Pediatric Bleeding Disorders and Thrombocytopenia. David Simon, MD Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Kaiser Permanente Downey Medical Center
|
|
|
- Blanche Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pediatric Bleeding Disorders and Thrombocytopenia David Simon, MD Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Kaiser Permanente Downey Medical Center 1
2 2
3 Case Presentations Case 1 12 month old male, no personal or family history, presents for WCC to PCP. Just began walking last week. After two days of walking (and falling) family noticed he stopped trying and seemed upset when they would try to make him walk for the video camera. Family upset they have no video of his first steps. PCP notices refusal to put weight on left leg and possibly swollen left ankle/foot 3
4 Case 1 12 month old male, no personal or family history, presents for WCC to PCP. Just began walking last week. After two days of walking (and falling) family noticed he stopped trying and seemed upset when they would try to make him walk for the video camera. Family upset they have no video of his first steps. PCP notices refusal to put weight on left leg and possibly swollen left ankle/foot WBC 5.7 Hgb 13.1 Plt: 344 PT: 10.3 PTT: 78 Fib: 344 Case 2 3 y/o male with no PMH presents to PCP with 2 days of sudden onset bruising and rash. No fever, very active, bouncing off walls (and off the exam table repeatedly). Normal vitals, bruising on the legs, arms, trunk and petechial rash. No bleeding. 4
5 Case 2 3 y/o male with no PMH presents to PCP with 2 days of sudden onset bruising and rash. No fever, very active, bouncing off walls (and off the exam table repeatedly). Normal vitals, bruising on the legs, arms, trunk and petechial rash. No bleeding. WBC 5.3 (nl diff) Hgb 12.1 Platelet 4 PT: 11.1 PT 29 Fibrinogen 278 5
6 Case 3 3 y/o with no past medical history presents to PCP complaining of increased sleeping for 1 week, less playful for 2-3 weeks, fever for 3-4 days and bruises for 2 days. This is 6 th visit to medical care in last 3 weeks, mother is not happy. Case 3 3 y/o with no past medical history presents to PCP complaining of increased sleeping for 1 week, less playful for 2-3 weeks, fever for 3-4 days and bruises for 2 days. This is 6 th visit to medical care in last 3 weeks, mother is not happy. WBC 39 (97% blasts) Hgb: 6.4 Plt: 9 PT: 12 PTT: 28 Fib: 189 6
7 Case 4 13 y/o girl, no past medical history, had menarche 6 months ago. First period 4 days. Then none for 2 months. Now with continuous bleeding for three months. PE: Slightly Pale, mildly fatigued. Mildly tachycardic. BP nl. Case 4 13 y/o girl, no past medical history, had menarche 6 months ago. First period 4 days. Then none for 2 months. Now with continuous bleeding for three months. PE: Pale, fatigued. Mildly tachycardic. BP nl. WBC 6.5 Hgb 6.8 Plt 265 PT: 12.1 PTT: 48 Fibrinogen: 311 7
8 Evaluation of the Patient with Suspected Bleeding Disorder History (Presentation and Past/Surg/Fam) Physical Exam Labs Presentation Presentation Mucous Membrane Bleeding (epistaxis, gingival, menstrual) Von Willebrand Disease (VWD), Thrombocytopenia, Platelet Function Defect Joints/Soft Tissues Hemophilia Umbilical Stump Factor XIII 8
9 Presentation Localized bleeding often not a bleeding disorder (caveats apply family history etc) Unilateral epistaxis in a child nose picking, allergies/congestion, friable superficial vessel Consider ENT first Bleeding after tonsillectomy: surgical trauma >> bleeding disorder Past History Medical Conditions Liver dysfunction, Connective Tissue Disorders, CCHD, Malabsorption Trauma was there excessive bleeding? Surgical was there excessive or unexpected bleeding? Transfusions? 9
10 Family History Abnormal bleeding? Site? Age at onset? Transfusion (esp for something unusual eg. Childbirth)? Get details (family with heavy periods may not realize it if everyone affected) Inheritance Pattern X-linked (hemophilia but up to 30% are spontaneous), Autosomal Dominant (VWD) Rare factor deficiencies tend to be Autosomal Recessive so likely no FHx Lab Workup But first some movies 10
11 INTRINSIC PATHWAY 11
12 Lab Workup CBC with diff Lab Workup CBC with diff PT PTT?von Willebrands 12
13 CBC Platelets Normal vs Low Size (large vs normal or small) WBC Differential PT and PTT A word about specimen collection 13
14 Prothrombin Time (PT) Measurement of Extrinsic Pathway Only clotting factor measured is Factor 7 Clinically significant deficiency is very rare Useful in monitoring of Coumadin (short half life of Factor 7) 14
15 Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) Measures extrinsic pathway Will be prolonged with deficiencies of: Factor 8 (hemophilia A) Factor 9 (hemophilia B) Factor 11 ( hemophilia C ) Factor 12 (NOT a bleeding disorder but very prolonged PTT) Von Willebrand Disease (+/-) heparin contamination Circulating inhibitor mixing study Mixing Study (PTT substituted) Mix normal plasma with patient plasma 1:1 If corrects to normal then there is a factor deficiency If does not correct to normal then there is a circulating inhibitor (Hemophilia with inhibitor, autoimmune disease, viral-induced) 15
16 Evaluation of lab tests in the patient with suspected bleeding disorder Normal Platelets, Normal PT Prolonged PTT Von Willebrand Disease Hemophilia A or B Factor 11 deficiency Factor 12 deficiency (not a bleeding disorder) 16
17 Normal Platelets, Normal PTT Prolonged PT Factor 7 deficiency Wafarin (Coumadin) Ingestion PT, PTT Prolonged Factor 5 or 10 deficiency (very rare) Prolonged exposure to Coumadin Liver dysfunction DIC Many bad things 17
18 Normal PT, PTT and Platelets Von Willebrand Disease Platelet Function Defect Low Platelets LATER 18
19 Factor 8 Von Willebrand Von Willebrand Disease CALL ME ERIK 19
20 Von Willebrand Disease Autosomal Dominant Diagnosed much more frequently in women Platelet plug formation is dependant on von Willebrand binding to exposed subendothelium Von Willebrand also serves as carrier protein for Factor 8 Von Willebrand Disease Prevalence 1:100 Incidence 1:1,000 Very heterogeneous presentation even among family members Type 1 Reduced amount of VW protein Most common Type 2 Qualitative problem with VW Type 3 Near absence very severe and rare 20
21 Tests VW Antigen Quantitative Assay Ristocetin Cofactor measure of activity VW Multimers Measures distribution of multimers present in circulation Factor 8 Activity VW carries Factor 8 in the plasma VW Multimers ADAMTS 13 21
22 Problems with testing Blood Type Group AB may have 60-70% higher VW antigen that Group O Acute Phase Reactant Hyper/Hypothyroidism Maybe as low as in hypo Stress Phlebotomy! 22
23 Type 1 VWD By far most common (~90%) Quantitative decrease in circulating VW Extremely common (up to 1%) Presentation Easy bruising, menorrhagia, post-op hemorrhage and epistaxis. Anemia Type 1 VWD Labs PTT prolonged (+/-) Depends on factor 8 level Ristocetin Cofactor: low VW Antigen: low Factor 8: normal or low Multimers: normal distribution 23
24 Type 1 VWD Treatment Desmopressin IV or Intranasal (Stimate) Aminocaproic Acid (Amicar) Plasma derived vwf/factor VIII (Humate-P) Cryoprecipitate Type 1 VWD Desmopressin ~75% of patients will respond Releases stored VW Antigen into circulation Must give trial dose to assure response IV most effective Intranasal efficacy slightly lower Probably due to variable absorption Good for heavy menses, nosebleeds, minor surgical procedures Must caution about free water restriction DO NOT use enuresis formulation of DDAVP 24
25 Type 1 VWD -Aminocaproic Acid (Amicar) Antifibrinolytic Useful for mucosal bleeding especially in conjunction with Stimate Type 1 VWD Plasma Derived VWF/FVIII (Humate-P) Replacement concentrate Contains normal VW multimer distribution For severe bleeding Surgical Prophylaxis and Post-op Routine Prophylaxis (more common in type 3) Factor VIII concentrates typically lack VW 25
