Abstract Objective In 1971 McEwen and colleagues suggested that the radiological changes of classic ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and the
|
|
|
- Elfreda McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57: EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive? P S Helliwell, P Hickling, V Wright* Rheumatology and Rehabilitation Research Unit, University of Leeds P S Helliwell V Wright Mount Gould Hospital, Plymouth P Hickling Correspondence to: Dr P S Helliwell, Rheumatology and Rehabilitation Research Unit, University of Leeds, 36 Clarendon Road, Leeds LS2 9NZ. *Professor Wright died on 31 January Accepted for publication 20 January 1998 Abstract Objective In 1971 McEwen and colleagues suggested that the radiological changes of classic ankylosing (AS), and the changes of the associated with inflammatory bowel disease diver in several respects from the radiological features of psoriatic and reactive. The findings of this study have never been confirmed. The aim of this study was to replicate the McEwen study comparing films blinded to diagnostic group. Methods The study population comprised 91 patients with classic AS, 15 patients with regional enteritis, 16 patients with ulcerative colitis, five patients with sexually acquired reactive, two with postdysenteric, and 34 with psoriatic. Blinded reading of spinal radiographs was undertaken, scoring for severity, symmetry, paravertebral ossification, size of syndesmophytes, ligamentous calcification, squaring, discitis, pseudofractures, zygoapophyseal joint involvement, and complete ankylosis. Results Comparison of the four groups classic, enteropathic, psoriatic, and reactive AS showed diverences with respect to symmetry of sacroiliitis, symmetry of lumbar spinal involvement, and frequency and size of syndesmophytes. Zygoapophyseal joint involvement was more frequent in the lumbar spine in classic and enteropathic but no between group diverences were found with respect to symphisitis, squaring, apophyseal joint involvement and ligamentous calcification in the lumbar spine, and other areas. Conclusions Some of the radiological diverences described by McEwen et al, notably the asymmetry, the less severe changes, and the distinctive syndesmophytes in psoriasis, have been confirmed. A number of hypotheses are proposed to explain these diverences including biomechanical, biochemical, and genetic factors. (Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57: ) In 1974 Moll and colleagues defined the concept of the seronegative spondylarthritides as a group of seronegative arthritides sharing clinical features, central to which was ankylosing (AS). 1 Common features of these conditions included a seronegative, anodular, peripheral inflammatory, mucocutaneous ulceration, psoriasiform skin lesions, ocular inflammation, familial aggregation (linked to the HLA-B27 antigen), and radiological sacroiliitis with or without AS. Included within this group of disorders were classic AS, psoriatic, reactive, inflammatory bowel disease, Whipple s disease, and Behcet s disease, although it has been argued that the latter two conditions should no longer be included in the group. 2 Despite the core feature of radiological sacroiliitis, it has been argued that the radiological features of enteropathic (the AS associated with inflammatory bowel disease, EnSp) and classic AS diver in several respects, radiologically, from the associated with psoriasis (PsSp) and reactive (ReSp). 3 5 The key study underlying these assertions was published in 1971 by McEwen and colleagues 6 and the findings of that paper are summarised in table 1. The major diverences were in the symmetry and severity of the radiological changes and in the shape and size of the syndesmophytes, although other diverences such as zygoapophyseal involvement, osteitis, and ligamentous calcification were also highlighted. The McEwen study has not been repeated formally, although a limited radiological comparison of classic AS and psoriatic was undertaken by Gladman and colleagues. 7 However, the diverences described by McEwen and colleagues have generally been accepted by the rheumatological community. 8 9 The advent of new imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging and spiral computed tomography overs the possibility of new approaches to defining these radiographic abnormalities but, as the findings of McEwen et al have never been confirmed, a straightforward replication of the original study was felt to
