The relationship between vitamin D level and disease activity and focal erosion in rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Letitia Tucker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Annals of Medical Research DOI: /annalsmedres ;26(1):37-41 Original Article The relationship between vitamin D level and disease activity and focal erosion in rheumatoid arthritis Burhan Fatih Kocyigit 1, Ahmet Akyol 2, Tuba Tulay Koca 1 1 Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Kahramanmaras, Turkey 2 Nizip State Hospital Clinic of, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Gaziantep, Turkey Copyright 2019 by authors and Annals of Medical Research Publishing Inc. Abstract Aim: Bone loss,fragility,and fractures are well-described complications that affect quality of life, morbidity, and health care costs during the course of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Besides its well-known role in bone metabolism, vitamin D is also an important immune modulator, meant to affect the disease activity of rheumatic disorders. However, conflicting results have been demonstrated about the relationship between levels of vitamin D and disease activity in RA. Primary aim of was to compare vitamin D levels and Bone Mineral Density (BMD) values between RA and control groups.the secondary aim was to assess the correlations between vitamin D and disease activity and radiologic damage in RA. Material and Methods: A total of 41 RA patients and 40 healthy controls were included in this study. The patient and control groups were between the ages of 18 and 65. Disease activity score 28 (DAS-28) was used to determine the severity of disease.sharp/van der Heijde method was performed to evaluate the radiologic changes.dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) was performed to measure Bone Mineral Density (BMD).Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) method was used to measure serum D vitamin concentrations. Results: Vitamin D levels, the BMD-lumbar spine, BMD-femur total and BMD-femur neck values were significantly lower in the patient group (p = 0.012, p < 0.001, p < and p < 0.001). No significant correlations were detected between vitamin D levels and BMD values, disease activity, and radiologic damage scores (p > 0.05). DAS-28 was significantly and negatively correlated with BMD values (p < 0.05). Conclusion: Our study suggests that RA patients have lower vitamin D levels, BMD-lumbar spine, BMD-femur total and BMD-femur neck values. Higher disease activity increases bone loss in RA. Vitamin D levels and BMD values should be monitored for the risk of osteoporosis and fracture in RA. Keywords: Rheumatoid Arthritis; Vitamin D; Bone Mineral Density; Disease Activity; Radiologic Damage. INTRODUCTION Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune rheumatic disorder with inflammation, synovitis, peripheral symmetrical arthritis, synovial cell proliferation and extraarticular manifestations (1,2). The etiopathogenesis of RA is complex and environmental factors induce disease in genetically sensitive individuals (3). Osteopenia and osteoporosis (OP) are well known complications of rheumatic diseases, particularly RA.Three types of osteoporosis have been described in RA: focal bone erosion, periarticular OP, and generalized OP (4). Increased disease activity, immobilization due to the pain and treatment with glucocorticoids are the major risk factors increasing bone loss in RA (5). Proinflammatory cytokines induce erosions and periarticular OP by stimulating osteoclast formation and activation. Additionally, osteoclasts are more likely to have increased functional activity in generalized OP. Thus, appropriate control of disease activity may reduce bone loss and low energy fractures in RA (6). Vitamin D, defined as a prohormone, influences the immune system as well as bone metabolism. Vitamin D receptors that mediate immune system regulatory functions have been isolated from active dendritic cells, antigen presenting cells, T and B lymphocytes (7,8). Vitamin D decreases the production of proinflammatory mediators such as interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-17 and Received: Accepted: Available online: Corresponding Author: Burhan Fatih Kocyigit, Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University Faculty of Medicine Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Kahramanmaras, Turkey, bfk2701@hotmail.com 37
2 tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) by inhibiting the immunological response of Th1 cells (9). Therefore, the risk of infection and autoimmune disease is increasing in case of the insufficient or deficient levels of vitamin D (10). Although some studies have demonstrated the relationship between levels of vitamin D and disease activity in RA, this issue has not been fully clarified in the literature (11). Our primary aim was to compare vitamin D levels and bone mineral density (BMD) values between RA and control groups. The secondary aim was to assess the correlations between vitamin D and disease activity and radiologic damage in RA. MATERIAL and METHODS Study Design & Participants This study has a case control design. A total of 52 RA patients who applied to a physical medicine and rehabilitation polyclinic and 40 healthy controls were assessed. Patients fulfilled the RA classification criteria of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology/ European League against Rheumatism (12). The patient and control groups were between the ages of 18 and 65. Exclusion criteria include a history of metabolic bone diseases, recent fractures, malnutrition, neoplasia, chronic infection, inflammatory bowel disease, diabetes mellitus, thyroid/parathyroid dysfunction, liver/renal diseases, drug use affecting metabolism of bone such as bisphosphonates, vitamin D supplementations, pregnancy, and breast-feeding. After the application of the exclusion criteria, 41 RA patients were remained and two groups were formed according to medication use, patients receiving TNF-α inhibitor and those receiving Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug (DMARD) groups.patients in the TNF-α inhibitor group were using infliximab, golimumab, adalimumab, or etanercept. Patients in the DMARD group were using methotrexate, salazopyrine or hydroxychloroquine. Data Sources & Measurement Data were recorded including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), duration of disease.disease activity score 28 (DAS- 28) was used to determine the severity of disease. We used c reactive protein (CRP) concentrations for calculating DAS-28. Radiologic Assessment Sharp/van der Heijde method was performed to evaluate the radiologic changes.radiographs were scored by a radiologist who was blinded to the patients identity. Joint space narrowing and erosion were determined and scored using the radiographs of hands and feet (13). Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) (HOLOGIC 4500 A) was performed to measure BMD in the lumbar spine (L1 - L4 anterior - posterior), total femur, and femur neck. The results are expressed as g/cm 2. Radiologic assessments were performed at the same day of the physical examination. After the physical examination, blood samples were obtained from participants between AM. Standard laboratory techniques were used to measure CRP (Cobas Integra 400 plus, Rotkreuz, Switzerland) and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (EventusVacuPlus ESR 100, Ankara, Turkey) concentrations.enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) method was used to measure serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) levels and results expressed in ng / ml (normal value 30 ng / ml). Ethical Consideration This study has been approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University. Statistical Analysis Statistical Package for Social Sciences for Windows version 20.0 package program (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used to perform statistical analysis.mean ± standard deviation, median (minimum-maximum), and number were used for the expression of results. Distribution