Effectiveness of Clemastine Fumarate for Treatment of Rhinorrhea and Sneezing Associated with the Common Cold
|
|
|
- Evan Lindsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 824 Effectiveness of Clemastine Fumarate for Treatment of Rhinorrhea and Sneezing Associated with the Common Cold Ronald B. Turner, Steven J. Sperber, James V. Sorrentino, Robert R. O Connor, James Rogers, Amir Reza Batouli, and Jack M. Gwaltney, Jr. From the Departments of Pediatrics and Laboratory Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, South Carolina; the Department of Internal Medicine, Hackensack University Medical Center, Hackensack, the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey New Jersey Medical School, Newark, and Sandoz Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, New Jersey; HealthCare Products Development, Norwalk, Connecticut; Research and Data Services, Bloomingdale, Illinois; and the Department of Internal Medicine, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia Limited data support the use of first-generation antihistamines for treatment of the common cold. The purpose of this study was to test the effectiveness of clemastine fumarate, a first-generation antihistamine, for treatment of sneezing and rhinorrhea associated with naturally occurring common colds. Four hundred three subjects (202 clemastine fumarate recipients and 201 placebo recipients) who reported new onset (õ24 hours) of cold symptoms that included rhinorrhea or sneezing were studied. At baseline (day 1), the mean symptom-severity scores { SEM for the clemastine fumarate and placebo groups were not significantly different. The mean rhinorrhea-severity score { SEM was not different on day 2; however, on day 3, the mean rhinorrhea-severity score { SEM was 1.02 { 0.07 for the clemastine fumarate group and 1.39 { 0.07 for the placebo group (P õ.001). This treatment effect persisted on day 4. A significant effect on sneezing was noted on days 2 4. Sedation occurred in 14% of the clemastine fumarate treated subjects and 1.5% of the placebo-treated subjects (P õ.0001). Viral upper respiratory tract infection is the most common toms. Although these studies generally found no, or very modest, treatment effects, critical review suggests that the studies illness in humans. Although it is generally a mild illness, the common cold is responsible for more days of work and school did not have sufficient experimental power to conclusively absence than all other illnesses combined [1]. There is also an establish a lack of efficacy [4 7]. A decrease in both rhinorrhea enormous cost associated with the common cold for physician and sneezing following treatment with clemastine fumarate, a visits and the purchase of cough and/or cold remedies by consumers. The symptomatic treatment of cold symptoms currently study of experimental rhinovirus colds [8]. The purpose of this first-generation antihistamine, was reported in a recent large relies on decongestants for nasal congestion, antitussives for study was to determine the efficacy of clemastine fumarate for cough, analgesics for headache and myalgia, and antihistamines treatment of rhinorrhea and sneezing in subjects with natural for rhinorrhea and sneezing. These agents are available without colds. prescription and are widely used [2]. The paucity of data that support the use of these various agents for treatment of the common cold was the subject of a recent review [3]. Materials and Methods Rhinorrhea and sneezing are important components of the Subjects. Male or female subjects, 18 years of age and common cold. Several studies have been conducted to establish older, were recruited at three study sites: the University of the efficacy of antihistamines for the treatment of these symp- Virginia (Charlottesville), Hackensack University Medical Center (Hackensack, NJ), and the Medical University of South Carolina (Charleston). The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Boards at the respective institutions, and all Received 7 November 1996; revised 19 March subjects gave written informed consent for participation. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects who participated in this Surveillance phase. Subjects in the surveillance phase of study, and the guidelines for human experimentation of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and those of the institutions where the study the study were recruited by newspaper and posted advertise- was conducted were followed in the conduct of this study. ments and were paid for participation. Approximately 1,000 Financial support: This work was supported by Sandoz Pharmaceuticals subjects were kept under surveillance at the three study sites (currently Novartis Consumer Health), East Hanover, New Jersey. Reprints or correspondence: Dr. Ronald B. Turner, Department of Pediatrics, at all times from September 1994 to April As subjects Medical University of South Carolina, 171 Ashley Avenue, Charleston, South discontinued participation or were enrolled in the treatment Carolina study, additional subjects were recruited to maintain the sur- Clinical Infectious Diseases 1997;25: veillance population. All subjects recorded the presence or ab by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved /97/ $03.00 sence of headache, muscle ache, runny nose, sneezing, stopped-
2 CID 1997;25 (October) Antihistamine Treatment of the Common Cold 825 up nose, sore throat, scratchy throat, cough, hoarseness, postna- was again evaluated in person to review any adverse events sal drip, feverishness, chilliness, and feeling sick in a diary and to conduct a final evaluation of symptoms. that was completed daily and reviewed by study staff at 2- to Data analysis. The demographics and symptom severity at 3-week intervals. The subjects were instructed to contact the the baseline evaluation were compared to document the compastudy staff with the first occurrence of any of these common rability of the treatment groups. A one-way analysis of variance cold symptoms to determine eligibility for the treatment phase (ANOVA) was used to compare age across treatment groups. of the trial. Race, gender, sneezing severity, and rhinorrhea severity were Treatment phase. Subjects who reported runny nose and/ compared by using either the x 2 or Fisher s exact test. or sneezing, had at least two different symptoms, had recorded The primary analysis for assessment of the effectiveness of symptoms in their diary for no more than 1 day, and responded clemastine fumarate was defined, a priori, as comparison of rhi- Yes to the question Have you had the onset of a cold norrhea- and sneezing-severity scores for the treated and control within the last 24 hours? were eligible for enrollment in the subjects on days 2 and 3 of the study. Comparison of other treatment study. Females of childbearing age were required to common cold symptoms in the two groups was done as a secondary have a negative pregnancy test and use effective birth control. analysis. The treatment groups were compared on days 2 4 Subjects with underlying illnesses that might be exacerbated by assessment of the change from baseline in response to the by antihistamines or that might affect the assessment of common study medication. The analysis of these results was done with a cold symptoms were excluded from the study. Subjects three-way ANOVA with treatment arm and study site as the who were taking medications that might interact with antihistamines between-groups factors and the interactive symptom scores on or alter common cold symptoms were also excluded days 2 6 as the repeated-measures factor. For analysis of the day from the study. Subjects with a history of seasonal or perennial 2 timed symptom-severity scores, a similar ANOVA model was allergic rhinitis must have responded No to the question used except that the different times (4, 8, and 12 hours after Are you suffering from allergies at the present time?. the morning dose) served as the repeated-measures factor, and Study medications. Study subjects received either 1.34 mg treatment contrasts were conducted at these times. of clemastine fumarate or identically appearing placebo tablets. All available data, including data for subjects who subse- The active and placebo tablets were randomly distributed in quently withdrew from the study, were included in the analyses. sequentially numbered blister packs provided to each study To validate the assumptions underlying the ANOVA, the data site. Subjects were then given the blister packs in numerical were also analyzed with nonparametric tests. The significance order as they were admitted to the treatment phase of the study. levels were essentially unchanged, and only the results of the The initial dose of study medication was administered by a ANOVA are presented. study nurse on day 1 of the study between 8:00 A.M. and noon. A post hoc analysis of the change in sneezing severity from The second dose on day 1 was self-administered Ç12 hours baseline for those subjects who reported at least moderate after the first dose. On study days 2 5, subjects took their (symptom-severity score, 2) sneezing at the time of enroll- medication at Ç8:00 A.M. and 8:00 P.M. Compliance with the ment and the change in rhinorrhea severity from baseline in study medications was encouraged by the study staff during those subjects who had at least moderate rhinorrhea at the time daily telephone contact, and the empty blister packs were col- of enrollment was done by using the methods described above. lected to confirm that all medications had been taken. Subjects The statistical significance of differences in incidence of side were instructed to take no other common cold remedies while effects in the treatment and placebo groups was determined by receiving the study medication. using a one-sided Fisher s exact test. Study procedures. Subjects participating in the surveillance The sample size was based on previous data on experimental phase of the study who contacted the study center and reported colds [8] and produced an estimate of 331 subjects per group, common cold symptoms were evaluated in person. Eligibility with P a Å.05 and P b Å.8 for a two-tailed test. The study criteria were reviewed, and an assessment of baseline symptoms protocol provided for two blinded interim analyses and a final was done. A symptom-severity score of 0 4, correspond- analysis. The interim analyses were examined by an indepen- ing to absent, mild, moderate, severe, and very severe symptoms, dent data review panel after enrollment of approximately one- respectively, was assigned to each of the symptoms of third of the planned number of subjects and again after enrolldent sneezing, rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction, sore throat, cough, ment of approximately two-thirds of the planned number of headache, malaise, chilliness, and postnasal drip. Each morning subjects. Treatment differences were considered statistically on subsequent study days (days 2 5), subjects were contacted significant if the P level was.021 at the second interim by telephone and asked to evaluate the severity of these symp- analysis. This P a at the second analysis, with corresponding toms over the previous 24-hour period. Subjects were instructed prospective adjustments of the P a at the first interim analysis to take the morning dose of study medication after reporting and final evaluation, provided overall protection against type their symptoms. In addition, on day 2, each subject was asked I error at the P level of.05. to record the severity of symptoms 4, 8, and 12 hours after the The a priori criterion for the effectiveness of clemastine morning dose of study medication. On study day 6, each subject fumarate for treatment of common cold symptoms was that the
