Review article. early diagnosis? HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for. Why subjects carrying HLA-B27 are prone. Jan Tore Gran, Gunnar Husby
|
|
|
- Wilfred Tucker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 _JMed Genet 1995;32: Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence to: Dr Gran. HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for early diagnosis? Jan Tore Gran, Gunnar Husby The seronegative spondyloarthropathy complex The seronegative spondyloarthropathy complex embraces a group of inflammatory rheumatic disorders linked together by certain clinical, laboratory, and radiological manifestations. Clinically, the disorders are characterised by asymmetrical peripheral oligoarthritis and involvement of the sacroiliac joints (table 1). Manifestations in the eyes, mucocutaneous membranes, and genitourinary system not infrequently accompany the often predominant arthritis. The patients lack detectable rheumatoid factors in serum, hence the term "seronegative". Other serum autoantibodies, often found in inflammatory rheumatic diseases, are notably absent in the spondyloarthropathies. Unlike in rheumatoid arthritis, radiological examinations of peripheral joints rarely show destructive changes. However, radiological sacroiliitis is essential for the diagnosis of many of these diseases. ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is regarded as the prototype of the seronegative spondyloarthropathies (table 1). In its classic but quite rare form, complete ankylosis of the whole spine develops within a few years. More often, however, the clinical picture is dominated by pain and stiffness of the back with radiological examination showing sacroiliitis and varying degrees of spinal inflammation.' Table 1 The seronegative spondyloarthropathy complex: disorders, common disease manifestations, and frequencies of HLA-B27 Disorders % Ankylosing spondylitis Reiter's disease Reactive arthritis Psoriatic arthritis 54 Arthritis in inflammatory bowel diseases 50 Manifestations Seronegativity for rheumatoid factors Absence of antinuclear antibodies Absence of rheumatic nodules Peripheral arthritis Genitourinary (urethritis, vaginitis, balanitis) Mucocutaneous (stomatitis, dermatitis) Intestinal (enteric infections or chronic inflammation) Radiological sacroiliitis Genetic (familial aggregation, HLA-B27) REACTIVE ARTHRITIS Reactive arthritis (ReA) is a term introduced by Aho et al2 in It denotes an asymmetrical non-infectious arthritis in a few joints, appearing days or weeks after infection elsewhere in the body, most often in the genitourinary or gastrointestinal system. Previously, the term postinfectious arthritis was preferred. PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS The arthritis associated with psoriasis is most often localised to a few joints in an asymmetrical pattern, frequently affecting the distal interphalangeal joints of the hands.3 It occasionally manifests radiological sacroiliitis, but complete ankylosis of the spine ("bamboo spine") is definitely less frequent than in AS. Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may also present a clinical picture almost indistinguishable from that of rheumatoid arthritis. Although serum rheumatoid factors are notably absent, this form of psoriatic arthritis affecting peripheral joints bears little resemblance to the other spondyloarthropathies. INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASES A seronegative arthritis may also accompany the inflammatory bowel disorders ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.4 As in other spondyloarthropathies, radiological sacroiliitis may be seen. A striking feature of the seronegative spondyloarthropathies is the association with the histocompatibility antigen HLA-B27. The association between HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy The study of products of genes located on a region of chromosome 6, known as the major histocompatibility complex, has provided valuable insight into many diseases of as yet unknown aetiology. In 1973, two independent groups of workers found a striking association between one of these genes, HLA-B27 and AS.56 Subsequently, associations between HLA-B27 and ReA and PsA were established.78 Why subjects carrying HLA-B27 are prone to develop spondyloarthropathy is not fully understood.9
2 498 Gran, Husby Table 2 Diagnostic criteria and tentative disease definitions for varzous seronegative spondyloarthropathies New York criteria for ankylosing spondylitis (1) Limitation of motion of the lumbar spine in all three planes (anterior flexion, lateral flexion, and extension). (2) HistQry or the presence of pain at the dorsolumbar junction or in the lumbar spine. (3) Limitation of chest expansion to 2-5 cm or less, measured at the level of the fourth intercostal space. The diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis requires the presence of grade 3-4 bilateral sacroiliitis with at least one clinical criterion, or grade 3-4 unilateral or grade 2 bilateral with criterion 1 or with both clinical criteria 2 and 3. Reactive arthritis A seronegative arthritis occurring shortly after infection in the genitourinary or gastrointestinal canal. Reiter's syndronie One or more episodes of urethritis or