of data was evaluated using the Shapiro- Wilk test. Determination the differences in the categorical variables was performed using the Chi-Square test. Comparison of independent groups was performed using the independent sample t test or Mann-Whitney U test according to the distribution of data. Spearman s rho test was performed for the correlation analysis. The statistical significance level was accepted as p < RESULTS In our study, 41 RA patients (31 females, 10 males) and 40 healthy controls (24 females, 16 males) were included. The mean ages in the patient and control groups were ± and ± years.age, sex and BMI were not significantly different between the patient and control groups (p > 0.05) (Table 1). Table 1. Demographic data of patient and control groups Patient Group (n = 41) Control Group (n = 40) Age (years) ± ± Sex Female (n) Male (n) P BMI (kg/m 2 ) ± ± n: number; BMI: body mass index Vitamin D level, the BMD-lumbar spine, BMD-femur total and BMD-femur neck values were significantly lower in the patient group (p = 0.012, p < 0.001, p < and p < 0.001) (Table 2). No significant differences were detected between the TNF-α inhibitor (n = 17) and DMARD (n = 24) groups in terms of 25-OHD, ESR and CRP concentrations, BMDlumbar spine, total BMD-femur and BMD - femur neck values (p> 0.05). No significant correlations were detected between 25- OHD concentrations and symptom duration,sharp/van 38
3 der Heijde scores, DAS-28, ESR, CRP,BMD-lumbar spine, BMD-femur total and BMD-femur neck in the patient group (p > 0.05) (Table 3). No significant correlations were detected between ESR, CRP and BMD values (p > 0.05). DAS-28 was significantly and negatively correlated with BMD-lumbar spine, BMDfemur total and BMD-femur neck values (r = , p = 0.001; r = , p = and r = , p = 0.008, respectively). Table 2. Comparison of bone mineral density and laboratory parameters between patient and control groups Patient Group (n = 41) Control Group (n = 40) median min-max Median min-max Vitamin D (ng/ml) BMD lumbar spine (g/ cm 2 ) < BMD femur total (g/ cm 2 ) < BMD femur neck (g / cm 2 ) < ESR (mm / h) < CRP (mg / L) n: number; min: minimum; max: maximum; BMD: bone mineral density; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C - reactive protein Table 3. Correlation analysis of clinic and laboratory parameters with 25-hydroxyvitamin D Symptom duration Sharp/van der Heijde- narrowing hand score Sharp/van der Heijde- narrowing foot score Sharp/van der Heijde- total narrowing score Sharp/van der Heijde- erosion hand score Sharp/van der Heijde- erosion foot score Sharp/van der Heijde- total erosion score Sharp/van der Heijde-total score DAS ESR (mm/h) CRP (mg/l) BMD - lumbar spine (g/cm 2 ) BMD - femur total (g/cm 2 ) BMD - femur neck (g/cm 2 ) DAS-28: disease activity score 28; ESR:erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C - reactive protein; BMD: bone mineral density DISCUSSION This study suggests that levels of 25-OHD were significantly lower in RA patients. No significant correlations were detected between 25-OHD concentrations and disease activity, radiologic changes and BMD values in RA patients.vitamin D is a secosteroid hormone and has rho P p substantial skeletal and non-skeletal biologic functions. Vitamin D deficiency causes a decrease in intestinal absorption of calcium and phosphorus. In the early period of vitamin D deficiency, hypophosphatemia is more prominent than hypocalcemia. If vitamin D deficiency persists, hypocalcemia develops and triggers secondary hyperparathyroidism that will cause phosphaturia. Vitamin deficiency induces the levels of alkaline phosphatase and causes variations in levels bone turnover markers (14). Immune cells including macrophages, T and B lymphocytes, and dendritic cells have been shown to express vitamin D receptors (15). Vitamin D influences immune responses via innate and adaptive immune systems. Vitamin D suppresses immune globulin production, B cell differentiation and T cell proliferation. Levels of proinflammatory cytokines are decreased and the immune activity of macrophages is inhibited. Additionally, vitamin D increases the anti-inflammatory response by activating T helper-2 and regulator T cell responses (16,17). Conflicting results have been demonstrated about the vitamin D and RA link. Similar to our results; Baykal et al. (18), Rossini et al. (19), Kostoglou-Athanassiou et al. (20) and Kroger et al. (21) reported lower concentrations of vitamin D in RA patients. In contrast; Nielen et al. (22), Cutolo et al. (23) and Turhanoglu et al. (24) reported no difference in vitamin D concentrations between RA patients and controls. In agreement with our results, no inverse correlations were found between vitamin D concentrations and disease activity in RA patients (25,26,27). On the contrary, significant inverse correlations have been reported between vitamin D concentrations and disease activity (23,28,29). There may be several explanations for the differences in the above mentioned studies. Variations in sample size, study population, ethnicity and season may cause these discrepancies. Additionally, severity of disease, vitamin D supplementation use, dietary vitamin D intake, disease duration, physical activity level and medication use may also affect the results. In our study, BMD-lumbar spine, BMD-femur total and BMD-femur neck values were significantly lower in RA patients. Bone loss and increased fracture risk have been demonstrated in RA patients (30). Kröger et al. (31) and Ladder et al. (32) reported lower BMD values in RA patients. Causes of bone loss in RA include joint inflammation, disease activity, reduced mobility, and steroid use (33). DAS-28, disease activity parameter, was significantly and inversely correlated with BMD values in this study. Shibuya et al. (34) reported that disease activity, duration of disease and BMI were associated with BMD in RA patients. Bone loss was predominantly observed in peripheral joints in this study. Early development of osteoporosis at the peripheral joints suggests that inflammation, cytokines and synovitis mainly affect bone loss in RA patients. In another study, negative correlations have been demonstrated between disease activity and BMD values (35). On the contrary, Sivas et al. (36) reported 39
4 no significant correlations between disease activity and lumbar and femur neck BMD values. Cytokines have direct and indirect effects on peripheral joints and systemic bones and enhances osteoclastogenesis in the tissue. Additionally, cytokines play a key regulatory role on RANKL and osteoprotegerin which are the important mediators for osteoclast differentiation and activation.cytokines activate osteoclastogenesis via RANKL which controls the activation, differentiation and survival of osteoclasts (37). Studies on normal populations have shown that low levels of inflammatory markers prevent bone loss and resorption (38). Another explanation for the inflammation and osteoporosis link might be that higher disease activity decreases physical activity and muscle strength. This condition causes a decrease in the loading on the bones and leads to bone loss in RA. In our study, BMD values were not found to be significantly different between the TNF-α inhibitor and DMARD groups. These results may be due to the lack of differences in vitamin D, ESR, and CRP levels between the groups. This study has some limitations. The sample size is small. The physical activity level, dietary habits and sunlight exposure frequencies were not assessed. This study has a cross-sectional design and patients were not followed-up prospectively. We did not question previous steroid use. RF or anti CCP levels were not evaluated in all RA patients. Finally; calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, parathormone and other bone turnover markers were not measured. CONCLUSION In conclusion, we found lower vitamin D concentrations in RA patients. Vitamin D concentrations were not associated with radiologic damage, disease activity parameters and BMD values. BMD values were lower than the healthy controls and disease activity was negatively correlated with BMD values. Disease activity and inflammation increase bone loss and the reduction of BMD starts in the early phase of RA; continues throughout the disease. Therefore, patients whose disease activity is severe and whose inflammation cannot be suppressed despite treatment should be monitored for the risk of osteoporosis and fracture. Vitamin D is a potential factor in the etiopathogenesis of RA. We believe that vitamin D levels should also be monitored and should be replaced if they are found to be deficient in RA patients. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interest. Financial Disclosure: There are no financial supports Ethical approval: This study has been approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Kahramanmaras Sutcu Imam University. Burhan Fatih Kocyigit ORCID: Ahmet Akyol ORCID: Tuba Tulay Koca ORCID: X REFERENCES 1. Cojocaru M, Cojocaru IM, Silosi I, et al. Extra-articular Manifestations in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Maedica (Buchar) 2010;5: Khurana R, Berney SM. Clinical aspects of rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology 2005;12: Malmström V, Catrina AI, Klareskog L. The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: from triggering to targeting.nat Rev Immunol 2017;17: Güler-Yüksel M, Bijsterbosch J, Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, et al. Bone mineral density in patients with recently diagnosed, active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66: Haugeberg G, Orstavik RE, Uhlig T, Bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a population-based cohort of 366 patients followed up for two years. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46: Colin EM, Asmawidjaja PS, van Hamburg JP, et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates Th17 polarization and interleukin-22 expression by memory T cells from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62: Tetlow LC, Smith SJ, Mawer EB, et al. Vitamin D receptors in the rheumatoid lesion: Expression by chondrocytes, macrophages, and synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 1999;58: Arnson Y, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y. Vitamin D and autoimmunity: new aetiological and therapeutic considerations. Ann Rheum Dis 2007;66: Yang J, Liu L, Zhang Q, et al. Effect of vitamin D on the recurrence rate of rheumatoid arthritis. ExpTher Med 2015;10: Cutolo M. Vitamin D or hormone D deficiency in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, including undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res Ther 2008;10: Rossini M, Bagnato G, Frediani B, et al. Relationship of focal erosions, bone mineral density, and parathyroid hormone in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2011;38: Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62: van der Heijde D. How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. J Rheumatol 2000;27: Kennel KA, Drake MT, Hurley DL. Vitamin D deficiency in adults: when to test and how to treat. Mayo Clin Proc 2010;85: Cutillos Marco E, Morales-Suarez-Varela M, Marquina-Vila A, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in patients with cutaneous lupus erythematosus in a Mediterranean region. Lupus 2010;19: Lequerre T, Richez C. Pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rev Prat 2012;62: Holick MF. Vitamin D: Extraskeletal health. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2012;38: Baykal T, Senel K, Alp F, et al. Is there an association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis? Bratisl Lek Listy 2012;113: Rossini M, Maddali Bongi S, La Montagna G, et al. Vitamin D deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence, determinants and associations with disease activity and disability. Arthritis Res Ther 2010;12:R Kostoglou-Athanassiou I, Athanassiou P, Lyraki A, Vitamin D and rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab 2012;3: Kroger H, Penttila IM, Alhava EM. Low serum vitamin D metabolities in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J 40
5 Rheumatol 1993;22: Nielen MM, van Schaardenburg D, Lems WF, et al. Vitamin D deficiency does not increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: comment on the article by Merlino et al. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54: Cutolo M, Otsa K, Laas K, et al. Circannual vitamin D serum levels and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: Northern versus Southern Europe. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2006;24: Turhanoglu AD, Güler H, Yönden Z, et al. The relationship between vitamin D and disease activity and functional health status in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 2011;31: Gopinath K, Danda D. Supplementation of 1,25dihydroxy vitamin D3 in patients with treatment naive early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised controlled trial. Int J Rheum Dis 2011;14: Baker JF, Baker DG, Toedter G, et al. Associations between vitamin D, disease activity, and clinical response to therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2012;30: Haga HJ, Schmedes A, Naderi Y, et al. Severe deficiency of 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) (25-OH-D (3)) is associated with high disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. ClinRheumatol 2013;32: Song GG, Bae SC, Lee YH. Association between vitamin D intake and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 2012;31: Craig SM, Yu F, Curtis JR, et al. Vitamin D status and its associations with disease activity and severity in African Americans with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2010;37: van Staa TP1, Geusens P, Bijlsma JW, et al. Clinical assessment of the long-term risk of fracture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54: Kröger H, Honkanen R, Saarikoski S, et al. Decreased axial bone mineral density in perimenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis-a population based study. Ann Rheum Dis 1994;53: Ladder MC, de Jong Z, Kostense PJ, et al. Bone mineral density in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: relation between disease severity and low bone mineral density. Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63: Laan RF, van Riel PL, van de Putte LB. Bone mass in patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1992;51: Shibuya K, Hagino H, Morio Y, et al. Cross-sectional and longitudinal study of osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 2002;21: Peng J, Gong Y, Zhang Y, et al. Bone Mineral Density in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and 4-Year Follow-up Results. J Clin Rheumatol 2016;22: Sivas F, Barça N, Önder M, et al. The relation between joint erosion and generalized osteoporosis and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 2006;26: Braun T, Zwerina J. Positive regulators of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2011;13: Ding C, Parameswaran V, Udayan R, et al. Circulating levels of inflammatory markers predict change in bone mineral density and resorption in older adults: a longitudinal study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:
Research Article Association between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 913804, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/913804 Research Article Association between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 913804, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/913804 Research Article Association between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Description of Study Protocol. Data Collection Summary
 AND Evidence Analysis Worksheet Citation Kostoglou-athanassiou I, AthanassiouP, Lyraki A, Raftakis I, Antoniadis C. Vitamin D and rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 3(6):181-7. Study
AND Evidence Analysis Worksheet Citation Kostoglou-athanassiou I, AthanassiouP, Lyraki A, Raftakis I, Antoniadis C. Vitamin D and rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 3(6):181-7. Study
Vitamin D levels in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Is it related to disease activity?