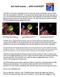
3 826 Turner et al. CID 1997;25 (October) Table 1. Demographic characteristics on 403 subjects at enrollment group, withdrew because of excessive drowsiness. Two subwho received either clemastine fumarate or placebo as treatment of jects in the treatment group withdrew when their symptoms rhinorrhea and sneezing associated with the common cold. resolved and one subject in the placebo group withdrew because of treatment failure. Fourteen subjects, eight in the treat- Clemastine fumarate Placebo ment group and six in the placebo group, withdrew for reasons recipients recipients unrelated to their illness or the study medication. Characteristic (n Å 202) (n Å 201) P value Effect of clemastine fumarate on sneezing. The mean symptom-severity scores { SEM for sneezing in the treatment Mean age { SEM* (y) 35.1 { { No. of whites: no. of blacks or and placebo groups at baseline were 1.17 { 0.06 and 1.32 { others 168:34 165: , respectively (P Å.39). On day 2, the mean sneezing- No. of females: no. of males 159:43 155:46.70 severity scores { SEM for the two groups were 0.74 { 0.06 Mean sneezing-severity score and 1.16 { 0.07, respectively (P õ.001). These decreases are { SEM 1.17 { { a mean change from baseline of 37% for the treatment group Mean rhinorrhea-severity score { SEM and 11% for the placebo group (P Å.007). The mean symptom { { severity scores { SEM for sneezing that were recorded 4, 8, * Analyzed by using a one-way analysis of variance. and 12 hours after the morning dose of medication on day 2 Analyzed by using a x 2 test. were also lower (P.002) for the treatment group. This Analyzed by using the Fisher s exact test. treatment effect persisted with statistically significant results on days 3 and 4 (figure 1). The 143 subjects (65 who received clemastine fumarate and 78 who received placebo) who remean change in symptom-severity score for rhinorrhea and ported sneezing of at least moderate severity at baseline resneezing would be greater in the treatment group than in the vealed similar findings. Treatment reduced sneezing severity placebo group on either day 2 or day 3 at a statistically signifiin this group of subjects 22.7%, 23.4%, and 21.5% relative to cant level. The study met the criterion for statistical significance the placebo group on days 2, 3, and 4, respectively. and was terminated after the second interim analysis. The data Effect of clemastine fumarate on rhinorrhea. The mean analysis revealed no difference in symptom severity or treatsymptom-severity scores { SEM for rhinorrhea at baseline ment effect by site of enrollment. were 1.73 { 0.07 and 1.65 { 0.07 for the clemastine fumarateand placebo-treated subjects, respectively (P Å.37). On day Results 2, the mean rhinorrhea-severity scores { SEM for the two groups were 1.46 { 0.07 and 1.58 { 0.08, respectively Four hundred three subjects were enrolled in the treatment (P Å.24). These decreases are a mean change from baseline phase of the study; 202 received clemastine fumarate, and 201 of 16% for the treatment group and 4% for the placebo group received placebo. Subject enrollment was similar at the three (P Å.1). The mean symptom-severity scores { SEM for rhi- study sites, with 164 subjects enrolled at the University of norrhea were lower for the clemastine fumarate treated subjects Virginia, 123 enrolled at the Medical University of South Carolina, 4, 8, and 12 hours after the morning dose on day 2; these and 116 enrolled at Hackensack University Medical Cen- differences were statistically significant at 8 hours (P Å.002) ter. Approximately 40% of the subjects who reported cold and 12 hours (P Å.01). symptoms while under surveillance met the enrollment criteria The effect of clemastine fumarate was more pronounced on for the treatment study. The most common reasons for not day 3, when the mean symptom-severity score { SEM for enrolling subjects were the presence of symptoms for ú24 rhinorrhea was 1.02 { 0.07 for the treatment group and 1.39 hours, a report of only a single symptom, or the absence of { 0.07 for the placebo group (P õ.001) and the mean change either rhinorrhea or sneezing as a symptom. from baseline was 42% for the treatment group and 16% for The demographic characteristics of the subjects enrolled in the placebo group (P õ.001). This treatment effect persisted the treatment and placebo groups were similar (table 1). There on day 4 (figure 2). A post hoc analysis of the 225 subjects were no significant differences in mean symptom-severity (120 clemastine fumarate recipients and 105 placebo recipients) scores between the two groups before treatment. There were who reported rhinorrhea of at least moderate severity when also no significant differences in demographic characteristics they were enrolled in the treatment phase of the study produced or baseline symptom severity at the study sites. The enrollment similar results. Treatment reduced rhinorrhea severity in this of subjects was evenly distributed throughout the study period group of subjects 21.2% and 17.7% relative to the placebo with the exception of February and March, when 182 (45%) group on days 3 and 4, respectively. of the subjects were enrolled. Effect of clemastine fumarate on secondary treatment vari- Twenty-three subjects, 16 who received clemastine fumarate ables. No treatment effect was seen on any of the secondary and seven who received placebo (P Å.08), withdrew from the variables with the exception of nasal congestion. On day 3, study before completion. Six subjects, all in the treatment compared with baseline severity scores, the mean nasal conges-
4 CID 1997;25 (October) Antihistamine Treatment of the Common Cold 827 tion severity score { SEM was improved for the treatment group (00.13 { 0.09) and was worse for the placebo group (/0.27 { 0.09) (P õ.001). Statistically significant differences in nasal congestion severity were not detected on the other days of observation. Side effects. The subjects were asked to report any potential side effects of the medication. In response, 56 (28%) of the clemastine fumarate recipients and 30 (15%) of the placebo recipients complained of adverse events. These adverse events were judged by the blinded investigators to be related to the treatment in 44 (22%) of the subjects in the clemastine fumarate group and 14 (7%) of the subjects in the placebo group (P õ.001). The difference was due mainly to sedation-related events (drowsiness, sleepiness, and tiredness) that occurred in 28 (14%) of the subjects who received clemastine fumarate and three (1.5%) of the subjects who received placebo Figure 2. Comparison of the effect of clemastine fumarate and placebo on rhinorrhea associated with the common cold. A. Mean rhinorrhea-severity score { SEM by day. Comparison of clemastine fumarate treated subjects with placebo-treated subjects revealed statistically significant differences (P õ.021) in mean rhinorrhea-severity scores { SEM on treatment days 3 and 4. B. Change in mean rhinorrhea-severity scores { SEM from baseline by day. Comparison of clemastine fumarate treated subjects with placebo-treated subjects revealed significantly greater changes (P õ.021) in mean rhinorrheaseverity scores { SEM from baseline for the clemastine fumarate treated subjects on treatment days 3 and 4. The results of this study demonstrate that clemastine fumarate is effective treatment for the nasal symptoms of rhinorrhea and sneezing in patients with naturally occurring common colds. Relative to placebo, clemastine fumarate reduced sneez- ing severity 26% and 22% and rhinorrhea 12% and 26% on Figure 1. Comparison of the effect of clemastine fumarate and placebo on sneezing associated with the common cold. A. Mean sneezing-severity score { SEM by day. Comparison of clemastine fumarate treated subjects with placebo-treated subjects revealed statistically significant differences (P õ.021) in mean sneezing-severity scores { SEM on treatment days 2 4. B. Change in mean sneezingseverity scores { SEM from baseline by day. Comparison of clemas- tine fumarate treated subjects with placebo-treated subjects revealed significantly greater changes (P õ.021) in mean sneezing-severity scores { SEM from baseline for the clemastine fumarate treated subjects on treatment days 2 and 4. (P õ.0001). The number of subjects who withdrew from the study because of sedation-related events was higher in the clemastine fumarate group than in the placebo group (six vs. zero, respectively; P Å.015). Most treatment-related adverse events were of either mild or moderate severity; however, 11 events in the clemastine fumarate group and six events in the placebo group were reported to be severe. Discussion
5 828 Turner et al. CID 1997;25 (October) days 2 and 3, respectively. Similar results were seen when the with the nonsedating antihistamines involved subjects with natural analysis was limited to those subjects who presented with at colds, and it would be interesting to study these drugs least moderate symptom severity. This result for natural colds under more controlled conditions with experimentally induced complements the results reported from a similar study of the colds. effect of clemastine fumarate on induced colds [8]. In that The hypothesis that the effect of the first-generation antihistamines study, clemastine fumarate was shown to reduce sneezing-severity on rhinorrhea is mediated by their anticholinergic acstudy, scores (50%), sneeze counts (57%), rhinorrhea scores tivity is also supported by the similarity of the effect of these (27%), and nasal mucus weights (35%). The difference in the drugs and that of ipratropium bromide, which has anticholinerapparent size of the treatment effect between the studies done gic but not antihistaminic activity [9, 10, 21]. Despite these in the natural setting and those done on induced colds appears data suggesting an anticholinergic mechanism of action, an to be a result of the less controlled conditions inherent in the antihistaminic effect cannot be ruled out. Allergic and nonallergic natural setting. Similar findings have been noted with other patients experimentally infected with rhinovirus have more therapeutic agents [9, 10]. sneezing and rhinorrhea in response to histamine challenge than Subjects were enrolled in the treatment phase of this study uninfected controls [22]. These results suggest that increased on the basis of the presence of symptoms typical of acute sensitivity to histamine normally present in the nasal secretions viral upper respiratory tract infection. Allergic rhinitis is also might result in the increase of rhinorrhea and sneezing associ- typically associated with sneezing and rhinorrhea, although ated with the common cold. If this is the case, it is plausible other components of the common cold symptom complex such