26 Type 1 VWD Cryoprecipitate Plasma component Rich in VW Used in situations where plasma derived concentrate unavailable Much more effective than FFP Type 2 VWD Many types Qualitative problems with VWD Fairly Rare Labs variable depending on type Distinguish from other diseases (eg. hemophilia A vs type 2N) Generally must be treated with plasma derived VWF/FVIII concentrates 26
27 Type 3 VWD Extremely rare Almost complete deficiency of VW (and consequently factor 8) Phenotype similar to severe hemophilia A Severe epistaxis Mucocutaneous hemorrhage Joint/muscle bleeding Treatment/Prophylaxis with plasma derived VWF/FVIII Hemophilia Recognized since biblical times First medical description in 10 th century Scientific Investigation began around turn of 19 th century Effect on history Queen Victoria passed gene for Hemophilia B to two daughters and subsequently to the royal families of Spain, Germany and Russia 27
28 Hemophilia Overall incidence 1:5,000 males Severity proportional to baseline factor level Severe <1% Moderate 1-5% Mild >5% Hemophilia A (Factor 8 deficiency) 80-85% of cases X-Linked Hemophilia B (Factor 9 deficiency) Identical clinical picture to Factor 8 deficiency 28
29 Clinical Presentation Most diagnosed at birth due to family history (~2/3) About 1/3 are due to spontaneous mutations Bleeding with circumcision (~30% will bleed) Without hemostatic challenge most present when crawling/walking with bruises, swollen joints, refusal to walk, oral bleeding (torn frenulum) Clinical presentation Toddler: most common site of bleed is ankle due to pressure from child trying to maintain upright position As child ages elbows and knees become more common 29
30 Lab Workup PT normal PTT prolonged Mixing Study corrects Factor 8 or 9 level low Complications Hemophilic Arthropathy 30
31 Complications Intramuscular Bleeding Very difficult to localize/diagnose High index of suspicion especially with abdominal pain Iliopsoas bleed is life threatening Characteristic hunch gait with pain upon extension of hip despite normal flexion and rotation Diagnose via CT 31
32 Complications Life threatening bleeding CNS Airway Exsanguination Inhibitor Development 14-25% of severe Hemophilia A patient Antibody inactivates Factor 8 Suspect with failure to respond to usual Factor replacement Complications 32
33 Treatment 1930s: Plasma infusions helped 1964: Cryoprecipitate discovered Higher concentration of factor : First plasma derived concentrates First attempts at prophylaxis 1980s: Lost generation Patient mistrust Mid 1980s: improved donor selection, heat inactivation, refined purification 1985: Genes for Factors 8 and 9 cloned 1989: First recombinant products 33
34 Treatment Principles Dose and duration based on: Site of bleed (joint vs muscle vs CNS) target? Patient Weight Product Being Used (factor vs DDAVP) Severity of bleed Surgical Prophylaxis Concomitant Antifibrinolytic (ie. Amicar) 34
35 Prophylaxis vs On-Demand Severe Hemophilia Almost all will benefit from prophylaxis Start when toddling after first bleed Central Venous Catheter needed Moderate Many will require prophylaxis Family History Useful Mild Generally treated with on-demand Thrombocytopenia Peripheral consumption/destruction Poor production ITP HUS Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia (NAIT) Neonatal autoimmune thrombocytopenia (like ITP) Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease Kasabach-Merritt Syndrome TTP Sepsis Acute Leukemia Aplastic Anemia Congenital Thrombocytopenias Drug Induced *Sequestration -hypersplenism -hypothermia -burns *Spurious -EDTA 35
36 Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) Accelerated destruction of antibody sensitized platelets by macrophages (predominantly of the spleen) Incidence: 1:10,000 children Acute: <6 months duration Chronic: >6 months duration Age >10 years and female gender associated with development of chronic Pathogenesis of ITP Autoantibodies to platelet surface glycoproteins (usually GP IIb-IIIa) coat platelets Splenic macrophages clear coated platelets Megakaryocytes are also cleared production is affected Viral infections and immunizations implicated in triggering the process causality is very poorly understood 36
37 Acute Chronic Most will have spontaneous recovery irrespective of therapy 50% by 4-8 weeks 2/3 by 3 months 76%-90% by 6 months Of the remaining 37% eventually had recovery Screen for autoimmune disease especially in teens 37
38 Presentation Abrupt onset of bruising and petechiae in almost every child. Overt bleeding more rare. Peak age 2-6 typically acute. Male:female Infant or Adolescent more often chronic with concomitant autoimmune disorders Female > Male 2:1 in adolescents History of preceeding viral illness or immunization supposedly. Epistaxis or oral mucosal bleeding (blood blisters): < 1/3 Hematuria/Hematochezia/Melena: < 10% Presentation Despite profoundly low platelet counts (<20,000) severe bleeding rare. Particularly compared to thrombocytopenia due to poor production New, large, sticky platelets are more prevalent Malaise, bone pain, adenopathy, fever, hepatosplenomegaly = trouble 38
39 Presentation Platelet count <20,000 in >80%, often less than 10,000 WBC and RBC should be normal Unless severe bleeding Bone marrow is unremarkable Usually only performed if patient fails frontline therapy and requires corticosteroids Treatment (or not) To Treat Americans Risk of ICH (0.9%) (0.1%-0.5%) Trauma ASA use Plt <20,000 Relatively few side effects of treatment Not to treat Europeans No great evidence that treatment prevents ICH Spontaneous remission rates high and unaffected by treatment Cost of treatment Side effects of treatment 39
40 Treatment First Line IVIG Anti Rh o (D) (WinRho) Second Line Corticosteroids Salvage Cytoxan, Cyclosporine, 6MP, Vincristne, Interferon-a, Danazol, Azathioprine Splenectomy New agents (TPO agonists) IVIG Primarily acts by blocking macrophages at the Fc receptor Good efficacy fairly rapid response can be repeated Duration 2-4 weeks Side effects (15-75%): Headaches, nausea, lightheaded, fever, rarely anaphylaxis (IgA deficient patients) Aseptic meningitis (10%) Expensive/Shortage 40
41 Anti-D (WinRho) Rh+ patients only Also acts by blocking macrophages (at the expense of some red cells!) About as effective as IVIG Shorter infusion time (but now longer post infusion observation required) Similar side effect profile Plus acute hemolytic anemic renal failure Corticosteroids Need for bone marrow before therapy? Traditional practice but studies argue against Inhibition of phagocytosis and antibody production Many different regimens: 21 day, pulse then taper, megadose pulse Very effective Side effects related to dose and duration: HTN, hyperglycemia, cushingoid facies, polydipsia/polyuria, weight gain, fluid retention, acne 41
42 Splenectomy Generally reserved for refractory cases in patients with high risk of, or proclivity toward bleeding. Eliminates the major site of both platelet destruction and antibody production Defer in children as long as possible Complete Remission 75%, partial in many more If poor response look for accessory spleen Prophylactic Vaccination Long term risks: Infection Emerging data on pulmonary hypertension, cardiac dysfunction New Agents 42
43 TPO agonists 60-80% effective Concern for rebound thrombocytopenia Marrow reticulin fibrosis Hepatotoxicity 43
44 44
Coagulation Disorders. Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU
 Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Bleeding disorders. Hemostatic failure: Inappropriate and excessive bleeding either spontaneous or in response to injury.
