Introduction. A Short Review of Cutaneous Vasculitis. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction
|
|
|
- Marcus Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Short Review of Cutaneous Vasculitis Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology, William Beaumont Oakland University School of Medicine Staff Dermatopathologist Beaumont Hospital-Royal Oak, MI September 10, 2016 Introduction The vasculopathic reaction pattern is an extensive catch all comprising vasculopathies as well as acute leukocytoclastic vasculitis, neutrophilic dermatoses, chronic lymphocytic vasculitis and granulomatous vasculitis Key feature of many systemic diseases that involve the skin 9/1/ Introduction Diseases of cutaneous vessels important cause of morbidity, and sometimes mortality Basis for extensive multidisciplinary collaboration among rheumatologists, dermatologists, and dermatopathologists Introduction Morphologic groups include: Non inflammatory purpuras: extravasation of erythrocytes without inflammation or occlusion, i.e., senile purpura Vasculopathy: Vascular occlusion with associated downstream changes, i.e., skin ulceration and localized necrosis Introduction Urticaria: Immunity changes leads to vascular changes, leakage of intravascular contents into dermis (can overlap with acute vasculitis) Acute vasculitis: True inflammation of vessel walls, with fibrinoid necrosis, infiltration by neutrophils, and leukocytoclasis (neutrophilic debris) Introduction Non neutrophilic vasculitis: Inflammation of vessel walls, but driven by either lymphocytes or histiocytes with formation of granulomatous changes Neutrophilic dermatoses (i.e., Sweet syndrome): Dermal infiltration by neutrophils but acute vasculitis is secondary, not primary 1
2 Case 1 16 year old female with erythematous papules and nodules on her lower extremities. The biopsy is from a nodule on the left lower leg. Question 1: What is the best diagnosis for this lesion? A. Lupus panniculitis B. Polyarteritis nodosa C. Subcutaneous panniculitis like T cell lymphoma D. Lipodermatosclerosus E. Subcutaneous granuloma annulare 2
3 Polyarteritis nodosa Inflammation of small and medium sized muscular arteries Involves visceral organs like kidneys, liver, gastrointestinal tract and nervous system Constitutional symptoms are present, including fever, weight loss, fatigue, arthralgia, myalgia 5 year survival=50% Polyarteritis nodosa Can have a cutaneous only version Patients present with nodules, livedo reticularis, and/or ulceration involving the lower limbs (palpable purpura) Mild constitutional symptoms such as fever can be present Prognosis is very good, but recurrent and chronic course Polyarteritis nodosa Many causes documented, including formation of immune complexes, angiogenic cytokines, hepatitis B and C, and preceding bacterial infections Treatment includes corticosteroids under occlusion for cutaneous lesions, oral corticosteroids, and non steroidal anti inflammatory agents such as mycophenolate mofetil Polyarteritis nodosa Superficial biopsies may show no findings, so a deep incisional biopsy is recommended If an ulcer is present, take a biopsy from near the center of the ulcer, as the affected artery may be directly underneath Acute inflammation of small and medium sized arteries Polyarteritis nodosa Fibrinoid necrosis of vessel walls, fibrin thrombi formation, and infusion of walls with acute inflammatory cells Leukocytoclasis can be present Partial to full involvement of the vessel may be seen Some vessels may be uninvolved Polyarteritis nodosa Can see vessels at all stages of involvement/development (none to partial to full; early and late lesions) Can see deposition of IgM and sometimes C3 in vessel walls on direct immunofluorescence Older lesions show intimal thickening and luminal obliteration with an accompanying mononuclear infiltrate 3
4 Question 2: What is an important histologic differential diagnostic consideration? A. Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum B. Nodular vasculitis C. Pancreatic panniculitis D. Lupus panniculitis E. NK/T cell lymphoma Nodular vasculitis Erythema induratum-nodular vasculitis thought to be the same entity, presumably related to tuberculosis, regardless of whether organisms are obtained from lesions via cultures or PCR methodology Characterized by recurrent crops of tender erythematous nodules, predilection for calves Nodular vasculitis Inflammatory changes within subcutis predominantly Diffuse lobular panniculitis, with granulomatous inflammation, focal necrosis, and vasculitis Granulomas are poorly formed, and accompanied by mixed inflammation Nodular vasculitis Vasculitis involves all sizes of arteries and veins (separating this entity from both thrombophlebitis and polyarteritis nodosa) In nodular vasculitis, vasculitis and inflammatory changes involves contiguous lobules (diffuse), whereas in polyarteritis nodosa, inflammatory changes limited to the vicinity of the involved vessel (localized) Case 2 55 year old woman with multiple new lesions which the patient thought were spider bites. 4
5 Question 3. What is the best diagnosis for this entity? A. Lichen planus B. Dermatitis herpetiformis C. Degos disease D. Mucha Habermann syndrome E. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ Malignant atrophic papulosis (Degos disease) Rare multisystem vaso-occlusive disease Associated with infarctive lesions of visceral sites, particularly GI tract Crops of papules develop, evolve slowly to become umbilicated with a porcelain center and telangiectatic rim Finally, lesions resolve with an atrophic scar 5
6 Malignant atrophic papulosis (Degos disease) There are cutaneous lesions-only versions which have a benign course Histology: epidermal atrophy with overlying hyperkeratosis and wedge shaped area of cutaneous ischemia Dense lymphocytic infiltrate Overlap histologically with lichen sclerosus or early morphea Malignant atrophic papulosis (Degos disease) Endothelial swelling is seen of venules and to a lesser extent, arterioles Extensive deposition of mucopolysaccharides in the dermis, thought to be a secondary event Question 4: The patient was found to have several year history of abdominal pain and bleeding. Her follow up was set up with various specialists. Who should follow this patient? A. Podiatrist B. Endocrinologist C. Neurologist/neurosurgeon D. Allergist E. Oncologist Patient should be followed by neurologist or neurosurgeon for CNS events Degos disease is thought to be a multi system vaso occlusive phenomenon CNS events is a potential avenue of fatality Case 3 54 year old man with 2 episodes of 3rd/4th right toe swelling, pruritus, and erythema. 6