that the effectiveness of antihistamines in the symptomatic as cough and sore throat are generally absent. In patients with treatment of the common cold may be due to their reduction allergic rhinitis, antihistamines reduce rhinorrhea by 20% 40% of the effect of normal histamine levels. compared with placebo [11 14]. The inadvertent inclusion of Although histamine and/or cholinergic mechanisms appear significant numbers of subjects with allergic rhinitis in our to play a role in rhinorrhea and sneezing, the constellation of study would have potentially affected our assessment of effi- symptoms that constitute the common cold syndrome appears cacy; we do not believe that this occurred in our study. to result from a complex pathogenesis that involves a number All patients enrolled in the treatment phase of the study of mediators as well as neurological mechanisms [23 26]. were under surveillance prior to enrollment and at the time of Thus, regardless of the mechanism of action, antihistamines enrollment were explicitly asked whether they were having a would not be expected to have a direct effect on the nasal cold. The surveillance phase of the study would be expected congestion, sore throat, headache, or cough associated with the to identify those subjects who had undiagnosed perennial rhini- cold. As a result, a detectable effect on a global symptom tis, and in a previous study on natural colds that used the assessment was not expected in this study and was not included surveillance model [15], subjects were found to be able to as an endpoint. accurately differentiate colds from allergic rhinitis. The risk The demonstration of a statistically significant effect of anti- that enrollment of patients with allergic rhinitis influenced the histamines for treatment of sneezing and rhinorrhea does not results of our study is further reduced by the fact that most address the issue of the clinical relevance of the observed effect. subjects were enrolled during the winter months, when the We believe that the results of this study were clinically meaningful. incidence of seasonal allergic rhinitis would be expected to The definition of a clinically significant endpoint was be low. established before the execution of the study and was met The mechanism of action of the therapeutic effect of the before enrollment of the entire calculated sample size. Also first-generation antihistamines on the common cold is not clear. relevant to assessment of the clinical significance of the results There is little information that addresses the mechanism of is the fact that the endpoints in this study were improvements action of the antihistamines for the treatment of sneezing. The in subjective symptom-severity scores. The determination of limited data regarding the mechanism of the effect on rhinorrhea clinical significance is more difficult when objective endpoints, suggest that the effect may be due to the anticholinergic such as sneezing counts or nasal mucus weights, are reported activity of these drugs. Histamine was not detectable in nasal without an assessment of whether the changes in these end- wash in two studies of the common cold [16, 17]. A more points are perceptible to the subjects. In this study, the symptom-severity recent study [18] found that histamine levels were increased scores directly assessed the subjects perception during colds in four of 15 subjects; however, there was no of their symptom burden. correlation between histamine levels and nasal or serum protein A final aid to assessment of the clinical relevance of these concentration in the nasal secretions. The suggestion that hista- results is a comparison to size of the treatment effect in other mine is not involved in the production of rhinorrhea is further illnesses or with other therapies that are generally accepted as supported by reports of the ineffectiveness of the nonsedating clinically meaningful. The magnitude of the treatment effects antihistamines (which have potent antihistamine activity but seen in this study is comparable with that previously reported lack significant anticholinergic activity) for treatment of rhinor- in studies of the treatment of allergic rhinitis with antihistamines rhea [19, 20]. These studies of treatment of the common cold [11 14]. The treatment of common cold symptoms with
6 CID 1997;25 (October) Antihistamine Treatment of the Common Cold 829 ipratropium bromide, recently approved by the U.S. Food and 3. Smith MBH, Feldman W. Over-the-counter cold medications. A critical review of clinical trials between 1950 and JAMA 1993;269: Drug Administration for treatment of rhinorrhea in patients with colds, also produces a similar reduction in rhinorrhea 4. Gaffey MJ, Gwaltney JM Jr, Sastre A, Dressler WE, Sorrentino JV, Hayseverity [9]. den FG. Intranasally and orally administered antihistamine treatment of Safety is an important consideration for therapies for the experimental rhinovirus colds. Am Rev Respir Dis 1987;136: common cold. Since the symptoms are relatively mild and selfmines 5. Howard JC Jr, Kantner TR, Lilienfield LS, et al. Effectiveness of antihista- in the symptomatic management of the common cold. JAMA limited and of short duration, cold remedies must be safe and 1979;242: free of serious side effects. In this study, the frequency of 6. Doyle WJ, McBride TP, Skoner DP, Maddern BR, Gwaltney JM Jr, Uhrin side effects, especially sedation-related effects, associated with M. A double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the effect of clemastine fumarate was higher than that associated with plaeustachian chlorpheniramine on the response of the nasal airway, middle ear and cebo. The frequency of sedation in this study was comparable tube to provocative rhinovirus challenge. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1988;7: with that reported in previous clinical trials with the first-gener- 7. Sakchainanont B, Ruangkanchanasetr S, Chantarojanasiri T, Tapasart C, ation antihistamines [12, 14, 27]. Suwanjutha S. Effectiveness of antihistamines in common cold. J Med The increased incidence of sedation-related side effects in Assoc Thai 1990;73: the clemastine fumarate treated subjects has potential implica- 8. Gwaltney JM Jr, Park J, Paul RA, Edelman DA, O Connor RR, Turner RB. Randomized controlled trial of clemastine fumarate for treatment tions for interpretation of the results of the study. The subjective of experimental rhinovirus colds. Clin Infect Dis 1996;22: assessment of symptoms of these mild and self-limited illnesses 9. Diamond L, Dockhorn RJ, Grossman J, et al. A dose-response study of is readily biased when subjects are unblinded by an inadequate the efficacy and safety of ipratropium bromide nasal spray in the treatment placebo control [28, 29]. In this study, subjects who developed of the common cold. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1995;95: drowsiness could have correctly concluded that they were retreatment of experimental rhinovirus infection. Antimicrob Agents Che- 10. Gaffey MJ, Hayden FG, Boyd JC, Gwaltney JM Jr. Ipratropium bromide ceiving the active treatment. Although sedation occurred sigmother 1988;32: nificantly more frequently in the clemastine fumarate treated 11. Mansmann HC Jr, Altman RA, Berman BA, et al. Efficacy and safety of subjects, only 14% reported this side effect. The subjects in cetirizine therapy in perennial allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy 1992;68: this study were not aware that rhinorrhea and sneezing were Kemp JP, Buckley CE, Gershwin ME, et al. Multicenter, double-blind, the primary variables of efficacy. The lack of an effect of placebo-controlled trial of terfenadine in seasonal allergic rhinitis and clemastine fumarate on the other common cold symptoms re- conjunctivitis. Ann Allergy 1985;54: corded as part of the symptom-severity score suggests that the 13. Falliers CJ, Brandon ML, Buchman E, et al. Double-blind comparison of observed effect on rhinorrhea and sneezing was not the result cetirizine and placebo in the treatment of seasonal rhinitis. Ann Allergy 1991;66: of bias introduced by unblinding of the subjects. 14. Berman BA. Perennial allergic rhinitis: clinical efficacy of a new antihista- The results of this study provide a basis for informed decimine. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1990;86(6 pt 2): sions about the use of antihistamines as therapy for the common 15. Williams RB III, Gwaltney JM Jr. Allergic rhinitis or virus cold? Nasal smear cold. It is likely that other antihistamines with anticholinergic eosinophilia in differential diagnosis. Ann Allergy 1972;30: activity similar to that of clemastine fumarate would have a 16. Eggleston PA, Hendley JO, Gwaltney JM Jr, Eggleston AW, Leavell BS Jr. Histamine in nasal secretions. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 1978; similar therapeutic effect. As with any common cold remedy, 57: the decision to use these agents rests with the patient and their 17. Naclerio RM, Proud D, Lichtenstein LM, et al. Kinins are generated during physician and must take into consideration the severity of the experimental rhinovirus colds. J Infect Dis 1988;157: target symptoms, the expected benefit, the potential occurrence 18. Igarashi Y, Skoner DP, Doyle WJ, White MV, Fireman P, Kaliner MA. Analysis of nasal secretions during experimental rhinovirus upper respiof side effects, and cost. ratory infections. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1993;92: Berkowitz RB, Tinkelman DG. Evaluation of oral terfenadine for treatment of the common cold. Ann Allergy 1991;67: Acknowledgments 20. Gaffey MJ, Kaiser DL, Hayden FG. Ineffectiveness of oral terfenadine in natural colds: evidence against histamine as a mediator of common cold The authors acknowledge the valuable contribution of the study symptoms. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1988;7: nurses for this study: Pat Beasley and Kathy Adams at the Univerblind, 21. Dockhorn R, Grossman J, Posner M, Zinny M, Tinkleman D. A double- sity of Virginia (Charlottesville), Genny Connelly and Polly Lanz placebo-controlled study of the safety and efficacy of ipratropium at the Medical University of South Carolina (Charleston), and bromide nasal spray versus placebo in patients with the common cold. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1992;90: Tammy Crupi, Carol Cianci, and Angela Casella at Hackensack 22. Doyle WJ, Skoner DP, Seroky JT, Fireman P, Gwaltney JM. Effect of University Medical Center (Hackensack, NJ). experimental rhinovirus 39 infection on the nasal response to histamine and cold air challenges in allergic and nonallergic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1994;93: References 23. Douglass JA, Dhami D, Gurr CE, et al. Influence of interleukin-8 challenge in the nasal mucosa in atopic and nonatopic subjects. Am J Respir Crit 1. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Vital and health statistics. Care Med 1994;150: Series 10. Hyattsville, MD: Government Printing Office, Proud D, Naclerio RM, Gwaltney JM, Hendley JO. Kinins are generated 2. Kogan MD, Pappas G, Yu SM, Kotelchuck M. Over-the-counter medica- in nasal secretions during natural rhinovirus colds. J Infect Dis 1990; tion use among US preschool-age children. JAMA 1994;272: :120 3.
