COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY ANKYLOSING SPONDYLIT-IS
|
|
|
- Melinda Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF EARLY ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS ADEL G. FAM, JOEL D. RUBENSTEIN, HYACINTH CHINSANG, and FRANCES Y. K. LEUNG Computed tomography (CT) was compared with plain radiography and quantitative sacroiliac (SI) scintigraphy in 28 patients with early ankylosing spondylitis (AS) of 510 years duration. Compared with conventional radiography, CT improved delineation of the SI joints and revealed more abnormalities and higher grades of sacroiliitis; this was significant in patients with early AS of 13 years duration. Quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy showed higher SI joint:sacrum ratios of radioisotope uptake in patients with AS compared with controls. However, its diagnostic usefulness was limited by the frequency of inconsistent results and the lack of specificity. CT examination of the SI joints may be a useful adjunct in the diagnosis of early AS. The clinical diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is largely based upon the radiologic demonstration of sacroiliitis (1,2). However, early radiographic changes are often subtle and subject to considerable observer error (36). Other imaging techniques have been used in the evaluation of sacroiliac (SI) joints, including special views of SI joints (7,8), conventional From the Division of Rheumatology, Department of Medicine, and the Department of Radiology, Sunnybrook Medical Centre, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Supported by a grant from the Sunnybrook Trust for Medical Research. Adel G. Fam, MD, FRCP(C): Associate Professor of Medicine; Joel D. Rubenstein, MD, FRCP(C): Assistant Professor of Radiology; Hyacinth ChinSang, MD, FRCP(C): Assistant Professor of Radiology; Frances Y. K. Leung, MD, FRCP(C): Lecturer in Medicine. Address reprint requests to Adel G. Fam, MD, Division of Rheumatology, Sunnybrook Medical Centre, 2075 Bayview Avenue, 'Toronto, Ontario, Canada M4N 3M5. Submitted for publication July 19, 1984; accepted in revised form February 8, tomography (9, lo), quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy (QSS) (1115), and more recently, computed tomography (CT) (4,1621). The role of CT in the diagnosis of sacroiliitis is controversial. Recent studies indicate that CT is more sensitive and accurate than plain radiography in the evaluation of inflammatory sacroiliitis (4,8,16,1921). However, other studies have not found CT to be superior in the detection of sacroiliitis (17,18). This study was designed to define the role of CT in the evaluation of sacroiliitis in patients with early symptomatic AS. Our results indicate that CT is useful in clarifying suspected SI joint abnormalities in those patients whose plain film findings are still equivocal. PATIENTS AND METHODS Patients. Between January 1982 and March 1984 we studied 28 consecutive patients with inflammatory low back pain of 5 10 years duration and clinical findings suggestive of AS. The group consisted of 22 men and 6 women with a mean age of 29.7 years (range 2143). AS was diagnosed in patients who were 1840 years of age at the time of onset of symptoms and had a typical history of chronic inflammatory back pain (22) in association with 1 or more of the following signs: tender SI joints, positive results of SI joint stress test (23), limited lumbar spine movement (modified Schober's test) (24), or restricted chest expansion. Inflammatory back pain was defined as the insidious onset of lumbar or thoracic pain for 2 3 months, that was improved by movement or light exercise, was aggravated by rest, and was associated with 230 minutes of morning back stiffness (22). We excluded those patients who fulfilled criteria for rheumatoid arthritis, metabolic bone disease, or other types of spondylarthropathy secondary to psoriasis, Reiter's syndrome, or inflammatory bowel disease. A standard anteroposterior radiograph of the SI joints with a 20" caudal tube angle, QSS, and CT of the SI joints were performed on all AS patients. For QSS, ratios of peak counts over each SI joint:peak sacral count, or SI:S Arthritis and Rheumatism, Vol. 28, No. 8 (August 1985)
