Todd A. Evans, Sharon N. Domorski, Wayne J. Sebastianelli, Margot Putukian, and Jay N. Hertel
|
|
|
- Natalie Bruce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Studies Forefoot Pain in a Female College Soccer Player Todd A. Evans, Sharon N. Domorski, Wayne J. Sebastianelli, Margot Putukian, and Jay N. Hertel Idiopathic forefoot pain, often termed metatarsalgia, is a common complaint among running athletes. Whereas several causes are often included in the differential diagnosis, Freiberg s infraction is rarely considered. The signs and symptoms present with Freiberg s infraction however, can mimic those present with more common forefoot injuries. The article presents the case of a female Division-I college soccer player who developed and was successfully treated for bilateral Freiberg s infraction. Her initial complaint of unilateral forefoot pain, induced only by vigorous running, progressed to intolerable bilateral forefoot pain with light exercise. Conservative treatment was unsuccessful, and therefore surgery was required to enable her continued athletic participation. As with all weight-bearing joints, clinicians need to be aware of the potential for progressive degenerative changes at the metatarsal heads and the steps used in the evaluation and subsequent treatment of Freiberg s infraction. Key Words: Freiberg s infraction, avascular necrosis, sclerosis, osteochondrosis, metatarsal head Evans TA, Domorski SN, Sebastianelli WJ, Putukian M, Hertel JN. Forefoot pain in a female college soccer player. J Sport Rehabil. 2003;12: Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Freiberg s infraction is not commonly considered when athletes present with atraumatic forefoot pain. Freiberg s infraction is osteochondrosis with associated flattening, fragmentation, and sclerosis of the metatarsal head. 1 Although classically associated with the second metatarsal, 1 Freiberg s infraction has been reported at the third, 2-6 fourth, 2,3 and first 7 metatarsal heads, as well. When a final diagnosis of Freiberg s infraction is made, conservative treatments, similar to those implemented with other forefoot injuries, are attempted to alleviate pain and restore function. If conservative efforts fail, however, surgical intervention is necessary. 3,4,7 Our purpose is to present the case of a female intercollegiate soccer player who underwent surgical debridement for bilateral Freiberg s infraction and successfully returned to competition. Evans is with the Division of Athletic Training, University of Northern Iowa, Cedar Falls, IA Domorski is with HealthAmerica, State College, PA Sebastianelli and Putukian are with the Center for Orthopaedic and Sports Medicine, and Hertel, the Athletic Training Research Laboratory, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
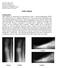
2 Forefoot Pain in a Soccer Player 273 Case Report During her sophomore season, a 20-year-old female intercollegiate soccer player experienced a burning, localized pain in her left forefoot, specifically over the second and third metatarsal heads. She denied trauma, prior injury, or bilateral symptoms. Her pain was persistent during running and pivoting but was relieved with rest. She denied numbness or tingling and had no ankle pain. Her examination by the team physician revealed localized swelling at the third metatarsal head and pain with passive and active range of motion at the third metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint. Distal metatarsal compression produced pain. Her distal neurovascular examination and ankle range of motion were normal. Radiographs revealed a crescent sign and collapse of her third left metatarsal head and deformation of the second right metatarsal head (Figure 1), consistent with Freiberg s disease. Figure 1 Plantar-view radiographs of the left and right forefeet. Note the deformity, flattening, and fragmentation of the third metatarsal head of the left foot and the second metatarsal head of the right foot.
3 274 Evans et al After consulting the team orthopedist, she chose conservative treatment over season-ending surgery. She was treated with prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, cold-water immersion, ultrasound, massage, and heel-cord stretching. Although she was able play in games, she eliminated excessive running or sprinting during practice, relying on pool running for conditioning. Although she displayed normal foot contact while walking, her running gait consisted exclusively of forefoot contact during foot strike, midsupport, and takeoff. To reduce forefoot contact forces, neutral orthotics with a metatarsal arch pad were prescribed. Attempts to alter her running style by encouraging heel strike were unsuccessful. Although still symptomatic, she completed her sophomore season. She improved once the season ended and her activity level decreased. As she began off-season conditioning, however, her symptoms returned. Kicking and jogging were now intolerable. In addition, she developed similar pain and stiffness in her right forefoot, with a bilateral decrease in forefoot motion. Follow-up radiographs revealed progressive deformity of the third left and second right metatarsal heads, with flattening of the articular surfaces, subchondral sclerosis, and early marginal spurring consistent with Freiberg s infraction. As is also consistent with Freiberg s disease, an MRI revealed joint effusion and flattening of the third left and second right MTP joints, with focal low-signal intensity seen in the subchondral region of third left and second right metatarsal heads. No acute fracture or free fragment was seen with either imaging technique. Because of the condition s progression and severity, the athlete elected surgery. In the spring, she underwent surgery on both feet, 1 month apart. The procedure on the third left metatarsal included an excisional arthroplasty and debridement of osteophytes in the dorsal half of the MTP joint. At the time of surgery, the capsule was noted to contain a large amount of gelatinous fluid with the development of a pseudoganglion. Small rice bodies in the joint were also removed. Two large, loose joint fragments attached by soft tissue to the periosteum but freely mobile within the joint were also debrided. The remaining dorsal 40% of the articular surface was completely free and peeled away from the bone and was nonsalvageable. The subchondral bone surface in this area was curetted to form a stable base and provide a more congruent joint surface (Figure 2). A K-wire was used to drill holes through the end of the sclerotic metatarsal head to ensure reinstitution of vascular supply and promote fibrocartilaginous ingrowth. Bleeding through these holes was easily seen postdrilling. The volar 30% of the joint had a normal subchondral structure and articular surface. The athlete s postoperative range of motion was significantly improved, and the articular surface appeared symmetric with that of the fourth ray (Figure 2, left). The right second metatarsal head had similar findings, and an almost identical procedure was performed on it (Figure 2, right).
