ASM NAWSHAD UDDIN AHMED, MD. MAHBUBUL HOQUE
|
|
|
- Brett Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (1): Review Article Is it Safe for a Mother Infected with Hepatitis B Virus to Breastfeed Her Baby? ASM NAWSHAD UDDIN AHMED, MD. MAHBUBUL HOQUE Summary: One third of the world s population has been infected by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), causing an enormous burden of chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted through contact with blood and blood products, by sexual contact, through close contact between children (horizontal transmission), or by perinatal transmission from a carrier mother to her baby. In Asia, perinatal transmission is the major mode of transmission and those who become infected perinatally with HBV are most likely to develop chronic infection. The question of whether breastfeeding by HBV-positive mothers is an additional mechanism by which infants may acquire HBV infection, has been asked for many years. Although small amounts of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) have been detected in some samples of breast milk, there is no evidence that breastfeeding by HBV-carrier mothers increase the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HBV. Infants born to known hepatitis B positive women should receive hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) and hepatitis B vaccine, effectively eliminating any theoretical risk of transmission through breastfeeding. However, neither screening of pregnant women for HBV infection nor use of HBIG is feasible in most developing countries. Routine immunization of infants with hepatitis B vaccine is therefore recommended by the World Health Organization. Bangladesh has already included hepatitis B vaccine as part of routine childhood immunization in EPI program since Also the risk must be balanced against the increased risk of morbidity and mortality due to malnutrition and diarrheal or other infectious diseases associated with replacement feeding. Malnutrition is responsible, directly or indirectly, for 6.5 million under 5 deaths annually. Thus, even where HBV infection is highly endemic and immunization against HBV is not available, breastfeeding remains the recommended method of feeding. Keywords: Hepatitis B virus, Perinatal transmission, Breastfeeding, Immunoprophylaxis Introduction: Hepatitis B is an infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver, causing damage to liver cells. Chronically infected persons with HBV are at increased risk for developing chronic liver disease or liver cancer in later life. Young children who become infected with HBV are the most likely to develop chronic infection. 1 In areas where persistent infection is highly endemic, transmission is mainly either perinatal, from a carrier mother to her newborn, or through close contact between children (horizontal transmission). 2,3 Breastfeeding has been suggested Associate Professor, Bangladesh Institute of Child Health, Dhaka Shishu Hospital, Sher-e-Bangla Nagar, Dhaka-1207 Correspondence: Dr. A.S.M. Nawshad Uddin Ahmed as an additional mechanism by which infants may acquire HBV infection, because small amounts of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) have been detected in some samples of breast milk from women who tested positive for hepatitis B. 3 Concern have been expressed by scientists, health professionals, environmentalists and mothers about the potential risks posed by the presence of this hepatitis B antigen in breast milk. The question of whether breastfeeding plays a significant role in the transmission of hepatitis B has been asked for many years. It is important given the critical role of breastfeeding and the fact that about 5 percent of mothers worldwide are chronic HBV carriers. 4
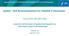
2 Is it Safe for a Mother Infected with Hepatitis B Virus BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (1) : 21 Although HBsAg can be detected in breast milk, several studies have shown that breastfeeding by hepatitis B positive mothers have not been demonstrated to be a mode of transmission of the virus. 5,6 Infants born to known hepatitis B positive women should receive hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) and hepatitis B vaccine at birth, effectively eliminating any theoretical risk of transmission through breastfeeding. 6,7 Also this risk must be balanced against the increased risk of morbidity and mortality due to malnutrition and diarrheal or other infectious diseases associated with replacement feeding. 8 Malnutrition is responsible, directly or indirectly, for about 60 percent of the 10.9 million deaths annually among children under 5 years of age. 9 Malnutrition among infants and young children, why remains as one of the most severe global public health problems. That is among the main reasons World Health Organization (WHO) strongly supports breastfeeding and all infants receive hepatitis B vaccine as part of routine childhood immunization. 10 In this paper we reviewed the issues relevant to breastfeeding and HBV transmission and provided guidance regarding breastfeeding by HBV carrier mothers. Breastfeeding: Breast milk is the ideal in infant nutrition, and breastfeeding the optimal delivery system. Appropriate feeding practices are essential for the growth, development, health, nutrition, and survival of infants and children everywhere. 8 In addition to meeting nutritional needs, breast milk provides increased resistance to diseases, allergy protection and psychosocial development, make it the most important, cost effective substance we have in medicine today. 11 It has been postulated that breastfeeding may also be related to the prevention of some adult health problems such as obesity, diabetes and coronary heart disease. 12,13 There is a considerable risk of morbidity and mortality among infants who are not breastfed. Numerous benefits of breastfeeding for mother (e.g., decreased risk for breast cancer) are well documented. In a recent recommendation, WHO and UNICEF have urged to strengthen activities to protect, promote and support exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months as a global public health recommendation, followed by safe and appropriate complementary foods, with continued breastfeeding for up to 2 years of age or beyond. 14 Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a double-stranded DNA virus in the Hepadnaviridae family, a highly infectious virus 50 to 100 times more infectious than the AIDS virus (HIV). Hepatitis B virus infection is of major public health importance worldwide. It can cause asymptomatic infection, clinical acute hepatitis, fulminant hepatitis, or persistent infection which is known as the chronic carrier state. 1 Chronic hepatitis B is a serious public health problem. 1 Hepatitis B virus is widespread in Asia and sub-saharan Africa, with 8 to 15 percent of the population being chronically infected. 1 (Fig.-1). Globally there are over 350 million chronic carriers of HBV who are at high risk of developing severe sequelae including chronic active hepatitis, cirrhosis, and primary hepatocellular carcinoma, complications which kill more than 1.2 million persons per year. 1,4 The risk of death from HBV-related liver cancer or cirrhosis is approximately 25 percent for persons who become chronically infected during childhood. 1 Worldwide, hepatitis B has been reported to be the 10 th leading causes of death. 4 Up to 80 percent of the world s primary liver cancer, which is currently the fifth most frequent cancer worldwide, is associated with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted through contact with blood or blood products, by intimate contact such as sexual intercourse, or through close contact between children (horizontal transmission). 1 According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), HBV is not spread through food or water, sharing eating utensils, breastfeeding, hugging, kissing, coughing, sneezing or by casual contact. 15 In highly endemic areas a major route of transmission from an infected mother (who is often unaware that she is a carrier and has chronic hepatitis B) to her baby is via contact with maternal blood and other body fluids during or soon after delivery. Being a carrier during pregnancy does not seem to cause damage to the unborn baby and when infection occurs,, hepatitis B in neonates rarely results in serious clinical illness. Rather, the principal morbidity of perinatal transmission is the development of a chronic HBsAg carrier state in neonates with the subsequent risk for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. 16 Although cesarean delivery has been proposed by some researchers as a means of reducing mother-to-child transmission (MCT) of HBV, 17 other researchers found no difference in maternal-infantile transmission of HBV between women with cesarean section and natural birth. 18 Delivery by cesarean
