The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
|
|
|
- Mark McGee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Factsheet for healthcare professionals about the neonatal selective immunisation programme for babies at risk of hepatitis B
2 Background All babies born on or after 1 August 2017 are now eligible for a hexavalent vaccine which includes hepatitis B (HepB) for their primary immunisations. This vaccine, called Infanrix hexa, will replace the pentavalent infant vaccines Infanrix -IPV+Hib and Pediacel. Whilst this should benefit infants at increased risk of hepatitis B (for example those born to an infected mother) as they are more likely to complete the full course of hepatitis B, these babies still require the critical early doses at birth and one month of age. Healthcare professionals administering the programme may mistakenly assume that these doses are no longer needed or find the schedule for high risk infants confusing or complicated. The following questions and answers are intended to provide healthcare professionals with more information about vaccinating high risk infants in light of the new universal hepatitis B infant programme. Answers to more general questions about the hexavalent vaccine may be found in The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB 6 in 1 combination vaccine: Information for healthcare practitioners about the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in the routine infant immunisation programme available on What is the selective neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme? All pregnant women are offered screening for infection with hepatitis B in every pregnancy. Babies born to mothers who, following screening, are found to be chronically infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or who have had acute hepatitis B during pregnancy are at risk of becoming infected with HBV. The objective of the selective neonatal immunisation programme is to provide post exposure immunisation to prevent mother to child transmission at or around the time of birth. To fulfil this objective, infected mothers need to be identified through antenatal screening and immunisation of the infant needs to start with a dose of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine at birth followed by a second dose at four weeks of age. Up until now, they received further doses at eight weeks of age and twelve months of age and a dose with their pre-school booster vaccines. As Infanrix hexa is now part of the universal childhood immunisation programme, it will continue to be delivered in primary care. Immuisation providers (Trust maternity and paediatric teams and primary care) will therefore need to ensure timely communication with child health offices on vaccines administered to avoid doses inadvertently being given or missed. Why is the selective neonatal immunisation programme continuing if all infants are going to receive hepatitis B vaccine as part of the routine childhood programme? Hepatitis B infection can be transmitted from infected mothers to their babies at or around the time of birth (perinatal transmission). 2
3 This occurs mainly because infected blood from the mother passes through the placenta to the baby during delivery. Babies acquiring infection at this time have a high risk of becoming chronically infected with the virus. The development of chronic infection in infants born to infected mothers after perinatal transmission can be prevented in over 90% of cases by appropriate post-exposure prophylactic vaccination starting at birth. Timely vaccination at birth and at four weeks of age is critical to preventing infection in the infant. The universal infant programme provides preexposure protection against hepatitis B virus which will benefit those who may have future risk of exposure to it. The dose that is given to all babies at eight weeks of age (as part of the universal programme) would be too late to prevent infection in those high risk babies who are exposed at or around birth. Will Hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) still be required? Yes. Babies born to highly infectious mothers should continue to receive HBIG as well as vaccine at birth (see Green Book Hepatitis B chapter). HBIG provides ready-made hepatitis B-specific antibodies and gives some immediate protection until the hepatitis B vaccine, which should be given at the same time, becomes effective. Giving HBIG concurrently with hepatitis B vaccine does not affect the development of active immunity to the vaccine. HBIG should be given in a different site to the vaccine. HBIG should be given as soon as possible, preferably within 48 hours of delivery (and within 24 hours of birth dose of vaccine), although it should still be considered up to a week after exposure. Does the Infanrix hexa vaccine provide the same protection as giving the pentavalent DTaP/IPV/ Hib vaccine with a monovalent hepatitis B vaccine? Large clinical studies have shown that Infanrix hexa produces a strong immune response against all the antigens contained in it in infants who have received a dose of hepatitis B vaccine at birth. 1 These studies have also shown that infants who received monovalent hepatitis B vaccines at birth followed by a three dose course of the Infanrix hexa vaccine achieve the same protection against hepatitis B as those who received the pentavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib vaccine with a monovalent HepB vaccine. 3
4 Vaccine scheduling What is the vaccine schedule for high risk infants? High risk infants should receive monovalent hepatitis B vaccine at birth and 4 weeks of age and then three doses of Infanrix hexa vaccine at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age. They should receive a booster dose of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine at 12 months of age, at which time they should also have a blood test to check for infection. Table one: Hepatitis B doses in the immunisation schedule for routine childhood and selective neonatal hepatitis B programmes Age Routine childhood Babies born to hepatits B Birth x * x programme infected mothers Monovalent HepB (Engerix B or HBvaxPRO Paediatric ) (with HBIG if indicated) 4 weeks Monovalent HepB (Engerix B or HBvaxPRO Paediatric ) (with HBIG if indicated) 8 week DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB 12 weeks DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB 16 weeks DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB x 1 year Monovalent HepB (Engerix B or HBvaxPRO Paediatric ) (with HBIG if indicated) *Newborn infants born to a hepatitis B negative woman but known to be going home to a household with another hepatitis B infected person may be at immediate risk of hepatitis B infection. In these situations, a monovalent dose of hepatitis B vaccine should be offered before discharge from hospital. They should then continue on the routine childhood schedule commencing at eight weeks. 4