4 Forefoot Pain in a Soccer Player 275 Figure 2 Six-month postoperative plantar-view radiographs of the left and right forefeet. Note the more congruent joint surface (compared with preoperative views) of the subchondral bone of the third metatarsal head of the left foot and the second metatarsal head of the right foot. Postoperative care included weight bearing as tolerated and a rigid-soled postoperative shoe. Aggressive rehabilitation began 2 weeks after each surgery and included active and passive MTP range of motion, massage to prevent adhesions, joint mobilization to promote normal forefoot motion, and thermal modalities. Over the next 3 months, as healing progressed, the athlete continued progressive exercise using pain as her guide. Three and a half months after surgery, she returned without limitations to begin her junior season. Throughout the season, however, she experienced bilateral pain, swelling, and stiffness. Conservative pain control included metatarsal pads fixed in orthotics, prescription NSAIDS, range-ofmotion exercises, and thermal modalities. Despite the continued discomfort, the athlete completed the season. She reduced her postseason activity, however, reducing her symptoms. The following spring, she participated in normal off-season workouts and successfully returned to complete her senior season without pain. She is currently 3 years postoperative and denies experiencing any significant pain
5 276 Evans et al in her feet, although she continues to wear orthotics. She continues to exercise regularly without foot pain. Currently she is coaching soccer but no longer playing competitively. Discussion Freiberg s infraction in the general or athletic population is not considered a common disorder, 4 although we found no specific epidemiological data as to its incidence. It has been reported in both men and women of various ages, 5-8 although the disorder is most common in adolescent females between 10 and 15 years of age and young athletes who perform on their toes in events such as sprinting, jumping, and dancing. 4,9-13 Bilateral occurrence is rare, being reported in only 6% of cases 2 to 10% of cases. 4,14 In a summary of 88 surgical cases of Freiberg s infraction, Gauthier and Elbaz 2 reported that 68% involved the second metatarsal head, 27% involved the third, and 3% involved the fourth. They reported no cases of multiple lesions unilaterally. 2 Although Freiberg s infraction was initially described as aseptic necrosis of the metatarsal heads, 15 there appears to be debate as to the true etiology of the disease. 7 Infraction implies that an incomplete fracture is present, and in adolescent cases this is true. It is generally accepted that in adolescents, the growing epiphysis is in some way affected, and the condition is therefore appropriately defined as avascular necrosis or osteochondrosis. This has been supported through scintigraphic imaging of adolescents displaying active revascularization surrounding the epiphysis before any significant radiographic findings. 10 This is a common indicator of avascular necrosis. Gauthier and Elbaz 2 classified the anatomic evolution of the disease in 5 specific stages: (0) subchondral fatigue fracture with normal X rays, (1) osteonecrosis without deformity, (2) osteonecrosis with crushing deformity, (3) cartilaginous tearing, and (4) degeneration of the MTP joint. In addition, Viladot and Viladot 15 described the progression of the disease, beginning with mechanical compression and subsequent spasm of the arteries supplying the metatarsal head. The spasm results in ischemia of the epiphysis, and continued compression causes arterial occlusion and necrosis. The necrotic epiphyseal bone will be resorbed and remodeled under the mechanical load. Devoid of adequate blood supply, however, the bone will subsequently collapse, resulting in arthrosis of the MTP joint. Similar to Osgood Schlatter and Legg Perthes disease, insult to the epiphysis adequately explains the adolescent manifestation of Freiberg s disease. Kehr 3 suggests that the symptoms of inflammation might resolve initially during adolescence but reappear later in life. The onset in adults, however, might also be linked to impingement of the osteochondral cartilage, in addition to a compromised blood supply that occurs after growth. Young et al 8 suggest that in skeletally mature adults, shearing forces during
6 Forefoot Pain in a Soccer Player 277 the toe-off phase are responsible for the pathogenesis of Freiberg s infraction, as opposed to vascular disruption. Based on cadaver examinations, they explain that during toe-off, the phalanges produce a shearing force at the dorsal aspect of the metatarsal heads, causing separation between the mineralized and nonmineralized articular cartilage at the metatarsal head. 8 This leads to the formation of osteochondritis dissecans and eventually degeneration within the MTP joint. Regardless of the true nature of the pathology, the cause is consistently linked to abnormal mechanical conditions at the affected metatarsal head. Gauthier and Elbaz 2 reported that the lesions were only present on the metatarsals bearing the most weight. Furthermore, they recounted that 50% of their cases were attributed to hallux