Blood-nourishing and Hard-softening Capsule Costs Less in the Management of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial
|
|
|
- David Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advance Access Publication 26 July 2005 ecam 2005;2(3) doi: /ecam/neh104 Original Article Blood-nourishing and Hard-softening Capsule Costs Less in the Management of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial Yuelong Cao 1, Yinyu Shi 1, Yuxing Zheng 1, Meiyu Shi 1 and Sing Kai Lo 1,2 1 Research Institute of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China and 2 Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences, Deakin University, Melbourne, Australia The blood-nourishing and hard-softening (BNHS) capsule is a traditional Chinese formula used in the symptomatic treatment of inflammation and pain. We conducted this randomized controlled trial to compare the efficacy of BNHS with other commonly prescribed drugs. We recruited 120 patients from two teaching hospitals; 30 patients in each hospital were randomly assigned to receive BNHS. In one hospital, the 30 controls were given another traditional Chinese drug; whereas a Western medicine (chondroprotection drug/viartril-s) was used as the control in the other hospital. Intervention was carried out over a period of 4 weeks. Primary outcome measures included self-reported pain level, and changes in stiffness and functional ability as measured by the Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis (WOMAC) index. Mixed models were used for statistical analysis. Substantial improvements in disease-specific symptoms were observed, after 4 weeks of treatment, in patients taking BNHS capsules. As assessed by the WOMAC index, pain level of the BNHS group decreased by 57% [95% confidence interval (CI) ¼ 50, 63], stiffness by 63% (95% CI ¼ 55, 71) and functional ability increased by 56% (95% CI ¼ 50, 63). No significant differences were found in any of the outcome measures between the BNHS group and either of the comparison groups. No severe adverse effects were reported. However, this study lacked a placebo group; therefore, we conclude that BNHS appears to be as effective as commonly prescribed medicines for the relief of pain and dysfunction in knee osteoarthritis patients, but costs a lot less than other Western and herbal drugs in the study. Keywords: Chinese herbal medicine chondroprotection drug WOMAC Introduction Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disease. Clinical manifestations of OA of the knee are joint pain, stiffness in the morning or after rest, pain at night, limited joint motion and/or joint deformity (1). Treatment modalities for knee OA include non-pharmacologic (e.g. physical and occupational therapy, aerobic exercise programs, weight control and patient education) and pharmacologic therapy [e.g. intra-articular steroid injections, paracetamol, topical analgesics, non-steroidal For reprints and all correspondence: Professor Sing Kai Lo, Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences, Deakin University, 221 Burwood Highway, Burwood, VIC 3125, Australia. Tel: þ ; Fax: þ ; singkai.lo@deakin.edu.au anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and opioid analgesics] (2). Although NSAIDs are the most widely prescribed drugs to reduce joint pain and stiffness, the inflammatory component of OA is usually minimal; therefore, the need for the anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs in this condition is controversial (3). Since the efficacy of NSAIDs in symptomatic treatment of OA of the knee depends on analgesic rather than anti-inflammatory effect, paracetamol has been recently recommended as the first-line oral drug. On the one hand, long-term use of paracetamol can lead to hepatic and renal impairment (4). On the other hand, inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis is directly related to many common and occasionally severe side effects including gastrointestinal bleeding, hypertension, congestive heart failure, hyperkalemia and renal Ó The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. The online version of this article has been published under an open access model. Users are entitled to use, reproduce, disseminate, or display the open access version of this article for non-commercial purposes provided that: the original authorship is properly and fully attributed; the Journal and Oxford University Press are attributed as the original place of publication with the correct citation details given; if an article is subsequently reproduced or disseminated not in its entirety but only in part or as a derivative work this must be clearly indicated. For commercial re-use, please contact journals.permissions@oupjournals.org
2 364 BNHS capsule for osteoarthritic knee pain insufficiency (5,6). These disadvantages call for an evaluation of the risks and benefits of the therapies in comparison with a less toxic one for OA. Thus, less toxic pain managing procedures, e.g. electroacupuncture or acupuncture as reported, as well as chondroprotection drugs are considered alternative treatments and they are widely prescribed in China. Evidence gathered from a systematic review show that herbal medicines, which appear relatively safe, may offer a much-needed alternative, and merit further attention (7). The blood-nourishing and hard-softening capsule (BNHS), which is an extract from Bai Shao (radix paeoniae alba), Qin Jiao (radix gentianae macrophyllae) and Gan Cao (radix glycyrrhizae), containing mainly paconiflorin and gentianine, is a traditional Chinese herb used for symptomatic treatment of inflammation and pain in OA. In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), OA is known as the Bi syndrome (painful obstruction), which means either the limbs or the joints are suffered from pain and malfunction, and herb therapy has long been a standard treatment. Only limited data are available on the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of traditional Chinese herbs in the treatment of OA of the knee. Therefore, we initiated this study to compare the efficacy of BNHS, another commonly prescribed Chinese herb counter osteophytes capsule, and Western medicine Viartril-s (chondroprotection drug) in short-term symptomatic treatment of OA of the knee. We hypothesized that BNHS is as effective as, but will cost less than, other commonly prescribed drugs chosen for comparison purposes. Materials and Methods Study Design This was a prospective two-center randomized controlled trial. All patients underwent a treatment period of 4 weeks, and followed for 2 weeks to check for adverse events. The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University in Shanghai. The trial was conducted under the Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines. All patients gave informed written consent. Patients We screened all outpatients, aged 50, who in 2002 attended the Department of Orthopaedics in two teaching hospitals in Shanghai. All of them suffered from painful OA of the knee according to American College of Rheumatology criteria (8). Additional inclusion criteria were as follows: intake of NSAIDs for at least 5 days before the study entry, but presented with adverse events from previous NSAID therapy; had pain intensity of 20 mm on the visual analog scales (VASs) in the previous 48 h when walking on a flat surface; radiological evidence of OA in the painful joint; at least grades II IV on the Kellgren Lawrence scale on an X-ray taken within 12 months; and reluctant to continue on previous drug but willing to change drug treatment. Exclusion criteria include concurrent medical/arthritic diseases such as secondary inflammatory arthritis, gout, episodes of acute monoarticular arthritis, isolated patellofemoral disease, a history of acute