conjunctivitis in connection with seronegative arthritis. Psonratic spondylitis Pain/stiffness of the spine with radiological examination showing sacroiliitis/spondylitis in a patient with psoriasis. Spondylitis in iniflanmnmatory bowel disease Pain/stiffness of the spine with radiological examination showing sacroiliitis/spondylitis in a patient with either Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. HLA-B27 IN SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES Approximately 95% of white patients with AS are HLA-B27 positive'0 (table 1). The prevalence of HLA-B27 among patients with ReA appears somewhat less, about 70-85%7 (table 1). In PsA, there is a clear association between HLA-B27 and the group of patients exhibiting radiological sacroiliitis,8 whereas the frequency of this tissue antigen among cases with symmetrical polyarthritis resembling rheumatoid arthritis equals that in the general population.8 In the inflammatory bowel disorders, HLA- B27 does not confer an increased risk of contracting peripheral arthritis,4 but a moderate association between HLA-B27 and spondylitic disease is present.4 HLA-B27 IN VARIOUS POPULATIONS The distribution of HLA-B27 among various ethnic groups appears strikingly uneven.'' Among certain North American Indians, Lapps, and inhabitants of northern Scandinavia the frequency of HLA-B27 ranges from 26 to 50%." Most European populations show B27 prevalences between 7 and 10%." In blacks, HLA-B27 is virtually absent." Diagnostic value of HLA-B27 in spondyloarthropathy DEFINITE DIAGNOSES The diagnostic criteria and tentative definitions of various seronegative spondyloarthropathies are given in table 2. Clearly, none of the diseases under consideration requires a positive HLA- B27 test for a definite diagnosis. All diagnoses are based on the appearance of certain clinical signs and symptoms, and for AS the demonstration of radiological sacroiliitis is mandatory for diagnosis.'2 SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY The diagnostic value of the HLA-B27 test for AS in a randomly selected person can be obtained by expressing the test sensitivity. Sensitivity is defined as the proportion of patients with positive test results, and is between 90 and 95% in AS. The specificity of the test gives the proportion of healthy subjects with negative test results (HLA-B27 negative). With a prevalence of AS of 0 1 %, a population frequency of HLA-B27 of 10%, and a sensitivity of 95%, the specificity of the HLA-B27 test in AS is 90-1%. If the prevalence of AS amounts to 1%, the specificity is 90-8%. PREDICTIVE VALUE OF A POSITIVE HLA-B27 TEST The predictive value indicates the proportion of HLA-B27 positive AS patients among persons with HLA-B27. Populations who have a prevalence of HLA-B27 of 10%, disease prevalences of 0 1 % and 1%, would give predictive values of 0 95% and 9 5%, respectively. These figures correspond well to the findings in epidemiological surveys, in which it has been calculated that between 1 and 6% of persons with HLA-B27 suffer from AS.'0 PREDICTIVE VALUE OF A NEGATIVE HLA-B27 TEST This figure gives the proportion of persons without HLA-B27 who are healthy. It can be calculated that the probability of not having AS for a HLA-B27 negative person is about 99.9%. INTERPRETATIONS OF THE STATISTICAL CALCULATIONS From the above mentioned statistical considerations, it can be concluded that although the HLA-B27 test exhibits both high sensitivity and specificity, the test cannot be used to diagnose AS in randomly selected persons. The predictive value of a positive test which is between 0 95 and 9-5% indicates that the overwhelming majority of HLA-B27 positive persons do not suffer from AS. Thus, HLA- B27 appears not to be useful as a screening test for AS among randomly selected persons. However, the predictive value of a negative test result for the absence of AS reaches exceptionally high values. Consequently, the chance ofhaving AS for a person without HLA- B27 is extremely low. The HLA-B27 test may therefore possess some value in clinical practice when dealing with randomly selected persons. A negative test result should be interpreted as an exclusion criterion for the diagnosis of AS. However, this is unrealistic as there is no reason to test for HLA-B27 in randomly selected persons. The HLA-B27 test should always be performed after clinical suspicion of seronegative spondyloarthropathy has been evoked. Thus, the discussion of the potential use of this test is reserved for cases presenting with symptoms and signs suggestive of seronegative spondyloarthropathy. PRETEST LIKELIHOOD In epidemiological surveys it has been found that the prevalence of AS among HLA-B27