 Original Article Vitamin D levels in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Is it related to disease activity? Burhan Fatih Kocyigit 1, Ahmet Akyol 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is an
Original Article Vitamin D levels in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: Is it related to disease activity? Burhan Fatih Kocyigit 1, Ahmet Akyol 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is an
Bull. of Egyp. Soc. Physiol. Sci. Serum Vitamin D levels in Rheumatoid arthritis and Relationship with disease activity
 Bull. Egypt. Soc. Physiol. Sci. 38(2), 175-184 Bull. of Egyp. Soc. Physiol. Sci. (Official Journal of Egyptian Society for Physiological Sciences) (pissn: 1110-0842; eissn: 2356-9514) Serum Vitamin D levels
Bull. Egypt. Soc. Physiol. Sci. 38(2), 175-184 Bull. of Egyp. Soc. Physiol. Sci. (Official Journal of Egyptian Society for Physiological Sciences) (pissn: 1110-0842; eissn: 2356-9514) Serum Vitamin D levels
Study of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and its Corelation with Severity of the Disease
 26 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and its Corelation with Severity of the Disease Liyakat Ali Gauri 1, Qadir Fatima 2, Sharanbasu Diggi 3, Asim
26 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and its Corelation with Severity of the Disease Liyakat Ali Gauri 1, Qadir Fatima 2, Sharanbasu Diggi 3, Asim
Role of vitamin D supplementation in improving disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: An exploratory study
 International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2017; 20: 825 831 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of vitamin D supplementation in improving disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: An exploratory study S. CHANDRASHEKARA
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2017; 20: 825 831 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of vitamin D supplementation in improving disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: An exploratory study S. CHANDRASHEKARA
Rheumatoid arthritis
 Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Rheumatoid arthritis 1 Definition Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common inflammatory disorders affecting the population worldwide. It is a systemic inflammatory disease which affects not only
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
Original Article Comparison between ESR and C-Reactive Protein(CRP) as a Marker of Disease activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Ali M.E. Yousef 1, Fatemah A. Elshabacy 2, Sherry K. Abdelrahman
Associations between vitamin D, disease activity, and clinical response to therapy in rheumatoid arthritis
 Associations between vitamin D, disease activity, and clinical response to therapy in rheumatoid arthritis J.F. Baker 1, D.G. Baker 2, G. Toedter 6, J. Shults 3, J.M. Von Feldt 4, M.B. Leonard 5,3 1 Department
Associations between vitamin D, disease activity, and clinical response to therapy in rheumatoid arthritis J.F. Baker 1, D.G. Baker 2, G. Toedter 6, J. Shults 3, J.M. Von Feldt 4, M.B. Leonard 5,3 1 Department
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Impact of obesity on rheumatoid arthritis: Relation with disease activity, joint damage, functional impairment and response to therapy
 International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology Impact of obesity on rheumatoid arthritis: Relation with disease activity, joint damage, functional impairment and response to therapy Background and Aim
International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology Impact of obesity on rheumatoid arthritis: Relation with disease activity, joint damage, functional impairment and response to therapy Background and Aim
Bone Mineral Density Changes in Patients with Recent-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Clinical Medicine Insights: Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Disorders Original Research Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Bone Mineral Density
Clinical Medicine Insights: Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Disorders Original Research Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Bone Mineral Density
Michael Ziegelasch 1*, Kristina Forslind 2,3, Thomas Skogh 1, Katrine Riklund 4, Alf Kastbom 1 and Ewa Berglin 5
 Ziegelasch et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:195 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1403-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Decrease in bone mineral density during three months after diagnosis of early rheumatoid
Ziegelasch et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:195 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1403-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Decrease in bone mineral density during three months after diagnosis of early rheumatoid
Association between vitamin D deficiency and disease activity in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56: 626-631 Original Association between vitamin D deficiency and disease activity in juvenile idiopathic arthritis Elif Çomak 1, Çağla Serpil Doğan 1, Arife Uslu-Gökçeoğlu
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56: 626-631 Original Association between vitamin D deficiency and disease activity in juvenile idiopathic arthritis Elif Çomak 1, Çağla Serpil Doğan 1, Arife Uslu-Gökçeoğlu
ABSTRACT. increasing anti-ccp2 antibody concentrations. Associations between BMD and anti-ccp2 antibody status and titer were
 Adv Ther (2018) 35:232 242 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-017-0657-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH Association of Low Bone Mineral Density with Anti- Citrullinated Protein Antibody Positivity and Disease Activity
Adv Ther (2018) 35:232 242 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-017-0657-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH Association of Low Bone Mineral Density with Anti- Citrullinated Protein Antibody Positivity and Disease Activity
Skeletal Manifestations
 Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
J. van Aken* H. van Dongen* S. le Cessie F.C. Breedveld T.W.J. Huizinga. * both authors contributed equally
 CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
CHAPTER Comparison of long term outcome of patients with rheumatoid arthritis presenting with undifferentiated arthritis or with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study J. van Aken* H. van
Vitamin D: Is it a superhero??