7 Question 5: What is the best diagnosis for this lesion? A. Lymphoma B. Pernio C. Bullous pemphigoid D. Syphilis E. Polymorphous light eruption Perniosis Localized inflammatory lesion which individuals experience secondary to cold weather Classic perniosis (chilblains): fingers, toes, sometimes ears Chilblain lupus: lesions occuring in the setting of lupus erythematosus that mimic pernio Equestrian perniosis: occurs on thighs and buttocks of female equestrians in winter Perniosis On histopathology, perniosis is considered a lymphocytic vasculitis Superficial and deep perivascular infiltrates of lymphocytes are seen as well as perieccrine inflammation Intramural inflammation and vessel wall thickening can be seen as well 7
8 Perniosis There can be subepidermal edema but this may not be fully formed Interface activity and dermal mucin deposition may accompany lesions of lupus erythematosus, and may be very extensive (more than cold related pernio) Perniosis A leukocytoclastic vasculitis is almost never seen Lack of subepidermal edema and deep infiltrate does not exclude this diagnosis: may depend on when along the disease process the biopsy was taken If lupus is suspected, further work up is indicated Question 6: Recently a study examined the expression of which marker in large atypical cells of pernio? A. CK5/6 B. PDL-1 C. Sox10 D. STAT-6 E. CD30 CD30 expression in large atypical lymphocytes A recent study from the Univ of Pennsylvania examined expression of CD30 in the large atypical cells of pernio Activated T cells that express CD30 can be a part of any inflammatory infiltrate and do not necessarily constitute a diagnosis of lymphoma Massey PR et al. Am J Dermatopathol Sep;36(9): Case 4 27 year old woman with right upper cheek lesion. 8
9 Question 7: What is the best diagnosis for this lesion? A. Granuloma faciale B. Eosinophilic fasciitis C. Arthropod bite reaction D. Lymphomatoid papulosis E. Mast cell disease Granuloma faciale Rare dermatosis manifesting as one or more brown red plaques or nodules Face, solitary Middle aged males Persistent, asymptomatic Thought to be a vasculitis 9
10 Granuloma faciale Dense polymorphous inflammatory infiltrate involving the reticular dermis Grenz zone Can extend to subcutis Eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes and histiocytes Endothelial swelling with perivascular deposition of fibrinoid material (toxic hyalin) Question 8: Granuloma faciale is thought to be related to which entity? A. Squamous cell carcinoma B. Mycosis fungoides C. Urticarial vasculitis D. Erythema elevatum diutinum E. Pityriasis rubra pilaris Erythema elevatum diutinum EED has many histologic similarities to GF but neutrophils tend to predominate over eosinophils No defined Grenz zone Toxic hyalin more well developed Clinical scenario very different EED is acrally and symmetrically distributed whereas GF is primarily on the face Case 5 52-year-old male with infectious process on the glans penis, now with 6 mm pustule with surrounding hyperpigmentation on the left foot. The clinical differential includes infectious vs. pustular arthropod vs. bullous disorder. 10
11 Question 9: What is the best diagnosis for these findings? A. Polyarteritis nodosa B. Vasculopathy C. Lupus D. Toxic epidermal necrolysis E. Impetigo Vascular occlusive diseases (vasculopathy) Complete or partial occlusion of vessels fibrin platelet thrombi, but also platelet rich thrombi (TTP), cryoglobulins, cholesterol plugs (atheromas), and fungi (Mucor) Clinically, can cause purpura, livedo reticularis, erythromelalgia, ulceration or infarction Vasculopathy Livedo reticularis=netlike pattern of interconnecting macular violaceous rings Primary livedo: increased visibility of venous plexus due to cold (most common cause of livedo) Secondary livedo: due to vasoocclusive disease Vasculopathy Vasculopathy Protein C/S deficiencies Prothrombin gene mutations Warfarin necrosis Disseminated intravascular coagulation Purpura fulminans Cryoglobulinemia Cholesterol/other emboli (infection for example) Antiphospholipid syndrome Factor V Leiden Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Protein C is a vitamin K dependent plasma glycoprotein which has important anticoagulation activities Homozygous deficiency=purpura fulminans as a child Heterozygous deficiency=venous thrombosis as an adult 11
12 Vasculopathy Can have acquired deficiencies as well, due to ulcerative colitis, infection, and anticoagulant therapy Protein S is a related vitamin K dependent protein that is a cofactor for activated protein C Deficiencies in protein S leads to same presentations as those of protein C Vasculopathy Disseminated intravascular coagulation=acquired disorder Activation of coagulation pathway results in thrombi formation in many organ microvasculatures Platelets and fibrin are consumed and lead to a hemorrhagic manifestation as well Vasculopathy Purpura fulminans: the skin manifestations of DIC Large cutaneous ecchymoses and hemorrhagic necrosis of the skin Majority are in infants and children, due to infection or severe protein C/S deficiency Erythematous macules that progress to central purpura Vasculopathy Cryoglobulinemia: immunoglobulins which precipitate from serum or plasma upon cooling Monoclonal (type I) and mixed (type II, type III) Type I=cryoglobulins can be seen in biopsies as intravascular deposits Type II, type III=vasculitis Vasculopathy Cholesterol/other emboli=can also include exogenous material or parts of tumor Atheromatous plaques often the source, particularly abdominal aorta Found often on lower legs, and include livedo reticularis, gangrene, ulceration, cyanosis, purpura High mortality Question 10: A key finding on histology of vasculopathy includes: A. Fibrin thrombi B. Leukocytoclasis C. Panniculitis D. Interface dermatitis E. Calcification 12