3 HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for early diagnosis? positive persons with back pain or stiffness is as high as 22-5%. ' This figure clearly contrasts the estimate of a 1 to 6% prevalence of AS among a random sample ofb27 positive people. Thus, selecting people with back pain and stiffness for B27 testing increases the likelihood of finding AS. However, more than 75% of cases with back pain and stiffness suffer from diseases other than AS. Thus, the pretest likelihood must be increased further to meet the cost-benefit demands. It has been calculated'3 that for a positive HLA-B27 test to provide an acceptable 95% chance that the diagnosis is correct, the physician must be more than 50% certain of the diagnosis before the test is performed. Unfortunately, the many attempts at constructing useful clinical diagnostic criteria for AS independent of radiological examination have all been unsuccessful.'415 At present it seems difficult to diagnose AS clinically with a 50% chance of correct diagnosis. Consequently, HLA-B27 does not appear helpful in differentiating spondyloarthropathies meeting traditional definitions from other causes of back complaints. THE CONCEPT OF UNDIFFERENTIATED SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY AND SPONDYLITIC DISEASE It has been suggested recently that the traditional clinical view on diagnosing seronegative spondyloarthropathies should be broadened.'6 Some workers have suggested that AS may manifest with clinical symptoms of inflammatory back pain but without the radiological features of classical AS.'6 In family studies this clinical picture appears significantly associated with HLA-B27. It has been found that between 13 and 18% of B27 positive first degree relatives of B27 positive cases express clinical symptoms of inflammatory spinal disease without concomitant radiological signs of the disease. The clinical picture has been entitled "spondylitic disease".'6 A new set of classification criteria for spondyloarthropathies has also been suggested'7 (table 3). According to these criteria, a diagnosis of undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy is preferred in patients who complain of inflammatory spinal pain or synovitis and in addition have psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, positive familial history, or enthesopathy. 17 If the concept of AS is broadened to include such clinical pictures, the value of HLA-B27 testing, especially in first degree relatives of AS Table 3 European Spondylarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) preliminary classification criteria for spondyloarthropathies Inflammatory spinal pain or synovitis Asymmetrical Predominantly in the lower limb And one of the following Positive family history Psoriasis Inflammatory bowel disease Alternate buttock pain Enthesopathy 499 probands, should be re-evaluated. Until the aetiology of AS has been described, these suggestions cannot be proven nor refuted. However, the eventual clinical usefulness of expanding the diagnostic net of spondyloarthropathies may be disputed. Evidently, no effective prophylaxis is available for either the classical spondyloarthropathies or for the "new" group of spondylitics. Thus, adding a new group of patients to the already existing cases of AS does not help to solve the primary task of medicine, to prevent disease development. Moreover, we do not know the effect of therapy on these new syndromes. To diagnose "spondylitic disease" for the benefit of early therapy, whether physical therapy or administration of drugs, does not seem justified. Furthermore, whether or not undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy in due time will lead to restricted mobility of the spine and chest as seen in AS is not yet known, so the purpose of physical therapy directed at increasing spinal mobility appears limited. Finally, another important problem is adequate patient information. At present, the possible risk of developing disease complications, such as cardiac conduction disturbances, dislocations of the upper cervical spine, and renal amyloidosis has not been studied properly. Thus, defining a new group of spondylitics creates the problem of offering adequate patient information regarding disease outcome. However, the concept of a wider spectrum of HLA-B27 associated spondyloarthropathy is intriguing and the cases under consideration should be subjected to research based follow up and further clinical and laboratory analyses. It should also be stressed that the new criteria'7 were primarily meant to serve as classification criteria and not as a diagnostic aid in everyday clinical practice. Unfortunately, classification criteria are often confused with diagnostic criteria and the confusion is not infrequently enhanced by the general accessibility of the HLA-B27 test. Therefore, it seems necessary to review the individual clinical syndromes of the seronegative spondyloarthropathy complex and their associations with HLA-B27. VALUE OF THE B27 TEST IN PATIENTS WITH ASYMMETRICAL PERIPHERAL OLIGOARTHRITIS The presence of asymmetrical peripheral arthritis in a few joints may raise the suspicion of either psoriatic arthritis (PsA) or reactive arthritis (ReA). In young and middle aged patients with an *acute onset of oligoarthritis in the absence of psoriasis, ReA is a likely diagnosis. A definite diagnosis is based on the findings of serological or microbiological evidence of genitourinary or gastrointestinal infection antedating the arthritis. As the prevalence of HLA-B27 among cases with ReA is lower than in AS, the predictive value of both a positive and a negative test is less when compared to AS. Although the presence of HLA-B27 may increase the
