MARSH BULLETIN. Pollen Morphological Study of the Dicots Wetland Plants of Southern Marshes of Iraq
|
|
|
- Clara Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Marsh Bulletin 7(2)(2012) MARSH BULLETIN Amaricf_Basra Pollen Morphological Study of the Dicots Wetland Plants of Southern Marshes of Iraq S.A. A. Al-Saadi and A.R.A. Al- Mayah Department of Biology, College of Science, University of Basra. Iraq Abstract Palynological features of the pollen grains of Dicots wetland plants of the Southern Marshlands of Iraq were studied. Forty nine species belong to twenty five families were investigated.the results showed that there were significant difference and high diversity in shape, size, ornamentation and apertures of the pollen grains of most genera and species studied. Most families and genera have their own characteristic pollen types. On the basis of ornamentation and apertural types, nineteen distinct pollen types were recognized. Pantoporate pollen grains were showed in several families such as Chenopodiaceae and Amaranthaceae. Most species contain three colpi as in Bacopa monniera, while Myriophyllum spicatum contains 4-5 clopi, but many species contained colp and pore as in most of Dicots species as in Compositae. Ornamentations were varied from psilate in the Utricularia australis to echinate in some species of Compositae. 1- Introduction Pollen morphology of sixteen species of aquatic angiosperms distributed in 14 families from Karachi has been studied by Perveen (1999). He showed that pollen grains were free, rarely united, mostly radically symmetrical, isopolar or apolar, occasionally heteropolar; simple aperture (porate or colpate), tectum was variable from reticulate to rugulate, striate, echinate, scabrate and areolate. Perveen (2000) provided pollen morphology of 353 species from Karachi, belonging to 67 families of angiosperms, distributed in 58 dicots and 9 monocots. The 15 species of genus Lycopus examined by Moon and Hong ( 2003)
2 170 showed that the pollen grains were hexacolpate, medium or small in size, the shape was oblate to prolate. Aftab and Perveen (2006) examined pollen morphology of 25 species belonging to 23 genera distributed in 13 families by light microscopy and scanning electron microscope. They showed that pollen grains occurred singly and rarely in polyads, 3-colporate in family Apocynaceae, however, the family Malvaceae had pantoporate pollen grains, tectum reticulate or regulate in addition to its scabrate and echinate. Alwadie (2008) studied pollen morphology of six aquatic angiosperms from Saudi Arabia, and showed several types; non-apertures pollen grains as in Elodea canadensis, Potamogeton crispus, P. pectinatus and Ruppia maritima, porate pollen as in Lemna gibba, and colpate pollen grains as in Myriophyllum spicatum. Few species of family Malvaceae have been studied by 2-Materials and methods Pollen samples were collected from plants of different locations in southern wetland of Iraq. Six stations in the marshes, namely Um Al-Naaj and Um Al-warid in Hewaiza marsh, Abo-Sobat and Abo Cholan in Chabaish marsh, and Burga and Nagara in east Hammar marsh, In addition to Shatt-Al-Arab, were chosen for sampling. The pollen samples were procured from closed mature anthers. The materials were suspended in glacial acetic acid, centrifuged and acetolysed (Erdtman, 1952). The acetolysis fluid was poured off and the sediments washed in distilled water (3 times) by shaking the tubes, centrifuged and decanted. Then pollen grains were mounted in Safranine stained glycerin jelly, and micro morphological observations were made with light microscope (Model: Leitz, Japan). Microphotographs were taken by using digital camera (Model: DC 2000) and measurements were made using an ocular Bibi et al. (2010) they showed that Malva parviflora is pantoporate, monocolpate, spherical to subspherical in polar view while it is reniform in equatorial view. There are no previous studies on pollen morphology of wetland and aquatic plants from Southern Iraq. The present study aims micrometer in the light- microscope, the measurements were based on readings from each specimen. Polar axis (P), equatorial diameter (E), colpi length, spine length and exine thickness were measured. The terminology used for the description is in accordance with Erdtman (1952), Faegri to study the pollen morphology of the species of wetland angiosperms in Southern Iraq and their major evolutionary trends. and Iversen (1964) and Moore and Webb (1978).
3 171 3-Results Wetland angiosperms exhibited great diversity in their pollen characters, such as shape, size, apertures, polarity and tectum type, but the exine pattern and aperture types are the most significant pollen characters. From the family Amaranthaceae, three species Alternanthera sessilis, Amaranthus 1.16 (plate1, table 1). Within Caryophyllaceae, one species Spergularia diandra was studied, pollen grains 3-5 colpate, psilate, isopolar, subprolate(plate 1,table 1). In Ceratophyllaceae, one species Ceratophyllum demersum was studied, pollen grains monoaperturate, diameter 25- graecizans and Amaranthus viridis were examined. Pollen grain was apolar and spheroidal. It was polypantoporate in the genus Amaranthus and12-forate in Alternanthera sessilis, all pollen grains were small in size, with spinulose tectum. Mean of largest pollen grains was recorded in Amaranthus graecizans μm and the smallest was in Alternanthera sessilis μm (plate1, table 1). In Apocynaceae one species Trachomitum venetum was studied, pollen grains were aggregate in tetrad, diameter μm, tetrahedral in shape, 4-6 pore in all pollen grains, subprolate in equatorial 47.5 μm, spheroidal, medium in size (plate 1, table 1). From the family Chenopodiaceae, six species were studied. Pollen grains were apolar, pantoporate, and spheroidal. Number of pores was variable among species, it was 30 pores in Salsola baryosma, pores in Chenopodium murale and Suaeda aegyptiaca, in Suaeda vermiculata and in Salicornia herbacea(plate 1,table 1). From the family Compositae, eight species were examined (plate 2, table 2). Those species were characterized by tricolporate type. Shape of pollen grain was prolate spheroidal in Eclipta alba and view, tectum reticulate(plate 1, table 1). In Asclepiadaceae one species Cynancum acutum was examined, pollen shed in aggregates, in the form of pollinia, with reticulate tectum (plate 1, table1). Capparaceae showed that Capparis spinosa with pollen grains tricolporate, isopolar, sub- Silybum marianum,oblate spheroidal in the rest species, the smallest pollen grain in Eclipta alba was μm, the largest in Silybum marianum was μm, tectum varies between the species, it was reticulate in Senecio vernalis, punctuate in Centaurea solstitialis and prolate, tectum generally spinulose, polar axis (18) 22.45(23.65) µm, and equatorial diameter (17) (24.2) µm. P/E ratio: spinules in the rest species. In Convolvulaceae, the species Cressa cretica was examined, pollen grains were
4 172 isopolar, tricolpate, shape of pollen in polar view was circular to semi-circular and in equatorial view was prolate spheroidal, with punctate tectum. Pollen morphology of two species of family Cruciferae (Brassicaceae) Cardaria draba(cardaria draba var. draba and Cardaria draba var. chalepensis) and Sinapis arvensis were examined. Pollen type is 3-colpate, it was prolate spheroidal in Cardaria draba, subprolate in Sinapis arvensis, exine thicker than nexine. Pollen grain size varies from medium to small size in Cardaria draba, medium size in Sinapis arvensis (plate 2, table 1). Myriophyllum spicatum (Haloragaceae ) pollen grains were isopolar, oblate spheroidal, 4-5-zonocolpate, elliptic, size: polar axis, 25.5(26) 30 μm, and equatorial diameter (25) 27.5 (32.5) μm, the mean of exine 0.85 μm thick, sexine thicker than nexine. Tectum was punctate (plate 3, table 3).One species of family Labiatae (Lycopus europaeus) was examined. Pollen grains mean of polar diameter was μm in A. graecorum and smallest 19 um in T. resupinatum, the largest mean of equatorial diameter was 24.5 μm in T. resupinatum and smallest, μm in A. graecorum (plate 3, table 3). Utricularia australis (Lentibularaceae) pollen grains were medium sized they were 25(26.50)27.5 μm in polar view and 30(32.75)35 μm in equatorial view, polycolporoidate, isopolar, the shape of the grains was suboblate, ornamentation was psilate (plate3, table 3). Pollen of Malva parviflora from family Malvaceae was polypantoporate echinate, spherical in shape with pollen diameter 95(98.33)105 μm. Pores are small with pore diameter of about 1(1.50)1.75 μm, circular in shape and located usually at the base of spine. Exine thickness was about 8(12.5)13 μm, tectum echinate. Spine number 25 (40)54, vary in size, larger one with spine height of μm (plate 4, table 3). were isopolar, (hexacolpate) 6-colpate, oblate spheroidal, medium in size, tectum reticulate (plate 3, table 3). Pollen morphology of the Leguminosae was examined for two species, Alhagi graecorum and Trifolium resupinatum, pollen grains were generally Menyanthaceae: tow species Nymphoides indica and N. peltata were studied. Pollen grains heteropolar, subprolate and suboblate in Nymphoides indica and N. peltata respectively, tricolpate, sexine thicker than nexine. Tectum spinulose in N. indica and reticulate in N. peltata(plate 4, isopolar, 3-colporate, the shape of pollen grain was prolate in A. graecorum and suboblate in T. resupinatum, sexine thicker than nexine, tectum baculate. The largest table 3). Nymphaceae: Nymphaea alba pollen grains monosculate, bilateral, heteropolar, boat-shaped, size in polar view (32.5) (37.5) μm and equatorial view
5 173 (25)26.87 (30) μm, tectum was wart (plate 4 table 3). Pollen grains in Ludwigia repens (Onagraceae) were isopolar, tricolporate, oblate spheroidal and wart tectum.mean of polar view was μm and μm in equatorial view, ratio of P/E was 0.89 (plate 4, table 3). Three species Polygonum monniera) were isopolar, oblate spheroidal, tricolpate, medium in size, reticulate tectum, the mean of polar view μm and μm in equatorial view (plate 5, table 3). Solanum nigrum (Solanaceae) pollen grain was isopolar, oblate spheroidal, tricolporate and psilate (plate 6, table 3). From the family Tamaricaceae five species aviculare, Persicaria salicifolia and Rumex dentatus from Polygonaceae family were examined, they had three types of pollen grains; they were tricolporate, pantopolyporate and tetracolporate respectively. Pollen morphology was more specialized in ornamentation; tectum was reticulate in Persicaria salicifolia and Rumex dentatus and punctate in Polygonum aviculare (plate 5, table 3). Pollen grain of Samolus valerandi from Primulaceae is 3- colporoidate, subprolate, small in size μm, tectum reticulate (plate 5, table3). Rannunculus sphaerospermus from the family Ranunculaceae was characterized by were examined. These species were characterized by tricolpate,small size with reticulate tectum. Shape of pollen grain was suboblate in T.arceuthoides, oblate spheroidal in T.aralensis and T.brachystachys, while prolate spheroidal in T. aphylla and T.ramosissima. The smallest pollen grain in equatorial view was in T. ramosissima x15 μm, and the largest was in T.brachystachys 18.14x μm (plate 6, table 4). In Verbenaceae, Phyla nodiflora pollen grains were tricolporate, isopolar, suboblate, size in polar view was (20) (27.5) μm and in equatorial view was (27.5)29 (32.5) tricolpate, isopolar grains; with punctuate tectum (plate 5, table 3). While Scruphularaceae pollen grains (Bacopa μm, tectum was reticulate (plate 6, table 3).