 1 Bleeding disorders Objectives: 1. Discuss briefly the physiology of hemostasis. 2. Define the mechanisms of thrombocytopenia and the relative bleeding risk at any given platelet count. 3. Be able to
1 Bleeding disorders Objectives: 1. Discuss briefly the physiology of hemostasis. 2. Define the mechanisms of thrombocytopenia and the relative bleeding risk at any given platelet count. 3. Be able to
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College
 Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN
 Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN The student should be able:» To identify the mechanism of homeostasis and the role of vessels, platelets
Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN The student should be able:» To identify the mechanism of homeostasis and the role of vessels, platelets
Bleeding Disorders. Dr. Mazen Fawzi Done by Saja M. Al-Neaumy Noor A Mohammad Noor A Joseph Joseph
 Bleeding Disorders Dr. Mazen Fawzi Done by Saja M. Al-Neaumy Noor A Mohammad Noor A Joseph Joseph Normal hemostasis The normal hemostatic response involves interactions among: The blood vessel wall (endothelium)
Bleeding Disorders Dr. Mazen Fawzi Done by Saja M. Al-Neaumy Noor A Mohammad Noor A Joseph Joseph Normal hemostasis The normal hemostatic response involves interactions among: The blood vessel wall (endothelium)
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood
 Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
The Child with a Hematologic Alteration
 47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
Platelet Disorders. By : Saja Al-Oran
 Platelet Disorders By : Saja Al-Oran Introduction The platelet arise from the fragmentation of the cytoplasm of megakaryocyte in the bone marrow. circulate in the blood as disc-shaped anucleate particles
Platelet Disorders By : Saja Al-Oran Introduction The platelet arise from the fragmentation of the cytoplasm of megakaryocyte in the bone marrow. circulate in the blood as disc-shaped anucleate particles
Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment. by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate
 Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate 2 Approach to a patient of bleeding diathesis 1. Clinical evaluation: History, Clinical features 2. Laboratory approach:
Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate 2 Approach to a patient of bleeding diathesis 1. Clinical evaluation: History, Clinical features 2. Laboratory approach:
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders
 HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
Hemostatic System - general information
 PLATELET DISORDERS Hemostatic System - general information Normal hemostatic system vessel wall circulating blood platelets blood coagulation and fibrynolysis Bleeding Diathesis inherited or acquired defects
PLATELET DISORDERS Hemostatic System - general information Normal hemostatic system vessel wall circulating blood platelets blood coagulation and fibrynolysis Bleeding Diathesis inherited or acquired defects
Bleeding Disorders HOPE Maram Al-anbar
 Bleeding Disorders HOPE Maram Al-anbar 9-9 - 2014 ^^ Attention Please ^^ We ( correction team of pediatric package^hope/2010^ ) had decided to make one lecture of bleeding disorders in place of the two
Bleeding Disorders HOPE Maram Al-anbar 9-9 - 2014 ^^ Attention Please ^^ We ( correction team of pediatric package^hope/2010^ ) had decided to make one lecture of bleeding disorders in place of the two
Pathology note 8 BLEEDING DISORDER
 Pathology note 8 BLEEDING DISORDER Slide75 ( Types of clotting factors deficiency): Today we will talk about public public factor deficiency it could be acquired or inherited, acquired diseases are more
Pathology note 8 BLEEDING DISORDER Slide75 ( Types of clotting factors deficiency): Today we will talk about public public factor deficiency it could be acquired or inherited, acquired diseases are more
Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives:
 Haematology Lec. 1 د.ميسم مؤيد علوش Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives: - Define haemostasis and what are the major components involved in haemostasis? - How to assess the coagulation status?
Haematology Lec. 1 د.ميسم مؤيد علوش Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives: - Define haemostasis and what are the major components involved in haemostasis? - How to assess the coagulation status?
Easy Bleeding General Presentation
 Easy Bleeding General Presentation It is not uncommon for children to bleed and bruise after experiencing trauma. However, a child may also have an underlying coagulopathy, which results in easy and possibly
Easy Bleeding General Presentation It is not uncommon for children to bleed and bruise after experiencing trauma. However, a child may also have an underlying coagulopathy, which results in easy and possibly
There are two main causes of a low platelet count
 Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which a person's blood has an unusually low level of platelets Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are found in a person's blood along with red blood
Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which a person's blood has an unusually low level of platelets Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are found in a person's blood along with red blood
PCCN Review Hematology
 PCCN Review Hematology Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Anemia Definition reduction in RBC concentration Causes iron deficiency
PCCN Review Hematology Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Anemia Definition reduction in RBC concentration Causes iron deficiency
Contemporary perspectives and initial management of pediatric ITP. William Beau Mitchell, MD Weill Cornell Medical College New York, NY USA
 Contemporary perspectives and initial management of pediatric ITP William Beau Mitchell, MD Weill Cornell Medical College New York, NY USA Case Presentation 5 year old female Bruises on trunk, extremities
Contemporary perspectives and initial management of pediatric ITP William Beau Mitchell, MD Weill Cornell Medical College New York, NY USA Case Presentation 5 year old female Bruises on trunk, extremities
POLICY NO. Printed copies are for reference only. Please refer to the electronic copy for the latest version.