2 CT IN EARLY AS 93 1 Table 1. Clinical and laboratory findings in 28 patients with ankvlosinrr srrondvlitis Characteristic' Number of patients Duration of back symptoms 53 years 15 >310 years 13 Morning back stiffness 230 minutes duration 26 Diminished chest expansion 8 Decreased lumbar mobility 15 SI joint tenderness 15 Positive results on SI joint stress test 9 Peripheral arthritis 9 Manubriosternal arthritis 3 Intis 3 Elevated ESR 8 HLAB27 25 * SI = sacroiliac; ESR = erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ratios, were cakuiated 3 hours after intravenous injection of 15 mci of *"Tclabeled methylene diphosphonate. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs were withheld for at least 10 days prior to scintigraphy. CT and plain radiographs of the SI joints were obtained on the same day in 12 patients. The interval of time between examinations was less than 3 months in 11 patients, and within 36 months in the remaining 5. Six to eight contiguous 5 mmthick CT sections were obtained through the SIjoints on a GE 8800 scanner with no gantry angulation. The correct anatomic level was localized on the scout view prior to CT examination, and only those sections through the synovial compartment of the joints (4) were assessed. Controls. Ten control patients (8 men and 2 women), with a mean age of 29. I years (range 1741) and no history of back pain, underwent pelvic radiography and CT for reasons other than arthritis (e.g., lymphoma, metastases). Computed Tomography Table 2. Comparison of computed tomography (CT) and plain radiography in the detection of sacroiliitis* ~~ ~ ~ No. of cases Control patients (n = 10) Agreement between methods Patients with AS (n = 28) 10 Agreement between methods 26 CT falsenegative result 1 Radiography falsenegative result 1 * Agreement statistic (kappa) = Fifty additional control patients underwent QSS. This group consisted of 10 patients with mechanical \ow back pain (9 men and 1 woman, mean age 29.5 years, age range 2938; all but 1 were HLAB27 negative) and 40 patients without back pain (23 men and 17 women, mean age 56.3 years, age range 3086) who had whole body bone scintigraphs for reasons other than suspected arthritis (e.g., metastatic disease or fracture). All radiographs and CT scans were examined independently by 3 observers (2 radiologists and 1 rheumatologist) who had no knowledge of the clinical diagnoses, HLA type, or scintigraphic findings. Each SI joint was graded separately using the New York criteria (I): grade 0 = normal; grade 1 = suspicious for erosions or sclerosis; grade 2 = mildly abnormal with definite erosions or sclerosis but without alteration In joint width; grade 3 = moderately abnormal with erosions, iliac and sacral sclerosis, joint space narrowing or widening and/or partial ankylosis; grade 4 = severe abnormality with complete ankylosis. The independent scores were reviewed, and for those on which the observers disagreed (5% of the initial readings), the radiographs and CT scans were reexamined by the 3 observers together, and a reconciled grade was recorded. Analysis of data. Data were anasyzed by Cohen's kappa agreement coefficient statistics (25), the chisquare test of independence, and Student's ttest of the means. A P level <OM was arbitrarily chosen as indicative of significant differences. % + Cra I 47 I Kappa statistic = 0.83 Figure 1. Interrater agreement statistic (kappa) between computed tomography and plain radiography in the detection of sacroiliitis in 28 ankylosing spondylitis patients and 10 control patients. Numbers are the total number of sacroiliac joints positive or negative for sacroiliitis, as evidenced by that technique. RESULTS Clinical findings. Table 1 summarizes the clinical and laboratory findings or the 28 patients with AS. By definition, all 28 patients had back symptoms for (10 years. Fifteen patients had back symptoms for 5 3 years, including 6 patients who were evaluated within 1 year of symptom onset. All but 3 patients were HLA 327 positive. The most common objective findings were tenderness of the SI joints and slight limitation of lumbar spine movements. Chest expansion was limited in 8 patients, most of whom had symptoms for >3 years. Nine patients had peripheral arthritis, and 3 had iritis. Manubriosternal arthritis was seen in 3 patients and was the presenting symptom in 1.
3 932 FAM ET AL Figure 2. A, Plain radiograph of the sacroiliac (SI) joints, showing no evidence of sacroiliitis. B, Computed tomography image through the synovial part of the SI joints of the same patient, obtained 3 days after the plain films, demonstrating sclerosis and erosions in right SI joint (arrows). The left SI joint shows irregular articular surfaces.
