Autoantibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
- Chester Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Autoantibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Y. Wada 1, T. Kuroda 1, A. Murasawa 4, N. Tanabe 2, M. Nakano 3, F. Gejyo 1 1 Division of Clinical Nephrology and Rheumatology, 2 Division of Health Promotion, Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Niigata; 3 School of Health Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, Niigata University, Niigata; 4 Rheumatic Center, Niigata Prefectural Senami Hospital, Niigata, Japan Abstract Objectives To examine the relationship between autoantibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxldl-abs) and the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Methods Fifty RA patients without evidence of risk factors for atherosclerosis (RA group) and 30 healthy volunteers (normal group) were investigated. The mean intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery (mean CCA-IMT) was measured by high-resolution B-mode ultrasonography. The titer of IgG oxldl-abs was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The relationships among mean CCA-IMT, IgG oxldl-ab titer and patient factors such as body mass index, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and serum lipid levels were examined. Results Mean CCA-IMT, CRP, ESR and titer of IgG oxldl-abs were significantly higher in the RA group than in the normal group. Although mean CCA-IMT showed a positive correlation only with age in multivariate analysis, IgG oxldl-ab titers in the RA group were positively associated with mean CCA-IMT and independently with age and sex by multiple regression analysis. Conclusions IgG oxldl-abs appear to be associated with the degree of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with RA, and are independent of traditional risk factors for atherosclerotic diseases. These results suggest a possible link between autoimmune mechanisms and accelerated atherosclerosis in RA. Key words Rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, autoantibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL). Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 2005; 23:
2 Yoko Wada, MD, PhD; Takeshi Kuroda, MD, PhD; Fumitake Gejyo, MD, PhD; Akira Murasawa, MD, PhD; Naohito Tanabe, MD, PhD; Masaaki Nakano, MD, PhD. Please address correspondence and re p r i n t requests to: Yoko Wada, MD, PhD, Division of Clinical Nephrology and Rheumatology, Niigata Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Asahimachi-dori, Niigata , Japan. youko.wada@ryumachi-jp.com Received on October 6, 2004; accepted in revised form on March 4, Copyright CLINICALAND EXPERIMEN- TAL RHEUMATOLOGY Introduction Coronary vascular disease and stroke are well recognized as major causes of mortality in patients with autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), (1, 2) and increased arterial intima-media thickness (IMT) has also been demonstrated in these patients (3, 4). Although traditional atherosclerosis risk factors play essential roles, several studies have also suggested the importance of systemic inflammation rather than traditional risk factors in the progression of atherosclerosis in autoimmune disorders (3-5). The potential mechanisms involved in the accelerated atherosclerosis associated with autoimmune disorders may involve various cellular and humoral inflammatory mediators, immune complex-mediated endothelial cell damage, prothrombotic states, and autoantibodies (6). Autoantibodies against oxidized lowdensity lipoprotein (oxldl-abs) have been reported to be one of the autoimmune agents associated with atherosclerosis (6), and the serum titer of oxldl-abs is reportedly increased in patients with atherosclerotic and autoimmune disorders (6-10). In the present study, we investigated the relationship between oxldl-abs and atherosclerosis in patients with RA. Patients and methods Subjects Between October 2002 and March 2003, 50 RA patients who had been referred to Niigata Prefectural Senami Hospital for surgery or rehabilitation were entered in the study (RA group). All patients fulfilled the diagnostic criteria of the American College of Rheumatology for RA and had no history of any atherosclerotic disorders, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, or other complications that might affect the measurements performed in the study. Thirty healthy volunteers (normal group) were selected for comparison. Informed consent was obtained from all 80 subjects. The background data for the RA and normal groups are summarized in Table I and II. In this s t u d y, body mass index was significantly lower in the RA group than in the normal group. Carotid ultrasonography Ultrasonography of the common carotid artery (CCA) was performed using a high resolution real-time scanner with a 7.5-MHz transducer (SSD-2200; Aloka Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), and all examinations were performed by a single observer who was unaware of the clinical and biochemical data for the subjects. Measurement of the mean CCA- IMTwas performed as described previously (11). All subjects were examined in the supine position and the bilateral C C A and carotid bifurcations were carefully scanned in the longitudinal and transverse views. The IMT w a s measured at 0.5, 1 and 2 cm below the bifurcation on each side in plaque-free arterial segments, and the average value was taken as the mean CCA- IMT. Anti-oxidized LDL antibodies and other measurements The titer of IgG oxldl-abs was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with a commercially available kit (OLAB; Biomedica, Wien, Austria), as described previously (12). Serum samples stored at -20 C were diluted 1:50 and tested in 96-well microtiter wells precoated with copperoxidized LDL. Double wavelength reading at 450 and 620 nm was performed and the difference in absorbance was calculated with a microplate r e a d e r. The titer was calculated from a Table I. Clinical characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA group) and healthy controls (normal group). RAgroup (n = 50) Normal group (n = 30) p Age, mean ± SD 60.5 ± ±12.9 NS Sex, male/female 4/46 2/28 NS Body mass index, mean ± SD 21.1 ± ± Smokers/non-smokers 4/46 3/27 NS 483