 Department Blood Bank POLICY NO. 4633 Department Of Pathology LBH Transfusion Criteria Version# 2 PAGE NO. 1 OF 9 Printed copies are for reference only. Please refer to the electronic copy for the latest
Department Blood Bank POLICY NO. 4633 Department Of Pathology LBH Transfusion Criteria Version# 2 PAGE NO. 1 OF 9 Printed copies are for reference only. Please refer to the electronic copy for the latest
BLEEDING (PLATELET) DISORDER. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BLEEDING (PLATELET) DISORDER 1 APPROACH The initial set of questions should establish the following: (1) the most common site and type of bleeding (e.g., mucocutaneous versus articular or deep muscle),
BLEEDING (PLATELET) DISORDER 1 APPROACH The initial set of questions should establish the following: (1) the most common site and type of bleeding (e.g., mucocutaneous versus articular or deep muscle),
Blood Components & Indications for Transfusion. Neda Kalhor
 Blood Components & Indications for Transfusion Neda Kalhor Blood products Cellular Components: Red blood cells - Leukocyte-reduced RBCs - Washed RBCs - Irradiated RBCs Platelets - Random-donor platelets
Blood Components & Indications for Transfusion Neda Kalhor Blood products Cellular Components: Red blood cells - Leukocyte-reduced RBCs - Washed RBCs - Irradiated RBCs Platelets - Random-donor platelets
V.N. KARAZIN KHARKOV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY
 V.N. KARAZIN KHARKOV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Kharkov Regional Centre of Cardiovascular surgery V.N. Karazin Kharkov National University Department of Internal Medicine Immune thrombocytopenic purpura Abduyeva
V.N. KARAZIN KHARKOV NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Kharkov Regional Centre of Cardiovascular surgery V.N. Karazin Kharkov National University Department of Internal Medicine Immune thrombocytopenic purpura Abduyeva
Commonly Encountered Hematologic Chief Complaints in the Pediatric Pa8ent Black Hills Pediatric Symposium 6/23/17 Sam Milanovich, MD Pediatric
 Commonly Encountered Hematologic Chief Complaints in the Pediatric Pa8ent Black Hills Pediatric Symposium 6/23/17 Sam Milanovich, MD Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Sanford Children s Specialty Clinic Sioux
Commonly Encountered Hematologic Chief Complaints in the Pediatric Pa8ent Black Hills Pediatric Symposium 6/23/17 Sam Milanovich, MD Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Sanford Children s Specialty Clinic Sioux
LifeBridge Health Transfusion Service Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Northwest Hospital Center BQA Transfusion Criteria Version#2 POLICY NO.
 LifeBridge Health Transfusion Service Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Northwest Hospital Center BQA 1011.02 Transfusion Criteria Version#2 Department POLICY NO. PAGE NO. Blood Bank Quality Assurance Manual
LifeBridge Health Transfusion Service Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Northwest Hospital Center BQA 1011.02 Transfusion Criteria Version#2 Department POLICY NO. PAGE NO. Blood Bank Quality Assurance Manual
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
Bleeding Disorders.2 MS Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD
 Bleeding Disorders.2 MS4.25.02.2019 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Case 6: GT 18 yr old female was admitted with pallor, abdominal pain and gum
Bleeding Disorders.2 MS4.25.02.2019 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Case 6: GT 18 yr old female was admitted with pallor, abdominal pain and gum
Blood Transfusion Guidelines in Clinical Practice
 Blood Transfusion Guidelines in Clinical Practice Salwa Hindawi Director of Blood Transfusion Services Associate Professor in Haematology and Transfusion Medicine King Abdalaziz University, Jeddah Saudi
Blood Transfusion Guidelines in Clinical Practice Salwa Hindawi Director of Blood Transfusion Services Associate Professor in Haematology and Transfusion Medicine King Abdalaziz University, Jeddah Saudi
COAGULATIONS. Dr. Hasan Fahmawi, MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin)
 COAGULATIONS Dr. Hasan Fahmawi, MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin) Haemostasis-blood must be maintained in a fluid state in order to function as a transport system, but must be able to solidify to form a clot following
COAGULATIONS Dr. Hasan Fahmawi, MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin) Haemostasis-blood must be maintained in a fluid state in order to function as a transport system, but must be able to solidify to form a clot following
Thrombocytopenia. Dr Lynda Vandertuin May 6, 2014
 Dr Lynda Vandertuin May 6, 2014 1 Presentation 1. Definition 2. Platelet Physiology, Thromboiesis, & Platelet Function 3. Bleeding Risk 4. Clinical Diagnosis 5. Differential Diagnosis 6. Classification
Dr Lynda Vandertuin May 6, 2014 1 Presentation 1. Definition 2. Platelet Physiology, Thromboiesis, & Platelet Function 3. Bleeding Risk 4. Clinical Diagnosis 5. Differential Diagnosis 6. Classification
TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE
 TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE Dr Susan Russell Director HTC Sydney Children s Hospital, Randwick HFA Meeting 2015 What is von Willebrand Factor? VWF is a large multimeric protein Two
TREATMENT & MANAGEMENT OF VON WILLEBRAND DISEASE Dr Susan Russell Director HTC Sydney Children s Hospital, Randwick HFA Meeting 2015 What is von Willebrand Factor? VWF is a large multimeric protein Two
Congenital bleeding disorders
 Congenital bleeding disorders Overview Factor VIII von Willebrand Factor Complex factor VIII von Willebrand factor (vwf) complex circulate as a complex + factor IX intrinsic pathway Platelets bind via
Congenital bleeding disorders Overview Factor VIII von Willebrand Factor Complex factor VIII von Willebrand factor (vwf) complex circulate as a complex + factor IX intrinsic pathway Platelets bind via
Effective Date: Approved by: Laboratory Director, Jerry Barker (electronic signature)
 1 of 5 Policy #: 702 (PHL-702-05) Effective Date: 9/30/2004 Reviewed Date: 8/1/2016 Subject: TRANSFUSION GUIDELINES Approved by: Laboratory Director, Jerry Barker (electronic signature) Approved by: Laboratory
1 of 5 Policy #: 702 (PHL-702-05) Effective Date: 9/30/2004 Reviewed Date: 8/1/2016 Subject: TRANSFUSION GUIDELINES Approved by: Laboratory Director, Jerry Barker (electronic signature) Approved by: Laboratory
von Willebrand Disease
 von Willebrand Disease Jeremy Robertson Paediatric Haematologist Royal Children s s Hospital & Pathology Queensland Foglo,, April 1924: the journey begins Oskar and Augusta sail to Helsinki... ...to o
von Willebrand Disease Jeremy Robertson Paediatric Haematologist Royal Children s s Hospital & Pathology Queensland Foglo,, April 1924: the journey begins Oskar and Augusta sail to Helsinki... ...to o
BLEEDING DISORDERS. JC Opperman 2012
 BLEEDING DISORDERS JC Opperman 2012 Primary and Secondary Clotting Laboratory Tests Routine screening tests Prothrombin time (PT) (INR) increased in neonates (12-18 sec) Partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
BLEEDING DISORDERS JC Opperman 2012 Primary and Secondary Clotting Laboratory Tests Routine screening tests Prothrombin time (PT) (INR) increased in neonates (12-18 sec) Partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
Developed by Stephanie Zachary, Sarah Weicker, Dr. Jeremy Friedman, Dr. Carolyn Beck, and Dr. Lauren Kitney for PedsCases.com.