 Vitamin D: Is it a superhero?? Dr. Ashraf Abdel Basset Bakr Prof. of Pediatrics 1 2 History of vitamin D discovery Sources of vitamin D and its metabolism 13 Actions of vitamin D 4 Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D: Is it a superhero?? Dr. Ashraf Abdel Basset Bakr Prof. of Pediatrics 1 2 History of vitamin D discovery Sources of vitamin D and its metabolism 13 Actions of vitamin D 4 Vitamin D deficiency
Correlation between Thyroid Function and Bone Mineral Density in Elderly People
 IBBJ Spring 2016, Vol 2, No 2 Original Article Correlation between Thyroid Function and Bone Mineral Density in Elderly People Ali Mirzapour 1, Fatemeh Shahnavazi 2, Ahmad Karkhah 3, Seyed Reza Hosseini
IBBJ Spring 2016, Vol 2, No 2 Original Article Correlation between Thyroid Function and Bone Mineral Density in Elderly People Ali Mirzapour 1, Fatemeh Shahnavazi 2, Ahmad Karkhah 3, Seyed Reza Hosseini
I mmunosuppressive pulse treatment with intravenous
 940 EXTENDED REPORT Bone loss in patients treated with pulses of methylprednisolone is not negligible: a short term prospective observational study G Haugeberg, B Griffiths, K B Sokoll, P Emery... See
940 EXTENDED REPORT Bone loss in patients treated with pulses of methylprednisolone is not negligible: a short term prospective observational study G Haugeberg, B Griffiths, K B Sokoll, P Emery... See
8/6/2018. Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? Disclosure. Objectives. Overview
 Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Original Research Article. Raj Kumar Bhimwal 1, Mohan Makwana 2 *, Harish Sanawadiya 1, Ratan Lal Bhati 2
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Bhimwal RK et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Aug;4(4):952-958 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20172568
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Bhimwal RK et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Aug;4(4):952-958 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20172568
Rheumatoid arthritis 2010: Treatment and monitoring
 October 12, 2010 By Yusuf Yazici, MD [1] The significant changes in the way rheumatoid arthritis has been managed include earlier, more aggressive treatment with combination therapy. Significant changes
October 12, 2010 By Yusuf Yazici, MD [1] The significant changes in the way rheumatoid arthritis has been managed include earlier, more aggressive treatment with combination therapy. Significant changes
The Pathogenesis of Bone Erosions in RA FULL VERSION
 The Pathogenesis of Bone Erosions in RA FULL VERSION 1 Key Learning Objectives Understand the role of osteoclasts in normal bone remodeling Comprehend the key processes in pathologic osteoclast functions
The Pathogenesis of Bone Erosions in RA FULL VERSION 1 Key Learning Objectives Understand the role of osteoclasts in normal bone remodeling Comprehend the key processes in pathologic osteoclast functions
Are glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis recommendations sufficient to determine antiosteoporotic treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:509-515 Are glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis recommendations sufficient to determine antiosteoporotic treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Joo-Hyun
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:509-515 Are glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis recommendations sufficient to determine antiosteoporotic treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Joo-Hyun
Research Article Vitamin D Is a Good Marker for Disease Activity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease
 Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 260725, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/260725 Research Article Vitamin D Is a Good Marker for Disease Activity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Firas Sultan
Disease Markers Volume 2015, Article ID 260725, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/260725 Research Article Vitamin D Is a Good Marker for Disease Activity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Firas Sultan
Efficacy of Anakinra in Bone: Comparison to Other Biologics
 Advances In Therapy Volume 19 No. 1 January/February 2002 Efficacy of Anakinra in Bone: Comparison to Other Biologics Stephen A. Paget, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery Department of Rheumatic Disease
Advances In Therapy Volume 19 No. 1 January/February 2002 Efficacy of Anakinra in Bone: Comparison to Other Biologics Stephen A. Paget, M.D. Hospital for Special Surgery Department of Rheumatic Disease
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904)
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
Osteoporosis. Overview
 v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases
 Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Research Article. Advance Research Journal of Multi-Disciplinary Discoveries ISSN NO : VITAMIN-D AND TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 VITAMIN-D AND TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Research Article ISSN CODE: 2456-1045 (Online) (ICV-MDS/Impact Value): 2.31 (GIF) Impact Factor: 1.272 Copyright@IJF 2016 Journal Code: ARJMD/MDS/V-7.0/I-1/C-10/NOV-2016
VITAMIN-D AND TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Research Article ISSN CODE: 2456-1045 (Online) (ICV-MDS/Impact Value): 2.31 (GIF) Impact Factor: 1.272 Copyright@IJF 2016 Journal Code: ARJMD/MDS/V-7.0/I-1/C-10/NOV-2016
A. Kopchev, S.Monov, D. Kyurkchiev, I.Ivanova, T. Georgiev (UMHAT St. Ivan Rilski, Medical University - Sofia, Bulgaria)
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 6 Issue 7 July 2017 PP. 08-12 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), cartilage oligomeric
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 6 Issue 7 July 2017 PP. 08-12 Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), cartilage oligomeric
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies
 Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
Research Article Serum Vitamin D and Pyridinoline Cross-Linked Carboxyterminal Telopeptide of Type I Collagen in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 543806, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/543806 Research Article Serum Vitamin D and Pyridinoline Cross-Linked Carboxyterminal Telopeptide of
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 543806, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/543806 Research Article Serum Vitamin D and Pyridinoline Cross-Linked Carboxyterminal Telopeptide of
Vitamin D. Vitamin functioning as hormone. Todd A Fearer, MD FACP
 Vitamin D Vitamin functioning as hormone Todd A Fearer, MD FACP Vitamin overview Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential in small amounts for normal metabolism They are different from minerals
Vitamin D Vitamin functioning as hormone Todd A Fearer, MD FACP Vitamin overview Vitamins are organic compounds that are essential in small amounts for normal metabolism They are different from minerals
MEDICAL POLICY EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/21/14 REVISED DATE: 04/16/15, 06/16/16, 07/20/17 SUBJECT: SCREENING FOR VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SCREENING FOR VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SCREENING FOR VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not
Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General
 Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General Rheumatology classification criteria) 34 ; erythrocyte
Supplemental Table 1. Key Inclusion Criteria Inclusion Criterion OPTIMA PREMIER 18 years old with RA (per 1987 revised American College of General Rheumatology classification criteria) 34 ; erythrocyte
Index. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) 775 780 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AACE (American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists), bone mineral density recommendations of,
Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) 775 780 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A AACE (American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists), bone mineral density recommendations of,
Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity
 7 Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity Charlotte Krieckaert* Anna Jamnitski* Mike Nurmohamed Piet Kostense
7 Comparison of long-term clinical outcome with etanercept and adalimumab treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with respect to immunogenicity Charlotte Krieckaert* Anna Jamnitski* Mike Nurmohamed Piet Kostense
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine Yoon-Sok CHUNG WCIM, COEX, Seoul, 27Oct2014 Case 1 71-year old woman Back pain Emergency
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine Yoon-Sok CHUNG WCIM, COEX, Seoul, 27Oct2014 Case 1 71-year old woman Back pain Emergency
Can bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis be prevented?