valgus, 30% demonstrated excessive length of the affected metatarsal, and 6% were associated with rapid weight gain. This concept (unusual loading) was supported by Bayliss and Klenerman, 5 who reported the cases of 3 adults who, after unrelated forefoot surgery, developed avascular necrosis in the lesser metatarsal heads as a result of altered forefoot mechanics. Freiberg s infraction has also been linked with other anomalies that can alter weight distribution, such as Morton s toe. 9 The high occurrence in women has been linked to wearing high-heeled shoes, which creates additional forces at the MTP joints and allows for greater MTP dorsiflexion during toe-off. In the case of our soccer player, we think that her running gait, which consisted of forefoot and toe contact only, was a causative factor. Analysis of her running gait revealed that it was devoid of any heel strike bilaterally. Whereas this is common during sprinting, it is unusual to maintain this pattern during an endurance event such as soccer. The initial symptom of Freiberg s infraction is typically localized pain over the affected MTP joint during standing, walking, running, or sprinting that ceases with rest. 4,13 High-heeled or pointed shoes might also produce pain. The athlete might complain of stiffness, and active and passive range of motion will be limited. 4,13 Dorsal effusion and signs of synovitis are often present, as well. 9,13 In the advanced stages of the disease, crepitus, locking, palpable osteophytic defects, hypertrophy of the joint surface, and extension contractures might be present. 3,13 These symptoms might resolve and then reappear later in life with an increase in activity or alteration in loading. 3 Although seldom reported symptomatically, evaluation of the contralateral side might enable early detection and preventive intervention before significant structural changes occur. 12 Imaging techniques can include simple radiographs including AP, lateral, and oblique views. These views will often reveal flattening, fragmentation, and a crescent sign with longstanding involvement of the metatarsal head. Occasionally, the plain-view X rays might only reveal a widened joint space resulting from chronic synovitis. When plain-view X rays do not reveal any significant findings, additional supplemental imaging techniques including bone scan and MRI can be helpful. With the progression of MRI techniques, however, bone scanning is becoming obsolete.
7 278 Evans et al Normal X rays in the presence of pain might indicate that nonsurgical treatments will be effective. This can include techniques such as those recommended by Canale, 9 including a short-leg walking cast with toe extension for approximately 6 12 weeks along with complete cessation of all painful activity. Ary 16 suggested the use of a donut pad surrounding the metatarsal head and timely steroid injections. Rigid forefoot orthotics that prevent dorsiflexion of the toes can reduce shear forces at the MP joint and can therefore be helpful in diminishing pain. In individuals with longstanding disease or progression of deformity, surgical intervention is often necessary. Techniques including excisional arthroplasty, internal fixation of the metatarsal-head fragment, and core decompression can be considered. 4,12 When fragment fixation is selected, the metatarsal head, articular surface, and underlying subchondral bone must be suitable to allow appropriate purchase of the fixation device in order to completely stabilize the metatarsal head to the metatarsal shaft. In most cases, however, clinical findings at the time of surgery do not allow fixation, because bone fragmentation has often occurred in the articular fragments. In these instances, drilling the remaining sclerotic distal metatarsal is necessary in order to reinstitute vascular supply to this surface so that a fibrocartilaginous cap can be developed. 7,12 Clearly, this is not as functional as articular cartilage, but it will facilitate improved MTP function. Overall, the goals in treatment and surgery are to minimize discomfort and improve function. High-demand athletes will clearly stretch the limits of surgical technique because of stress that is applied to the metatarsophalangeal joints during running and jumping activities. This injury often ultimately leads to complete cessation of sporting activity and the untimely discontinuation of an athlete s sport or career. This case represents a successful outcome for a female intercollegiate soccer player with Freiberg s disease. Her case was unique not only because Freiberg s infraction is rarely presented as an athletic injury but also because her symptoms manifested beyond adolescence and occurred bilaterally. Conservative treatment was unsuccessful so surgery was necessary. Although it is impossible to establish a causal relationship, she might have developed Freiberg s infraction as a result of her toes only running style. This disorder can be misinterpreted as more common stress-related persistent foot injuries, even though the signs and symptoms are specific to the metatarsal heads. Acknowledgment This project was presented at the 51st Annual Meeting of the National Athletic Trainers Association (Nashville, Tenn, June 29, 2000).