4 CT IN EARLY AS 933 Table 3. Comparison of plain radiography and computed tomography in the grading of sacroiliitis in 28 patients with ankylosing soondvlitis* Sacroiliitis grade Plain radiography (56 joints) Computed tomography scans (56 joints) * Pooled results of 3 observers. Numbers are the total number of joints positive for that grade. Differences not statistically significant (P < 0.09). CT findings. In the control patients and in the patients with AS, there was good correlation between interpretations of sacroiliitis from plain radiographs and from CT (Figure 1). CT did not significantly increase the probability of detecting sacroiliitis, compared with plain radiography (Table 2). However, in 5 SI joints, CT demonstrated changes of sacroiliitis that were not evident radiographically (Figure 1). This included 1 AS patient who had a positive CT result but a negative result on plain films (Table 2 and Figures 2A and B). One patient had unilateral grade 1 sacroiliitis by radiography... but a negative.....~.~~ CT result (Table 2). Plain radiographs and CT were'negative for sacroiliitis in all 10 control patients (those without history of back pain undergoing radiography and CT for lymphoma, metastases, etc.). Three CT scans showed focal iliac sclerosis that was not visible on plain radiographs: this finding has been recently described in CT of normal SI joints (21). In patients with AS, CT revealed more SI joint abnormalities (erosions, sclerosis, and joint space narrowing or widening) and higher grades of sacroiliitis, compared with conventional radiography (Table 3), but the differences were not statistically significant (x2 = 6.53, 3 df, P < 0.09). However, in patients with early AS, there was a significant change in sacroiliitis grade when evaluated by CT (Table 4). Eleven of 15 patients (17 of 30 SI joints) with disease of 53 years had a higher grade of sacroiliitis shown on CT, compared with plain films (Figures 3A and B). In the group with disease duration of >3 years, only 6 of 13 patients, or 7 of 26 SIjoints, demonstrated a change in grade (x2 = 3.89, 1 df, P < 0.05 versus patients with disease of 13 years). Therefore, CT was useful in patients with disease duration of 13 years and normal or equivocal results on plain films, but was of littie additional value in interpreting advanced grades of sacroiliitis (Figures 4A and B). Table 4. Comparison of computed tomography (CT) and plain radiography in the detection of sacroiliitis, according to disease duration Duration of ankylosing spondylitis 53 years >3 years (15 patients) (13 patients) Stable, CT and plain films showed same grade of sacroiliitis Change, CT showed higher grade 17 7* of sacroiliitis than did plain films Total number of sacroiliac joints * P < 0.05 compared with patients with disease duration of 53 years. Quantitative sacroiliac seintigraphy. Patients with AS had significantly higher SI : S ratios compared with nonrheumatic disease controls (P < 0.001) and compared with those with mechanical low back pain (P < 0.003), but there was frequent overlap between these groups (Table 5 and Figure 5). The SI:S ratios were significantly higher in patients with early AS of 53 years duration compared with those with AS for >3 years (P < 0.03) (Table 5 and Figure 5). DISCUSSION The diagnostic criteria for AS that are presently being used are too restrictive and are heavily dependent upon the detection of unequivocal radiologic evidence of sacroiliitis (1,2). Clinical diagnosis of early AS is often difficult because of the high incidence of back pain in the general population (26), the nonspecificity of objective findings (23,27), and because of difficulties in radiologic diagnosis of early inflammatory changes of the SI joints (36). The curved and oblique orientation of the SI joints, the overlying soft tissues, and the presence of unrelated degenerative changes (28,29) complicate the radiologic interpretation of inflammatory sacroiliitis (36). A number of diagnostic methods have been proposed as being superior to plain radiography in the evaluation of early sacroiliitis. These include special views of the SI joints (7,8), conventional tomography (9,10), QSS (1113, and CT (4,1621). However, special radiographic projections of the SI joints, including oblique views, have not been shown to significantly increase the accuracy of diagnosis of sacroiliitis (7,8). Although conventional tomography improves the definition of the SI joints, it is associated with high radiation exposure (9,lO).
5 934 FAM ET AL Figure 3. A, Plain radiograph of the sacroiliac (SI) joints, showing minimal bilateral iliac and sacral sclerosis. B, Computed tomography image of the SI joints of the same patient, obtained 22 days after the plain films, demonstrating irregular sclerosis, erosions, and pseudowidening of the right SI joint, and sclerosis and indistinct articular margins of the left SI joint. Quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy revealed higher SI: S ratios in our patients with AS, particularly those with early disease of 53 years duration, compared with the controls. Although the probability of detecting sacroiliitis was increased in the presence of a high SI : S ratio, QSS was not consistently diagnostic in differentiating patients with AS from the control patients and from those with mechanical low back pain. These findings are in agreement with recent studies that have shown that radionuclide scanning of SIjoints
6 CT IN EARLY AS 935 Figure 4. Advanced (grade 3) sacroiliitis. A, Plain radiograph; B, Computed tomography image, showing large erosions and irregular sclerosis in both joints. is too nonspecific for effective diagnosis of inflammatory sacroiliitis (1316,30,31). CT of the SI joints is associated with low radiation exposure (16). The technique seems ideally suited to studying the curved, oblique SI joints in a transaxial plane, thereby minimizing interference from the overlying soft tissues and bony structures (4,16,17,21). The tomographic nature of CT images also enhances the definition of changes in the SI joint (20). Although it was not always possible to obtain simultaneous plain radiographs and CT scans in our patients, the interval of time between the 2 procedures was short and, in the majority of cases, did not exceed 3 months.