13 Vasculopathy: Histology On histology, fibrin or fibrin-platelet thrombi may be present in arterioles and/or venules in deep dermis and subcutis Surrounding hemorrhage may be present Small capillaries and arteries in the superficial dermis may also be involved Vasculopathy: Histology There is overlying wedge shaped necrosis If fibrin or fibrin-platelet thrombi, the thrombi may be PAS positive Vasculitis is not usually seen (except in type II/type III cryoglobulinemia) Vasculopathy: Histology In infectious septic emboli, organisms can be found in emboli via special stains Cholesterol and other emboli: need multiple sections to find cholesterol crystals in arterioles in lower dermis Case 6 67 year old woman with diagnosis of rule out polyarteritis nodosa. 13
14 Question 11: What is the best diagnosis for these findings? A. Polyarteritis nodosa B. Wegener s granulomatosis C. Lethal midline granuloma D. Allergic granulomatosis (Churg Strauss granuloma) E. Erythema annulare centrifugum Churg Strauss Syndrome First described in 1951 Syndrome of asthma, fever, peripheral eosinophilia Can have/lead to cardiac failure, renal damage and peripheral neuropathy Tissue diagnosis: tissue eosinophilia, necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis, extravascular granulomas Churg Strauss Syndrome Distinguished from classic polyarteritis nodosa and classic Wegener s granulomatosis (granulomatosis with polyangiitis, GPA) Now called eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) Churg Strauss Syndrome (EGPA) ANCA positive entity, along with GPA and MPA (microscopic polyangiitis) Classically thought of as Th2 mediated disease Can be limited in involvement and in these cases, diagnosis made on histology (these situations are rare) Churg Strauss Syndrome (EGPA) ACR (American College of Rheumatology) criteria: Asthma Eosinophilia greater than 10% Neuropathy Extravascular eosinophils on biopsy Paranasal sinus abnormalities Nonfixed lung infiltrates 14
15 Churg Strauss Syndrome (EGPA) ANCA-subsets Positive in only 38% of cases Tend to have glomerulonephritis, peripheral neuropathy and purpura ANCA negative: endomyocardial and lung involvement more prevalent Question 12: The entity with nearly identical clinical and histologic features is: A. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis B. Kawasaki syndrome C. Pityriasis lichenoides D. Hypereosinophilic syndrome E. Sarcoidosis Churg Strauss Syndrome (EGPA) Major differential diagnosis: Hypereosinophilic syndrome Persistent pronounced peripheral eosinophilia (greater than 1550/mL) Organ involvement Absence of a reactive component (i.e., infection, drug, allergy, autoimmune, immune mediated disease) Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) Pathogenesis driven classification Myeloid/lymphoid neoplasms with abnormalities in PDGFRA, PDGFRB, or FGFR1 Chronic eosinophilic leukemia Lymphocytic variant that can progress to a leukemia Idiopathic Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) Cardiac and pulmonary manifestations can be similar in EGPA and HES, particularly idiopathic HES Idiopathic HES will not usually have asthma, sinusitis, or purpura Tissue biopsies do not show vasculitis in idiopathic HES but will show eosinophilia ANCA negative in idiopathic HES Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) ANCA negative EGPA vs HES: very difficult! Important because of the neoplastic component of HES (warrants long term follow up) 15
16 Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) Eotaxin-3 (eosinophil-attracting chemokine) Serum levels significantly increased in EGPA vs other eosinophil rich DDX considerations like HES Cut off level of 80 pg/ml had 87% sensitivity, 99% specificity for EGPA over HES Case 7 49 year old male with psoriasis who developed pain and swelling of the right ear helix 3 months ago. Erythematous scaly edematous plaque on helix. 16
17 Question 13: What is the best diagnosis for this entity? A. Chondrodermatitis nodularis helicis B. Relapsing polychondritis C. Lupus erythematosus D. Infection E. Cutaneous mucinosis Relapsing polychondritis Rare multisystem disease manifesting as recurrent inflammatory events attacking cartilagenous organs Ears, nose, and tracheobronchial areas particularly affected Tenderness and reading of one or both ears common presentation Polyarthritis, cardiac lesions, ocular inflammation, and vasculitis Relapsing polychondritis Associated with psoriasis and Behcet s, among other entities Progressive destruction of cartilage with deformity Death occurs in up to 25% of patients, due to respiratory and cardiovascular complications Relapsing polychondritis Histology: degeneration of chondrocytes which become vacuolated with pyknotic nuclei Florid perichondritis Decrease in basophilia of involved cartilage A vasculitis is sometimes present Cartilage can be replaced by fibrous tissue in later stages Question 14: What other entity closely mimics relapsing polychondritis? A. Microscopic thromboangiitis B. Polyarteritis nodosa C. Hypereosinophilic syndrome D. Wegener s granulomatosis E. Churg Strauss granuloma Wegener s granulomatosis c ANCA is positive, which is not reported in relapsing polychondritis On histology a true necrotizing leukocytoclastic vasculitis with granulomas is seen, unlike relapsing polychondritis 17
18 Wegener s granulomatosis Wegener s granulomatosis has a very similar clinical presentation Lung and nasal lesions occur in both entities WG has necrotizing vasculitis rather than primarily a lymphocytic vasculitis with primary destruction of collagen Otitis media can occur but external ear involvement is not present Summary and Conclusions The vasculopathic reaction pattern is protean and can present in numerous ways Key categories include vascular occlusion, acute vasculitis, neutrophilic dermatoses, chronic lymphocytic vasculitis, and granulomatous vasculitides Accurate diagnosis and classification requires clinicopathologic correlation 18
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Mohammad Reza Shakibi M.D Kerman university of medical sciences (KMU) Shafa Hospital, Rheumatology ward
 VASCULITIS SYNDROMES Mohammad Reza Shakibi M.D Kerman university of medical sciences (KMU) Shafa Hospital, Rheumatology ward ILLUSTRATED CASE 1 A 56 years old lady refered me for prolonged fever, arthritis