 Osteoporos Int (2013) 24:2541 2553 DOI 10.1007/s00198-013-2334-5 REVIEW Can bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis be prevented? M. Vis & M. Güler-Yüksel & W. F. Lems Received: 17 December 2012 / Accepted:
Osteoporos Int (2013) 24:2541 2553 DOI 10.1007/s00198-013-2334-5 REVIEW Can bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis be prevented? M. Vis & M. Güler-Yüksel & W. F. Lems Received: 17 December 2012 / Accepted:
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
Rheumatoid Arthritis Ajay Bhatia Rheumatology Consultant Hillingdon Hospital ajay.bhatia@thh.nhs.uk Rheumatoid Arthritis When to refer to secondary care? Why early referral is beneficial for the patient?
Randomized withdrawal of long-term prednisolone treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: effects on inflammation and bone mineral density
 Scand J Rheumatol 2007;36:351 358 351 Randomized withdrawal of long-term prednisolone treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: effects on inflammation and bone mineral density B Tengstrand 1, E Larsson 1, L
Scand J Rheumatol 2007;36:351 358 351 Randomized withdrawal of long-term prednisolone treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: effects on inflammation and bone mineral density B Tengstrand 1, E Larsson 1, L
The role of IL-17A in postmenopausal inflammatory events, such as in osteoporosis
 The role of IL-17A in postmenopausal inflammatory events, such as in osteoporosis 1 Ildikó Molnár, MD, CSc, 2 Ilona Bohaty, MD, 1 Éva Somogyiné-Vári 1 Immunoendocrinology and Osteoporosis Centre, 2 Regional
The role of IL-17A in postmenopausal inflammatory events, such as in osteoporosis 1 Ildikó Molnár, MD, CSc, 2 Ilona Bohaty, MD, 1 Éva Somogyiné-Vári 1 Immunoendocrinology and Osteoporosis Centre, 2 Regional
Study of secondary causes of male osteoporosis
 Study of secondary causes of male osteoporosis Suárez, S.M., Giunta J., Meneses G., Costanzo P.R., Knoblovits P. Department of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Nuclear Medicine of Hospital Italiano of Buenos
Study of secondary causes of male osteoporosis Suárez, S.M., Giunta J., Meneses G., Costanzo P.R., Knoblovits P. Department of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Nuclear Medicine of Hospital Italiano of Buenos
Decreased Plasma Vitamin D Levels in Patients with Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Decreased Plasma Vitamin D Levels in Patients with Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Sukran Erten 1, Orhan Kucuksahin 2,AliSahin 3, Alpaslan Altunoglu 4, Mesut
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Decreased Plasma Vitamin D Levels in Patients with Undifferentiated Spondyloarthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Sukran Erten 1, Orhan Kucuksahin 2,AliSahin 3, Alpaslan Altunoglu 4, Mesut
Based on review of available data, the Company may consider the use of denosumab (Prolia) for the
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
denosumab (Prolia ) Policy # Original Effective Date: 07/21/2011 Current Effective Date: 04/19/2017
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future
 Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future Lai-Ling Winchow FCP(SA) Cert Rheum(SA) Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand Outline of presentation
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Past, the Present and the Future Lai-Ling Winchow FCP(SA) Cert Rheum(SA) Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand Outline of presentation
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC
 Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC Update on the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Sabrina Fallavollita MDCM McGill University Canadian Society of Internal Medicine
Canadian Society of Internal Medicine Annual Meeting 2016 Montreal, QC Update on the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Sabrina Fallavollita MDCM McGill University Canadian Society of Internal Medicine
TREAT-TO-TARGET IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 TREAT-TO-TARGET IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS To receive up to 10 CME credits for this activity, complete the evaluation, attestation and post-test answer sheet (minimum passing grade of 70%) and return all
TREAT-TO-TARGET IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS To receive up to 10 CME credits for this activity, complete the evaluation, attestation and post-test answer sheet (minimum passing grade of 70%) and return all
Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes
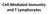 Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes T helper (Th) Cells Peripheral lymhoid tissue thymus Lymphoid stem cell CD8+ CD4+ CD4+ Treg CD8+ CTL + antigen Cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD4+ Th Helper T cell CD4+
Cell-Mediated Immunity and T Lymphocytes T helper (Th) Cells Peripheral lymhoid tissue thymus Lymphoid stem cell CD8+ CD4+ CD4+ Treg CD8+ CTL + antigen Cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD4+ Th Helper T cell CD4+
B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis?
 Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
The long-term impact of early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis on radiographic progression: a population-based cohort study
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2011;50:1106 1110 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keq424 Advance Access publication 21 January 2011 Concise report The long-term impact of early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis on
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2011;50:1106 1110 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keq424 Advance Access publication 21 January 2011 Concise report The long-term impact of early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis on
Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News
 Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News Jeffrey R. Lisse, M.D. Ethel P. McChesney Bilby Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Rheumatology University of Arizona School of Medicine
Treating Rheumatologic Disease in Arizona: Good News, Bad News Jeffrey R. Lisse, M.D. Ethel P. McChesney Bilby Professor of Medicine Chief, Section of Rheumatology University of Arizona School of Medicine
Clinical Policy: Etanercept (Enbrel) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid
 Clinical Policy: (Enbrel) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Enbrel ) is tumor necrosis
Clinical Policy: (Enbrel) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.250 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Enbrel ) is tumor necrosis
Clinical Policy: Certolizumab (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid
 Clinical Policy: (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Cimzia ) is a tumor necrosis
Clinical Policy: (Cimzia) Reference Number: PA.CP.PHAR.247 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 08/17 Line of Business: Medicaid Coding Implications Revision Log Description (Cimzia ) is a tumor necrosis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor
 Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Non-commercial use only
 Reumatismo, 2013; 65 (3): 113-120 original Regional differences of vitamin D deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Italy M. Rossini 1, G. D Avola 2, M. Muratore 3, N. Malavolta 4, F. Silveri 5,
Reumatismo, 2013; 65 (3): 113-120 original Regional differences of vitamin D deficiency in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Italy M. Rossini 1, G. D Avola 2, M. Muratore 3, N. Malavolta 4, F. Silveri 5,
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Improving Outcomes in RA: Three Pillars. RA: Chronic Joint Destruction and Disability What We Try to Prevent
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Modern Management of Common Problems in Rheumatology: Rheumatoid Arthritis Jonathan Graf, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine, UCSF Division of Rheumatology, SFGH Director, UCSF Rheumatoid
Rheumatoid Arthritis Modern Management of Common Problems in Rheumatology: Rheumatoid Arthritis Jonathan Graf, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine, UCSF Division of Rheumatology, SFGH Director, UCSF Rheumatoid
Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine and Gerontology, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland 4
 Original papers Efficacy and safety of golimumab as add-on therapy to standard disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: Results of the GO-MORE study in the Polish population Sławomir Jeka 1,A,B,D F, Bogdan
Original papers Efficacy and safety of golimumab as add-on therapy to standard disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: Results of the GO-MORE study in the Polish population Sławomir Jeka 1,A,B,D F, Bogdan
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: , Volume 2, Issue 7, August 2014
 HYPOVITAMINOSIS D IN INDIAN FEMALES WITH POSTMENOPAUSAL OSTEOPOROSIS DR. SHAH WALIULLAH 1 DR. VINEET SHARMA 2 DR. R N SRIVASTAVA 3 DR. YASHODHARA PRADEEP 4 DR. A A MAHDI 5 DR. SANTOSH KUMAR 6 1 Research
HYPOVITAMINOSIS D IN INDIAN FEMALES WITH POSTMENOPAUSAL OSTEOPOROSIS DR. SHAH WALIULLAH 1 DR. VINEET SHARMA 2 DR. R N SRIVASTAVA 3 DR. YASHODHARA PRADEEP 4 DR. A A MAHDI 5 DR. SANTOSH KUMAR 6 1 Research
C. Assess clinical response after the first three months of treatment.
 Government Health Plan (GHP) of Puerto Rico Authorization Criteria Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNFα) Adalimumab (Humira ) Managed by MCO Section I. Prior Authorization Criteria A. Physician must submit
Government Health Plan (GHP) of Puerto Rico Authorization Criteria Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNFα) Adalimumab (Humira ) Managed by MCO Section I. Prior Authorization Criteria A. Physician must submit
Prior treatment with non-biologic Disease- Modifying Antirheumatic. Not to be used in combination with another biologic DMARD
 Abatacept (Orencia) 1, 2, 7, 11, 13, 14, 18, 24, 31, 44, 48, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57 J0129 Alpha 1 - Proteinase inhibitor (Prolastin-C) 5, 6, 10, 12, 40 Medically Necessary (if all the following criteria apply):
Abatacept (Orencia) 1, 2, 7, 11, 13, 14, 18, 24, 31, 44, 48, 49, 51, 53, 55, 57 J0129 Alpha 1 - Proteinase inhibitor (Prolastin-C) 5, 6, 10, 12, 40 Medically Necessary (if all the following criteria apply):
Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis: results of a 1-year study
 Rheumatol Int (2006) 26: 427 431 DOI 10.1007/s00296-005-0004-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J. D. Ringe Æ H. Faber Æ P. Farahmand Æ A. Dorst Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis:
Rheumatol Int (2006) 26: 427 431 DOI 10.1007/s00296-005-0004-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J. D. Ringe Æ H. Faber Æ P. Farahmand Æ A. Dorst Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis:
Elecsys bone marker panel. Optimal patient management starts in the laboratory
 bone marker panel Optimal patient management starts in the laboratory Complete solution for osteoporosis The most complete bone metabolism panel on a single platform bone marker assays are important diagnostic
bone marker panel Optimal patient management starts in the laboratory Complete solution for osteoporosis The most complete bone metabolism panel on a single platform bone marker assays are important diagnostic
SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
 SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS Essam Tewfik Attwa and S. Al-Beltagy* Rheumatology & Rehabilitation Department, Zagazig University Faculty of Medicine
SIGNIFICANCE OF ELEVATED INTERLEUKIN-6 LEVEL IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS Essam Tewfik Attwa and S. Al-Beltagy* Rheumatology & Rehabilitation Department, Zagazig University Faculty of Medicine
Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 1. Title: Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis 2. Background: The population of older individuals with rheumatoid arthritis
1. Title: Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis 2. Background: The population of older individuals with rheumatoid arthritis
Preventing the Progression From Undifferentiated Arthritis to Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Clinical and Economic Implications