ligamentous or meniscal injury of the study joint within the previous 2 years and arthroscopy of the affected knee in the 3 months before the study entry, which could confound or interfere with the evaluation of efficacy. Subjects with hypersensitivity to one of the ingredients of the BNHS or rescue medication, asthma attacks, episodes of urticaria or acute rhinitis after administration of aspirin or other NSAIDs were not included in the study. Patients with severe heart, renal or liver insufficiency including increased liver function tests, blood urea nitrogen test, alanine aminotransferase test and other biochemistry tests three times higher than the upper limit of normal range, or with acute or suspected gastrointestinal bleeding, active gastric or duodenal ulcer, ulcer diagnosed endoscopically within the previous 28 days, steroid injection <3 months were also excluded. Procedures A total of 120 patients, 60 in each hospital, were recruited from eligible patients. They were randomly (using the sealed envelope method) and blindly assigned to treatment (BNHS) or control care (counter osteophytes capsule, another traditional Chinese drug) in Hospital A. Since Hospital B used Western medicine (Viartril-s, a chondroprotection drug) as control care, and there are pharmacokinetical differences between Chinese and Western medicine, we could only blind the clinician who performed the assessments. On Day 0 (Visit 1), patients stopped their previous NSAID therapy and started taking either BNHS (Experimental) or counter osteophytes capsule (Control 1) or Viartril-s capsule (Control 2) with a daily dose of 3.15, 5.25 and 2.25 g, respectively. On Day 14 patients returned for an interim visit (Visit 2). On Day 28 the final visit took place (Visit 3). Thus, the duration of treatment was 4 weeks. Two weeks after Visit 3 or after discontinuation the patient was contacted to check for adverse events. As a pain rescue medication, patients were allowed to take paracetamol 500 mg on demand, e.g. in the event of breakthrough pain, with a maximum dose of 4 g day 1. We counted and recorded all returned tablets at each visit. There were no study-specific restrictions with regard to previous and concomitant medication and treatments, except that co-administration of NSAIDs was not allowed during the study period. Low-dose aspirin (<100 mg d 1 ) was allowed, provided the dosage was not changed during the study period and had been stable for months. Clinical Endpoints and Outcome Measures The endpoints used for the study included pain when walking on a flat surface, pain, stiffness and functional ability. To be specific, the radiological severity of OA was assessed at Day 0 using the Kellgren Lawrence index. At each visit (Days 0, 14 and 28) the patients were rested in a sitting position
3 ecam 2005;2(3) 365 for 10 min before monitoring the vital signs. They were also asked to complete the following questionnaires: (i) patient s global assessment of treatment satisfaction (5-point scale; 0 ¼ poor, 4 ¼ excellent); (ii) patient s assessment of pain when walking on a flat surface (VAS; 0 ¼ no pain, 100 ¼ major pain) (9); (iii) Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis (WOMAC) LK 3.1; and (iv) global assessment of treatment response (5-point scale; 0 ¼ very well, 4 ¼ very very poor) completed by the same investigator (Y.C.). Tolerability and Safety Spontaneously reported adverse events were recorded throughout the study. Vital signs were monitored at every visit. Laboratory investigations including hematology, blood chemistry and urinalysis were performed at Days 0 and 28, and repeated on a need basis. For all adverse events the intensity, relation to test drug and actions taken were recorded. Statistical Analysis Data analysis was performed according to the intention-totreat (last observation carried forward) principle using SPSS V12.0. Mixed models, treating group as the between-subject factor and time as the within-subject factor, were formulated to compare outcome scores between groups and over time. When significant interaction between group and time was detected, analysis of covariance was used to compare groups at Days 14 and 28 after adjusted for baseline values. While the overall significance level was set at 0.05, the Sharpened Bonferroni procedure (10) was used to adjust individual alpha level when multiple testing was performed. Results In the two hospitals, 136 patients were approached before 120 agreed to participate. The primary diagnosis was knee OA. The radiological Kellgren Lawrence index was II (slight OA) in 22.5% of the patients and III (moderate OA) or IV (major OA) in 54.2 and 23.3%, respectively. One hundred sixteen subjects completed the study per protocol (three experienced adverse events and one refused to take the study drug, all after Visit 2), but analyses were carried out using all the 120 patients ( last observation carried forward for the four incomplete patients). One-third of the randomized participants were males and the mean age was 69 (SD ¼ 8) years. No significant differences in mean age or gender ratios were observed between the BNHS and the control groups (Table 1). WOMAC As assessed by the WOMAC index, pain decreased by 57% [95% confidence interval (CI) ¼ 50, 63; P < 0.001], stiffness by 63% (95% CI ¼ 55, 71; P < 0.001) and functional ability increased by 56% (95% CI ¼ 50, 63; P < 0.001) over the course (i.e. 4 weeks) of the study in BNHS patients. As shown in Tables 2 4, the improvement from Days 14 to 28 (percent improvement varied from 33 to 51% depending on the outcome measure and Hospital) was substantially more than that to Week 2 (percent improvement varied from 23 to 32%), although statistical significance was not reached in some outcome measures among patients in Hospital A. However, for the sample size we had, we found no significant differences in the pattern of change to Day 28 between the treatment and the control groups, regardless of whether the control was TCM herb or Western medicine, as none of the interaction terms were significant. We also noted that although most of the WOMAC scores (except pain) were significantly different between patients in the three treatment regimes (i.e. BNHS, Chinese herb control and Western medicine control) at Day 0, the scores were very similar at Day 28. This seems to suggest that regardless of the initial clinical situation of the patient, there is a threshold such that once the limit is reached the patient cannot improve further, at least for the drugs used in this study and after 4 weeks of treatment. Other Outcome Measures The outcome measures also included assessment of pain when walking on a flat surface, investigator s global assessment of treatment response as well as patient s global assessment of treatment satisfaction. The results are shown in Tables 3 and 4. By and large, none of these outcome measures were significantly different between the BNHS and the control groups. The patterns of the results for pain when walking on a flat surface, whether it was the change to Weeks 2 or 4, or the absolute scores obtained at end of study, were very similar to those of the WOMAC scores. However, patients in the BNHS group in Hospital A appeared to be slightly more satisfied than the controls (Good/Excellent: 50 versus 30%; P ¼ 0.095), although the differences were marginally non-significant. Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the participants Hospital A (Chinese medicine control) Hospital B (Western medicine control) BNHS* (n ¼ 30) Counter osteophytes P-value BNHS* (n ¼ 30) Viartril-s (n ¼ 30) P-value capsule (n ¼ 30) Age (years) 59 ± 7 60 ± ± 9 62 ± Female gender 22 (73.3%) 17 (56.7%) (80.0%) 17 (56.7%) Disease duration (years) 11 ± 8 10 ± ± 8 11 ± *BNHS ¼ blood-nourishing and hard-softening capsule.