8 Forefoot Pain in a Soccer Player 279 References 1. Freiberg A. Infraction of the 2nd metatarsal bone a typical injury. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1914;19: Gauthier G, Elbaz R. Freiberg s infraction: a subchondral bone fatigue fracture. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1979;142: Kehr LE. A new surgical technique for the correction of Freiberg s infraction. J Am Podiatry Assoc. 1982;72(3): Sproul J, Klaaren H, Mannarino F. Surgical treatment of Freiberg s infraction in athletes. Am J Sports Med. 1993;21(3): Bayliss NC, Klenerman L. Avascular necrosis of lesser metatarsal heads following surgery. Foot Ankle. 1989;10(3): Gurin J. Joint occurrence of aseptic necrosis of the head of the 3rd metacarpal and Freiberg s disease. Acta Chirurg Hung. 1985;26(1): Maresca G, Adriani E, Falez F, Mariani PP. Arthroscopic treatment of bilateral Freiberg s infraction. Arthroscopy. 1996;12(1): Young MC, Fornasier VL, Cameron HU. Osteochondral disruption of the 2nd metatarsal: a variant of Freiberg s infraction. Foot Ankle. 1987;8(2): Canale ST. Osteochondroses and related problems of the foot and ankle. In: Delee JC, Drez D, eds. Orthopaedic Sports Medicine: Principles and Practice. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders; 1994: Mandell GA, Harcke HT. Scintigraphic manifestations of infraction of the 2nd metatarsal (Freiberg s disease). J Nucl Med. 1987;28(2): Fu FH, Gomez W. Bilateral avascular necrosis of the first metatarsal head in adolescence: a case report. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1989;246: Freiberg A, Freiberg R. Core decompression as a novel treatment for early Freiberg s infraction of the 2nd metatarsal head. Orthopedics. 1995;18(12): Scartozzi G, Schram A, Janigian J. Freiberg s infraction of the 2nd metatarsal head with formation of multiple loose bodies [review]. J Foot Surg. 1989;28(3): Ozonoff MB. Pediatric Orthopedic Radiology. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders; Viladot A, Viladot A. Osteochondroses: aseptic necrosis of the foot. In: Jahss M, ed. Disorders of the Foot and Ankle. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders; 1991: Ary KR, Turbino M. Freiberg s infraction: an osteochondritis of the metatarsal head. J Am Podiatry Assoc. 1979;69(2):
FREIBERG S INFRACTION TREATMENT WITH METATARSAL NECK DORSAL CLOSING WEDGE OSTEOTOMY: REPORT OF TWO CASES
 FREIBERG S INFRACTION TREATMENT WITH METATARSAL NECK DORSAL CLOSING WEDGE OSTEOTOMY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Sung-Yen Lin, 1 Yuh-Min Cheng, 1,2 and Peng-Ju Huang 1,2 1 Department of Orthopedics, Kaohsiung
FREIBERG S INFRACTION TREATMENT WITH METATARSAL NECK DORSAL CLOSING WEDGE OSTEOTOMY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Sung-Yen Lin, 1 Yuh-Min Cheng, 1,2 and Peng-Ju Huang 1,2 1 Department of Orthopedics, Kaohsiung
6/5/2018. Forefoot Disorders. Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust (Barnet & Chase Farm Hospitals) Hallux Rigidus
 Forefoot Disorders Mr Pinak Ray (MS, MCh(Orth), FRCS, FRCS(Tr&Orth)) Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust (Barnet & Chase Farm Hospitals) E: ray.secretary@uk-conslutants Our
Forefoot Disorders Mr Pinak Ray (MS, MCh(Orth), FRCS, FRCS(Tr&Orth)) Highgate Private Hospital (Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust (Barnet & Chase Farm Hospitals) E: ray.secretary@uk-conslutants Our
Dorsiflexory Wedge Osteotomy to Treat Freiberg s Infraction of the Second Metatarsal Head: A case report
 Open Access Publication Dorsiflexory Wedge Osteotomy to Treat Freiberg s Infraction of the Second Metatarsal Head: A case report 1 2 by Georgeanne Botek, DPM, FACFAS, Martha A. Anderson, DPM, George Balis,
Open Access Publication Dorsiflexory Wedge Osteotomy to Treat Freiberg s Infraction of the Second Metatarsal Head: A case report 1 2 by Georgeanne Botek, DPM, FACFAS, Martha A. Anderson, DPM, George Balis,
30 Freiberg's Disease
 30 Freiberg's Disease T.W.D. SMITH D.N. KREIBICH Infraction of the second metatarsal bone was first described by Cincinnati surgeon Albert Freiberg in 1914. 1 In much of the English-speaking world the
30 Freiberg's Disease T.W.D. SMITH D.N. KREIBICH Infraction of the second metatarsal bone was first described by Cincinnati surgeon Albert Freiberg in 1914. 1 In much of the English-speaking world the
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot. Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada.
 Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Hallux Rigidus. Normal. Normal Arthritis Arthritis
 Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Hallux Rigidus Explanation: Hallux Rigidus is characterized as degeneration
Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Hallux Rigidus Explanation: Hallux Rigidus is characterized as degeneration
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries
 Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Juvenile Osteochondroses
 Juvenile Osteochondroses Nathalie Gaulier, MD Sports Medicine Physician Cook Children s Medical Center Definition General term for disorders that affect one or more ossification centers in children Encompasses
Juvenile Osteochondroses Nathalie Gaulier, MD Sports Medicine Physician Cook Children s Medical Center Definition General term for disorders that affect one or more ossification centers in children Encompasses
Modified Weil Osteotomy for the Treatment of Freiberg s Disease
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:300-306 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.300 Modified Weil Osteotomy for the Treatment of Freiberg s Disease Jiyoun Kim, MD, Woo Jin Choi, MD*,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:300-306 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.300 Modified Weil Osteotomy for the Treatment of Freiberg s Disease Jiyoun Kim, MD, Woo Jin Choi, MD*,
Injuries to the Foot. NOCROP Sports Medicine and Therapy
 Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months.
 Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Elbow Injuries in Young Athletes!
 Elbow Injuries in Young Athletes! Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM! Director Sports Medicine Campbell University! Head Team Physician, Associate Professor Sports Medicine Disclosures None based on the content
Elbow Injuries in Young Athletes! Andrew Martin DO, MBA, CAQSM! Director Sports Medicine Campbell University! Head Team Physician, Associate Professor Sports Medicine Disclosures None based on the content
Anterior ankle impingement in sports Hrefna Thorbjorg Hakonardottir
 Anterior ankle impingement in sports Hrefna Thorbjorg Hakonardottir Anterior ankle impingement in sports Ankle impingement syndromes are classified by their anatomical location around the tibiotalar joint
Anterior ankle impingement in sports Hrefna Thorbjorg Hakonardottir Anterior ankle impingement in sports Ankle impingement syndromes are classified by their anatomical location around the tibiotalar joint
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
Clinical Case Series (vs. Case Study) Patient #1 Progression Male Soccer Athlete 5/26/2016
 Patellar Chondroplasty With Gel-One Cross-Linked Hyaluronate Injection for the Treatment of Grade III Patellar Chondromalacia in Collegiate Male Athletes: A Case Series David Tomchuk, MS, ATC, LAT, CSCS
Patellar Chondroplasty With Gel-One Cross-Linked Hyaluronate Injection for the Treatment of Grade III Patellar Chondromalacia in Collegiate Male Athletes: A Case Series David Tomchuk, MS, ATC, LAT, CSCS
9180 KATY FREEWAY, STE. 200 (713)
 OSTEOCHONDRAL AUTOGRAFT TRANSPLANTATION Patella/Trochlea Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Goals: - Protection of healing tissue from load and shear forces - Decrease pain
OSTEOCHONDRAL AUTOGRAFT TRANSPLANTATION Patella/Trochlea Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Goals: - Protection of healing tissue from load and shear forces - Decrease pain
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
Hallux Rigidus & Silastic Total Implants
 Hallux Rigidus & Silastic Total Implants JOSHUA L. MOORE, DPM FACFAS ASSISTANT DEAN OF EDUCATIONAL AFFAIRS TUSPM CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF SURGERY Definitions Hallux Limitus 1 st MTPJ range of motion
Hallux Rigidus & Silastic Total Implants JOSHUA L. MOORE, DPM FACFAS ASSISTANT DEAN OF EDUCATIONAL AFFAIRS TUSPM CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF SURGERY Definitions Hallux Limitus 1 st MTPJ range of motion
Bunions. A bunion is a painful bony bump that develops on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. Bunions are often referred to as hallux valgus.