3 Table II. Clinical characteristics of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RAgroup). Disease duration, mean ± SD 12.4 ± 11.4 yrs. DMARDs, yes/no 44/6 Glucocorticoid, yes/no 33/17 Functional class RAstage I 3 I 4 II 17 II 6 III 26 III 17 IV 4 IV 23 Functional class: RA functional status determined by American College of Rheumatology criteria; RA stage: determined by Steinbrocker criteria; DMARDs: disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Results Table III shows the laboratory findings and the mean CCA-IMT in the RA group and the normal group; as expected, ESR was significantly higher in the RAgroup than in the normal group. Although there were no significant differences in serum cholesterol levels between the two groups, the titer of oxldl-abs and the mean CCA-IMT were significantly higher in the patients with RA. Figure 1 shows the distributions of the titers of oxldl-abs in the R A and normal groups. OxLDL-Abs were elevated over the cut-off value in 9 patients (18%) in the RAgroup. Table IVshows the correlation between mean CCA-IMT and other variables in the RA and normal groups. Although the mean CCA-IMT was correlated only with age in patients with RA, it was positively correlated with age, systolic blood pressure, CRP, and ESR in the normal group. We also examined the correlations between CCA-IMT and the clinical features of the RA patients listed in Table II; however, no significant relationships were apparent (data not shown). To examine the factors that correlated independently with mean CCA-IMT in patients with RA, stepwise multiple regression analysis was performed for each group (Table V). Although age and titer of oxldl-abs were selected as independent variables that showed a significant positive correlation with CCA-IMT in the RA group, only age standard curve produced using the standard samples provided with the kit. In this study, the 95th percentile in normal group was taken as the cut-off value (518.5 mu/ml). Total cholesterol and triglycerides were measured by enzymatic methods. High density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol was measured by a dextran sulfate precipitation method. LDL cholesterol was calculated using the formula of Friedewald e t a l. C-reactive protein (CRP) was measured by nepherometry. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and rheumatoid factor (RF) were measured by routine laboratory methods. IgG antibodies against cardiolipine (acls) was measured by ELISA with a commercially available kit (MESACUP c a r d i o l i p i n e test, MBLCo., Ltd. Japan). Statistical analysis Statistical differences between the RA group and normal group were determined with the Student s t-test or We l c h s t-test. Correlations between mean CCA-IMT and each variable were analyzed by Pearson s correlation c o e fficient and stepwise multiple regression analysis. A value of p < 0.05 was taken to indicate statistical significance. Table III. Laboratory findings and intima-media thickness of the common carotid artery (CCA-IMT) in RAgroup and normal group. RAgroup (n = 50) Normal group (n = 30) p ESR (mm/hour) 56.0 ± ± 12.8 < CRP(mg/dl) 2.65 ± ± 0.33 < RF (IU/ml) ± ± 3.05 < TC (mmol/l) 4.83 ± ± 0.72 NS TG (mmol/l) 0.92 ± ± HDLC (mmol/l) 1.56 ± ± 0.41 NS LDLC (mmol/l) 2.91 ± ± 0.64 NS sbp(mmhg) ± ± 10.8 NS dbp(mmhg) 74.7 ± ± 7.4 NS OxLDL-Ab (EU/ml) ± ± acl(u/ml) 1.49 ± ± CCA-IMT(mm) 0.61 ± ± Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-reactive protein; RF: rheumatoid factor; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; HDLC: high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLC: low density lipoprotein cholesterol; sbp: systolic blood pressure; dbp: diastolic blood pressure; oxldl-ab: antibodies aginst oxidized-ldl; acl: anticardiolipin antibodies; CCA-IMT: mean intima-media thickness of common carotid artery. Fig. 1. The titers of autoantibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein in the RA and normal groups. The lower, middle, and upper horizontal lines represent 25 th, 50 th, and 75 th percentiles, while vertical lines extend from the 10 th to 90 th percentile. 484
4 was selected in the normal group. The next analysis was performed on all study subjects (n = 80) using RA status and the interaction between RA status and oxldl-abs as additional independent variables. Table VI shows that age, RA status and interaction between RAstatus and oxldl-abs were selected as independent variables in multiple regression analysis in all subjects. Discussion oxldl-abs are known as one of the autoimmune agents associated with atherosclerosis (6), and the serum titer of oxldl-abs is reported to be elevated in many pathological conditions, including cardiovascular diseases and autoimmune disorders (6-10). However, the mechanism by which these autoantibodies act against the development of atherosclerosis remains controversial. Salonen et al. reported a positive correlation between progression of atherosclerosis and serum levels of oxldl- Abs (7), and Hulthe et al. also demonstrated a positive correlation between CCA-IMT and oxldl-abs in healthy subjects (13). Increased levels of ox- LDL-Abs are also found in cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and peripheral arterial disease (8,14,15). These studies suggest that elevated levels of oxldl-abs may predict the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disorders. On the other hand, several studies have suggested an inverse correlation between CCA-IMT and oxldl-abs in healthy subjects (6, 12). Our study also indicated a similar inverse trend, without statistical significance, in the normal group. In addition, immunization with oxldl results in a reduction of atherosclerotic lesions with increased levels of oxldl-abs in experimental animal models (16). OxLDL-Abs are known to be detectable in healthy subjects as well as in patients with atherosclerotic diseases, and humoral immunity to oxidized LDLs is thought to reduce the incidence of atherosclerosis by neutralizing them (17). These apparently conflicting results may be due, at least in part, to methodological differences in the detection of oxldl-abs. There are several antigenic forms of LDLused in immunoassay, and the nature of their antigenic Table IV. Correlation coefficient between mean CCA-IMT and each variable in RAgroup and normal group. epitopes remains uncertain (6, 18). Ox- LDL-Abs also belong to different subclasses, such as IgA, IgG, and IgM (6), RAgroup (n = 50) Normal group (n = 30) Sex (male = 1/female = 0) Age 0.57*** 0.78*** Body mass index ESR (1 hour) ** CRP * RF TC TG HDLC LDLC sbp * dbp OxLDL-Ab acl * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-reactive protein; RF: rheumatoid factor; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; HDLC: high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLC: low density lipoprotein cholesterol; sbp: systolic blood pressure; dbp: diastolic blood pressure; oxldl-ab: antibodies aginst oxidized-ldl; acl: anticardiolipin antibodies; CCA-IMT: mean intima-media thickness of common carotid artery. Table V. Results of stepwise multiple regression analysis of factors affecting CCA-IMT in RAgroup and normal group. Selected variables* Standardized Beta p RAgroup (n = 50) Age 0.57 < OxLDL-Ab Normal group (n = 30) Age 0.78 < *Selected from Sex, Age, BMI, ESR, CRP, RF, TC, TG, HDLC, LDLC, sbp, dbp, and OxLDL-Ab. CCA-IMT: mean intima-media thickness of common carotid artery; BMI: body mass index; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-reactive protein; RF: rheumatoid factor; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; HDLC: high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLC: low density lipoprotein cholesterol; sbp: systolic blood pressure; dbp: diastolic blood pressure; oxldl-ab: antibodies aginst oxidized- LDL. Table VI. Results of stepwise multiple regression analysis of factors affecting CCA-IMTin all subjects (n = 80). Selected variables* Standardized Beta P Age 0.61 < Interaction RAstatus and OxLDL-Ab RAstatus (RA= 1/normal = 0) *Selected from Sex, Age, BMI, ESR, CRP, RF, TC, TG, HDLC, LDLC, sbp, dbp, and OxLDL-Ab. CCA-IMT: mean intima-media thickness of common carotid artery; BMI: body mass index; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-reactive protein; RF: rheumatoid factor; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; HDLC: high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLC: low density lipoprotein cholesterol; sbp: systolic blood pressure; dbp: diastolic blood pressure; oxldl-ab: antibodies aginst oxidized- LDL. and Karvonen et al. reported that only IgM oxldl-abs had an inverse association with carotid atherosclerosis 485