5 This schedule was agreed by the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) in October The Committee considered various schedule options and agreed that there was no evidence of increased reactogenicity or adverse events associated with multiple doses of hepatitis B-containing vaccine and the schedule option chosen for babies born to hepatitis B infected mothers (shown in the table above) reduced the risk of missing doses. Is it safe for high risk infants to receive a total of six doses when they previously only received four doses in infancy? The JCVI considered the various different options for vaccinating high risk infants following the introduction of the hexavalent hepatitis B-containing vaccine into the routine immunisation schedule for all infants. It was agreed that having two different vaccines being used in the infant programme (pentavalent and hexavalent) would be confusing and securing a continuous supply of the small amount of pentavalent vaccine would be difficult. Therefore JCVI concluded that it is better to recommend that all high risk infants receive additional doses of hepatitis B vaccine in the hexavalent vaccine. Hepatitis B vaccine is well tolerated and additional doses should not be harmful. If a high risk infant misses their 4 week dose of hepatitis B vaccine and then receives hexavalent vaccine at 8, 12 and 16 weeks, should a dose of hepatitis B vaccine still be given to replace the 4 week missed dose even if given late? No. The key to giving optimal protection is the timing of the early doses. The doses given at birth, 4 and 8 weeks old should stimulate immunity in time to prevent the hepatitis B virus replicating to high levels. The doses normally given at 12 and 16 weeks, and the booster at one year of age, will help to provide longer term protection and boosting. Where an early dose (eg at 4 weeks) is missed or delayed, this may increase the risk of the child becoming infected, but cannot be reversed by adding additional doses later. Immunisation providers in primary care that are not responsible for giving the monovalent HepB doses before 8 weeks of age should ensure that their medical records clearly identify at risk infants so that they are aware when a dose has been missed or delayed. In the situation described above, it is very important that the child is tested to check whether they were infected early in life as they missed an early dose of vaccine. The best approach to preventing these infants becoming hepatitis B positive is to ensure all scheduled doses of a hepatitis B containing vaccine are given on time. What do you do if a high risk infant attends late for their first or second dose of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine but before six weeks of age? The infant should receive a dose of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine as early doses of vaccine are of critical importance in preventing maternallyacquired hepatitis B infection. The first primary Infanrix hexa dose, rotavirus, PCV and MenB vaccines should then be scheduled routinely at 8 weeks of age, irrespective of the timing of the late monovalent hepatitis B vaccine dose, in order not to delay protection against the other infections, A shorter interval between doses of hepatitis B vaccine in this situation is unlikely to be detrimental to the infant s overall protection against HBV. In the situation described above, it is very important that the child is tested to check whether they were infected early in life as they missed an early dose of vaccine. 5
6 What do you do if a high risk infant attends late for their first or second dose of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine after 6 weeks of age? Do you give monovalent vaccine or a dose of Infanrix hexa early? While Infanrix hexa is approved for use from six weeks of age, in Northern Ireland, Child Health will continue to call babies for their first dose at eight weeks of age. Infants who attend Trust paediatric clinics after six weeks of age should be assessed for the need for monovalent hepatitis B vaccine. It is safe to give the monovalent vaccine and the hexavalent within a short time interval. What should be done if the pentavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib vaccine is given in error to a high risk infant who should have received hepatitis B-containing hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB vaccine? Immunisation providers in primary care that have not provided the monovalent doses before 8 weeks of age should ensure that medical records clearly identify at risk infants so that they are able to recognise this error. If a child at high risk of hepatitis B inadvertently receives the pentavalent vaccine at 8 weeks of age, they should be urgently offered a monovalent hepatitis B vaccine. No additional vaccination is required if the same error occurs at the 12 or 16 week dose appointment. Should high risk infants born before August 2017 transfer onto the new schedule? No. Infants born before August 2017 should continue to receive the monovalent hepatitis B vaccine as per the previous 0, 1, 2, 12 month schedule with a blood test at 12 months to check whether they acquired infection. If any babies have not yet received their 2 month/8 week dose of hepatitis B however, this can be offered as Infanrix hexa. What should be given to other infants at risk of exposure to hepatitis B, for example those born into a family where there is a household contact (other than the mother) who is hepatitis B positive? Infants born to a hepatitis B negative mother but known to be going home to a household with another hepatitis B infected person may be at risk of hepatitis B infection. Whilst the risk of transmission to these infants is lower than for infants born to infected mothers who have already been exposed at birth, these infants should be given pre-exposure immunisation. Where there is an immediate risk of exposure, a monovalent dose of hepatitis B should be offered as soon as possible after birth. They can then continue to receive the routine doses of hexavalent vaccine at 8, 12 and 16 weeks old so that they receive a total of four doses of a hepatitis B containing vaccine. They do not require a dose at 4 weeks of age or a booster at 12 months of age. Other infants, who are not at immediate risk, can be vaccinated routinely at 8, 12 and 16 weeks of age. Infants who do not receive this dose at birth should receive it as soon as the need for it is realised. A risk assessment should be carried out as to the potential that the infant has been infected prior to this dose being given and therefore the need to test for infection at 12 months of age. If the infant is less than six weeks of age when the need for protection against hepatitis B in this situation is realised, they should be given a dose of monovalent hepatitis B vaccine. Doses of Infanrix hexa should then be given as per the infant schedule at 8, 12 and 16 weeks, irrespective of the timing of the late monovalent hepatitis B vaccine dose, in order not to delay protection against the other infections. If it is only realised that the infant needs protection against hepatitis B after they are six weeks of age, instead of giving monovalent hepatitis B vaccine, they should start their infant immunisation schedule early and receive their first dose of Infanrix hexa along with their first dose of rotavirus, MenB and PCV vaccines. 6