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) CPS Podcast These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) CPS Podcast These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of
INHERITED COAGULOPATHY
 Disorder Etiology Pathophysiology and Presentation Lab Findings and Diagnosis Treatment INHERITED COAGULOPATHY HEMOPHILIA A and B Hemophilia A: deficiency in XIII (85%) Hemophilia B: deficiency in IX (15%)
Disorder Etiology Pathophysiology and Presentation Lab Findings and Diagnosis Treatment INHERITED COAGULOPATHY HEMOPHILIA A and B Hemophilia A: deficiency in XIII (85%) Hemophilia B: deficiency in IX (15%)
Haemorrhagic Disorders. Dr. Bashar Department of Pathology Mosul Medical College
 Haemorrhagic Disorders Dr. Bashar Department of Pathology Mosul Medical College Hemorrhagic Disorders These include Disorders of platelets. Disorders of blood vessels. Disorders of coagulation & fibrinolysis.
Haemorrhagic Disorders Dr. Bashar Department of Pathology Mosul Medical College Hemorrhagic Disorders These include Disorders of platelets. Disorders of blood vessels. Disorders of coagulation & fibrinolysis.
The importance of thrombocytopenia and its causes
 SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT NO 4 2017 SEED HAEMATOLOGY The importance of thrombocytopenia and its causes Key words: Thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic, low levels of platelets What is
SYSMEX EDUCATIONAL ENHANCEMENT AND DEVELOPMENT NO 4 2017 SEED HAEMATOLOGY The importance of thrombocytopenia and its causes Key words: Thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic, low levels of platelets What is
Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient
 Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient Kristina Haley, DO March 10, 2012 Jovita Reyes Memorial Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient Kristina Haley, DO March 10, 2012 Jovita Reyes Memorial Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
Hemostasis. PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures
 Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
For platelet control as individual as you
 For platelet control as individual as you Explore the possibilities of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) treatment. Important Risk Information WARNING: INTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS (IVH) Intravascular hemolysis
For platelet control as individual as you Explore the possibilities of Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) treatment. Important Risk Information WARNING: INTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS (IVH) Intravascular hemolysis
Heme (Bleeding and Coagulopathies) in the ICU
 Heme (Bleeding and Coagulopathies) in the ICU General Topics To Discuss Transfusions DIC Thrombocytopenia Liver and renal disease related bleeding Lack of evidence in managing critical illness related
Heme (Bleeding and Coagulopathies) in the ICU General Topics To Discuss Transfusions DIC Thrombocytopenia Liver and renal disease related bleeding Lack of evidence in managing critical illness related
Bleeding Disorders: (Hemorrhagic Diatheses) Tests used to evaluate different aspects of hemostasis are the following:
 Bleeding Disorders: (Hemorrhagic Diatheses) Excessive bleeding can result from: 1. Increased fragility of vessels. 2. Platelet deficiency or dysfunction. 3. Derangement of coagulation. 4. Combinations
Bleeding Disorders: (Hemorrhagic Diatheses) Excessive bleeding can result from: 1. Increased fragility of vessels. 2. Platelet deficiency or dysfunction. 3. Derangement of coagulation. 4. Combinations
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89
 Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Document Title: Hemostasis: Platelet and Coagulation Disorders. Author(s): Joseph H. Hartmann (University of Michigan), DO 2012
 Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Hemostasis: Platelet and Coagulation Disorders Author(s): Joseph H. Hartmann (University of Michigan), DO 2012 License: Unless otherwise
Project: Ghana Emergency Medicine Collaborative Document Title: Hemostasis: Platelet and Coagulation Disorders Author(s): Joseph H. Hartmann (University of Michigan), DO 2012 License: Unless otherwise
GUIDELINES FOR THE TRANSFUSION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS
 CHILDREN S HOSPITALS AND CLINICS OF MINNESOTA Introduction: GUIDELINES FOR THE TRANSFUSION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS These guidelines have been developed in conjunction with the hospital Transfusion Committee.
CHILDREN S HOSPITALS AND CLINICS OF MINNESOTA Introduction: GUIDELINES FOR THE TRANSFUSION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS These guidelines have been developed in conjunction with the hospital Transfusion Committee.
It s a bird, It s a plane, No It s a. Presented by Julie Kirkegaard & Miche Swofford
 It s a bird, It s a plane, No It s a Presented by Julie Kirkegaard & Miche Swofford 55 year old woman admitted 11/23/2015 for colon cancer that metastasized to her liver History of 3 pregnancies Surgery
It s a bird, It s a plane, No It s a Presented by Julie Kirkegaard & Miche Swofford 55 year old woman admitted 11/23/2015 for colon cancer that metastasized to her liver History of 3 pregnancies Surgery
Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No
 SEED Coagulation Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No 2 2016 An approach to the bleeding patient The purpose of this newsletter is to provide an overview of the approach to the bleeding patient
SEED Coagulation Sysmex Educational Enhancement and Development No 2 2016 An approach to the bleeding patient The purpose of this newsletter is to provide an overview of the approach to the bleeding patient
Overview 5/8/2017. Management Strategies for Bleeding and Thrombocytopenia in the Neonate
 Management Strategies for Bleeding and Thrombocytopenia in the Neonate Kyle Annen, DO Medical Director Blood Bank, Transfusion Service and Hematology Mount Sinai Beth Israel Assistant Professor, Department
Management Strategies for Bleeding and Thrombocytopenia in the Neonate Kyle Annen, DO Medical Director Blood Bank, Transfusion Service and Hematology Mount Sinai Beth Israel Assistant Professor, Department
GLANZMANN S THROMBASTHENIA. Stacey Shiovitz January 13, 2012
 GLANZMANN S THROMBASTHENIA Stacey Shiovitz January 13, 2012 HELP!! MY PATIENTHASGT DO YOU EVEN KNOW WHAT THAT IS? CASE 27yo woman presented tdto gynecology clinic i for menorrhagia x 10 days Bleeding started
GLANZMANN S THROMBASTHENIA Stacey Shiovitz January 13, 2012 HELP!! MY PATIENTHASGT DO YOU EVEN KNOW WHAT THAT IS? CASE 27yo woman presented tdto gynecology clinic i for menorrhagia x 10 days Bleeding started
CrackCast Episode 7 Blood and Blood Components
 CrackCast Episode 7 Blood and Blood Components Episode Overview: 1) Describe the 3 categories of blood antigens 2) Who is the universal donor and why? 3) Define massive transfusion 4) List 5 physiologic
CrackCast Episode 7 Blood and Blood Components Episode Overview: 1) Describe the 3 categories of blood antigens 2) Who is the universal donor and why? 3) Define massive transfusion 4) List 5 physiologic
Routine preoperative coagulation tests: are they necessary?