4 500 suspicion of ReA, it remains unhelpful as an aid to diagnosis. In PsA, the association between spondylitis and HLA-B27 is less pronounced than that of AS and ReA.8 At most, the frequency of HLA- B27 in psoriatic spondylitis is about 50%.8 Consequently, the predictive diagnostic value of the HLA-B27 test in psoriatic spondylitis does not meet the demands ofclinical medicine. THE VALUE OF HLA-B27 IN JUVENILE CHRONIC ARTHRITIS In contrast to adult AS, juvenile AS less frequently causes symptoms of axial skeleton disease at onset.'8 Perhaps as few as 24% of children complain of pain and stiffness of the lumbar spine.'8 Instead, manifestations from the peripheral joints often dominate the initial clinical picture. The association between juvenile AS and HLA-B27 is, however, as strong as that in adult disease.'8 In patients with established juvenile chronic arthritis a positive HLA-B27 test can be of help in focusing the diagnosis towards development of AS later on. However, the test shows the same limitations as in adult AS, and cannot be regarded as of diagnostic value. THE VALUE OF HLA-B27 IN ACUTE UVEITIS It has been found that the prevalence of HLA- B27 is increased to about 50% in acute anterior uveitis (AAU),'9 and that between 15 and 25% of the patients have clinical and radiographic evidence of AS.'9 Thus, even in the absence of concomitant AS, AAU seems to be associated with HLA-B27, and the test appears to be of limited value in diagnosing coexisting AS. Patients with AAU should not undergo routine rheumatological examinations. Only those cases with AAU who report significant stiffness or pain of the back or peripheral joints should be referred to a rheumatologist for further examination. SCREENING FOR HLA-B27 IN FAMILIES OF AS PROBANDS As HLA-B27 is inherited in a codominant fashion, the prevalence of HLA-B27 among first degree family members will be in the order of 25 to 100%, depending on homozygosity and HLA status of the mate. The prevalence of AS among first degree relatives of AS probands has been estimated as 1-3 to 11%.2021 Consequently, only a small proportion of HLA- B27 positive probands will develop AS as defined by traditional diagnostic criteria. Moreover, as no prophylaxis is available to prevent the development of AS, there is no cause for routine testing of HLA-B27 among family members. The determination of HLA-B27 in first degree relatives of AS probands will only increase the risk of introducing "iatrogenic HLA-B27-itis". As discussed earlier, clinical spondylitic disease is suggested to occur quite frequently among HLA-B27 positive family members of AS probands.'6 It is the authors' opinion that the prbblems associated with this diagnosis are Gran, Husby so significant that HLA-B27 typing based on the assumption of clinical spondylitic disease is not justified. HLA-B27 AS A CONFIRMATORY TEST IN AS The diagnosis ofas rests on the demonstration of radiological sacroiliitis in patients having pain or stiffness ofthe back. The demonstration of a negative HLA-B27 test in such cases will not alter the diagnosis. The absence of HLA- B27 in a patient with AS should, however, alert the physician to the possibility of concurrent psoriasis or inflammatory bowel disease. There are undoubtedly, however, true cases of HLA- B27 negative cases of AS.showing no signs of concurrent dermatological or intestinal disease. HLA-B27 AND PROGNOSIS IN AS Apart from a higher prevalence ofaau in B27 positive subjects compared to B27 negative cases, the clinical picture appears similar in B27 positive and B27 negative AS.22 As more than 90% of AS patients carry B27, and only 25% contract AAU, tissue typing is of no help in selecting those cases that are prone to develop eye complications. Conclusions HLA-B27 is essential to the aetiopathogenesis of spondyloarthropathies. This statement has been so widely accepted that the term "HLA- B27 associated disease" is sometimes used to replace "the seronegative spondyloarthropathy complex" introduced by Moll et al.21 However, for the practising physician it is important to bear in mind that only a minority of HLA-B27 positive subjects contract a "B27 associated disease" and that the overwhelming majority of patients with musculoskeletal complaints do not suffer from inflammatory rheumatic disease. These two simple facts should serve as guidelines to the use of the HLA-B27 test in everyday clinical practice. It is our conviction that the benefit of the HLA-B27 test is very limited. The test cannot be used for confirming a diagnosis of spondyloarthropathy or predicting the prognosis in patients with an established diagnosis of inflammatory rheumatic disease. The test can be used in three ways. First, if the likelihood of spondyloarthropathy based on symptoms and signs is greater than 50%, a B27 positive test result significantly increases the chance of a correct diagnosis. Such a high pretest likelihood, however, requires reliable clinical diagnostic criteria which are not readily available in rheumatology. It is, however, our hope that such criteria will be developed in the near future. Secondly, in patients with back pain and stiffness, a negative B27 test result very strongly indicates that the complaints are caused by diseases other than AS. In the absence of concurrent psoriasis or inflammatory bowel disease, a negative B27 test result virtually excludes a diagnosis of AS, provided the test is properly done.