6 174 Table (1) Some pollen morphological characters of dicotyledons species.
7 Table (2) Some pollen morphological characters of Compositae species. 175
8 176 Table (3) Some pollen morphological characters of dicotyledons species.
9 177 Table (4) Some pollen morphological characters of Tamarix species. Table (5) types of pollen grains Type Monosulcate wart monoaperturate (porate) psilate tricolpate reticulate tricolpate spinuliferous tricolpate psilate tricolpate punctate hexacolpate reticulate tricolporate spinuliferous tricolporate punctate Tricolporate reticulate tricolporate warted tetracolporate reticulate tricolporate psilate polypantoporate reticulate pantoporate spinuleferous pantoporate scabrate polypantoporate spinuleferous polycolporoidate psilate tetracolpate punctate Taxa Nymphaea alba (Nymphaceae) Ceratophyllum demersum species in family Tamarixaceae, Cardaria draba and Sinapis arvensis (Cruciferae), Nymphoides peltata (Menyanthaceae), Bacopa monniera and Samalus valerandis Nymphoidesindica Spergularia diandra (Caryophyllaceae) Trifolium resupinatum. Alhagi graecorum, Cressa cretica and Ranunculus sphaerospermus Lycopus europaeus, Compositae, and Capparis spinosa Centurea and Polygonum aviculare Phylla nodiflorae and Sencio vernalis Ludwgia repans Rumex dentatus Solanum nigrum. Persicaria salicifolia. Amaranthaceae and Chenopodiaceae. Suaeda Malva parviflora, Utricularia australis Myriophyllum spicatum.
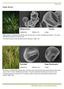
10 178 Plate(1 )Pollen grains A- Alternanthera sissilis(12 porate) B- Amaramnthus graecizans (pantoporate) C- Cynanchum acutum D- Trachomitum venetum E-Capparis spinosa(3-colporate, polar view) F- Capparis spinos (Equatorial view) GSpergularia diandra(3-colpate) H- Spergularia diandra (4-colpate) I-Spergularia diandra (5colpate) J-Ceratophyllum demersum (monoaperturate) K- Halocnemum strobilaceum (pantoporate) L- Suaeda vermiculata M- Salsola baryosma N- Salicornia herbacea (scale bar = 10 μm)
11 179 Plate(2 )Pollen grains A-B,D (3-colporate, polar view) A- Aster tripolium B- Eclipta alba C Centaurea solstitialis (equatorial view) D- Centaurea solstitialis (3-colporate, polar view) E - Senecio desfontainei (equatorial view) F- Senecio vernalis (polar view) G- Silybum marianum (polar view) H- Sonchus maritimus I- Pluchea tomentosa (polar view) J- Cressa cretica(3-colpate, polar view) K- Sinapis arvensis (3- colpate, polar view ) L- Sinapis arvensis(reticulate tectum) (scale bar = 10 μm)
12 180 Plate(3)Pollen grains A- Myriophyllum spicatum(5-colpate) B- Myriophyllum spicatum(4colpate) C Myriophyllum spicatum (equatorial view) D-E-Lycopus europaeus ( 6colpate) F- Lycopus europaeus (reticulate tectum) G- Trifolium resupinatum (equatorial view) H- Trifolium resupinatum (polar view) I- Alhagi graecorum(polar and equatorial view) J-L- Utricularia australis (polycolporoidate) (scale bar = 10 μm).
13 181 Plate (4) Pollen grains A-C- Malva parviflora (polypantoporate) D-E- Nymphoides indica, 3colpate (D-polar view E- equatorial view) F- G-Nymphoides peltata (3-colpate, F-polar view, G- equatorial view) H-I-Nymphaea alba (monosulcate) J-Ludwigia repens (equatorial view) K- Ludwigia repens( tricolporate,polar view) (scale bar = 10 μm).
14 182 Plate (5) Pollen grains A-B- polygonum aviculare, 3-colporate (A-polar view B- equatorial view) C Persicaria salcifolia (pantopolyporate) D- Rumex dentatus (tetracolporate :polar view) E-L- 3-colpate, E- Samolus valerandi(polar view) F- Samolus valerandi (equatorial view) G-I- Ranunculus sphaerospermu (G- polar view H- equatorial view I- ornamentation) J-L- Bacopa manniera(j- polar view K- equatorial view L- ornamentation ) (scale bar = 10 μm).
15 183 Plate (6) Pollen grains A-B- Solanum nigrum,3-colporate (A- equatorial view B- polar view) C E- Tamarix aralensis (C- 3-colpate, polar view D- equatorial view E- reticulate ornamentation) F-H- Tamarix brachystachys (F- polar view G- equatorial view) H- reticulate sculpture) I-K- Phyla nodiflora (3-colporate) (scale bar = 10 μm).
16 184 4-Discussion Pollen grains are usually free, rarely united or tetrad, the shapes of pollen grains were sub-prolate in Nymphaea and Nymphoides, and oblate or oblate spheroidal in Myriophyllum spicatum and Ranunculus spherospermus. Plants of wetlands showed clear differences in apertural types. On the basis of ornamentation and apertural types, nineteen distinct pollen types were recognized (table 5), type I : is monosulcate wart, this type includes Nymphaea alba (Nymphaceae).The pollen morphology of Nymphaeaceae was extremely distinct from the rest of the dicotyledonous families by the presence of monosulcate, heteropolar, bilateral symmetric grains, the shape subprolate (boat-shaped), and tectum warts (plate 4, table 3), these results agree with (Perveen,2000). Whereas (Erdtman, 1952) and Walker (1972) reported 2 3 sulcate grains in the Nymphaea genus. The presence Ceratophyllum demersum represents this of the most primitive types of pollen grain boat shaped, monosulcate grains clearly indicates the primitive nature of order Nymphaeales (Magnoliidae) (Takhtajan, 1969; Sporne, 1972; Doyle et al. 1975). These primitive types of pollen were restricted to the subclass Magnoliidae and monocots. Pollen type 2: is characterized resupinatum and Alhagi graecorum (Leguminosae), Cressa cretica (Convolvulaceae) and Ranunculus sphaerospermus (Ranunculaceae). Many authors mentioned that Ranunculaceae have a more advanced type than monocolpate and nonaperturate pollen grains, as well as having three characteristics colpi, isopolar and three apertures. Perveen (2000) said that Ranunculidae are considered the first tricolpate derived subclass, a basic type by its monoaperturate (porate) psilate pollen. Only a single species, type. Pollen type 3: is readily delimited by having tricolpate reticulate; ten species were included in this pollen type, species in family Tamarixaceae, Cardaria draba and Sinapis arvensis (Cruciferae), Nymphoides peltata (Menyanthaceae), Bacopa monniera (Scrophulariaceae) and Samalus valerandi (Primulaceae). Pollen type 4: was readily delimited by having tricolpate spinuliferous, one species was included in this pollen type Nymphoides indica. While Pollen type 5: was easily recognized by having tricolpate psilate, including Spergularia diandra (Caryophyllaceae). Van Campo (1976) reported that an evolutionary trend from colpate to polycolpate was clearly seen in the genus Spergularia of Caryophyllaceae in which tri- pantocolpate pollen grains were found. Pollen type 6: is characterized by its tricolpate punctate and includes Trifolium