VASCULITIS SYNDROMES Mohammad Reza Shakibi M.D Kerman university of medical sciences (KMU) Shafa Hospital, Rheumatology ward ILLUSTRATED CASE 1 A 56 years old lady refered me for prolonged fever, arthritis
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Vasculitis. Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology. Vasculitis
 Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Spongiotic Dermatitis
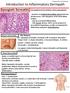 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Inflammatory Dermpath Spongiotic Dermatitis intraepidermal intercellular edema (spongiosis) - presence of widened intercellular spaces between keratinocytes, with
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Inflammatory Dermpath Spongiotic Dermatitis intraepidermal intercellular edema (spongiosis) - presence of widened intercellular spaces between keratinocytes, with
PAEDIATRIC VASCULITIS
 PAEDIATRIC VASCULITIS Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. OUTLINE Introduction
PAEDIATRIC VASCULITIS Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. OUTLINE Introduction
Vasculitis and Vasculitides. OMONDI OYOO Physician/Rheumatologist; Senior Lecturer, Department of Medicine University of Nairobi
 Vasculitis and Vasculitides OMONDI OYOO Physician/Rheumatologist; Senior Lecturer, Department of Medicine University of Nairobi Definition Presence of leucocytes in the vessel wall with reactive damage
Vasculitis and Vasculitides OMONDI OYOO Physician/Rheumatologist; Senior Lecturer, Department of Medicine University of Nairobi Definition Presence of leucocytes in the vessel wall with reactive damage
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123
 BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
The histological assessment of cutaneous vasculitis
 Histopathology 2010, 56, 3 23. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03443.x REVIEW The histological assessment of cutaneous vasculitis J Andrew Carlson Department of Pathology, Divisions of Dermatology and Dermatopathology,
Histopathology 2010, 56, 3 23. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03443.x REVIEW The histological assessment of cutaneous vasculitis J Andrew Carlson Department of Pathology, Divisions of Dermatology and Dermatopathology,
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
December 6, 2010 Asthma and Rheumatic Disorders and Vasculitis
 December 6, 2010 Asthma and Rheumatic Disorders and Vasculitis Lanny J. Rosenwasser, M.D. Dee Lyons/Missouri Endowed Chair in Immunology Research Professor of Pediatrics Allergy-Immunology Division Childrens
December 6, 2010 Asthma and Rheumatic Disorders and Vasculitis Lanny J. Rosenwasser, M.D. Dee Lyons/Missouri Endowed Chair in Immunology Research Professor of Pediatrics Allergy-Immunology Division Childrens
Done by: Shatha Khtoum
 Done by: Shatha Khtoum Overview Vasculitis -Vasculitis is a general term for vessel wall inflammation -Symptoms and signs depend on the tissue of which the vessels are affected. (slide 2) -There are usually
Done by: Shatha Khtoum Overview Vasculitis -Vasculitis is a general term for vessel wall inflammation -Symptoms and signs depend on the tissue of which the vessels are affected. (slide 2) -There are usually
Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature Monira waked Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 5, June 2008 Al Houd Al Marsod Hospital Submitted for publication: May 25 th, 2008 Accepted
Degos Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literature Monira waked Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 5, June 2008 Al Houd Al Marsod Hospital Submitted for publication: May 25 th, 2008 Accepted
Inflammatory Dermatopathology
 Inflammatory Dermatopathology Steven D. Billings Jenny Cotton Inflammatory Dermatopathology A Pathologist s Survival Guide Second Edition Steven D. Billings, MD Professor of Pathology and Co-Director
Inflammatory Dermatopathology Steven D. Billings Jenny Cotton Inflammatory Dermatopathology A Pathologist s Survival Guide Second Edition Steven D. Billings, MD Professor of Pathology and Co-Director
Plan. Sarcoidosis 21/07/2017. Sarcoidosis Liver involvement. Sarcoidosis GI involvement. Sarcoidosis Diagnosis
 Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
VASCULITIC SYNDROMES. Howard L. Feinberg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I., F.A.C.R. OPSC 2018
 VASCULITIC SYNDROMES Howard L. Feinberg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I., F.A.C.R. OPSC 2018 2012 REVISED CHAPEL HILL CONSENSUS CONFERENCE Large vessel Takayasu arteritis Giant cell arteritis Medium Vessel Polyarteritis
VASCULITIC SYNDROMES Howard L. Feinberg, D.O., F.A.C.O.I., F.A.C.R. OPSC 2018 2012 REVISED CHAPEL HILL CONSENSUS CONFERENCE Large vessel Takayasu arteritis Giant cell arteritis Medium Vessel Polyarteritis
Diagnostic Procedures for Vasculitis
 Diagnostic Procedures for Vasculitis Toshiharu Matsumoto, MD Clinical Professor of Department of Diagnostic Pathology Juntendo University Nerima Hospital, Tokyo, Japan Introduction In 1994, the International
Diagnostic Procedures for Vasculitis Toshiharu Matsumoto, MD Clinical Professor of Department of Diagnostic Pathology Juntendo University Nerima Hospital, Tokyo, Japan Introduction In 1994, the International
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
CPC. Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand
 CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
Overview. = inflammation of vessel wall. Symptoms and signs depend on the tissue of which the vessels are affected
 Vasculitis (1+2) Overview = inflammation of vessel wall Symptoms and signs depend on the tissue of which the vessels are affected Often with systemic symptoms fever, myalgia, arthralgia, malaise etc. Most
Vasculitis (1+2) Overview = inflammation of vessel wall Symptoms and signs depend on the tissue of which the vessels are affected Often with systemic symptoms fever, myalgia, arthralgia, malaise etc. Most
Vasculitis Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie
 Vasculitis 08-21-2018 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Agenda Anatomy and histology Vasculitis: Chapel Hill Classification Examples Giant cell arteritis Single organ vasculitis Artery or Vein?
