A Comparison of Acupuncture with Advice and Exercises on the Symptomatic Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Hip A Randomised Controlled Trial
|
|
|
- Brittany Butler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Comparison of Acupuncture with Advice and Exercises on the Symptomatic Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Hip A Randomised Controlled Trial Roisin Haslam Summary Acupuncture is becoming a common technique within the physiotherapy profession as a treatment modality for pain relief; however, few randomised controlled trials have been undertaken to assess the effectiveness of acupuncture, particularly in the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) of the hip. Therefore, a randomised trial to compare the effectiveness of acupuncture with advice and exercises on the symptomatic treatment of OA of the hip was carried out. Thirty-two patients awaiting a total hip arthroplasty were randomly allocated to either the experimental group, (A), to have six sessions of acupuncture each lasting up to 25 minutes, or the control group, (B), to be given advice and exercises for their hip over a six week period. Group A consisted of three men and 13 women, and group B consisted of four men and eight women. The average age in group A was 66 years and in group B it was 68 years. Patients were assessed for pain and functional ability, using a modified version of the WOMAC questionnaire, pre-treatment, immediately post-treatment and at eight weeks post-treatment. The pre-treatment WOMAC scores in the two groups were similar (p=0.85). There was a significant improvement in group A (decrease in WOMAC score) immediately post-treatment (p=0.002) and this was maintained at the eightweek follow-up (p=0.03). There were no significant changes in group B. When the changes in WOMAC scores were compared between groups, a significantly greater improvement was found between pre-treatment and immediately post-treatment in group A, compared with group B (p=0.02). The changes between pre-treatment and the eight-week follow-up also showed a significant improvement in group A compared with group B (p=0.03). In conclusion, this trial supports the hypothesis that acupuncture is more effective than advice and exercises in the symptomatic treatment of OA of the hip. Keywords Acupuncture, pain relief, osteoarthritis, hip joint, exercises, randomised controlled trial. Introduction Osteoarthritis (OA) is an extremely common disease. In an ageing population, one in five individuals suffer from OA. 1 The underlying disease process involves destruction of the articular cartilage leading to proliferation and remodelling of the subchondral bone. 2 Patients present with pain, swelling and stiffness, causing a reduction in functional ability, particularly if a weight-bearing joint is affected. 3 Conservative treatment of OA is aimed at pain relief through the use of anti-inflammatory drugs. Side effects from such drugs have been documented to include gastrointestinal haemorrhage, renal toxicity and an increased risk of hypertension. 4 Another form of conservative treatment is physiotherapy. Current treatment focuses on advice and education about the disease process, how patients can help themselves, the latter having been identified as an important part of treating OA, 5 and stretching and strengthening exercises for the muscles around the pelvis, aimed at stabilising the joint. 5 King (1997) suggests that Roisin Haslam senior physiotherapist Princess Margaret Hospital Swindon haslamroisin@ hotmail.com 19
2 this form of management may help to extend the time before a total hip replacement is necessary. 6 Patients can wait many months for surgery, during which time the disease process progresses, and the patients quality of life decreases. This may be one reason why patients and practitioners are seeking alternative or complementary treatments for the symptoms of OA. Acupuncture is becoming increasingly popular in the symptomatic treatment of OA. In the United Kingdom, it has been reported that between 25 to 54% of patients with OA have sought alternative practitioners. 7 Few studies exist on the effectiveness of acupuncture and OA of the hip. 8 Ernst (1997) performed a systematic review of studies on acupuncture as a symptomatic treatment of OA: 2 a Medline search ( ) and a search of a database specialising in complementary medicine highlighted 13 studies. Most of the studies used pain scales as outcome measures and employed formula acupuncture (predefined set of points). The review found inconsistencies in the effectiveness of acupuncture to relieve pain. Seven of the studies reported an apparent relief of pain compared with the control groups, 9-15 whilst the other six did not ;27 Of the former seven, however, several failed to control for placebo effects, some were not randomised trials, had small sample sizes and lacked formal statistical analysis. Such factors jeopardise the quality of the research and indicate the need for further randomised controlled trials to determine the specific efficacy of acupuncture on pain relief in this condition. As a consequence of this lack of research, and a trend found in the researcher s own practice, it was decided to investigate the treatment of OA of the hip with acupuncture, compared with one type of current physiotherapy practice. A randomised trial was designed, the null hypothesis being that there was no difference between acupuncture and advice and exercises in the symptomatic treatment of OA of the hip. Method This trial was conducted with a group of 32 patients on the waiting list for a total hip arthroplasty. The number of patients was derived from those available at the time of the study, given the author s time and resource constraints, rather than from a formal power analysis. Swindon Research Ethics Committee approved the study and all patients gave informed consent prior to the start of the trial. All patients included in the study had radiographic changes consistent with OA. Patients were excluded from the study if they had rheumatoid arthritis, previous hip injury or surgery, intra-articular steroid injection in the last three months, if they were pregnant, had epilepsy, or had an allergy to metal. The patients were randomly allocated, using a random number table, to group A or B, with 16 in each group. Group A received a course of acupuncture, and group B received advice and exercises for their hip. The total study period was 14 weeks. The setting for the study was a physiotherapy department in a District General Hospital. Group A received six sessions of acupuncture. The first session lasted ten minutes, with the patient side-lying with their affected hip uppermost. Acupuncture points used were: GB29, GB30, GB34, GB43, ST44, LI4 bilaterally, and four ah shi points around the greater trochanter, in a north, south, east, west formation. The majority of points chosen were on the Gall Bladder meridian, which is said to have an influence on muscles and tendons, and the course of which passes over the lateral and posterior aspects of the hip. ST44 and LI4 were chosen because of their general pain relieving influence, 21 and the ah shi points to isolate the greater trochanter and its muscle attachments, which support the hip. Viva sterile disposable acupuncture needles (0.25mm diameter, 25mm length) were used. Longer needles were used at GB30 (0.25mm diamater, 40mm length). The needles were manufactured by Helio Medical Supplies Inc, Santa Clara, CA 95050, USA. Each 20