 n report n Preventing the Progression From Undifferentiated Arthritis to Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Clinical and Economic Implications Michael H. Schiff, MD Introduction Over the past few years, the management
n report n Preventing the Progression From Undifferentiated Arthritis to Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Clinical and Economic Implications Michael H. Schiff, MD Introduction Over the past few years, the management
Osteoporosis challenges
 Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
Osteoporosis challenges Osteoporosis challenges Who should have a fracture risk assessment? Who to treat? Drugs, holidays and unusual adverse effects Fracture liaison service? The size of the problem 1
Aromatase Inhibitors & Osteoporosis
 Aromatase Inhibitors & Osteoporosis Miss Sarah Horn Consultant Oncoplastic Breast Surgeon April 2018 Aims Role of Aromatase Inhibitors (AI) in breast cancer treatment AI s effects on bone health Bone health
Aromatase Inhibitors & Osteoporosis Miss Sarah Horn Consultant Oncoplastic Breast Surgeon April 2018 Aims Role of Aromatase Inhibitors (AI) in breast cancer treatment AI s effects on bone health Bone health
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases
 Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Pharmacy Management Drug Policy
 SUBJECT: - Forteo (teriparatide), Prolia (denosumab), Tymlos (abaloparatide) POLICY NUMBER: Pharmacy-35 EFFECTIVE DATE: 9/07 LAST REVIEW DATE: 9/29/2017 If the member s subscriber contract excludes coverage
SUBJECT: - Forteo (teriparatide), Prolia (denosumab), Tymlos (abaloparatide) POLICY NUMBER: Pharmacy-35 EFFECTIVE DATE: 9/07 LAST REVIEW DATE: 9/29/2017 If the member s subscriber contract excludes coverage
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them. Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey
 Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Coverage Criteria: Express Scripts, Inc. monograph dated 12/15/ months or as otherwise noted by indication
 BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Kineret (anakinra subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
BENEFIT DESCRIPTION AND LIMITATIONS OF COVERAGE ITEM: PRODUCT LINES: COVERED UNDER: DESCRIPTION: CPT/HCPCS Code: Company Supplying: Setting: Kineret (anakinra subcutaneous injection) Commercial HMO/PPO/CDHP
Department of Studies & Planning, Statistics Section, The Research Council, Muscat 130, Oman
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 285854, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/285854 Clinical Study Evaluation of Anti-Mutated Citrullinated Vimentin Antibodies, Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 285854, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/285854 Clinical Study Evaluation of Anti-Mutated Citrullinated Vimentin Antibodies, Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide
Osteoporosis and Rheumatic Diseases
 Osteoporosis and Rheumatic Diseases This is an area which is often neglected and is a burden too heavy to be carried by the weakened bones! There is an increased risk of osteoporosis (OP) in rheumatic
Osteoporosis and Rheumatic Diseases This is an area which is often neglected and is a burden too heavy to be carried by the weakened bones! There is an increased risk of osteoporosis (OP) in rheumatic
Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Mod Rheumatol (2007) 17:28 32 Japan College of Rheumatology 2007 DOI 10.1007/s10165-006-0532-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hisashi Yamanaka Yoshiya Tanaka Naoya Sekiguchi Eisuke Inoue Kazuyoshi Saito Hideto Kameda
Mod Rheumatol (2007) 17:28 32 Japan College of Rheumatology 2007 DOI 10.1007/s10165-006-0532-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hisashi Yamanaka Yoshiya Tanaka Naoya Sekiguchi Eisuke Inoue Kazuyoshi Saito Hideto Kameda
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
 EFFICACY OF COMBINATION THERAPY OF METHOTREXATE WITH HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE OR SULFASALAZINE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS IN KUMAON REGION: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Suyash Bharat 1, Bhavana Srivastava 2, Paramjeet
EFFICACY OF COMBINATION THERAPY OF METHOTREXATE WITH HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE OR SULFASALAZINE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS IN KUMAON REGION: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Suyash Bharat 1, Bhavana Srivastava 2, Paramjeet
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink
 Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Examining the prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in data from the Clinical Practice Research Datalink Julian Gardiner, Michael Soljak, Department of Primary Care & Public Health Benjamin Ellis, Arthritis
Osteoporosis. When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of.
 Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Center for Rheumatology, Maxima Medical Center Eindhoven, The Netherlands; 4
 High incidence rate of vertebral fractures during chronic prednisone treatment, in spite of bisphosphonate or alfacalcidol use. Extension of the Alendronate or alfacalcidol in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis-trial
High incidence rate of vertebral fractures during chronic prednisone treatment, in spite of bisphosphonate or alfacalcidol use. Extension of the Alendronate or alfacalcidol in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis-trial
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis
 Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Management of postmenopausal osteoporosis Yeap SS, Hew FL, Chan SP, on behalf of the Malaysian Osteoporosis Society Committee Working Group for the Clinical Guidance on the Management of Osteoporosis,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial (ADOPT), 194 Adaptive immunity, 129 131 ADOPT (A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial), 194 Aging, vitamin
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial (ADOPT), 194 Adaptive immunity, 129 131 ADOPT (A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial), 194 Aging, vitamin
The Impact of Proinflammatory Cytokynes of Rheumatoid Polyarthritis on the Generalized Loss of Bone Mass
 The Impact of Proinflammatory Cytokynes of Rheumatoid Polyarthritis on the Generalized Loss of Bone Mass RALUCA BARZOI 1, ELENA REZUS 2 *, CODRUTA BADESCU 3 *, RAZAN AL NAMAT 4, MANUELA CIOCOIU 1 1 Grigore
The Impact of Proinflammatory Cytokynes of Rheumatoid Polyarthritis on the Generalized Loss of Bone Mass RALUCA BARZOI 1, ELENA REZUS 2 *, CODRUTA BADESCU 3 *, RAZAN AL NAMAT 4, MANUELA CIOCOIU 1 1 Grigore
Index. B BMC. See Bone mineral content BMD. See Bone mineral density Bone anabolic impact, Bone mass acquisition
 A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
Clinical Policy: Tocilizumab (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44
 Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 09/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Clinical Policy: (Actemra) Reference Number: ERX.SPMN.44 Effective Date: 10/16 Last Review Date: 09/16 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory
Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis. August 2009
 Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Abatacept (Orencia) for active rheumatoid arthritis August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