5 (19). These studies suggest possible functional differences according to epitope or isotype, and it will be important to determine these differences in order to clarify the relationship between ox- LDL-Abs and the development of atherosclerosis. Apart from these problems, immunological status in patients with autoimmune disorders seems quite different from that in healthy subjects. Elevated levels of oxldl-abs have been found in patients with several autoimmune disorders, and oxldl-ab titers in SLE and RA patients are reportedly related to disease severity (9, 10). Although in this study we found no significant correlation between acl and oxldl-abs in RA patients, cross-reactivity between acl and oxldl-abs has been reported in several autoimmune disorders (6). These findings suggest that levels of oxldl-abs reflect abnormal immunological activity in autoimmune disorders, such as high production of autoantibodies or immunoglobulins. Although it remains unknown whether oxldl-abs have a promotive or protective role in the development of atherosclerosis, these observations indicate that the process of atherosclerosis might involve some kind of immunological abnormality or autoimmunological mechanism. Recently, several studies have examined the relationship between carotid atherosclerosis and markers associated with systemic inflammation in patients with RA (3,4). Kumeda et al. demonstrated that the duration and clinical severity of RA were independently associated with increased CCA-IMT (3). Rincon et al. showed that increased CCA-IMT and the presence of carotid plaque were associated with markers of systemic inflammation such as CRP and ESR both in RA patients and in healthy subjects (4). These studies have suggested a close relationship between systemic inflammation and the progression of atherosclerosis in patients with RA. Although we have suggested that the positive correlation between CCA-IMT and oxldl-abs is affected by RA status, in this study CCA-IMT was not correlated with serum inflammatory markers or clinical features in R A patients. As RA disease activity may be modified by changes in lifestyle or medication, it may be difficult to evaluate disease status by examination at a single time-point. An appropriate marker of long-term disease activity is needed for future studies. In summary, this study has demonstrated a positive correlation between carotid atherosclerosis and oxldl-abs in patients with RA, independent of age, sex, or other traditional risk factors. As our findings suggest a possible link between autoimmune mechanisms and acceleration of atherosclerosis in RA, further studies will be needed to investigate the functional role of these autoantibodies in the human body in various immunological states. References 1. WARD MM: Premature morbidity from cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 1999; 42: WOLFE F, FREUNDLICH B, STRAUS W L: Increase in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease prevalence in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2003; 30: KUMEDA Y, INABA M, GOTO H et al.: Increased thickness of the arterial intima-media detected by ultrasonography in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46: D E L RINCON I, WILLIAMS K, STERN W M, FREEMAN GL, O LEARY DH, ESCALANTE A: Association between carotid atherosclerosis and markers of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy subjects. Arthri - tis Rheum 2003; 48: D E L RINCON I, WILLIAMS K, STERN MP, FREEMAN GL, ESCALANTE A: High incidence of cardiovascular events in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort not explained by traditional cardiac risk factors. Arthritis Rheum 2001; 46: S T E I N E R O VA A, RACEK J, STO Z I C K Y F, Z I M A T, FIALOVA L, LAPIN A: A n t i b o d i e s against oxidized LDL theory and clinical use. Physiol Res 2001; 50: S A L O N E N J T, Y L A - H E RT T U A L A S, YA M A- M O TO R et al.: Autoantibody against oxidized LDLand progression of carotid atherosclerosis. Lancet 1992; 339: INOUE T, YAGUCHI I, UCHIDA T et al.: Clinical significance of the antibody against oxidized low-density lipoprotein in acute myocardial infarction. C a rd i o l o g y 2002; 98: CVETKOVIC JT, WALLENBERG-JONSSON S, AHMED E, RANTAPAA-DAHLQVIST S, LEF- VERT AK: Increased levels of autoantibodies against copper-oxidized low density lipoprotein, malondialdehyde-modified low density lipoprotein and cardiolipine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. R h e u m a t o l o g y ; 41: GOMEZ-ZUMAQUERO JM, TINAHONES FJ, DE RAMON E, CAMPS M, GARRIDO L, SORIGUER FJ: Association of biological markers of activity of systemic lupus erythematosus with levels of anti-oxidized lowdensity lipoprotein antibodies. R h e u m a t o l - ogy 2004; 43: BENEDETTO FA, MALLAMACI F, TRIPEPI G, ZOCCALI C: Prognostic value of ultrasonographic measurement of carotid intima media thickness in dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001; 12: FUKUMOTO M, SHOJI T, EMOTO M, KAWAG- ISHI T, OKUNO Y, NISHIZAWAY: Antibodies against oxidized LDLand carotid artery intima-media thickness in a healthy population. A rterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000; 20: H U LTHE J, BOKEMARK L, FAGERBERG B: Antibodies to oxidized LDLin relation to intima-media thickness in carotid and femoral arteries in 58-year-old subjectively clinically healthy men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001; 21: MAGGI E, MARCHESI E, RAVETTA V, MAR- TIGNONI A, FINARDI G, BELLOMO G: Presence of autoantibodies against oxidatively modified low-density lipoprotein in essential hypertension: a biochemical signature of an enhanced in vivo low-density lipoprotein oxidation. J Hypertens 1995; 13: BERGMARK C, WU R, DE FAIRE U, LEFVERT AK, SWEDENBORG J: Patients with earlyonset peripheral vascular disease have increased levels of autoantibodies against oxidized LDL. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1995; 15: F R E I G A N G S, SOHVI H, MILLER E, W I T Z- T U M JL, PA L I N S K I W: Immunization of LDL receptor-deficient mice with homologous malondialdehyde-modified and native LDL reduces progression of atherosclerosis by mechanisms other than induction of high titers of antibodies to oxidative neoepitopes. A rterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1998; 18: SHOENFELD Y, WU R, DEARING LD, MAT- SUURA E: Are anti-oxidized low-density lipoprotein antibodies pathogenic or pretective? Circulation 2004; 110: KARVONEN J, PAIVANSALO M, KESANIEMI YA, HORKKO S: Immunogloburin M type of autoantibodies to oxidized low-density lipoprotein has an inverse relation to carotid artery atherosclerosis. Circulation 2003; 108: VAARALA O: Antibodies to oxidized LDL. Lupus 2000; 9:
A Study of Atherosclerosis in Systemic Vasculitis
 Original Article A Study of Atherosclerosis in Systemic Vasculitis Silas Supragya Nelson, Sonjjay Pande, Avadhesh Pratap Singh Kushwah 3 Assistant Professor in the Department of Medicine, NSCB Medical
Original Article A Study of Atherosclerosis in Systemic Vasculitis Silas Supragya Nelson, Sonjjay Pande, Avadhesh Pratap Singh Kushwah 3 Assistant Professor in the Department of Medicine, NSCB Medical
CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS. Dimitrios N. Nikas, MD, PhD, FESC Interventional Cardiologist Ioannina University Hospital
 CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS Dimitrios N. Nikas, MD, PhD, FESC Interventional Cardiologist Ioannina University Hospital I, DIMITRIOS N. NIKAS, MD, PHD, FESC, HAVE NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE RELATED
CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS Dimitrios N. Nikas, MD, PhD, FESC Interventional Cardiologist Ioannina University Hospital I, DIMITRIOS N. NIKAS, MD, PHD, FESC, HAVE NO CONFLICT OF INTEREST TO DECLARE RELATED
Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic
 Supplementary Information The title of the manuscript Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic stroke Xin-Wei He 1, Wei-Ling Li 1, Cai Li
Supplementary Information The title of the manuscript Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic stroke Xin-Wei He 1, Wei-Ling Li 1, Cai Li
Serum lipids and anti-oxidized LDL antibodies in primary antiphospholipid syndrome
 Serum lipids and anti-oxidized LDL antibodies in primary antiphospholipid syndrome M. Bećarević 1, S. Andrejević 2, P. Miljić 3, B. Bonači-Nikolić 2, N. Majkić-Singh 1 1 Institute for Medical Biochemistry,
Serum lipids and anti-oxidized LDL antibodies in primary antiphospholipid syndrome M. Bećarević 1, S. Andrejević 2, P. Miljić 3, B. Bonači-Nikolić 2, N. Majkić-Singh 1 1 Institute for Medical Biochemistry,
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
 Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. An Independent Risk Factor for Endothelial Dysfunction in Women
 Systemic Lupus Erythematosus An Independent Risk Factor for Endothelial Dysfunction in Women Masoud El-Magadmi, MB; Helena Bodill, MSc; Yasmeen Ahmad, MB, MRCP; Paul N. Durrington, MD, F Med Sci; Michael
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus An Independent Risk Factor for Endothelial Dysfunction in Women Masoud El-Magadmi, MB; Helena Bodill, MSc; Yasmeen Ahmad, MB, MRCP; Paul N. Durrington, MD, F Med Sci; Michael
Influence of age and sex on levels of anti-oxidized LDL antibodies and anti-ldl immune complexes in the general population
 Influence of age and sex on levels of anti-oxidized LDL antibodies and anti-ldl immune complexes in the general population Francisco J. Tinahones, 1, * Juan Miguel Gómez-Zumaquero, Lourdes Garrido-Sánchez,
Influence of age and sex on levels of anti-oxidized LDL antibodies and anti-ldl immune complexes in the general population Francisco J. Tinahones, 1, * Juan Miguel Gómez-Zumaquero, Lourdes Garrido-Sánchez,
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings?
 Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 27, No. 1, 2013; 67-72
 Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE. Review. 120 Clinical Dermatology 2013; 1 (2):
 Review Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE Andrea Doria Division of Rheumatology University of Padua, Italy Address for correspondence: Division of Rheumatology University of
Review Cardio-metabolic comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and SLE Andrea Doria Division of Rheumatology University of Padua, Italy Address for correspondence: Division of Rheumatology University of
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
STUDIES ON ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION AND INTIMA- MEDIA THICKNESS USING ULTRASOUND TECHNIQUE. Morteza Rohani
 STUDIES ON ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION AND INTIMA- MEDIA THICKNESS USING ULTRASOUND TECHNIQUE Morteza Rohani Stockholm 2008 DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE, HUDDINGE KAROLINSKA INSTITUTET, STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN STUDIES
STUDIES ON ARTERIAL ENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION AND INTIMA- MEDIA THICKNESS USING ULTRASOUND TECHNIQUE Morteza Rohani Stockholm 2008 DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE, HUDDINGE KAROLINSKA INSTITUTET, STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN STUDIES
HDL and Arterial Wall
 JIFA January 31th 2014 HDL and Arterial Wall P-J TOUBOUL INSERM698 Bichat University Conflict of Interest M Ath intellectual property owner Involvement in R & D for atherosclerosis software developments
JIFA January 31th 2014 HDL and Arterial Wall P-J TOUBOUL INSERM698 Bichat University Conflict of Interest M Ath intellectual property owner Involvement in R & D for atherosclerosis software developments
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both
 Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
MEASURING AUTOANTIBODY AGAINST MODIFIED LDL IN CARDIOVASCULAR PATIENTS
 Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 7 (1) 899-903 (2007) ISSN: 0973-0028 Original Article MEASURING AUTOANTIBODY AGAINST MODIFIED LDL IN CARDIOVASCULAR PATIENTS ASGARY, S.,? NADERI, G., GHARIPOOR,
Journal of Cell and Tissue Research Vol. 7 (1) 899-903 (2007) ISSN: 0973-0028 Original Article MEASURING AUTOANTIBODY AGAINST MODIFIED LDL IN CARDIOVASCULAR PATIENTS ASGARY, S.,? NADERI, G., GHARIPOOR,
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease
 Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Lupus as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease SØREN JACOBSEN Department Rheumatology, Rigshospitalet Søren Jacobsen Main sponsors: Gigtforeningen Novo Nordisk Fonden Rigshospitalet Disclaimer: Novo
Original Research Article
 A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
How would you manage Ms. Gold
 How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure
 801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
Received: March 2008; in final form May 2008.