3 needle was manually stimulated for approximately ten seconds half way through the treatment. Subsequent sessions lasted 25 minutes, with manual stimulation of each needle, for approximately ten seconds, every five minutes. Each patient received one session per week over a six-week period. Each session was conducted by the author at a similar time of day and in the same room. Group B attended the department three times over the same time period. Each session lasted 30 minutes. The first session involved giving each patient an advice sheet on OA, and on self-help. 22 The advice sheet also contained a set of five exercises that were demonstrated to the patient, 3 who then practiced them to the author s satisfaction. Three weeks later the patients came back for a review to check that they were doing their exercises correctly, and they were advised, if appropriate, on how to gently progress. Three weeks later the patients came back for their final review and were encouraged to continue with the exercises and follow the advice given. Each session was conducted by the author at a similar time of day and in the same room. Neither the author nor the patients were blinded to the treatments received. A slightly modified version of the WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities) osteoarthritis index was used as the outcome measure (Appendix 1). A previous study by Berman et al (1994) used the original questionnaire as an outcome measure on the efficacy of traditional Chinese acupuncture in the treatment of symptomatic knee OA. 23 The WOMAC questionnaire is a three-dimensional, disease specific, self-administered measure of health status. 24 It defines clinical and patient relevant symptoms in the areas of pain, stiffness and physical function in patients with OA of the hip or knee. It is valid, reliable and sufficiently sensitive to identify changes in health status following a variety of interventions including physiotherapy. 24 The questionnaire was given to all patients in both groups on their first attendance to establish a baseline of their pain and functional ability. Levels were measured on a 100mm point visual analogue scale. There were 16 questions in total, therefore each subject was scored out of The greater the WOMAC score, the more pain and dysfunction the patient reports. A body chart was also completed to establish the main area of pain, and this was compared with subsequent questionnaires to identify changes in areas of pain post-treatment. Patients were also asked to state how much analgesia they took on average per day for the pain in their hip. Patients were given back their pre-trial questionnaire at the end of the six-week period to establish their score post-treatment. A new questionnaire was sent to all patients eight weeks later, to identify any longer term effects of their treatment. Data from the questionnaires were tested for normality, and intra-group comparisons were performed using the paired t-test. Inter-group comparisons were performed using the unpaired t- test, and checked with the Mann-Whitney test where normality of the sample scores was in question. Results Sixteen patients were randomly allocated to each group at the start of the study. Group A remained intact but in group B, four patients withdrew from the study during the intervention period. One patient was admitted for arthroplasty, another withdrew after the first session after having a fall at home, another withdrew after the first session due to difficulty in getting to the department because of poor mobility. The fourth patient attended the first session then did not attend the second and could not be re-contacted. Three further patients dropped out of group B between the post-treatment assessment and the eight-week follow-up. One reported having had an arthroplasty and the other two were not contactable. One patient dropped out of group A during this period to have a total hip replacement. 21
4 Table 1 Demographic Data Group A Group B Number of patients Male : female ratio 3 : 13 4 : 8 Mean age (yrs) Age range (yrs) Mean duration of symptoms (yrs) 9 6 Table 2 WOMAC Scores Group A Group B MEAN SD MEAN SD Pre-treatment 870* Post-treatment 696* Eight-week follow-up 732* *p<0.05 for the inter-group comparisons of the changes in scores between pre-treatment and immediately post-treatment, and between pre-treatment and eight-week follow-up. The demographic data for both groups is illustrated in Table 1. Analysis confirmed that the data were normally distributed at all stages, with the exception, in group A, of the difference in scores between preand immediately post-treatment. No significant difference was found between the pre-treatment scores of group A and group B (p=0.85), confirming that the groups were similar at baseline. Figure 1 Mean WOMAC scores for group A and group B p values represent intra-group changes p=0.002 Group A Group B NS Pre-treatment Post-treatment Eight-weeks follow-up NS p=0.03 WOMAC scores decreased significantly in group A from pre- to immediately post-treatment (p=0.002), and from pre-treatment to the eightweek follow-up (p=0.03)(see figure 1). A significant difference was found in the pre- to immediately post-treatment change when the two groups were compared (p=0.02). This comparison was made using the unpaired t-test, and the result confirmed with the Mann-Whitney test, as one of the sets of figures was non-normal. Five subjects (31%) in group A, and three (25%) in group B had reduced their analgesia intake by the end of the treatment course. At the eight-week follow-up, four subjects in group A, and one in group B had maintained this reduction. Six subjects (38%) in group A, and three (25%) in group B reported fewer symptoms on their body chart at the end of the treatment course. At the eight-week follow-up, three subjects in group A and one in group B reported the maintenance of fewer symptoms. Discussion To summarise the findings of this study, there was a significant improvement in pain relief and function in the acupuncture group compared with that in the group receiving advice and exercises, and this benefit lasted for at least two months. Further, almost a third (31%) of subjects in group A managed to reduce the analgesic drug intake for their hip by the end of the treatment session, compared with only a quarter of those in group B. These results provide evidence for the effectiveness of acupuncture compared with a more traditional approach in the treatment of both the pain and dysfunction associated with OA of the hip joint. There are several limitations to this study. There was no control for the needle, so this trial is not able to determine the specific effect of the needling within the acupuncture intervention. The sample size was relatively small, and this questions whether the results can be generalised to the population as a whole. There was a relatively high number of dropouts, with seven of the 22
5 original 16 patients lost between pre-treatment and the eight-week follow-up in group B, compared with the loss of only one from group A. The high dropout rate may have been prevented by recruiting patients who had just been put on the waiting list for total hip arthroplasty, because the length of the wait is such that they would not have reached surgery within the trial period. The dropout rate for group B could also have been attributed to patients within this group wanting to have acupuncture and lacking faith in the advice and exercise intervention, which requires more co-operation and self-motivation on the part of the patient. This issue was identified pre-treatment, and the relevant patients were offered a course of acupuncture once the trial had finished. The outcome measure used in this trial (WOMAC) has been tested as a valid and reliable way of measuring health status changes in patients with OA of the hip and was therefore deemed appropriate for this trial. 24 The modified version that was used involved asking fewer questions from the third section of the questionnaire that covers functional tasks. The researcher identified specific tasks relevant to the hip, thus keeping the questionnaire shorter, so that patients were not daunted by being posed too many questions of a similar nature. This may have reduced the validity and reliability of the outcome measure; however, compared with previous studies, it appears more valid and reliable than having purely subjective outcome measures. 25 The WOMAC questionnaire can be used with either a visual analogue scale or a Likert scale. In validation studies of the questionnaire, the visual analogue scale proved the slightly more sensitive of the two, so it was chosen for the current trial. Some patients reported a difficulty, however, in translating their subjective levels of pain and stiffness to a 100mm line, with some patients reporting subjective changes in pain that were not consistent with their questionnaires. The reliability of such data must therefore be questioned, and in order to try and eliminate this problem in future research, the Likert scale may be the more reliable outcome measure to use amongst this sample group. It was also decided for the current trial to use the same questionnaire, post-treatment, that the patients had completed pre-treatment. Whether patients should be shown their prior scores remains controversial. This was addressed as part of a validation study for the WOMAC, and no statistically significant differences were found between blind and informed administration of the questionnaire. 