7 Booster doses and blood tests Why do high risk children still require a blood test a 12 months if they are receiving six doses of hepatitis B vaccine? Although the hepatitis B vaccine is highly effective at preventing infection if given at birth, a few infants may still acquire infection despite vaccination and HBIG. Infants with hepatitis B infection are usually asymptomatic and do not display any signs of infection so testing infants at 12 months of age (when they attend for their booster dose) is important to enable a timely assessment of their infection status. Finding out if the infant is infected at this point allows for prompt referral to specialist care to reduce the risk of long term complications in later life. Additionally, if the infant s blood test is negative, parents can be reassured that transmission has been avoided and no further action is required. The purpose of the 12 month blood test is to check for infection, not to check or measure response to the vaccine in the way that a healthcare worker s response is checked. Numerous studies have already demonstrated that the vast majority of infants who do not become infected make a protective response to a course of hepatitis B given in the first year of life. Why do some babies acquire hepatitis B infection despite vaccination and HBIG? If infection has already become established before the full response to immunisation is made, virus replication may not be inhibited completely by HBIG or vaccine. This is why it is important that the child is tested at one year of age. However, severe illness and, most importantly, development of the chronic, persistently infected, state which can lead to serious liver disease and liver cancer, may still be prevented by immunisation. Why do high risk children who receive Infanrix hexa no longer require a pre-school booster dose of hepatitis B vaccine? Increasing evidence has now shown that protection from hepatitis B vaccine is long-lasting and studies demonstrate that, among successfully vaccinated immunocompetent individuals, protection against chronic infection persists for years or more. The World Health Organization (WHO) has concluded from this that there is no compelling evidence for recommending a booster dose of hepatitis B vaccine in routine immunisation programmes. 2 Booster doses are only recommended for: healthcare workers, including students and trainees, who should be offered a single booster dose of vaccine, once only, around five years after primary immunisation patients with renal failure; at the time of a subsequent significant exposure. When is the pre-school hepatitis B booster dose for high risk children going to be dropped from the schedule? A further dose of hepatitis B-containing vaccine at 3 years and 4 months will no longer be recommended for those children who have completed their routine primary immunisations with the hexavalent hepatitis B-containing vaccine. Immunisation providers are reminded however, to use the opportunity of the pre-school booster appointment (for MMR and DTaP/IPV or dtap/ipv vaccinations), to check that high risk children have received all of the required doses and been tested for HBsAg to exclude infection. A high risk child who has missed a dose of hepatitis B in infancy could be offered a dose of Infanrix hexa instead of the routine pre-school booster vaccine. 7
8 Useful resources Dhilllon S. DTPa-HBV-IPV/Hib vaccine (Infanrix hexa ) A Review of its Use as a Primary and Booster Vaccination. Drugs 2010: 70(8): Available at: Infanrix hexa Summary of Product Characteristics. Available at: Public Health England. Immunisation against infectious disease (The Green Book) Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Polio, Hib and Hepatitis B chapters. Available at: References 1. Dhilllon S. DTPa-HBV-IPV/Hib vaccine (Infanrix hexa ) A Review of its Use as a Primary and Booster Vaccination. Drugs 2010: 70(8): Available at: 2. World Health Organization Global Hepatitis Report Public Health Agency, Linenhall Street, Belfast BT2 8BS. Tel: (local rate). Adapted from text published by Public Health England and reproduced with permission. 08/17
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the neonatal selective immunisation programme for babies at high risk (babies born to hepatitis B positive mothers)
The hexavalent combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the neonatal selective immunisation programme for babies at high risk (babies born to hepatitis B positive mothers)
WELSH HEALTH CIRCULAR
 WELSH HEALTH CIRCULAR WHC (2017) 022 Issue Date: 12 May 2017 STATUS: ACTION CATEGORY: PUBLIC HEALTH Title: Change of vaccine for the routine primary infant immunisation Date of Expiry / Review N/A For
WELSH HEALTH CIRCULAR WHC (2017) 022 Issue Date: 12 May 2017 STATUS: ACTION CATEGORY: PUBLIC HEALTH Title: Change of vaccine for the routine primary infant immunisation Date of Expiry / Review N/A For
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB combination vaccine Greenwich Practice Nurse Forum Oct 17 th 2017 Introduction of a hexavalent infant vaccine From autumn 2017, all babies born on or after 1 August 2017
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB combination vaccine Greenwich Practice Nurse Forum Oct 17 th 2017 Introduction of a hexavalent infant vaccine From autumn 2017, all babies born on or after 1 August 2017
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the introduction of the hexavalent vaccine into the routine infant immunisation programme
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the introduction of the hexavalent vaccine into the routine infant immunisation programme
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1Neonatal hepatitis
NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1Neonatal hepatitis
Guideline on Immunisation schedule from Autumn 2017
 Guideline on Immunisation schedule from Autumn 2017 Change: Introduction of Hexavalent combination vaccine (this includes Hepatitis B) for babies born on or after 1 st Aug. Those born before to stay on
Guideline on Immunisation schedule from Autumn 2017 Change: Introduction of Hexavalent combination vaccine (this includes Hepatitis B) for babies born on or after 1 st Aug. Those born before to stay on
Childhood Immunisations Template Guide 2017
 Childhood Immunisations Template Guide 2017 1 Template Control Page Childhood Immunisations Template Guide Title Childhood Immunisations Author CEG Description Supports the schedule of Childhood Immunisations
Childhood Immunisations Template Guide 2017 1 Template Control Page Childhood Immunisations Template Guide Title Childhood Immunisations Author CEG Description Supports the schedule of Childhood Immunisations
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in the routine infant immunisation programme July 2017
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in the routine infant immunisation programme July 2017
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for healthcare practitioners about the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in the routine infant immunisation programme About Public Health
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for healthcare practitioners about the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in the routine infant immunisation programme About Public Health
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for healthcare practitioners about the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in the routine infant immunisation programme About Public Health
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for healthcare practitioners about the inclusion of hepatitis B vaccine in the routine infant immunisation programme About Public Health
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the introduction of the hexavalent vaccine into the routine infant immunisation programme
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/HepB combination vaccine Information for registered healthcare practitioners about the introduction of the hexavalent vaccine into the routine infant immunisation programme
2018/19 Immunisation programmes list of additional and enhanced services
 2018/19 Immunisation programmes list of additional and enhanced services 2018/19 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional and enhanced services Version number: 1 First published: April 2018 Prepared