2 136 Helliwell, Hickling, Wright Table 1 Summary of radiological diverences reported by McEwen et al 6 Feature and of ulcerative colitis and regional enteritis Spondylitis associated with psoriasis and reactive Sacroiliitis Severe and symmetrical Sacroiliitis sometimes unilateral or bilaterally asymmetrical Symphisitis More frequent Less frequent Osteoporosis More frequent Less frequent Lumbar straightening More frequent Less frequent Apophyseal joint involvement More frequent Less frequent Squaring More frequent Less frequent Syndesmophytes More frequent, usually symmetrical Less frequent, usually asymmetrical Shape and size of syndesmophytes Marginal (see text) Usually other than marginal (see text) Ligamentous ossification More frequent Less frequent Progression of syndesmophytes Lumbar to dorsal to cervical Random progression be necessary, comparing films blinded to diagnostic group. Methods Most of the patients were recruited from rheumatology outpatient clinics in Leeds. In 12 cases spinal radiographs and all clinical data were mailed from rheumatology colleagues in other areas: in all these cases the films were read blind. The only entry criterion was AS diagnosed using the modified New York criteria. 10 Further subdivision was based on coexisting disorders. was diagnosed using the criteria of Calin et al. 11 All patients with psoriasis had seen a dermatologist and all patients with inflammatory bowel disease were under the care of a gastroenterologist: most had been examined by barium series and biopsy. In addition to basic demographic details the following clinical data were collected: history of heel involvement, history of uveitis, lumbar flexion by the modified Schober s method, 12 and chest expansion measured at the level of the xiphisternum. Recent (within 12 months) radiographs were read blind to diagnosis by two readers in tandem: no attempt to measure interobserver or intraobserver agreement was made. Pelvic radiographs were scored for sacroiliitis according to the New York criteria 13 where changes are graded from 0 (normal), 1 (doubtful), 2 (mild irregularity and sclerosis)), 3 (marked erosion without ankylosis), and 4 (complete ankylosis). Sacroiliitis was graded asymmetrical if a diverence of more than one grade occurred between sides. Symphisitis was graded using a similar system to that for sacroiliitis. Ischial and iliac enthesitis were graded from 0 4 where a score of 4 represented florrid new bone formation over the avected site. Hips were also graded 0 4 with 0 1 normal or doubtful, 2 mild loss of joint space, 3 moderate loss of joint space with sclerosis, and 4 complete loss of joint space (arthroplasty was graded as 4). Spine radiographs were graded for overall severity as follows: normal (0); isolated erosion of the superior anterior border of a vertebra, the eponymous Romanus lesion, (1); three or fewer syndesmophytes (2); more than three syndesmophytes (3); and complete ankylosis (4). If ankylosis of the zygoapophyseal joints occurred throughout the region the films were graded as 4 independent of the other changes. Symmetry was defined as greater than or equal to 50% matching of syndesmophytes in the anteroposterior film. Thus if only three syndesmophytes were seen and two were matched that film would be scored as symmetrical. The presence of other features was recorded as follows. Paravertebral ossification as defined and described by Bywaters and Dixon, 14 ligamentous calcification (usually interspinous ligament), squaring of the anterior border of the vertebra without erosion/sclerosis, discitis (narrowing of disc space with erosion, and new bone formation in adjacent vertebrae), spinal pseudarthrosis (a fracture line through a fused spine with reactive new bone formation at either side of the lesion), bamboo spine (complete ankylosis of vertebrae due to contiguous syndesmophyte formation), and ankylosis of zygoapophyseal joints. Syndesmophytes were classified as chunky or marginal based on their size and shape. Marginal syndesmophytes were defined as discrete vertically oriented areas of calcification extending from the corner of one vertebra to the next. Chunky syndesmophytes were defined as more extensive areas of calcification extending vertically from the vertebral corner included within this group were the non-marginal and inverted comma syndesmophytes of McEwen et al. 6 Table 2 Demographic details of study group χ 2 (df=3)* Significant Number Male/female 67/24 15/16 26/8 7/ NS Age (y) median (range) 46 (18 71) 48 (34 75) 46 (25 83) 43 (25 47) 6.58 NS Duration disease (y) median (range) 18 (1 44) 15 (6 39) 16 (0 56) 8 (5 12) 7.15 NS Number (%) heel involvement 12/82 (15) 3/17 (18) 4/21 (20) 1/4 (25) Number (%) uveitis 19/83 (23) 14/21 (67) 4/23 (18) 1/5 (20) Schober s (cm) median (range) 2 (0 7) 4 (0 7) 4.85 (1 8) 5.5 (4 7.5) Chest expansion (cm) median (range) 3 (0 6.5) 4 (0 6) 4 (0 6) 3 (0 6) 1.36 NS Number (%) B27 positive 31/37 (84) 8/10 (80) 4/6 (67) 2/2 (100) *χ 2 on 2 4 tables. Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance, χ 2 statistic for interval scale data. p Values multiplied by 8 to allow for multiple comparisons. Comparison not made because minimum expected frequency in two cells was <2.