24 Informed administration of the questionnaire was used in the current trial in an attempt to make it easier for the patients to judge their levels of pain and function pre- and posttreatment, because of the difficulties that some of them experienced in interpreting the visual analogue scale. Despite such methodological problems, the results do seem consistent with other acupuncture studies, in that there was a significant benefit in the acupuncture group. McIndoe et al (1995) compared acupuncture with intra-articular steroid injections and found that both groups had pain relief, but that there was no statistically significance difference between them. 8 Gaw et al (1975) studied the efficacy of acupuncture on OA pain in 40 subjects. 26 The active group received treatment at classical acupuncture points and the control group at placebo points. They found that both groups showed significant improvements in tenderness and subjective reporting of pain, but they found no significant difference between the groups. Such inconclusive research will continue to cast doubts on the effectiveness of acupuncture as a form of pain relief for OA. The findings from the current trial, however, should encourage its use. Patients were compliant with treatment, and there were no reported side-effects. Large numbers of patients can be treated within a relatively short space of time, making it time efficient. With some patients reporting a reduction in analgesia intake post-treatment, this has potential cost and health benefit implications for the patient. 23
6 For acupuncture to become a more accepted form of pain relief for OA of the hip, further randomised controlled trials need to be undertaken, with larger sample sizes, adequate control for the needling intervention, and with long term follow up. The aim of such research should be to determine whether acupuncture can be used as a long-term treatment for the symptoms of OA of the hip to improve patients quality of life whilst awaiting surgery. In conclusion, this study shows that acupuncture is effective in treating the symptoms of OA of the hip with patients waiting for a total hip arthroplasty and that such benefits can lasts for at least two months post-treatment. Acknowledgements The author would like to thank Mr J Ivory and Mr S Ward for their help, support and encouragement through the course of this study. Reference list 1. Lawrence RC, Hochberg MC, Kelsy JL, McDuffie FC, Medsger TA. Estimates of the prevalence of selected arthritic and musculoskeletal diseases in the United States. J Rheumatol 1989;16(4): Ernst E. Acupuncture as a symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis. A systematic review. Scand J Rheumatol 1997;26(6): Fagerson T. The Hip Handbook. Butterwoth-Heinemann; Griffin FR, Ray WA, Shaffner W. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use and death from peptic ulcer in elderly patients. Ann Int Med 1988;109(5): Dieppe P. Management of hip osteoarthritis. BMJ 1995;311(7009): King L. Case study: Physical therapy management of hip osteoarthritis prior to total hip arthroplasty. J Sport Phys Ther 1997;26(1): Visser GJ, Peters L, Rasker JJ. Rheumatologists and their patients who seek alternative care: An agreement to disagree. Br J Rheumatol 1992;31(7): McIndoe AK, Young K, Bone ME. A comparison of acupuncture with intra-articular steroid injection as analgesia for osteoarthritis of the hip. Acupunct Med 1995;13(2): Coan RM, Wong G, Coan PL. The acupuncture treatment of neck pain: a randomised controlled study. Am J Chin Med 1982;9:326-32, in reference Junnila SYT. Acupuncture superior to piroxicam in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Am J Acupunct 1982;10:341-7, in reference Loy TT. Treatment of cervical spondylosis. Med J Aust 1983;2:32-4, in reference Petrie JP, Langley GB. Acupuncture in the treatment of chronic cervical pain. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1983;1:333-5, in reference Petrou P, Winkler V, Genti G, Balint G. Double blind trial to evaluate the effect of acupuncture treatment on knee osteoarthrosis. Scand J Acupunct 1988;3:112-5, in reference Dickens W, Lewith GT. A single-blind, controlled and randomised clinical trial to evaluate the effect of acupuncture in the treatment of trapezometacarpal osteoarthritis. Compl Med Res 1989;3:5-8, in reference Christensen BV, Ichl IU, Vilbeck H, Bulow HH, Dreijer NC, Ramussen HF. Acupuncture treatment of severe knee osteoarthrosis. A long term study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1992;36:519-25, in reference Petrie JP, Hazleman BL. A controlled study of acupuncture in neck pain. Br J Rheumatol 1986;25:271-5, in reference Ammer K, Petschnig R. Vergleich der wirksamkeit von akupunktur und physiotherapie bei ambulante gonarthrose patienten. Wien Med Wochenschr 1988;22:566-9, in reference Thomas M, Eriksson SV, Lundeberg T. A comparative study of diazepam and acupuncture in patients with osteoarthritis pain. Am J Chin Med 1991;14:95-100, in reference Takeda W, Wessel J. Acupuncture for the treatment of pain of osteoarthritic knees. Arthritis Care Res 1994;7:118-22, in reference Fink MG, de Groot M, Kunsebeck HW, Gutenbrunner CH, Lambrecht F, Gehrke A. Standardized acupuncture v s placebo-acupuncture in coxarthrosis. Forrrsch Kompl Med 1996; (abstract) in reference Ellis N. Acupuncture in clinical practice. 1 st edition. Chapman and Hall; Downie A and Tidswell E. Cash s Textbook of orthopaedics and rheumatology for physiotherapists. 2 nd edition. Mosby-Year Book Europe; Berman BM, Lao L, Greene M, Anderson R, Wong RH, Longernberg P, Hochenberg MC. Efficacy of traditional Chinese acupuncture in the treatment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a pilot study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 1995;3(2): Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt L. Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee. Br Journal Rheumat 1988;15(12): Loy TT. Treatment of cervical spondylosis. Medical Journal of Austria 1983;3(1): Gaw AC, Chang LW, Shaw LC. Efficacy of acupuncture on osteoarthritic pain, A controlled double blind study. N Eng J Med 1975;293(8):
7 Appendix 1 HIP QUESTIONNAIRE Please answer the following questions considering the pain / stiffness you have experienced over the last week in your hip. All the questions require an answer in the form of a mark on the scale, this is between two extremes. Please place your mark straight down across the scale, e.g. The whole form should not take more than 10 minutes to complete. 1. Please mark on the line your level of pain a) when walking b) stair climbing c) at night d) at rest 2. Please mark on the line the degree of stiffness in your hip a) in the mornings b) later in the day 3. Please mark on the line the level of difficulty you have in performing a) sit-stand b) bending to the floor c) walking
8 d) putting on socks and tights e) sitting 4. Please mark on the line the level of difficulty you have in your normal leisure activities 5. Please mark on the line the level at which you generally feel a) anxious b) depressed c) relaxed d) happy 6. Please state the name of the medication you take as pain relief for your hip. 7. Please state the average number of these tablets you take daily. 8. Please draw on the chart where you got pain from your hip in the last week. THANK YOU FOR COMPLETING THIS QUESTIONNAIRE Roisin Haslam SYMPTOMS
Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of the Knee
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research article Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of Dimitar Tonev 1 *, Stoyka Radeva 2 and
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research article Effectiveness of True Acupuncture as an Adjunct to Standard Care or Electro-Physiotherapy in Osteoarthritis of Dimitar Tonev 1 *, Stoyka Radeva 2 and
Acupuncture for Osteoarthritis of the Knee
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 44, No. 4, April 2001, pp 819 825 2001, American College of Rheumatology Published by Wiley-Liss, Inc. Acupuncture for Osteoarthritis of the Knee A Systematic Review Jeanette
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 44, No. 4, April 2001, pp 819 825 2001, American College of Rheumatology Published by Wiley-Liss, Inc. Acupuncture for Osteoarthritis of the Knee A Systematic Review Jeanette
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.144 Effect of acupuncture on the pain management
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.144 Effect of acupuncture on the pain management
Supervised exercise plus acupuncture for moderate to severe knee osteoarthritis: a small randomised controlled trial
 1 Department of Rheumatology, The Great Western Hospital, Swindon, Wiltshire, UK 2 Department of Physiotherapy, The Great Western Hospital, Swindon, Wiltshire, UK Correspondence to Dr Lyn Williamson, Department