7 936 FAM ET AL P Y L * t w t I. Table 5. Sacroiliac joint: sacrum (SI: S) ratios in 40 control patients, 10 patients with mechanical low back pain, and 28 patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), according to results of quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy Mechanical AS patients low back Disease duration Disease duration Controls pain All 53 years >3 years No. of SI joints Mean SI:S ratio * 1.55t 1.40 SD ' '0.27 SEM * P < compared with controls, P < compared with patients with mechanical low back pain. t P < 0.03 compared with AS patients with disease duration >3 years. " "... : " I CONTROLS MECHANICAL ANKYLOIINO ANKYLOSINO (N=*Ol BACK SCONDYLITIS SPONDYLITIS PAY <3 YEARS >a YEARS (N.20) (N=30) (N=26) Figure 5. Results of quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy, showing sacroiliac (SI) joint:sacrum uptake ratios and mean values (horizontal bars) for 40 control patients, 10 patients with mechanical back pain, and 28 patients with ankylosing spondylitis (grouped according to disease duration). Each SI joint is considered individually. The upper and lower bars for patient controls represent the 95% confidence limits for this group. See Patients and Methods for details.. CT images showed better delineation of the SI joints and revealed more abnormalities and higher grades of sacroiliitis, particularly in patients with early AS, than did plain radiographs. Although CT did not significantly increase the diagnostic capability beyond that with plain radiography, mild SI joint abnormalities were more clearly evident on CT. This allowed for greater confidence and accuracy of diagnosis, particularly in patients who did not have limited chest expansion, limited movement of the lumbar spine, and definite radiographic changes at the SI joints, all of which are necessary for a diagnosis of AS by established criteria. However, the technique was of no added value in interpreting higher grades of sacroiliitis. Therefore, CT cannot be recommended for the routine assessment of inflammatory sacroiliitis (32). Rather, it should be reserved for the few patients in whom the diagnosis remains in doubt after results of clinical and radiographic evaluations have been reviewed. CT would be a reasonable next step in patients with an atypical presentation or incompletely expressed AS who fail to manifest overt erosive and sclerotic radiographic changes at the SI joints. It has been established that AS may be symptomatic for years before sacroiliitis becomes manifest on radiographs (33,34). Recognition of the disease in its early stages will allow for patient education, institution of correct therapy including high doses of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, and avoidance of inappropriate investigative procedures (35). We believe that CT of the SI joints may be a useful adjunct in the evaluation of inflammatory sacroiliitis of recent onset and, hence, in the diagnosis of early AS. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors wish to thank Dr. John Szalai and Marko Katic for help with statistical analysis, and Sylvia Fader for secretarial assistance.
8 CT IN EARLY AS Bennett PH, Wood PHN: Population Studies of the Rheumatic Diseases: Proceedings of the Third International Symposium, New York, June Amsterdam, Excerpta Medica, 1968, pp , Van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A: Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis: a proposal for the modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361368, MacRae IF, Baslock DI, Wright V: Grading of films for sacroiliitis in population studies. Ann Rheum Dis 30: 5866, Lawson TL, Foley WD, Carrera GF, Berland LL: The sacroiliac joints: anatomic, plain roentgenographic, and computed tomographic analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 6:307314, Hollingsworth PN, Cheah PS, Dawkins RL, Owen ET, Calin A, Wood PHN: Observer variation in grading sacroiliac radiographs in HLAB27 positive individuals. J Rheumatol 10:247254, Forrester DM, Hollingsworth PN, Dawkins RL: Difficulties in the radiographic diagnosis of sacroiliitis. Clin Rheum Dis 9:323332, Wasner C, Kraines RG, Kaye RL: Oblique view radiographs in the diagnosis of sacroiliitis (abstract). Arthritis Rheum 22:671, Ryan LM, Carrera GF, Lightfoot RW Jr, Hoffman RG, Kozin F: The radiographic diagnosis of sacroiliitis: a comparison of different views with computed tomograms of the sacroiliac joint. Arthritis Rheum 26: , Wilkinson M, Meikle JA: Tomography of the sacroiliac joints. Ann Rheum Dis 25:433440, De Smet AA, Gardner JD, Lindsley HB, Goin JE, Fritz SL: Tomography for evaluation of sacroiliitis. AJR 139:577581, Russell AS, Lentle BC, Percy JS: Investigation of sacroiliac