2018/19 Immunisation programmes list of additional and enhanced services 2018/19 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional and enhanced services Version number: 1 First published: April 2018 Prepared
2017/18 Immunisation programmes list of additional and enhanced services
 2017/18 Immunisation programmes list of additional and enhanced services 2017/18 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional and enhanced services Version number: 1 First published: April 2017 Prepared
2017/18 Immunisation programmes list of additional and enhanced services 2017/18 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional and enhanced services Version number: 1 First published: April 2017 Prepared
Classification: official 1
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
immunisation in New Zealand
 This appendix details the history of. Section A1.1 is a brief summary of when each vaccine was introduced to the National Immunisation Schedule (the Schedule). This summary includes vaccines which were
This appendix details the history of. Section A1.1 is a brief summary of when each vaccine was introduced to the National Immunisation Schedule (the Schedule). This summary includes vaccines which were
Rotavirus. Factsheet for parents. Immunisation for babies up to a year old
 Rotavirus Factsheet for parents This factsheet describes the rotavirus infection and the vaccine that protects against it. It also provides the background to the development and introduction of the vaccination
Rotavirus Factsheet for parents This factsheet describes the rotavirus infection and the vaccine that protects against it. It also provides the background to the development and introduction of the vaccination
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C
 Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C Presentation 5 October 2018 0 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to: Demonstrate an increased knowledge and understanding of opportunities
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C Presentation 5 October 2018 0 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to: Demonstrate an increased knowledge and understanding of opportunities
Childhood Immunisations Template Guide 2016
 Childhood Immunisations Template Guide 2016 1 Template Control Page Childhood Immunisations Template Guide Title Childhood Immunisations Author CEG Version 9 Description Supports the schedule of Childhood
Childhood Immunisations Template Guide 2016 1 Template Control Page Childhood Immunisations Template Guide Title Childhood Immunisations Author CEG Version 9 Description Supports the schedule of Childhood
2016/17 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional services and enhanced services
 2016/17 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional services and enhanced services 2016/17 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional services and enhanced services Version number: 1 First published:
2016/17 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional services and enhanced services 2016/17 Vaccination and Immunisation list of additional services and enhanced services Version number: 1 First published:
in pregnancy Document Review History Version Review Date Reviewed By Approved By
 GYNAECOLOGY/ ANTENATAL CARE WIRRAL WOMEN & CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Guideline No: Hepatitis B management in pregnancy VERSION 1 AMENDMENTS MADE: N/A DATE OF ISSUE: May 2012 DATE OF REVIEW: May 2015 REVIEW INTERVAL:
GYNAECOLOGY/ ANTENATAL CARE WIRRAL WOMEN & CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Guideline No: Hepatitis B management in pregnancy VERSION 1 AMENDMENTS MADE: N/A DATE OF ISSUE: May 2012 DATE OF REVIEW: May 2015 REVIEW INTERVAL:
Current National Immunisation Schedule Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office.
 Current National Immunisation Schedule 2012 Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office Objectives To outline immunisation schedules in Ireland Primary childhood schedule Vaccine uptake rates School
Current National Immunisation Schedule 2012 Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office Objectives To outline immunisation schedules in Ireland Primary childhood schedule Vaccine uptake rates School
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers
 Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers April 2016 Health Protection Scotland is a division of NHS National Services Scotland.
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) an update for registered healthcare practitioners Questions and Answers April 2016 Health Protection Scotland is a division of NHS National Services Scotland.
Chapter 5 Serology Testing
 Chapter 5 Serology Testing 49 50 This page intentionally left blank. Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Diagnosis of HBV infection (acute vs. chronic) is based on clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic
Chapter 5 Serology Testing 49 50 This page intentionally left blank. Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Diagnosis of HBV infection (acute vs. chronic) is based on clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic
Summary of Key Points. WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017
 Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
3. Title Vaccination and immunisation data return collected through the COVER
 1. Record Type? 2. Unique Number Reassessment R00019 3. Title Vaccination and immunisation data return collected through the COVER 4. Collection Type National 5. Other Reference 6. Description Cover of
1. Record Type? 2. Unique Number Reassessment R00019 3. Title Vaccination and immunisation data return collected through the COVER 4. Collection Type National 5. Other Reference 6. Description Cover of
National Immunisation News
 July 2015 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office CONTENTS Changes to the Primary Childhood Immunisation Programme BCG Shortage Pertussis Vaccine Mumps Order Vaccines
July 2015 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office CONTENTS Changes to the Primary Childhood Immunisation Programme BCG Shortage Pertussis Vaccine Mumps Order Vaccines
Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
 Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Last reviewed: October 2014 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Last reviewed: October 2014 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy
 Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Issue Date: July 2012 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy Purpose
Document ID: MATY031 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Jo McMullan, CMM Issue Date: July 2012 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2016 Hepatitis B Positive: Care of Mother Policy Purpose
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
 TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
TEMPORARY PROGRAMME PERTUSSIS VACCINATION FOR PREGNANT WOMEN Richard Smithson Neil Irvine Maureen McCartney Consultant Health Protection October 2012 Pertussis/whooping cough The disease Whooping Cough
GENERAL PRACTITIONER DATA PACK GUIDANCE
 RESTRICTED For CQC internal use only This should NOT be shared outside CQC GENERAL PRACTITIONER DATA PACK GUIDANCE PRIMARY CARE DATA PACKS AND INSPECTION TEAM - November 2015 - Table of Contents Introduction...
RESTRICTED For CQC internal use only This should NOT be shared outside CQC GENERAL PRACTITIONER DATA PACK GUIDANCE PRIMARY CARE DATA PACKS AND INSPECTION TEAM - November 2015 - Table of Contents Introduction...