3 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (1) : 22 section for the purpose of reducing MCT of HBV is not presently recommended by either the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) 15 or the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). 19 For women developing acute hepatitis B in the third trimester, the rate of transmission to neonates approaches 90 percent, virtually all becoming chronic carriers. In contrast, hepatitis B acquired earlier in pregnancy results in perinatal transmission in only 10 percent of cases. 20,21 This disparity is related to the fact that mothers infected earlier in pregnancy have generally cleared HBsAg by the time of labor and delivery which would result in a much lower rate of transmission to the neonate. In Asia approximately 40 percent of HBV carrier women of childbearing age are also positive for the hepatitis e antigen (HBeAg) and these mothers have a 70 to 90 percent chance of infecting their newborn perinatally. 22 In Asia, perinatal transmission accounts for approximately 25 to 30 percent of the carrier pool. Young children who become infected with HBV are the most likely to develop chronic infection. 1,23 About 90 percent of infants infected during the first year of life, 25 percent of infected young children and fewer infected adults develop chronic infection. 1 Vaccines are available for the prevention of hepatitis B. According to WHO recommendations, many countries including Bangladesh have included hepatitis B vaccine as part of routine childhood immunization. Three injections are given as pentavalent vaccine (along with diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus and Hib vaccines) at 6, 10 and 14 weeks of age. In recent ASMNU Ahmed, MM Hoque years, Lamivudine has been used in the latter half of pregnancy in an attempt to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection with mixed results. One study suggests that, in highly viremic HBsAg-positive mothers, reduction of viremia by Lamivudine therapy in the last month of pregnancy may be an effective and safe measure to reduce the risk of child vaccination breakthrough, 24 whereas another study opinioned that, Lamivudine therapy might not prevent perinatal transmission of HBV infection in every newborn. 25 Results of a recent randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study suggest that, Lamivudine reduced HBV transmission from highly viremic mothers to their infants who received passive/ active immunization. 26 However, the data is limited, and this approach should be evaluated in a large controlled trial. Breastfeeding and Hepatitis B: Even though the HBV antigen has been detected in breast milk, examination of relevant studies indicates that there is no evidence that breastfeeding by HBV carrier mothers increases the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HBV. 3,27 A follow up study of 147 infants born to mothers known to be carriers of HBV in Taiwan found similar rates of HBV infection in 92 children who were breastfed compared to 55 who were bottle fed. 3 Another study in Britain, involving 126 subjects, also showed no additional risk for breastfed versus non breastfed infants of carrier mothers. 28 These findings suggest strongly that breastfeeding of the infant by an HBsAg-positive mother poses no additional risk for acquisition of HBV infection by the Fig.-1. Geographic Distribution of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Worldwide, 2006
4 Is it Safe for a Mother Infected with Hepatitis B Virus BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (1) : 23 infant. There is no need to delay initiation of breastfeeding until after the infant is immunized. 29 Experts on hepatitis, however, do have concerns that breast pathology such as cracked or bleeding nipples or lesions with serous exudates could expose the infant to infectious doses of HBV. 30 Appropriate hepatitis B immunoprophylaxis can prevent the development of persistent carrier state in such situation. 5,6 World Health Organization recommends that all infants receive hepatitis B vaccine as part of routine childhood immunization, the first dose to be given within 48 hr of birth when feasible. 10 Breastfeeding remains the recommended method of feeding. 10 A statement prepared jointly by the Global Programme for Vaccines and Immunization (GPV) and the Divisions of Child Health and Development (CHD), and Reproductive Health (Technical Support ) (RHT) World Health Organization recommends that active immunization with hepatitis B vaccine is effective for the prevention of both perinatal and horizontal transmission of HBV. 30 Immunization can prevent development of the persistent carrier state in 70 to 90 percent of infants of carrier mothers, and in up to 95 percent of infants who are infected horizontally Administration of HBIG within 24 hours of birth together with the first dose of vaccine increases the protection up to 85 to 90 percent in infants of HBV carrier mothers. 27 However, neither screening of pregnant women for HBV infection nor use of HBIG is feasible in most developing countries. Routine immunization of infants with hepatitis B vaccine is therefore recommended, the first dose to be given within 48 hours of birth, and subsequent doses with routine childhood immunizations. But in majority of cases contact with the immunization system does not take place for several weeks after birth. Delivery of hepatitis B vaccine at birth may be possible with clinic or hospital deliveries but is more difficult following home deliveries, where majority of deliveries take place in our country. 34 A dose of hepatitis B vaccine around the time of birth is more important in Asia where perinatal transmission is commoner. Infants who have received their first dose of vaccine can safely breastfeed. 35 Introduction of hepatitis B vaccine as part of routine childhood immunization in endemic areas, as recommended by WHO, will substantially reduce perinatal transmission, and virtually eliminate any risk of transmission through breastfeeding. But this would not be possible without birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine in areas where persistent HBV infection is highly endemic. Immunization of infants will also prevent infection from all other modes of HBV transmission. WHO and UNICEF recommend that all infants be exclusively breastfed for at least 4 and if possible 6 months, and that they continue to breastfeed up to two years of age or beyond with the addition of adequate complementary foods after completion of 6 months of age. 8 Government of Bangladesh has also recommended exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months. There is a considerable risk of morbidity and mortality among infants who are not breastfed. Importance of Hepatitis B Birth dose? Hepatitis B vaccine administered to newborns before hospital discharge may minimize the risk of infection due to errors in maternal HBsAg testing or reporting, or from exposure to persons with chronic hepatitis B infection in the household. It is estimated that over 40% of infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers will become infected without prophylaxis. An estimated 90% of infants who become infected by perinatal transmission develop chronic HBV infection and as many as 25% will die from chronic liver disease as adults. Although not a substitute for immunoprophylaxis, routine administering Hepatitis B vaccine to infants at birth regardless of the mothers HBsAg status can serve as a safety net. Studies have shown that administering hepatitis B vaccine without HBIG beginning <12 hours after birth in a 3- or 4-dose schedule can prevent 70-95% of perinatal HBV infections among infants born to HBsAg-positive mothers. Noted medical groups the Advisory Commission on Immunization Practices (ACIP), American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), and American Academy of Family Physicians recommended health care providers routinely administer the first dose of hepatitis B vaccine to infants soon after birth and before hospital discharge. 36 Hepatitis B birth dose acts a safety net when A pregnant woman is HBsAg positive but her status is not communicated to the nursery; is misinterpreted, or is mistranscribed in her prenatal records. A chronically infected woman is tested by mistake for hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-hbs) instead of HBsAg.