17 185 from which other types have been derived (Walker, 1972, Walker and Doyle, 1975). In many taxa of Ranunculaceae pollen grain were same as of Centrospermous families like, Amaranthaceae, Caryophyllaceae and Chenopodiaceae (Nowicke & Skvarla 1979). However our study showed different pollen types. vernalis (Compositae) and Phyla nodiflora (Verbenaceae). Pollen type 11: is easily delimited by its tricolporate warted in Ludwigia repens, while pollen type 12: is characterized by its tetracolporate reticulate included one species Rumex dentatus. Pollen type 13: is characterized by its tricolporate psilate, one species including Solanum Pollen type 7: is easily recognized by having hexacolpate reticulate, it includes one species Lycopus europaeus, this results agree with Moon and Hong (2003). Pollen type 8: is characterized by its tricolporate spinuliferous in some genera of Compositae, and genus Capparis. Two families Brassicaceae and Capparaceae placed in order Tamaricales, they have tricolpate pollen grains, therefore, the separation order Tiliales proposed by Hutchinson (1948) seems to be justified on palynological results. Takhtajan (1969) and Cronquist (1968) reported that Asteridae (including Asteraceae and Scrophulariaceae) was most advanced subclass; the data of pollen morphology also supports this idea. In Asteraceae pollen grains was tricolporate, with echinate tectum, in Scrophulariaceae usually tricolporate grains were also found. Pollen type 9: is characterized by its tricolporate punctate in Centaurea and Polygonum aviculare. Pollen type 10: is recognized by having tricolporate reticulate, two species including in this type Senecio nigrum. Type 14: is characterized by its polypantoporate reticulate in Persicaria salicifolia. Polygonaceae were more specialized by having tricolporate and pantoporate pollen grains, in addition to simple (porate, colpate) grains, the tectum also varied from reticulate to punctate types. Our data agree with ( Perveen, 2000), in spite of the Polygonaceae is a eurypalynous family, but palynological data do not agree with Takhtajan (1969) who suggested that the Polygonaceae is probably derived from the same stock as the Caryophyllales Pollen type 15: is characterized by its pantoporate spinuleferous Amaranthaceae and Chenopodiaceae. Pollen type 16: is characterized by its pantoporate scabrate in Suaeda. In Chenopodiaceae and Amaranthaceae most taxa have pantoporate grains, number of pores 22 50, both often have spinulose tectum. Amaranthaceae and Chenopodiaceae have long been considered closely related families by having small inflorescence, reductive flower, 2 3 carpelled, unilocular ovary and also show
18 186 some distinct pollen morphological characters by having many apertures (pantoporate) (Preveen, 2000). Pollen type 17: is characterized by its polypantoporate spinuleferous in Malva parviflora, the present study showed that the family Malvaceae is more advanced than the other families above, because of having echinate and polypantoporate pollen grains which agree with (Preveen, 2000). Pollen type 18: is characterized by its polycolporoidate psilate in Utricularia australis. While Pollen type 19: is characterized by its tetracolpate punctate in Myriophyllum spicatum. From the pollen types mentioned above,it is clear that the pollen morphology can help in some cases, to solve systematic problems such as the cases in polygonaceae, where the pantoporate pollen type support separation of Polygonum persicaria from Polygonum( a colporate type) to a distinct genus Persecaria. The same cases showed in the polyporate and the 2nd gives rise to tricolpate then tricolporate and polycolporate. genus Spergularia in Caryophyllaceae. In other cases pollen grain features may be of very little taxonomic importance such as the case in the pollen types of Tamaricaceae and Cruciferae which are often tricolpate reticulate. The evolutionary trends in the pollen grains of the aquatic and wetland plants of Southern Iraq may be suggested as follow: Monosulcate may gives rise to two branches the 1st gives rise to monoporate then to Massachusettes. Faegri, K. and Iversen, J. (1964). Textbook of pollen analysis. Copenhagen: 295 pp. Hutchinson J. (1948). British flowering plants. 374pp. London. Moon, H.K. and Hong, S.P. (2003).Pollen morphology of the genus Lycopus (Lamiaceae). Ann. Bot. Fennici. 40: References Alwadie,H.M. (2008). Pollen morphology of six aquatic angiosperms from Saudi Arabia. Asian Journal of Biological Sciences, 1: Bibi, N.; Akhtar, N.; Hussain, M. and Khan, M. A. (2010). Systematic Implications of pollen morphology in the family Malvaceae from north west frontier province, Pakistan.. Pak. J. Bot., 42(4): Doyle J.A., Van Campo M, Lugardom B. (1975). Observations on exine structure of Eucommiidites and lower Cretaceous angiosperm pollen. Pollen et Spores 17: Erdtman, G. (1952). Pollen morphology and plant taxonomy. Angiosperms. Chronica Botanica Co., Waltham,
19 187 Moore P.D. and Webb J.A. (1978). An Illustrated Guide to Pollen Analysis. Hodder and Stoughton, London. Nowicke, J.W. and Skvarla,J.J. (1979). Pollen morphology: The potential influence in higher order systematics. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard., 66: Perveen, A. (1999). A palynological survey Dicotyledons. New Phytol. 71: Takhtajan A. (1969). Flowering Plants (Originand dispersal). Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh. Van Campo M. (1976). Patterns of pollen morphological variation within taxa. In: Ferguson I.K. and Müller, J. (eds.). of aquatic Flora of Karachi-Pakistan. Tr. J. of Botany. 23: Perveen, A. (2000). Pollen characters and their evolutionary significance with special reference to the flora of Karachi. Turk J. Biol. 24: Perveen, A. (2006). A contribution to the pollen morphology of family Gramineae. World applied sciences journal. 1 (2): Sporne, K.R. (1972). Some Observations on the evolution of pollen types in The Evolutionary Significance of the Exine. Academic Press, London. Walker J.W. (1972). Aperture evolution in the pollen of primitive angiosperms. American Journal of Botany 61: Walker, J.W. and J.A. Doyle. (1975). The basis of Angiosperm phylogeny: Palynology. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard., 62:
20 188 دراﺳﺔ ﻣظﻬرﯾﺔ ﻟﺣﺑوب اﻟﻠﻘﺎح ﻓﻲ ﻧﺑﺎﺗﺎت اﻻراﺿﻲ اﻟرطﺑﺔ ﻓﻲ اﻟﺟزء اﻟﺟﻧوﺑﻲ ﻣن اﻟﻌراق ﺳﺣر ﻋﺑد اﻟﻌﺑﺎس ﻣﺎﻟك و ﻋﺑد اﻟرﺿﺎ اﻛﺑر ﻋﻠوان اﻟﻣﯾﺎح ﻗﺳم ﻋﻠوم اﻟﺣﯾﺎة / ﻛﻠﯾﺔ اﻟﻌﻠوم / ﺟﺎﻣﻌﺔ اﻟﺑﺻرة اﻟﺧﻼﺻﺔ درﺳت ﺣﺑوب اﻟﻠﻘﺎح ﻟﻧﺑﺎﺗﺎت ذوات اﻟﻔﻠﻘﺗﯾن واﻟﻣﺗواﺟدة ﻓﻲ اﻻراﺿﻲ اﻟرطﺑﺔ وﺷﻣﻠت ﺗﺳﻌﺔ وأرﺑﻌﯾن ﻧوﻋﺎ" ﺗﻌود اﻟﻰ ﺧﻣﺳﺔ وﻋﺷرﯾن ﻋﺎﺋﻠﺔ. ﺗﺑﯾن ﻣن اﻟﻧﺗﺎﺋﺞ ان ﻫﻧﺎك ﺗﻐﺎﯾ ار" واﺿﺣﺎ" ﻓﻲ ﺷﻛل وﺣﺟم وﻓﺗﺣﺎت ﺣﺑوب اﻟﻠﻘﺎح ﺑﯾن اﻻﻧواع اﻟﻣدروﺳﺔ وﻋﻠﻰ اﺳﺎس ﻧوع اﻟﻔﺗﺣﺎت واﻟزﺧرﻓﺔ أﻣﻛن ﺗﻣﯾﯾز ﺗﺳﻌﺔ ﻋﺷر ط ار از" ﻣن ﺣﺑوب اﻟﻠﻘﺎح ﻓﻘد ﺗﻣﯾز اﻟطراز اﻟﻣﺗﻌدد اﻟﺛﻘوب pantoporate ﻓﻲ اﻟﻌﺎﺋﻠﺗﯾن اﻟرﻣراﻣﯾﺔ chenopodiaceae وﻋﺎﺋﻠﺔ ﻋرف اﻟدﯾك.Amaranthaceae ﻛﻣﺎ ﺗﺑﺎﯾﻧت اﻋداد اﻻﺧﺎدﯾد ﻓﻲ اﻻﻧواع اﻟﻣدروﺳﺔ ﻓﺑدت أﻧﻬﺎ ﺗﺣﺗوي ﻋﻠﻰ ﺛﻼﺛﺔ أﺧﺎدﯾد ﻓﻲ اﻟﺟﻧس Bacopa ﻓﻲ ﺣﯾن اﺣﺗوت ﻋﻠﻰ 5-4 أﺧﺎدﯾد ﻓﻲ اﻟﻧوع Myriophyllum spicatum وﻗد اﺣﺗوت ﺑﻌض اﻻﻧواع ﻋﻠﻰ ﺛﻘوب وأﺧﺎدﯾد ﻛﻣﺎ ﻓﻲ اﻧواع اﻟﻌﺎﺋﻠﺔ اﻟﻣرﻛﺑﺔ اﻣﺎ اﻟزﺧﺎرف ﻓﻘد ﺗﺑﺎﯾﻧت ﺑﯾن اﻟزﺧرﻓﺔ اﻟﻣﻠﺳﺎء ﻓﻲ ﺣﺎﻣول اﻟﻣﺎء Utricularia australis اﻟﻰ ﺷوﻛﯾﺔ ﻓﻲ ﺑﻌض اﻧواع اﻟﻌﺎﺋﻠﺔ اﻟﻣرﻛﺑﺔ.
POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN XLI. CUSCUTACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 36(3): 475480, 2004. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN XLI. CUSCUTACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MOHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan Abstract Pollen morphology
Pak. J. Bot., 36(3): 475480, 2004. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN XLI. CUSCUTACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MOHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan Abstract Pollen morphology
STUDIES ON THE POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE GENUS ARABIDOPSIS (BRASSICACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN
 Pak. J. Bot., 36(2): 229-234, 2004. STUDIES ON THE POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE GENUS ARABIDOPSIS (BRASSICACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN Department of Botany, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Sciences & Technology,
Pak. J. Bot., 36(2): 229-234, 2004. STUDIES ON THE POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE GENUS ARABIDOPSIS (BRASSICACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN Department of Botany, Federal Urdu University of Arts, Sciences & Technology,
A PALYNOLOGICAL SURVEY OF WETLAND PLANTS OF PUNJAB, PAKISTAN
 Pak. J. Bot., 45(6): 2131-2140, 2013. A PALYNOLOGICAL SURVEY OF WETLAND PLANTS OF PUNJAB, PAKISTAN ANDLEEB ANWAR SARDAR 1*, ANJUM PERVEEN 2 AND ZAHEER-UD-DIN KHAN 1 1 Department of Botany, Govt College
Pak. J. Bot., 45(6): 2131-2140, 2013. A PALYNOLOGICAL SURVEY OF WETLAND PLANTS OF PUNJAB, PAKISTAN ANDLEEB ANWAR SARDAR 1*, ANJUM PERVEEN 2 AND ZAHEER-UD-DIN KHAN 1 1 Department of Botany, Govt College
localities in South India, mostly from Kerala. The taxa studied and their sources are provided in Appendices I and II. Verification of species
 3 MATERIALS AND METHODS Polleniferous materials were procured from plants growing in different localities in South India, mostly from Kerala. The taxa studied and their sources are provided in Appendices
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS Polleniferous materials were procured from plants growing in different localities in South India, mostly from Kerala. The taxa studied and their sources are provided in Appendices
Pollen Morphology of Some Desertic Crucifers
 Pollen Morphology of Some Desertic Crucifers Anil Arora and Archana Modi* Palynology and Aerobiology Lab, P. G. Department of Botany, Govt. Dungar College, Bikaner *Author for Correspondence: E-mail: dr.archana.modi@gmail.com
Pollen Morphology of Some Desertic Crucifers Anil Arora and Archana Modi* Palynology and Aerobiology Lab, P. G. Department of Botany, Govt. Dungar College, Bikaner *Author for Correspondence: E-mail: dr.archana.modi@gmail.com
POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN L. RANUNCULACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(3): 499-509, 2006. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN L. RANUNCULACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen morphology
Pak. J. Bot., 38(3): 499-509, 2006. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN L. RANUNCULACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen morphology
POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN XXXVIII. PLANTAGINACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 36(1): 19-24, 2004. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN XXXVIII. PLANTAGINACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND M. QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen morphology
Pak. J. Bot., 36(1): 19-24, 2004. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN XXXVIII. PLANTAGINACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND M. QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen morphology
Pollen morphology of some selected mangrove flora
 INT J CURR SCI 2016, 19(4): E 153-157 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 2250-1770 Pollen morphology of some selected mangrove flora Lovly MS and MV Merlee Teresa Department of Botany, St Teresas College, Ernakulam-682
INT J CURR SCI 2016, 19(4): E 153-157 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 2250-1770 Pollen morphology of some selected mangrove flora Lovly MS and MV Merlee Teresa Department of Botany, St Teresas College, Ernakulam-682
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THALICTRUM L., SPECIES (RANUNCULACEAE) IN TURKEY
 Pak. J. Bot., 37(2): 203-212, 2005. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THALICTRUM L., SPECIES (RANUNCULACEAE) IN TURKEY SEVCAN TATLIDIL *, ADEM BICAKCI, HULUSI MALYER AND K.H. CAN BASER ** Department of Biology, Science
Pak. J. Bot., 37(2): 203-212, 2005. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THALICTRUM L., SPECIES (RANUNCULACEAE) IN TURKEY SEVCAN TATLIDIL *, ADEM BICAKCI, HULUSI MALYER AND K.H. CAN BASER ** Department of Biology, Science
SYSTEMATIC IMPLICATIONS OF POLLEN MORPHOLOGY IN THE FAMILY MALVACEAE FROM NORTH WEST FRONTIER PROVINCE, PAKISTAN
 Pak. J. Bot., 42(4): 2205-2214, 2010. SYSTEMATIC IMPLICATIONS OF POLLEN MORPHOLOGY IN THE FAMILY MALVACEAE FROM NORTH WEST FRONTIER PROVINCE, PAKISTAN NOREEN BIBI 1*, NAVEED AKHTAR 2, MANZOOR HUSSAIN 3
Pak. J. Bot., 42(4): 2205-2214, 2010. SYSTEMATIC IMPLICATIONS OF POLLEN MORPHOLOGY IN THE FAMILY MALVACEAE FROM NORTH WEST FRONTIER PROVINCE, PAKISTAN NOREEN BIBI 1*, NAVEED AKHTAR 2, MANZOOR HUSSAIN 3
POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LXV. BERBERIDACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 42(1): 1-6, 2010. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LXV. BERBERIDACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER 1 Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan 1 Federal Urdu University
Pak. J. Bot., 42(1): 1-6, 2010. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LXV. BERBERIDACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER 1 Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan 1 Federal Urdu University
PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOME CULTIVATED SPECIES OF GENUS HIBISCUS FROM NORTH WEST FRONTIER PROVINCE (N.W.F.P.) PAKISTAN
 Pak. J. Bot., 40(4): 1561-1569, 2008. PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOME CULTIVATED SPECIES OF GENUS HIBISCUS FROM NORTH WEST FRONTIER PROVINCE (N.W.F.P.) PAKISTAN NOREEN BIBI *1, MANZOOR HUSSAIN 2 AND NAVEED
Pak. J. Bot., 40(4): 1561-1569, 2008. PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOME CULTIVATED SPECIES OF GENUS HIBISCUS FROM NORTH WEST FRONTIER PROVINCE (N.W.F.P.) PAKISTAN NOREEN BIBI *1, MANZOOR HUSSAIN 2 AND NAVEED
A PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOME CULTIVATED TREES FROM KARACHI
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 15-28, 2006. A PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOME CULTIVATED TREES FROM KARACHI RUKHSHINDA AFTAB AND ANJUM PERVEEN Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan. Abstract
Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 15-28, 2006. A PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOME CULTIVATED TREES FROM KARACHI RUKHSHINDA AFTAB AND ANJUM PERVEEN Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan. Abstract
Comparative Study of Pollen Morphology of some members of Euphorbiaceae family
 Standard Research Journal of Agricultural Sciences Vol 2 (4): 054-058, May2014 (ISSN: 2311-2751) http://www.standresjournals.org/journals/srjas Research Article Comparative Study of Pollen Morphology of
Standard Research Journal of Agricultural Sciences Vol 2 (4): 054-058, May2014 (ISSN: 2311-2751) http://www.standresjournals.org/journals/srjas Research Article Comparative Study of Pollen Morphology of
Palynological Properties of the Genus Haplophyllum (Rutaceae) in Jordan
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 281-287 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Palynological Properties of the Genus Haplophyllum (Rutaceae) in Jordan Dawud Al-Eisawi* and Mariam
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 281-287 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Palynological Properties of the Genus Haplophyllum (Rutaceae) in Jordan Dawud Al-Eisawi* and Mariam
PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOIL SAMPLE COLLECTED FROM AN ARCHAEOLOGICAL SITE (GULABI BAGH) IN LAHORE, PAKISTAN ABSTRACT
 Khola and Hanif The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 22(4): 2012, Page: 1113-1117 J. Anim. Plant Sci. 22(4):2012 ISSN: 1018-7081 PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOIL SAMPLE COLLECTED FROM AN ARCHAEOLOGICAL SITE
Khola and Hanif The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 22(4): 2012, Page: 1113-1117 J. Anim. Plant Sci. 22(4):2012 ISSN: 1018-7081 PALYNOLOGICAL STUDY OF SOIL SAMPLE COLLECTED FROM AN ARCHAEOLOGICAL SITE
Palynological studies in tribe Chlorideae (Poaceae) from salt range of Pakistan
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(44), pp. 8909-8913, 15 August, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB10.2512 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(44), pp. 8909-8913, 15 August, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB10.2512 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LVI. VALERIANACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 39(6): 1889-1896, 2007. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LVI. VALERIANACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi -75270, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen
Pak. J. Bot., 39(6): 1889-1896, 2007. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LVI. VALERIANACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi -75270, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen
POLLEN GRAIN MORPHOLOGY OF THREE SPECIES AND A VARIETY OF OCIMUM LINN. (LAMIACEAE) IN SOUTHWESTERN NIGERIA
 Journal of Science and Technology, Vol. 29, No. 3 (2009), pp 1-7 1 2009 Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) POLLEN GRAIN MORPHOLOGY OF THREE SPECIES AND A VARIETY OF OCIMUM LINN.
Journal of Science and Technology, Vol. 29, No. 3 (2009), pp 1-7 1 2009 Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) POLLEN GRAIN MORPHOLOGY OF THREE SPECIES AND A VARIETY OF OCIMUM LINN.
I J R B A T, Issue (VI), Vol. I, Jan 2018: 49-56
 Page49 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCHES IN BIOSCIENCES, AGRICULTURE AND TECHNOLOGY VISHWASHANTI MULTIPURPOSE SOCIETY (Global Peace Multipurpose Society) R. No. MH-659/13(N) www.ijrbat.in LIGHT MICROSCOPIC
Page49 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCHES IN BIOSCIENCES, AGRICULTURE AND TECHNOLOGY VISHWASHANTI MULTIPURPOSE SOCIETY (Global Peace Multipurpose Society) R. No. MH-659/13(N) www.ijrbat.in LIGHT MICROSCOPIC
1) The myrtalean group of families is primarily characterized by two. distinctive wood anatomical features the combination of
 6 SUMMARY 1) The myrtalean group of families is primarily characterized by two distinctive wood anatomical features the combination of bicollateral vascular bundles in the primary stem and vestured pits
6 SUMMARY 1) The myrtalean group of families is primarily characterized by two distinctive wood anatomical features the combination of bicollateral vascular bundles in the primary stem and vestured pits
Palyonological studies of the semi-desert plant species from Pakistan
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 9 (24), pp. 35273535, 14 June, 2010 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2010 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Palyonological
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 9 (24), pp. 35273535, 14 June, 2010 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 2010 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Palyonological
Pollen Characteristics of Polygala, Salomonia and Xanthophyllum (Polygalaceae) in Thailand