Annual Immunisation and Vaccine Preventable Diseases Report for Northern Ireland
 Annual Immunisation and Vaccine Preventable Diseases Report for Northern Ireland 2016-17 Acknowledgements The Public Health Agency immunisation team would like to thank everyone who works so hard across
Annual Immunisation and Vaccine Preventable Diseases Report for Northern Ireland 2016-17 Acknowledgements The Public Health Agency immunisation team would like to thank everyone who works so hard across
National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office
 February 2015 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office CONTENTS Changes to the PCI programme Uptake statistics Pneumovax name change Flu season Common queries School
February 2015 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office CONTENTS Changes to the PCI programme Uptake statistics Pneumovax name change Flu season Common queries School
MA PERINATAL HEPATITIS B PREVENTION PROGRAM
 MA PERINATAL HEPATITIS B PREVENTION PROGRAM Massachusetts Department of Public Health Immunization Program MIAP 2016 1 1 Presenter Disclosure Information I, Theodora Wohler, have been asked to disclose
MA PERINATAL HEPATITIS B PREVENTION PROGRAM Massachusetts Department of Public Health Immunization Program MIAP 2016 1 1 Presenter Disclosure Information I, Theodora Wohler, have been asked to disclose
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
Syrian Programme Refugees Advice on assessment of immunisation status and recommendations for additional immunisation
 Syrian Programme Refugees Advice on assessment of immunisation status and recommendations for additional immunisation Background Information Immunisation services in Syria Syria had good immunisation services,
Syrian Programme Refugees Advice on assessment of immunisation status and recommendations for additional immunisation Background Information Immunisation services in Syria Syria had good immunisation services,
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.9 DTaP/IPV and dtap/ipv pre-school booster immunisation programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.9 DTaP/IPV and dtap/ipv pre-school booster immunisation programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.9 DTaP/IPV and dtap/ipv pre-school booster immunisation programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
Data Flows for Direct Commissioning v1.54 Activity Reporting Programme Child Immunisations UNIFY Collections: Guidance
 Data Flows for Direct Commissioning (COVER) UNIFY Collections: Guidance v1.54 Activity Reporting Programme UNIFY Collections: Guidance Page 1 of 11 (COVER) UNIFY Collections: Guidance This document aims
Data Flows for Direct Commissioning (COVER) UNIFY Collections: Guidance v1.54 Activity Reporting Programme UNIFY Collections: Guidance Page 1 of 11 (COVER) UNIFY Collections: Guidance This document aims
EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
Whooping. pregnancy. Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby. the safest way to protect yourself and your baby
 Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby the safest way to protect yourself and your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who
Whooping cough and pregnancy Your questions answered on how to help protect your baby the safest way to protect yourself and your baby There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who
Hepatitis B (Hep-B) is one of the most
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 50 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Influence of Hepatitis B immunization to prevent vertical transmission of Hep-B virus in infants born from Hep-B positive mother Liza
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 50 November NUMBER 6 Original Article Influence of Hepatitis B immunization to prevent vertical transmission of Hep-B virus in infants born from Hep-B positive mother Liza
Immunisations for. young people. Your questions answered
 Immunisations for young people Your questions answered about the HPV, Td/IPV and MenACWY vaccinations given between 11 and 19 years of age (school years 7 to 13) the safest way to protect your health This
Immunisations for young people Your questions answered about the HPV, Td/IPV and MenACWY vaccinations given between 11 and 19 years of age (school years 7 to 13) the safest way to protect your health This
Hepatitis B protocol (CG487)
 Hepatitis B protocol (CG487) Approval and Authorisation Approved by Maternity Clinical Guidelines Committee Job Title or Chair of Committee Chair, Maternity Clinical Governance Committee Date 6 th April
Hepatitis B protocol (CG487) Approval and Authorisation Approved by Maternity Clinical Guidelines Committee Job Title or Chair of Committee Chair, Maternity Clinical Governance Committee Date 6 th April
Childhood immunisation
 Childhood immunisation Guidance notes for professionals 2011/12 edition the safest way to protect our children Consent Informed consent which can be either written or oral (depending on local Trust policy)
Childhood immunisation Guidance notes for professionals 2011/12 edition the safest way to protect our children Consent Informed consent which can be either written or oral (depending on local Trust policy)
Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention
 Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Purpose 2 The primary goal of the Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Program (PHBPP) is to identify all pregnant women who are infected with hepatitis b and prevent perinatal
Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Purpose 2 The primary goal of the Perinatal Hepatitis b Prevention Program (PHBPP) is to identify all pregnant women who are infected with hepatitis b and prevent perinatal
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women
 Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
Pertussis immunisation for pregnant women Introduction The routine childhood immunisation programme has been very effective in reducing the overall numbers of cases of pertussis. Before the introduction
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.5 Rotavirus immunisation programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.5 Rotavirus immunisation programme Classification: official 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.5 Rotavirus immunisation programme Classification: official 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification
March 2015: Issue 6. I would like to highlight some of the topics in this edition of Transmit where we have focused on Vaccine Preventable Diseases
 March 2015: Issue 6 Foreword I would like to highlight some of the topics in this edition of Transmit where we have focused on Vaccine Preventable Diseases The Duty Room Update has information about the
March 2015: Issue 6 Foreword I would like to highlight some of the topics in this edition of Transmit where we have focused on Vaccine Preventable Diseases The Duty Room Update has information about the
Seroprotection after Hepatitis B Vaccination among Newborn Infants: a Review
 Center for Global Health Seroprotection after Hepatitis B Vaccination among Newborn Infants: a Review Rania Tohme, MD, MPH Team Lead Global Immunization Division, US CDC Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board
Center for Global Health Seroprotection after Hepatitis B Vaccination among Newborn Infants: a Review Rania Tohme, MD, MPH Team Lead Global Immunization Division, US CDC Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy. Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011
 HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
Immunizations are among the most cost effective and widely used public health interventions.
 Focused Issue of This Month Recommended by the Korean Pediatric Society, 2008 Hoan Jong Lee, MD Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine E mail : hoanlee@snu.ac.kr J Korean
Focused Issue of This Month Recommended by the Korean Pediatric Society, 2008 Hoan Jong Lee, MD Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine E mail : hoanlee@snu.ac.kr J Korean
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.7 Hib/MenC vaccination programme NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.7 Hib/MenC vaccination programme NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information
Blood-Borne Viruses and Pregnancy. Prof Ashley Brown Imperial Healthcare NHS Trust
 Blood-Borne Viruses and Pregnancy Prof Ashley Brown Imperial Healthcare NHS Trust Hepatitis B and Pregnancy Global Prevalence of Chronic HBV Chronic HBV prevalence (% of population) Chronic HBV in the
Blood-Borne Viruses and Pregnancy Prof Ashley Brown Imperial Healthcare NHS Trust Hepatitis B and Pregnancy Global Prevalence of Chronic HBV Chronic HBV prevalence (% of population) Chronic HBV in the
CARE OF HEPATITIS B POSITIVE MOTHER
 CARE OF HEPATITIS B POSITIVE MOTHER SCOPE All medical and midwifery staff employed by Hutt Valley DHB. All Hutt Valley DHB Maternity access holders. All Special Care Baby Unit staff PURPOSE The purpose
CARE OF HEPATITIS B POSITIVE MOTHER SCOPE All medical and midwifery staff employed by Hutt Valley DHB. All Hutt Valley DHB Maternity access holders. All Special Care Baby Unit staff PURPOSE The purpose
National Immunisation News The Newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office
 December 2017 National Immunisation News The Newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office Contents Flu Vaccine Campaign 2017/2018 Flu vaccine campaign 2017/2018 Updated NIAC Guidelines for influenza
December 2017 National Immunisation News The Newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office Contents Flu Vaccine Campaign 2017/2018 Flu vaccine campaign 2017/2018 Updated NIAC Guidelines for influenza
UNSCHEDULED VACCINATION OF CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WHO HAVE OUTSTANDING ROUTINE IMMUNISATIONS. Service Specification
 UNSCHEDULED VACCINATION OF CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WHO HAVE OUTSTANDING ROUTINE IMMUNISATIONS Service Specification National Enhanced Service Specification For The Unscheduled Vaccination Of Children
UNSCHEDULED VACCINATION OF CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WHO HAVE OUTSTANDING ROUTINE IMMUNISATIONS Service Specification National Enhanced Service Specification For The Unscheduled Vaccination Of Children
The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues. Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office.