1 Department of Rheumatology, The Great Western Hospital, Swindon, Wiltshire, UK 2 Department of Physiotherapy, The Great Western Hospital, Swindon, Wiltshire, UK Correspondence to Dr Lyn Williamson, Department
The effectiveness of acupuncture for osteoarthritis of the knee a systematic review
 The effectiveness of acupuncture for osteoarthritis of the knee a systematic review Adrian White, Nadine Foster, Mike Cummings, Panos Barlas Adrian White clinical research fellow Peninsula Medical School
The effectiveness of acupuncture for osteoarthritis of the knee a systematic review Adrian White, Nadine Foster, Mike Cummings, Panos Barlas Adrian White clinical research fellow Peninsula Medical School
International Journal of Orthopaedics Sciences 2017; 3(1): Dr. Sunil Kumar TR and Dr. Harish YS
 2017; 3(1): 658-663 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 658-663 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 07-11-2016 Accepted: 08-12-2016 Dr. Sunil Kumar TR Senior Resident, ESIC Medical College and Model Hospital
2017; 3(1): 658-663 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 658-663 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 07-11-2016 Accepted: 08-12-2016 Dr. Sunil Kumar TR Senior Resident, ESIC Medical College and Model Hospital
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, Osteoarthritis Research Society /98/ $12.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, 79 86 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063 4584/98/020079 + 08 $12.00/0 Comparison of the WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities) osteoarthritis index
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, 79 86 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063 4584/98/020079 + 08 $12.00/0 Comparison of the WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities) osteoarthritis index
Collected Scientific Research Relating to the Use of Osteopathy with Knee pain including iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome
 Collected Scientific Research Relating to the Use of Osteopathy with Knee pain including iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome Important: 1) Osteopathy involves helping people's own self-healing abilities
Collected Scientific Research Relating to the Use of Osteopathy with Knee pain including iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome Important: 1) Osteopathy involves helping people's own self-healing abilities
Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture
 Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Dr Panos Barlas School of Health and Rehabilitation Keele University Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Applications of acupuncture Principles
Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Dr Panos Barlas School of Health and Rehabilitation Keele University Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Applications of acupuncture Principles
Osteoarthritis Research Society /98/ $12.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, (Supplement A), 31 36 9 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/98/030031 + 06 $12.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Efficacy and tolerability of oral chondroitin
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1998) 6, (Supplement A), 31 36 9 1998 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/98/030031 + 06 $12.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Efficacy and tolerability of oral chondroitin
About the Measure. Pain, Pain (Type and Intensity), Impairment, Arthritis/Osteoarthritis, Exercise Capacity/Six-Minute Walk Test
 About the Measure Domain: Geriatrics Measure: Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Definition: Purpose: Essential PhenX Measures: Related PhenX Measures: A self-administered questionnaire to assess the patient
About the Measure Domain: Geriatrics Measure: Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Definition: Purpose: Essential PhenX Measures: Related PhenX Measures: A self-administered questionnaire to assess the patient
Type of intervention Treatment. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Costs and effectiveness of pre- and post-operative home physiotherapy for total knee replacement: randomized controlled trial Mitchell C, Walker J, Walters S, Morgan A B, Binns T, Mathers N Record Status
Costs and effectiveness of pre- and post-operative home physiotherapy for total knee replacement: randomized controlled trial Mitchell C, Walker J, Walters S, Morgan A B, Binns T, Mathers N Record Status
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
H. L. Mitchell 1, A. J. Carr 1 and D. L. Scott 1,2
 Rheumatology 2006;45:771 776 Advance Access publication 3 February 2006 The management of knee pain in primary care: factors associated with consulting the GP and referrals to secondary care H. L. Mitchell
Rheumatology 2006;45:771 776 Advance Access publication 3 February 2006 The management of knee pain in primary care: factors associated with consulting the GP and referrals to secondary care H. L. Mitchell
LOW PRIORITY PROCEDURE - Policy T18a Hip replacement
 LOW PRIORITY PROCEDURE - Policy T18a Hip replacement Policy author: NHS Suffolk Public Health Team Policy start date: June 2007 (formally T9) Revision date: January 2011 Review date: January 2013 Referral
LOW PRIORITY PROCEDURE - Policy T18a Hip replacement Policy author: NHS Suffolk Public Health Team Policy start date: June 2007 (formally T9) Revision date: January 2011 Review date: January 2013 Referral
Acupuncture for the Treatment of Pain of Osteoarthritic Knees
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Acupuncture for the Treatment of Pain of Osteoarthritic Knees Wendy Takeda and lean Wessel Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine whether acupuncture was more effective
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Acupuncture for the Treatment of Pain of Osteoarthritic Knees Wendy Takeda and lean Wessel Objective. The purpose of this study was to determine whether acupuncture was more effective
Double-blind randomized controlled trial of isoxicam vs piroxicam in elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1986), 22, 149S-155S Double-blind randomized controlled trial of isoxicam vs piroxicam in elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee N. BELLAMY"'2, W. W. BUCHANAN2
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1986), 22, 149S-155S Double-blind randomized controlled trial of isoxicam vs piroxicam in elderly patients with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee N. BELLAMY"'2, W. W. BUCHANAN2
Patient Pain and Function Survey
 FORCE-TJR QI Data Elements Patient Contact Information/ Demographic data Education Level Employment status Race or Ethnicity Gender Marital status Age Body Mass Index Smoking status General health status
FORCE-TJR QI Data Elements Patient Contact Information/ Demographic data Education Level Employment status Race or Ethnicity Gender Marital status Age Body Mass Index Smoking status General health status
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Fam Community Health. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 January 25.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Fam Community Health. 2008 ; 31(3): 247 254. doi:10.1097/01.fch.0000324482.78577.0f. Acupuncture and Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Fam Community Health. 2008 ; 31(3): 247 254. doi:10.1097/01.fch.0000324482.78577.0f. Acupuncture and Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A
A comparison of Ketoprofen and Diclofenac for acute musculoskeletal pain relief: a prospective randomised clinical trial
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A comparison of Ketoprofen and Diclofenac for acute musculoskeletal pain relief: a prospective randomised clinical trial P Ng, CW Kam, HH Yau Objectives: To compare
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine A comparison of Ketoprofen and Diclofenac for acute musculoskeletal pain relief: a prospective randomised clinical trial P Ng, CW Kam, HH Yau Objectives: To compare
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate to Severe Osteoarthritis Pain in Adults?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 Is Phlogenzym Effective in Reducing Moderate
Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee Pain in Adults With Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Ginger Effective in Reducing Knee
Effectiveness of passive and active knee joint mobilisation following total knee arthroplasty: Continuous passive motion vs. sling exercise training.