Vasculitis 08-21-2018 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Agenda Anatomy and histology Vasculitis: Chapel Hill Classification Examples Giant cell arteritis Single organ vasculitis Artery or Vein?
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies
 My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
My Method for Approaching Skin Biopsies P A U L H A U N, MD, MS, F A A D A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R D E R M A T O L O G Y A N D D E R M A T O P A T H O L O G Y D E P A R T M E N T O F D E R M
GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS
 What is granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)? Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict
What is granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA)? Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict
Patterns and mechanisms of inflammatory skin conditions: the pathologist s survival kit SALVADOR J. DIAZ-CANO BAHRAIN, APRIL 2017
 Patterns and mechanisms of inflammatory skin conditions: the pathologist s survival kit SALVADOR J. DIAZ-CANO 0000-0003-1245-2859 BAHRAIN, APRIL 2017 Basic Elements of Lesions Repair Injury Time & Intensity
Patterns and mechanisms of inflammatory skin conditions: the pathologist s survival kit SALVADOR J. DIAZ-CANO 0000-0003-1245-2859 BAHRAIN, APRIL 2017 Basic Elements of Lesions Repair Injury Time & Intensity
SHO Teaching. Dr. Amir Bhanji Consultant Nephrologist, Q.A hospital, Portsmouth
 SHO Teaching Vasculitis Renal medicine Dr. Amir Bhanji Consultant Nephrologist, Q.A hospital, Portsmouth OUTLINE What is vasculitis Causes Classification Brief look into ANCA Associated Vasculitis (AAV)
SHO Teaching Vasculitis Renal medicine Dr. Amir Bhanji Consultant Nephrologist, Q.A hospital, Portsmouth OUTLINE What is vasculitis Causes Classification Brief look into ANCA Associated Vasculitis (AAV)
The Vasculitis Syndromes
 The Vasculitis Syndromes Definition Inflammation and damage of blood vessels Single organ skin Several organ systems Primary Secondary Heterogeneity Overlap Primary Vasculitis Syndromes Wegener s granulomatosis
The Vasculitis Syndromes Definition Inflammation and damage of blood vessels Single organ skin Several organ systems Primary Secondary Heterogeneity Overlap Primary Vasculitis Syndromes Wegener s granulomatosis
2/23/18. Disclosures. Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood. Making Room for Rheumatology. I have nothing to disclose. James J.
 Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Making Room for Rheumatology James J. Nocton, MD Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Rheumatic Diseases of Childhood Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ANCA vasculitis. See Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated (ANCA) vasculitis Angiography 54 Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody correlation
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ANCA vasculitis. See Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated (ANCA) vasculitis Angiography 54 Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody correlation
a mimicker of Wegener s Granulomatosis
 a mimicker of Wegener s Granulomatosis Combined Meeting October 2009 a story of 2 ladies Madam JA 56 year-old Madam RH 36 year-old Madam JA 56 year-old Apr 2008 May Jun Jul Aug Sept Oct Nov 2008 Madam
a mimicker of Wegener s Granulomatosis Combined Meeting October 2009 a story of 2 ladies Madam JA 56 year-old Madam RH 36 year-old Madam JA 56 year-old Apr 2008 May Jun Jul Aug Sept Oct Nov 2008 Madam
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of
 Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Cutaneous Mucinoses Nathan C. Walk, M.D. Mucinoses Diverse group of disorders which have in common deposition of basophilic, finely granular and stringy material in the connective tissues of the dermis.
Vasculitis (Polyarteritis Nodosa, Microscopic Polyangiitis, Wegener s Granulomatosis, Henoch- Schönlein Purpura)
 Vasculitis (Polyarteritis Nodosa, Microscopic Polyangiitis, Wegener s Granulomatosis, Henoch- Schönlein Purpura) J. Charles Jennette Ronald J. Falk The kidneys are affected by a variety of systemic vasculitides
Vasculitis (Polyarteritis Nodosa, Microscopic Polyangiitis, Wegener s Granulomatosis, Henoch- Schönlein Purpura) J. Charles Jennette Ronald J. Falk The kidneys are affected by a variety of systemic vasculitides
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Cutaneous vasculitides and vasculopathies. Review. Giampiero Girolomoni Paolo Rosina. severity.