 Routine preoperative coagulation tests: are they necessary? Dr Azzah Alzahrani MD Pediatrics Hematology /Oncology PSMMS Outline Introduction. Brief review of hemostatic mechanisms. A clinical aspect of
Routine preoperative coagulation tests: are they necessary? Dr Azzah Alzahrani MD Pediatrics Hematology /Oncology PSMMS Outline Introduction. Brief review of hemostatic mechanisms. A clinical aspect of
Guidelines for Shared Care Centres and Community Staff
 Reference: CG1410 Written by: Dr Jeanette Payne Peer reviewer Dr Jenny Welch Approved: February 2016 Approved by D&TC: 8th January 2016 Review Due: February 2019 Intended Audience This document contains
Reference: CG1410 Written by: Dr Jeanette Payne Peer reviewer Dr Jenny Welch Approved: February 2016 Approved by D&TC: 8th January 2016 Review Due: February 2019 Intended Audience This document contains
Platelet disorders. Information for families. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust
 Platelet disorders Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust Platelets are the cells responsible for making blood clot so platelet disorders mean that injured
Platelet disorders Information for families Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust Platelets are the cells responsible for making blood clot so platelet disorders mean that injured
BLEEDING DISORDERS Simple complement:
 BLEEDING DISORDERS Simple complement: 1. Select the statement that describe the thrombocytopenia definition: A. Marked decrease of the Von Willebrandt factor B. Absence of antihemophilic factor A C. Disorder
BLEEDING DISORDERS Simple complement: 1. Select the statement that describe the thrombocytopenia definition: A. Marked decrease of the Von Willebrandt factor B. Absence of antihemophilic factor A C. Disorder
GOOD MORNING! Thursday, July Heidi Murphy, MD Leslie Carter-King, MD
 GOOD MORNING! Thursday, July 10 2014 Heidi Murphy, MD Leslie Carter-King, MD PREP QUESTION Almost all infants experience a transient increase in bilirubin concentrations known as physiologic jaundice during
GOOD MORNING! Thursday, July 10 2014 Heidi Murphy, MD Leslie Carter-King, MD PREP QUESTION Almost all infants experience a transient increase in bilirubin concentrations known as physiologic jaundice during
Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP
 Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP OVERVIEW Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder in humans, with an estimated prevalence ranging upward
Introduction to von Willebrand Disease Mary Lesh RN, MS, CPNP OVERVIEW Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder in humans, with an estimated prevalence ranging upward
GUIDELINES. for the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease (VWD)
 GUIDELINES for the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease (VWD) The Canadian Hemophilia Society (CHS) is committed to improve the health and quality of life of all people with inherited bleeding
GUIDELINES for the diagnosis and management of von Willebrand disease (VWD) The Canadian Hemophilia Society (CHS) is committed to improve the health and quality of life of all people with inherited bleeding
Miss. kamlah ahmed 1
 Miss. kamlah ahmed 1 Anatomy & Physiology Blood has two compartments: 1- a fluid portion called plasma. 2- a cellular portion known as the formed elements of the blood. Which are RBC (erythrocytes), WBC
Miss. kamlah ahmed 1 Anatomy & Physiology Blood has two compartments: 1- a fluid portion called plasma. 2- a cellular portion known as the formed elements of the blood. Which are RBC (erythrocytes), WBC
PLASMA EXCHANGE J MANION NEPEAN HOSPITAL
 PLASMA EXCHANGE J MANION NEPEAN HOSPITAL PLASMA The fluid portion of blood Normally approx 5% body weight or 3.5L in 70kg male Clots on standing unless anticoagulated Common plasma proteins are albumin,
PLASMA EXCHANGE J MANION NEPEAN HOSPITAL PLASMA The fluid portion of blood Normally approx 5% body weight or 3.5L in 70kg male Clots on standing unless anticoagulated Common plasma proteins are albumin,
Assessing thrombocytopenia in the intensive care unit: The past, present, and future
 Assessing thrombocytopenia in the intensive care unit: The past, present, and future Ryan Zarychanski MD MSc FRCPC Sections of Critical Care and of Hematology, University of Manitoba Disclosures FINANCIAL
Assessing thrombocytopenia in the intensive care unit: The past, present, and future Ryan Zarychanski MD MSc FRCPC Sections of Critical Care and of Hematology, University of Manitoba Disclosures FINANCIAL
GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN. All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding
 GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN Reference: Bruising / Bleeding / NAI Version No: 1 Applicable to All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding Classification
GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN Reference: Bruising / Bleeding / NAI Version No: 1 Applicable to All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding Classification
Blood Components Transfusion Criteria
 Adults 1. Packed Cells: Dosage one unit of red blood cells will raise the Hbg by 1 gram; Hct by 3% in a 70Kg adult. Red Blood Cells should be transfused based on clinical need. In the absence of acute
Adults 1. Packed Cells: Dosage one unit of red blood cells will raise the Hbg by 1 gram; Hct by 3% in a 70Kg adult. Red Blood Cells should be transfused based on clinical need. In the absence of acute
Platelet vs. Coagulation Bleeding. Qualitative and Quantitative Platelet Disorders. Laboratory Tests. Platelet Signaling. Jeffrey S. Jhang, M.D.
 Qualitative and Quantitative Platelet isorders Platelet vs. Coagulation Bleeding Findings Petechiae Hematomas and Hemarthroses elayed Bleeding Coagulation Rare Common Common Platelet Common Rare Rare Bleeding
Qualitative and Quantitative Platelet isorders Platelet vs. Coagulation Bleeding Findings Petechiae Hematomas and Hemarthroses elayed Bleeding Coagulation Rare Common Common Platelet Common Rare Rare Bleeding
Chapter 46. Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder
 Chapter 46 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Components of the Blood Red
Chapter 46 Care of the Patient with a Blood or Lymphatic Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Components of the Blood Red
Most Common Hemostasis Consults: Thrombocytopenia
 Most Common Hemostasis Consults: Thrombocytopenia Cindy Neunert, MS MSCS Assistant Professor, Pediatrics CUMC Columbia University TSHNA Meeting, April 15, 2016 Financial Disclosures No relevant financial
Most Common Hemostasis Consults: Thrombocytopenia Cindy Neunert, MS MSCS Assistant Professor, Pediatrics CUMC Columbia University TSHNA Meeting, April 15, 2016 Financial Disclosures No relevant financial
Anemia. A case-based approach. David B. Sykes, MD, PhD Hematology, MGH Cancer Center June 8, 2017
 Anemia A case-based approach David B. Sykes, MD, PhD Hematology, MGH Cancer Center June 8, 2017 Recognizing trends Learning Objectives MCV, RDW, Ferritin, LDH, Reticulocytes Managing complex patients 1.