4 366 BNHS capsule for osteoarthritic knee pain Table 2. Comparison of WOMAC scores between the treatment groups Baseline 2 weeks 4 weeks Percent changed Baseline 2 weeks 4 weeks Percent changed Hospital A BNHS (n ¼ 30) Counter osteophytes capsule (n ¼ 30) Total x (% changed) 24 ± ± 11 (29) 11 ± 10 (38) ± ± 12 (24) 13 ± 10 (32) Pain x (% changed) 28 ± ± 13 (27) 14 ± 12 (33) ± ± 11 (28) 15 ± 9 (29) Stiffness x (% changed) 26 ± ± 17 (23) 12 ± 14 (46)* ± ± 18 (26) 15 ± 16 (25) Disability x (% changed) 23 ± ± 12 (28) 11 ± 11 (36) ± ± 13 (25) 13 ± 11 (33) Hospital B BNHS (n ¼ 30) Viartril-s (n ¼ 30) Total x (% changed) 32 ± 4 22 ± 4 (32) 12 ± 5 (45)** ± 6 23 ± 5 (32) 13 ± 5 (43) Pain x (% changed) 29 ± 5 20 ± 4 (30) 11 ± 5 (46)** ± 8 24 ± 7 (29) 14 ± 7 (42) Stiffness x (% changed) 33 ± 9 22 ± 7 (33) 11 ± 6 (51)** ± 9 26 ± 8 (32) 14 ± 7 (46) Disability x (% changed) 32 ± 4 22 ± 4 (32) 12 ± 5 (44)** ± 6 22 ± 5 (33) 12 ± 5 (45) No significant differences between the two groups at baseline in any of the measurements. z P-value for group by time interaction, i.e. testing whether the change was different between the two groups or not. x Percent changed from the previous time period. *P < **P < 0.01 as compared with the changed to Week 2 (analysis for BNHS only). Table 3. Comparison of other outcome measures between the groups: pain when walking on a flat surface Baseline 2 weeks 4 weeks Percent changed Baseline 2 weeks 4 weeks Percent changed Hospital A BNHS (n ¼ 30) Counter osteophytes capsule (n ¼ 30) Pain (VAS) x (% changed) 31 ± ± 19 (23) 15 ± 19 (45)* ± ± 23 (32) 13 ± 17 (38) Hospital B BNHS (n ¼ 30) Viartril-s (n ¼ 30) Pain (VAS) x (% changed) 47 ± ± 9 (36) 18 ± 9 (44)** ± ± 11 (31) 20 ± 10 (43) No significant differences between the two groups at baseline in any of the measurements. z P-value for group by time interaction, i.e. testing whether the change was different between the two groups or not. x Percent changed from the previous time period. *P < **P < 0.01 as compared with the changed to Week 2 (analysis for BNHS only). Table 4. Comparison of other outcome measures between the groups: patient satisfaction and investigator s assessment of treatment response P-value z P-value z Patient satisfaction Investigator s assessment of treatment response BNHS (n ¼ 30) Control (n ¼ 30) P-value* BNHS (n ¼ 30) Control (n ¼ 30) P-value* Hospital A Poor (%) Fair (%) Good (%) Excellent (%) Hospital B Poor (%) Fair (%) Good (%) Excellent (%) *P-values comparing BNHS and control within each hospital. Adverse Events One BNHS case in Hospital A had macule that could be related to treatment. Four patients, all in the BNHS group in Hospital A, withdrew from the trial due to obstipation (one case), gum swelling (two cases) and bitter feeling in the mouth (one case). None of these were considered serious by the investigators. No severe adverse cardiovascular events or deep vein thrombosis were observed. No hospitalization or death
5 ecam 2005;2(3) 367 occurred due to adverse events. No adverse events occurred in Hospital B. Switch Pattern In the telephone survey, 2 weeks after completion of the 4 week study, 61% (35/57) had decided to stay on BNHS capsule and 60% (18/30) on Viartril-s capsule, but only 48% (14/29) preferred to stay on counter osteophytes capsule; however, the differences were not statistically significant. Dosage and Cost All the 116 subjects who completed the study had a 100% dose taking record. To be specific, 88.2 g BNHS, 147 g counter osteophytes or 63 g Viartril-s drugs were taken by each patient in the treatment and two control groups, respectively, during the 4 week period. For the dosage used in this study, the cost for BNHS was only 80% compared with counter osteophytes capsule and 12% compared with Viartril-s. Discussion This study documents the benefits of treating OA of the knee with BNHS for OA patients who were either unresponsive to or presented with adverse events from previous NSAID therapy. We found that BNHS significantly improved WOMAC pain, stiffness and function over 4 weeks. Although lots of reports show that Chinese herbs are potentially effective in the treatment of OA, few of them were carried out in accordance with the GCP principle. We have followed the GCP guidelines as close as possible when conducting the study. Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of the COX-2 specific NSAIDs in the treatment of pain and inflammation due to OA, as well as its efficacy profile relative to classical (non-cox-2 specific) high-dose NSAIDs (11 14). Other studies have demonstrated the superior safety profile of such drugs compared with classical NSAIDs, with a particular focus on upper gastrointestinal adverse events such as perforation, ulcers and bleeding (15). As COX-2 specific NSAIDs is a relatively new drug, more research, especially long-term follow-ups and examination of adverse effects, are needed before its efficacy is established. Hence, we have not chosen COX-2 specific NSAIDs as the Western control medicine. Numerous TCM methods have been used in the treatment of OA. The most widely studied method was acupuncture, with several studies examining the short-term and long-term effectiveness of the treatment in relieving clinical pain (16 18). Nevertheless, flaws and limitations in these studies have been reported (19). These included inadequate sessions of treatment, failure to control concomitant therapies and no sham, placebo or controlled group. However, scientific data on the efficacy of herbal formulae in the treatment of OA are rarely available. It was difficult to choose the kind of Chinese medicine for comparison purposes. We finally decided to use a drug that is commonly prescribed. OA is a disease in which compliance and persistence are known to be rather poor. In this study, the BNHS was generally safe and well tolerated. After 4 weeks of treatment, 61% still preferred to stay on BNHS. Compared with NSAIDs, the anti-pain mechanism of BNHS is still unclear. The specific way NSAIDs develop effect is through the inhibition of COX. Meanwhile, the most common renal effects of conventional NSAIDs attributable to the inhibition of COX are a reduction in both glomerular filtration rate and excretion of sodium, with the attendant potential for fluid retention and edema (19). Viartril-s mainly consists of chondroitin sulfate, which is a chondroprotection agent and a key component of the extracellular matrix of cartilage. Studies have documented that glucosamine is absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract with 26% bioavailability and incorporated into plasma proteins. The supplement has anti-inflammatory properties but not analgesic properties (20). A previous study showed that BNHS could improve pain threshold of rats, and BNHS could inhibit the expression of matrix metalloproteases-3 of chondrocyte in vitro. BNHS is a complex formula, the effectiveness of which appeared to be comprehensive and similar to chondroprotection or degeneration protection (21). However, the exact mechanism requires further investigations. The major limitation of the present study was the lack of a placebo group. We cannot rule out the possibility that patients got better despite any treatments they received, especially symptoms in OA often improve with no treatment and undergo a fluctuating course. The lack of any significant differences across the three treatments might well be explained by this. However, as the two comparison drugs were commonly prescribed in the two participating hospitals, including a control arm with, say, paracetamol but without the chosen control drugs would be extremely difficult for the researchers to obtain ethical approval. The finding that BNHS is as effective as both controlled drugs is itself very encouraging, as it implies that the costeffectiveness of BNHS could be substantially higher. This is due to the fact BNHS is 88% less expensive than the Western drug Viartril-s. Although BNHS is only marginally cheaper than the other Chinese herbal medicine, the dosage required to achieve similar effects is lower (88.2 versus 147 g per case), hence the total cost is substantially lower. It must also be mentioned that compared with boiled herbal formula, capsules are more likely to be accepted. One limitation of this study was that sample size was not very large. Nevertheless, the effect sizes (in terms of mean differences between the Experimental and the Controls divided by the standard deviations, as shown in Table 2) were fairly small, indicating that the non-significant differences could not be explained by sample size alone; there were in fact no apparent differences in any of the outcome measures between the groups. Yet, any conclusive remarks on equivalence can only be made after a proper bioequivalence study with a much larger sample is conducted. Another limitation was the lack of long-term follow-up and evaluation. However, the duration chosen in the present study was in line with acute