 Review Cutaneous vasculitides and vasculopathies Giampiero Girolomoni Paolo Rosina Department of Medicine Section of Dermatology University of Verona, Italy Address for correspondence: Paolo Rosina, MD
Review Cutaneous vasculitides and vasculopathies Giampiero Girolomoni Paolo Rosina Department of Medicine Section of Dermatology University of Verona, Italy Address for correspondence: Paolo Rosina, MD
Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
 To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice
 Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Update in deposition diseases
 Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Genoa, Italy Update in deposition diseases Prof. Franco Rongioletti, Section of Dermatology, Chair of Dermatopathology, University of Genoa,Italy Cutaneous deposition disorders Endogenous Exogenous Cutaneous
Contents. Part I Genodermatoses
 Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin
 Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Cutaneous Lymphoid Proliferations: A Comprehensive Textbook of Lymphocytic Infiltrates of the Skin Magro, Cynthia M., MD ISBN-13: 9780471695981 Table of Contents Chapter One: Introduction to the Classification
Common Cutaneous Signs of Medical Illnesses
 Common Cutaneous Signs of Medical Illnesses DR COLIN THENG MBBS, MMED (FAM. MED), MRCP(UK), FAMS SENIOR CONSULTANT DERMATOLOGIST THE SKIN SPECIALISTS & LASER CLINIC MOUNT ALVERNIA MEDICAL CENTRE D, #07-61
Common Cutaneous Signs of Medical Illnesses DR COLIN THENG MBBS, MMED (FAM. MED), MRCP(UK), FAMS SENIOR CONSULTANT DERMATOLOGIST THE SKIN SPECIALISTS & LASER CLINIC MOUNT ALVERNIA MEDICAL CENTRE D, #07-61
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
QUESTION 53 Endothelial cell pathology on renal biopsy is most characteristic of which one of the following diagnoses? A. Pre-eclampsia B. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome C. Lupus nephritis D. Immunoglobulin
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM VASCULITIS
 What is central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis? Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is among a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which restricts blood flow
What is central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis? Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is among a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which restricts blood flow
Vasculitis Update. A selective review of what s new. Dr Jonathan Akikusa MBBS FRACP
 Vasculitis Update A selective review of what s new Dr Jonathan Akikusa MBBS FRACP Consultant Paediatric Rheumatologist Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne Honorary Research Fellow Murdoch Children s Research
Vasculitis Update A selective review of what s new Dr Jonathan Akikusa MBBS FRACP Consultant Paediatric Rheumatologist Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne Honorary Research Fellow Murdoch Children s Research
Small Vessel Vasculitis
 Small Vessel Vasculitis Paul A Brogan Professor of Vasculitis and Consultant Paediatric Rheumatologist Department of Rheumatology Institute of Child Health and Great Ormond St Hospital, London UK P.brogan@ucl.ac.uk
Small Vessel Vasculitis Paul A Brogan Professor of Vasculitis and Consultant Paediatric Rheumatologist Department of Rheumatology Institute of Child Health and Great Ormond St Hospital, London UK P.brogan@ucl.ac.uk
Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis -A Case Report Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis -A Case Report Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Wen-Yu Chang Gwo-Shing Chen Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is a rare entity first described by Ackerman
Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis -A Case Report Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis Wen-Yu Chang Gwo-Shing Chen Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is a rare entity first described by Ackerman
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months
 A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
Dermatopathology. Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia
 Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
Dermatopathology Dr. Rafael Botella Estrada. Hospital La Fe de Valencia DERMATOPATHOLOGY CASE CHALLENGE: RECOGNIZING MIMIS AND MASQUERADERS Rosalie Elenitsas. University of Pennsylvania Spectrum Lupus
Granuloma annulare is a benign self-limited disease, first described by Colcott-Fox 1 in 1895 and Radcliffe-Crocker in 1902.
 Granuloma Annulare Granuloma annulare is a benign self-limited disease, first described by Colcott-Fox 1 in 1895 and Radcliffe-Crocker in 1902. EPIDEMIOLOGY Granuloma annulare is a relatively common disorder.
Granuloma Annulare Granuloma annulare is a benign self-limited disease, first described by Colcott-Fox 1 in 1895 and Radcliffe-Crocker in 1902. EPIDEMIOLOGY Granuloma annulare is a relatively common disorder.
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus. Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016
 Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016 Introduction: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus LE is an autoimmune disease with a range of clinical manifestations
Skin Deep: Cutaneous Lupus Dr Sarah Sasson Immunology Registrar, Liverpool Hospital 2016 Introduction: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus LE is an autoimmune disease with a range of clinical manifestations
CUTANEOUS VASCULITIS. Katharine Warburton ST6 Dermatology
 CUTANEOUS VASCULITIS Katharine Warburton ST6 Dermatology AIMS Clinical cases introduction The theory Categorising cutaneous vasculitis Features presenting in the skin Mimics/pitfalls How to initially manage
CUTANEOUS VASCULITIS Katharine Warburton ST6 Dermatology AIMS Clinical cases introduction The theory Categorising cutaneous vasculitis Features presenting in the skin Mimics/pitfalls How to initially manage
Direct immunofluorescence testing in vasculitis A single institution experience with Henoch-Schönlein purpura
 Received: 11 August 2017 Revised: 21 September 2017 Accepted: 29 September 2017 DOI: 10.1111/cup.13054 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Direct immunofluorescence testing in vasculitis A single institution experience with
Received: 11 August 2017 Revised: 21 September 2017 Accepted: 29 September 2017 DOI: 10.1111/cup.13054 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Direct immunofluorescence testing in vasculitis A single institution experience with
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
Primary Cutaneous CD30-Positive T-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A spectrum of related conditions originating from transformed or activated CD30-positive T-lymphocytes May coexist in individual
THE TIP OF THE ICEBERG SAMER BOLIS, DO PGY-3 LEHIGH VALLEY HEALTH NETWORK, ALLENTOWN PA