5 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (1) : 24 A pregnant woman is not tested for HBsAg prenatally or in hospital at time of delivery. A high-risk woman tests negative early in pregnancy but develops hepatitis B infection later in pregnancy. A mother is HBsAg negative but the infant is exposed postnatally from another family member or caregiver. This accounts for two-thirds of childhood transmission. Conclusion: With appropriate immunoprophylaxis, including hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine, breastfeeding of infants of chronic HBV-carriers poses no additional risk for the transmission of the hepatitis B virus. There is no evidence that breastfeeding from a HBV-infected mother poses an additional risk of HBV infection to her infant, even without immunization. 3,27,30 Thus, even where HBV infection is highly endemic and immunization against HBV is not available, breastfeeding remains the recommended method of infant feeding. References: 1. World Health Organization. Hepatitis B fact sheet number 204. Available from: mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en/. Accessed on: 12 May Doganci T, Uysal G, Kir T, Bakirtas A, Kuyucu N, Doganci L. Horizontal transmission of hepatitis B virus in children with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11: Wong VC, Lee AK, Ip HM. Transmission of hepatitis B antigens from symptom free carrier mothers to the fetus and the infant. Br J Obstetric Gynaecol 1980; 87: Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. J Viral Hepat 2004; 11: Davis AR, Rosenthal P. Hepatitis B in Children. Pediatr Rev 2008; 29; Hill JB, Shefûeld JS, Kim MJ, Alexander JM, Sercely B, Wendel Jr GD. Risk of hepatitis B transmission in breast-fed infants of chronic hepatitis B carriers. Obstetric Gynecol 2002; 99: Wang JS, Zhu QR, Wang XH. Breastfeeding does not pose any additional risk of immunoprophylaxis ASMNU Ahmed, MM Hoque failure on infants of HBV carrier mothers. Int J Clin Pract 2003; 57: WHO Collaborative Study Team on the Role of Breastfeeding on the Prevention of Infant Mortality. Effect of breastfeeding on infant and child mortality due to infectious diseases in less developed countries: a pooled analysis. Lancet 2000; 355: World Health Assembly. Childhood Nutrition and Progress in Implementing the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes. Available from: PDF/WHA55/ea5514.pdf. Accessed on: 12 May World Health Organization, Child and Adolescent Health and Development. Hepatitis B and Breastfeeding. Update No 22, November Available from: New_Publications/ NUTRITION/updt-22.htm. Accessed on: 12 May American Academy of Pediatrics policy statement. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 1997; 100: Deckelbaum RJ, Williams CL. Childhood obesity: the health issue. Obes Res 2001; 9: S239-S Martorell R, Stein AD, Schroeder DG. Early nutrition and later adiposity. J Nutr 2001; 131: S874-S World Health Assembly. Infant and Young Child Nutrition. Resolution WHA54.2. Available from: ea54r2.pdf. Accessed on: 12 May Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines MMWR May 10, 2002/ 51(RR06); Available from: htm#hepatitis B. Accessed on: 21 May Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the World Cancer Burden. Globocan Int J Cancer 2001; 94: Lin HH, Kao JH, Hsu HY, Mizokami M, Hirano K, Chen DS. Least microtransfusion from mother to fetus in elective cesarean delivery. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1996; 87: Wang J, Zhu Q, Zhang X. Effect of delivery mode on maternal-infant transmission of hepatitis B
6 Is it Safe for a Mother Infected with Hepatitis B Virus BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2011; VOL 35 (1) : 25 virus by immunoprophylaxis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2002; 115: American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Practice Bulletin No. 86: Viral hepatitis in pregnancy. Obstetric Gynecol 2007; 110: Wiseman E, Fraser MA, Holden S, Glass A, Kidson BL, Heron LG, et al. Perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus: an Australian experience. The Medical Journal of Australia 2009; 190: Reinus J, Leikin E. Viral hepatitis in pregnancy. Clin Liver Dis 1999; 3: Protocol for assessing prevalence of Hepatitis B infection in antenatal patients, World Health Organization, WHO/EPI/GEN/90.6. Available from: DocsPDF01/www613.pdf. Accessed: 21 May Nishioka K. Predominant Mode of Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus. In: Vyas GN, Dlenstag JL, Hoofnagle VH, editors. Viral hepatitis and Liver Disease. Orlando FL, Grune and Stratton P van Zonneveld M, van Nunen AB, Niesters HG, de Man RA, Schalm SW, Janssen HL. Lamivudine treatment during pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat 2003; 10: Kazim SN, Wakil SM, Khan LA, Hasnain SE, Sarin SK. Vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus despite maternal lamivudine therapy. Lancet 2002; 359: Xu WM, Cui YT, Wang L, Yang H, Liang ZQ, Li XM, et al. Lamivudine in late pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection: a multicentre, randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study. J Viral Hepat 2009; 16: de Martino M, Appendino C, Resti M, Rossi ME, Muccioli AT, Vierucci A. Should hepatitis B surface antigen positive mothers breast feed? Arch Dis Child 1985; 60: Woo D, Davies PA, Harvey DR, Hurley R, Waterson AP. Vertical transmission of hepatitis B surface antigen in carrier mothers in two west London hospitals. Arch Child Dis 1979; 54: The Red Book, American Academy of Pediatrics, 2009 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases Transmission of Infectious Agents via Human Milk p Hepatitis B and breastfeeding, A statement prepared jointly by the Global Programme for Vaccines and Immunization (GPV) and the Divisions of Child Health and Development (CHD), and Reproductive Health (Technical Support ) (RHT) World Health Organization. WHO-DOCS 9, 22 November Available from: documents/pdfs/hepatitis_b_and_ breastfeeding.pdf. Accessed: 17 May Bracciale L, Fabbiani M, Sansoni A, Luzzi L, Bernini L, Zanelli G. Impact of Hepatitis B Vaccination in Children Born to HBsAg-Positive Mothers: a 20-year Retrospective Study. Infection 2009; 37: Wong VC, Ip HM, Reesink HW, Lelie PN, Reerink-Brongers EE, Yeung CY, Ma HK. Prevention of the HBsAg carrier state in newborn infants of mothers who are chronic carriers of HBsAg and HBeAg by administration of Hepatitis B vaccine and hepatitis B immunoglobulin. Lancet 1984; 1: Maynard JE, Kane MA, Hadler SC. Global control of hepatitis B through vaccination: role of hepatitis B vaccine in the expanded programme on immunization. Rev Infect Dis 1989; 11: S574- S Akhter HH, Rahman MH, Mannan I, Elahi ME, Khan AK. Review of performance of trained TBAs. Dhaka: Bangladesh Institute of Research for Promotion of Essential and Reproductive Health and Technologies (BIRPERHT), August Tseng AKY, Lam CWK, Tam J. Breastfeeding babies of HBsAg-positive mothers. Lancet 1988; 2: Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule - United States, 2002, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR) Vol. 51, January 18, Available from: mm5102a4.htm. Accessed: 17 May 2010.
OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program
 OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Dear Colleague, This letter is to introduce myself and explain the role I play with the Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis B Program. Alaska
OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Dear Colleague, This letter is to introduce myself and explain the role I play with the Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis B Program. Alaska
perinatology.com Infections During Pregnancy
 perinatology.com Infections During Pregnancy Search Translate Back Site Map Agencies and Organizations Calculators Critical Care Exposures Chemicals Drugs Infection Physical Agent Genetics Images Labs
perinatology.com Infections During Pregnancy Search Translate Back Site Map Agencies and Organizations Calculators Critical Care Exposures Chemicals Drugs Infection Physical Agent Genetics Images Labs
Epatite B: fertilità, gravidanza ed allattamento, aspetti clinici e terapeutici. Ivana Maida
 Epatite B: fertilità, gravidanza ed allattamento, aspetti clinici e terapeutici Ivana Maida Positivity for HBsAg was found in 0.5% of tested women In the 70s and 80s, Italy was one of the European countries
Epatite B: fertilità, gravidanza ed allattamento, aspetti clinici e terapeutici Ivana Maida Positivity for HBsAg was found in 0.5% of tested women In the 70s and 80s, Italy was one of the European countries
AN ECONOMIC EVALUATION OF UNIVERSAL INFANT VACCINATION STRATEGIES AGAINST HEPATITIS B IN THAILAND: AN ANALYTIC DECISION APPROACH TO COST-EFFECTIVENESS
 AN ECONOMIC EVALUATION OF UNIVERSAL INFANT VACCINATION STRATEGIES AGAINST HEPATITIS B IN THAILAND: AN ANALYTIC DECISION APPROACH TO COST-EFFECTIVENESS Thosporn Vimolket 1 and Yong Poovorawan 2 1 Department
AN ECONOMIC EVALUATION OF UNIVERSAL INFANT VACCINATION STRATEGIES AGAINST HEPATITIS B IN THAILAND: AN ANALYTIC DECISION APPROACH TO COST-EFFECTIVENESS Thosporn Vimolket 1 and Yong Poovorawan 2 1 Department
Elimination of Perinatal Hepatitis B Transmission
 Elimination of Perinatal Hepatitis B Transmission Trudy V. Murphy, MD Division of Viral Hepatitis NCHHSTP, CDC December 19, 2013 Hep B United and WHIAAPI Webinar Background q Hepatitis B is an infection
Elimination of Perinatal Hepatitis B Transmission Trudy V. Murphy, MD Division of Viral Hepatitis NCHHSTP, CDC December 19, 2013 Hep B United and WHIAAPI Webinar Background q Hepatitis B is an infection
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview
 Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Acknowledgment. Natural history of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Background on hepatitis B
 : How to prevent perinatal HBV transmission Immunization Action Coalition (IAC) Acknowledgment Trudy V. Murphy, MD, (retired), formerly Team Lead, Vaccine Research and Policy, Division of Viral Hepatitis,
: How to prevent perinatal HBV transmission Immunization Action Coalition (IAC) Acknowledgment Trudy V. Murphy, MD, (retired), formerly Team Lead, Vaccine Research and Policy, Division of Viral Hepatitis,
APEC Guidelines Immunizations
 Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
HEPATITIS B: PREGNANCY AND LABOR MANAGEMENT MICHAEL P. NAGEOTTE, M.D.
 HEPATITIS B: PREGNANCY AND LABOR MANAGEMENT MICHAEL P. NAGEOTTE, M.D. Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to resolve. I will not discuss any unapproved
HEPATITIS B: PREGNANCY AND LABOR MANAGEMENT MICHAEL P. NAGEOTTE, M.D. Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to resolve. I will not discuss any unapproved
The Hep B Moms Program: A Primary Care Model for Management of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy
 The Hep B Moms Program: A Primary Care Model for Management of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy Janice Lyu, MS Senior Hepatitis B Program Associate Charles B. Wang Community Health Center (CBWCHC) Charles B Wang
The Hep B Moms Program: A Primary Care Model for Management of Hepatitis B in Pregnancy Janice Lyu, MS Senior Hepatitis B Program Associate Charles B. Wang Community Health Center (CBWCHC) Charles B Wang
PERINATAL HEPATITIS B
 PERINATAL HEPATITIS B A Prevention Strategy Douglas County Health Department, Omaha, NE Why Prevention is Important About 1.25 million people in the U.S. have chronic hepatitis B infection Hepatitis B
PERINATAL HEPATITIS B A Prevention Strategy Douglas County Health Department, Omaha, NE Why Prevention is Important About 1.25 million people in the U.S. have chronic hepatitis B infection Hepatitis B
EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
Viral Hepatitis in Reproductive Health
 Viral Hepatitis in Reproductive Health Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2010 Dr José M Bengoa Dr Pierre Jean Malè Consultants Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Viral Hepatitis in Reproductive Health Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva 2010 Dr José M Bengoa Dr Pierre Jean Malè Consultants Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Hepadnaviridae family (DNA) Numerous antigenic components Humans are only known host May retain infectivity for more than 7 days at room temperature
 Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
The Evolving Landscape of Preventing Maternal-Fetal Hepatitis B Infections
 The Evolving Landscape of Preventing Maternal-Fetal Hepatitis B Infections Neil S. Silverman, M.D. Center for Fetal Medicine and Women s Ultrasound Clinical Professor, Obstetrics/Gynecology David Geffen
The Evolving Landscape of Preventing Maternal-Fetal Hepatitis B Infections Neil S. Silverman, M.D. Center for Fetal Medicine and Women s Ultrasound Clinical Professor, Obstetrics/Gynecology David Geffen
Hepatitis B Disease Burden: A Model for Global Estimates and Impact of Vaccination. Susan A. Wang, MD, MPH Division of Viral Hepatitis
 Hepatitis B Disease Burden: A Model for Global Estimates and Impact of Vaccination Susan A. Wang, MD, MPH Division of Viral Hepatitis Barriers to Appreciating HBV Disease Burden and Vaccine Impact Chronic
Hepatitis B Disease Burden: A Model for Global Estimates and Impact of Vaccination Susan A. Wang, MD, MPH Division of Viral Hepatitis Barriers to Appreciating HBV Disease Burden and Vaccine Impact Chronic
Summary of Key Points. WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017
 Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Hepatitis and pregnancy
 Hepatitis and pregnancy Pierre-Jean Malè MD Training Course in Reproductive Health Research WHO Geneva 2008 26.02.2008 Liver disease and pregnancy: three possible etiologic relationship the patient has
Hepatitis and pregnancy Pierre-Jean Malè MD Training Course in Reproductive Health Research WHO Geneva 2008 26.02.2008 Liver disease and pregnancy: three possible etiologic relationship the patient has
Chapter 5 Serology Testing
 Chapter 5 Serology Testing 49 50 This page intentionally left blank. Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Diagnosis of HBV infection (acute vs. chronic) is based on clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic
Chapter 5 Serology Testing 49 50 This page intentionally left blank. Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Diagnosis of HBV infection (acute vs. chronic) is based on clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic
Hepatitis B vaccine alone or with HBIG in neonates of HBsAg+/HBeAg- mothers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 Hepatitis B vaccine alone or with HBIG in neonates of HBsAg+/HBeAg- mothers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Vana Papaevangelou (Greece) National and Kapodistrian University of Athens Chang SemFNM
Hepatitis B vaccine alone or with HBIG in neonates of HBsAg+/HBeAg- mothers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Vana Papaevangelou (Greece) National and Kapodistrian University of Athens Chang SemFNM
Hepatitis B: A Preventable Cause of Liver Cancer. Saira Khaderi MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Surgery Associate Director, Project ECHO June 17, 2016
 Hepatitis B: A Preventable Cause of Liver Cancer Saira Khaderi MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Surgery Associate Director, Project ECHO June 17, 2016 Overview Epidemiology HBV and cancer Screening, Diagnosis