 Bunions A bunion is a painful bony bump that develops on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. Bunions are often referred to as hallux valgus. Bunions develop slowly. Pressure on the big toe joint
Bunions A bunion is a painful bony bump that develops on the inside of the foot at the big toe joint. Bunions are often referred to as hallux valgus. Bunions develop slowly. Pressure on the big toe joint
OSTEOCHONDRAL AUTOGRAFT TRANSPLANTATION
 OSTEOCHONDRAL AUTOGRAFT TRANSPLANTATION FEMORAL CONDYLE REHABILITATION PROGRAM PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Protection of healing tissue from load and shear forces Decrease pain and effusion
OSTEOCHONDRAL AUTOGRAFT TRANSPLANTATION FEMORAL CONDYLE REHABILITATION PROGRAM PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Protection of healing tissue from load and shear forces Decrease pain and effusion
Trainers. Anne-Marie O Connor Musculoskeletal Podiatrist
 Trainers Anne-Marie O Connor Musculoskeletal Podiatrist Agenda Background Tarso-navicular stress fractures Case Study Interventions and research Further Research Anatomy Anatomically, wedged between the
Trainers Anne-Marie O Connor Musculoskeletal Podiatrist Agenda Background Tarso-navicular stress fractures Case Study Interventions and research Further Research Anatomy Anatomically, wedged between the
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
fitting shoes, or repetitive stress. It also frequently arises from unknown causes.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
BUCKS MSK: FOOT AND ANKLE PATHWAY GP MANAGEMENT. Hallux Valgus. Assessment: Early Management. (must be attempted prior to any referral to imsk):
 Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS
 CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon. Monday, 29 April 13
 Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April 2013 Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Monday, 29 April 13 Topics Forefoot pain Hindfoot/Ankle pain Hallux rigidus Bunions Toe deformity Mortons
Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April 2013 Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Monday, 29 April 13 Topics Forefoot pain Hindfoot/Ankle pain Hallux rigidus Bunions Toe deformity Mortons
How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia
 220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Foot & Ankle. Mr Peter Black, FRCSEd. Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Anglesea Clinic Orthopaedics
 Foot & Ankle Mr Peter Black, FRCSEd Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Anglesea Clinic Orthopaedics Foot & Ankle Problems - Myths and Leg-ends All foot and ankle surgery is cripplingly painful There s no point
Foot & Ankle Mr Peter Black, FRCSEd Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Anglesea Clinic Orthopaedics Foot & Ankle Problems - Myths and Leg-ends All foot and ankle surgery is cripplingly painful There s no point
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Case report. Your Diagnosis?
 Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity
 Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
Re+Line Bunion Correction System for Correction of Hallux Abducto Valgus Deformity Amber M. Shane, DPM, FACFAS 1, Christopher L. Reeves, DPM, FACFAS 1 1. Orlando Foot & Ankle Clinic, Orlando, FL Abstract
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses. Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital
 Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
Current Thinking of the Osteochondroses Diego Jaramillo, M.D., M.P.H. Department of Radiology Stanford Children s Hospital What is an osteochondrosis? Abnormal endochondral ossification and epiphyseal
Rehabilitation Protocol:
 Rehabilitation Protocol: Patellofemoral resurfacing: Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS), Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) and Microfracture Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey
Rehabilitation Protocol: Patellofemoral resurfacing: Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS), Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) and Microfracture Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey
Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Treatment and evolution.
 Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Treatment and evolution. J. R. Valentí Nín; M. Leyes; D. Schweitzer ABSTRACT We performed a retrospective study on 21 patients affected by unilateral spontaneous
Spontaneous osteonecrosis of the knee. Treatment and evolution. J. R. Valentí Nín; M. Leyes; D. Schweitzer ABSTRACT We performed a retrospective study on 21 patients affected by unilateral spontaneous
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Knee Arthroscopy The knee is the body's largest joint, and the place where the femur, tibia, and patella meet to form a hinge-like joint. These bones are supported by a large
Foot and ankle update
 Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Burwood Road, Concord Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Turf Toe Injury By Todd Gothelf Foot, Ankle, Shoulder History
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 119 Lethbridge Street, Penrith 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Turf Toe Injury By Todd Gothelf Foot, Ankle, Shoulder History
Localized collection of pus in a cavity
 Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia
 Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Section 6: Preoperative Planning
 Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines
 Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Brace: Protect healing tissue from load and shear forces Decrease pain and effusion Restore full passive knee extension
Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Brace: Protect healing tissue from load and shear forces Decrease pain and effusion Restore full passive knee extension
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery
 Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
KNEE MICROFRACTURE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE
 KNEE MICROFRACTURE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Progression is time and criterion-based, dependent on soft tissue healing, patient demographics and clinician evaluation. Contact Ohio State Sports Medicine
KNEE MICROFRACTURE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE Progression is time and criterion-based, dependent on soft tissue healing, patient demographics and clinician evaluation. Contact Ohio State Sports Medicine
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed.
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
These are rehabilitation guidelines for OSU Sports Medicine patients. Please contact us at if you have any questions.