disease: comparative evaluation of radiological and radionuclide techniques. J Rheumatol 2:4551, Namey TC, McIntyre J, Buse M, LeRoy EC: Nucleographic studies of axial spondarthritides. I. Quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy in early HLAB27associated sacroiliitis. Arthritis Rheum 20: , Goldberg RP, Genant HK, Shimshak R, Shames D: Applications and limitations of quantitative sacroiliac joint scintigraphy. Radiology 128:683686, Ho G Jr, Sadovnikoff N, Malhotra CM, Claunch BC: Quantitative sacroiliac joint scintigraphy: a critical assessment. Arthritis Rheum 22:837844, Esdaile JM, Rosenthall L, Terkeltaub R, Kloiber R: Prospective evaluation of sacroiliac scintigraphy in chronic inflammatory back pain. Arthritis Rheum 23: , Carrera GF, Foley WD, Kozin F, Ryan L, Lawson TL: CT of sacroiliitis. AJR 136:4146, Borlaza GS, Seigel R, Kuhns LR, Good AE, Rapp R, Martel W: Computed tomography in the evaluation of sacroiliac arthritis. Radiology 139:437440, Khan MA, Miron SD, Kushner I, Ballou SP, Wiesen EJ, Bellon EM: The comparative value of standard radiography, quantitative scintigraphy and computerized tomography in sacroiliitis (abstract). Arthritis Rheum (suppl) 24:S119, Kozin F, Carrera GF, Ryan LM, Foley D, Lawson T: Computed tomography in the diagnosis of sacroiliitis. Arthritis Rheum 24: , Carrera GF: Computed tomography in sacroiliitis. Clin Rheum Dis 9:403415, Vogler JB, Brown WH, Helms CA, Genant HK: The normal sacroiliac joint: a CT study of asymptomatic patients. Radiology 151:433437, Calin A, Porta J, Fries J, Schurman DJ: Clinical history as a screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. JAMA 237: , Russell AS, Maksymowych W, LeClercq S: Clinical examination of the sacroiliac joints: a prospective study. Arthritis Rheum 24: , Moll JMH, Wright V: Normal range of spinal mobility: an objective clinical study. Ann Rheum Dis 30:381386, I Fleiss JL: The measurement of interrater agreement, Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions. Second edition. New York, John Wiley & Sons, 1981, pp Grabias SL, Mankin HJ: Pain in the lower back. Bull Rheum Dis 30: , Blower PW, Griffin AJ: Clinical sacroiliac tests in ankylosing spondylitis and other causes of low back pain2 studies. Ann Rheum Dis 43:192195, Cohen AS, McNeill JM, Calkins E, Sharp JT, Schubart A: The normal sacroiliac joint. AJR , Resnick D, Niwayama G, Goergen TG: Comparison of radiographic abnormalities of the sacroiliac joint in degenerative disease and ankylosing spondylitis. AJR 128: , Spencer DG, Adams FG, Horton PW, Buchanan W: Scintiscanning in ankylosing spondylitis: a clinical, radiological and quantitative radioisotopic study. J Rheumatol 6: , Snaith ML, Calvin SEJ, Short MD: The value of quantitative radioisotope scanning in the differential diagnosis of low back pain and sacroiliac disease. J Rheumatol 9~435440, Calin A: Abuse of computed tomography (letter). Arthritis Rheum 25: , Parry CBW: Management of ankylosing spondylitis. Proc R SOC Med 59:619623, Bluestone R: Ankylosing spondylitis, Arthritis and Allied Conditions. Ninth edition. Edited by DJ McCarty. Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, 1979, pp Ankylosing spondylitis and its early diagnosis (editorial). Lancet , 1977
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SACROILIITIS
 1479 COMPUTED TOMOGRPHY IN THE DIGNOSIS OF SCROILIITIS FRNKLIN KOZIN, GUILLERMO F. CRRER, LWRENCE M. RYN, DENIS FOLEY, and THOMS LWSON Computed tomography (CT) and conventional radiography of the sacroiliac
1479 COMPUTED TOMOGRPHY IN THE DIGNOSIS OF SCROILIITIS FRNKLIN KOZIN, GUILLERMO F. CRRER, LWRENCE M. RYN, DENIS FOLEY, and THOMS LWSON Computed tomography (CT) and conventional radiography of the sacroiliac
The Clinical Usefulness of Multidetector Computed Tomography of the Sacroiliac Joint for Evaluating Spondyloarthropathies
 The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:171-177, 2007 The Clinical Usefulness of Multidetector Computed Tomography of the Sacroiliac Joint for Evaluating Spondyloarthropathies You-Hyun Lee, M.D.,
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:171-177, 2007 The Clinical Usefulness of Multidetector Computed Tomography of the Sacroiliac Joint for Evaluating Spondyloarthropathies You-Hyun Lee, M.D.,
Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Clinical Study Diagnosis and Progression of Sacroiliitis in Repeated Sacroiliac Joint Computed Tomography
 Arthritis Volume 2013, Article ID 659487, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/659487 Clinical Study Diagnosis and Progression of Sacroiliitis in Repeated Sacroiliac Joint Computed Tomography Mats Geijer,