Hepatitis B: A Preventable Cause of Liver Cancer Saira Khaderi MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Surgery Associate Director, Project ECHO June 17, 2016 Overview Epidemiology HBV and cancer Screening, Diagnosis
PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases
 PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Viruses in July (ViJ), 2004 Overview Epidemiology Perinatal transmission
PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Viruses in July (ViJ), 2004 Overview Epidemiology Perinatal transmission
Chronic hepatitis B in pregnancy: unique challenges and opportunities
 The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2011;17:1-8 DOI: 10.3350/kjhep.2011.17.1.1 Review Chronic hepatitis B in pregnancy: unique challenges and opportunities Kumaresan Yogeswaran and Scott K. Fung Department
The Korean Journal of Hepatology 2011;17:1-8 DOI: 10.3350/kjhep.2011.17.1.1 Review Chronic hepatitis B in pregnancy: unique challenges and opportunities Kumaresan Yogeswaran and Scott K. Fung Department
Yakima Health District BULLETIN
 Yakima Health District BULLETIN Volume 12, Issue 4 December, 2013 Overview Prevention of Perinatal Hepatitis B Transmission Perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus (HBV) is preventable through universal
Yakima Health District BULLETIN Volume 12, Issue 4 December, 2013 Overview Prevention of Perinatal Hepatitis B Transmission Perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus (HBV) is preventable through universal
Prevention of Infections in Mothers & Infants
 Helen Y. Chu, MD MPH Division of Allergy & Infectious Diseases University of Washington Prevention of Infections in Mothers & Infants June 2, 2015 Midwives Association of Washington State Conference Financial
Helen Y. Chu, MD MPH Division of Allergy & Infectious Diseases University of Washington Prevention of Infections in Mothers & Infants June 2, 2015 Midwives Association of Washington State Conference Financial
Hepatitis B (Hep-B) is one of the most
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 50 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Influence of Hepatitis B immunization to prevent vertical transmission of Hep-B virus in infants born from Hep-B positive mother Liza
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 50 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Influence of Hepatitis B immunization to prevent vertical transmission of Hep-B virus in infants born from Hep-B positive mother Liza
Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective
 Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective Infectious A E Enterically transmitted Viral hepatitis NANB Serum B D F, G,? other C Parenterally transmitted Before the discovery of hepatitis A virus (HAV) and
Viral Hepatitis - Historical Perspective Infectious A E Enterically transmitted Viral hepatitis NANB Serum B D F, G,? other C Parenterally transmitted Before the discovery of hepatitis A virus (HAV) and
in pregnancy Document Review History Version Review Date Reviewed By Approved By
 GYNAECOLOGY/ ANTENATAL CARE WIRRAL WOMEN & CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Guideline No: Hepatitis B management in pregnancy VERSION 1 AMENDMENTS MADE: N/A DATE OF ISSUE: May 2012 DATE OF REVIEW: May 2015 REVIEW INTERVAL:
GYNAECOLOGY/ ANTENATAL CARE WIRRAL WOMEN & CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Guideline No: Hepatitis B management in pregnancy VERSION 1 AMENDMENTS MADE: N/A DATE OF ISSUE: May 2012 DATE OF REVIEW: May 2015 REVIEW INTERVAL:
Media centre. WHO Hepatitis B. Key facts. 1 of :12 AM.
 1 of 5 2013-08-02 7:12 AM Media centre Hepatitis B Share Print Fact sheet N 204 Updated July 2013 Key facts Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic
1 of 5 2013-08-02 7:12 AM Media centre Hepatitis B Share Print Fact sheet N 204 Updated July 2013 Key facts Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic
Carrier state and chronic infection state. At-risk populations
 John T. Stutts, MD, MPH University of Louisville School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Carrier state and chronic infection state -
John T. Stutts, MD, MPH University of Louisville School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Carrier state and chronic infection state -
Michigan Guidelines: HIV, Syphilis, HBV in Pregnancy
 Michigan Guidelines: HIV, Syphilis, HBV in Pregnancy Presenter: Theodore B. Jones, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine Beaumont Dearborn Hospital HIV, Syphilis, HBV in
Michigan Guidelines: HIV, Syphilis, HBV in Pregnancy Presenter: Theodore B. Jones, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine Beaumont Dearborn Hospital HIV, Syphilis, HBV in
universal vaccination
 Vol. 21No. 2149 8 HB B universal vaccination Blumberg HBs B 40 B HBV HBV HBV HBs WHO 1992 HBV B HB universal vaccination 1997 HB universal vaccination HBV high risk HBV universal vaccination B HBV universal
Vol. 21No. 2149 8 HB B universal vaccination Blumberg HBs B 40 B HBV HBV HBV HBs WHO 1992 HBV B HB universal vaccination 1997 HB universal vaccination HBV high risk HBV universal vaccination B HBV universal
MA PERINATAL HEPATITIS B PREVENTION PROGRAM
 MA PERINATAL HEPATITIS B PREVENTION PROGRAM Massachusetts Department of Public Health Immunization Program MIAP 2016 1 1 Presenter Disclosure Information I, Theodora Wohler, have been asked to disclose
MA PERINATAL HEPATITIS B PREVENTION PROGRAM Massachusetts Department of Public Health Immunization Program MIAP 2016 1 1 Presenter Disclosure Information I, Theodora Wohler, have been asked to disclose
HBV vaccination: Optimizing coverage and efficacy. Alex Vorsters, Pierre Van Damme Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board
 HBV vaccination: Optimizing coverage and efficacy. Alex Vorsters, Pierre Van Damme Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board 2 nd Hepatitis Cure and Eradication Meeting 11 12 November 2015 Declaration of Interest
HBV vaccination: Optimizing coverage and efficacy. Alex Vorsters, Pierre Van Damme Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board 2 nd Hepatitis Cure and Eradication Meeting 11 12 November 2015 Declaration of Interest
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy. Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011
 HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
Hepatitis B Update. Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL. Gastroenterology
 Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
Hepatitis B Update Jorge L. Herrera, M.D. University of South Alabama Mobile, AL Deciding Who to Treat Is hepatitis B a viral disease or a liver disease? Importance of HBV-DNA Levels in the Natural History
VIRAL HEPATITIS: SITUATION ANALYSIS AND PERSPECTIVES IN THE AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Secretariat. CONTENTS Paragraphs BACKGROUND...
 8 April 2014 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH PROGRAMME SUBCOMMITTEE Sixty-fourth session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 9 11 June 2014 Provisional agenda item 6 VIRAL HEPATITIS: SITUATION
8 April 2014 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH PROGRAMME SUBCOMMITTEE Sixty-fourth session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 9 11 June 2014 Provisional agenda item 6 VIRAL HEPATITIS: SITUATION
STATE TDAP VACCINE PROGRAM
 STATE TDAP VACCINE PROGRAM CDPH provides free Tdap vaccine for local public health departments. This vaccine then is distributed to clinics through out county. Vaccine to be specifically given to: Woman
STATE TDAP VACCINE PROGRAM CDPH provides free Tdap vaccine for local public health departments. This vaccine then is distributed to clinics through out county. Vaccine to be specifically given to: Woman
Eliminating Chronic Hepatitis B Disparities among Asian Pacific Islanders: A Model for Transforming Public Health in the Pacific
 Eliminating Chronic Hepatitis B Disparities among Asian Pacific Islanders: A Model for Transforming Public Health in the Pacific Augustina Manuzak, MD, MPH, PhD Augustina.manuzak@doh.hawaii.gov 10/10/2012
Eliminating Chronic Hepatitis B Disparities among Asian Pacific Islanders: A Model for Transforming Public Health in the Pacific Augustina Manuzak, MD, MPH, PhD Augustina.manuzak@doh.hawaii.gov 10/10/2012
VIRAL HEPATITIS: SITUATION ANALYSIS AND PERSPECTIVES IN THE AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Secretariat. CONTENTS Paragraphs BACKGROUND...