3 Radiological changes of classic ankylosing 137 Table 3 Sacroiliitis, symphisitis, pelvic enthesitis, and hip involvement Number of films available (no of cases) 91/91 31/31 34/34 7/7 Worst SI grade (number (%)) grades (92) 30 (97) 28 (82) 7 (100) Symmetry (number (%)) 77 (85) 31 (100) 25 (74) 3 (43) Symphisitis (number (%)) grades (31) 9 (30) 8 (25) 1 (14) Iliac enthesitis (number (%)) grades (7) 1 (4) 1 (4) 0 Ischial enthesitis (number (%)) grades (30) 4 (14) 6 (22) 0 Hip involvement (number (%)) grades (26) 4 (14) 7 (23) 0 Lateral heel radiographs were scored at three sites (posterior calcaneal, inferior calcaneal, and tarsal) as follows: normal (0), doubtful (1), spur less than 3 mm (2), spur 3 8 mm (3), spur greater than 8 mm (4). STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Non-parametric statistics were used throughout. As members of the ReSp group were younger and had a shorter duration of disease and, as the ReSp group was much smaller than the other three groups, statistical comparisons of spinal features specifically excluded this group of patients. In 2xk contingency tables we followed the advice of Cochran 15 who recommended that the χ 2 test be used providing df<30 and minimum expected cell frequency >2. Results Table 2 gives the demographic details and clinical data. Most of the patients had classic AS, as expected, so that the total figures were 91 for AS, 31 for EnSp, 34 for PsSp, and seven for ReSp. The were sex diverences between the groups: the AS, PsSp, and ReSp groups were predominantly male whereas the EnSp group had an equal sex distribution. A significant difference in the amount of lumbar movement (as measured by the modified Schober s method) was found across the groups; this was largely because of the limited mobility of the AS group. Measures of chest expansion were similar. Tables 3 6 compare the radiological features of the groups. PELVIC FILMS Severity of sacroiliac involvement, defined by the worst grade of sacroiliitis, did not diver significantly between the groups. However, the major groups (AS, EnSp, and PsSp) did diver when scored for symmetry (χ 2 = 7.97, df=2, p=0.02). No diverences were found between the groups with respect to symphisitis, iliac and ischial enthesitis, and hip involvement. SPINAL FILMS Spinal films were analysed by region. Tables 4 6 give the percentage of films in each group demonstrating the recorded features for lumbar, thoracic, and cervical spine regions. The appearances were not uniform throughout the spine. Films from patients with AS showed more severe changes, particularly in the lumbar spine, with a higher percentage of grades 3 to 4 involvement, more zygoapophyseal involvement, and more cases of complete ankylosis. Patients with EnSp also showed more severe changes in the lumbar spine. Among the major diagnostic groups (AS, EnSp, and PsSp) these diverences were significant (lumbar severity: χ 2 =7.95, df=2, p=0.02, lumbar zygoapophyseal: χ 2 =6.93, df=2, p=0.03). The inter-regional pattern of severity also divered between the four diagnostic groups but not consistently between groups; for AS the worst avected area was the lumbar spine but there was little diverence between the spinal areas (lumbar 55% grades 3 4; thoracic 45%; cervical 50%). For the EnSp the worst affected area was the cervical spine but, again, the range was small (lumbar 40% grades 3 4; thoracic 31%; cervical 45%). In the PsSp group the worst avected area was easily the cervical spine (lumbar 25% grades 3 4; thoracic 36%; cervical 47%). Syndesmophyte morphology, as recorded by the percentage of chunky syndesmophytes, was not significantly diverent between the major groups (AS, EnSp, and PsSP). However, consistent diverences between the groups were found throughout the spine with respect to this feature, with the PsSp and ReSp groups having a larger percentage of chunky syndesmophytes. Furthermore, the degree of symmetry Table 4 Lumbar spine involvement Number of films available (no of cases) 78/91 25/31 28/34 5/7 Worst grade (number (%)) grades (55) 10 (40) 7 (25) 1 (20) Number (%) symmetry* 38/52 (73) 8/16 (50) 4/14 (29) 2/3 (67) Paravertebral ossification (number (%)) 1 (1) 1 (4) 1 (4) 0 Chunky syndesmophytes (number (%))* 12/52 (23) 3/16 (19) 5/14 (36) 1/3 (33) Ligamentous calcification (number (%)) 11 (14) 1 (4) 1 (4) 0 Squaring (number (%)) 15 (19) 1 (4) 1 (4) 0 Romanus lesion (number (%)) 17 (22) 0 4 (14) 3 (60) Spinal pseudarthrosis (number (%)) 2 (3) 0 1 (4) 0 Zygoapophyseal ankylosis (number (%)) 16 (21) 4 (16) 0 0 Discitis (number (%)) 5 (6) 2 (8) 1 (4) 0 Bamboo spine (number (%)) 9 (12) 3 (12) 0 0 *Note data on symmetry and syndesmophyte morphology only apply to severity grades 2 4: the number of available films is given by the denominator.