Arthritis Volume 2013, Article ID 659487, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/659487 Clinical Study Diagnosis and Progression of Sacroiliitis in Repeated Sacroiliac Joint Computed Tomography Mats Geijer,
Vertebral sclerosis in adults
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation
 ~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 741-745 Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27 ADRIAN B. BECKINGSALE, JONATHAN DAVIES, JONATHAN M. GIBSON, AND A. RALPH ROSENTHAL
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 741-745 Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27 ADRIAN B. BECKINGSALE, JONATHAN DAVIES, JONATHAN M. GIBSON, AND A. RALPH ROSENTHAL
predicts radiographic change
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
The usefulness of bone SPECT/CT imaging with volume of interest analysis in early axial spondyloarthritis
 Kim et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:9 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0465-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The usefulness of bone SPECT/CT imaging with volume of interest analysis in early axial spondyloarthritis
Kim et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:9 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0465-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The usefulness of bone SPECT/CT imaging with volume of interest analysis in early axial spondyloarthritis
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies
 Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: Atlantoaxial Ankylosis and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R
 The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Moderate to Severe Ankylosing Spondylitis
 MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement
 \>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
\>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
Abstract Objective In 1971 McEwen and colleagues suggested that the radiological changes of classic ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and the
 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
Department of Radiology, Aarhus University Hospital, Aarhus, Denmark; 4. Key words MRI, sacroiliitis, ankylosing spondylitis, axial spondyloarthritis.
 Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
Gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI sequence does not have an incremental value in the assessment of sacroiliitis in patients with early inflammatory back pain by using MRI in combination with pelvic radiographs:
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis?
 Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis? Dr. Omar Azmat*, Dr. Zaid Jibri, Dr. Vimarsha Swami, Dr. Babak Maghdoori, Dr. Kent Greep,
Is intra-articular gas within the SI Joints a confounding factor in the false negative diagnosis of sacroiliitis? Dr. Omar Azmat*, Dr. Zaid Jibri, Dr. Vimarsha Swami, Dr. Babak Maghdoori, Dr. Kent Greep,
Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Axial Spondyloarthritis. Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital
 Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Dr Tracey Kain. Associate Professor Ed Gane
 Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Osteoporotic insufficiency fractures of the pelvis. Khong, PL; Peh, WCG; Ho, WY; Yeung, HWD; Luk, KDK
 Title Osteoporotic insufficiency fractures of the pelvis Author(s) Khong, PL; Peh, WCG; Ho, WY; Yeung, HWD; Luk, KDK Citation Journal of the Hong Kong Medical Association, 1994, v. 46 n. 3, p. 242-246
Title Osteoporotic insufficiency fractures of the pelvis Author(s) Khong, PL; Peh, WCG; Ho, WY; Yeung, HWD; Luk, KDK Citation Journal of the Hong Kong Medical Association, 1994, v. 46 n. 3, p. 242-246
6/6/2017. Spondyloarthritis and Osteopathic Primary Care: Facts and Challenges. Progression of Ankylosing Spondylitis Classic Disease
 1 Outline Talk 1 Introduction of spondyloarthritis (SpA) Clinical case challenge The problem of low back pain (LBP) in primary care and in osteopathic primary care Talk 2 What is SpA today? How many people
1 Outline Talk 1 Introduction of spondyloarthritis (SpA) Clinical case challenge The problem of low back pain (LBP) in primary care and in osteopathic primary care Talk 2 What is SpA today? How many people
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
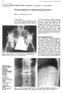 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
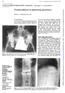 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
APPLICATION FOR SUBSIDY BY SPECIAL AUTHORITY
 APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1620 Etanercept INITIAL APPLICATION - juvenile idiopathic arthritis Applications only from a named specialist rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months.
APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1620 Etanercept INITIAL APPLICATION - juvenile idiopathic arthritis Applications only from a named specialist rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months.
A mong the inflammatory rheumatic diseases
 659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging
 Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
Sacroiliac Joint Imaging Jacob Jaremko, MD, PhD Edmonton, Canada SPR, May 2017 Longview, Alberta Overview SI joint anatomy Sacroiliitis pathophysiology Sacroiliitis imaging Disease features Imaging protocols
RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1998;37:760 765 RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS P. RAHMAN, D. D. GLADMAN,* R. J. COOK, Y. ZHOU, G. YOUNG and D. SALONEN Department of Medicine and Institute
British Journal of Rheumatology 1998;37:760 765 RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS P. RAHMAN, D. D. GLADMAN,* R. J. COOK, Y. ZHOU, G. YOUNG and D. SALONEN Department of Medicine and Institute
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Introduction: Inflammatory arthritis is the most common extraintestinal manifestation in patients with inflammatory
PREVALENCE OF SPONDYLOARTHROPATHY IN PUERTO RICAN PATIENTS WITH INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Introduction: Inflammatory arthritis is the most common extraintestinal manifestation in patients with inflammatory
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
Active (acute) inflammation on MRI highly suggestive of sacroiliitis associated with SpA
 MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
MRI findings of active and chronic sacroiliitis in light of recent ASAS criteria for diagnosing axial spondyloarthritis: what the radiologist should know Poster No.: C-1955 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
APPLICATION FOR SUBSIDY BY SPECIAL AUTHORITY
 APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1621 Adalimumab INITIAL APPLICATION - rheumatoid arthritis Applications only from a rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months. The patient has had an initial
APPLICANT (stamp sticker acceptable) Page 1 Fm SA1621 Adalimumab INITIAL APPLICATION - rheumatoid arthritis Applications only from a rheumatologist. Approvals valid f 6 months. The patient has had an initial
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics
 Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation
 Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
SERRATUS ANTERIOR MUSCLE
 AND THE SERRATUS ANTERIOR MUSCLE James D. Collins, MD, Richard K. J. Los Angeles, California Brown, MD, and Poonam Batra, MD Twenty-seven patients with a history of asbestos exposure were reviewed at the
AND THE SERRATUS ANTERIOR MUSCLE James D. Collins, MD, Richard K. J. Los Angeles, California Brown, MD, and Poonam Batra, MD Twenty-seven patients with a history of asbestos exposure were reviewed at the
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Review article. early diagnosis? HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for. Why subjects carrying HLA-B27 are prone. Jan Tore Gran, Gunnar Husby
 _JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
_JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
T he spondyloarthritides (SpA) comprise five subtypes:
 1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G)
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:66-71 THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G) S. D. JONES, A. STEINER,* S. L. GARRETT and A. CALIN Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases,
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:66-71 THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G) S. D. JONES, A. STEINER,* S. L. GARRETT and A. CALIN Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases,
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1
 Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
Key words Ankylosing spondylitis, radiographic scoring methods, intra- and interobserver reliability, BASRI, msasss.
 Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score F. Salaffi 1, M.
Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score F. Salaffi 1, M.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
Ankylosing Spondylitis*
 Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/30/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 18 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/30/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 18 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 220 Patients
 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases
 Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS
 ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis
 Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
5/4/2018. Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis. Learning Objectives. Outcome Measures Clinical Outcome Assessments
 Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis Marina N Magrey MD Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives What are outcome measures
Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis Marina N Magrey MD Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives What are outcome measures
PROFFESOR THAMER AHMED HAMDAN M.B.CH.B, F.R.C.S(ED), F.R.C.P(ED), F.A.C.S,F.I.C.S CHANCELLOR OF BASRA UNIVERSITY SICOT VICE PRESEDENT
 PROFFESOR THAMER AHMED HAMDAN M.B.CH.B, F.R.C.S(ED), F.R.C.P(ED), F.A.C.S,F.I.C.S CHANCELLOR OF BASRA UNIVERSITY SICOT VICE PRESEDENT DR.RAFID A. ALADAB M.B.CH.B,F.I.C.M.S(ORTHO),SICOT DIPLOMA ORTHOPEDIC
PROFFESOR THAMER AHMED HAMDAN M.B.CH.B, F.R.C.S(ED), F.R.C.P(ED), F.A.C.S,F.I.C.S CHANCELLOR OF BASRA UNIVERSITY SICOT VICE PRESEDENT DR.RAFID A. ALADAB M.B.CH.B,F.I.C.M.S(ORTHO),SICOT DIPLOMA ORTHOPEDIC
González-Sistal, A. Diagnostic Imaging Modalities of Osteoblastic Metastases. Hospital Imaging & Radiology Europe, 2 (1): (2007)
 Post print version: González-Sistal, A. Diagnostic Imaging Modalities of Osteoblastic Metastases. Hospital Imaging & Radiology Europe, 2 (1): 16-17 (2007) Tittle: Diagnostic imaging modalities of osteoblastic
Post print version: González-Sistal, A. Diagnostic Imaging Modalities of Osteoblastic Metastases. Hospital Imaging & Radiology Europe, 2 (1): 16-17 (2007) Tittle: Diagnostic imaging modalities of osteoblastic
Digital tomosynthesis (DT) has been well described as a
 Case Report The Usefulness of Digital Tomosynthesis (DT) in Assisting in Cases of Doubtful Routine Radiography and/or Computed Tomography (CT) Image. Abstract Digital tomosynthesis is useful in assisting
Case Report The Usefulness of Digital Tomosynthesis (DT) in Assisting in Cases of Doubtful Routine Radiography and/or Computed Tomography (CT) Image. Abstract Digital tomosynthesis is useful in assisting
SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro?
 Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no :
 Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no : 201715579 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : Complains of pain in the middle &lower 1/3 rd junction
Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no : 201715579 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : Complains of pain in the middle &lower 1/3 rd junction
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Sequential Sacral Insufficiency Fracture After Unilateral Pubic Fractures - A Case Report -
 CASE REPORT Vol. 19, No. 1, 2012 Sequential Sacral Insufficiency Fracture After Unilateral Pubic Fractures - A Case Report - Kyung-Soon Park, Dong-Hyun Lee, Indra Peni, Taek-Rim Yoon * Department of Orthopaedic
CASE REPORT Vol. 19, No. 1, 2012 Sequential Sacral Insufficiency Fracture After Unilateral Pubic Fractures - A Case Report - Kyung-Soon Park, Dong-Hyun Lee, Indra Peni, Taek-Rim Yoon * Department of Orthopaedic
Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF AGE OF ONSET IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia Rheumatica
 The Open General and Internal Medicine Journal, 29, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia
The Open General and Internal Medicine Journal, 29, 3, 53-57 53 Open Access Scintigraphic Findings and Serum Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in Patients with Polymyalgia
ABSTRACT Objective: To validate and refine two sets of candidate criteria for the classification/diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis
 1 Rheumatology, Med Klinik I, Charité, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany; 2 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; 3 Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, The Netherlands;
1 Rheumatology, Med Klinik I, Charité, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany; 2 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; 3 Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, The Netherlands;
MDP on Improving Refractory Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and CRP. Guo Dan, Shuai Ping
 5th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Computer Science (ICAMCS 2016) MDP on Improving Refractory Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and CRP Guo Dan, Shuai
5th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Computer Science (ICAMCS 2016) MDP on Improving Refractory Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate and CRP Guo Dan, Shuai
RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
Combined SPECT/CT bone scintigraphy; a superior technique for diagnosis of benign and malignant conditions in the spine.
 Combined SPECT/CT bone scintigraphy; a superior technique for diagnosis of benign and malignant conditions in the spine. Poster No.: C-1686 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational
Combined SPECT/CT bone scintigraphy; a superior technique for diagnosis of benign and malignant conditions in the spine. Poster No.: C-1686 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational
Studies with an enthesis index as a method of clinical
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 197-202 Studies with an enthesis index as a method of clinical assessment in ankylosing spondylitis MICHELLE MANDER, JUDY M SIMPSON, ALISON McLELLAN, DAVID WALKER,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 197-202 Studies with an enthesis index as a method of clinical assessment in ankylosing spondylitis MICHELLE MANDER, JUDY M SIMPSON, ALISON McLELLAN, DAVID WALKER,
Incidental Detection of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm on Skeletal Scintigraphy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 3 Number 2 Incidental Detection of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm on Skeletal Scintigraphy B Cumarasingam, R Mansberg, V Mansberg Citation B Cumarasingam,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 3 Number 2 Incidental Detection of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm on Skeletal Scintigraphy B Cumarasingam, R Mansberg, V Mansberg Citation B Cumarasingam,
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