5 HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for early diagnosis? Thirdly, a positive B27 test in children with established inflammatory joint disease may help the physician focus on a possible development of seronegative spondyloarthropathy. Today's increasing demands for an effective and rationalised health system do not allow uncritical use of expensive laboratory tests. The results of such tests may at worst lead to incorrect diagnoses and initiation oftherapeutic strategies of virtually no benefit to the patients. 1 Gran JT, Husby G. Ankylosing spondylitis: a comparative study of patients in an epidemiological survey and those admitted to a department of rheumatology..7 Rheumatol 1984;11: Aho K, Ahvonen P, Lassus A, Sievers K, Tiilikainen A. HLA antigen 27 and reactive arthritis. Lancet 1973; ii: Wright V. Arthropathia psoriatica. A clinical entity? Scand.7 Rheumatol 1980;suppl 32: Gran JT, Husby G. Joint manifestations in gastrointestinal diseases. Dig Dis 1992;10: Brewerton DA, Hart FD, Nicholls A, Caffrey M, James DCO, Sturrock RD. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A27. Lancet 1973;i: Schlosstein L, Terasaki PI, Bluestone R, Pearson CM. High association of an HL-A antigen, w27, with ankylosing spondylitis. N Engl J7 Med 1973;288: Calin A. Reiter's syndrome: epidemiology and immunogenetics. ScandJ Rheumatol 1980;suppl 32: Scarpa R, Oriente P, Pucino A. The clinical spectrum of psoriatic spondylitis. Br _7 Rheumatol 1988;27: Khan MA. Spondyloarthropathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1993;5: Gran JT, Husby G, Hordvik M. Prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis in males and females in a young middle-aged population in Troms0, northern Norway. Ann Rheum Dis 1985;44: Gran JT, Husby G. The epidemiology of ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1993;22: Moll JMH, Wright V. New York clinical criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 1973;32: Hawkins BR, Dawkins RL, Christiansen FT, Zilko PJ. Use of the B27 test in the diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis: a statistical evaluation. Arthritis Rheum 1981;24: Gran JT. An epidemiological survey of the signs and symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 1985;4: Baron M, Zeidel I. HLA-B27 testing in ankylosing spondylitis: an analysis of pretest assumptions. _7 Rheumatol 1989;16: Khan MA, van der Linden SM, Kushner I, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Spondylitic disease without radiologic evidence of sacroiliitis in relatives of HLA-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis patients. Arthritis Rheum 1985;28: Khan MA, van der Linden SM. Ankylosing spondylitis and other spondyloarthropathies. Rheunz Dis Clin North Am 1990;16: Cassidy JT, Petty RE. Spondyloarthropathy. In: Cassidy JT, Petty RE, eds. Textbook ofpediatric rheumatology. 2nd ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1990: Brewerton DA, Webley M, Murphy AH, Ward AM. The alpha-1-antitrypsin phenotype MZ in acute anterior uveitis. Lancet 1978;i: Rogoff B, Freyberg RH. The familial incidence of rheumatoid spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 1949;8: van der Linden SM, Valkenburg HA, de Jongh BM, Cats A. The risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis in HLA- B27 positive individuals. Arthritis Rheum 1984;27: Linssen A, Feltkamp TEW. B27 positive diseases versus B27 negative diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 1988;47: Moll JM, Haslock I, Macrae IF, Wright V. Associations between ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, Reiter's disease, the intestinal arthropathies and Behcet's syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974;53: J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 July Downloaded from on 13 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 504-509 HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis J. C. WOODROW, AND C. J. EASTMOND From the Department of Medicine, Liverpool University SUMMARY One
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 504-509 HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis J. C. WOODROW, AND C. J. EASTMOND From the Department of Medicine, Liverpool University SUMMARY One
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT
 THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT J.M.H. MOLL Emeritus Consultant Rheumatologist, Sheffield, UK SUMMARY In the 1960s, Professor Verna Wright became increasingly interested
THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT J.M.H. MOLL Emeritus Consultant Rheumatologist, Sheffield, UK SUMMARY In the 1960s, Professor Verna Wright became increasingly interested
Histocompatibility antigens in inflammatory
 Gut, 1976, 17, 906-910 Histocompatibility antigens in inflammatory bowel diseaset Their clinical significance and their association with arthropathy with special reference to HLA-B27 (W27) ELIAS G. MALLAS,
Gut, 1976, 17, 906-910 Histocompatibility antigens in inflammatory bowel diseaset Their clinical significance and their association with arthropathy with special reference to HLA-B27 (W27) ELIAS G. MALLAS,
HLA haplotype A33-B58-Cw10 may modulate radiographic development of bamboo spine in Taiwanese patients with primary ankylosing spondylitis
 Disease Markers 26 (2009) 93 96 93 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0619 IOS Press HLA haplotype A33-B58-Cw10 may modulate radiographic development of bamboo spine in Taiwanese patients with primary ankylosing spondylitis
Disease Markers 26 (2009) 93 96 93 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0619 IOS Press HLA haplotype A33-B58-Cw10 may modulate radiographic development of bamboo spine in Taiwanese patients with primary ankylosing spondylitis
Axial Spondyloarthritis. Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital
 Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro?
 Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Genetics of B27-associated diseases 1
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 135 Genetics of B27-associated diseases 1 J. C. WOODROW From the Department of Medicine, University of Liverpool, Liverpool The genetic analysis of those conditions
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 135 Genetics of B27-associated diseases 1 J. C. WOODROW From the Department of Medicine, University of Liverpool, Liverpool The genetic analysis of those conditions
Dr Tracey Kain. Associate Professor Ed Gane
 Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Overview of axial spondyloarthritis
 Chapter 2 Overview of axial spondyloarthritis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises ankylosing spondylitis (AS), reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis
Chapter 2 Overview of axial spondyloarthritis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises ankylosing spondylitis (AS), reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling. Rheumatic Diseases
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA)
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation
 ~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Ankylosing Spondylitis*
 Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
Antibody producing capacity to the bacteriophage
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 883-888 Antibody producing capacity to the bacteriophage 4X174 in yersinia arthritis ROGER BUCKNALL,' MARJATTA LEIRISALO-REPO,2 OSSI LAITINEN,2 AND JOHN VERRIER
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 883-888 Antibody producing capacity to the bacteriophage 4X174 in yersinia arthritis ROGER BUCKNALL,' MARJATTA LEIRISALO-REPO,2 OSSI LAITINEN,2 AND JOHN VERRIER
Ileocolonoscopy in Seronegative Spondylarthropathy
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1989;96:339-44 Ileocolonoscopy in Seronegative Spondylarthropathy M. DE vas, c. CUVELIER, H. MIELANTS, E. VEYS, F. BARBIER, and A:ELEWAUT Departments of Gastroenterology, Pathology, and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1989;96:339-44 Ileocolonoscopy in Seronegative Spondylarthropathy M. DE vas, c. CUVELIER, H. MIELANTS, E. VEYS, F. BARBIER, and A:ELEWAUT Departments of Gastroenterology, Pathology, and
Update on Enthesitis-Related Arthritis, a Subtype of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
 Hong Kong Bull Rheum Dis 2010;10:15-19 Review Article Update on Enthesitis-Related Arthritis, a Subtype of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Tsz-Leung Lee Abstract: Keywords: Enthesitis related arthritis (ERA)
Hong Kong Bull Rheum Dis 2010;10:15-19 Review Article Update on Enthesitis-Related Arthritis, a Subtype of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Tsz-Leung Lee Abstract: Keywords: Enthesitis related arthritis (ERA)
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide for Macular Edema in HLA-B27 Negative Ankylosing Spondylitis
 105 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
105 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Introduction: Inflammatory arthritis is the most common extraintestinal manifestation in patients with inflammatory
PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Introduction: Inflammatory arthritis is the most common extraintestinal manifestation in patients with inflammatory
CLOSER LOOK AT SpA. Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi. Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH
 CLOSER LOOK AT SpA Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH Closer look at SpA I. Categories II. SIGN & SYMPTOMS III. X-RAY IV. MRI V. MANAGMENT Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
CLOSER LOOK AT SpA Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH Closer look at SpA I. Categories II. SIGN & SYMPTOMS III. X-RAY IV. MRI V. MANAGMENT Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London
 Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London Background Extraintestinal manifestations of IBD are well recognised. They include:- Arthritis - peripheral and axial Eye complications
Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London Background Extraintestinal manifestations of IBD are well recognised. They include:- Arthritis - peripheral and axial Eye complications
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 741-745 Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27 ADRIAN B. BECKINGSALE, JONATHAN DAVIES, JONATHAN M. GIBSON, AND A. RALPH ROSENTHAL
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 741-745 Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27 ADRIAN B. BECKINGSALE, JONATHAN DAVIES, JONATHAN M. GIBSON, AND A. RALPH ROSENTHAL
A Tailored Approach to Uveitis and Associated Systemic Conditions Anthony DeWilde O.D.
 A Tailored Approach to Uveitis and Associated Systemic Conditions Anthony DeWilde O.D. I. Introduction II. III. IV. A. Why I am giving this talk B. What to take from lecture Diagnosis 1. Better understanding
A Tailored Approach to Uveitis and Associated Systemic Conditions Anthony DeWilde O.D. I. Introduction II. III. IV. A. Why I am giving this talk B. What to take from lecture Diagnosis 1. Better understanding
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 23, No. 4, August, 2016
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 23, No. 4, August, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2016.23.4.234 Original Article Human Leukocyte Antigen B27 and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Classification
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 23, No. 4, August, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2016.23.4.234 Original Article Human Leukocyte Antigen B27 and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Classification
Assessment of Pulmonary Function Test (Pft) In Patients of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. X (Aug. 2017), PP 63-68 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Pulmonary Function Test (Pft)
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 8 Ver. X (Aug. 2017), PP 63-68 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Pulmonary Function Test (Pft)
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care
 Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
9 Lecture. Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม
 9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES
 www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES What is it? The juvenile spondyloarthropathies constitute are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints (arthritis) and
www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES What is it? The juvenile spondyloarthropathies constitute are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints (arthritis) and
B27 positive diseases versus B27 negative diseases
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 431-4 Viewpoint B27 positive diseases versus B27 negative diseases A LINSSEN AND T E W FELTKAMP From the Netherlands Ophthalmic Research Institute, Amsterdam
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 431-4 Viewpoint B27 positive diseases versus B27 negative diseases A LINSSEN AND T E W FELTKAMP From the Netherlands Ophthalmic Research Institute, Amsterdam
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 220 Patients
 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
Abstract Objective In 1971 McEwen and colleagues suggested that the radiological changes of classic ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and the
 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
A mong the inflammatory rheumatic diseases
 659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION
 European Medicines Agency London, 20 September 2007 Product name: Remicade Procedure number: EMEA/H/C/240/II/95 SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION 7 Westferry Circus, Canary Wharf, London, E14 4HB, UK Tel. (44-20)
European Medicines Agency London, 20 September 2007 Product name: Remicade Procedure number: EMEA/H/C/240/II/95 SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION 7 Westferry Circus, Canary Wharf, London, E14 4HB, UK Tel. (44-20)
U ntil the pioneering work of Wright1 and Baker,2. Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis REPORT. P S Helliwell, W J Taylor...