6 368 BNHS capsule for osteoarthritic knee pain OA flare episodes, and the study was long enough to document BNHS s rapid onset of action and its sustained efficacy over 4 weeks. Although WOMAC is an internationally recognized measurement method, it has never been used as an outcome measure in clinical trials of Chinese herbs; but we do not see why it could have caused any concerns. Given the differences between Chinese herbs and Western medicine, it was difficult to employ a double-blind design in Hospital B. Unfortunately, the degree of potential bias introduced was simply not estimable. In conclusion, this study suggests that BNHS improves disease-specific symptoms, such as pain, stiffness and decreased function in patients with painful knee OA within 4 weeks, and has similar effects compared with other commonly prescribed Western and Chinese herbal drugs, but the prescription costs less. Acknowledgements This study was supported by a grant from the Science and Technology Committee, Shanghai, People s Republic of China (No ). References 1. Altman RD, Hochberg MC. Degenerative joint disease. Clin Rheum Dis 1983;9: Hochberg MC, Altman RD, Brandt KD, Clark BM, Dieppe PA, Griffin MR, et al. Guidelines for the medical management of osteoarthritis. Part II. Osteoarthritis of the knee. American College of Rheumatology. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38: Bradley JD, Brandt KD, Katz BP, Kalasinski LA, Ryan SI. Comparison of anti inflammatory dose of ibuprofen, an analgesic dose of ibuprofen, and acetaminophen in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med 1991;325: Buckalew VM,Jr. Habitual use of acetaminophen as a risk factor for chronic renal failure: a comparison with phenacein. Am J Kidney Dis 1996;28: Griffin MR, Piper JM, Daugherty JR, Snowden M, Ray WA. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and increased risk for peptic ulcer disease in elderly persons. Ann Intern Med 1991;114: Soll AH, Weinstein WM, Kurata J, McCarthy D. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs and peptic ulcer disease. Ann Intern Med 1991;114: Long L, Soeken K, Ernst E. Herbal medicines for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a systematic review. J Rheumatol 2001;40: Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G, Borenstein D, Brandt K, et al. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis: classification of OA of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 1986;29: Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes, to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 1988;15: Hochberg Y, Benjamini Y. More powerful procedure for multiple significance testing. Stat Med 1990;9: Scott LJ, Lamb HM. Rofecoxib. Drugs 1999;58: Day R, Morrison B, Luza A, Castaneda O, Strusberg A, Helgetveit KB, et al. A randomized trial of the efficacy and tolerability of the COX-2 inhibitor rofecoxib vs. ibuprofen in patients with osteoarthritis. Arch Intern Med 2000;160: Saag K, van der Heijde D, Fisher C, Samara A, De Tora L, Bolognese J, et al. Rofecoxib, a new cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor, shows sustained efficacy, comparable with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: a 6-week and a 1-year trial in patients with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Studies Group. Arch Fam Med 2000;9: Geba GP, Weaver AL, Polis AB, Dixon ME, Schnitzer TJ. Efficacy of Refecoxib, celecoxib, and acetaminophen in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Am Med Assoc 2002;287: Deeks JJ, Smith LA, Bradley MD. Efficacy, tolerability, and upper gastrointestinal safety of celecoxib for treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Br Med J 2002;325: Berman BM, Singh BB, Lao L, Langenberg P, Li H, Hadhazy V, et al. A randomized trial of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatology 1999;38: Takeda W, Wessel J. Acupuncture for the treatment of pain of osteoarthritic knees. Arthritis Care Res 1994;7: Lao L, Bergman S, Langenberg P, Wong RH, Berman B. Efficacy of Chinese acupuncture on postoperative oral surgery pain. Oral Surg Med Oral Pathol 1995;79: Berman BM. Clinical applications of acupuncture: an overview of the evidence. J Altern Complement Med 2001;7:S Brater DC, Harris C, Redfern JS, Gertz BJ. Renal effects of COX-2 selective inhibitors. Am J Nephrol 2001;21: Cao YL, Shi YY, Wei F, Li ZJ. Experimental study of PGE expression on osteoarthritis treated with YuanGuLi. Chin J Orthop Traumatol 2001;14: (Chinese). Received April 20, 2005; accepted July 3, 2005
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis Research Society /98/ $12.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, (Supplement A), 31 36 9 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/98/030031 + 06 $12.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Efficacy and tolerability of oral chondroitin
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, (Supplement A), 31 36 9 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/98/030031 + 06 $12.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Efficacy and tolerability of oral chondroitin
This document has not been circulated to either the industry or Consultants within the Suffolk system.
 New Medicine Report Document Status COX II Inhibitors In Acute Analgesia For Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee Date of Last Revision 15 th February 2002 Reviewer s Comments There seems to be a growing
New Medicine Report Document Status COX II Inhibitors In Acute Analgesia For Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee Date of Last Revision 15 th February 2002 Reviewer s Comments There seems to be a growing
Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of the Knee
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research article Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of Dimitar Tonev 1 *, Stoyka Radeva 2 and
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research article Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of Dimitar Tonev 1 *, Stoyka Radeva 2 and
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 26 November 2008
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 26 November 2008 CHONDROSULF 400 mg, capsule Box containing 84 capsules (CIP: 335 917-3) CHONDROSULF 400 mg, granules
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 26 November 2008 CHONDROSULF 400 mg, capsule Box containing 84 capsules (CIP: 335 917-3) CHONDROSULF 400 mg, granules
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Tue, 01 Jan 2019 02:42:38 GMT) CTRI Number CTRI/2008/091/000063 [Registered on: 08/07/2008] - Last Modified On Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Tue, 01 Jan 2019 02:42:38 GMT) CTRI Number CTRI/2008/091/000063 [Registered on: 08/07/2008] - Last Modified On Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of
Safety and efficacy of flavocoxid compared with naproxen in subjects with osteoarthritis of the knee: a pilot study
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 15(suppl B):B91 Safety and efficacy of flavocoxid compared with naproxen in subjects with osteoarthritis of the knee: a pilot study Levy R*, Saikovsky R, Shmidt E, Khokhlov
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 15(suppl B):B91 Safety and efficacy of flavocoxid compared with naproxen in subjects with osteoarthritis of the knee: a pilot study Levy R*, Saikovsky R, Shmidt E, Khokhlov
NOTOPAIN CAPLETS. Diclofenac Sodium + Paracetamol. Composition. Each tablet contains: Diclofenac Sodium BP 50mg Paracetamol BP 500mg.