7 830 Turner et al. CID 1997;25 (October) 25. Proud D, Gwaltney JM Jr, Hendley JO, Dinarello CA, Gillis S, Schleimer 27. Kaiser HB. H 1 -receptor antagonist treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. RP. Increased levels of interleukin-1 are detected in nasal secretions of J Allergy Clin Immunol 1990;86(6 pt 2): volunteers during experimental rhinovirus colds. J Infect Dis 1994;169: 28. Karlowski TR, Chalmers TC, Frenkel LD, Kapikian AZ, Lewis TL, Lynch JM. Ascorbic acid for the common cold. A prophylactic and therapeutic 26. Turner RB. Elaboration of interleukin 8 from fibroblast cells and human trial. JAMA 1975;231: nasal epithelium in response to rhinovirus challenge [abstract no B43]. 29. Farr BM, Conner EM, Betts RF, Oleske J, Minnefor A, Gwaltney JM Jr. In: Program and abstracts of the 34th Interscience Conference on Anti- Two randomized controlled trials of zinc gluconate lozenge therapy of microbial Agents and Chemotherapy (Orlando, FL). Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology, experimentally induced rhinovirus colds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1987;31:
Symptom Severity Patterns in Experimental Common Colds and Their Usefulness in Timing Onset of Illness in Natural Colds
 MAJOR ARTICLE Symptom Severity Patterns in Experimental Common Colds and Their Usefulness in Timing Onset of Illness in Natural Colds Jack M. Gwaltney, Jr., 1 J. Owen Hendley, 2 and James T. Patrie 3 Departments
MAJOR ARTICLE Symptom Severity Patterns in Experimental Common Colds and Their Usefulness in Timing Onset of Illness in Natural Colds Jack M. Gwaltney, Jr., 1 J. Owen Hendley, 2 and James T. Patrie 3 Departments
The role of histamine in allergic rhinitis
 The role of histamine in allergic rhinitis Robert M. Naclerio, MD Baltimore, Maryland Studies using nasal provocation followed by nasal lavage have demonstrated that histamine plays a n important role
The role of histamine in allergic rhinitis Robert M. Naclerio, MD Baltimore, Maryland Studies using nasal provocation followed by nasal lavage have demonstrated that histamine plays a n important role
The role of antihistamines in upper respiratory tract infections
 The role of antihistamines in upper respiratory tract infections Robert C. Welliver, MD Buffalo, N.Y. Antihistamines are commonly administered for URI, but their efficacy cannot be easily demonstrated.
The role of antihistamines in upper respiratory tract infections Robert C. Welliver, MD Buffalo, N.Y. Antihistamines are commonly administered for URI, but their efficacy cannot be easily demonstrated.
Treatment of Naturally Acquired Common Colds with Zinc: A Structured Review
 MAJOR ARTICLE Treatment of Naturally Acquired Common Colds with Zinc: A Structured Review Thomas J. Caruso, 1 Charles G. Prober, 2 and Jack M. Gwaltney, Jr. 3 1 Stanford University School of Medicine and
MAJOR ARTICLE Treatment of Naturally Acquired Common Colds with Zinc: A Structured Review Thomas J. Caruso, 1 Charles G. Prober, 2 and Jack M. Gwaltney, Jr. 3 1 Stanford University School of Medicine and
A dose-response study of the efficacy and safety of ipratropium bromide nasal spray in the treatment of the common cold
 A dose-response study of the efficacy and safety of ipratropium bromide nasal spray in the treatment of the common cold Louis Diamond, PhD, Robert J. Dockhorn, MD, b Jay Grossman, MD, c James C. Kisicki,
A dose-response study of the efficacy and safety of ipratropium bromide nasal spray in the treatment of the common cold Louis Diamond, PhD, Robert J. Dockhorn, MD, b Jay Grossman, MD, c James C. Kisicki,
A Winter Free of Cold Understanding the Common Cold and Flu. Camille Aizarani, MD Family Medicine Specialist
 A Winter Free of Cold Understanding the Common Cold and Flu Camille Aizarani, MD Family Medicine Specialist Outline Introduction Is it a cold or flu? The Common Cold Symptoms of Common Cold Tansmission
A Winter Free of Cold Understanding the Common Cold and Flu Camille Aizarani, MD Family Medicine Specialist Outline Introduction Is it a cold or flu? The Common Cold Symptoms of Common Cold Tansmission
Sponsor Novartis Consumer Health, SA. Generic Drug Name
 Sponsor Novartis Consumer Health, SA Generic Drug Name Xylometazoline Hydrochloride Trial Indication(s) For the symptomatic relief of nasal congestion due to colds, hayfever or other allergic rhinitis,
Sponsor Novartis Consumer Health, SA Generic Drug Name Xylometazoline Hydrochloride Trial Indication(s) For the symptomatic relief of nasal congestion due to colds, hayfever or other allergic rhinitis,
SYNOPSIS. A Multi-center, Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Parallel Group, Phase II Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of RHINOCORT
 Drug product: RHINOCORT AQUA Drug substance(s): Budesonide Edition No.: Final Study code: D5360C00703 Date: 8 November 2005 SYNOPSIS A Multi-center, Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Parallel
Drug product: RHINOCORT AQUA Drug substance(s): Budesonide Edition No.: Final Study code: D5360C00703 Date: 8 November 2005 SYNOPSIS A Multi-center, Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Parallel
13.2 Elements for a Public Summary
 13.2 Elements for a Public Summary 13.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The common cold is one of the most prevalent diseases in humans and is the most common condition for which family doctors are
13.2 Elements for a Public Summary 13.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The common cold is one of the most prevalent diseases in humans and is the most common condition for which family doctors are
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 2 Zinc Lozenges May Shorten the Duration of Colds: A Systematic Review
 Supplementary Material 2 The Open Respiratory Medicine Journal, 2011, Volume 5 i SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 2 Zinc Lozenges May Shorten the Duration of Colds: A Systematic Review Harri Hemilä Department of
Supplementary Material 2 The Open Respiratory Medicine Journal, 2011, Volume 5 i SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL 2 Zinc Lozenges May Shorten the Duration of Colds: A Systematic Review Harri Hemilä Department of
Respiratory System Virology
 Respiratory System Virology Common Cold: Rhinitis. A benign self limited syndrome caused by several families of viruses. The most frequent acute illness in industrialized world. Mild URT illness involving:
Respiratory System Virology Common Cold: Rhinitis. A benign self limited syndrome caused by several families of viruses. The most frequent acute illness in industrialized world. Mild URT illness involving:
BIBLIOGRAPHY: DONALD KAY RIKER, Ph.D.!