 Effectiveness of passive and active knee joint mobilisation following total knee arthroplasty: Continuous passive motion vs. sling exercise training. Mau-Moeller, A. 1,2, Behrens, M. 2, Finze, S. 1, Lindner,
Effectiveness of passive and active knee joint mobilisation following total knee arthroplasty: Continuous passive motion vs. sling exercise training. Mau-Moeller, A. 1,2, Behrens, M. 2, Finze, S. 1, Lindner,
Is Curcumin Effective in Reducing Pain in Arthritis Patients?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Curcumin Effective in Reducing Pain
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Curcumin Effective in Reducing Pain
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Linking osteoarthritis-specific health-status measures to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health (ICF)
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 519 523 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00086-4 Linking osteoarthritis-specific
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 519 523 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00086-4 Linking osteoarthritis-specific
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2013) 2(10):
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 10 (2013) pp. 369-381 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A Prospective Clinical Evaluation between Intra - Articular Injections of Methyl Prednisolone and Triamcinolone
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 2 Number 10 (2013) pp. 369-381 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A Prospective Clinical Evaluation between Intra - Articular Injections of Methyl Prednisolone and Triamcinolone
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hinman RS, McCrory, irotta M, et al. Acupuncture for chronic knee pain: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.12660. etable 1: Exclusion criteria etable
Supplementary Online Content Hinman RS, McCrory, irotta M, et al. Acupuncture for chronic knee pain: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.12660. etable 1: Exclusion criteria etable
Migraine and Acupuncture
 BRIEFING PAPER No 1 Migraine and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council June 1998 The Evidence
BRIEFING PAPER No 1 Migraine and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council June 1998 The Evidence
THE TRUTH ABOUT OSTEOARTHRITIS. By GRAHAM NELSON RUSSELL VISSER
 THE TRUTH ABOUT OSTEOARTHRITIS By GRAHAM NELSON RUSSELL VISSER WWW.NWPG.COM.AU THE TRUTH ABOUT OSTEOARTHRITIS 2 ABOUT NORTHWEST PHYSIOTHERAPY GROUP Northwest Physiotherapy Group was first established as
THE TRUTH ABOUT OSTEOARTHRITIS By GRAHAM NELSON RUSSELL VISSER WWW.NWPG.COM.AU THE TRUTH ABOUT OSTEOARTHRITIS 2 ABOUT NORTHWEST PHYSIOTHERAPY GROUP Northwest Physiotherapy Group was first established as
Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
 Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2014 Nov;93(11 Suppl 3):S108-21. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000115. Intraarticular platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: review and recommendations.
Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo in Reducing Pain in Patients with Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo
Osteoarthritis of the hip
 North Yorkshire and York Osteoarthritis of the hip Information for patients considering surgery Arthritis of the hip is common and affects approximately 10% of the population. The most common cause is
North Yorkshire and York Osteoarthritis of the hip Information for patients considering surgery Arthritis of the hip is common and affects approximately 10% of the population. The most common cause is
Osteoarthritis of the neck
 1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
Received: 18 October 2001 Accepted: 21 March 2002
 BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine BioMed Central BMC 22002, Complementary and Alternative Medicine x Research article Electroacupuncture versus Diclofenac in symptomatic treatment of Osteoarthritis
BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine BioMed Central BMC 22002, Complementary and Alternative Medicine x Research article Electroacupuncture versus Diclofenac in symptomatic treatment of Osteoarthritis
Blood-nourishing and Hard-softening Capsule Costs Less in the Management of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Advance Access Publication 26 July 2005 ecam 2005;2(3)363 368 doi:10.1093/ecam/neh104 Original Article Blood-nourishing and Hard-softening Capsule Costs Less in the Management of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain:
Advance Access Publication 26 July 2005 ecam 2005;2(3)363 368 doi:10.1093/ecam/neh104 Original Article Blood-nourishing and Hard-softening Capsule Costs Less in the Management of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain:
Received: 11 Sep 2006 Revisions requested: 6 Nov 2006 Revisions received: 3 Jan 2007 Accepted: 31 Jan 2007 Published: 31 Jan 2007
 Vol 9 No 1 Research article Evaluation of the Patient Acceptable Symptom State in a pooled analysis of two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies evaluating lumiracoxib and celecoxib
Vol 9 No 1 Research article Evaluation of the Patient Acceptable Symptom State in a pooled analysis of two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies evaluating lumiracoxib and celecoxib
In the Treatment of Patients With Knee Joint Osteoarthritis, Are Platelet Rich Plasma Injections More Effective Than Hyaluronic Acid Injections?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 In the Treatment of Patients With Knee
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 In the Treatment of Patients With Knee
Physiotherapy Services. Physiotherapy Guide. Hip Replacement
 Physiotherapy Services Physiotherapy Guide to Hip Replacement AGH 01535 293656 Bingley Hospital 01274 563438 Ilkley Coronation Hospital 01943 609666 ext 241 Skipton General Hospital 01756 701726 Settle
Physiotherapy Services Physiotherapy Guide to Hip Replacement AGH 01535 293656 Bingley Hospital 01274 563438 Ilkley Coronation Hospital 01943 609666 ext 241 Skipton General Hospital 01756 701726 Settle
Home based exercise programme for knee pain and knee osteoarthritis: randomised controlled trial
 Home based exercise programme for knee pain and knee osteoarthritis: randomised controlled trial K S Thomas, K R Muir, M Doherty, A C Jones, S C O Reilly, E J Bassey on behalf of the Community Osteoarthritis
Home based exercise programme for knee pain and knee osteoarthritis: randomised controlled trial K S Thomas, K R Muir, M Doherty, A C Jones, S C O Reilly, E J Bassey on behalf of the Community Osteoarthritis
The Effects of Joint Protection on Task Performance in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics 2010 The Effects of Joint Protection on Task Performance in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ryan Farwell Pacific University
Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics 2010 The Effects of Joint Protection on Task Performance in Rheumatoid Arthritis Ryan Farwell Pacific University
Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review: February 2007
 Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review:
Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-945-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Month/Year of Review: January 2012 Date of Last Review:
Regain your freedom. Authorised Representative Genzyme Europe B.V. Gooimeer DD Naarden The Netherlands
 Regain your freedom Authorised Representative Genzyme Europe B.V. Gooimeer 10 1411 DD Naarden The Netherlands Genzyme Limited 4620 Kingsgate Cascade Way Oxford Business Park South Oxford OX4 2SU Tel: 01865
Regain your freedom Authorised Representative Genzyme Europe B.V. Gooimeer 10 1411 DD Naarden The Netherlands Genzyme Limited 4620 Kingsgate Cascade Way Oxford Business Park South Oxford OX4 2SU Tel: 01865
THE BEST TIME IS NOW.