4 138 Helliwell, Hickling, Wright Table 5 Thoracic spine involvement Number of films available (no of cases) 64/91 13/31 14/34 4/7 Worst grade (number (%)) grades (45) 4 (31) 5 (36) 1 (25) Number (%) symmetry* 24/40 (60) 4/5 (80) 2/6 (33) 0 Paravertebral ossification (number (%)) 1 (2) Chunky syndesmophytes (number (%))* 2/40 (5) 0 4/6 (67) 1/2 (50) Ligamentous calcification (number (%)) 9 (14) 0 2 (14) 0 Squaring (number (%)) 7 (11) Romanus lesions (number (%)) 9 (14) 0 2 (14) 1 (25) Spinal pseudarthrosis (number (%)) 1 (2) Zygoapophyseal ankylosis (number (%)) 7 (11) Discitis (number (%)) 4 (6) Bamboo spine (number (%)) 8 (13) 2 (15) 0 0 *Note data on symmetry and syndesmophyte morphology only apply to severity grades 2 4: the number of available films is given by the denominator. Table 6 Cervical spine involvement Enteropathi c Number of films available (no of cases) 58/91 11/31 19/34 5/7 Worst grade (number (%)) grades (50) 5 (45) 9 (47) 0 Number (%) symmetry* 19/19 (100) 2/4 (50) 7/7 (100) 0 Paravertebral ossification (number (%)) 1 (2) 0 2 (11) 0 Chunky syndesmophytes (number (%))* 3/34 (9) 1/6 (17) 5/12 (42) 1/1 (100) Ligamentous calcification (number (%)) 1 (2) 2 (18) 0 0 Squaring (number (%)) 3 (5) Romanus lesions (number (%)) 1 (2) Spinal pseudarthrosis (number (%)) 1 (2) 1 (9) 0 0 Zygoapophyseal ankylosis (number (%)) 10 (17) 0 2 (11) 0 Discitis (number (%)) 0 1 (9) 0 0 Bamboo spine (number (%)) 5 (9) 0 1 (5) 0 *Note data on symmetry and syndesmophyte morphology only apply to severity grades 2 4: the number of available films is given by the denominator. It was not possible to evaluate cervical symmetry in 23 cases because syndesmophytes were only seen on lateral radiographs. of syndesmophytes divered: this diverence was particularly apparent in the lumbar spine for groups AS, EnSp, and PsSp (χ 2 = 6.4, df=2, p=0.04). No diverences were found between the groups with respect to paravertebral ossification, ligamentous calcification, squaring, discitis, Romanus lesions, and spinal pseudarthrosis. Radiographs of the heel were not available for all patients. Grades 3 4 plantar enthesopathy were found in the following numbers (%): AS, 8 of 40 (20%); EnSp, 0 of 5; PsSp, 1 of 7(13%); ReSp, 0 of 2. At the Achilles tendon insertion the figures were 3 of 39(8%), 0 of 4, 2 of 8(25%), and 0 of 2 for AS, EnSp, PsSp, and ReSp respectively. Discussion We have shown some diverences between the radiological features of classic AS and the features found in enteropathic, psoriatic, and reactive AS. The diverences are mainly in the severity of involvement, the symmetry of sacroiliitis and syndesmophytes, and the morphology of syndesmophytes. Our findings did not enable us to justify the grouping suggested by McEwen et al that is, pairing AS/EnSp and PsSp/ReSp except in the case of zygoapophyseal involvement of the lumbar spine. Other diverences noted by McEwen, such as symphisitis, squaring, and ligamentous calcification, have not been found. The unequal numbers of patients in each group is a reflection of our clinic population rather than an attempt to overrepresent classic AS. The disproportion is in contrast with the study by McEwen et al where the numbers of patients in each group was 29, 38, 39, and 34 for classic AS, EnSp, PsSp, and ReSp respectively. The disease definitions used by McEwen et al were not explicitly stated but clearly Reiter s disease was more common among their clinic population (New York, 1971) than Leeds, Our patients with ReSp were younger with shorter duration of disease than patients in the other groups and for this reason we could not include them in the analysis between groups. Given a similar disease duration the changes in the PsSp group were less severe overall, in agreement with McEwen et al. Furthermore, Gladman and colleagues noted more severe sacroiliitis, more frequent classic syndesmophytes, and less cervical spine involvement in AS compared with PsSp but their radiological definitions were imprecise and their cohorts not matched for age. 7 In this study severity of involvement was based on the number and extent of syndesmophytes and this may, in part, explain the asymmetry found in PsSp. We have previously noted, in peripheral psoriatic, that symmetry is a function of frequency of joint involvement so that the greater the number of sites involved the more chance that these sites will be matched and recorded as symmetrical. 16 For example, where syndesmophytes were recorded in the lumbar spine, 50% of films from PsSp patients had three or fewer syndesmophytes whereas this figure was only 19% in classic AS. In this study, therefore, asymmetry may be a function of paucity of syndesmophytes. Additionally, it is worth noting that a judgement on symmetry in the cervical spine was sometimes impossible to