 The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office : Dates vaccines introduced into the Irish immunisation schedule Vaccine 1937-1999 Date introduced
The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office : Dates vaccines introduced into the Irish immunisation schedule Vaccine 1937-1999 Date introduced
Table of Contents. 1.0 INFANRIX hexa VACCINE...3
 Table of Contents 1.0 INFANRIX hexa VACCINE...3 1.1 What is INFANRIX hexa vaccine?...3 1.2 When will INFANRIX hexa be introduced?...3 1.3 What is the difference between INFANRIX hexa and Pediacel?...3
Table of Contents 1.0 INFANRIX hexa VACCINE...3 1.1 What is INFANRIX hexa vaccine?...3 1.2 When will INFANRIX hexa be introduced?...3 1.3 What is the difference between INFANRIX hexa and Pediacel?...3
OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program
 OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Dear Colleague, This letter is to introduce myself and explain the role I play with the Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis B Program. Alaska
OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Dear Colleague, This letter is to introduce myself and explain the role I play with the Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis B Program. Alaska
OVERVIEW OF THE NATIONAL CHILDHOOD IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN SINGAPORE
 OVERVIEW OF THE NATIONAL CHILDHOOD IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN SINGAPORE Dr Tiong Wei Wei, MD, MPH Senior Assistant Director Policy and Control Branch, Communicable Diseases Division Ministry of Health 9
OVERVIEW OF THE NATIONAL CHILDHOOD IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN SINGAPORE Dr Tiong Wei Wei, MD, MPH Senior Assistant Director Policy and Control Branch, Communicable Diseases Division Ministry of Health 9
VII THE CHILDHOOD IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN SINGAPORE 7. 7
 VII THE CHILDHOOD IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN SINGAPORE IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN 2002 7. 7 The childhood immunisation programme in Singapore offers vaccination against tuberculosis, hepatitis B, diphtheria,
VII THE CHILDHOOD IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN SINGAPORE IMMUNISATION PROGRAMME IN 2002 7. 7 The childhood immunisation programme in Singapore offers vaccination against tuberculosis, hepatitis B, diphtheria,
Acknowledgements. Introduction. Structure of the video
 Educators Guide Acknowledgements The Ministry of Health would like to thank Blue Bicycle Flicks. Thanks also to the staff and students from Evans Bay Intermediate School who contributed to the shooting
Educators Guide Acknowledgements The Ministry of Health would like to thank Blue Bicycle Flicks. Thanks also to the staff and students from Evans Bay Intermediate School who contributed to the shooting
Highland NHS Board 6 October 2015 Item 5.1 NEW VACCINATION PROGRAMMES
 Highland NHS Board 6 October 2015 Item 5.1 NEW VACCINATION PROGRAMMES Report by Abhayadevi Tissington, Nurse Consultant Health Protection and Ken Oates, Consultant in Public Health on behalf of Hugo Van
Highland NHS Board 6 October 2015 Item 5.1 NEW VACCINATION PROGRAMMES Report by Abhayadevi Tissington, Nurse Consultant Health Protection and Ken Oates, Consultant in Public Health on behalf of Hugo Van
National Immunisation News
 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office July 2016 Changes to the Primary Childhood Immunisation Programme The National Immunisation Advisory Committee (NIAC) has
National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office July 2016 Changes to the Primary Childhood Immunisation Programme The National Immunisation Advisory Committee (NIAC) has
Pregnant? There are many ways to help protect you and your baby. Immunise against: Flu (Influenza) Whooping cough (Pertussis) German measles (Rubella)
 Pregnant? There are many ways to help protect you and your baby Immunise against: Flu (Influenza) Whooping cough (Pertussis) German measles (Rubella) mmunisation This leaflet describes the vaccinations
Pregnant? There are many ways to help protect you and your baby Immunise against: Flu (Influenza) Whooping cough (Pertussis) German measles (Rubella) mmunisation This leaflet describes the vaccinations
Hepatitis B prevention in Malaysia
 Hepatitis B prevention in Malaysia Presented by Dr A aisah binti Senin Head of Vaccine Preventable Diseases & Food and Water Bourne Diseases Disease Control Division, Ministry of Health Malaysia 1990 1991
Hepatitis B prevention in Malaysia Presented by Dr A aisah binti Senin Head of Vaccine Preventable Diseases & Food and Water Bourne Diseases Disease Control Division, Ministry of Health Malaysia 1990 1991
abcdefghijklm abcde abc a `ÜáÉÑ=jÉÇáÅ~ä=lÑÑáÅÉê=aáêÉÅíçê~íÉ= HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B (HIB) VACCINE FOR YOUNG CHILDREN CATCH-UP PROGRAMME
 abcdefghijklm `ÜáÉÑ=jÉÇáÅ~ä=lÑÑáÅÉê=aáêÉÅíçê~íÉ= HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B (HIB) VACCINE FOR YOUNG CHILDREN CATCH-UP PROGRAMME This letter explains a Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccination
abcdefghijklm `ÜáÉÑ=jÉÇáÅ~ä=lÑÑáÅÉê=aáêÉÅíçê~íÉ= HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE TYPE B (HIB) VACCINE FOR YOUNG CHILDREN CATCH-UP PROGRAMME This letter explains a Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccination
Hepatitis B. Could I be at risk?