 NOTOPAIN CAPLETS Diclofenac Sodium + Paracetamol Composition Each tablet contains: Diclofenac Sodium BP 50mg Paracetamol BP 500mg Pharmacology Phamacodynamics Diclofenac relieves pain and inflammation
NOTOPAIN CAPLETS Diclofenac Sodium + Paracetamol Composition Each tablet contains: Diclofenac Sodium BP 50mg Paracetamol BP 500mg Pharmacology Phamacodynamics Diclofenac relieves pain and inflammation
Received: 18 October 2001 Accepted: 21 March 2002
 BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine BioMed Central BMC 22002, Complementary and Alternative Medicine x Research article Electroacupuncture versus Diclofenac in symptomatic treatment of Osteoarthritis
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine BioMed Central BMC 22002, Complementary and Alternative Medicine x Research article Electroacupuncture versus Diclofenac in symptomatic treatment of Osteoarthritis
Efficacy and tolerability of celecoxib in osteoarthritis patients who previously failed naproxen and ibuprofen: results from two trials
 International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology A - Efficacy and tolerability of celecoxib in osteoarthritis patients who previously failed naproxen and ibuprofen: results from two trials Aims: To evaluate
International Journal of Clinical Rheumatology A - Efficacy and tolerability of celecoxib in osteoarthritis patients who previously failed naproxen and ibuprofen: results from two trials Aims: To evaluate
REXON-AGE therapy in the treatment of arthrosis
 Presidio Ospedaliero di Cittadella Unità Operativa Autonoma ANESTESIA RIANIMAZIONE E TERAPIA DEL DOLORE Direttore: Dott. Giandomenico BABBOLIN Via Riva Ospedale 35013 Cittadella / Padova Tel. 049.942.48.01/3
Presidio Ospedaliero di Cittadella Unità Operativa Autonoma ANESTESIA RIANIMAZIONE E TERAPIA DEL DOLORE Direttore: Dott. Giandomenico BABBOLIN Via Riva Ospedale 35013 Cittadella / Padova Tel. 049.942.48.01/3
Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee Pain in Adults With Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee
Summary. Introduction
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 290 296 2002 Published by Elsevier Science Ltd on behalf of OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/01/040290+07 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0510,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 290 296 2002 Published by Elsevier Science Ltd on behalf of OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/01/040290+07 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0510,
Risk Management Plan Etoricoxib film-coated tablets
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Pain or stiffness in joints after periods of inactivity or excessive use
 Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
SELECTED ABSTRACTS. Figure. Risk Stratification Matrix A CLINICIAN S GUIDE TO THE SELECTION OF NSAID THERAPY
 SELECTED ABSTRACTS A CLINICIAN S GUIDE TO THE SELECTION OF NSAID THERAPY The authors of this article present a 4-quadrant matrix based on 2 key clinical parameters: risk for adverse gastrointestinal (GI)
SELECTED ABSTRACTS A CLINICIAN S GUIDE TO THE SELECTION OF NSAID THERAPY The authors of this article present a 4-quadrant matrix based on 2 key clinical parameters: risk for adverse gastrointestinal (GI)
Gastrointestinal Safety of Coxibs and Outcomes Studies: What s the Verdict?
 Vol. 23 No. 4S April 2002 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S5 Proceedings from the Symposium The Evolution of Anti-Inflammatory Treatments in Arthritis: Current and Future Perspectives Gastrointestinal
Vol. 23 No. 4S April 2002 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S5 Proceedings from the Symposium The Evolution of Anti-Inflammatory Treatments in Arthritis: Current and Future Perspectives Gastrointestinal
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 9 January 2013
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 9 January 2013 The opinion adopted by the Transparency Committee on 4 July 2012 was given a hearing on 5 December
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 9 January 2013 The opinion adopted by the Transparency Committee on 4 July 2012 was given a hearing on 5 December
Is Curcumin Effective in Reducing Pain in Arthritis Patients?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Curcumin Effective in Reducing Pain
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Curcumin Effective in Reducing Pain
Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets , Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
 Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets 23.5.2016, Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg film-coated
Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets 23.5.2016, Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg film-coated
Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review: February 2007
 Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review:
Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review:
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 1111e1118 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.004 An analgesic model
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 1111e1118 ª 2006 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.05.004 An analgesic model
Pain therapeutics. Acetaminophen/NSAIDs Acute pain Osteoarthritis Migraine Acute Gout Neuropathic pain
 Pain therapeutics Acetaminophen/NSAIDs Acute pain Osteoarthritis Migraine Acute Gout Neuropathic pain James McCormack, Pharm.D. Professor Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, UBC Common types of pain killers
Pain therapeutics Acetaminophen/NSAIDs Acute pain Osteoarthritis Migraine Acute Gout Neuropathic pain James McCormack, Pharm.D. Professor Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, UBC Common types of pain killers
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2007) 15, 454e461 ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.10.008 Three-month efficacy
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2007) 15, 454e461 ª 2006 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.10.008 Three-month efficacy
OSTEOARTHRITIS; EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF ACECLOFENAC IN THE TREATMENT: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL VERSUS DICLOFENAC
 The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-416 OSTEOARTHRITIS; EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF ACECLOFENAC IN THE TREATMENT: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL VERSUS
The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-416 OSTEOARTHRITIS; EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF ACECLOFENAC IN THE TREATMENT: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL VERSUS
Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo in Reducing Pain in Patients with Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo
COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT
 JANUARY 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Osteoarthritis Pain
JANUARY 2012 COMPOUNDING PHARMACY SOLUTIONS PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING WWW.CPSRXS. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Osteoarthritis Pain
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a major cause of pain
 Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 138 143 DOI: 10.1097/01.GME.0000087983.28957.5D 2004 The North American Menopause Society Text printed on acid-free paper.
Menopause: The Journal of The North American Menopause Society Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 138 143 DOI: 10.1097/01.GME.0000087983.28957.5D 2004 The North American Menopause Society Text printed on acid-free paper.
O steoarthritis is a major source of morbidity, disability,
 70 EXTENDED REPORT First line treatment of knee osteoarthritis in outpatients in France: adherence to the EULAR 2000 recommendations and factors influencing adherence L Denoeud, B Mazières, C Payen-Champenois,
70 EXTENDED REPORT First line treatment of knee osteoarthritis in outpatients in France: adherence to the EULAR 2000 recommendations and factors influencing adherence L Denoeud, B Mazières, C Payen-Champenois,
Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) Produced by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination Copyright 2017 University of York.
 A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
A comparison of the cost-effectiveness of five strategies for the prevention of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced gastrointestinal toxicity: a systematic review with economic modelling Brown
Prevention Diagnosis Assessment Prescription and /or application of wide range of interventions and PRM program management
 OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
Osteoarthritis (OA), the most common joint
 Effect of Rofecoxib Therapy on Measures of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Osteoarthritis Elliot W. Ehrich, MD; James A. Bolognese, MStat; Douglas J. Watson, PhD; and Sheldon X. Kong, PhD
Effect of Rofecoxib Therapy on Measures of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Osteoarthritis Elliot W. Ehrich, MD; James A. Bolognese, MStat; Douglas J. Watson, PhD; and Sheldon X. Kong, PhD
Canadian Chiropractic Guideline Initiative (CCGI) Guideline Summary
 Canadian Chiropractic Guideline Initiative (CCGI) Guideline Summary Title of guideline Osteoarthritis: care and management Clinical guideline Author of guideline National Institute for Health and Care
Canadian Chiropractic Guideline Initiative (CCGI) Guideline Summary Title of guideline Osteoarthritis: care and management Clinical guideline Author of guideline National Institute for Health and Care
Iroko Pharmaceuticals Receives FDA Approval for VIVLODEX - First Low Dose SoluMatrix Meloxicam for Osteoarthritis Pain
 Iroko Pharmaceuticals Receives FDA Approval for VIVLODEX - First Low Dose SoluMatrix Meloxicam for Osteoarthritis Pain VIVLODEX Developed to Align with FDA NSAID Recommendations Proven Efficacy at Low
Iroko Pharmaceuticals Receives FDA Approval for VIVLODEX - First Low Dose SoluMatrix Meloxicam for Osteoarthritis Pain VIVLODEX Developed to Align with FDA NSAID Recommendations Proven Efficacy at Low
Maria Lourdes R. Bernardo and Alfredo C. Azarcon, Jr. Department of Rehabi/itation Medicine, Veterans Memorial Medica! Center
 A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of Oral Collagen Treatment on the Media) Knee Joint Space aod Functional Outcome among Veterans Memorial Medical Center Patients Diagnosed with Osteoarthritis
A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of Oral Collagen Treatment on the Media) Knee Joint Space aod Functional Outcome among Veterans Memorial Medical Center Patients Diagnosed with Osteoarthritis
T Pincus, G Koch, H Lei, B Mangal, T Sokka, R Moskowitz, F Wolfe, A Gibofsky, L Simon, S Zlotnick, J G Fort...