5 Radiological changes of classic ankylosing 139 make as syndesmophytes were noted only in the lateral radiographs. The cross sectional nature of this study precluded any meaningful conclusions about the onset and progression of the radiological changes. McEwen et al were less inhibited by the design of their study, using cohorts of patients based on disease duration. On this basis they concluded that in AS/EnSp the presents with early, progressive, symmetrical sacroiliac involvement and extends progressively from the lumbar into the dorsal and finally the cervical spine. In contrast, PsSp/ReSp demonstrated frequent asymmetrical and occasionally unilateral sacroiliitis progressing in random fashion througout the spine. We were unable to confirm this pattern. The morphology of syndesmophytes needs further clarification and new imaging techniques may permit better anatomical description of these abnormalities. Digital radiographs will allow quantification of the area of the syndesmophytes; we have used this technique in conventional radiographs using planimetry but it is sometimes diycult to define the (normal) margins of the vertebral body. The use of three dimensional techniques such as spiral computed tomography will encounter similar diyculties but three dimensional images would improve visualisation of the syndesmophyte morphology. Classic marginal syndesmophytes, which represent calcification in the outer fibres of the annulus fibrosis of the disc, are the predominant form in all of the spondylarthritides. Can the broader, bulky looking syndesmophytes that occur commonly, although not exclusively, in patients with PsSp correctly be called syndesmophytes? Resnick and Niwayama 3 describe these areas as paravertebral ossification but allow that, as they progress, they fuse with the underlying disc and bone ultimately producing appearances normally associated with divuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis and, on occasions, disc degeneration. More detailed pathological data on the origin and progression of these changes are required. Peripheral psoriatic is characterised pathologically by intense osteoblastic proliferation surrounding the periosteum and it is possible that similar changes are occurring in the vertebra adjacent to the disc associated with an enthesopathy at the attachment of the annulus fibrosis, as in classic AS. 17 Perhaps the initiating lesion is common to all types of but the intense osteoblastosis in PsSp and ReSp sometimes produces bulkier syndesmophytes. An alternative explanation for the excessive new bone formation at the spinal enthesis found in PsSp has been suggested by de Vlam and colleagues. 18 They postulate that reduced spinal mobility associated with involvement of apophyseal joints (as seen more commonly in AS) is associated with classic syndesmophyte formation, whereas if posterior spinal mobility is maintained greater tensile forces are experienced anteriorly resulting in increased inflammation/repair and consequently more bone formation. At these sites of high mechanical stress transforming growth factor β or interleukin 6 may be the principal mediators of new bone formation in the inflammatory tissue. To examine this theory further it would be necessary to make detailed observations of syndesmophyte morphology and zygoapophyseal involvement at each vertebral level. The hypothesis does provide a plausible explanation for the observed diverences in syndesmophyte morphology and might also explain the radiological changes found in divuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Other factors may underlie the diverences noted above, particularly genetic variation. The major histocompatability gene-hla-b27 is pivotal to all the seronegative spondylarthritides but other genes related to both the major histocompatability complex and elsewhere may contribute to the unique expression of each of these disorders. Both HLA-B38 and HLA-DR4 seem to be associated with psoriatic 19 and the role of these and other genes in reactive needs further study. Although we have been unable to justify grouping reactive and psoriatic these conditions share other clinical features that suggest grouping them together, particularly the skin lesions (keratoderma blenorrhagica may be indistinguishable from pustular psoriasis of the foot: a similar rash is not seen in classic AS and enteropathic ) the pattern of peripheral (particularly the destructive changes in distal inter-phalangeal joints) and the enthesopathy, particularly around the heel (although this feature was not prominent in this study). Furthermore, an explosive and severe form of psoriasis may follow infection with HIV, and a 10-fold increase in the prevalence of psoriatic has been reported in patients infected with HIV. 20 Other infective triggers may be common to both reactive and psoriatic ; for example, some authors have suggested that psoriatic is a reactive to bacteria carried in psoriatic plaques. 21 In summary, we have confirmed that some radiological features distinguish psoriatic, classic, and enteropathic. The mechanisms underlying these diverences remain obscure and require further clarification. We are grateful to Dr Luay Zebouni for help with data collection. We would like to thank the following colleagues for providing films for this study: Professor H Bird, Dr J M Iveson, Dr J Lambert, Dr F McKenna, and Dr M Snaith. 1 Moll JMH, Haslock I, Macrae IF, Wright V. Associations between ankylosing, psoriatic, Reiter s disease, the intestinal arthropathies and Behcet s syndrome. Medicine 1974;53: Helliwell PS, Wright V. Seronegative spondarthritides. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol 1987;1: Resnick D, Niwayama G. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. Philadelphia:W B Saunders, 1981: Wright V.. In: Scott JT, ed. Copeman s textbook of the rheumatic diseases. 6th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1986: Helliwell PS, Wright V.. In: Klippel JH, Dieppe PA, eds. Rheumatology. London: Mosby Year Book Europe, 1994: chapter McEwen C, DiTata D, Lingg C, Porini A, Good A, Rankin T. and accompanying ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis, psoriasis and Reiter s disease. Arthritis Rheum 1971;14: Gladman DD, Brubacher B, Buskila D, Langevitz P, Farewell V. DiVerences in the expression of spondyloarthropathy: a comparison between ankylosing and psoriatic. Clin Invest Med 1993;16:1 7.