 THE TIP OF THE ICEBERG SAMER BOLIS, DO PGY-3 LEHIGH VALLEY HEALTH NETWORK, ALLENTOWN PA Case The patient is a 48 year-old female, who recently returned from a trip to Puerto Rico. She presents to the ED
THE TIP OF THE ICEBERG SAMER BOLIS, DO PGY-3 LEHIGH VALLEY HEALTH NETWORK, ALLENTOWN PA Case The patient is a 48 year-old female, who recently returned from a trip to Puerto Rico. She presents to the ED
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE
 HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
HYPERTENSIVE VASCULAR DISEASE Cutoffs in diagnosing hypertension in clinical practice sustained diastolic pressures >90 mm Hg, or sustained systolic pressures >140 mm Hg Malignant hypertension A small
A. Smržová. III. Interní klinika FN Olomouc nefrologická, revmatologická a endokrinologická
 A. Smržová III. Interní klinika FN Olomouc nefrologická, revmatologická a endokrinologická Systemic vasculitis destructive inflamatory of the walls of blood vessels. Pathologist Inflammatory destruction
A. Smržová III. Interní klinika FN Olomouc nefrologická, revmatologická a endokrinologická Systemic vasculitis destructive inflamatory of the walls of blood vessels. Pathologist Inflammatory destruction
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
vasculitis Patomorfologia vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections
 Patomorfologia Lecture 12 prof hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek VASCULITIS infectious vasculitis non-infectious causes: Aspergillus Rickettsiae vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections Mucormycosis syphylis
Patomorfologia Lecture 12 prof hab. n. med. Andrzej Marszałek VASCULITIS infectious vasculitis non-infectious causes: Aspergillus Rickettsiae vasculitis (arteritis) caused by infections Mucormycosis syphylis
Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2015), PP 31-35 www.iosrjournals.org Lymphomatoid Papulosis 3 Case Reports
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Clinicopathologic Evaluation of Nodular Cutaneous Lesions of Behçet Syndrome
 Anatomic Pathology / NODULAR CUTANEOUS LESIONS OF BEHÇET SYNDROME Clinicopathologic Evaluation of Nodular Cutaneous Lesions of Behçet Syndrome Cuyan Demirkesen, MD, 1 Nükhet Tüzüner, MD, 1 Cem Mat, MD,
Anatomic Pathology / NODULAR CUTANEOUS LESIONS OF BEHÇET SYNDROME Clinicopathologic Evaluation of Nodular Cutaneous Lesions of Behçet Syndrome Cuyan Demirkesen, MD, 1 Nükhet Tüzüner, MD, 1 Cem Mat, MD,
IgG4 Disease. General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman
 IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
Scleritis LEN V KOH OD
 Scleritis LEN V KOH OD 2014 PUCO 1 Introduction A painful, destructive, and potentially blinding disorder Highly symptomatic High association with systemic disease Immunosuppresssive agents 2014 PUCO 2
Scleritis LEN V KOH OD 2014 PUCO 1 Introduction A painful, destructive, and potentially blinding disorder Highly symptomatic High association with systemic disease Immunosuppresssive agents 2014 PUCO 2
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
My ear won t stop hurting!
 This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept for DLE, 493 for SLE, 497 Ablative therapies, localized, for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, 502 506. See also Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma,
A number of factors point to the likelihood of a person with RA developing RV:
 What is rheumatoid vasculitis (RV)? Rheumatoid vasculitis (RV) is a rare but serious complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) an inflammatory disease that causes severe joint pain and damage, and can
What is rheumatoid vasculitis (RV)? Rheumatoid vasculitis (RV) is a rare but serious complication of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) an inflammatory disease that causes severe joint pain and damage, and can
Diploma examination. Dermatopathology: First paper. Tuesday 21 March Candidates must answer FOUR questions ONLY. Time allowed: Three hours
 Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 21 March 2017 1. Discuss the role of fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) and emerging molecular techniques in the diagnosis of cutaneous melanocytic lesions,
Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases
 Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 246 251 CASE REPORT Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases RASHMI JINDAL* & NADIA SHIRAZI** *Department of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy, Himalayan
Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 246 251 CASE REPORT Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases RASHMI JINDAL* & NADIA SHIRAZI** *Department of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy, Himalayan
EDITORIAL. Issue Seventeen, October Editorial Team. Issue Seventeen. Info link
 EDITORIAL, October 2004 Welcome to the Spring 2004 Edition of InfoLink. The feature article in this edition has been written by Dr Rodger Laurent, Head of Department, PaLMS Rheumatology Laboratory. The
EDITORIAL, October 2004 Welcome to the Spring 2004 Edition of InfoLink. The feature article in this edition has been written by Dr Rodger Laurent, Head of Department, PaLMS Rheumatology Laboratory. The
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING
 AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
Breast involvement in Wegener's granulomatosis
 J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 343-347 Breast involvement in Wegener's granulomatosis H. PAMBAKIAN AND J. R. TIGHE From the Department of Surgical Pathology, St Thomas's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS Two cases
J. clin. Path., 1971, 24, 343-347 Breast involvement in Wegener's granulomatosis H. PAMBAKIAN AND J. R. TIGHE From the Department of Surgical Pathology, St Thomas's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS Two cases
Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
 Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN) Background Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is defined as any glomerular disease characterized by extensive crescents (usually >50%) as the principal histologic
Crescentic Glomerulonephritis (RPGN) Background Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is defined as any glomerular disease characterized by extensive crescents (usually >50%) as the principal histologic
Classification of Vasculitis
 106S Classification of Vasculitis Joseph L. Jorizzo A working classification of necrotizing vasculitis based on size of the affected vessel is proposed. The classification proposed by Gilliam and Fink
106S Classification of Vasculitis Joseph L. Jorizzo A working classification of necrotizing vasculitis based on size of the affected vessel is proposed. The classification proposed by Gilliam and Fink
Content. Polyarteritis nodosa. Vasculitis. Giant cell arteritis. Primary cerebral angiitis. Other autoimmune CNS disease.