 OSU Sports Medicine Knee Microfracture Rehabilitation Guidelines These are rehabilitation guidelines for OSU Sports Medicine patients. Please contact us at 614-293-2385 if you have any questions. Rehabilitation
OSU Sports Medicine Knee Microfracture Rehabilitation Guidelines These are rehabilitation guidelines for OSU Sports Medicine patients. Please contact us at 614-293-2385 if you have any questions. Rehabilitation
Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery
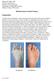 Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery A bunion (also called hallux
Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Bunionectomy-Forefoot Surgery A bunion (also called hallux
No Disclosures. Topics. Pediatric ACL Tears
 Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes No Disclosures Zachary Stinson, M.D. 2 Topics ACL Tears and Tibial Eminence Fractures Meniscus Injuries Discoid Meniscus Osteochondritis Dessicans Patellar
Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries
 369 ORIGINAL Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries Naoto Suzue 1, Tetsuya Matsuura 1, Toshiyuki Iwame 2, Daisuke Hamada 1, Tomohiro Goto 1, Yoichiro Takata 1, Takenobu
369 ORIGINAL Prevalence of childhood and adolescent soccer-related overuse injuries Naoto Suzue 1, Tetsuya Matsuura 1, Toshiyuki Iwame 2, Daisuke Hamada 1, Tomohiro Goto 1, Yoichiro Takata 1, Takenobu
HEMI IMPLANT ARTHROPLASTY FOR THE SECOND METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINT
 C H A P T E R 1 5 HEMI IMPLANT ARTHROPLASTY FOR THE SECOND METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINT Joe T. Southerland, DPM Mickey D. Stapp, DPM INTRODUCTION Hemi-implant arthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal
C H A P T E R 1 5 HEMI IMPLANT ARTHROPLASTY FOR THE SECOND METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINT Joe T. Southerland, DPM Mickey D. Stapp, DPM INTRODUCTION Hemi-implant arthroplasty of the first metatarsophalangeal
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Rehabilitation Protocol: Distal Femoral/Proximal Tibial Microfracture and Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS)
 Rehabilitation Protocol: Distal Femoral/Proximal Tibial Microfracture and Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS) Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington 781-744-8650
Rehabilitation Protocol: Distal Femoral/Proximal Tibial Microfracture and Osteochondral Autograft Transplantation (OATS) Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington 781-744-8650
WHAT IS ARTHRITIS OF THE BIG TOE (HALLUX RIGIDUS)?
 Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS ARTHRITIS OF THE BIG TOE (HALLUX RIGIDUS)? A common term for arthritis of the metatarsophalangeal
Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS ARTHRITIS OF THE BIG TOE (HALLUX RIGIDUS)? A common term for arthritis of the metatarsophalangeal
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM
 AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
Comparison of Hallux Rigidus Surgical Treatment Outcomes Between Active Duty and Non Active Duty Populations
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Hallux Rigidus Surgical Treatment Outcomes Between Active Duty and Non Active Duty Populations A Retrospective Review Marc D. Jones, DPM* Kerry J. Sweet, DPM Background:
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Hallux Rigidus Surgical Treatment Outcomes Between Active Duty and Non Active Duty Populations A Retrospective Review Marc D. Jones, DPM* Kerry J. Sweet, DPM Background:
A Patient s Guide to Hallux Rigidus
 A Patient s Guide to Hallux Rigidus Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Hallux Rigidus Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Anatomy 1% 29% 64% 6%
 Mortons Neuroma Perineural fibrosis of the plantar digital nerve Females 8-10 3 rd plantar webspace most commonly effected Burning pain Sensory changes 3&4 digits / interdigital space Etiology Excessive
Mortons Neuroma Perineural fibrosis of the plantar digital nerve Females 8-10 3 rd plantar webspace most commonly effected Burning pain Sensory changes 3&4 digits / interdigital space Etiology Excessive
Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol
 Brian E. Camilleri, DO 2610 Enterprise Dr Anderson, IN 46013 Phone: (765) 683-4400 Fax: (765) 642-7903 www.ciocenter.com Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide
Brian E. Camilleri, DO 2610 Enterprise Dr Anderson, IN 46013 Phone: (765) 683-4400 Fax: (765) 642-7903 www.ciocenter.com Meniscus Repair Rehabilitation Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide
Increased pressures at
 Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
9180 KATY FREEWAY, STE. 200 (713)
 AUTOLOGOUS CHONDROCYTE IMPLANTATION Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Goals: - Protect healing tissue from load and shear forces - Decrease pain and effusion
AUTOLOGOUS CHONDROCYTE IMPLANTATION Femoral Condyle Rehabilitation Guidelines PHASE I - PROTECTION PHASE (WEEKS 0-6) Goals: - Protect healing tissue from load and shear forces - Decrease pain and effusion
The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the
 The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE
 POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
POSTERIOR TIBIAL TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Posterior tibial tendon rupture is a complete tear of the posterior tibial tendon. This structure is the tendon attachment of leg muscles (posterior
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
June 2013 Case Study. Author: T. Walker Robinson, MD, MPH, Nationwide Children s Hospital
 June 2013 Case Study Author: T. Walker Robinson, MD, MPH, Nationwide Children s Hospital Chief Complaint: Right ankle pain HPI: A 10 year old female dancer presents to the clinic with a five day history
June 2013 Case Study Author: T. Walker Robinson, MD, MPH, Nationwide Children s Hospital Chief Complaint: Right ankle pain HPI: A 10 year old female dancer presents to the clinic with a five day history