 Hepatitis B Could I be at risk? Contents Page no What is hepatitis B? 2 How could I get hepatitis B? 3 How do I know if I have the virus? 5 What if the test result is negative? 5 What if the test result
Hepatitis B Could I be at risk? Contents Page no What is hepatitis B? 2 How could I get hepatitis B? 3 How do I know if I have the virus? 5 What if the test result is negative? 5 What if the test result
3 rd dose. 3 rd or 4 th dose, see footnote 5. see footnote 13. for certain high-risk groups
 Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
Immunisation Update for Occupational Health
 Immunisation Update for Occupational Health Dr Gayatri Amirthalingam Immunisation, Hepatitis & Blood Safety department Public Health England 29 th April 2016 Session Outline Epidemiology of vaccine preventable
Immunisation Update for Occupational Health Dr Gayatri Amirthalingam Immunisation, Hepatitis & Blood Safety department Public Health England 29 th April 2016 Session Outline Epidemiology of vaccine preventable
Communicable Disease Update; Vol. 16 (1), February 2017
 Communicable Disease Update; Vol. 16 (1), February 017 Item Type Other Authors Health Service Executive (HSE) South (South East), Department of Public Health Publisher Health Service Executive (HSE) South
Communicable Disease Update; Vol. 16 (1), February 017 Item Type Other Authors Health Service Executive (HSE) South (South East), Department of Public Health Publisher Health Service Executive (HSE) South
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases
 PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Viruses in July (ViJ), 2004 Overview Epidemiology Perinatal transmission
PERINATAL HEPATIDES AND HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS (HIV) Pamela Palasanthiran Staff Specialist, Paediatric Infectious Diseases Viruses in July (ViJ), 2004 Overview Epidemiology Perinatal transmission
APEC Guidelines Immunizations
 Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Questions & Answers 1 November 2005 Vaccine Schedule
 Questions & Answers 1 November 2005 Vaccine Schedule General Questions Q. When can clinics order the new vaccine? A. From early October 2005. Orders will be placed on back order & stock will be sent out
Questions & Answers 1 November 2005 Vaccine Schedule General Questions Q. When can clinics order the new vaccine? A. From early October 2005. Orders will be placed on back order & stock will be sent out
Report to Health and Well- Being Board on Childhood Immunisation Programmes in Barnet 14 th September 2017/18
 Report to Health and Well- Being Board on Childhood Immunisation Programmes in Barnet 14 th September 2017/18 Report on Section 7a Immunisation Programmes in London Borough of Barnet Prepared by: Amanda
Report to Health and Well- Being Board on Childhood Immunisation Programmes in Barnet 14 th September 2017/18 Report on Section 7a Immunisation Programmes in London Borough of Barnet Prepared by: Amanda
Whooping cough. If you are pregnant you should get vaccinated to protect your baby
 Whooping cough If you are pregnant you should get vaccinated to protect your baby Cases of whooping cough are on the increase by getting the vaccine while pregnant you can protect your baby There were
Whooping cough If you are pregnant you should get vaccinated to protect your baby Cases of whooping cough are on the increase by getting the vaccine while pregnant you can protect your baby There were
Vaccines Work Version
 Vaccines Work 2018 Version European Immunisation Week (EIW) is celebrated across the European Region every April to raise awareness of the importance of immunisation for people s health and well-being.
Vaccines Work 2018 Version European Immunisation Week (EIW) is celebrated across the European Region every April to raise awareness of the importance of immunisation for people s health and well-being.
Acknowledgment. Natural history of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Background on hepatitis B
 : How to prevent perinatal HBV transmission Immunization Action Coalition (IAC) Acknowledgment Trudy V. Murphy, MD, (retired), formerly Team Lead, Vaccine Research and Policy, Division of Viral Hepatitis,
: How to prevent perinatal HBV transmission Immunization Action Coalition (IAC) Acknowledgment Trudy V. Murphy, MD, (retired), formerly Team Lead, Vaccine Research and Policy, Division of Viral Hepatitis,
Release Notes. Medtech Evolution General Practice. Version Build (June 2016)
 Release Notes Medtech Evolution General Practice Version 1.5.7 Build 1.5.7.72 (June 2016) These release notes contain important information for Medtech Evolution users. Please ensure that they are circulated
Release Notes Medtech Evolution General Practice Version 1.5.7 Build 1.5.7.72 (June 2016) These release notes contain important information for Medtech Evolution users. Please ensure that they are circulated
Decision to amend access criteria for some vaccines
 3 July 2015 Decision to amend access criteria for some vaccines PHARMAC is pleased to announce the following changes to the funding access criteria for a number of vaccines. The changes in criteria follow
3 July 2015 Decision to amend access criteria for some vaccines PHARMAC is pleased to announce the following changes to the funding access criteria for a number of vaccines. The changes in criteria follow
Changes to the Meningococcal C conjugate (MenC) vaccine schedule. Questions and Answers
 Changes to the Meningococcal C conjugate (MenC) vaccine schedule Questions and Answers Background The meningococcal C (MenC) vaccination programme was first introduced into the UK routine immunisation
Changes to the Meningococcal C conjugate (MenC) vaccine schedule Questions and Answers Background The meningococcal C (MenC) vaccination programme was first introduced into the UK routine immunisation
National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office
 February 2014 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office CONTENTS Adverse Local Reactions following 4 in 1 booster 2013 Immunisation Guidelines for Ireland Flu Season
February 2014 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office CONTENTS Adverse Local Reactions following 4 in 1 booster 2013 Immunisation Guidelines for Ireland Flu Season
BCG vaccine and tuberculosis
 PART 2: Vaccination for special risk groups 2.1 Vaccination for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people historically had a very high burden of infectious
PART 2: Vaccination for special risk groups 2.1 Vaccination for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people historically had a very high burden of infectious
The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues. Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office.