6 140 Helliwell, Hickling, Wright 8 Genant HK. Radiology of rheumatic diseases. In: McCarty DJ, ed. Arthritis and allied conditions. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger, 1985: Brower AC. Spondloarthropathies:imaging. In: Klippel JH, Dieppe PA, eds. Rheumatology. London: Mosby Year Book, 1994: The HSG, Steven MM, van der Linden SM, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing : a comparison of the Rome, NY, and modified NY criteria in patients with a positive clinical history screening test for ankylosing. Br J Rheumatol 1985;24: Calin A. Reiter s syndrome. In Calin A, ed. Spondylarthropathies. New York: Grune and Stratton, 1984: Macrae IF, Wright V. Measurement of back movement. Ann Rheum Dis 1969;28: Bennet PH, Burch TA. New York Symposium on population studies in the rheumatic diseases: new diagnostic criteria. Bull Rheum Dis 1967;17: Bywaters EGL, Dixon AJ. Paravertebral ossification in psoriatic arthitis. Ann Rheum Dis 1965;24: Cochran WG. Some methods for strengthening the chi-squared tests. Biometrics 1954;10: Helliwell PS, Marchesoni A, Peters M, Barker M, Wright V. A re-evaluation of the osteoarticular manifestations of psoriasis. Br J Rheumatol 1991;30: Ball J. Enthesopathy of rheumatoid and ankylosing. Ann Rheum Dis 1971:30: de Vlam K, Mielants H, Veys EM. Association between ankylosing and divuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: reality or fiction? Clin Exp Rheum 1996;14: Eastmond CJ. Genetics and HLA antigens. In: Wright V, Helliwell PS, eds.. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol 1994;8: Solinger AM, Hess EV. Rheumatic diseases and AIDS: is the association real? J Rheumatol 1993;20: Vasey FB, Espinoza LR. arthropathy. In: Calin A, ed. Spondylarthropathies. New York: Grune and Stratton, 1984: Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases - Visitors to the world wide web can now access Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases either through the BMJ Publishing Group s home page ( or directly by using its individual URL ( There they will find the following: x Current contents list for the journal x Contents lists of previous issues x Members of the editorial board x Subscribers information x Instructions for authors x Details of reprint services A hotlink gives access to: x BMJ Publishing Group home page x British Medical Association web site x Online books catalogue x BMJ Publishing Group books The web site is at a preliminary stage and there are plans to develop it into a more sophisticated site. Suggestions from visitors about features they would like to see are welcomed. They can be left via the opening page of the BMJ Publishing Group site or, alternatively, via the journal page, through about this site.
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT
 THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT J.M.H. MOLL Emeritus Consultant Rheumatologist, Sheffield, UK SUMMARY In the 1960s, Professor Verna Wright became increasingly interested
THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT J.M.H. MOLL Emeritus Consultant Rheumatologist, Sheffield, UK SUMMARY In the 1960s, Professor Verna Wright became increasingly interested
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Spondylarthropathies
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
U ntil the pioneering work of Wright1 and Baker,2. Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis REPORT. P S Helliwell, W J Taylor...
 ii3 REPORT Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis P S Helliwell, W J Taylor... Background: The study of psoriatic arthritis is difficult and has lagged behind the study of other
ii3 REPORT Classification and diagnostic criteria for psoriatic arthritis P S Helliwell, W J Taylor... Background: The study of psoriatic arthritis is difficult and has lagged behind the study of other
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS
 ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Elective Student P. H.
 Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Review article. early diagnosis? HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for. Why subjects carrying HLA-B27 are prone. Jan Tore Gran, Gunnar Husby
 _JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
_JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Introduction: Inflammatory arthritis is the most common extraintestinal manifestation in patients with inflammatory
PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Introduction: Inflammatory arthritis is the most common extraintestinal manifestation in patients with inflammatory
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
9 Lecture. Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม
 9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling. Rheumatic Diseases
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
Axial Spondyloarthritis. Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital
 Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA)
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Bone formers: osteophyte and enthesophyte formation are positively associated
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1997;56:85 9 85 EXTENDED REPORTS Bone formers: osteophyte and enthesophyte formation are positively associated Juliet Rogers, Lee Shepstone, Paul Dieppe Rheumatology Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1997;56:85 9 85 EXTENDED REPORTS Bone formers: osteophyte and enthesophyte formation are positively associated Juliet Rogers, Lee Shepstone, Paul Dieppe Rheumatology Unit,
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Dr Tracey Kain. Associate Professor Ed Gane
 Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES
 www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES What is it? The juvenile spondyloarthropathies constitute are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints (arthritis) and
www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES What is it? The juvenile spondyloarthropathies constitute are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints (arthritis) and
Peripheral arthropathies in inflammatory bowel disease: their articular distribution and natural history
 Gut 1998;42:387 391 387 Gastroenterology Unit, NuYeld Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, RadcliVe Infirmary, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK T R Orchard D P Jewell Musculoskeletal Research
Gut 1998;42:387 391 387 Gastroenterology Unit, NuYeld Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, RadcliVe Infirmary, Woodstock Road, Oxford OX2 6HE, UK T R Orchard D P Jewell Musculoskeletal Research
Studies with an enthesis index as a method of clinical
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 197-202 Studies with an enthesis index as a method of clinical assessment in ankylosing spondylitis MICHELLE MANDER, JUDY M SIMPSON, ALISON McLELLAN, DAVID WALKER,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 197-202 Studies with an enthesis index as a method of clinical assessment in ankylosing spondylitis MICHELLE MANDER, JUDY M SIMPSON, ALISON McLELLAN, DAVID WALKER,
Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
Psoriatic Spondylitis: A Clinical and Radiological Description of the Spine in Psoriatic Arthritis
 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series XLVI, No. 8, pp. -5, October 977 Psoriatic Spondylitis: A Clinical and Radiological Description of the Spine in Psoriatic Arthritis J. R. LAMBERT AND V. WRIGHT
Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series XLVI, No. 8, pp. -5, October 977 Psoriatic Spondylitis: A Clinical and Radiological Description of the Spine in Psoriatic Arthritis J. R. LAMBERT AND V. WRIGHT
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies
 A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Clinical application of the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis compared to other existing criteria
 Clinical application of the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis compared to other existing criteria L. Congi 1 and E. Roussou 2 1 Rheumatology Department, Whittington Hospital, London, United Kingdom;
Clinical application of the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis compared to other existing criteria L. Congi 1 and E. Roussou 2 1 Rheumatology Department, Whittington Hospital, London, United Kingdom;
Jurnal Medical Aradean (Arad Medical Journal) Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 2015, pp Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.
 Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 15, pp. 4-45 15 Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.ro) DEMOGRAPHIC AND CLINICAL PARAMETERS EVALUATION FOR PATIRNTS WITH PSORIATIC VERSUS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Camelia Ciacli
Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 15, pp. 4-45 15 Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.ro) DEMOGRAPHIC AND CLINICAL PARAMETERS EVALUATION FOR PATIRNTS WITH PSORIATIC VERSUS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Camelia Ciacli
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 220 Patients
 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
CLOSER LOOK AT SpA. Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi. Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH
 CLOSER LOOK AT SpA Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH Closer look at SpA I. Categories II. SIGN & SYMPTOMS III. X-RAY IV. MRI V. MANAGMENT Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
CLOSER LOOK AT SpA Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH Closer look at SpA I. Categories II. SIGN & SYMPTOMS III. X-RAY IV. MRI V. MANAGMENT Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
Rheumatology. Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications. Definition of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Spondyloarthropathies
 Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
arthritis: a clinical, radiological and immunogenetic study
 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 73-77 2nd Divisione di Medicina (Unita Reumatologica), USL N9, Reggio Emilia, Italy C Salvarani P Macchioni F Rossi N Capozzoli R Baricchi I Portioli 2 Dipartimento
Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 73-77 2nd Divisione di Medicina (Unita Reumatologica), USL N9, Reggio Emilia, Italy C Salvarani P Macchioni F Rossi N Capozzoli R Baricchi I Portioli 2 Dipartimento
Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: Atlantoaxial Ankylosis and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Health Technology Appraisal: etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (rev 104, 125)
 Health Technology Appraisal: etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (rev 104, 125) Personal view of etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for psoriatic arthritis
Health Technology Appraisal: etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (rev 104, 125) Personal view of etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab for psoriatic arthritis
Radiography is typically the first imaging study in evaluation for arthritis. On radiographs, one critical assessment is differentiating inflammatory
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology
 Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
Relation between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A study of 40 patients
 2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis
 CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004?