Lesser Toe Correction
 Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Lesser Toe Correction Lesser toe deformities are classified
Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Lesser Toe Correction Lesser toe deformities are classified
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Inter Digital Neuralgia (Morton s Neuroma)
 A Patient s Guide to Inter Digital Neuralgia (Morton s Neuroma) The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of two specialist
A Patient s Guide to Inter Digital Neuralgia (Morton s Neuroma) The foot and ankle unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of two specialist
A Patient s Guide to Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head
 A Patient s Guide to Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information
A Patient s Guide to Osteonecrosis of the Humeral Head 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information
Goals. Initial management skeletal trauma. Physical Exam ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT 12/4/2010
 ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
HALLUX LIMITUS VS. TURF TOE
 VS. TURF TOE EATA Conference 2015 { Dr Jim Sullivan DPM ATC North Smithfield Podiatry Foot and Ankle Consultant: University of Rhode Island Athletics Providence College Athletics Providence Bruins USA
VS. TURF TOE EATA Conference 2015 { Dr Jim Sullivan DPM ATC North Smithfield Podiatry Foot and Ankle Consultant: University of Rhode Island Athletics Providence College Athletics Providence Bruins USA
A Patient s Guide to Hallux Rigidus
 A Patient s Guide to Hallux Rigidus Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Hallux Rigidus Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
pull your toes and foot toward your head, you will feel this tissue tighten. WHAT CAUSES PLANTAR
 PLANTAR FASCIITIS AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? Plantar fasciitis is pain felt at the bottom of the heel. It is usually felt on the first step out of bed in the morning or when walking again
PLANTAR FASCIITIS AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? Plantar fasciitis is pain felt at the bottom of the heel. It is usually felt on the first step out of bed in the morning or when walking again
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Osteochondritis Dissecans
 Osteochondritis Dissecans Introduction Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a problem that affects the knee, mostly at the end of the big bone of the thigh (the femur). A joint surface damaged by OCD doesn't
Osteochondritis Dissecans Introduction Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) is a problem that affects the knee, mostly at the end of the big bone of the thigh (the femur). A joint surface damaged by OCD doesn't
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity
 REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
REVIEW Proximal metatarsal osteotomy and distal soft tissue reconstruction as treatment for hallux valgus deformity Michael J. Coughlin and J. Speight Grimes Boise, Idaho, USA (Received for publication
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective
 LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective Debra A. Zillmer, M.D. M&M Orthopaedics, Ltd 18 Year Old Experienced Cross Country Runner: Sept Sr Year Pain in left lower leg with running Pain now prevents
LEG LENGTH INEQUALITY: Sports Medicine Perspective Debra A. Zillmer, M.D. M&M Orthopaedics, Ltd 18 Year Old Experienced Cross Country Runner: Sept Sr Year Pain in left lower leg with running Pain now prevents
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT
 C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
Clinical results of modified Mitchell s osteotomy for hallux valgus augmented with oblique lesser metatarsal osteotomy
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):245-252 Clinical results of modified Mitchell s osteotomy for hallux valgus augmented with oblique lesser metatarsal osteotomy K Yamamoto, A Imakiire, Y Katori,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):245-252 Clinical results of modified Mitchell s osteotomy for hallux valgus augmented with oblique lesser metatarsal osteotomy K Yamamoto, A Imakiire, Y Katori,
Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion
 Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Proximal Inter-Phalangeal (PIP) Fusion Prepared in consultation with: Phinit Phisitkul, MD Department of Orthopedics and Rehabilitation University of Iowa
Dr. Huff Modified Brostrom Repair Rehabilitation Protocol:
 Dr. Huff Modified Brostrom Repair Rehabilitation Protocol: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of a patient who has undergone
Dr. Huff Modified Brostrom Repair Rehabilitation Protocol: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of a patient who has undergone
A Ware Injury in Collegiate Athletics- The Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocation
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 281-286 O 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. A Ware Injury in Collegiate Athletics- The Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocation Keith M. Gorse, Graham Johnstone, and Jennifer
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1993, 2, 281-286 O 1993 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. A Ware Injury in Collegiate Athletics- The Lisfranc Fracture-Dislocation Keith M. Gorse, Graham Johnstone, and Jennifer
Rehabilitation after ankle injuries
 Rehabilitation after ankle injuries Ahmed Thabet, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso What are our objectives?
Rehabilitation after ankle injuries Ahmed Thabet, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center El Paso What are our objectives?
Management of Chronic Elbow Pain
 Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY
 FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