 BIBLIOGRAPHY: DONALD KAY RIKER, Ph.D. Publications & Presentations Berkowitz, B.B., Tinkelman, D.G., Geist, F.C., Witek, T.J. & Riker, D.K. 1992, "Evaluation of phenindamine tartrate in the treatment of
BIBLIOGRAPHY: DONALD KAY RIKER, Ph.D. Publications & Presentations Berkowitz, B.B., Tinkelman, D.G., Geist, F.C., Witek, T.J. & Riker, D.K. 1992, "Evaluation of phenindamine tartrate in the treatment of
BIBLIOGRAPHY: DONALD KAY RIKER, Ph.D. Publications & Presentations in Descending Chronological Order
 BIBLIOGRAPHY: DONALD KAY RIKER, Ph.D. Publications & Presentations in Descending Chronological Order Colds & Allergy Witek, T.J., Ramsey D.L., Carr A.N., Riker D.K. 2015, The Natural History of Community-Acquired
BIBLIOGRAPHY: DONALD KAY RIKER, Ph.D. Publications & Presentations in Descending Chronological Order Colds & Allergy Witek, T.J., Ramsey D.L., Carr A.N., Riker D.K. 2015, The Natural History of Community-Acquired
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults
 Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
A clinical trial of ipratropium bromide nasal spray in patients with perennial nonallergic rhinitis
 A clinical trial of ipratropium bromide nasal spray in patients with perennial nonallergic rhinitis Edwin A. Bronsky, MD, Howard Druce, MD, Steven R. Findlay, MD, Frank C. Hampel, MD, Harold Kaiser, MD,
A clinical trial of ipratropium bromide nasal spray in patients with perennial nonallergic rhinitis Edwin A. Bronsky, MD, Howard Druce, MD, Steven R. Findlay, MD, Frank C. Hampel, MD, Harold Kaiser, MD,
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS
 EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS PAUL H. RATNER 1 ; FRANK HAMPEL 2 ; AURORA BREAZNA 3 ; CYNTHIA F. CARACTA 3 ; SUDEESH
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS PAUL H. RATNER 1 ; FRANK HAMPEL 2 ; AURORA BREAZNA 3 ; CYNTHIA F. CARACTA 3 ; SUDEESH
British Journal of Nutrition
 (2011), 105, 118 122 doi:10.1017/s000711451000317x q The Authors 2010. The online version of this article is published within an Open Access environment subject to the conditions of the Creative Commons
(2011), 105, 118 122 doi:10.1017/s000711451000317x q The Authors 2010. The online version of this article is published within an Open Access environment subject to the conditions of the Creative Commons
Common cold and high-dose ipratropium bromide: Use of anticholinergic medication as an indicator of reflex-mediated hypersecretion*
 Rhinology, 35, 58 62, 1997 Common cold and high-dose ipratropium bromide: Use of anticholinergic medication as an indicator of reflex-mediated hypersecretion* Birgitte Østberg, Birgit Winther, Peter Borum,
Rhinology, 35, 58 62, 1997 Common cold and high-dose ipratropium bromide: Use of anticholinergic medication as an indicator of reflex-mediated hypersecretion* Birgitte Østberg, Birgit Winther, Peter Borum,
IASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2001) 19:
 IASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2001) 19: 171-175 A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, and Randomized Study of Loratadine (Clarityne) Syrup for the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis in Children
IASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2001) 19: 171-175 A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, and Randomized Study of Loratadine (Clarityne) Syrup for the Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis in Children
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS
 EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS GARY GROSS 1 ; FRANK HAMPEL 2 ; AURORA BREAZNA 3 ; CYNTHIA F. CARACTA 3 ; SUDEESH K.
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY FOR THE TREATMENT OF SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS GARY GROSS 1 ; FRANK HAMPEL 2 ; AURORA BREAZNA 3 ; CYNTHIA F. CARACTA 3 ; SUDEESH K.
We ll be our lifesaver. We ll get the flu vaccine.
 We ll be our lifesaver. We ll get the flu vaccine. The flu vaccine is a lifesaver for healthcare workers and the people they care for. www.immunisation.ie Flu Vaccine 2017-18 Healthcare workers prevent
We ll be our lifesaver. We ll get the flu vaccine. The flu vaccine is a lifesaver for healthcare workers and the people they care for. www.immunisation.ie Flu Vaccine 2017-18 Healthcare workers prevent
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
IT S A LIFESAVER EVERY YEAR FLU CAUSES SEVERE ILLNESS AND DEATH. GET YOUR FLU VACCINE NOW. IF YOU ARE: worker
 FLU VACCINE Information FOR Health care workers EVERY YEAR FLU CAUSES SEVERE ILLNESS AND DEATH. IF YOU ARE: A health care worker Over 65 Have a longterm illness Pregnant GET YOUR FLU VACCINE NOW. IT S
FLU VACCINE Information FOR Health care workers EVERY YEAR FLU CAUSES SEVERE ILLNESS AND DEATH. IF YOU ARE: A health care worker Over 65 Have a longterm illness Pregnant GET YOUR FLU VACCINE NOW. IT S
We ll be our lifesaver. We ll get the flu vaccine.
 We ll be our lifesaver. We ll get the flu vaccine. www.hse.ie/flu Flu Vaccine 2018-19 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and save lives every year by getting vaccinated with the flu vaccine.
We ll be our lifesaver. We ll get the flu vaccine. www.hse.ie/flu Flu Vaccine 2018-19 Healthcare workers prevent the spread of flu and save lives every year by getting vaccinated with the flu vaccine.
Cold, Flu, or Allergy?
 Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Introduction: A cold, the flu, and allergies all affect the respiratory system and have many similar symptoms. It can be difficult to tell whether someone has a cold, the flu, or
Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Introduction: A cold, the flu, and allergies all affect the respiratory system and have many similar symptoms. It can be difficult to tell whether someone has a cold, the flu, or
ALLERGIC RHINITIS Eve Kerr, M.D., M.P.H.
 - 63-3. ALLERGIC RHINITIS Eve Kerr, M.D., M.P.H. We conducted a MEDLINE search of review articles on rhinitis between the years of 1990-1995 and selected articles pertaining to allergic rhinitis. We also
- 63-3. ALLERGIC RHINITIS Eve Kerr, M.D., M.P.H. We conducted a MEDLINE search of review articles on rhinitis between the years of 1990-1995 and selected articles pertaining to allergic rhinitis. We also
Repeated antigen challenge in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis to house dust mites
 Allergology International (2003) 52: 207 212 Original Article Repeated antigen challenge in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis to house dust mites Minoru Gotoh, Kimihiro Okubo and Minoru Okuda Department
Allergology International (2003) 52: 207 212 Original Article Repeated antigen challenge in patients with perennial allergic rhinitis to house dust mites Minoru Gotoh, Kimihiro Okubo and Minoru Okuda Department
UCLA Nutrition Bytes. Title. Permalink. Journal ISSN. Author. Publication Date. Zinc Lozenges as a Cure for the Common Cold: Fact or Fiction?
 UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Zinc Lozenges as a Cure for the Common Cold: Fact or Fiction? Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/00m8p8h1 Journal Nutrition Bytes, 3(1) ISSN 1548-601X Author Smith, Matthew
UCLA Nutrition Bytes Title Zinc Lozenges as a Cure for the Common Cold: Fact or Fiction? Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/00m8p8h1 Journal Nutrition Bytes, 3(1) ISSN 1548-601X Author Smith, Matthew
How to spot allergies. What are allergies? What can your patients do about allergies? How allergies cause sinusitis. Module 5 Allergies
 Module 5 Allergies What are allergies? Allergies occur when a patient s immune system has a hypersensitive response to a substance that the body comes into contact with 1a. These substances, called allergens,
Module 5 Allergies What are allergies? Allergies occur when a patient s immune system has a hypersensitive response to a substance that the body comes into contact with 1a. These substances, called allergens,
Treatment Of Allergic Rhinitis
 Treatment Of Allergic Rhinitis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Treatment Of Allergic Rhinitis Galphimia Glauca, Histaminum Hydrochlo-ride, Cardiospermum Halicacabum and Amni Visnaga are effective homeopathic medicines
Treatment Of Allergic Rhinitis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Treatment Of Allergic Rhinitis Galphimia Glauca, Histaminum Hydrochlo-ride, Cardiospermum Halicacabum and Amni Visnaga are effective homeopathic medicines
COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT
 1 COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT P.O. Box 900 Morristown, NJ 07963 (973) 631-5485 (973) 631-5490 Fax www.morrishealth.org 2012-2013 Influenza Season FREQUENTLY
1 COUNTY OF MORRIS DEPARTMENT OF LAW & PUBLIC SAFETY OFFICE OF HEALTH MANAGEMENT P.O. Box 900 Morristown, NJ 07963 (973) 631-5485 (973) 631-5490 Fax www.morrishealth.org 2012-2013 Influenza Season FREQUENTLY
Middleton Chapter 42b (pages ): Allergic and Nonallergic Rhinitis Prepared by: Tammy Peng, MD
 FIT Board Review Corner November 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner November 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
Derriford Hospital. Peninsula Medical School
 Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis iti What is the Connection? Hisham Khalil Consultant ENT Surgeon Clinical Senior Lecturer, PMS Clinical Sub-Dean GP Evening 25 June 2008 Plymouth Derriford Hospital Peninsula
Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis iti What is the Connection? Hisham Khalil Consultant ENT Surgeon Clinical Senior Lecturer, PMS Clinical Sub-Dean GP Evening 25 June 2008 Plymouth Derriford Hospital Peninsula
Eli O. Meltzer, MD, a John M. Weiler, MD, b and Michael D. Widlitz, MD c
 Comparative outdoor study of the efficacy, onset and duration of action, and safety of cetirizine, Ioratadine, and placebo for seasonal allergic rhinitis Eli O. Meltzer, MD, a John M. Weiler, MD, b and
Comparative outdoor study of the efficacy, onset and duration of action, and safety of cetirizine, Ioratadine, and placebo for seasonal allergic rhinitis Eli O. Meltzer, MD, a John M. Weiler, MD, b and
ARIA. At-A-Glance Pocket Reference 2007
 ARIA_Glance_2007_8pg:ARIA_Glance_English 9/14/07 3:10 PM Page 1 ARIA At-A-Glance Pocket Reference 2007 1 st Edition NEW ARIA UPDATE BASED ON THE ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ITS IMPACT ON ASTHMA WORKSHOP REPORT
ARIA_Glance_2007_8pg:ARIA_Glance_English 9/14/07 3:10 PM Page 1 ARIA At-A-Glance Pocket Reference 2007 1 st Edition NEW ARIA UPDATE BASED ON THE ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ITS IMPACT ON ASTHMA WORKSHOP REPORT
Flu. is a killer. If you are at risk you should have your free flu vaccination every year.