 5 November 2014 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-fourth session Cotonou, Republic of Benin, 3 7 November 2014 Provisional agenda item 11 VIRAL HEPATITIS: SITUATION ANALYSIS AND PERSPECTIVES
5 November 2014 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-fourth session Cotonou, Republic of Benin, 3 7 November 2014 Provisional agenda item 11 VIRAL HEPATITIS: SITUATION ANALYSIS AND PERSPECTIVES
Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention
 Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Purpose 2 The primary goal of the Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Program (PHBPP) is to identify all pregnant women who are infected with hepatitis b and prevent perinatal
Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Purpose 2 The primary goal of the Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Program (PHBPP) is to identify all pregnant women who are infected with hepatitis b and prevent perinatal
24. Screening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection
 Part D. Infectious Diseases 24. Screening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection RECOMMENDATION Screening with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) to detect active (acute or chronic) hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection
Part D. Infectious Diseases 24. Screening for Hepatitis B Virus Infection RECOMMENDATION Screening with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) to detect active (acute or chronic) hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection
Hepatitis STARS Program. Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003
 Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis B Virus in Pregnancy
 REVIEW REVIEW Hepatitis B Virus in Pregnancy Tram T. Tran, M.D. Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains an important worldwide cause of chronic liver disease, which may lead to the development
REVIEW REVIEW Hepatitis B Virus in Pregnancy Tram T. Tran, M.D. Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains an important worldwide cause of chronic liver disease, which may lead to the development
Should we treat hepatitis B positive pregnant women to prevent mother to child transmission?
 Should we treat hepatitis B positive pregnant women to prevent mother to child transmission? Daniel Shouval Liver Unit Hadassah-Hebrew University Hospital Jerusalem, Israel VHPB Vienna June 1-2, 2017 Background
Should we treat hepatitis B positive pregnant women to prevent mother to child transmission? Daniel Shouval Liver Unit Hadassah-Hebrew University Hospital Jerusalem, Israel VHPB Vienna June 1-2, 2017 Background
Hepatitis B and Hepatitis B Vaccine
 Hepatitis B and Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine- Preventable Diseases Note to presenters: Images of vaccine-preventable diseases are available from the Immunization Action Coalition website at http://www.vaccineinformation.org/photos/index.asp
Hepatitis B and Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine- Preventable Diseases Note to presenters: Images of vaccine-preventable diseases are available from the Immunization Action Coalition website at http://www.vaccineinformation.org/photos/index.asp
The Hepatitis B Vaccine: What Went Wrong?
 The Hepatitis B Vaccine: What Went Wrong? By F. Edward Yazbak, MD, FAAP On Dec. 23, 2005, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (1) in which
The Hepatitis B Vaccine: What Went Wrong? By F. Edward Yazbak, MD, FAAP On Dec. 23, 2005, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (1) in which
Summary of Seroprotection after Recombinant Hepatitis B Vaccine Administered to Newborn Infants (defined as the first 30 days of Life) Background:
 Prepared by: TV Murphy, MD, September 16, 2016 Summary of Seroprotection after Recombinant Hepatitis B Vaccine Administered to Newborn Infants (defined as the first 30 days of Life) Background: The primary
Prepared by: TV Murphy, MD, September 16, 2016 Summary of Seroprotection after Recombinant Hepatitis B Vaccine Administered to Newborn Infants (defined as the first 30 days of Life) Background: The primary
Management of Viral Infection during Pregnancy
 Vaccination Management of Viral Infection during Pregnancy JMAJ 45(2): 69 74, 2002 Takashi KAWANA Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Teikyo University Mizonokuchi Hospital Abstract: Viral infection
Vaccination Management of Viral Infection during Pregnancy JMAJ 45(2): 69 74, 2002 Takashi KAWANA Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Teikyo University Mizonokuchi Hospital Abstract: Viral infection
Blood-Borne Viruses and Pregnancy. Prof Ashley Brown Imperial Healthcare NHS Trust
 Blood-Borne Viruses and Pregnancy Prof Ashley Brown Imperial Healthcare NHS Trust Hepatitis B and Pregnancy Global Prevalence of Chronic HBV Chronic HBV prevalence (% of population) Chronic HBV in the
Blood-Borne Viruses and Pregnancy Prof Ashley Brown Imperial Healthcare NHS Trust Hepatitis B and Pregnancy Global Prevalence of Chronic HBV Chronic HBV prevalence (% of population) Chronic HBV in the
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Factsheet for healthcare professionals about the neonatal selective immunisation programme for babies at risk of hepatitis B Background All babies born
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Factsheet for healthcare professionals about the neonatal selective immunisation programme for babies at risk of hepatitis B Background All babies born
TOWARDS ELIMINATION OF MOTHER TO CHILD TRANSMISSION OF HIV
 TOWARDS ELIMINATION OF MOTHER TO CHILD TRANSMISSION OF HIV Gladwel Muthoni KPA Conference 24 th April, 2018 OUTLINE Burden of HIV in PMTCT Mechanism and timing of Mother to Child Transmission (MTCT) Four
TOWARDS ELIMINATION OF MOTHER TO CHILD TRANSMISSION OF HIV Gladwel Muthoni KPA Conference 24 th April, 2018 OUTLINE Burden of HIV in PMTCT Mechanism and timing of Mother to Child Transmission (MTCT) Four
Hepatitis B Birth Dose: A Self-Study Module for the Maternal and Child Health Nurse
 Hepatitis B Birth Dose: A Self-Study Module for the Maternal and Child Health Nurse With a special feature on frequently asked questions about vaccines Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to expand
Hepatitis B Birth Dose: A Self-Study Module for the Maternal and Child Health Nurse With a special feature on frequently asked questions about vaccines Purpose: The purpose of this activity is to expand
Contraindications to breast feeding. Dr. Ahmed Isam
 Contraindications to breast feeding Dr. Ahmed Isam When should a mother avoid breastfeeding? Health professionals agree that human milk provides the most complete form of nutrition for infants, including
Contraindications to breast feeding Dr. Ahmed Isam When should a mother avoid breastfeeding? Health professionals agree that human milk provides the most complete form of nutrition for infants, including
Balance Sheets 1. CHILD HEALTH... PAGE NUTRITION... PAGE WOMEN S HEALTH... PAGE WATER AND ENVIRONMENTAL SANITATION...
 Balance Sheets A summary of the goals, gains and unfinished business of the 1990-2000 decade as included in the Report of the Secretary-General, 'We the Children: End-decade review of the follow-up to
Balance Sheets A summary of the goals, gains and unfinished business of the 1990-2000 decade as included in the Report of the Secretary-General, 'We the Children: End-decade review of the follow-up to
Update: ACIP Recommendations for Hepatitis B Vaccination
 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Update: ACIP Recommendations for Hepatitis B Vaccination Sarah Schillie, MD, MPH, MBA Summit for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and
National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Update: ACIP Recommendations for Hepatitis B Vaccination Sarah Schillie, MD, MPH, MBA Summit for the Elimination of Hepatitis B and
Toronto Declaration: Strategies to control and eliminate viral hepatitis globally. A call for coordinated action
 Toronto Declaration: Strategies to control and eliminate viral hepatitis globally A call for coordinated action Hepatitis B National Action Plan All countries should develop a national and/or regional
Toronto Declaration: Strategies to control and eliminate viral hepatitis globally A call for coordinated action Hepatitis B National Action Plan All countries should develop a national and/or regional
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the neonatal selective immunisation programme for babies at high risk (babies born to hepatitis B positive mothers)
The hexavalent combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the neonatal selective immunisation programme for babies at high risk (babies born to hepatitis B positive mothers)
Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program. Purpose
 Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Presented by: Carolyn Perry, RN, BSN Purpose 2 The primary goal of the Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program (PHBPP) is to identify all pregnant women who are
Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Presented by: Carolyn Perry, RN, BSN Purpose 2 The primary goal of the Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program (PHBPP) is to identify all pregnant women who are
Viral Hepatitis. Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital
 Viral Hepatitis Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Viral Hepatitis HAV HBV HCV HDV HEV Other viral: CMV, EBV, HSV Unknown Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Transmitted via the faecal-oral route
Viral Hepatitis Dr Melissa Haines Gastroenterologist Waikato Hospital Viral Hepatitis HAV HBV HCV HDV HEV Other viral: CMV, EBV, HSV Unknown Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Transmitted via the faecal-oral route
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1Neonatal hepatitis
NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1Neonatal hepatitis
Confirmed (Laboratory Tests) Serum positive for IgM anti-hbc or, hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg).