 Content Other autoimmune CNS disease Philippe Demaerel Vasculitis Systemic lupus erythematosus Wegener granulomatosis Behçet disease Rhombencephalitis - CLIPPERS Neurosarcoidosis Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Content Other autoimmune CNS disease Philippe Demaerel Vasculitis Systemic lupus erythematosus Wegener granulomatosis Behçet disease Rhombencephalitis - CLIPPERS Neurosarcoidosis Langerhans cell histiocytosis
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
AN OVERVIEW OF ANCA-ASSOCIATED VASCULITIS
 GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (GPA), MICROSCOPIC POLYANGIITIS (MPA), and EOSINOPHILIC GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (EGPA) AN OVERVIEW OF ANCA-ASSOCIATED VASCULITIS What is ANCA-associated Vasculitis?
GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (GPA), MICROSCOPIC POLYANGIITIS (MPA), and EOSINOPHILIC GRANULOMATOSIS WITH POLYANGIITIS (EGPA) AN OVERVIEW OF ANCA-ASSOCIATED VASCULITIS What is ANCA-associated Vasculitis?
CASE year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland
 CASE 1 55 year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland Case 1 Adrenal gland parenchyma partly replaced by a spindle cell tumour with mild nuclear pleomorphism Atypical mitoses present
CASE 1 55 year old male with a PET avid nodule in the left adrenal gland Case 1 Adrenal gland parenchyma partly replaced by a spindle cell tumour with mild nuclear pleomorphism Atypical mitoses present
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
RARE JUVENILE PRIMARY SYSTEMIC VASCULITIS
 www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it RARE JUVENILE PRIMARY SYSTEMIC VASCULITIS WHAT IS IT? Vasculitis is an inflammation of blood vessels. Vasculitides cover a wide group of diseases. Primary vasculitis
www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it RARE JUVENILE PRIMARY SYSTEMIC VASCULITIS WHAT IS IT? Vasculitis is an inflammation of blood vessels. Vasculitides cover a wide group of diseases. Primary vasculitis
Inpatient dermatopathology. Inpatient dermatopathology. Inpatient dermatopathology: Histologic patterns that matter most
 Inpatient dermatopathology: Histologic patterns that matter most Beth S. Ruben, M.D. Associate Clinical Professor University of California, San Francisco Departments of Dermatology and Pathology Dermatopathology
Inpatient dermatopathology: Histologic patterns that matter most Beth S. Ruben, M.D. Associate Clinical Professor University of California, San Francisco Departments of Dermatology and Pathology Dermatopathology
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE
 Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Title: Erythema annulare centrifugum associated with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia Authors: Helbling I, Walewska R, Dyer MJS, Bamford M, Harman KE Sir, A wide range of conditions have been described as
Vasculitis and the Dermatologist: General approach, pitfalls, and pearls
 Vasculitis and the Dermatologist: General approach, pitfalls, and pearls Robert G. Micheletti, MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology and Medicine Director, Cutaneous Vasculitis Clinic, Penn Vasculitis
Vasculitis and the Dermatologist: General approach, pitfalls, and pearls Robert G. Micheletti, MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology and Medicine Director, Cutaneous Vasculitis Clinic, Penn Vasculitis
DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY. Daniel A. West, MD I HAVE NO RELEVENT RELATIONSHIPS WITH ANY COMPANIES
 DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Daniel A. West, MD I HAVE NO RELEVENT RELATIONSHIPS WITH ANY COMPANIES The most likely diagnosis is: A. Allergic contact dermatitis B. Pemphigus vulgaris
DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Daniel A. West, MD I HAVE NO RELEVENT RELATIONSHIPS WITH ANY COMPANIES The most likely diagnosis is: A. Allergic contact dermatitis B. Pemphigus vulgaris
Diploma Examination. Dermatopathology: First paper. Tuesday 20 March Candidates must answer FOUR questions. Time allowed: 3 hours
 Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 20 March 2018 Candidates must answer FOUR questions Time allowed: 3 hours 1. Give an account of the genetic aberrations encountered in Spitzoid neoplasms and how these
Dermatopathology: First paper Tuesday 20 March 2018 Candidates must answer FOUR questions Time allowed: 3 hours 1. Give an account of the genetic aberrations encountered in Spitzoid neoplasms and how these
الفتوي الاصفر الحبيبوم = Xanthogranuloma_Juvenile JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9
 JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA
 What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA Neurologist in Chief, Tufts Medical Center Professor and Chair
What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA Neurologist in Chief, Tufts Medical Center Professor and Chair
KAWASAKI DISEASE. What is Kawasaki disease? Causes
 What is Kawasaki disease? Kawasaki disease is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage vital organs and
What is Kawasaki disease? Kawasaki disease is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage vital organs and
Neuropathology lecture series. III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease. Physiology of cerebral blood flow
 Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
MOSTLY SEPTAL PANNICULITIS
 Margot S. Peters, M.D. Professor of Dermatology and Laboratory Medicine & Pathology, Mayo Clinic PANNICULITIS C017 Essential Dermatopathology, What You Need to Know for Clinical Practice: Inflammatory.
Margot S. Peters, M.D. Professor of Dermatology and Laboratory Medicine & Pathology, Mayo Clinic PANNICULITIS C017 Essential Dermatopathology, What You Need to Know for Clinical Practice: Inflammatory.
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD
 CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
Interactive Workshops. Practical Follow-up of DVT and PE patients
 Interactive Workshops Practical Follow-up of DVT and PE patients Vascular acrosyndromes Unusual site thrombosis Women s health issues WHAT IS IT? 18/04/2016 49 WHAT IS IT? 1. Acrocyanosis 2. Raynaud s
Interactive Workshops Practical Follow-up of DVT and PE patients Vascular acrosyndromes Unusual site thrombosis Women s health issues WHAT IS IT? 18/04/2016 49 WHAT IS IT? 1. Acrocyanosis 2. Raynaud s
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