 931 EXTENDED REPORT Patient Preference for Placebo, Acetaminophen (paracetamol) or Celecoxib Efficacy Studies (PACES): two randomised, double blind, placebo controlled, crossover clinical trials in patients
931 EXTENDED REPORT Patient Preference for Placebo, Acetaminophen (paracetamol) or Celecoxib Efficacy Studies (PACES): two randomised, double blind, placebo controlled, crossover clinical trials in patients
Received: 11 Sep 2006 Revisions requested: 6 Nov 2006 Revisions received: 3 Jan 2007 Accepted: 31 Jan 2007 Published: 31 Jan 2007
 Vol 9 No 1 Research article Evaluation of the Patient Acceptable Symptom State in a pooled analysis of two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies evaluating lumiracoxib and celecoxib
Vol 9 No 1 Research article Evaluation of the Patient Acceptable Symptom State in a pooled analysis of two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies evaluating lumiracoxib and celecoxib
Type of intervention Treatment. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Costs and effectiveness of pre- and post-operative home physiotherapy for total knee replacement: randomized controlled trial Mitchell C, Walker J, Walters S, Morgan A B, Binns T, Mathers N Record Status
Costs and effectiveness of pre- and post-operative home physiotherapy for total knee replacement: randomized controlled trial Mitchell C, Walker J, Walters S, Morgan A B, Binns T, Mathers N Record Status
CHOLINE MAGNESIUM TRISALICYLATE VS NAPROXEN IN THE SYMPTOMATIC TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol 5, Issue 1, 212 ISSN - 974-2441 Research Article CHOLINE MAGNESIUM TRISALICYLATE VS NAPROXEN IN THE SYMPTOMATIC TREATMENT OF
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol 5, Issue 1, 212 ISSN - 974-2441 Research Article CHOLINE MAGNESIUM TRISALICYLATE VS NAPROXEN IN THE SYMPTOMATIC TREATMENT OF
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (26) 14, A14eA18 ª 26 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:116/j.joca.26.2.22 Assessment of joint space narrowing
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (26) 14, A14eA18 ª 26 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:116/j.joca.26.2.22 Assessment of joint space narrowing
OSTEOARTHRITIS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research
 infoaging guides DISEASES OF AGING OSTEOARTHRITIS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS? Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
infoaging guides DISEASES OF AGING OSTEOARTHRITIS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS? Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
ClinialTrials.gov Identifier: Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
Shared Decision Making
 Deciding what to do about carpal This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your carpal. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you make a decision about what's right
Deciding what to do about carpal This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your carpal. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you make a decision about what's right
A Comparison of Acupuncture with Advice and Exercises on the Symptomatic Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Hip A Randomised Controlled Trial
 A Comparison of Acupuncture with Advice and Exercises on the Symptomatic Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Hip A Randomised Controlled Trial Roisin Haslam Summary Acupuncture is becoming a common technique
A Comparison of Acupuncture with Advice and Exercises on the Symptomatic Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Hip A Randomised Controlled Trial Roisin Haslam Summary Acupuncture is becoming a common technique
ARD Online First, published on April 13, 2004 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on April 13, 2004 as 10.1136/ard.2003.020313 Patient preference for, or Celecoxib Efficacy Studies (PACES): Two randomized placebo-controlled cross-over clinical trials in patients
ARD Online First, published on April 13, 2004 as 10.1136/ard.2003.020313 Patient preference for, or Celecoxib Efficacy Studies (PACES): Two randomized placebo-controlled cross-over clinical trials in patients
Shared Decision Making Osteoarthritis of the Knee Next clinical review date March 2018
 Shared Decision Making Osteoarthritis of the Knee Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what to do about Osteoarthritis of the Knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about
Shared Decision Making Osteoarthritis of the Knee Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what to do about Osteoarthritis of the Knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about
Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Acute pain usually responds to medication and should settle in less than three months. Inadequate pain relief may lead to other
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Acute pain usually responds to medication and should settle in less than three months. Inadequate pain relief may lead to other
NONSTEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS
 NONSTEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS MRS. M.M. HAS A 3 YR. HX OF PROGRESSIVE RIGHT HIP PAIN. THE PAIN INCREASES WITH WEIGHT BEARING ACTIVITY. PT. HAS BEEN ON ACETAMINOPHEN WITHOUT RELIEF. PERTINENT LABS
NONSTEROIDAL ANTI- INFLAMMATORY DRUGS MRS. M.M. HAS A 3 YR. HX OF PROGRESSIVE RIGHT HIP PAIN. THE PAIN INCREASES WITH WEIGHT BEARING ACTIVITY. PT. HAS BEEN ON ACETAMINOPHEN WITHOUT RELIEF. PERTINENT LABS
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
T he choice of an outcome measure is a major step in the
 29 EXTENDED REPORT Evaluation of clinically relevant changes in patient reported outcomes in knee and hip osteoarthritis: the minimal clinically important improvement F Tubach, P Ravaud, G Baron, B Falissard,
29 EXTENDED REPORT Evaluation of clinically relevant changes in patient reported outcomes in knee and hip osteoarthritis: the minimal clinically important improvement F Tubach, P Ravaud, G Baron, B Falissard,
High Impact Rheumatology
 High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
Children Enteric coated tablet : 1-3 mg/kg per day in divided doses.
