chimeric monoclonal antibodies, IgG monoclonal antibodies and IgG polyclonal antibodies. Most of these antibodies can be used in neutralization experiments, but also for other applications such as flow cytometry, immunochemistry and Western blotting. - Anti-HA antibody is provided to detect the expression of TLR proteins fused to the HA tag by Western blot or immunoprecipitation.
3 TLR Ligands TLR Inhibition TLR Ligand Detection InvivoGen offers the largest choice of ligands known to activate specific TLRs, that can serve as controls in genetic and pharmaceutical studies on TLRs. The ligands are available individually or in kits. InvivoGen provides a number of tools that should prove useful to help elucidate the molecular mechanisms involved in TLR signaling. These tools include dominant negative TLRs, short hairpin RNAs (shrnas) that silence TLR and adaptor genes and inhibitors of TLR signaling. Endotoxin Detection: InvivoGen provides the HEK-Blue LPS Detection Kit, a simple, rapid and reliable system to detect the presence of lipopolysaccharides in your samples. TLR Ligand Screening: InvivoGen has developed an innovative method to determine whether a compound is recognized by TLRs and acts either as an agonist or antagonist.
4 TLR Ligands The Largest Collection of TLR Agonists Toll-like receptors recognize a wide variety of ligands, called pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), discriminating gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria from fungi and other pathogens. InvivoGen offers the most comprehensive choice of ligands known to activate specific TLRs, that can serve as controls in genetic and pharmaceutical studies on TLRs. InvivoGen strives to provide TLR ligands of the highest quality. All ligands are tested for induction on TLRs and endotoxin levels.tlr ligands are provided individually or as TLR Agonist kits TLR2 Ligands : TLR2 is involved in the recognition of a wide array of microbial molecules representing broad groups of species such as Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as mycoplasma and yeast. TLR3 Ligand : TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA (dsrna), a molecular pattern associated with viral infection. Polyinosine-polycytidylic acid (poly(i:c)), a synthetic analog of dsrna, is the ligand of choice for TLR3. TLR4 Ligands : TLR4 is the receptor for Gram-negative lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipid A, its toxic moiety. InvivoGen offers LPS from various bacteria and monophosphoryl lipid A. TLR5 Ligands : TLR5 recognizes flagellin, the major component of the bacterial flagellar filament, from both Gram+ and Gram- bacteria. InvivoGen provides flagellin purified from B.subtilis (Gram+) and S.typhimurium (Gram-) bacteria and a new recombinant form. TLR7/8 Ligands: TLR7 and TLR8 are involved in the response to viral infection. They recognize GU-rich short single-stranded RNA as well as small synthetic molecules such as imidazoquinolines and nucleoside analogues. TLR9 Ligands : TLR9 recognizes specific unmethylated CpG-ODN sequences that distinguish microbial DNA from mammalian DNA. Three types of stimulatory ODNs have been described: type A, B and C. InvivoGen also provides inhibitory ODNs as well as control ODNs. Labeled TLR Ligands: Labeled ligands are useful to study their cellular uptake and localization. InvivoGen offers CpG-ODNs that are labeled with FITC at their 3 terminus and E.coli lipopolysaccharide labeled with biotin. NOD Ligands: NOD1 and NOD2 are intracellular pathogen-recognition molecules that sense bacterial peptidoglycan (PGN). InvivoGen provides insoluble and soluble PGNs from Gram- and Gram+ bacteria and bioactive fragments of PGN such as ie-dap and MDP. IFN Inducer: Double-stranded B DNA is a very potent inducer of type I interferons that is obtained by complexing the synthetic double-stranded DNA, poly(dadt) poly(dt-da), with cationic lipids. NF- : InvivoGen provides two known activators of the transcription factor NF- Factor alpha (TNF-
5 TLR Agonist kits : The TLR agonist kits represent convenient and economical tools to study the stimulation of 96-well plate).
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity. Jan 8 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Relative sizes of infectious agents
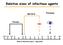 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS
 Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Inflammation - Molecular events
 Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity
 Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
Pathogen Recognition and Inflammatory Signaling in Innate Immune Defenses
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Basic immunology. Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Innate Immunity. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury. Journal Club December 16, 2004
 Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Innate immunity. Monika Raulf. Lecture Tasks of the immune system. Body protection against damaging influences
 Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
MICR2209. Innate Immunity. Dr Allison Imrie
 MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis
 The Open Inflammation Journal, 2011, 4, (Suppl 1-M5) 31-48 31 Open Access Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis Lesley Doughty* Division of Critical
The Open Inflammation Journal, 2011, 4, (Suppl 1-M5) 31-48 31 Open Access Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis Lesley Doughty* Division of Critical
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No
 Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity. Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada
 Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Early Goal-Directed Therapy Rivers E et al. NEJM 345:1368-77,
Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Early Goal-Directed Therapy Rivers E et al. NEJM 345:1368-77,
State of the Art. Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung CONTENTS AT A GLANCE COMMENTARY 1.