 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BRACHIAL ARTERY FLOW- MEDIATED DILATION AND CAROTID ARTERY INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN THE MIDDLE-AGED SUBJECTS WITH LOW CARDIOVASCULAR RISK GERMAINE SĂVOIU*, LAVINIA NOVEANU**, O. FIRA-MLADINESCU*,
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BRACHIAL ARTERY FLOW- MEDIATED DILATION AND CAROTID ARTERY INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN THE MIDDLE-AGED SUBJECTS WITH LOW CARDIOVASCULAR RISK GERMAINE SĂVOIU*, LAVINIA NOVEANU**, O. FIRA-MLADINESCU*,
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria
 Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Intima-Media Thickness
 European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
Dyslipidaemia. Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram
 Dyslipidaemia Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram PhD,FACP,FCPS(Medicine) Professor(c.c.) & Head Department of Medicine Rajshahi Medical College Rajshahi-6000 New features of ATP III
Dyslipidaemia Is there any new information? Dr. A.R.M. Saifuddin Ekram PhD,FACP,FCPS(Medicine) Professor(c.c.) & Head Department of Medicine Rajshahi Medical College Rajshahi-6000 New features of ATP III
The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Smoking The Impact of Smoking on Acute Ischemic Stroke Wei-Chieh Weng, M.D. Department of Neurology, Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital, Kee-Lung, Taiwan Smoking related mortality Atherosclerotic vascular disease
Andrejs Kalvelis 1, MD, PhD, Inga Stukena 2, MD, Guntis Bahs 3 MD, PhD & Aivars Lejnieks 4, MD, PhD ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Riga Stradins University
 CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do We Correctly Assess the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease? Characteristics of Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Depending on the Sex and Age of Patients
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do We Correctly Assess the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease? Characteristics of Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Depending on the Sex and Age of Patients
Small dense low-density lipoprotein is a risk for coronary artery disease in an urban Japanese cohort: The Suita study
 Small dense low-density lipoprotein is a risk for coronary artery disease in an urban Japanese cohort: The Suita study Hidenori Arai 1, Yoshihiro Kokubo 2, Makoto Watanabe 2, Tatsuya Sawamura 3, Tomonori
Small dense low-density lipoprotein is a risk for coronary artery disease in an urban Japanese cohort: The Suita study Hidenori Arai 1, Yoshihiro Kokubo 2, Makoto Watanabe 2, Tatsuya Sawamura 3, Tomonori
Serum Ferritin Level in Male with Established Coronary Artery Disease
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 12 Ver. I (Dec. 2014), PP 58-62 Serum Ferritin Level in Male with Established Coronary Artery
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 12 Ver. I (Dec. 2014), PP 58-62 Serum Ferritin Level in Male with Established Coronary Artery
Carotid intima media thickness as a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: a case control study
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Saigal R et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Nov;3(4):942-946 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20163728
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Saigal R et al. Int J Adv Med. 2016 Nov;3(4):942-946 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20163728
Annals of RSCB Vol. XIV, Issue 1
 THE ROLE OF URIC ACID AS A RISK FACTOR FOR ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION Corina Şerban 1, Germaine Săvoiu 2, Lelia Şuşan 3, Alina Păcurari 3, A. Caraba 3, Anca Tudor 4, Daniela Ionescu 5, I. Romosan 3, A. Cristescu
THE ROLE OF URIC ACID AS A RISK FACTOR FOR ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION Corina Şerban 1, Germaine Săvoiu 2, Lelia Şuşan 3, Alina Păcurari 3, A. Caraba 3, Anca Tudor 4, Daniela Ionescu 5, I. Romosan 3, A. Cristescu
Clinical Investigation and Reports. Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Clinical Investigation and Reports Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Elisabet Svenungsson, MD; Kerstin Jensen-Urstad, MD, PhD; Mikael Heimbürger, MD, PhD; Angela Silveira,
Clinical Investigation and Reports Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Elisabet Svenungsson, MD; Kerstin Jensen-Urstad, MD, PhD; Mikael Heimbürger, MD, PhD; Angela Silveira,
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness. The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study
 Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
Original Article. To Study Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis
 26 To Study Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis SS Nelson 1, AK Khan 2 Original Article Abstract Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with an increased morbidity and mortality.
26 To Study Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis SS Nelson 1, AK Khan 2 Original Article Abstract Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with an increased morbidity and mortality.
Supplemental Figures and Legends
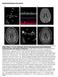 Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Number of patients 14
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1 Number of patients 14 Age, years 54.9 ± 10.0 Female gender, n (%) 6 (42.9) Diabetes, n (%) 2 (14.3) History of hypertension, n (%) 5 (35.7) Ever smoker, n (%)
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1 Number of patients 14 Age, years 54.9 ± 10.0 Female gender, n (%) 6 (42.9) Diabetes, n (%) 2 (14.3) History of hypertension, n (%) 5 (35.7) Ever smoker, n (%)
Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia
 Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia Christian Delles, Catriona E Brown, Joanne Flynn, David M Carty Institute of Cardiovascular and Medical Sciences University of Glasgow United
Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia Christian Delles, Catriona E Brown, Joanne Flynn, David M Carty Institute of Cardiovascular and Medical Sciences University of Glasgow United
Tracking a Killer Molecule
 Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
Tracking a Killer Molecule Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA www.mercodia.com Mercodia Oxidized LDL ELISA products Product Catalog No Kit size Oxidized LDL ELISA 10-1143-01 96 wells Oxidized LDL competitive
CVD Risk Assessment. Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic
 CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
How to detect early atherosclerosis ; focusing on techniques
 How to detect early atherosclerosis ; focusing on techniques Jang-Ho Bae, MD., PhD. Heart Center Konyang University Hospital Daejeon city, S. Korea Surrogates for Atherosclerosis Measures of endothelial
How to detect early atherosclerosis ; focusing on techniques Jang-Ho Bae, MD., PhD. Heart Center Konyang University Hospital Daejeon city, S. Korea Surrogates for Atherosclerosis Measures of endothelial
Identification of autoantibodies in human plasma recognizing an apob-100 LDL receptor binding site peptide
 Identification of autoantibodies in human plasma recognizing an apob-100 LDL receptor binding site peptide Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, 1, *, Göran Berglund,* Ragnar Alm,* Jan-Åke Nilsson,* Prediman K. Shah,
Identification of autoantibodies in human plasma recognizing an apob-100 LDL receptor binding site peptide Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, 1, *, Göran Berglund,* Ragnar Alm,* Jan-Åke Nilsson,* Prediman K. Shah,
Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients With Coronary Atherosclerosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
Identifying and Quantifying Dynamic Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Identifying and Quantifying Dynamic Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Mandana Nikpour A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
Identifying and Quantifying Dynamic Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Mandana Nikpour A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
Mandana Nikpour 1,2, Murray B Urowitz 1*, Dominique Ibanez 1, Paula J Harvey 3 and Dafna D Gladman 1. Abstract
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Autoantibodies, Chronic Infections, and Carotid Atherosclerosis in a Population-Based Study
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 12, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.024
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 47, No. 12, 2006 2006 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/06/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.024
Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 CM&R Rapid Release. Published online ahead of print February 26, 2009 as doi:10.3121/cmr.2008.828 Original Research Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus José María Calvo-Romero,
CM&R Rapid Release. Published online ahead of print February 26, 2009 as doi:10.3121/cmr.2008.828 Original Research Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus José María Calvo-Romero,
Plasma fibrinogen level, BMI and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
IS PRE-CLINICAL AUTOIMMUNITY BENIGN?