 Ultrafen Tablet/SR Tablet/Suppository/Gel Description Ultrafen is a preparation of Diclofenac is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent with marked analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
Ultrafen Tablet/SR Tablet/Suppository/Gel Description Ultrafen is a preparation of Diclofenac is a non-steroidal antiinflammatory agent with marked analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS
 Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS Objective Outline some clinical features that are not well appreciated in OA patients Recent advances in knowledge and management of OA
Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS Objective Outline some clinical features that are not well appreciated in OA patients Recent advances in knowledge and management of OA
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE
 Dr C S Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE The knee is the largest joint in the body, and is also the joint most
Dr C S Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE The knee is the largest joint in the body, and is also the joint most
NSAIDs: Side Effects and Guidelines
 NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2004) 12, 389 399 2004 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2004.02.001 International Cartilage
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2004) 12, 389 399 2004 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2004.02.001 International Cartilage
Evaluation of Ostolief (Polyherbal Formulation) in the Management of Osteoarthritis: A Double-blind, Randomized, 12-Week Comparative Study
 Volume 17, Number 5 October 2006 Special Reprint Evaluation of Ostolief (Polyherbal Formulation) in the Management of Osteoarthritis: A Double-blind, Randomized, 12-Week Comparative Study DG Langade* SRSinha**
Volume 17, Number 5 October 2006 Special Reprint Evaluation of Ostolief (Polyherbal Formulation) in the Management of Osteoarthritis: A Double-blind, Randomized, 12-Week Comparative Study DG Langade* SRSinha**
AN NSAID WITH A BALANCED COX-1 & COX-2 INHIBITORY EFFECT
 AN NSAID WITH A BALANCED COX-1 & COX-2 INHIBITORY EFFECT A balanced cox-1 and cox-2 inhibitor Metabolisim and Bioavailabillty of Lornoxicam (3) Relative selectivity of agents as inhibitors of cox-1 and
AN NSAID WITH A BALANCED COX-1 & COX-2 INHIBITORY EFFECT A balanced cox-1 and cox-2 inhibitor Metabolisim and Bioavailabillty of Lornoxicam (3) Relative selectivity of agents as inhibitors of cox-1 and
... REPORTS... The Use and Effect of Analgesics in Patients Who Regularly Drink Alcohol. Richard C. Dart, MD, PhD
 ... REPORTS... The Use and Effect of Analgesics in Patients Who Regularly Drink Alcohol Richard C. Dart, MD, PhD Abstract Analgesic consumption poses special risks for regular users of alcohol. Among the
... REPORTS... The Use and Effect of Analgesics in Patients Who Regularly Drink Alcohol Richard C. Dart, MD, PhD Abstract Analgesic consumption poses special risks for regular users of alcohol. Among the
Drug Class Review Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
 Drug Class Review Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Preliminary Scan Report #2 May 2014 Last Report: Update #4 (November 2010) Last Preliminary Scan: July 2013 The purpose of reports is to make
Drug Class Review Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Preliminary Scan Report #2 May 2014 Last Report: Update #4 (November 2010) Last Preliminary Scan: July 2013 The purpose of reports is to make
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 26 November 2008
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 26 November 2008 ZONDAR 50 mg, capsules Pack of 30 capsules (CIP: 335 530-01) Applicant : PHARMA 2000 Diacerein ATC
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 26 November 2008 ZONDAR 50 mg, capsules Pack of 30 capsules (CIP: 335 530-01) Applicant : PHARMA 2000 Diacerein ATC
Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? 2. What are the ingredients of Algaea-X? 3. How does Algaea-X work?
 Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? Algaea-X is a topical cream developed to help relieve pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and helps the regeneration of damaged cartilage. Developed by utilizing
Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? Algaea-X is a topical cream developed to help relieve pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and helps the regeneration of damaged cartilage. Developed by utilizing
Pain in Osteoarthritis
 Pain in Osteoarthritis By Edward L. Treadwell, MD Professor of Medicine- Rheumatology/Immunology Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University School of Medicine Greenville, NC 27834 E-mail: treadwelle@ecu.edu
Pain in Osteoarthritis By Edward L. Treadwell, MD Professor of Medicine- Rheumatology/Immunology Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University School of Medicine Greenville, NC 27834 E-mail: treadwelle@ecu.edu
Ketorolac injection. Supportive care
 Supportive care Ketorolac injection Supportive care: specialist medicines This leaflet provides information on a medicine called ketorolac which is used to treat pain that is difficult to control. It is
Supportive care Ketorolac injection Supportive care: specialist medicines This leaflet provides information on a medicine called ketorolac which is used to treat pain that is difficult to control. It is
The legally binding text is the original French version
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 July 2009 ENDOSTA 625 mg, tablet Box of 60 (CIP: 380 534-2) Box of 180 (CIP: 380 535-9) Applicant: EXPANSCIENCE
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 July 2009 ENDOSTA 625 mg, tablet Box of 60 (CIP: 380 534-2) Box of 180 (CIP: 380 535-9) Applicant: EXPANSCIENCE
Keywords: Prescribing pattern, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis
 Human Journals Research Article May 2016 Vol.:6, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Anjali.C et al. A Prospective Observational Study to Assess Prescription Pattern in Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis
Human Journals Research Article May 2016 Vol.:6, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Anjali.C et al. A Prospective Observational Study to Assess Prescription Pattern in Osteoarthritis & Rheumatoid Arthritis
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW. Issue 6 February Economic Assessment: Celecoxib and Rofecoxib for Patients with Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis
 TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW Issue 6 February 2002 Economic Assessment: Celecoxib and Rofecoxib for Patients with Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis Publications can be requested from: CCOHTA 110-955 Green
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW Issue 6 February 2002 Economic Assessment: Celecoxib and Rofecoxib for Patients with Osteoarthritis or Rheumatoid Arthritis Publications can be requested from: CCOHTA 110-955 Green
Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate to Severe Osteoarthritis Pain in Adults?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate
Say goodbye to your agonizing joint pain FAST and kick start TRUE HEALING with these powerful holistic therapies
 Say goodbye to your agonizing joint pain FAST and kick start TRUE HEALING with these powerful holistic therapies As I read the results of a recent osteoarthritis (OA) study in a major medical journal they
Say goodbye to your agonizing joint pain FAST and kick start TRUE HEALING with these powerful holistic therapies As I read the results of a recent osteoarthritis (OA) study in a major medical journal they
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: , VERSION 1.
 RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: 07-10-2016, VERSION 1.2 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib Orion
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: 07-10-2016, VERSION 1.2 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib Orion
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of platelet-rich plasma injections for knee osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis can develop
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of platelet-rich plasma injections for knee osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis can develop
Quality measures in osteoarthritis
 Quality measures in osteoarthritis M.C. Hochberg Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH, Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, University
Quality measures in osteoarthritis M.C. Hochberg Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH, Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, University
Papers. Abstract. Introduction. Methods. Jonathan J Deeks, Lesley A Smith, Matthew D Bradley
 Efficacy, tolerability, and upper gastrointestinal safety of celecoxib for treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review of randomised controlled trials Jonathan J Deeks, Lesley
Efficacy, tolerability, and upper gastrointestinal safety of celecoxib for treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review of randomised controlled trials Jonathan J Deeks, Lesley
Effective Health Care Program
 Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 38 Effective Health Care Program Analgesics for Osteoarthritis: An Update of the 2006 Comparative Effectiveness Review Executive Summary Background Osteoarthritis
Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 38 Effective Health Care Program Analgesics for Osteoarthritis: An Update of the 2006 Comparative Effectiveness Review Executive Summary Background Osteoarthritis
Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
 Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Helpline No:
 ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION Registered Nonprofit Organisation - No. 002-847 NPO Helpline No: 0861 30 30 30 DRUGS AND ARTHRITIS This information leaflet is published by the Arthritis Foundation as part of our
ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION Registered Nonprofit Organisation - No. 002-847 NPO Helpline No: 0861 30 30 30 DRUGS AND ARTHRITIS This information leaflet is published by the Arthritis Foundation as part of our
Arthritis of the Shoulder
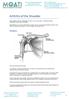 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Knee
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
UPDATES ON MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS
 UPDATES ON MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS August 10, 2014 Dr. Suneil Kapur Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Ottawa Associate Staff Rheumatologist, The Ottawa Hospital Learning Objectives Upon
UPDATES ON MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS August 10, 2014 Dr. Suneil Kapur Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Ottawa Associate Staff Rheumatologist, The Ottawa Hospital Learning Objectives Upon
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hinman RS, McCrory, irotta M, et al. Acupuncture for chronic knee pain: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.12660. etable 1: Exclusion criteria etable
Supplementary Online Content Hinman RS, McCrory, irotta M, et al. Acupuncture for chronic knee pain: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.12660. etable 1: Exclusion criteria etable
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is the most common type of joint disease. It represents a group of conditions that result in changes
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is the most common type of joint disease. It represents a group of conditions that result in changes
302 Scand J Rheumatol 2005;34:
 302 Scand J Rheumatol 2005;34:302 308 A powder made from seeds and shells of a rose-hip subspecies (Rosa canina) reduces symptoms of knee and hip osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
302 Scand J Rheumatol 2005;34:302 308 A powder made from seeds and shells of a rose-hip subspecies (Rosa canina) reduces symptoms of knee and hip osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
Coverage Guideline. BioniCare System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) DEFINITION COVERAGE CRITERIA MEDICAL BACKGROUND
 Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Glucosamine May Reduce Pain in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis
 1 Glucosamine May Reduce Pain in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis Prepared by: Jacqueline Pierce, MSc (PT) candidate, Queen's University Date: April 2005 (planned review date April 2007) Clinical Scenario:
1 Glucosamine May Reduce Pain in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis Prepared by: Jacqueline Pierce, MSc (PT) candidate, Queen's University Date: April 2005 (planned review date April 2007) Clinical Scenario:
Analgesic Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 1 March 2016
 Analgesic Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 1 March 2016 (minutes for web publishing) The Analgesic Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology and
Analgesic Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 1 March 2016 (minutes for web publishing) The Analgesic Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology and
Original Article COMPARING THE EFFECTS OF GINGER (ZINGIBER OFFICINALE) EXTRACT AND IBUPROFEN ON PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS
 Arch Iranian Med 2005; 8 (4): 267 271 Original Article COMPARING THE EFFECTS OF GINGER (ZINGIBER OFFICINALE) EXTRACT AND IBUPROFEN ON PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS Masoud Haghighi PhD *, Ali Khalvat MD**,
Arch Iranian Med 2005; 8 (4): 267 271 Original Article COMPARING THE EFFECTS OF GINGER (ZINGIBER OFFICINALE) EXTRACT AND IBUPROFEN ON PATIENTS WITH OSTEOARTHRITIS Masoud Haghighi PhD *, Ali Khalvat MD**,
V Roy*, U Gupta*, S Sharma**, B K Dhaon***, N P Singh****, P Gulati*****
 Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Nimesulide and Piroxicam in Osteoarthritis with Specific Reference to Chondroprotection : A Double Blind Randomised Study V Roy*, U Gupta*, S Sharma**, B K Dhaon***,
Comparative Efficacy and Tolerability of Nimesulide and Piroxicam in Osteoarthritis with Specific Reference to Chondroprotection : A Double Blind Randomised Study V Roy*, U Gupta*, S Sharma**, B K Dhaon***,
In the Treatment of Patients With Knee Joint Osteoarthritis, Are Platelet Rich Plasma Injections More Effective Than Hyaluronic Acid Injections?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 In the Treatment of Patients With Knee
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 In the Treatment of Patients With Knee
Effective pain management begins with OFIRMEV (acetaminophen) injection FIRST Proven efficacy with rapid reduction in pain 1
 Effective pain management begins with OFIRMEV (acetaminophen) injection FIRST Proven efficacy with rapid reduction in pain 1 Fast onset of pain relief with 7% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) scores
Effective pain management begins with OFIRMEV (acetaminophen) injection FIRST Proven efficacy with rapid reduction in pain 1 Fast onset of pain relief with 7% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) scores
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2013) 2(10):
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 10 (2013) pp. 369-381 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A Prospective Clinical Evaluation between Intra - Articular Injections of Methyl Prednisolone and Triamcinolone
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 10 (2013) pp. 369-381 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A Prospective Clinical Evaluation between Intra - Articular Injections of Methyl Prednisolone and Triamcinolone
Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture
 Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Dr Panos Barlas School of Health and Rehabilitation Keele University Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Applications of acupuncture Principles
Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Dr Panos Barlas School of Health and Rehabilitation Keele University Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Applications of acupuncture Principles
Is Regenerative Injection Therapy (Prolotherapy) Effective at Reducing Pain Associated With Knee Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Regenerative Injection Therapy (Prolotherapy)
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Regenerative Injection Therapy (Prolotherapy)
Academic address / Address for correspondence
 TITLE PAGE Title: Safety and efficacy of Arthronat in Indian subjects with painful Osteoarthritis of hips, knees, shoulders, neck or wrists Authors (Qualifications) Dr. Jyoti rao Hegde Dr. Lakshmi Bantwal
TITLE PAGE Title: Safety and efficacy of Arthronat in Indian subjects with painful Osteoarthritis of hips, knees, shoulders, neck or wrists Authors (Qualifications) Dr. Jyoti rao Hegde Dr. Lakshmi Bantwal
International Journal of Orthopaedics Sciences 2018; 4(1): Varun GBS, Vignesh Kumar V, Raj Lavadi and Muralidhar N
 2018; 4(1): 1094-1098 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1094-1098 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 07-11-2017 Accepted: 10-12-2017 Varun GBS Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Vydehi
2018; 4(1): 1094-1098 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1094-1098 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 07-11-2017 Accepted: 10-12-2017 Varun GBS Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Vydehi
Non-Steroidal Anti- Inflammatory Drugs. ATPE 410 Chapter 6
 Non-Steroidal Anti- Inflammatory Drugs ATPE 410 Chapter 6 Inflammatory Process A normal, beneficial process that begins immediately after injury to facilitate repair and return the tissue to normal function
Non-Steroidal Anti- Inflammatory Drugs ATPE 410 Chapter 6 Inflammatory Process A normal, beneficial process that begins immediately after injury to facilitate repair and return the tissue to normal function
Diagnosis & Nonoperative Treatment of the Osteoarthritic Knee. Randall R Wroble MD Orthopedic One Columbus OH
 Diagnosis & Nonoperative Treatment of the Osteoarthritic Knee Randall R Wroble MD Orthopedic One Columbus OH There are 2 things a good doctor does First Step: Finds out what's wrong Second step Makes the
Diagnosis & Nonoperative Treatment of the Osteoarthritic Knee Randall R Wroble MD Orthopedic One Columbus OH There are 2 things a good doctor does First Step: Finds out what's wrong Second step Makes the
Double-blind randomized controlled trial of isoxicam vs piroxicam in elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1986), 22, 149S-155S Double-blind randomized controlled trial of isoxicam vs piroxicam in elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee N. BELLAMY"'2, W. W. BUCHANAN2
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1986), 22, 149S-155S Double-blind randomized controlled trial of isoxicam vs piroxicam in elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee N. BELLAMY"'2, W. W. BUCHANAN2