 THE BEST TIME to tackle osteoarthritis knee pain IS NOW. 1. TAKE ACTION 2. Consider synvisc-one Synvisc-One (hylan G-F 20) is indicated for the treatment of pain in osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee in patients
THE BEST TIME to tackle osteoarthritis knee pain IS NOW. 1. TAKE ACTION 2. Consider synvisc-one Synvisc-One (hylan G-F 20) is indicated for the treatment of pain in osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee in patients
Effect of Preoperative Physiotherapy Patient Education on Early Functional Mobility of Post-Operative Total Knee Arthroplasty Subjects
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2018, 10[2]:1-14 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Effect
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2018, 10[2]:1-14 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4 Effect
A pre-operative group rehabilitation programme provided limited benefit for people with severe hip and knee osteoarthritis
 http://informahealthcare.com/dre ISSN 0963-8288 print/issn 1464-5165 online Disabil Rehabil, Early Online: 1 6! 2014 Informa UK Ltd. DOI: 10.3109/09638288.2014.895428 RESEARCH PAPER A pre-operative group
http://informahealthcare.com/dre ISSN 0963-8288 print/issn 1464-5165 online Disabil Rehabil, Early Online: 1 6! 2014 Informa UK Ltd. DOI: 10.3109/09638288.2014.895428 RESEARCH PAPER A pre-operative group
Osteoarthritis of the hip
 1 What is osteoarthritis of the hip? The hip joint is formed by the top of the thigh bone and the pelvis. Its primary functions are to support the weight of the body and enable the legs to move. The hip
1 What is osteoarthritis of the hip? The hip joint is formed by the top of the thigh bone and the pelvis. Its primary functions are to support the weight of the body and enable the legs to move. The hip
REXON-AGE therapy in the treatment of arthrosis
 Presidio Ospedaliero di Cittadella Unità Operativa Autonoma ANESTESIA RIANIMAZIONE E TERAPIA DEL DOLORE Direttore: Dott. Giandomenico BABBOLIN Via Riva Ospedale 35013 Cittadella / Padova Tel. 049.942.48.01/3
Presidio Ospedaliero di Cittadella Unità Operativa Autonoma ANESTESIA RIANIMAZIONE E TERAPIA DEL DOLORE Direttore: Dott. Giandomenico BABBOLIN Via Riva Ospedale 35013 Cittadella / Padova Tel. 049.942.48.01/3
Is Regenerative Injection Therapy (Prolotherapy) Effective at Reducing Pain Associated With Knee Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Regenerative Injection Therapy (Prolotherapy)
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Regenerative Injection Therapy (Prolotherapy)
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
 TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET This leaflet has been produced to help answer some questions you may have following your knee replacement. However if you still have any concerns or queries
Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group: Plain Language Summary (PLS) Guide for Authors
 Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group: Plain Language Summary (PLS) Guide for Authors Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group, October 2011 Contents 1. About Cochrane Plain Language Summaries (PLS)... 2 Who is this guide
Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group: Plain Language Summary (PLS) Guide for Authors Cochrane Musculoskeletal Group, October 2011 Contents 1. About Cochrane Plain Language Summaries (PLS)... 2 Who is this guide
The Effect of Type 1 Mobilization of Patello-femoral Joint on Reduction of Knee Joint Stiffness
 Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 3 [12] November 2014: 129-133 2014 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
Bulletin of Environment, Pharmacology and Life Sciences Bull. Env. Pharmacol. Life Sci., Vol 3 [12] November 2014: 129-133 2014 Academy for Environment and Life Sciences, India Online ISSN 2277-1808 Journal
ACUPUNCTURE AND OSTEOARTHRITIS
 ACUPUNCTURE AND OSTEOARTHRITIS About osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis involves damage to articular cartilage and other structures in and around joints, with variable levels of inflammation.(hunter 2006) The
ACUPUNCTURE AND OSTEOARTHRITIS About osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis involves damage to articular cartilage and other structures in and around joints, with variable levels of inflammation.(hunter 2006) The
Shared Decision Making Osteoarthritis of the Knee Next clinical review date March 2018
 Shared Decision Making Osteoarthritis of the Knee Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what to do about Osteoarthritis of the Knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about
Shared Decision Making Osteoarthritis of the Knee Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what to do about Osteoarthritis of the Knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
New Medicines Profile
 New Medicines Profile May 2008 Issue No. 08/05 (Alateris ) Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Brand Name, (Manufacturer): Alateris (William Ransom &
New Medicines Profile May 2008 Issue No. 08/05 (Alateris ) Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Brand Name, (Manufacturer): Alateris (William Ransom &
PIRPROFEN IN TREATMENT OF NON-ARTICULAR RHEUMATISM IN PAKISTANI OUTPATIENTS, A MULTICENTRE STUDY
 Abstract PIRPROFEN IN TREATMENT OF NON-ARTICULAR RHEUMATISM IN PAKISTANI OUTPATIENTS, A MULTICENTRE STUDY Pages with reference to book, From 265 To 268 N,A.Jaffer ( Ciba-Geigy (Pakistan) Limited, Karachi.