Anemia A case-based approach David B. Sykes, MD, PhD Hematology, MGH Cancer Center June 8, 2017 Recognizing trends Learning Objectives MCV, RDW, Ferritin, LDH, Reticulocytes Managing complex patients 1.
Risk of ID transmission. Patient Blood Management - Blood Safety and Component Utilization. Transfusion and Cancer 4/9/2014
 Patient Blood Management - Blood Safety and Component Utilization Lowell Tilzer M.D. Pathology and Lab Medicine Kansas University Med Center Risk of ID transmission Pre NAT Post NAT HIV 1:607,000 ~1:2.5
Patient Blood Management - Blood Safety and Component Utilization Lowell Tilzer M.D. Pathology and Lab Medicine Kansas University Med Center Risk of ID transmission Pre NAT Post NAT HIV 1:607,000 ~1:2.5
Bleeding Disorders.1 MS4.24.Feb.19. Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Professor
 Bleeding Disorders.1 MS4.24.Feb.19 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Professor Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Hemostasis BV Injury Neural Contact Damage/contact. Blood Vessel Constriction Reduced
Bleeding Disorders.1 MS4.24.Feb.19 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD. FRCP.FRCPath Professor Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Hemostasis BV Injury Neural Contact Damage/contact. Blood Vessel Constriction Reduced
Diagnosis / Lab Findings
 Diagnosis / Lab Findings During at acute episode may see Peripheral smear bite cells, Heinz bodies Reticulocytosis Increased indirect bilirubin G6PD will be normal or high during an acute crisis Repeat
Diagnosis / Lab Findings During at acute episode may see Peripheral smear bite cells, Heinz bodies Reticulocytosis Increased indirect bilirubin G6PD will be normal or high during an acute crisis Repeat
Easy bruising vs Coagulopathy
 Easy bruising vs Coagulopathy Sept. 19, 2015 Lakehead Summer School Chris Hillis, MD MSc FRCPC hillis@hhsc.ca @HemeHillis Aim & Objectives Aim: To increase comfort in detecting non-pathologic bleeding
Easy bruising vs Coagulopathy Sept. 19, 2015 Lakehead Summer School Chris Hillis, MD MSc FRCPC hillis@hhsc.ca @HemeHillis Aim & Objectives Aim: To increase comfort in detecting non-pathologic bleeding
Evaluation Of Bleeding Disorders /AAP Baton Rouge. Raj Warrier
 Evaluation Of Bleeding Disorders /AAP Baton Rouge Raj Warrier Evaluation and approach to management of a bleeding child Raj Warrier Ochsner /Tulane/LSU Manipal University University Of Queenland Objectives
Evaluation Of Bleeding Disorders /AAP Baton Rouge Raj Warrier Evaluation and approach to management of a bleeding child Raj Warrier Ochsner /Tulane/LSU Manipal University University Of Queenland Objectives
Thrombocytopenia: a practial approach
 Thrombocytopenia: a practial approach Dr. med. Jeroen Goede FMH Innere Medizin, Medizinische Onkologie, Hämatologie FAMH Hämatologie Chefarzt Hämatologie Kantonsspital Winterthur Outline Introduction and
Thrombocytopenia: a practial approach Dr. med. Jeroen Goede FMH Innere Medizin, Medizinische Onkologie, Hämatologie FAMH Hämatologie Chefarzt Hämatologie Kantonsspital Winterthur Outline Introduction and
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation
 Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation HIHIM 409 WBC count RBC count WBC differential Hemoglobin (HGB) Hematocrit (HCT) % of volume occupied by RBCs CBC Red cell indices Mean cell volume (MCV) average
Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation HIHIM 409 WBC count RBC count WBC differential Hemoglobin (HGB) Hematocrit (HCT) % of volume occupied by RBCs CBC Red cell indices Mean cell volume (MCV) average
WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME. An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency
 WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency WHAT IS WISKOTT ALDRICH SYNDROME? Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (WAS) is a serious medical condition that causes problems both with the immune system
WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency WHAT IS WISKOTT ALDRICH SYNDROME? Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (WAS) is a serious medical condition that causes problems both with the immune system
LAMA SHATAT TTP, ITP, DIC
 TTP, ITP, DIC Reduction in platelet number (thrombocytopenia) constitutes an important cause of generalized bleeding. A count less than 100,000 platelets/μl is generally considered to constitute thrombocytopenia.
TTP, ITP, DIC Reduction in platelet number (thrombocytopenia) constitutes an important cause of generalized bleeding. A count less than 100,000 platelets/μl is generally considered to constitute thrombocytopenia.
Hemophilia. Hemophilia A Hemophilia B. Justine Cuaresma Cesia Cisneros Natalia Giles
 Hemophilia Hemophilia A Hemophilia B Justine Cuaresma Cesia Cisneros Natalia Giles Hemophilia is A rare blood disorder in which the patient s blood clots do not normally function. Patients tend to bleed
Hemophilia Hemophilia A Hemophilia B Justine Cuaresma Cesia Cisneros Natalia Giles Hemophilia is A rare blood disorder in which the patient s blood clots do not normally function. Patients tend to bleed
Abnormal blood counts in children Dr Tina Biss Consultant Paediatric Haematologist Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
 Abnormal blood counts in children Dr Tina Biss Consultant Paediatric Haematologist Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Regional Paediatric Specialty Trainees teaching 4 th July 2017 Scope
Abnormal blood counts in children Dr Tina Biss Consultant Paediatric Haematologist Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Regional Paediatric Specialty Trainees teaching 4 th July 2017 Scope
DIC. Disseminated intravascular coagulation, is a life threatening pathological process in which clotting factors are abnormally activated.
 Miss. kamlah 1 DIC Disseminated intravascular coagulation, is a life threatening pathological process in which clotting factors are abnormally activated. Resulting in wide spread of clot formation in the
Miss. kamlah 1 DIC Disseminated intravascular coagulation, is a life threatening pathological process in which clotting factors are abnormally activated. Resulting in wide spread of clot formation in the
Learning Objectives: At the end of this exercise, the student will be able to:
 Applications in Transfusion Medicine- A CBL Exercise- Student Guide 1 Title: Applications in Transfusion Medicine A CBL Exercise Purpose: At the conclusion of this exercise, students will be able to apply
Applications in Transfusion Medicine- A CBL Exercise- Student Guide 1 Title: Applications in Transfusion Medicine A CBL Exercise Purpose: At the conclusion of this exercise, students will be able to apply
INVESTIGATION OF ADVERSE TRANSFUSION REACTIONS TABLE OF RECOMMENDED TESTS. Type of Reaction Presentation Recommended Tests Follow-up Tests
 Minor Allergic (Urticarial) Urticaria, pruritis, flushing, rash If skin reaction only and mild hives/ rash
Minor Allergic (Urticarial) Urticaria, pruritis, flushing, rash If skin reaction only and mild hives/ rash
KASABACH MERRITT SYNDROME
 KASABACH MERRITT SYNDROME Pages with reference to book, From 159 To 161 Shahina Qureshi, Zaheer Abbasi, Naheed Qadeer, Naila Yaqoob ( Children's Hospital, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad.