 State of the Art Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung Bastian Opitz 1, Vincent van Laak 1, Julia Eitel 1, and Norbert Suttorp 1 1 Department of Internal Medicine/Infectious
State of the Art Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung Bastian Opitz 1, Vincent van Laak 1, Julia Eitel 1, and Norbert Suttorp 1 1 Department of Internal Medicine/Infectious
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
1. The barriers of the innate immune system to infection
 Section 3.qxd 16/06/05 2:11 PM Page 12 12 SECTION THREE: Fleshed out 1. The barriers of the innate immune system to infection Questions What are the three characteristics of the innate immune system? What
Section 3.qxd 16/06/05 2:11 PM Page 12 12 SECTION THREE: Fleshed out 1. The barriers of the innate immune system to infection Questions What are the three characteristics of the innate immune system? What
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Biochemistry of the immune system. B. Sopko
 Biochemistry of the immune system B. Sopko Content The innate immune system Introduction Cells Immediate Innate Immunity Early Induced Innate Immunity Adaptive immunity Introduction Humoral Immunity Cell-Mediated
Biochemistry of the immune system B. Sopko Content The innate immune system Introduction Cells Immediate Innate Immunity Early Induced Innate Immunity Adaptive immunity Introduction Humoral Immunity Cell-Mediated
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER. Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma
 INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF)
 F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF) Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus, Department of
F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF) Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus, Department of
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
Immunity to Microbes. Cellular and Molecular Immunology (7 th : Chap 15)
 Immunity to Microbes Cellular and Molecular Immunology (7 th : Chap 15) Infection Entry of the microbe Invasion and colonization of host tissues, Evasion of host immunity Tissue injury or functional impairment
Immunity to Microbes Cellular and Molecular Immunology (7 th : Chap 15) Infection Entry of the microbe Invasion and colonization of host tissues, Evasion of host immunity Tissue injury or functional impairment
Anti-infectious Immunity
 Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity. Kingston H.G. Mills
 TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity Kingston H.G. Mills Immunology Research Centre and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland Abstract Autoimmune disease can
TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity Kingston H.G. Mills Immunology Research Centre and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland Abstract Autoimmune disease can
Immunity to Viruses. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly September 25, 2008
 Immunity to Viruses Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly September 25, 2008 The Immune System Deals with a Huge Range of Pathogens Roitt, 2003 Immune Responses to Viruses Viruses are dependent on the host cell
Immunity to Viruses Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly September 25, 2008 The Immune System Deals with a Huge Range of Pathogens Roitt, 2003 Immune Responses to Viruses Viruses are dependent on the host cell
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections
 ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with. unipartite and bipartite structure. Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2
 Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
MAST CELL RESPONSES TO DANGER SIGNALS
 Department of Medicine, Clinical Immunology and Allergy Unit, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden MAST CELL RESPONSES TO DANGER SIGNALS Mattias Enoksson Stockholm 2012 All previously published papers
Department of Medicine, Clinical Immunology and Allergy Unit, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden MAST CELL RESPONSES TO DANGER SIGNALS Mattias Enoksson Stockholm 2012 All previously published papers
Microbial recognition and the immune response Dr. Dana Philpott
 Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Masmudur M. Rahman and Grant McFadden* Department of Molecular Genetics and Microbiology, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32610
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 12505 12517 Vol. 85, No. 23 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00410-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Myxoma Virus Lacking
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 12505 12517 Vol. 85, No. 23 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00410-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Myxoma Virus Lacking
The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition
 International Immunology, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 317 337 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxp017 ª The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2009. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
International Immunology, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 317 337 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxp017 ª The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2009. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD. Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany
 Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
The innate immune system: Contributions to Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins
 The innate immune system: Contributions to Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins Daniela Verthelyi, M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory of Immunology Division of Therapeu8c Proteins OBP, CDER, FDA Map to the talk:
The innate immune system: Contributions to Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins Daniela Verthelyi, M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory of Immunology Division of Therapeu8c Proteins OBP, CDER, FDA Map to the talk:
Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity. Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity)
 Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity) : ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY: AN OVERVIEW OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Adaptive Immunity
Unit 6: Adaptive Immunity Adaptive Immunity (Humoral Immunity; Cell-Mediated Immunity; Immunodeficiency; Hypersensitivity) : ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY: AN OVERVIEW OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Adaptive Immunity
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection
 Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Unit 5 The Human Immune Response to Infection Unit 5-page 1 FOM Chapter 21 Resistance and the Immune System: Innate Immunity Preview: In Chapter 21, we will learn about the branch of the immune system
Overview of immunology
 Introduction Overview of immunology Masayuki Miyasaka, MD, PhD Interdisciplinary Program for Biomedical Sciences WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center (IFReC) Osaka University Inside our body, we have
Introduction Overview of immunology Masayuki Miyasaka, MD, PhD Interdisciplinary Program for Biomedical Sciences WPI Immunology Frontier Research Center (IFReC) Osaka University Inside our body, we have
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
SINGLE CHOICE. 5. The gamma invariant chain binds to this molecule during its intracytoplasmic transport. A TCR B BCR C MHC II D MHC I E FcγR
 A Name: Group: SINGLE CHOICE 1. Which is the most important ligand of TLR5? A endospore B flagellin C polysaccharide capsule D DNA E pilus 2. The antibody-binding site is formed primarily by... A the constant
A Name: Group: SINGLE CHOICE 1. Which is the most important ligand of TLR5? A endospore B flagellin C polysaccharide capsule D DNA E pilus 2. The antibody-binding site is formed primarily by... A the constant
The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors
 The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors Taro Kawai 1,2 & Shizuo Akira 1,2 The discovery of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) as components that recognize conserved
The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors Taro Kawai 1,2 & Shizuo Akira 1,2 The discovery of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) as components that recognize conserved
االستاذ المساعد الدكتور خالد ياسين الزاملي \مناعة \المرحلة الثانية \ التحليالت المرضية \ المعهد التقني كوت
 Complement System The term complement refers to the ability of a system of some nonspecific proteins in normal human serum to complement, i.e., augment the effects of other components of immune system,
Complement System The term complement refers to the ability of a system of some nonspecific proteins in normal human serum to complement, i.e., augment the effects of other components of immune system,
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 11 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 11 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 11: Advanced in Clinical Immunomodulation Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 11 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 11: Advanced in Clinical Immunomodulation Prepared by
Two signal models in innate immunity
 Mary F. Fontana Russell E. Vance Two signal models in innate immunity Authors address Mary F. Fontana 1, Russell E. Vance 1 1 Division of Immunology & Pathogenesis, Department of Molecular & Cell Biology,
Mary F. Fontana Russell E. Vance Two signal models in innate immunity Authors address Mary F. Fontana 1, Russell E. Vance 1 1 Division of Immunology & Pathogenesis, Department of Molecular & Cell Biology,
Test Bank for The Immune System 4th Edition by Parham
 Test Bank for The Immune System 4th Edition by Parham CHAPTER 3: INNATE IMMUNITY: THE INDUCED RESPONSE TO INFECTION 3 1 C-type lectins are so called because of the role of in facilitating receptor:ligand
Test Bank for The Immune System 4th Edition by Parham CHAPTER 3: INNATE IMMUNITY: THE INDUCED RESPONSE TO INFECTION 3 1 C-type lectins are so called because of the role of in facilitating receptor:ligand
IFNγ Inhibits the Cytosolic Replication of Shigella flexneri via the Cytoplasmic RNA Sensor RIG-I
 IFNγ Inhibits the Cytosolic Replication of Shigella flexneri via the Cytoplasmic RNA Sensor RIG-I The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
IFNγ Inhibits the Cytosolic Replication of Shigella flexneri via the Cytoplasmic RNA Sensor RIG-I The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you.
APPLICATIONS. Updated: July 2015
 APPLICATIONS Updated: July 2015 1 Contents APPLICATIONS... 3 Principles of immunomodulation and immune stimulation in animals... 3 What is immune stimulation?... 3 Rationale for targeting the innate immune
APPLICATIONS Updated: July 2015 1 Contents APPLICATIONS... 3 Principles of immunomodulation and immune stimulation in animals... 3 What is immune stimulation?... 3 Rationale for targeting the innate immune
Immune receptors Y Y. Multiple immune responses CLR TLR NLR ITAM RLR. C-type lectin. ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif
 C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells
 Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis. Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University
 Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
A calculated response: control of inflammation by the innate immune system
 Review series A calculated response: control of inflammation by the innate immune system Gregory M. Barton Division of Immunology, Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley,
Review series A calculated response: control of inflammation by the innate immune system Gregory M. Barton Division of Immunology, Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley,
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release. Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation. Neutrophils & Innate Defense
 Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
The cutaneous innate immune response in patients with atopic dermatitis
 Clinical reviews in allergy and immunology Series editors: Donald Y. M. Leung, MD, PhD, and Dennis K. Ledford, MD The cutaneous innate immune response in patients with atopic dermatitis I-Hsin Kuo, MS,
Clinical reviews in allergy and immunology Series editors: Donald Y. M. Leung, MD, PhD, and Dennis K. Ledford, MD The cutaneous innate immune response in patients with atopic dermatitis I-Hsin Kuo, MS,
Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade
 Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade Bryan L. Martin, DO, MMAS, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FACOI, FACP Emeritus Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics President, American College of Allergy,
Clinical Basis of the Immune Response and the Complement Cascade Bryan L. Martin, DO, MMAS, FACAAI, FAAAAI, FACOI, FACP Emeritus Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics President, American College of Allergy,
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases
 محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F Lyon
 Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
Antibodies for human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells studies Dendritics SAS, 60 avenue Rockefeller, F-69008 Lyon www.dendritics.net Human plasmacytoïd dendritic cells (PDCs) are considered the main sentinels