 Flu is a killer. If you are at risk you should have your free flu vaccination every year. What is flu? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. It is not
Flu is a killer. If you are at risk you should have your free flu vaccination every year. What is flu? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. It is not
Viral-Induced Asthma:
 Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
COMMON UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN
 ١ ٢ COMMON UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr mostafavi SN Pediatric Infectious Disease Department Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Case 1 ٣ An 18 month old infant brought with high
١ ٢ COMMON UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr mostafavi SN Pediatric Infectious Disease Department Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Case 1 ٣ An 18 month old infant brought with high
lozenge/spray) within the previous 8 hours; a longer acting or slow-release analgesic during the previous 24 hours (e.g. piroxicam, naproxen); any
 Benzocaine: Primary: Chrubasik S, Beime B, Maora F. Efficacy of a benzocaine lozenge in the treatment of uncomplicated sore throat. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2012; 269:571-77. Extended Abstract: Study
Benzocaine: Primary: Chrubasik S, Beime B, Maora F. Efficacy of a benzocaine lozenge in the treatment of uncomplicated sore throat. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2012; 269:571-77. Extended Abstract: Study
We ll be our own lifesavers. We ll get the flu vaccine.
 We ll be our own lifesavers. We ll get the flu vaccine. The flu vaccine is a lifesaver for older people and those with long-term health conditions. www.immunisation.ie Flu Vaccine 2017-18 What is seasonal
We ll be our own lifesavers. We ll get the flu vaccine. The flu vaccine is a lifesaver for older people and those with long-term health conditions. www.immunisation.ie Flu Vaccine 2017-18 What is seasonal
University Hospital Pharmacy Update: June 1987 v. 2, no. 5
 Boston University OpenBU BU Publications http://open.bu.edu University Hospital Pharmacy Update 1987-06 University Hospital Pharmacy Update: June 1987 v. 2, no. 5 Boston University Medical Center The University
Boston University OpenBU BU Publications http://open.bu.edu University Hospital Pharmacy Update 1987-06 University Hospital Pharmacy Update: June 1987 v. 2, no. 5 Boston University Medical Center The University
Frequency and Natural History of Rhinovirus Infections in Adults during Autumn
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1997, p. 2864 2868 Vol. 35, No. 11 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Frequency and Natural History of Rhinovirus Infections
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1997, p. 2864 2868 Vol. 35, No. 11 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Frequency and Natural History of Rhinovirus Infections
PRINCIPAL MEDICATION OPTIONS FOR RHINITIS
 SEE INDICATED SUMMARY STATEMENT (SS#) DISCUSSION FOR SUPPORTING DATA ALLERGIC RHINITIS (AR): SEASONAL (SAR) AND PERENNIAL (PAR) MONOTHERAPY ORAL Antihistamines, oral (H1 receptor antagonists) (SS# 61-64)
SEE INDICATED SUMMARY STATEMENT (SS#) DISCUSSION FOR SUPPORTING DATA ALLERGIC RHINITIS (AR): SEASONAL (SAR) AND PERENNIAL (PAR) MONOTHERAPY ORAL Antihistamines, oral (H1 receptor antagonists) (SS# 61-64)
Nonallergic Rhinitis: Developing Drug Products for Treatment Guidance for Industry
 Nonallergic Rhinitis: Developing Drug Products for Treatment Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding
Nonallergic Rhinitis: Developing Drug Products for Treatment Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding
Respiratory Outbreaks Including Influenza. Module 6
 Respiratory Outbreaks Including Influenza Module 6 Learner Outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: Outline the case definition for a respiratory outbreak. Outline the case definition for
Respiratory Outbreaks Including Influenza Module 6 Learner Outcomes By the end of this module you will be able to: Outline the case definition for a respiratory outbreak. Outline the case definition for
PFIZER INC. GENERIC DRUG NAME and/or COMPOUND NUMBER: 5% Spironolactone Cream/ PF
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
Allergic Rhinitis. Dr. Sasan Dabiri. Otorhinolaryngologist Head & Neck Surgeon January 2011 Imam Hospital complex - Tehran
 In the name of God Dr. Sasan Dabiri Otorhinolaryngologist Head & Neck Surgeon January 2011 Imam Hospital complex - Tehran Rhinitis Allergic Rhinitis Infectious Rhinitis Nonallergic Rhinitis Neoplastic
In the name of God Dr. Sasan Dabiri Otorhinolaryngologist Head & Neck Surgeon January 2011 Imam Hospital complex - Tehran Rhinitis Allergic Rhinitis Infectious Rhinitis Nonallergic Rhinitis Neoplastic
The common cold: Current therapy and natural history
 The common cold: Current therapy and natural history Sheldon L. Spector, MD Los Angeles, Calif Despite its prevalence, the common cold is complicated and can be difficult to treat, even symptomatically.
The common cold: Current therapy and natural history Sheldon L. Spector, MD Los Angeles, Calif Despite its prevalence, the common cold is complicated and can be difficult to treat, even symptomatically.
allergic rhinitis 3C47E65837E D1B E Allergic Rhinitis 1 / 6
 Allergic Rhinitis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Allergic Rhinitis Allergic rhinitis is a diagnosis associated with a group of symptoms affecting the nose. These symptoms occur when you breathe in something you are
Allergic Rhinitis 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Allergic Rhinitis Allergic rhinitis is a diagnosis associated with a group of symptoms affecting the nose. These symptoms occur when you breathe in something you are
Is intranasal zinc effective and safe for the common cold? A systematic review and meta-analysis
 ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPERS Is intranasal zinc effective and safe for the common cold? A and meta-analysis Hubert D Cruze MBBS; 1 Bruce Arroll MBChB, PhD; 2 Tim Kenealy MBChB, PhD 3 1 General practitioner
ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC PAPERS Is intranasal zinc effective and safe for the common cold? A and meta-analysis Hubert D Cruze MBBS; 1 Bruce Arroll MBChB, PhD; 2 Tim Kenealy MBChB, PhD 3 1 General practitioner
Opinion 8 January 2014
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 8 January 2014 WYSTAMM 1 mg/ml, oral solution 120 ml vial with syringe for oral administration (CIP: 34009 222 560
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 8 January 2014 WYSTAMM 1 mg/ml, oral solution 120 ml vial with syringe for oral administration (CIP: 34009 222 560
An Update on Allergic Rhinitis. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital
 An Update on Allergic Rhinitis Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital Allergic Rhinitis Common condition with increasing prevalence
An Update on Allergic Rhinitis Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Department of Paediatrics University of Cape Town Red Cross Hospital Allergic Rhinitis Common condition with increasing prevalence
Cold, Flu, or Allergy?
 A monthly newsletter from the National Institutes of Health, part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services October 2014 Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Know the Difference for Best Treatment You re feeling
A monthly newsletter from the National Institutes of Health, part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services October 2014 Cold, Flu, or Allergy? Know the Difference for Best Treatment You re feeling
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults Guideline
 Member Groups Requesting Changes: Lakeview Clinic Marshfield Clinic Mayo Clinic South Lake Pediatrics Response Report for Review and Comment January 2013 Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness
Member Groups Requesting Changes: Lakeview Clinic Marshfield Clinic Mayo Clinic South Lake Pediatrics Response Report for Review and Comment January 2013 Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness
ODACTRA House Dust Mite (Dermatophagoides farina & Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus) allergen extract sublingual tablet
 pteronyssinus) allergen extract sublingual tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan.
pteronyssinus) allergen extract sublingual tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan.