Abstract PIRPROFEN IN TREATMENT OF NON-ARTICULAR RHEUMATISM IN PAKISTANI OUTPATIENTS, A MULTICENTRE STUDY Pages with reference to book, From 265 To 268 N,A.Jaffer ( Ciba-Geigy (Pakistan) Limited, Karachi.
Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty
 Rheumatology 2002;41:142 147 Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty J. F. Maillefert 1,4,A.Gueguen
Rheumatology 2002;41:142 147 Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty J. F. Maillefert 1,4,A.Gueguen
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2004) 12, 389 399 2004 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2004.02.001 International Cartilage
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2004) 12, 389 399 2004 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2004.02.001 International Cartilage
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of platelet-rich plasma injections for knee osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis can develop
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of platelet-rich plasma injections for knee osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis can develop
Resources for patients, carers and clinicians. Referral indicators. Patient with previous THR - loosening/wear, pain
 Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians. Referral indicators Red flags -infection in previous Total Hip Replacement (THR) -pathological fracture Hip arthritis Patient with previous
Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians. Referral indicators Red flags -infection in previous Total Hip Replacement (THR) -pathological fracture Hip arthritis Patient with previous
Coverage Guideline. BioniCare System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) DEFINITION COVERAGE CRITERIA MEDICAL BACKGROUND
 Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Coverage Guideline System (formerly the BIO-1000 System) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan updates Coverage Guidelines throughout the year. A printed version may not be most up to date version
Ankle Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet. Under review. Page 1
 Ankle Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Ankle Fracture Welcome to the Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust. This leaflet will provide you with information regarding the diagnosis
Ankle Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Ankle Fracture Welcome to the Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust. This leaflet will provide you with information regarding the diagnosis
OSTEOARTHRITIS; EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF ACECLOFENAC IN THE TREATMENT: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL VERSUS DICLOFENAC
 The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-416 OSTEOARTHRITIS; EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF ACECLOFENAC IN THE TREATMENT: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL VERSUS
The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-416 OSTEOARTHRITIS; EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF ACECLOFENAC IN THE TREATMENT: A RANDOMIZED DOUBLE-BLIND COMPARATIVE CLINICAL TRIAL VERSUS
Physiotherapy for anterior knee pain: a randomised controlled trial
 700 Department of Orthopaedics, City Hospital Nottingham D I Clark N Downing Department of Physiotherapy, City Hospital Nottingham J Mitchell Trent Institute for Health Services Research, The Medical School
700 Department of Orthopaedics, City Hospital Nottingham D I Clark N Downing Department of Physiotherapy, City Hospital Nottingham J Mitchell Trent Institute for Health Services Research, The Medical School
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2013: Vol.-3, Issue-1, P
 Original article: Effectiveness between supervised clinical exercise with Maitland manual therapy and Home exercise program in treating osteoarthritis of knee: Comparative study 1Dr.Mrs. Swati Sandeep
Original article: Effectiveness between supervised clinical exercise with Maitland manual therapy and Home exercise program in treating osteoarthritis of knee: Comparative study 1Dr.Mrs. Swati Sandeep
1. Effectiveness, Volume of Evidence, Applicability / Generalisability and Consistency / Clinical impact
 Meeting Date: 21 June 2017 Topic: The effectiveness of injection of steroid into the hip as a form of interventional pain management Purpose This purchasing guidance (considered judgement) document accompanies
Meeting Date: 21 June 2017 Topic: The effectiveness of injection of steroid into the hip as a form of interventional pain management Purpose This purchasing guidance (considered judgement) document accompanies
Glucosamine May Reduce Pain in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis
 1 Glucosamine May Reduce Pain in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis Prepared by: Jacqueline Pierce, MSc (PT) candidate, Queen's University Date: April 2005 (planned review date April 2007) Clinical Scenario:
1 Glucosamine May Reduce Pain in Individuals with Knee Osteoarthritis Prepared by: Jacqueline Pierce, MSc (PT) candidate, Queen's University Date: April 2005 (planned review date April 2007) Clinical Scenario:
Knee arthroscopy surgery
 Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Knee arthroscopy surgery Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk Arthroplasty
Golden Jubilee National Hospital NHS National Waiting Times Centre Knee arthroscopy surgery Patient information guide Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk Arthroplasty
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Risk Management Plan Etoricoxib film-coated tablets
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
Osteoarthritis (OA), the most common joint
 Effect of Rofecoxib Therapy on Measures of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Osteoarthritis Elliot W. Ehrich, MD; James A. Bolognese, MStat; Douglas J. Watson, PhD; and Sheldon X. Kong, PhD
Effect of Rofecoxib Therapy on Measures of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Osteoarthritis Elliot W. Ehrich, MD; James A. Bolognese, MStat; Douglas J. Watson, PhD; and Sheldon X. Kong, PhD
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000. b) 330,000.
 1 WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000 b) 330,000 c) 650,000 2. What disease is the leading cause of disability in the U.S.? a)
1 WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000 b) 330,000 c) 650,000 2. What disease is the leading cause of disability in the U.S.? a)
D. Lazik, S. Gutschow, S. Luther, M. Erdmann, J. Woltersdorf
 Clinical studies were conducted in cooperation with Specialist Hospital in Vogelsang-Gommern (Deutsches Zentrum fur Knorpel-und Knochentransplantationen DZKKT / klinische Abteilung fur ORTHOPADIE - German
Clinical studies were conducted in cooperation with Specialist Hospital in Vogelsang-Gommern (Deutsches Zentrum fur Knorpel-und Knochentransplantationen DZKKT / klinische Abteilung fur ORTHOPADIE - German
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
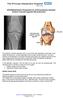 GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
GG10Rehabilitation Programme for Arthroscopically Assisted Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Femur ACL Graft Fibula Tibia The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the main ligaments in the
Maria Lourdes R. Bernardo and Alfredo C. Azarcon, Jr. Department of Rehabi/itation Medicine, Veterans Memorial Medica! Center
 A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of Oral Collagen Treatment on the Media) Knee Joint Space aod Functional Outcome among Veterans Memorial Medical Center Patients Diagnosed with Osteoarthritis
A Randomized Controlled Trial on the Effects of Oral Collagen Treatment on the Media) Knee Joint Space aod Functional Outcome among Veterans Memorial Medical Center Patients Diagnosed with Osteoarthritis
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Facet joint injection advice
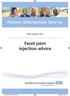 Patient Information Service Day surgery unit Facet joint injection advice SOU425_034175_0615_V1.indd 1 26/02/2016 09:11 Facet joints (Also known as Zygoapophyseal joints) Facet joints are the joints between
Patient Information Service Day surgery unit Facet joint injection advice SOU425_034175_0615_V1.indd 1 26/02/2016 09:11 Facet joints (Also known as Zygoapophyseal joints) Facet joints are the joints between
Myofascial Pain Massage Trigger point injection Heat, cold, acupuncture, relaxation training, and biofeedback Treatments. Pain medicines Exercise
 Myofascial Pain Myo is a Greek word for muscle. Fascia is the tough outer lining of a muscle that holds it in place. Myofascial pain is the term used to describe pain in the muscles and fascia. Myofascial
Myofascial Pain Myo is a Greek word for muscle. Fascia is the tough outer lining of a muscle that holds it in place. Myofascial pain is the term used to describe pain in the muscles and fascia. Myofascial
Generic and condition-specific outcome measures for people with osteoarthritis of the knee
 Rheumatology 1999;38:870 877 Generic and condition-specific outcome measures for people with osteoarthritis of the knee J. E. Brazier, R. Harper, J. Munro, S. J. Walters and M. L. Snaith1 School for Health
Rheumatology 1999;38:870 877 Generic and condition-specific outcome measures for people with osteoarthritis of the knee J. E. Brazier, R. Harper, J. Munro, S. J. Walters and M. L. Snaith1 School for Health
OPAS OSTEOARTHRITIS PROGRAMME AT SPORTS SURGERY CLINIC.