KASABACH MERRITT SYNDROME Pages with reference to book, From 159 To 161 Shahina Qureshi, Zaheer Abbasi, Naheed Qadeer, Naila Yaqoob ( Children's Hospital, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad.
Use of Intravenous Anti-RhD Immunoglobulin (RhIG) in the Treatment of Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia
 Use of Intravenous Anti-RhD Immunoglobulin (RhIG) in the Treatment of Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia KRISTINA WILLIAMS ABSTRACT Commercialized intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) products have been used
Use of Intravenous Anti-RhD Immunoglobulin (RhIG) in the Treatment of Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia KRISTINA WILLIAMS ABSTRACT Commercialized intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) products have been used
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing. IgA & ttg IgA
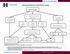 Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP)
 Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) ITP - What is it? ITP is a blood disorder affecting platelets in the blood. Platelets are small cells in your blood that help your blood to clot. In ITP the body s immune
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) ITP - What is it? ITP is a blood disorder affecting platelets in the blood. Platelets are small cells in your blood that help your blood to clot. In ITP the body s immune
M B Garvey. University of Toronto
 Do I really need that test??? M B Garvey Professor Emeritus University of Toronto St Michael s Hospital No relevant conflicts of interest 1 HEMOSTASIS IS LIKE LOVE Everybody talks about it, nobody understands
Do I really need that test??? M B Garvey Professor Emeritus University of Toronto St Michael s Hospital No relevant conflicts of interest 1 HEMOSTASIS IS LIKE LOVE Everybody talks about it, nobody understands
INTRODUCTION TO SET FORTH APROACH TO MANAGING ADULTS TO SET FORTH APROACH PRIMARY ( PRIMARY AUTOIMMUNE) AUTOIMMUNE ITP FROM ASH & THE BRITISH
 HOW I TREAT IDIOPATHIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA Dauglas B. Cines, James B Bussel. Blood Oktober 2005:106(7):2244-22512251 INTRODUCTION TO SET FORTH APROACH TO MANAGING ADULTS PRIMARY (AUTOIMMUNE) ITP FROM
HOW I TREAT IDIOPATHIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA Dauglas B. Cines, James B Bussel. Blood Oktober 2005:106(7):2244-22512251 INTRODUCTION TO SET FORTH APROACH TO MANAGING ADULTS PRIMARY (AUTOIMMUNE) ITP FROM
General approach to the investigation of haemostasis. Jan Gert Nel Dept. of Haematology University of Pretoria 2013
 General approach to the investigation of haemostasis Jan Gert Nel Dept. of Haematology University of Pretoria 2013 Clinical reasons to investigate haemostasis Investigating a clinically suspected bleeding
General approach to the investigation of haemostasis Jan Gert Nel Dept. of Haematology University of Pretoria 2013 Clinical reasons to investigate haemostasis Investigating a clinically suspected bleeding
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
 Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Title of Guideline Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for the management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura Dr S Stokley, Consultant
Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Title of Guideline Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for the management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura Dr S Stokley, Consultant
Crossmatching and Issuing Blood Components; Indications and Effects.
 Crossmatching and Issuing Blood Components; Indications and Effects. Alison Muir Blood Transfusion, Blood Sciences, Newcastle Trust Topics Covered Taking the blood sample ABO Group Antibody Screening Compatibility
Crossmatching and Issuing Blood Components; Indications and Effects. Alison Muir Blood Transfusion, Blood Sciences, Newcastle Trust Topics Covered Taking the blood sample ABO Group Antibody Screening Compatibility
ACQUIRED COAGULATION ABNORMALITIES
 ACQUIRED COAGULATION ABNORMALITIES ACQUIRED COAGULATION ABNORMALITIES - causes 1. Liver disease 2. Vitamin K deficiency 3. Increased consumption of the clotting factors (disseminated intravascular coagulation
ACQUIRED COAGULATION ABNORMALITIES ACQUIRED COAGULATION ABNORMALITIES - causes 1. Liver disease 2. Vitamin K deficiency 3. Increased consumption of the clotting factors (disseminated intravascular coagulation
Case Presentation. A Case from the Clinic. Additional Data. Examination and Data 10/27/2013
 Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Treatment of Severe Thrombocytopenia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Role of New Agents Disclosures: Advisory Board: Incyte Corporation Speaker
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine Treatment of Severe Thrombocytopenia in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Role of New Agents Disclosures: Advisory Board: Incyte Corporation Speaker
Anaemia / SCD/ Bleeding disorders in Children
 Anaemia / SCD/ Bleeding disorders in Children Dr Neil Kennedy Handouts by Steve Graham Learning Outcomes Describe mechanisms of anaemia in Malawian children Discuss important causes of anaemia Describe
Anaemia / SCD/ Bleeding disorders in Children Dr Neil Kennedy Handouts by Steve Graham Learning Outcomes Describe mechanisms of anaemia in Malawian children Discuss important causes of anaemia Describe
GOOD MORNING! July 3, 2014
 GOOD MORNING! July 3, 2014 OUR PATIENT 4yo Female with: 2 days of fever, sore throat, swollen nodes in neck and abdominal pain PMH: Tonsillectomy age 2 Immunizations: UTD NKDA DIFFERENTIAL: OUR PATIENT
GOOD MORNING! July 3, 2014 OUR PATIENT 4yo Female with: 2 days of fever, sore throat, swollen nodes in neck and abdominal pain PMH: Tonsillectomy age 2 Immunizations: UTD NKDA DIFFERENTIAL: OUR PATIENT
Things to never miss in the office. Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC
 Things to never miss in the office Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty / Speaker s name: Brett Houston / Leonard Minuk Relationships with commercial
Things to never miss in the office Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty / Speaker s name: Brett Houston / Leonard Minuk Relationships with commercial
Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease Olga Olevsky, M.D. and Stephen Wong, M.D. Von Willebrand s Disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Low levels of Von
CLINICAL VIGNETTE Diagnosis and Management of Von Willebrand Disease Olga Olevsky, M.D. and Stephen Wong, M.D. Von Willebrand s Disease is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Low levels of Von
Pathologist-in-chief. Professor of Medicine and Pathology. School of Medicine
 Michael Laposata MD, PhD Pathologist-in-chief Vanderbilt University Hospital Professor of Medicine and Pathology Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Rosemary Jaromin Godmother of patient Jazmin Corinne
Michael Laposata MD, PhD Pathologist-in-chief Vanderbilt University Hospital Professor of Medicine and Pathology Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Rosemary Jaromin Godmother of patient Jazmin Corinne