C o u g h s n e e z i n g h o t f l a s r u n n y n o
 C o u g h s n e e z i n g h o t f l a s r u n n y n o WebMD Symptom Checker helps you find the most common medical conditions indicated by the symptoms Cough and Hot flashes and including Common cold,
C o u g h s n e e z i n g h o t f l a s r u n n y n o WebMD Symptom Checker helps you find the most common medical conditions indicated by the symptoms Cough and Hot flashes and including Common cold,
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 21 July 2010
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 21 July 2010 GRAZAX 75 000 SQ-T, oral lyophilisate B/30 (CIP: 378 011-6) B/100 (CIP code: 378 012-2) B/90 (CIP code:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 21 July 2010 GRAZAX 75 000 SQ-T, oral lyophilisate B/30 (CIP: 378 011-6) B/100 (CIP code: 378 012-2) B/90 (CIP code:
Influenza Vaccine and Healthcare Workers
 Influenza Vaccine and Healthcare Workers Dr Elyce McGovern Department Public Health HSE SE Influenza Viral infection- types A, B & C Asymptomatic Severe illness Death Illness more severe in elderly, young
Influenza Vaccine and Healthcare Workers Dr Elyce McGovern Department Public Health HSE SE Influenza Viral infection- types A, B & C Asymptomatic Severe illness Death Illness more severe in elderly, young
Calling Acute Bronchitis a Chest Cold May Improve Patient Satisfaction with Appropriate Antibiotic Use
 Calling Acute Bronchitis a Chest Cold May Improve Patient Satisfaction with Appropriate Antibiotic Use T. Grant Phillips, MD, and John Hickner, MD, MS Background: Overuse of antibiotics for acute respiratory
Calling Acute Bronchitis a Chest Cold May Improve Patient Satisfaction with Appropriate Antibiotic Use T. Grant Phillips, MD, and John Hickner, MD, MS Background: Overuse of antibiotics for acute respiratory
Research Institute. Disclosures: Drs Danzig, Yao, and Staudinger are employees of Schering-Plough
 A placebo-controlled study of the nasal decongestant effect of phenylephrine and pseudoephedrine in the Vienna Challenge Chamber Friedrich Horak, MD* ; Petra Zieglmayer, MD*; René Zieglmayer, DI ; and
A placebo-controlled study of the nasal decongestant effect of phenylephrine and pseudoephedrine in the Vienna Challenge Chamber Friedrich Horak, MD* ; Petra Zieglmayer, MD*; René Zieglmayer, DI ; and
SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS NASAL SYMPTOMS AND QUALITY OF LIFE WITH OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY
 SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS NASAL SYMPTOMS AND QUALITY OF LIFE WITH OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY GARY N. GROSS 1 ; GARY BERMAN 2 ; NIRAN J. AMAR 3 ; CYNTHIA F. CARACTA 4 ; SUDEESH K. TANTRY
SEASONAL ALLERGIC RHINITIS NASAL SYMPTOMS AND QUALITY OF LIFE WITH OLOPATADINE/MOMETASONE COMBINATION NASAL SPRAY GARY N. GROSS 1 ; GARY BERMAN 2 ; NIRAN J. AMAR 3 ; CYNTHIA F. CARACTA 4 ; SUDEESH K. TANTRY
Introduction. Methods. Results 12/7/2012. Immunotherapy in the Pediatric Population
 12/7/212 Introduction Immunotherapy in the Pediatric Population Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Allergen
12/7/212 Introduction Immunotherapy in the Pediatric Population Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Allergen
Allergy and inflammation
 and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
Nasonex vs claritin The Borg System is 100 % Retrievable & Reusable Nasonex vs claritin
 Nasonex vs claritin The Borg System is 100 % Nasonex vs claritin Claritin (loratadine) is a once-daily medicine for allergies that won't make you as sleepy as other medicines that work like it. Zyrtec
Nasonex vs claritin The Borg System is 100 % Nasonex vs claritin Claritin (loratadine) is a once-daily medicine for allergies that won't make you as sleepy as other medicines that work like it. Zyrtec
1
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Scratch and Sniff All About Allergies Doug Jones, MD Program Director, Family Medicine, DHMG What is an allergic reaction? The immune system identifies things that are foreign and protects
1 2 3 4 5 6 Scratch and Sniff All About Allergies Doug Jones, MD Program Director, Family Medicine, DHMG What is an allergic reaction? The immune system identifies things that are foreign and protects
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Support for Acetaminophen 1000 mg Over-the-Counter Dose:
 Support for Acetaminophen 1000 mg Over-the-Counter Dose: The Dental Impaction Pain Model and Efficacy and Safety Results from McNeil Randomized, Double-Blind, Single-Dose Study of Acetaminophen 1000 mg,
Support for Acetaminophen 1000 mg Over-the-Counter Dose: The Dental Impaction Pain Model and Efficacy and Safety Results from McNeil Randomized, Double-Blind, Single-Dose Study of Acetaminophen 1000 mg,
Flu. Flu is a killer. Flu vaccination
 Flu Flu is a killer Flu vaccination 2015-16 Why is flu serious? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. There are outbreaks every year, usually in winter.
Flu Flu is a killer Flu vaccination 2015-16 Why is flu serious? Flu spreads easily and can cause serious illnesses which need to be treated in hospital. There are outbreaks every year, usually in winter.
SYNOPSIS. The study results and synopsis are supplied for informational purposes only.
 SYNOPSIS INN : FEXOFENADINE Study number : PJPR0024 Study title : A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel study comparing the efficacy and safety of three dosage strengths of MDL 16,455A
SYNOPSIS INN : FEXOFENADINE Study number : PJPR0024 Study title : A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel study comparing the efficacy and safety of three dosage strengths of MDL 16,455A
I M VACCINATING FOR TWO NOW. IT S A LIFESAVER. Pregnant women and their babies are at risk from flu. Protect you and your baby - get your flu vaccine.
 I M VACCINATING FOR TWO NOW. Pregnant women and their babies are at risk from flu. Protect you and your baby - get your flu vaccine. IT S A LIFESAVER www.im munisation.ie For more information, talk to
I M VACCINATING FOR TWO NOW. Pregnant women and their babies are at risk from flu. Protect you and your baby - get your flu vaccine. IT S A LIFESAVER www.im munisation.ie For more information, talk to
Influenza Fact Sheet
 What is influenza? Influenza, also known as the flu, is caused by a virus that affects the nose, throat, bronchial airways, and lungs. There are two types of flu that affect humans, types A and B. Influenza
What is influenza? Influenza, also known as the flu, is caused by a virus that affects the nose, throat, bronchial airways, and lungs. There are two types of flu that affect humans, types A and B. Influenza
OTC Cough and Cold Products: Not For Infants and Children Under 2 Years of Age
 U.S. Food and Drug Administration Protecting and Promoting Your Health OTC Cough and Cold Products: Not For Infants and Children Under 2 Years of Age http://www.fda.gov/forconsumers/consumerupdates/ucm048682.htm
U.S. Food and Drug Administration Protecting and Promoting Your Health OTC Cough and Cold Products: Not For Infants and Children Under 2 Years of Age http://www.fda.gov/forconsumers/consumerupdates/ucm048682.htm
Does rhinitis. lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma
 Does rhinitis lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma For a better management of allergies in Europe Allergy
Does rhinitis lead to asthma? Does sneezing lead to wheezing? What allergic patients should know about the link between allergic rhinitis and asthma For a better management of allergies in Europe Allergy
090177e182b31c5d\0.1\Draft\Versioned On:16-Dec :12
 MAH: / Product: IBU/PSE Protocol Number EudraCT number (if applicable) Trial report number PMID / D.O.I. (if applicable) Date of trial Is the trial Trial design Background for conducting the trial Participants
MAH: / Product: IBU/PSE Protocol Number EudraCT number (if applicable) Trial report number PMID / D.O.I. (if applicable) Date of trial Is the trial Trial design Background for conducting the trial Participants
What is Allergic Rhinitis?