 The Natural History Journal of Chulalongkorn University 9(1): 27-34, April 2009 2009 by Chulalongkorn University Pollen Characteristics of Polygala, Salomonia and Xanthophyllum (Polygalaceae) in Thailand
The Natural History Journal of Chulalongkorn University 9(1): 27-34, April 2009 2009 by Chulalongkorn University Pollen Characteristics of Polygala, Salomonia and Xanthophyllum (Polygalaceae) in Thailand
Palynology Of Six Species Of Solanum (Solanaceae) Gamal M. A. Lashin
 Palynology Of Six Species Of Solanum (Solanaceae) Gamal M. A. Lashin Department of Botany, Faculty of Sciences, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt. gamasabaa@yahoo.com Abstract: This paper presents the
Palynology Of Six Species Of Solanum (Solanaceae) Gamal M. A. Lashin Department of Botany, Faculty of Sciences, Zagazig University, Zagazig, Egypt. gamasabaa@yahoo.com Abstract: This paper presents the
POLLEN GRAINS OF SOME POISONOUS BEE PLANTS OF ETHIOPIA
 POLLEN GRAINS OF SOME POISONOUS BEE PLANTS OF ETHIOPIA A. Nuru 1, H.R. Hepburn 2 1 Holetta Bee Research Centre P. O. Box 17, Tel. 251 1 370120, Ethiopia, current address: Oakdene house, private Bag 1025,
POLLEN GRAINS OF SOME POISONOUS BEE PLANTS OF ETHIOPIA A. Nuru 1, H.R. Hepburn 2 1 Holetta Bee Research Centre P. O. Box 17, Tel. 251 1 370120, Ethiopia, current address: Oakdene house, private Bag 1025,
Pollen Grain Surface Pattern Terminology
 Pollen Grain Surface Pattern Terminology (NOTE: The top panel of the cartoon images below reflects the first plane of focus for the pollen grain. The lighter areas are indicative of protruding structures,
Pollen Grain Surface Pattern Terminology (NOTE: The top panel of the cartoon images below reflects the first plane of focus for the pollen grain. The lighter areas are indicative of protruding structures,
Systematic importance of pollen morphology of some plants of Lamiaceae
 Original Article Current Botany 2016, 7: 5-10 http://scienceflora.org/journals/index.php/jp/ doi:10.19071/cb.2016.v7.3029 Systematic importance of pollen morphology of some plants of Lamiaceae M. F. Azzazy*
Original Article Current Botany 2016, 7: 5-10 http://scienceflora.org/journals/index.php/jp/ doi:10.19071/cb.2016.v7.3029 Systematic importance of pollen morphology of some plants of Lamiaceae M. F. Azzazy*
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF DILLENIACEAE IN THAILAND
 Pak. J. Bot., 50(4): 1551-1562, 2018. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF DILLENIACEAE IN THAILAND SARAYUT RAKARCHA 1, PIYAPORN SAENSOUK 1,2* AND SURAPON SAENSOUK 2,3 1 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Mahasarakham
Pak. J. Bot., 50(4): 1551-1562, 2018. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF DILLENIACEAE IN THAILAND SARAYUT RAKARCHA 1, PIYAPORN SAENSOUK 1,2* AND SURAPON SAENSOUK 2,3 1 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Mahasarakham
POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN MALVACEAE- GREWIOIDEAE LII
 Pak. J. Bot., 39(1): 1-7, 2007. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN MALVACEAE- GREWIOIDEAE LII ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen
Pak. J. Bot., 39(1): 1-7, 2007. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN MALVACEAE- GREWIOIDEAE LII ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi-75270, Pakistan. Abstract Pollen
Pollen Flora of Pakistan - X. Leguminosae (Subfamily: Caesalpinioideae)
 Tr. J. of Botany 22 (1998) 145-150 TÜBİTAK A. PERVEEN, M. QAISER Research Article Pollen Flora of Pakistan - X. Leguminosae (Subfamily: Caesalpinioideae) Anjum PERVEEN, Mohammad QAISER Department of Botany,
Tr. J. of Botany 22 (1998) 145-150 TÜBİTAK A. PERVEEN, M. QAISER Research Article Pollen Flora of Pakistan - X. Leguminosae (Subfamily: Caesalpinioideae) Anjum PERVEEN, Mohammad QAISER Department of Botany,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pollen morphology of millets-exine surface ultrastructure. Kashikar Neha and Kalkar S. A Institute of Science, Nagpur
 ASIAN J. EXP. BIOL. SCI.SPL.2010 :85-90 Society of Applied Sciences ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pollen morphology of millets-exine surface ultrastructure Institute of Science, Nagpur ABSTRACT Pollen morphology of
ASIAN J. EXP. BIOL. SCI.SPL.2010 :85-90 Society of Applied Sciences ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pollen morphology of millets-exine surface ultrastructure Institute of Science, Nagpur ABSTRACT Pollen morphology of
Sakun Publishing House (SPH): IJPLS. Research Article [Ramakrishna et al., 6(1): Jan., 2015: ] CODEN (USA): IJPLCP ISSN:
![Sakun Publishing House (SPH): IJPLS. Research Article [Ramakrishna et al., 6(1): Jan., 2015: ] CODEN (USA): IJPLCP ISSN: Sakun Publishing House (SPH): IJPLS. Research Article [Ramakrishna et al., 6(1): Jan., 2015: ] CODEN (USA): IJPLCP ISSN:](/thumbs/94/122220800.jpg) INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES (Int. J. of Pharm. Life Sci.) pollen in the arborescent plants of Karimnagar district, Telangana state, India J. Kailas Ganga, H. Ramakrishna* and R. Prabhakar
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES (Int. J. of Pharm. Life Sci.) pollen in the arborescent plants of Karimnagar district, Telangana state, India J. Kailas Ganga, H. Ramakrishna* and R. Prabhakar
BASELINE INVENTORY FOR ANGIOSPERMIC POLLEN DIVERSITY IN OSMANABAD DISTRICT (MS), INDIA
 Bioscience Discovery, 2 (3):288-293, July 2011 ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print) BASELINE INVENTORY FOR ANGIOSPERMIC POLLEN DIVERSITY IN OSMANABAD DISTRICT (MS), INDIA Devarkar V D Department of Botany, Shri Chhatrapati
Bioscience Discovery, 2 (3):288-293, July 2011 ISSN: 2229-3469 (Print) BASELINE INVENTORY FOR ANGIOSPERMIC POLLEN DIVERSITY IN OSMANABAD DISTRICT (MS), INDIA Devarkar V D Department of Botany, Shri Chhatrapati
POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LIV. RUBIACEAE
 Pak. J. Bot., 39(4): 999-1015, 2007. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LIV. RUBIACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi - 75270, Pakistan Abstract Pollen morphology
Pak. J. Bot., 39(4): 999-1015, 2007. POLLEN FLORA OF PAKISTAN LIV. RUBIACEAE ANJUM PERVEEN AND MUHAMMAD QAISER Department of Botany, University of Karachi, Karachi - 75270, Pakistan Abstract Pollen morphology
Taxonomic Implication of Palynological Characters in the Genus Malva L., Family Malvaceae from Pakistan
 American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 6 (6): 716-722, 2009 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 2009 Taxonomic Implication of Palynological Characters in the Genus Malva L., Family Malvaceae from
American-Eurasian J. Agric. & Environ. Sci., 6 (6): 716-722, 2009 ISSN 1818-6769 IDOSI Publications, 2009 Taxonomic Implication of Palynological Characters in the Genus Malva L., Family Malvaceae from
Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Arak University, , Arak, Iran
 Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print), 2222-3045 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 6, No. 4, p. 53-64, 2015 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pollen morphology of
Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print), 2222-3045 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 6, No. 4, p. 53-64, 2015 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pollen morphology of
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE FAMILY CRASSULACEAE FROM PAKISTAN AND KASHMIR AND ITS TAXONOMIC IMPLICATIONS
 Pak. J. Bot. 47(4): 1481-1493, 2015. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE FAMILY CRASSULACEAE FROM PAKISTAN AND KASHMIR AND ITS TAXONOMIC IMPLICATIONS MUHAMMAD QAISER, ANJUM PERVEEN AND GHULAM RASOOL SARWAR Centre
Pak. J. Bot. 47(4): 1481-1493, 2015. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE FAMILY CRASSULACEAE FROM PAKISTAN AND KASHMIR AND ITS TAXONOMIC IMPLICATIONS MUHAMMAD QAISER, ANJUM PERVEEN AND GHULAM RASOOL SARWAR Centre
POLLEN AND SEED MORPHOLOGY OF CRAMBE SPECIES OF TURKEY ABSTRACT
 Bülbül et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 27(4): 2017, Page: The J. 1331-1339 Anim. Plant Sci. 27(4):2017 ISSN: 1018-7081 POLLEN AND SEED MORPHOLOGY OF CRAMBE SPECIES OF TURKEY A. S. Bülbül¹
Bülbül et al., The Journal of Animal & Plant Sciences, 27(4): 2017, Page: The J. 1331-1339 Anim. Plant Sci. 27(4):2017 ISSN: 1018-7081 POLLEN AND SEED MORPHOLOGY OF CRAMBE SPECIES OF TURKEY A. S. Bülbül¹
STUDIES ON PRODUCTION, MORPHOLOGY AND FREE AMINO ACIDS OF POLLEN OF FOUR MEMBERS IN THE GENUS NYMPHAEA L. (NYMPHAEACEAE)
 I.J.S.N., VOL. 3(3) 2012: 705-718 ISSN 2229 6441 STUDIES ON PRODUCTION, MORPHOLOGY AND FREE AMINO ACIDS OF POLLEN OF FOUR MEMBERS IN THE GENUS NYMPHAEA L. (NYMPHAEACEAE) Debasis Bhunia & Amal Kumar Mondal
I.J.S.N., VOL. 3(3) 2012: 705-718 ISSN 2229 6441 STUDIES ON PRODUCTION, MORPHOLOGY AND FREE AMINO ACIDS OF POLLEN OF FOUR MEMBERS IN THE GENUS NYMPHAEA L. (NYMPHAEACEAE) Debasis Bhunia & Amal Kumar Mondal
South American Compositae Meeting São Paulo, Brazil Cytogenetic and palynological studies in species of Chrysolaena (Vernonieae, Asteraceae)
 South American Compositae Meeting São Paulo, Brazil. 2011. Cytogenetic and palynological studies in species of Chrysolaena (Vernonieae, Asteraceae) Via do Pico Gisela M. & Dematteis Massimiliano Instituto
South American Compositae Meeting São Paulo, Brazil. 2011. Cytogenetic and palynological studies in species of Chrysolaena (Vernonieae, Asteraceae) Via do Pico Gisela M. & Dematteis Massimiliano Instituto
PALYNOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE GENUS CALENDULA (CALENDULEAE-COMPOSITAE) FROM PAKISTAN
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(3): 511-520, 2006. PALYNOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE GENUS CALENDULA (CALENDULEAE-COMPOSITAE) FROM PAKISTAN AKBAR ALI MEO AND MIR AJAB KHAN * Department of Biology, Government College,
Pak. J. Bot., 38(3): 511-520, 2006. PALYNOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE GENUS CALENDULA (CALENDULEAE-COMPOSITAE) FROM PAKISTAN AKBAR ALI MEO AND MIR AJAB KHAN * Department of Biology, Government College,
Department of Plant Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan. Keywords: Pedicularis L.; Deosai plateau; Pollen morphology; SEM analysis.
 Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 19(1): 1-5, 2012 (June) 2012 Bangladesh Association of Plant Taxonomists POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF FOUR ENDEMIC SPECIES OF PEDICULARIS L. FROM ALPINE ZONE OF THE DEOSAI PLATEAU, HIMALAYAN
Bangladesh J. Plant Taxon. 19(1): 1-5, 2012 (June) 2012 Bangladesh Association of Plant Taxonomists POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF FOUR ENDEMIC SPECIES OF PEDICULARIS L. FROM ALPINE ZONE OF THE DEOSAI PLATEAU, HIMALAYAN
Palynology Spore/Pollen Morphology
 Palynology Spore/Pollen Morphology http://incredibleworld.net/wp-content/uploads/2010/04/pollen-grains-2.jpg Mohamed K Zobaa, PhD Department of Geology Faculty of Science, Benha University, EGYPT mohamed.zobaa@fsc.bu.edu.eg
Palynology Spore/Pollen Morphology http://incredibleworld.net/wp-content/uploads/2010/04/pollen-grains-2.jpg Mohamed K Zobaa, PhD Department of Geology Faculty of Science, Benha University, EGYPT mohamed.zobaa@fsc.bu.edu.eg
Pollen morphology of selected species of the subfamily Bombacoideae (Malvaceae sensu lato) 1
 Acta Botanica Brasilica 28(3): 352-360. 2014. doi: 10.1590/0102-33062014abb3482 Pollen morphology of selected species of the subfamily Bombacoideae (Malvaceae sensu lato) 1 Vanessa Holanda Righetti de
Acta Botanica Brasilica 28(3): 352-360. 2014. doi: 10.1590/0102-33062014abb3482 Pollen morphology of selected species of the subfamily Bombacoideae (Malvaceae sensu lato) 1 Vanessa Holanda Righetti de
Angiosperms. The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species.
 Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
Angiosperms The most diverse group of plants, with about 14,000 genera and 257,000 species. Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms? Angiosperms How do angiosperms differ from gymnosperms?
1 BIOL 3242 VASCULAR FLORA OF MANITOBA 2017
 1 BIOL 3242 VASCULAR FLORA OF MANITOBA 2017 Course Description (expanded from description in course calendar) This course is an introduction to the principles and methods of plant taxonomy (the science
1 BIOL 3242 VASCULAR FLORA OF MANITOBA 2017 Course Description (expanded from description in course calendar) This course is an introduction to the principles and methods of plant taxonomy (the science
Pollen morphology of the genera Onobrychis and Hedysarum (Hedysareae, Fabaceae) in Bulgaria
 Ann. Bot. Fennici 37: 207 217 ISSN 0003-3847 Helsinki 27 September 2000 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 2000 Pollen morphology of the genera Onobrychis and Hedysarum (Hedysareae, Fabaceae)
Ann. Bot. Fennici 37: 207 217 ISSN 0003-3847 Helsinki 27 September 2000 Finnish Zoological and Botanical Publishing Board 2000 Pollen morphology of the genera Onobrychis and Hedysarum (Hedysareae, Fabaceae)
Summer Pollen Sources to Apis dorsata honey bees collected from Bramhapuri forest area of Chandrapur District of Maharashtra State (India)
 Int. J. of Life Sciences, 2014, Vol. 2(2): 160-164 ISSN: 2320-7817 eissn: 2320-964X RESEARCH ARTICLE Summer Pollen Sources to Apis dorsata honey bees collected from Bramhapuri forest area of Chandrapur
Int. J. of Life Sciences, 2014, Vol. 2(2): 160-164 ISSN: 2320-7817 eissn: 2320-964X RESEARCH ARTICLE Summer Pollen Sources to Apis dorsata honey bees collected from Bramhapuri forest area of Chandrapur
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE SUBFAMILY ARECOIDEAE GRIFF. (FAMILY-ARECACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN AND KASHMIR
 Pak. J. Bot., 48(3): 1051-1060, 2016. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE SUBFAMILY ARECOIDEAE GRIFF. (FAMILY-ARECACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN AND KASHMIR ABID ARZOO RASHEED 1*, ANJUM PERVEEN 1, ROOHI ABID 1 AND MUHAMMAD
Pak. J. Bot., 48(3): 1051-1060, 2016. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF THE SUBFAMILY ARECOIDEAE GRIFF. (FAMILY-ARECACEAE) FROM PAKISTAN AND KASHMIR ABID ARZOO RASHEED 1*, ANJUM PERVEEN 1, ROOHI ABID 1 AND MUHAMMAD
Pollen morphology of Centaurea L. (Asteraceae) in Iran
 Acta Botanica Brasilica 27(4): 669-679. 2013. Pollen morphology of Centaurea L. (Asteraceae) in Iran Elaheh Sadat Bagheri Shabestari 1,3, Farideh Attar 2, Hosein Riahi 1 and Masoud Sheidai 1 Received:
Acta Botanica Brasilica 27(4): 669-679. 2013. Pollen morphology of Centaurea L. (Asteraceae) in Iran Elaheh Sadat Bagheri Shabestari 1,3, Farideh Attar 2, Hosein Riahi 1 and Masoud Sheidai 1 Received:
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AS AN AID TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF CHRYSANTHEMUM SPECIES (COMPOSITAE ANTHEMIDEAE) FROM PAKISTAN
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 29-41, 2006. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AS AN AID TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF CHRYSANTHEMUM SPECIES (COMPOSITAE ANTHEMIDEAE) FROM PAKISTAN AKBAR ALI MEO * AND MIR AJAB KHAN ** *Department of Biology,
Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 29-41, 2006. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AS AN AID TO THE IDENTIFICATION OF CHRYSANTHEMUM SPECIES (COMPOSITAE ANTHEMIDEAE) FROM PAKISTAN AKBAR ALI MEO * AND MIR AJAB KHAN ** *Department of Biology,
Pollen grain morphology of selected allergenic species native to southern South America
 Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134(4), 2007, pp. 527 533 Pollen grain morphology of selected allergenic species native to southern South America Luis Palazzesi 1,2 and Roberto R. Pujana MACN -
Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134(4), 2007, pp. 527 533 Pollen grain morphology of selected allergenic species native to southern South America Luis Palazzesi 1,2 and Roberto R. Pujana MACN -
STUDY OF THE CYTOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND GERMINATION POTENTIAL OF SOME PEACH CULTIVARS FROM RSFG CONSTANŢA
 Scientific Papers. Series B, Horticulture. Vol. LXII, 2018 Print ISSN 2285-5653, CD-ROM ISSN 2285-5661, Online ISSN 2286-1580, ISSN-L 2285-5653 STUDY OF THE CYTOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND GERMINATION
Scientific Papers. Series B, Horticulture. Vol. LXII, 2018 Print ISSN 2285-5653, CD-ROM ISSN 2285-5661, Online ISSN 2286-1580, ISSN-L 2285-5653 STUDY OF THE CYTOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND GERMINATION
The Investigation of Morphologic Analysis of Pollen Grains Which are Economically Important and Collected by Apis mellifera L.
 HACETTEPE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Volume 35, Issue 1, January 2007 Hacettepe J. Biol. & Chem., 2007, 35 (1), 31-38 Research Article The Investigation of Morphologic Analysis of Pollen Grains Which
HACETTEPE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Volume 35, Issue 1, January 2007 Hacettepe J. Biol. & Chem., 2007, 35 (1), 31-38 Research Article The Investigation of Morphologic Analysis of Pollen Grains Which
Sadar et al., Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. (2015) 12(4):9-13
 APPRAISAL OF ETHNOBOTANICAL USES OF THE WETLAND PLANTS OF PUNJAB, PAKISTAN Andleeb Anwar Sardar 1, Zaheer-ud-din Khan 1, Anjum Perveen 2 and Arifa Zereen 1 1 University of Education Lower Mall Campus Lahore,
APPRAISAL OF ETHNOBOTANICAL USES OF THE WETLAND PLANTS OF PUNJAB, PAKISTAN Andleeb Anwar Sardar 1, Zaheer-ud-din Khan 1, Anjum Perveen 2 and Arifa Zereen 1 1 University of Education Lower Mall Campus Lahore,
Lagerstroemia , International Research Center for Japanese Studies, 3-2 Oeyama-cho, Goryo, Nishikyo-ku, Kyoto , Japan
 10 2 p. 91 99 2001 10 Jpn. J. Histor. Bot. 1 2 1 Lagerstroemia Toshiyuki Fujiki 1, Arata Momohara 2 and Yoshinori Yasuda 1 : Morphology of fossil Lagerstroemia pollen in the interglacial sediments in Japan
10 2 p. 91 99 2001 10 Jpn. J. Histor. Bot. 1 2 1 Lagerstroemia Toshiyuki Fujiki 1, Arata Momohara 2 and Yoshinori Yasuda 1 : Morphology of fossil Lagerstroemia pollen in the interglacial sediments in Japan
Morphological Features of Pollen Grains in Portulaca
 pissn 2287-5123 eissn 2287-4445 http://dx.doi.org/10.9729/am.2013.43.2.75 Morphological Features of Pollen Grains in Portulaca InSun Kim* Department of iology, College of Natural Sciences, Keimyung University,
pissn 2287-5123 eissn 2287-4445 http://dx.doi.org/10.9729/am.2013.43.2.75 Morphological Features of Pollen Grains in Portulaca InSun Kim* Department of iology, College of Natural Sciences, Keimyung University,
 In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
In cladistics, a synapomorphy or synapomorphic character state is a trait that is shared ("symmorphy") by two or more taxa and inferred to have been present in their most recent common ancestor, whose
Analysis of pollen grains in different honey samples from the region of Newasa tehsil in Maharashtra
 2018; 7(3): 3438-3442 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2018; 7(3): 3438-3442 Received: 07-03-2018 Accepted: 12-04-2018 Ashwini S Dhawan Kulbhushan W Pawar Ashwini A Lokhande Analysis of pollen grains
2018; 7(3): 3438-3442 E-ISSN: 2278-4136 P-ISSN: 2349-8234 JPP 2018; 7(3): 3438-3442 Received: 07-03-2018 Accepted: 12-04-2018 Ashwini S Dhawan Kulbhushan W Pawar Ashwini A Lokhande Analysis of pollen grains
The optimal sample size in pollen morphological studies using the example of Rosa canina L. (Rosaceae)
 Palynology, 2015 Vol. 39, No. 1, 56 75, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01916122.2014.933748 The optimal sample size in pollen morphological studies using the example of Rosa canina L. (Rosaceae) Dorota Wronska-Pilarek
Palynology, 2015 Vol. 39, No. 1, 56 75, http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/01916122.2014.933748 The optimal sample size in pollen morphological studies using the example of Rosa canina L. (Rosaceae) Dorota Wronska-Pilarek
Pollen morphology of the genus Paliurus (Rhamnaceae)
 Grana ISSN: 0017-3134 (Print) 1651-2049 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/sgra20 Pollen morphology of the genus Paliurus (Rhamnaceae) Carsten Schirarend To cite this article: Carsten
Grana ISSN: 0017-3134 (Print) 1651-2049 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/sgra20 Pollen morphology of the genus Paliurus (Rhamnaceae) Carsten Schirarend To cite this article: Carsten
Title. Author(s)Sawara, A.K.M. Golam. Issue Date DOI. Doc URL. Type. File Information. Pollen Morphology and Its Systematic Significance in
 Title Pollen Morphology and Its Systematic Significance in Author(s)Sawara, A.K.M. Golam Issue Date 2007-03-23 DOI 10.14943/doctoral.k8187 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46925 Type theses (doctoral)
Title Pollen Morphology and Its Systematic Significance in Author(s)Sawara, A.K.M. Golam Issue Date 2007-03-23 DOI 10.14943/doctoral.k8187 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46925 Type theses (doctoral)
LABORATORY 2: Flowers
 LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
LABORATORY 2: Flowers INTRODUCTION The goal of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize you with flowers, their structure, variation, and importance to the plant. By the end of today s laboratory exercise
Ethnic uses of some wetland plants by the Bodo community in Udalgiri district of Assam, India
 Pleione 7(1): 155-159. 2013. ISSN: 0973-9467 East Himalayan Society for Spermatophyte Taxonomy Ethnic uses of some wetland s by the Bodo community in Udalgiri district of Assam, India A. Boro 1 and G.