 IS PRE-CLINICAL AUTOIMMUNITY BENIGN? Darcy S. Majka MD, MS Disclosures I have no significant financial or other relationship with the manufacturers of any product or services. Dr. Teodorescu (coauthor)
IS PRE-CLINICAL AUTOIMMUNITY BENIGN? Darcy S. Majka MD, MS Disclosures I have no significant financial or other relationship with the manufacturers of any product or services. Dr. Teodorescu (coauthor)
Marc Frerix 1*, Johannes Stegbauer 2, Alexander Kreuter 3 and Stefan Markus Weiner 4
 Frerix et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R54 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Atherosclerotic plaques occur in absence of intima-media thickening in both systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus:
Frerix et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R54 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Atherosclerotic plaques occur in absence of intima-media thickening in both systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus:
Patients with Wegener s granulomatosis: a long-term follow-up study
 Patients with Wegener s granulomatosis: a long-term follow-up study K. de Leeuw 1, A.M. van der Graaf 1, J. Bijzet 1, C.A Stegeman 2, A.J Smit 3, C.G Kallenberg 1, M. Bijl 1 Departments of 1 Rheumatology
Patients with Wegener s granulomatosis: a long-term follow-up study K. de Leeuw 1, A.M. van der Graaf 1, J. Bijzet 1, C.A Stegeman 2, A.J Smit 3, C.G Kallenberg 1, M. Bijl 1 Departments of 1 Rheumatology
Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
 Supplement issue Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Jane E. Salmon, MD, a,b and Mary J. Roman, MD b a Mary Kirkland Center for Lupus Research, Hospital
Supplement issue Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Jane E. Salmon, MD, a,b and Mary J. Roman, MD b a Mary Kirkland Center for Lupus Research, Hospital
CRP and fibrinogen imply clinical outcome of patients with type-2 diabetes. and coronary artery disease
 CRP and fibrinogen imply clinical outcome of patients with type-2 diabetes and coronary artery disease Marijan Bosevski 1, *, Golubinka Bosevska 1, Lily Stojanovska 2, Vasso Apostolopoulos 2, * 1 University
CRP and fibrinogen imply clinical outcome of patients with type-2 diabetes and coronary artery disease Marijan Bosevski 1, *, Golubinka Bosevska 1, Lily Stojanovska 2, Vasso Apostolopoulos 2, * 1 University
Research Article Carotid Intima Media Thickness as a Marker of Atherosclerosis in Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Research Article Carotid Intima Media Thickness as a Marker of Atherosclerosis in Ankylosing Spondylitis Naveen Gupta, 1 Renu Saigal, 2,3 Laxmikant Goyal, 1 Abhishek Agrawal, 1 Rajat Bhargava, 1 and Arun
Research Article Carotid Intima Media Thickness as a Marker of Atherosclerosis in Ankylosing Spondylitis Naveen Gupta, 1 Renu Saigal, 2,3 Laxmikant Goyal, 1 Abhishek Agrawal, 1 Rajat Bhargava, 1 and Arun
Objective Calcium score carotid IMT hs-crp
 P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT
 Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
Role of imaging in risk assessment models: the example of CIMT Diederick E. Grobbee, MD, PhD, FESC Professor of Clinical Epidemiology Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical
Correspondence should be addressed to Huijuan Zhang;
 Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 3510275, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3510275 Research Article Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 Levels Are Associated with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness
Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 3510275, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3510275 Research Article Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 Levels Are Associated with Carotid Intima-Media Thickness
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA
 Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
cubital tunnel syndrome CTS 19 ~ ± cm 1. 1 CSA / CSA CSA CSA CSA 1. 3 SPSS 11.
 558 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 33 6 2011 6 1674-6309 2011 06-0558 - 04 1 2 3 3 1. 750004 2. 750004 3. 750004 39 CTS 40 20 40 CSA P < 0. 05 CSA MNCV r = - 0. 933 P < 0. 01 R445. 1 A cubital tunnel
558 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 33 6 2011 6 1674-6309 2011 06-0558 - 04 1 2 3 3 1. 750004 2. 750004 3. 750004 39 CTS 40 20 40 CSA P < 0. 05 CSA MNCV r = - 0. 933 P < 0. 01 R445. 1 A cubital tunnel
Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Jichi Medical University Saitama Medical Center, Japan
 Association between continuously elevated C-reactive protein and restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention using drug-eluting stent in angina patients Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Jichi
Association between continuously elevated C-reactive protein and restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention using drug-eluting stent in angina patients Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Jichi
John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam
 Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
Latest Insights from the JUPITER Study John J.P. Kastelein MD PhD Professor of Medicine Dept. of Vascular Medicine Academic Medial Center / University of Amsterdam Inflammation, hscrp, and Vascular Prevention
Know Your Number Aggregate Report Single Analysis Compared to National Averages
 Know Your Number Aggregate Report Single Analysis Compared to National s Client: Study Population: 2242 Population: 3,000 Date Range: 04/20/07-08/08/07 Version of Report: V6.2 Page 2 Study Population Demographics
Know Your Number Aggregate Report Single Analysis Compared to National s Client: Study Population: 2242 Population: 3,000 Date Range: 04/20/07-08/08/07 Version of Report: V6.2 Page 2 Study Population Demographics
Prediction of epileptic seizures: are nonlinear methods relevant?