 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
SIXTY-SECOND WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A62/22 Provisional agenda item April Viral hepatitis. Report by the Secretariat
 SIXTY-SECOND WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A62/22 Provisional agenda item 12.17 16 April 2009 Viral hepatitis Report by the Secretariat THE DISEASES AND BURDEN 1. The group of viruses that cause acute and/or chronic
SIXTY-SECOND WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A62/22 Provisional agenda item 12.17 16 April 2009 Viral hepatitis Report by the Secretariat THE DISEASES AND BURDEN 1. The group of viruses that cause acute and/or chronic
Incomplete Hepatitis B Immunization, Maternal Carrier Status, and Increased Risk of Liver Diseases: A 20-Year Cohort Study of 3.8 Million Vaccinees
 Incomplete Hepatitis B Immunization, Maternal Carrier Status, and Increased Risk of Liver Diseases: A 20-Year Cohort Study of 3.8 Million Vaccinees Yin-Chu Chien, 1 Chyi-Feng Jan, 2 Chun-Ju Chiang, 3 Hsu-Sung
Incomplete Hepatitis B Immunization, Maternal Carrier Status, and Increased Risk of Liver Diseases: A 20-Year Cohort Study of 3.8 Million Vaccinees Yin-Chu Chien, 1 Chyi-Feng Jan, 2 Chun-Ju Chiang, 3 Hsu-Sung
Hepatitis B surface antigen HBsAg Hepatitis B e antigen HBeAg 1) B
 292 14 4 B Effects of the Vaccination Against Hepatitis B Virus for All Infants in Taiwan Chang-Kuen Tien, Nobutaka Kurihara, Hiroyuki Yanagisawa and Osamu Wada (Hygiene and Preventive Medicine, Saitama
292 14 4 B Effects of the Vaccination Against Hepatitis B Virus for All Infants in Taiwan Chang-Kuen Tien, Nobutaka Kurihara, Hiroyuki Yanagisawa and Osamu Wada (Hygiene and Preventive Medicine, Saitama
Give Birth to the End of Hepatitis B
 Give Birth to the End of Hepatitis B LiverConnects Feb 14, 2017 Rosalyn Singleton MD MPH Research Physician, ANTHC ris2@cdc.gov risingleton@anthc.org Annie Peterson-Lewis RN State of Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis
Give Birth to the End of Hepatitis B LiverConnects Feb 14, 2017 Rosalyn Singleton MD MPH Research Physician, ANTHC ris2@cdc.gov risingleton@anthc.org Annie Peterson-Lewis RN State of Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Time to Eliminate Hepatitis B John W. Ward, M.D. Division of Viral Hepatitis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 Time to Eliminate Hepatitis B John W. Ward, M.D. Division of Viral Hepatitis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Division of Viral Hepatitis National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and
Time to Eliminate Hepatitis B John W. Ward, M.D. Division of Viral Hepatitis Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Division of Viral Hepatitis National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and
Hepatitis B vaccination worldwide: Lessons learnt and the way forward
 Hepatitis B vaccination worldwide: Lessons learnt and the way forward VHPB Russia meeting Oct 2018 Pierre Van Damme MD, PhD History Hepatitis B vaccines have been available since early 1980 s First recommended
Hepatitis B vaccination worldwide: Lessons learnt and the way forward VHPB Russia meeting Oct 2018 Pierre Van Damme MD, PhD History Hepatitis B vaccines have been available since early 1980 s First recommended
Maternal Immunization: Unique considerations of public health value of vaccines given to pregnant women
 Maternal Immunization: Unique considerations of public health value of vaccines given to pregnant women Estimating the full public health value of vaccines Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine
Maternal Immunization: Unique considerations of public health value of vaccines given to pregnant women Estimating the full public health value of vaccines Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine
Hepatitis B at a Glance
 Return completed form, preferably within 30 days of U.S. date of arrival, to address on reverse side of this form. Review overseas medical exam if available and document immunization dates. Indicate if
Return completed form, preferably within 30 days of U.S. date of arrival, to address on reverse side of this form. Review overseas medical exam if available and document immunization dates. Indicate if
A study on hepatitis-b in pregnant women and their neonatal outcome
 International Journal of Medical and Health Research ISSN: 2454-9142, Impact Factor: RJIF 5.54 www.medicalsciencejournal.com Volume 3; Issue 2; February 2017; Page No. 126-130 A study on hepatitis-b in
International Journal of Medical and Health Research ISSN: 2454-9142, Impact Factor: RJIF 5.54 www.medicalsciencejournal.com Volume 3; Issue 2; February 2017; Page No. 126-130 A study on hepatitis-b in
Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
 Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Issue Date: July 2012 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy Purpose
Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Issue Date: July 2012 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy Purpose
Protecting Infants and Children from Pertussis and Influenza
 September 23, 2016 Paulomi Shah, DO, FAAP Pediatrician, Medical Director Children s Medical Services, Sonoma County Alan Shotkin, MD, FAAP Neonatologist, Medical Director Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Protecting
September 23, 2016 Paulomi Shah, DO, FAAP Pediatrician, Medical Director Children s Medical Services, Sonoma County Alan Shotkin, MD, FAAP Neonatologist, Medical Director Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Protecting
HBsAg(+) mothers is a transient
 Perinatal HBV viremia in newborns of HBsAg(+) mothers is a transient phenomenon that does not necessarily imply HBV infection transmission Vana Papaevangelou (Greece) National and Kapodistrian University
Perinatal HBV viremia in newborns of HBsAg(+) mothers is a transient phenomenon that does not necessarily imply HBV infection transmission Vana Papaevangelou (Greece) National and Kapodistrian University
Hepatitis B. Data from the Travel Health Surveillance Section of the Health Protection Agency Communicable Disease Surveillance Centre
 Hepatitis B Introduction Hepatitis B virus is one of the most prevalent viruses worldwide and is a major cause of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. It is a hepadnavirus, consisting of
Hepatitis B Introduction Hepatitis B virus is one of the most prevalent viruses worldwide and is a major cause of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. It is a hepadnavirus, consisting of
2018 Perinatal Hepatitis B Summit. Eva Hansson, RN, MSN Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Coordinator
 2018 Perinatal Hepatitis B Summit Eva Hansson, RN, MSN Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Coordinator Overview of Summit Summary of perinatal Hepatitis B in the US & Texas ACIP Hepatitis B Prevention recommendations
2018 Perinatal Hepatitis B Summit Eva Hansson, RN, MSN Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Coordinator Overview of Summit Summary of perinatal Hepatitis B in the US & Texas ACIP Hepatitis B Prevention recommendations
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women
 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women March 2012 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women Abstracted from recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MARCH 2012 Risk
Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women March 2012 Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women Abstracted from recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MARCH 2012 Risk
These precautions should be followed for 7 days after symptom onset or 24 hours after resolution of symptoms, whichever is longer.