 ii3 REPORT Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis P S Helliwell, W J Taylor... Background: The study of psoriatic arthritis is difficult and has lagged behind the study of other
ii3 REPORT Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis P S Helliwell, W J Taylor... Background: The study of psoriatic arthritis is difficult and has lagged behind the study of other
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Peripheral arthropathies in inflammatory bowel disease: their articular distribution and natural history
 Gut 1998;42:387 391 387 Gastroenterology Unit, NuYeld Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, RadcliVe Infirmary, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK T R Orchard D P Jewell Musculoskeletal Research
Gut 1998;42:387 391 387 Gastroenterology Unit, NuYeld Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, RadcliVe Infirmary, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK T R Orchard D P Jewell Musculoskeletal Research
Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients
 Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients E. Koumakis, L. Gossec, M. Elhai, V. Burki, A. Durnez, I. Fabreguet, M. Meyer, J. Payet, F. Roure, S. Paternotte, M. Dougados
Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients E. Koumakis, L. Gossec, M. Elhai, V. Burki, A. Durnez, I. Fabreguet, M. Meyer, J. Payet, F. Roure, S. Paternotte, M. Dougados
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN AFRICAN BLACKS
 1366 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN AFRICAN BLACKS IAN. CHALERS Over a period of years in a large African teaching hospital, only 8 patients with ankylosing spondylitis were seen. This small number supports
1366 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN AFRICAN BLACKS IAN. CHALERS Over a period of years in a large African teaching hospital, only 8 patients with ankylosing spondylitis were seen. This small number supports
Clinical application of the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis compared to other existing criteria
 Clinical application of the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis compared to other existing criteria L. Congi 1 and E. Roussou 2 1 Rheumatology Department, Whittington Hospital, London, United Kingdom;
Clinical application of the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis compared to other existing criteria L. Congi 1 and E. Roussou 2 1 Rheumatology Department, Whittington Hospital, London, United Kingdom;
4/16/2018. Go with your gut: the gutjoint. Learning objectives: Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest. Collaboration: OpenBiome
 Go with your gut: the gutjoint axis James T. Rosenbaum April 27, 2018 Rheumatology Research Foundation Spondylitis Association of America Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest Collaboration: OpenBiome Funding:
Go with your gut: the gutjoint axis James T. Rosenbaum April 27, 2018 Rheumatology Research Foundation Spondylitis Association of America Disclosure of Conflicts of Interest Collaboration: OpenBiome Funding:
Spondylarthropathies
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
Human Leukocyte Antigen B27 in 453 Asian Indian Patients with Seronegative Spondyloarthropathy
 SHORT PAPER Human Leukocyte Antigen B27 in 453 Asian Indian Patients with Seronegative Spondyloarthropathy Mahendra Narain Mishra 1*, Vinay Singal 2 ¹ Department of Pathology, Command Hospital (SC), ²
SHORT PAPER Human Leukocyte Antigen B27 in 453 Asian Indian Patients with Seronegative Spondyloarthropathy Mahendra Narain Mishra 1*, Vinay Singal 2 ¹ Department of Pathology, Command Hospital (SC), ²
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R
 The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
Review Article Gender and Spondyloarthropathy-Associated Uveitis
 Ophthalmology Volume 2013, Article ID 928264, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928264 Review Article Gender and Spondyloarthropathy-Associated Uveitis Wendy M. Smith MayoClinic,200FirstStreetSW,Rochester,MN55905,USA
Ophthalmology Volume 2013, Article ID 928264, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928264 Review Article Gender and Spondyloarthropathy-Associated Uveitis Wendy M. Smith MayoClinic,200FirstStreetSW,Rochester,MN55905,USA
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Curr Opin Rheumatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 January 20.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
Arthritis and Crohn's disease
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis. Dr Johan Siebert
 JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases
 Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
HL-A 27 and acute anterior uveitis
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 270 HL-A 27 and acute anterior uveitis * R. MAPSTONE AND tj. C. WOODROW From * St Paul's Eye Hospital, Liverpool, and tnuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department of Medicine,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 270 HL-A 27 and acute anterior uveitis * R. MAPSTONE AND tj. C. WOODROW From * St Paul's Eye Hospital, Liverpool, and tnuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department of Medicine,
Prevalence, Clinical Features, and Radiological Features of Iraqi Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Prevalence, Clinical Features, and Radiological Features of Iraqi Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Khudhir Z. Mayouf Al-Bedri Department. of Medicine, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Baghdad,
Prevalence, Clinical Features, and Radiological Features of Iraqi Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Khudhir Z. Mayouf Al-Bedri Department. of Medicine, College of Medicine, University of Baghdad, Baghdad,
LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS
 ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
I J Sørensen,15 R Valle-Oñate,16 U Weber,17 J Wei,18 J Sieper,1,19
 See Editorial, pg 1 Additional data (supplementary table) are published online only. To view these fi les please visit the journal online (http://ard.bmj. com). 1 Department of Medicine, Charité University
See Editorial, pg 1 Additional data (supplementary table) are published online only. To view these fi les please visit the journal online (http://ard.bmj. com). 1 Department of Medicine, Charité University
Remicade (Infliximab)
 Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Impact of Chronic Conditions on Health-Related Quality of Life
 BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Conditions on Health-Related Quality of Life Chronic joint pain conditions have an important impact on health-related quality of life Note: a larger negative
BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Conditions on Health-Related Quality of Life Chronic joint pain conditions have an important impact on health-related quality of life Note: a larger negative
Jurnal Medical Aradean (Arad Medical Journal) Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 2015, pp Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.
 Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 15, pp. 4-45 15 Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.ro) DEMOGRAPHIC AND CLINICAL PARAMETERS EVALUATION FOR PATIRNTS WITH PSORIATIC VERSUS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Camelia Ciacli
Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 15, pp. 4-45 15 Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.ro) DEMOGRAPHIC AND CLINICAL PARAMETERS EVALUATION FOR PATIRNTS WITH PSORIATIC VERSUS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Camelia Ciacli
Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: Atlantoaxial Ankylosis and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Rheumatology. Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications. Definition of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Spondyloarthropathies
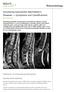 Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Sudan JMS Vol. 11, No.2. Jun
 Vtáx exñéüà Mohammed MasaudRab 1, Mahmoud H. Milad 2 and Abdalla M. Gamal 3* ABSTRACT Background: Ankylosing spondylitis is a relatively common worldwide chronic inflammatory disease that usually affects
Vtáx exñéüà Mohammed MasaudRab 1, Mahmoud H. Milad 2 and Abdalla M. Gamal 3* ABSTRACT Background: Ankylosing spondylitis is a relatively common worldwide chronic inflammatory disease that usually affects
A STUDY OF CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA FOR A DIAGNOSIS OF JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 274 A STUDY OF CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA FOR A DIAGNOSIS OF JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS J. T. CASSIDY, J. E. LEVINSON, J. C. BASS, J. BAUM, E. J. BREWER, JR., C. W. FINK, V. HANSON, J. C. JACOBS, A. T.
274 A STUDY OF CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA FOR A DIAGNOSIS OF JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS J. T. CASSIDY, J. E. LEVINSON, J. C. BASS, J. BAUM, E. J. BREWER, JR., C. W. FINK, V. HANSON, J. C. JACOBS, A. T.
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies
 Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics
 Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 6, June 2016, pp 1415 1421 DOI 10.1002/art.39542 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 6, June 2016, pp 1415 1421 DOI 10.1002/art.39542 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING
 ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING July 23, 2013 sbla 125057/323: adalimumab for the treatment of Active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in adults with objective signs of inflammation by elevated
ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING July 23, 2013 sbla 125057/323: adalimumab for the treatment of Active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in adults with objective signs of inflammation by elevated
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Objectives. Joint Pain. Case 1. Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) 12/4/2010
 Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 930/06
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 930/06 BEFORE: V. Marafioti: Vice-Chair HEARING: May 8, 2006 at Sudbury Oral Post-hearing activity completed on August 31, 2007 DATE OF DECISION:
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 930/06 BEFORE: V. Marafioti: Vice-Chair HEARING: May 8, 2006 at Sudbury Oral Post-hearing activity completed on August 31, 2007 DATE OF DECISION:
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation
 Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
Subpopulations within juvenile psoriatic arthritis: A review of the literature
 Clinical & Developmental Immunology, June December 2006; 13(2 4): 377 380 Subpopulations within juvenile psoriatic arthritis: A review of the literature MATTHEW L STOLL 1 & PETER A NIGROVIC 1,2, 1 Division
Clinical & Developmental Immunology, June December 2006; 13(2 4): 377 380 Subpopulations within juvenile psoriatic arthritis: A review of the literature MATTHEW L STOLL 1 & PETER A NIGROVIC 1,2, 1 Division
Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March. (minutes for web publishing)
 Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March 2011 (minutes for web publishing) Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 8 March 2011 (minutes for web publishing) Ad-Hoc Rheumatology Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the