Pleione 7(1): 155-159. 2013. ISSN: 0973-9467 East Himalayan Society for Spermatophyte Taxonomy Ethnic uses of some wetland s by the Bodo community in Udalgiri district of Assam, India A. Boro 1 and G.
MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF POLLEN GRAINS FOR SOME GENERA OF SUBFAMILY PAPILIONOIDEAE
 Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 2, 2017 pp. 1711172 ISSN 09725210 MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF POLLEN GRAINS FOR SOME GENERA OF SUBFAMILY PAPILIONOIDEAE Shaemaa Muhi ALAmery and Nedaa Adnan AbuSerag Department of
Plant Archives Vol. 17 No. 2, 2017 pp. 1711172 ISSN 09725210 MORPHOLOGICAL STUDY OF POLLEN GRAINS FOR SOME GENERA OF SUBFAMILY PAPILIONOIDEAE Shaemaa Muhi ALAmery and Nedaa Adnan AbuSerag Department of
Circumscription of Codonopsis and the allied genera Campanumoea and Leptocodon (Campanulaceae: Campanuloideae). I. Palynological data
 Morris Bot. Bull. and Acad. Lammers Sin. (1997) Pollen 38: of 277-284 Codonopsis 277 Circumscription of Codonopsis and the allied genera Campanumoea and Leptocodon (Campanulaceae: Campanuloideae). I. Palynological
Morris Bot. Bull. and Acad. Lammers Sin. (1997) Pollen 38: of 277-284 Codonopsis 277 Circumscription of Codonopsis and the allied genera Campanumoea and Leptocodon (Campanulaceae: Campanuloideae). I. Palynological
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF ENDEMIC NE ANATOLIAN CIRSIUM TAXA (ASTERACEAE)
 Pak. J. Bot., 50(3): 1181-1185, 2018. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF ENDEMIC NE ANATOLIAN CIRSIUM TAXA (ASTERACEAE) FUNDA ERŞEN BAK * AND MELAHAT OZCAN Department of Forest Engineering, Faculty of Forestry, Artvin
Pak. J. Bot., 50(3): 1181-1185, 2018. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF ENDEMIC NE ANATOLIAN CIRSIUM TAXA (ASTERACEAE) FUNDA ERŞEN BAK * AND MELAHAT OZCAN Department of Forest Engineering, Faculty of Forestry, Artvin
Pollen morphology of some species of the genus Veronica (Scrophulariaceae) in Iran
 Wulfenia 13 (2006): 1 10 Mitteilungen des Kärntner Botanikzentrums Klagenfurt Pollen morphology of some species of the genus Veronica (Scrophulariaceae) in Iran Shahryar Saeidi-Mehrvarz & Mehdi Zarrei
Wulfenia 13 (2006): 1 10 Mitteilungen des Kärntner Botanikzentrums Klagenfurt Pollen morphology of some species of the genus Veronica (Scrophulariaceae) in Iran Shahryar Saeidi-Mehrvarz & Mehdi Zarrei
POLLEN-WALL PROTEINS: ELECTRON- MICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF ACID PHOSPHATASE IN THE INTINE OF CROCUS VERNUS
 J. Cell Sci. 8, 727-733 (197O 727 Printed in Great Britain POLLEN-WALL PROTEINS: ELECTRON- MICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF ACID PHOSPHATASE IN THE INTINE OF CROCUS VERNUS R.B. KNOX* AND J. HESLOP-HARRISONf
J. Cell Sci. 8, 727-733 (197O 727 Printed in Great Britain POLLEN-WALL PROTEINS: ELECTRON- MICROSCOPIC LOCALIZATION OF ACID PHOSPHATASE IN THE INTINE OF CROCUS VERNUS R.B. KNOX* AND J. HESLOP-HARRISONf
Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring First Hourly Exam 4/22/10
 Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
Name: Lab sect. (TA name/time): BIOLOGY 317 Spring 2011 First Hourly Exam 4/22/10 1) (24 pts) Match the letter of the family given on the right with the characteristics for a plant described on the left.
(.Botanical Museum and Herbarium, Utrecht)
 Pollen morphology of some European Rosaceae Tj. Reitsma (.Botanical Museum and Herbarium, Utrecht) {received February 17th, 1966) Abstract In this preliminary investigation attention was paid to pollen
Pollen morphology of some European Rosaceae Tj. Reitsma (.Botanical Museum and Herbarium, Utrecht) {received February 17th, 1966) Abstract In this preliminary investigation attention was paid to pollen
FLOWERS, FRUITS, SEEDS, AND POLLEN OF LANDEENIA
 American Journal of Botany 87(12): 1909 1914. 2000. FLOWERS, FRUITS, SEEDS, AND POLLEN OF LANDEENIA GEN. NOV., AN EXTINCT SAPINDALEAN GENUS FROM THE EOCENE OF WYOMING 1 STEVEN R. MANCHESTER 2 AND ELIZABETH
American Journal of Botany 87(12): 1909 1914. 2000. FLOWERS, FRUITS, SEEDS, AND POLLEN OF LANDEENIA GEN. NOV., AN EXTINCT SAPINDALEAN GENUS FROM THE EOCENE OF WYOMING 1 STEVEN R. MANCHESTER 2 AND ELIZABETH
EFFECTS OF SOME FUNGICIDES ON POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF TOMATO (LYCOPERSİCON ESCULENTUM MILL.)
 Pak. J. Bot., 37(1): 23-30, 2005. EFFECTS OF SOME FUNGICIDES ON POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF TOMATO (LYCOPERSİCON ESCULENTUM MILL.) * N. TORT, İ. ÖZTÜRK AND A. GÜVENSEN Department Botany, Science Faculty,
Pak. J. Bot., 37(1): 23-30, 2005. EFFECTS OF SOME FUNGICIDES ON POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ANATOMY OF TOMATO (LYCOPERSİCON ESCULENTUM MILL.) * N. TORT, İ. ÖZTÜRK AND A. GÜVENSEN Department Botany, Science Faculty,
Seed Plants Lab. Learning Objectives. Procedure and Questions
 Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
Seed Plants Lab Learning Objectives Define the terms (meanings of the names) angiosperm and gymnosperm State what type of cells create eggs and what type of cells create sperm in gymnosperms and angiosperms
Department of Botany, Faculty of Biology, University of Sofia, blvd. Dragan Tzankov 8, 1164 Sofia, Bulgaria
 Genetics and Plant Physiology 2016, Volume 6(1 2), pp. 27 42 2016 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology and Genetics Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.ifrg-bg.com POLLEN
Genetics and Plant Physiology 2016, Volume 6(1 2), pp. 27 42 2016 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology and Genetics Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.ifrg-bg.com POLLEN
Pollen morphology of Vochysiaceae tree species in the State of Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil
 Pollen morphology of Vochysiaceae tree species in the State of Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil Ortrud Monika Barth 1,2 & Cynthia Fernandes Pinto da Luz 3 1. Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Fiocruz, Avenida Brasil
Pollen morphology of Vochysiaceae tree species in the State of Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil Ortrud Monika Barth 1,2 & Cynthia Fernandes Pinto da Luz 3 1. Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Fiocruz, Avenida Brasil
EVOLUTION OF ANGIOSPERM Lu Lu, 2,3 Alexandra H. Wortley, 4 De-zhu Li, 2,3 POLLEN. 2. THE Hong Wang, 2,3* and Stephen Blackmore 4 BASAL ANGIOSPERMS 1
 EVOLUTION OF ANGIOSPERM Lu Lu, Alexandra H. Wortley, 4 De-zhu Li, POLLEN. 2. THE Hong Wang, * and Stephen Blackmore 4 BASAL ANGIOSPERMS ABSTRACT Recently, evolutionary relationships among the five major
EVOLUTION OF ANGIOSPERM Lu Lu, Alexandra H. Wortley, 4 De-zhu Li, POLLEN. 2. THE Hong Wang, * and Stephen Blackmore 4 BASAL ANGIOSPERMS ABSTRACT Recently, evolutionary relationships among the five major
Pollen Atlas of Santiniketan, West Bengal, with Reference to Aeropalynology
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(6): 983-1000 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 5 (2016) pp. 983-1000 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(6): 983-1000 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 5 (2016) pp. 983-1000 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com
International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)
 International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 6, Issue 9 (September 2017), PP.36-44 Melittopalynological Investigation of Winter Honeys
International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 6, Issue 9 (September 2017), PP.36-44 Melittopalynological Investigation of Winter Honeys
(Sapindaceae) taxonomically (Van der Ham, 1977a). microscope (SEM), and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The LM studies were
 BLUMEA 23 (1977) 301 335 Pollenmorphologyof the genus Mischocarpus (Sapindaceae) R.W.J. van der Ham Rijksherbarium, Leiden, The Netherlands Contents Summary 301 I. Introduction 301 II. General morphology
BLUMEA 23 (1977) 301 335 Pollenmorphologyof the genus Mischocarpus (Sapindaceae) R.W.J. van der Ham Rijksherbarium, Leiden, The Netherlands Contents Summary 301 I. Introduction 301 II. General morphology
Pollen morphology and ultrastructure of selected species of Magnoliaceae
 Pollen morphology and ultrastructure of selected species of Magnoliaceae By: Feng-Xia Xu a, *, Bruce K. Kirchoff b Xu, Feng-Xia, and B. K. Kirchoff. 2008. Pollen morphology and ultrastructure of selected
Pollen morphology and ultrastructure of selected species of Magnoliaceae By: Feng-Xia Xu a, *, Bruce K. Kirchoff b Xu, Feng-Xia, and B. K. Kirchoff. 2008. Pollen morphology and ultrastructure of selected
Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências ISSN: Academia Brasileira de Ciências Brasil
 Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências ISSN: 0001-3765 aabc@abc.org.br Academia Brasileira de Ciências Brasil SOUSA, SAULO M.; PIERRE, PATRÍCIA M.O.; TORRES, GIOVANA A.; DAVIDE, LISETE C.; VICCINI, LYDERSON
Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências ISSN: 0001-3765 aabc@abc.org.br Academia Brasileira de Ciências Brasil SOUSA, SAULO M.; PIERRE, PATRÍCIA M.O.; TORRES, GIOVANA A.; DAVIDE, LISETE C.; VICCINI, LYDERSON
POLLEN CARDS OF THE GENISTA RADIATA GROUP (GENISTEAE, FABACEAE)
 Studia Geobotanica. Voi. 19: 39-48 (2000) POLLEN CARDS OF THE GENISTA RADIATA GROUP (GENISTEAE, FABACEAE) Loredana RIZZI LONGO, Laura FEOLI CHIAPELLA, Tiziana CUSMA VELARI and Vera KOSOVEL Dipartimento
Studia Geobotanica. Voi. 19: 39-48 (2000) POLLEN CARDS OF THE GENISTA RADIATA GROUP (GENISTEAE, FABACEAE) Loredana RIZZI LONGO, Laura FEOLI CHIAPELLA, Tiziana CUSMA VELARI and Vera KOSOVEL Dipartimento
Pollen Grains of Nigerian Plants
 Grana ISSN: 0017-3134 (Print) 1651-2049 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/sgra20 Pollen Grains of Nigerian Plants M. A. Sowunmi To cite this article: M. A. Sowunmi (1973) Pollen
Grana ISSN: 0017-3134 (Print) 1651-2049 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/sgra20 Pollen Grains of Nigerian Plants M. A. Sowunmi To cite this article: M. A. Sowunmi (1973) Pollen
inspection. It appeared that it was necessary
 Suggestions towards unification of descriptive terminology of Angiosperm pollen grains Tj. Reitsma Botanical Museum and Herbarium, State University, Utrecht (The Netherlands) (Received February 16, 1970)
Suggestions towards unification of descriptive terminology of Angiosperm pollen grains Tj. Reitsma Botanical Museum and Herbarium, State University, Utrecht (The Netherlands) (Received February 16, 1970)
Pollen Morphology of Four Species in Family Euphorbiaceae
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 1 Pollen Morphology of Four Species in Family Euphorbiaceae Thi Thi Htun Abstract The taxonomic descriptions and pollen morphology of 4 species belonging
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 1 Pollen Morphology of Four Species in Family Euphorbiaceae Thi Thi Htun Abstract The taxonomic descriptions and pollen morphology of 4 species belonging
COMPARATIVE POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND
 American Journal of Botany 87(2): 161 175. 2000. COMPARATIVE POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE CALLITRICHACEAE 1 RANESSA L. COOPER, 2,4 JEFFREY M. OSBORN, 2,5 AND C. THOMAS PHILBRICK 3 2 Division
American Journal of Botany 87(2): 161 175. 2000. COMPARATIVE POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE CALLITRICHACEAE 1 RANESSA L. COOPER, 2,4 JEFFREY M. OSBORN, 2,5 AND C. THOMAS PHILBRICK 3 2 Division
Pollen morphology of selected taxa of the genus Solanum from Southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India
 Rheedea Vol. 25(2) 128-145 2015 ISSN: 0971-2313 Pollen morphology of selected taxa of the genus Solanum from Southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India Anil Kumar V.S., Maya Nair C. 1 and Murugan K.* Department
Rheedea Vol. 25(2) 128-145 2015 ISSN: 0971-2313 Pollen morphology of selected taxa of the genus Solanum from Southern Western Ghats, Kerala, India Anil Kumar V.S., Maya Nair C. 1 and Murugan K.* Department
COMPARISON OF POLLEN MORPHOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF SOME TAXA BELONGING TO ASPARAGUS
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 36(2): 111-120, 2007 (December) COMPAISON OF POLLEN MOPHOLOICAL STUCTUES OF SOME TAXA BELONIN TO ASPAAUS L. AND FITILLAIA L. (LILIACEAE) FOM TUKEY H. OZLE* AND S. PEHLIVAN1 The Ministry
Bangladesh J. Bot. 36(2): 111-120, 2007 (December) COMPAISON OF POLLEN MOPHOLOICAL STUCTUES OF SOME TAXA BELONIN TO ASPAAUS L. AND FITILLAIA L. (LILIACEAE) FOM TUKEY H. OZLE* AND S. PEHLIVAN1 The Ministry
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF CALYCERACEAE
 32 LUNDELLIA DECEMBER, 2007 POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF CALYCERACEAE Melanie L. DeVore, 1 Zaiming Zhao, 2 Robert K. Jansen, 2 and John J. Skvarla 3 1 Department of Biology and Environmental
32 LUNDELLIA DECEMBER, 2007 POLLEN MORPHOLOGY AND ULTRASTRUCTURE OF CALYCERACEAE Melanie L. DeVore, 1 Zaiming Zhao, 2 Robert K. Jansen, 2 and John J. Skvarla 3 1 Department of Biology and Environmental
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS SJIF Impact Factor: 5.088
 wjpls, 2018, Vol. 4, Issue 9, 149-156 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Borkar et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 5.088 MELITTOPALYNOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF WINTER HONEYS COLLECTED FROM APIS
wjpls, 2018, Vol. 4, Issue 9, 149-156 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Borkar et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 5.088 MELITTOPALYNOLOGICAL INVESTIGATION OF WINTER HONEYS COLLECTED FROM APIS
Photographs of pollen grains from plants in NE Siberia
 Photographs of pollen grains from plants in NE Siberia Pim de Klerk, Bastian Niemeyer, Elena Raschke, Larisa Savelieva, Annette Teltewskoi, Martin Theuerkauf, Hans Joosten Appendix to: De Klerk P, Teltewskoi
Photographs of pollen grains from plants in NE Siberia Pim de Klerk, Bastian Niemeyer, Elena Raschke, Larisa Savelieva, Annette Teltewskoi, Martin Theuerkauf, Hans Joosten Appendix to: De Klerk P, Teltewskoi
Collection date: SEM date: 14/1/6 Location:
 Page 176 Family: Poaceae SEM images courtesy: Rachel Neville Phleum pratense Timothy Collection date: SEM date: 14/1/6 Location: Phleum pratense is a monoporate grain with the exine verrucate. Porus is
Page 176 Family: Poaceae SEM images courtesy: Rachel Neville Phleum pratense Timothy Collection date: SEM date: 14/1/6 Location: Phleum pratense is a monoporate grain with the exine verrucate. Porus is
World Pollen and Spore Flora 23. Malvaceae Adams. P.p. Subfamilies: Grewioideae, Tilioideae, Brownlowioideae
 Grana ISSN: 0017-3134 (Print) 1651-2049 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/sgra20 World Pollen and Spore Flora 23. Malvaceae Adams. P.p. Subfamilies: Grewioideae, Tilioideae, Brownlowioideae
Grana ISSN: 0017-3134 (Print) 1651-2049 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/sgra20 World Pollen and Spore Flora 23. Malvaceae Adams. P.p. Subfamilies: Grewioideae, Tilioideae, Brownlowioideae
SEM SURVEY OF POLLEN IRANIAN SPECIES OF (SOLANACEAE) MORPHOLOGY IN HYOSCYAMUS L. M. Khatamsaz & E. Zangirian
 SEM SURVEY OF POLLEN IRANIAN SPECIES OF (SOLANACEAE) MORPHOLOGY IN HYOSCYAMUS L. M. Khatamsaz & E. Zangirian Khatamsaz, M. & E. Zangirian 199805 25: SEM survey of pollen morphology in Iranian species of
SEM SURVEY OF POLLEN IRANIAN SPECIES OF (SOLANACEAE) MORPHOLOGY IN HYOSCYAMUS L. M. Khatamsaz & E. Zangirian Khatamsaz, M. & E. Zangirian 199805 25: SEM survey of pollen morphology in Iranian species of
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
Chapter 38. Plant Reproduction 1 Animal vs. Plant life cycle Animal multicellular 2n Plant multicellular sporophyte 2n gametes 1n spores 1n unicellular gametes 1n multicellular gametophyte 1n 2 Alternation
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES
 USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
USEFUL FIELD CHARACTERISTICS OF REPRESENTATIVE FAMILIES Modified 2004 Magnoliaceae -trees & shrubs -flowers large and showy -floral parts numerous, separate, spirally arranged -elongate receptacle Lauraceae
POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF GENUS ERITRICHIUM SCHRAD. (BORAGINACEAE) FROM PAN HIMALAYA AND CHINA (POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF ERITRICHIUM SCHARD.
 Pak. J. Bot., 50(4): 1539-1550, 2018. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF GENUS ERITRICHIUM SCHRAD. (BORAGINACEAE) FROM PAN HIMALAYA AND CHINA (POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF ERITRICHIUM SCHARD.SPECIES) PARAS MAZARI#*, JIA-CHEN
Pak. J. Bot., 50(4): 1539-1550, 2018. POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF GENUS ERITRICHIUM SCHRAD. (BORAGINACEAE) FROM PAN HIMALAYA AND CHINA (POLLEN MORPHOLOGY OF ERITRICHIUM SCHARD.SPECIES) PARAS MAZARI#*, JIA-CHEN
KARYOTYPE ANALYSIS OF TWO SPECIES OF SALSOLA FROM YAZD, IRAN
 KARYOTYPE ANALYSIS OF TWO SPECIES OF SALSOLA FROM YAZD, IRAN Rahavi Mostafa 1, 2, Zarei Gholamreza *3, Yazdanbakhsh Zahra 4 1-Department of Botany, Fars Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University,
KARYOTYPE ANALYSIS OF TWO SPECIES OF SALSOLA FROM YAZD, IRAN Rahavi Mostafa 1, 2, Zarei Gholamreza *3, Yazdanbakhsh Zahra 4 1-Department of Botany, Fars Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University,
Cladistics, part 2. Reading for this topic: Worobey et al Contaminated polio vaccine theory refuted. Nature 428: 820.
 Cladistics, part 2 Reading for this topic: Worobey et al. 2004. Contaminated polio vaccine theory refuted. Nature 428: 820. [note: when requesting this, request a color copy] III. Uses of Cladograms A.
Cladistics, part 2 Reading for this topic: Worobey et al. 2004. Contaminated polio vaccine theory refuted. Nature 428: 820. [note: when requesting this, request a color copy] III. Uses of Cladograms A.