 1 of 5 11/15/2009 10:34 AM H1N1 Flu November 10, 2009 4:30 PM ET This interim guidance has been updated to replace previously posted guidance entitled Considerations Regarding Novel H1N1 Flu Virus in Obstetric
1 of 5 11/15/2009 10:34 AM H1N1 Flu November 10, 2009 4:30 PM ET This interim guidance has been updated to replace previously posted guidance entitled Considerations Regarding Novel H1N1 Flu Virus in Obstetric
Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
 Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Last reviewed: October 2014 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Last reviewed: October 2014 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C
 S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
A VIEW OF DEMOGRAPHIC FACTORS OF HEPATITIS B VIRUS INFECTION IN DURRES REGION DURING
 Interdisplinary Journal of Research and Development Alexander Moisiu University, Durrës, Albania Vol (IV), No.2, 2017 Paper presented in 1 -st International Scientific Conference on Professional Sciences,
Interdisplinary Journal of Research and Development Alexander Moisiu University, Durrës, Albania Vol (IV), No.2, 2017 Paper presented in 1 -st International Scientific Conference on Professional Sciences,
Wang Linhong, Deputy Director, Professor National Center for Women and Children s Health, China CDC
 Maternal and Child Health in China Wang Linhong, Deputy Director, Professor National Center for Women and Children s Health, China CDC Table of Contents 1 MCH Development and Situation in China 2 MCH Resources
Maternal and Child Health in China Wang Linhong, Deputy Director, Professor National Center for Women and Children s Health, China CDC Table of Contents 1 MCH Development and Situation in China 2 MCH Resources
Best Practices for Infection Prevention and Control in Perinatology In All Health Care Settings that Provide Obstetrical and Newborn Care, PIDAC 2012
 Best Practices for Infection Prevention and Control in Perinatology In All Health Care Settings that Provide Obstetrical and Newborn Care, PIDAC 2012 Perinatal Infections Mary Vearncombe, MD, FRCPC Chair,
Best Practices for Infection Prevention and Control in Perinatology In All Health Care Settings that Provide Obstetrical and Newborn Care, PIDAC 2012 Perinatal Infections Mary Vearncombe, MD, FRCPC Chair,
Hepatitis B. What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013
 Hepatitis B What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013 Some quick facts about Hepatitis B Worldwide: 350-400 Million are chronic infections
Hepatitis B What's the impact on the risk? Dr Himanshu Bhatia, Asia Chief Medical Officer ALUCA, Brisbane, Sept 2013 Some quick facts about Hepatitis B Worldwide: 350-400 Million are chronic infections
Health Care Worker (Pregnant) - Infectious Diseases Risks and Exposure
 1. Purpose The purpose of this guideline is to provide accurate information on the risks to pregnant Health Care Workers (HCWs) in the event of an exposure to a transmissible infectious disease at the
1. Purpose The purpose of this guideline is to provide accurate information on the risks to pregnant Health Care Workers (HCWs) in the event of an exposure to a transmissible infectious disease at the
Immunization Update: What s New?
 Immunization Update: What s New? Joseph A. Bocchini, Jr. MD, FAAP Professor and Chairman Department of Pediatrics Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport Red Stick Potpourri LA Chapter-American
Immunization Update: What s New? Joseph A. Bocchini, Jr. MD, FAAP Professor and Chairman Department of Pediatrics Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport Red Stick Potpourri LA Chapter-American
REVIEW ARTICLE. Breastfeeding of Newborns by Mothers Carrying Hepatitis B Virus
 ONLINE FIRST REVIEW ARTICLE Breastfeeding of Newborns by Mothers Carrying Hepatitis B Virus A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review Zhongjie Shi, MD; Yuebo Yang, MD; Hao Wang, MD; Lin Ma, MD; Ann Schreiber,
ONLINE FIRST REVIEW ARTICLE Breastfeeding of Newborns by Mothers Carrying Hepatitis B Virus A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review Zhongjie Shi, MD; Yuebo Yang, MD; Hao Wang, MD; Lin Ma, MD; Ann Schreiber,
Hepatitis B infection
 Hepatitis B infection Kenneth Kabagambe Executive Director The National Organization for People Living with Hepatitis B (NOPLHB Uganda General introduction: Viral hepatitis in Uganda Viruses that affect
Hepatitis B infection Kenneth Kabagambe Executive Director The National Organization for People Living with Hepatitis B (NOPLHB Uganda General introduction: Viral hepatitis in Uganda Viruses that affect
Prevention and control of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B and C VIENNA, AUSTRIA 1-2 June 2017
 Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Prevention and control of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B and C VIENNA, AUSTRIA 1-2 June 2017 Objectives To provide an overview of the current epidemiology of mother-to-child
Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board Prevention and control of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B and C VIENNA, AUSTRIA 1-2 June 2017 Objectives To provide an overview of the current epidemiology of mother-to-child
CHILD HEALTH. There is a list of references at the end where you can find more information. FACT SHEETS
 SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing. Origins of Liver Science
 Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Treatment of hepatitis B : the guidelines and real life
 Treatment of hepatitis B : the guidelines and real life Prince of Songkla University, Thailand Teerha Piratvisuth MD. NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure Statement of Financial
Treatment of hepatitis B : the guidelines and real life Prince of Songkla University, Thailand Teerha Piratvisuth MD. NKC Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure Statement of Financial
Immunization Update Richard M. Lampe M.D.
 Immunization Update 2012 Richard M. Lampe M.D. Immunization Update List the Vaccines recommended for Health Care Personnel Explain why Health Care Personnel are at risk Recognize the importance of these
Immunization Update 2012 Richard M. Lampe M.D. Immunization Update List the Vaccines recommended for Health Care Personnel Explain why Health Care Personnel are at risk Recognize the importance of these
The management of hepatitis B virus (HBV) Management of hepatitis B in pregnancy: Weighing the options ABSTRACT PERINATAL TRANSMISSION KEY POINTS
 TRAM T. TRAN, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Geffen ULA School of Medicine Medical Director, Liver Transplantation, enter for Liver Disease and Transplantation, edars-sinai Medical enter Los Angeles,
TRAM T. TRAN, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Geffen ULA School of Medicine Medical Director, Liver Transplantation, enter for Liver Disease and Transplantation, edars-sinai Medical enter Los Angeles,
Transmission/Prevention
 Transmission/Prevention Section Three Transmission/Prevention Hepatitis C is transmitted by blood-to-blood contact. Any break in the skin may allow HCV to enter the body, even if no blood is visible. The
Transmission/Prevention Section Three Transmission/Prevention Hepatitis C is transmitted by blood-to-blood contact. Any break in the skin may allow HCV to enter the body, even if no blood is visible. The
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update. Primary Causes of Chronic Liver Disease in the U.S. Hepatitis Definition. Hepatitis Viruses.
 Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
patients with blood borne viruses Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled Document Lead:
 CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
How does HBV affect the liver?
 Hepatitis B Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It s the largest solid organ in the body and is located under your rib cage on the upper right
Hepatitis B Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It s the largest solid organ in the body and is located under your rib cage on the upper right