 Prediction of epileptic seizures: are nonlinear methods relevant? a b c d EEG Variance C(r ) C(r ) 2 2 3 2.6.4.2.6.5.4.3.2. To the editor Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological disorders,
Prediction of epileptic seizures: are nonlinear methods relevant? a b c d EEG Variance C(r ) C(r ) 2 2 3 2.6.4.2.6.5.4.3.2. To the editor Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological disorders,
The Comparison of Acute Myocardial Infarction Serum Anticardiolipin Antibody with Healthy Subjects, in Gorgan (Northern Iran)
 Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences 16 (2): 92-96, 2013 ISSN 1028-8880 I DOI: 10.3923/pjbs.2013.92.96 2013 Asian Network for Scientific Information The Comparison of Acute Myocardial Infarction Serum
Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences 16 (2): 92-96, 2013 ISSN 1028-8880 I DOI: 10.3923/pjbs.2013.92.96 2013 Asian Network for Scientific Information The Comparison of Acute Myocardial Infarction Serum
Inflammation and and Heart Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease
 Inflammation and Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease What is the link between een inflammation and atherosclerotic disease? What is the role of biomarkers in predicting cardiovascular
Inflammation and Heart Disease in Women Inflammation and Heart Disease What is the link between een inflammation and atherosclerotic disease? What is the role of biomarkers in predicting cardiovascular
Not only...but also : factors that contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis and premature coronary heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus
 Rheumatology 2005;44:1492 1502 Advance Access publication 18 October 2005 Review doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei142 Michael Mason Prize Essay Not only...but also : factors that contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis
Rheumatology 2005;44:1492 1502 Advance Access publication 18 October 2005 Review doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei142 Michael Mason Prize Essay Not only...but also : factors that contribute to accelerated atherosclerosis
Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome
 243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
Correlation between triglyceride level and carotid intima media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
 International Journal of Clinical Trials Bendwal K et al. Int J Clin Trials. 2018 May;5(2):97-101 http://www.ijclinicaltrials.com pissn 2349-3240 eissn 2349-3259 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3259.ijct20181051
International Journal of Clinical Trials Bendwal K et al. Int J Clin Trials. 2018 May;5(2):97-101 http://www.ijclinicaltrials.com pissn 2349-3240 eissn 2349-3259 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3259.ijct20181051
Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE)
 Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE) Thomas Dayspring, MD, FACP Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Medicine and Dentistry
Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE) Thomas Dayspring, MD, FACP Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Medicine and Dentistry
Spotty Calcification as a Marker of Accelerated Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis : Insights from Serial Intravascular Ultrasound
 Spotty Calcification as a Marker of Accelerated Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis : Insights from Serial Intravascular Ultrasound Department of Cardiovascular Medicine Heart and Vascular Institute
Spotty Calcification as a Marker of Accelerated Progression of Coronary Atherosclerosis : Insights from Serial Intravascular Ultrasound Department of Cardiovascular Medicine Heart and Vascular Institute
Recent studies suggest that the immune system modulates
 Identification of Immune Responses Against Aldehyde-Modified Peptide Sequences in ApoB Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, Bo Hedblad, Göran Berglund, Ragnar Alm, Mikko Ares,
Identification of Immune Responses Against Aldehyde-Modified Peptide Sequences in ApoB Associated With Cardiovascular Disease Gunilla Nordin Fredrikson, Bo Hedblad, Göran Berglund, Ragnar Alm, Mikko Ares,
Table S1. Read and ICD 10 diagnosis codes for polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TEXT Text S1. Multiple imputation TABLES Table S1. Read and ICD 10 diagnosis codes for polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis Table S2. List of drugs included as immunosuppressant
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL TEXT Text S1. Multiple imputation TABLES Table S1. Read and ICD 10 diagnosis codes for polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis Table S2. List of drugs included as immunosuppressant
ADHD and Adverse Health Outcomes in Adults
 Thomas J. Spencer, MD This work was supported in part by a research grant from Shire (Dr. Spencer) and by the Pediatric Psychopharmacology Council Fund. Disclosures Dr. Spencer receives research support
Thomas J. Spencer, MD This work was supported in part by a research grant from Shire (Dr. Spencer) and by the Pediatric Psychopharmacology Council Fund. Disclosures Dr. Spencer receives research support
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1
 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
Department of Internal Medicine and Molecular Science, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University, Osaka, Japan. 4
 146 Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis Original Articles Vol. 11, No. 3 Clinical Features of Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Japan in a Database from 1996 1998 by the Research Committee of the
146 Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis Original Articles Vol. 11, No. 3 Clinical Features of Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Japan in a Database from 1996 1998 by the Research Committee of the
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL
 CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL Kirui K Fredrick MBCHB,MMED KEMRI/WRP HIV PROGRAM KERICHO EPIDEMIOLOGY Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL Kirui K Fredrick MBCHB,MMED KEMRI/WRP HIV PROGRAM KERICHO EPIDEMIOLOGY Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease
Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases
 Original article: Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Dept of Medicine,
Original article: Study of relationship of serum Lipid Profile and etiological factors of Ischaemic Heart Diseases Dr Abhijit Nikam, Dr Sonu Yadav, Dr Vivek Chiddarwar, Dr A L Kakrani Dept of Medicine,
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4):
 300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
D Terentes-Printzios, C Vlachopoulos, G Vyssoulis, N Ioakeimidis, P Xaplanteris, K Aznaouridis, E Christoforatou, A Samentzas, A Siama, C Stefanadis
 Peripheral Vessels Unit, 1st Department of Cardiology Athens Medical School Hippokration Hospital, Athens, Greece D Terentes-Printzios, C Vlachopoulos, G Vyssoulis, N Ioakeimidis, P Xaplanteris, K Aznaouridis,
Peripheral Vessels Unit, 1st Department of Cardiology Athens Medical School Hippokration Hospital, Athens, Greece D Terentes-Printzios, C Vlachopoulos, G Vyssoulis, N Ioakeimidis, P Xaplanteris, K Aznaouridis,
Associations of blood pressure with carotid intima-media thickness in elderly Finns with diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance
 (2003) 17, 705 711 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Associations of blood pressure with carotid intima-media thickness in elderly
(2003) 17, 705 711 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Associations of blood pressure with carotid intima-media thickness in elderly
Key words: antiphospholipid syndrome, trombosis, pathogenesis
 26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 10 Page October 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients
 2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
The principal cause of cerebrovascular diseases is atherosclerosis.