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries OPAS AT SPORTS SURGERY CLINIC www.sportssurgeryclinic.com INTRODUCTION Osteoarthritis Normal Joint Destruction of Cartilage
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries OPAS AT SPORTS SURGERY CLINIC www.sportssurgeryclinic.com INTRODUCTION Osteoarthritis Normal Joint Destruction of Cartilage
Recent Progress in Clinical Research of Acupuncture
 23 28 2009 1 Recent Progress in Clinical Research of Acupuncture Adrian WHITE Clinical Research Fellow, General practice and Primary Care, Institute of Health and Social Care, Peninsula Medical School,
23 28 2009 1 Recent Progress in Clinical Research of Acupuncture Adrian WHITE Clinical Research Fellow, General practice and Primary Care, Institute of Health and Social Care, Peninsula Medical School,
Knee arthroscopy surgery
 Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
Patient information Knee arthroscopy surgery i Important information for all orthopaedic patients undergoing knee arthroscopy surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY
main/1103_new 01/11/06
 Search date May 2006 Allan Binder QUESTIONS What are the effects of treatments for people with uncomplicated neck pain without severe neurological deficit?...3 What are the effects of treatments for acute
Search date May 2006 Allan Binder QUESTIONS What are the effects of treatments for people with uncomplicated neck pain without severe neurological deficit?...3 What are the effects of treatments for acute
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE
 Dr C S Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE The knee is the largest joint in the body, and is also the joint most
Dr C S Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE The knee is the largest joint in the body, and is also the joint most
Analgesic Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 1 March 2016
 Analgesic Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 1 March 2016 (minutes for web publishing) The Analgesic Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology and
Analgesic Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 1 March 2016 (minutes for web publishing) The Analgesic Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology and
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021
 Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
BIG TOE FUSION. Patient Information
 Patient Information BIG TOE FUSION This may have been caused by an old injury, previous surgery or a long-standing bunion deformity. Pain at the joint can start to affect your daily activities and even
Patient Information BIG TOE FUSION This may have been caused by an old injury, previous surgery or a long-standing bunion deformity. Pain at the joint can start to affect your daily activities and even
Elbow Replacement Guide
 Elbow Replacement Guide IM-CNOH-12 Rev. 1 Issue Date: March 2011 Review Date: March 2012 Founded 1908 C A P PA G H N AT I O N A L O RT H O PA E D I C H O S P I TA L FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. TEL: 01 814 0429
Elbow Replacement Guide IM-CNOH-12 Rev. 1 Issue Date: March 2011 Review Date: March 2012 Founded 1908 C A P PA G H N AT I O N A L O RT H O PA E D I C H O S P I TA L FINGLAS, DUBLIN 11. TEL: 01 814 0429
Current Concepts in Management of OA Knee
 Current Concepts in Management of OA Knee The Arthritis Society 60 Years of Arthritis Research and Programs From unproven remedies to evidence based practice Rose McKenna BSc PT Arthritis Rehabilitation
Current Concepts in Management of OA Knee The Arthritis Society 60 Years of Arthritis Research and Programs From unproven remedies to evidence based practice Rose McKenna BSc PT Arthritis Rehabilitation
QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture.
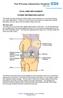
 The Hip Andrew Pearse Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedics Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Introduction Brief anatomy and topography History & examination Osteoarthritis Investigations Referral
The Hip Andrew Pearse Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedics Worcestershire Acute Hospitals NHS Trust Introduction Brief anatomy and topography History & examination Osteoarthritis Investigations Referral
SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS
 SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common rheumatological disorder. It is a degenerative joint disorder characterized by destruction of articular cartilage and formation of a new bone (lipping)
SUMMARY & CONCLUSIONS Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common rheumatological disorder. It is a degenerative joint disorder characterized by destruction of articular cartilage and formation of a new bone (lipping)
Shared Decision Making osteoarthritis of the knee. Deciding what to do about Osteoarthritis of the Knee
 Shared Decision Making osteoarthritis of the knee Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what to do about Osteoarthritis of the Knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about
Shared Decision Making osteoarthritis of the knee Next clinical review date March 2018 Deciding what to do about Osteoarthritis of the Knee This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about
KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA) A physiotherapist s perspective. When to refer?
 KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA) A physiotherapist s perspective When to refer? Beyond Wear & Tear Traditional & still common viewpoint Wear & tear Degenerative joint disease Progressive destruction of articular
KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA) A physiotherapist s perspective When to refer? Beyond Wear & Tear Traditional & still common viewpoint Wear & tear Degenerative joint disease Progressive destruction of articular
What is the Difference Between Myotherapy and Remedial Massage?
 What is the Difference Between Myotherapy and Remedial Massage? We can only imagine how difficult life must have been for the sick a hundred or more years ago. When they were sick they had very limited
What is the Difference Between Myotherapy and Remedial Massage? We can only imagine how difficult life must have been for the sick a hundred or more years ago. When they were sick they had very limited
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Keep moving. Self-help and daily living Keep moving. and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis.
 Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
Self-help and daily living This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about how to exercise if you have arthritis. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely from