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
Palaeopathology of spinal osteophytosis, vertebral ankylosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and vertebral hyperostosis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 113-120 Palaeopathology of spinal osteophytosis, vertebral ankylosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and vertebral hyperostosis JULIET ROGERS, IAIN WATT, AND PAUL DIEPPE
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 113-120 Palaeopathology of spinal osteophytosis, vertebral ankylosis, ankylosing spondylitis, and vertebral hyperostosis JULIET ROGERS, IAIN WATT, AND PAUL DIEPPE
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions
 Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN AFRICAN BLACKS
 1366 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN AFRICAN BLACKS IAN. CHALERS Over a period of years in a large African teaching hospital, only 8 patients with ankylosing spondylitis were seen. This small number supports
1366 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN AFRICAN BLACKS IAN. CHALERS Over a period of years in a large African teaching hospital, only 8 patients with ankylosing spondylitis were seen. This small number supports
Muhammad Haroon 1* Oliver FitzGerald 4. , Muddassar Ahmad 1, Muhammad Nouman Baig 2, Olivia Mason 3, John Rice 2 and
 Haroon et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:73 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1565-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Inflammatory back pain in psoriatic arthritis is significantly more responsive to corticosteroids
Haroon et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:73 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1565-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Inflammatory back pain in psoriatic arthritis is significantly more responsive to corticosteroids
RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review
 Insights Imaging (2011) 2:177 191 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0061-4 PICTORIAL REVIEW Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review Anne Grethe Jurik Received: 3 August 2010 /Revised: 6 November 2010 /Accepted:
Insights Imaging (2011) 2:177 191 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0061-4 PICTORIAL REVIEW Imaging the spine in arthritis a pictorial review Anne Grethe Jurik Received: 3 August 2010 /Revised: 6 November 2010 /Accepted:
Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Antunes da Cunha Oliveira
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Antunes da Cunha Oliveira
Skeletal Radiology. Productive osseous changes about the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis. Robert M. Cantor, M.D., and Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D.
 Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16: 397-402 Skeletal Radiology Productive osseous changes about the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis Robert M. Cantor, M.D., and Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. Department of Radiology, University
Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16: 397-402 Skeletal Radiology Productive osseous changes about the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis Robert M. Cantor, M.D., and Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. Department of Radiology, University
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
I n 1995, the ASsessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis
 127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Disclosures. Enteropathic Arthritis. Definition. Outline. Pathogenesis 5/4/2018. How Often do Patients with SpA Have Intestinal Inflammation?
 Disclosures Enteropathic Arthritis Site PI on UCB NR-Ax-SpA trial Site PI on Abbvie AS trial Mark C. Fisher, MD MPH Outline SpA and Colitis IBD and Arthritis Other intestinal processes associated with
Disclosures Enteropathic Arthritis Site PI on UCB NR-Ax-SpA trial Site PI on Abbvie AS trial Mark C. Fisher, MD MPH Outline SpA and Colitis IBD and Arthritis Other intestinal processes associated with
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation
 ~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
Vertebral sclerosis in adults
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis
 C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro?
 Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Ankylosing Spondylitis*
 Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London
 Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London Background Extraintestinal manifestations of IBD are well recognised. They include:- Arthritis - peripheral and axial Eye complications
Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London Background Extraintestinal manifestations of IBD are well recognised. They include:- Arthritis - peripheral and axial Eye complications
Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott)
 adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott) 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott) 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Differentiating Inflammatory and Mechanical Back Pain
 This resource was organised and funded by AbbVie. It has been developed in collaboration with Claire Harris, Susan Gurden, Dr Jane Martindale, Claire Jeffries and NASS. For UK healthcare professionals
This resource was organised and funded by AbbVie. It has been developed in collaboration with Claire Harris, Susan Gurden, Dr Jane Martindale, Claire Jeffries and NASS. For UK healthcare professionals
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care
 Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics
 Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
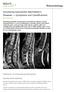
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
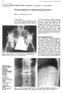 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
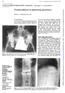 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Ankylosing Spondylitis. DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017
 Ankylosing Spondylitis DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
Ankylosing Spondylitis DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review
 Copyright 2006, Barrow Neurological Institute Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review Hamidreza Aliabadi, MD David Biglari, DO L. Fernando Gonzalez, MD
Copyright 2006, Barrow Neurological Institute Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis versus Ankylosing Spondylitis: Brief Case Review Hamidreza Aliabadi, MD David Biglari, DO L. Fernando Gonzalez, MD