 What is Allergic Rhinitis? Hay fever is the common name for allergic rhinitis; rhino meaning of the nose and its meaning inflammatory. Thus, allergic rhinitis is defined as an inflammation of the nose
What is Allergic Rhinitis? Hay fever is the common name for allergic rhinitis; rhino meaning of the nose and its meaning inflammatory. Thus, allergic rhinitis is defined as an inflammation of the nose
Montelukast: a better alternative than antihistaminics in allergic rhinitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kaur G et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 017 Apr;():17- http://www.ijorl.com pissn -99 eissn -97 Original Research Article
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kaur G et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 017 Apr;():17- http://www.ijorl.com pissn -99 eissn -97 Original Research Article
Bristol Children s Vaccine Centre
 Bristol Children s Vaccine Centre Bristol Children s Vaccine Centre Level 6, UHB Education Centre, Upper Maudlin St., Bristol, BS2 8AE, UK Tel: +44 (0)117 342 0172, Fax: +44 (0)117 342 0209 E-mail: bcvc-study@bristol.ac.uk,
Bristol Children s Vaccine Centre Bristol Children s Vaccine Centre Level 6, UHB Education Centre, Upper Maudlin St., Bristol, BS2 8AE, UK Tel: +44 (0)117 342 0172, Fax: +44 (0)117 342 0209 E-mail: bcvc-study@bristol.ac.uk,
Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Ast. Rhinitis: A Risk Factor for Asthma? Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
 Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Ast Rhinitis: A Risk Factor for Asthma? Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Rhinitis and asthma SIT-SLIT Evidence A SIT-SLIT Evidence A? SIT Evidence? Rhinitis
Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Ast Rhinitis: A Risk Factor for Asthma? Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Rhinitis and asthma SIT-SLIT Evidence A SIT-SLIT Evidence A? SIT Evidence? Rhinitis
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) was first synthesized RESEARCH PAPERS
 PAIN MEDICINE Volume 4 Number 2 2003 RESEARCH PAPERS Effects of Acetylsalicylic Acid on Sore Throat Pain and Other Pain Symptoms Associated With Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection Ron Eccles, DSc,*
PAIN MEDICINE Volume 4 Number 2 2003 RESEARCH PAPERS Effects of Acetylsalicylic Acid on Sore Throat Pain and Other Pain Symptoms Associated With Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection Ron Eccles, DSc,*
As-needed use of fluticasone propionate nasal spray reduces symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis
 As-needed use of fluticasone propionate nasal spray reduces symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis Albert Jen, MD, Fuad Baroody, MD, Marcy detineo, BSN, Lauran Haney, BSc, Christopher Blair, BSc, and Robert
As-needed use of fluticasone propionate nasal spray reduces symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis Albert Jen, MD, Fuad Baroody, MD, Marcy detineo, BSN, Lauran Haney, BSc, Christopher Blair, BSc, and Robert
Pediatric Allergies in America: A Landmark Survey of Nasal Allergy Sufferers
 Pediatric Allergies in America: A Landmark Survey of Nasal Allergy Sufferers EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Prepared for Nycomed Conducted by Schulman, Ronca and Bucuvalas, Inc. May 8, 2007 Supported by: Study Design
Pediatric Allergies in America: A Landmark Survey of Nasal Allergy Sufferers EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Prepared for Nycomed Conducted by Schulman, Ronca and Bucuvalas, Inc. May 8, 2007 Supported by: Study Design
Influenza. What Is Influenza?
 Flu is usually a mild, but uncomfortable disease. You can treat it yourself by staying home and drinking plenty of fluids. What Is?, often just called the flu, is the most common disease in the world,
Flu is usually a mild, but uncomfortable disease. You can treat it yourself by staying home and drinking plenty of fluids. What Is?, often just called the flu, is the most common disease in the world,
Intranasal Recombinant Alfa-2b Interferon Treatment
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Feb. 1988, p. 224-230 0066-4804/88/020224-07$02.00/0 Copyright 0 1988, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 2 Intranasal Recombinant Alfa-2b Interferon
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Feb. 1988, p. 224-230 0066-4804/88/020224-07$02.00/0 Copyright 0 1988, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 2 Intranasal Recombinant Alfa-2b Interferon
Discover the connection
 Susan lives with daily rhinitis symptoms. Pollen House dust mites Timothy grass Underlying allergens affect rhinitis Discover the connection Specific IgE blood testing helps you identify allergic triggers,
Susan lives with daily rhinitis symptoms. Pollen House dust mites Timothy grass Underlying allergens affect rhinitis Discover the connection Specific IgE blood testing helps you identify allergic triggers,
2.0 Synopsis. Adalimumab M Clinical Study Report R&D/04/900. (For National Authority Use Only) Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume:
 2. Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Name of Active Ingredient: Title of Study: Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National Authority Use Only) Phase
2. Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Name of Active Ingredient: Title of Study: Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National Authority Use Only) Phase
2.0 Synopsis. ABT-711 M Clinical Study Report R&D/06/573. (For National Authority Use Only) to Part of Dossier: Volume:
 2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Depakote ER Name of Active Ingredient: Divalproex sodium (ABT-711) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National
2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Depakote ER Name of Active Ingredient: Divalproex sodium (ABT-711) Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National
Pharmacy Coverage Guidelines are subject to change as new information becomes available.
 RAGWITEK (Short Ragweed Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage Guideline
RAGWITEK (Short Ragweed Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage Guideline
Get well sooner... with Cold EEZE
 Get well sooner... with Cold EEZE Cold EEZE cold remedy is clinically proven to reduce the severity and duration of the common cold. But what exactly is Cold EEZE? It s a natural cold remedy made with
Get well sooner... with Cold EEZE Cold EEZE cold remedy is clinically proven to reduce the severity and duration of the common cold. But what exactly is Cold EEZE? It s a natural cold remedy made with
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 - 1 - - - 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم This sheet was made from record section 1 all information are included - Introduction Our respiratory tract is divided anatomically to upper (URT),middle and
- 1 - - - 1 P a g e بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم This sheet was made from record section 1 all information are included - Introduction Our respiratory tract is divided anatomically to upper (URT),middle and
INFLUENZA WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST THE FLU?
 INFLUENZA WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST THE FLU? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED! FLU VACCINE WHAT IS INFLUENZA? Seasonal influenza
INFLUENZA WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST THE FLU? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED! FLU VACCINE WHAT IS INFLUENZA? Seasonal influenza
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Telehealth Care
 American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Telehealth Care Educational Information for Telephone Triage Nurses Educational Information for Telephone Triage Nurses Volume 6 Number 2 April 2009 Editor Andrew
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Telehealth Care Educational Information for Telephone Triage Nurses Educational Information for Telephone Triage Nurses Volume 6 Number 2 April 2009 Editor Andrew
A Guide for Parents. Protect your child. What parents should know. Flu Information The Flu:
 Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
Flu Information The Flu: A Guide for Parents Influenza (also known as flu) is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs. Flu is different from
Fluzone High-Dose Vaccine and FIM12 Efficacy Trial Results
 Fluzone High-Dose Vaccine and FIM12 Efficacy Trial Results Corey A. Robertson, MD, MPH Director, Scientific and Medical Affairs, Sanofi Pasteur 1 Older Adults Suffer Disproportionately from Influenza-related
Fluzone High-Dose Vaccine and FIM12 Efficacy Trial Results Corey A. Robertson, MD, MPH Director, Scientific and Medical Affairs, Sanofi Pasteur 1 Older Adults Suffer Disproportionately from Influenza-related
Allergic Rhinitis. What Does Allergic Rhinitis Mean? Published on: 9 Jul 2014
 Published on: 9 Jul 2014 Allergic Rhinitis What Does Allergic Rhinitis Mean? Allergic rhinitis is the way doctors describe an allergy that affects the nose. What happens when you have an allergy? To understand
Published on: 9 Jul 2014 Allergic Rhinitis What Does Allergic Rhinitis Mean? Allergic rhinitis is the way doctors describe an allergy that affects the nose. What happens when you have an allergy? To understand
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Salmeterol (Serevent)
 Prior to administration: Assess for presence/history of chronic asthma, exercise induced asthma, acute asthma attacks, and acute upper airway obstruction. Assess respiratory rate and lung sounds, pulse
Prior to administration: Assess for presence/history of chronic asthma, exercise induced asthma, acute asthma attacks, and acute upper airway obstruction. Assess respiratory rate and lung sounds, pulse
10/6/2014. INFLUENZA: Why Should We Take The Vaccine? OUTLINE INFLUNZA VIRUS INFLUENZA VIRUS INFLUENZA VIRUS
 INFLUENZA: Why Should We Take The Vaccine? Baptist Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital J. Milton Gaviria, MD, FACP October 17, 2014 Homestead Hospital Mariners Hospital Baptist Cardiac
INFLUENZA: Why Should We Take The Vaccine? Baptist Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital J. Milton Gaviria, MD, FACP October 17, 2014 Homestead Hospital Mariners Hospital Baptist Cardiac
What are the causes of nasal congestion?
 Stuffy Noses Nasal congestion, stuffiness, or obstruction to nasal breathing is one of the oldest and most common human complaints. For some, it may only be a nuisance; for others, nasal congestion can
Stuffy Noses Nasal congestion, stuffiness, or obstruction to nasal breathing is one of the oldest and most common human complaints. For some, it may only be a nuisance; for others, nasal congestion can
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Superiority of an Intranasal Corticosteroid Compared With an Oral Antihistamine in the As-Needed Treatment of Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis Scott M. Kaszuba, MD; Fuad M. Baroody, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Superiority of an Intranasal Corticosteroid Compared With an Oral Antihistamine in the As-Needed Treatment of Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis Scott M. Kaszuba, MD; Fuad M. Baroody, MD;