 The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office Objectives To outline immunisation schedules in Ireland Primary childhood schedule Vaccine uptake
The National Immunisation Schedule Update and Current issues Dr Brenda Corcoran National Immunisation Office Objectives To outline immunisation schedules in Ireland Primary childhood schedule Vaccine uptake
In February 2015, the Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation (JCVI) *
 Background In 2015, Public Health England (PHE) reported a continued increase in meningococcal serogroup W cases in England. The rise was initially recorded in 2009 and since this time, cases have steadily
Background In 2015, Public Health England (PHE) reported a continued increase in meningococcal serogroup W cases in England. The rise was initially recorded in 2009 and since this time, cases have steadily
NHS GRAMPIAN IMMUNISATION PROGRAMMES ANNUAL REPORT 2010/11
 NHS GRAMPIAN IMMUNISATION PROGRAMMES ANNUAL REPORT 2010/11 NHS GRAMPIAN IMMUNISATION STEERING GROUP March 2012 1 Table of Content 1. Purpose of this report.3 2. Uptake of immunisation: key points during
NHS GRAMPIAN IMMUNISATION PROGRAMMES ANNUAL REPORT 2010/11 NHS GRAMPIAN IMMUNISATION STEERING GROUP March 2012 1 Table of Content 1. Purpose of this report.3 2. Uptake of immunisation: key points during
WHO Recommendations and Guidelines for the Prevention of Perinatal Hepatitis B and Use of Hepatitis B Vaccines
 WHO Recommendations and Guidelines for the Prevention of Perinatal Hepatitis B and Use of Hepatitis B Vaccines Steven Wiersma,, Medical Officer WHO/EPI EPI,, Geneva March, 2006 Epidemiology Strategy WHO
WHO Recommendations and Guidelines for the Prevention of Perinatal Hepatitis B and Use of Hepatitis B Vaccines Steven Wiersma,, Medical Officer WHO/EPI EPI,, Geneva March, 2006 Epidemiology Strategy WHO
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus (HPV) programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus (HPV) programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus (HPV) programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus
Enhanced immunisation schedule Victoria
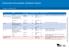 Children from March 2016 Age Disease Vaccine brand Birth Hepatitis B H-B-Vax-II Paediatric 2 months - from 6 weeks Diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis, poliomyelitis-hepatitis B- Reconstitute Site given Route
Children from March 2016 Age Disease Vaccine brand Birth Hepatitis B H-B-Vax-II Paediatric 2 months - from 6 weeks Diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis, poliomyelitis-hepatitis B- Reconstitute Site given Route
CHILDHOOD VACCINATION
 EPI (3) Age of Child How and Where is it given? CHILDHOOD VACCINATION Nicolette du Plessis Block 10 28/02/2012 10 weeks DTaP-IPV/Hib (2) Diphtheria, Tetanus, Acellular pertussis, Inactivated polio vaccine,
EPI (3) Age of Child How and Where is it given? CHILDHOOD VACCINATION Nicolette du Plessis Block 10 28/02/2012 10 weeks DTaP-IPV/Hib (2) Diphtheria, Tetanus, Acellular pertussis, Inactivated polio vaccine,
Whooping cough. help protect your baby. Don t take the risk act now to protect your baby from whooping cough from birth
 Whooping cough help protect your baby 2014 Don t take the risk act now to protect your baby from whooping cough from birth There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who are too young
Whooping cough help protect your baby 2014 Don t take the risk act now to protect your baby from whooping cough from birth There is a lot of whooping cough around at the moment and babies who are too young
VACCINATION AND IMMUNISATION PROGRAMMES 2016/17
 VACCINATION AND IMMUNISATION PROGRAMMES 2016/17 GUIDANCE AND AUDIT REQUIREMENTS Publication Gateway Reference Number 05245 Contents Section 1 Introduction 4 Introduction 4 Working with patient data 4 Verification
VACCINATION AND IMMUNISATION PROGRAMMES 2016/17 GUIDANCE AND AUDIT REQUIREMENTS Publication Gateway Reference Number 05245 Contents Section 1 Introduction 4 Introduction 4 Working with patient data 4 Verification
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C
 Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C January 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to:- Demonstrate an increased knowledge and
Prevention of and Immunisation against Hepatitis B and C January 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to:- Demonstrate an increased knowledge and
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.6 Meningococcal C (MenC) containing vaccine immunisation programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.6 Meningococcal C (MenC) containing vaccine immunisation programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.6 Meningococcal C (MenC) containing vaccine immunisation programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
GOVERNING BOARD. Date of Meeting 15 May 2013 Agenda Item No 13. Title Immunisation and Vaccination Report 2012/13
 GOVERNING BOARD Date of Meeting 15 May 2013 Agenda Item No 13 Title Immunisation and Vaccination Report 2012/13 Purpose of Paper To update the CCG on the performance and quality of vaccination programmes
GOVERNING BOARD Date of Meeting 15 May 2013 Agenda Item No 13 Title Immunisation and Vaccination Report 2012/13 Purpose of Paper To update the CCG on the performance and quality of vaccination programmes
The Use of Combination Vaccines in the United States
 The Use of Combination Vaccines in the United States John W Ward, MD Senior Scientist, CDC Director, Program for Viral Hepatitis Elimination Task Force for Global Health Revised 2018 Combination Vaccine
The Use of Combination Vaccines in the United States John W Ward, MD Senior Scientist, CDC Director, Program for Viral Hepatitis Elimination Task Force for Global Health Revised 2018 Combination Vaccine
IMMUNISATION OF CHILDREN DURING and AFTER CANCER THERAPY
 NATIONAL GUIDELINES PAEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY AND HAEMATOLOGY For the Care of Childhood Cancer in Specialist Child Cancer and Shared Care Centres. IMMUNISATION OF CHILDREN DURING and AFTER CANCER THERAPY Date
NATIONAL GUIDELINES PAEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY AND HAEMATOLOGY For the Care of Childhood Cancer in Specialist Child Cancer and Shared Care Centres. IMMUNISATION OF CHILDREN DURING and AFTER CANCER THERAPY Date