 Autoantibodies Against Oxidatively Modified LDL Do Not Constitute a Risk Factor for Stroke A Nested Case-Control Study Ejaz Ahmed, MD; Jasmina Trifunovic, MSc; Birgitta Stegmayr, MD, PhD; Göran Hallmans,
Autoantibodies Against Oxidatively Modified LDL Do Not Constitute a Risk Factor for Stroke A Nested Case-Control Study Ejaz Ahmed, MD; Jasmina Trifunovic, MSc; Birgitta Stegmayr, MD, PhD; Göran Hallmans,
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 06 Page June 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
Anti β 2. -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PREDICTIVE VALUE OF ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES Anti β -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PREDICTIVE VALUE OF ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES Anti β -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With
Assessing Cardiovascular Risk to Optimally Stratify Low- and Moderate- Risk Patients. Copyright. Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution
 CLINICAL Viewpoint Assessing Cardiovascular Risk to Optimally Stratify Low- and Moderate- Risk Patients Copyright Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution By Ruth McPherson, MD, PhD, FRCPC Unauthorised
CLINICAL Viewpoint Assessing Cardiovascular Risk to Optimally Stratify Low- and Moderate- Risk Patients Copyright Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution By Ruth McPherson, MD, PhD, FRCPC Unauthorised
IMPACT OF LONG TERM-STEROID TREATMENT PRESCRIBED FOR SYSTEMIC AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS.
 1 IMPACT OF LONG TERM-STEROID TREATMENT PRESCRIBED FOR SYSTEMIC AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS. A NETWORK ORGANIZED BY THE EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE Coordination:
1 IMPACT OF LONG TERM-STEROID TREATMENT PRESCRIBED FOR SYSTEMIC AND AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS. A NETWORK ORGANIZED BY THE EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF INTERNAL MEDICINE Coordination:
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Atherosclerosis. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Atherosclerosis. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher
Katsuyuki Nakajima, PhD. Member of JCCLS International Committee
 Katsuyuki Nakajima, PhD Member of JCCLS International Committee Visiting Professor and Scientist Tufts University, Boston, MA & Framingham Offspring Study, Framingham, MA August 20 th, 2011, Tokyo Framingham
Katsuyuki Nakajima, PhD Member of JCCLS International Committee Visiting Professor and Scientist Tufts University, Boston, MA & Framingham Offspring Study, Framingham, MA August 20 th, 2011, Tokyo Framingham
A: Epidemiology update. Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups
 A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
The formation of atherosclerosis is increasingly. Autoantibodies to Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Coronary Artery Disease
 AJH 2001; 14:149 154 Autoantibodies to Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Coronary Artery Disease Yaniv Sherer, Alexander Tenenbaum, Miri Blank, Joseph Shemesh, Dror Harats, Enrique Z. Fisman, Sonja Praprotnik,
AJH 2001; 14:149 154 Autoantibodies to Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein in Coronary Artery Disease Yaniv Sherer, Alexander Tenenbaum, Miri Blank, Joseph Shemesh, Dror Harats, Enrique Z. Fisman, Sonja Praprotnik,
S. I. Smiyan et al. ISSN IJMMR 2017 Vol. 3 Issue 2. S. I. Smiyan, B. O. Koshak, I. V. Gnatko
 International Journal of Medicine and Medical Research 2017, Volume 3, Issue 2, p. 5-9 copyright 2017, TSMU, All Rights Reserved DOI 10.11603/ijmmr.2413-6077.2017.2.7935 ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION AND CARDIOVASCULAR
International Journal of Medicine and Medical Research 2017, Volume 3, Issue 2, p. 5-9 copyright 2017, TSMU, All Rights Reserved DOI 10.11603/ijmmr.2413-6077.2017.2.7935 ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION AND CARDIOVASCULAR
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /07/$32.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.081
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.081
Progression of Early Carotid Atherosclerosis Is Only Temporarily Reduced After Antibiotic Treatment of Chlamydia pneumoniae Seropositivity
 Progression of Early Carotid Atherosclerosis Is Only Temporarily Reduced After Antibiotic Treatment of Chlamydia pneumoniae Seropositivity Dirk Sander, MD; Kerstin Winbeck, MD; Jürgen Klingelhöfer, MD;
Progression of Early Carotid Atherosclerosis Is Only Temporarily Reduced After Antibiotic Treatment of Chlamydia pneumoniae Seropositivity Dirk Sander, MD; Kerstin Winbeck, MD; Jürgen Klingelhöfer, MD;
Current limitations in the management of cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis
 Current limitations in the management of cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis I.C. Scott 1,2,3, F. Ibrahim 2, D. Johnson 3, D.L. Scott 2,4, G.H. Kingsley 2,3 1 Department of Rheumatology, Guy s
Current limitations in the management of cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis I.C. Scott 1,2,3, F. Ibrahim 2, D. Johnson 3, D.L. Scott 2,4, G.H. Kingsley 2,3 1 Department of Rheumatology, Guy s
Flatter Diurnal Cortisol Slope on Workdays is Associated with Pre-clinical Atherosclerosis
 Flatter Diurnal Cortisol Slope on Workdays is Associated with Pre-clinical Atherosclerosis Karissa G. Miller, B.A., Thomas W. Kamarck, Ph.D., Matthew F. Muldoon, M.D., Peter J. Gianaros, Ph.D., & Stephen
Flatter Diurnal Cortisol Slope on Workdays is Associated with Pre-clinical Atherosclerosis Karissa G. Miller, B.A., Thomas W. Kamarck, Ph.D., Matthew F. Muldoon, M.D., Peter J. Gianaros, Ph.D., & Stephen
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration. EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006
 Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population
 + Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
+ Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
PULSE WAVE VELOCITY AS A NEW ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 PULSE WAVE VELOCITY AS A NEW ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR ATHEROSCLEROSIS Introduction Hirohide Yokokawa, M.D., Ph.D. 1 , Aya Goto, M.D., MPH, Ph.D. 2 , and Seiji Yasumura, M.D., Ph.D.
PULSE WAVE VELOCITY AS A NEW ASSESSMENT TOOL FOR ATHEROSCLEROSIS Introduction Hirohide Yokokawa, M.D., Ph.D. 1 , Aya Goto, M.D., MPH, Ph.D. 2 , and Seiji Yasumura, M.D., Ph.D.
