The late stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis
|
|
|
- Albert Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
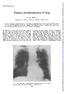
1 Postgraduate Medical Journal (August 1970) 46, The late stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis J. G. SCADDING The Brompton Hospital, London, S. W.3 Summary Pulmonary sarcoidosis is frequently preceded by bilateral hilar lymph-node enlargement (BHL). Although it is normally difficult to be certain in a patient without BHL that a stage of BHL has not in fact occurred in the past but been missed, there is good evidence that some cases of pulmonary sarcoidosis arise without preceding BHL. Although a prefibrotic infiltration of the lungs will usually show signs either of resolution or of developing fibrosis within 2 years, such an infiltration may remain apparently nonprogressive, producing little functional defect, for much longer than this, and in such a case, substantial resolution remains possible. A high proportion of those who develop fibrosis show a characteristic pattern of strand-like fibrosis in the middle zones and lower part of the upper zones of the lungs, with emphysematous changes above and below. In densely fibrotic parts of the lungs, cavities may appear, probably from necrosis at the centres of large masses of hyaline fibrosis. A rare complication is the development of a 'fungus ball' due to the growth of Aspergillus in such a cavity. Occasionally, fine focal fibrosis develops without distortion of lung architecture, but with severe disability. A rare but important event is the development of bronchial stenoses. These may affect main, segmental or subsegmental bronchi, more especially the proximal parts of segmental or subsegmental bronchi. Calcification has been observed to develop in a characteristic symmetrical fashion in the hilar lymphnodes and occasionally in small foci in the lungs in about 5% of patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis who initially had BHL, followed for periods ranging from 5 to 20 years. In the late stages of sarcoid fibrosis of the lungs, the specific granuloma may be no longer convincingly demonstrable. It will be helpful, before discussing the late stages of pulmonary sarcoidosis, to survey briefly the commoner early patterns of mediastinal lymph-node and pulmonary sarcoidosis. These are so well recognized that radiographic record of a characteristic sequence of changes may be sufficient to establish diagnosis with little risk of error. Bilateral hilar lymph-node enlargement (BHL), sometimes evidently involving also the right paratracheal group, is often the first evidence of the disease. It may be discovered in persons with few or no symptoms as a result of routine radiography, or may be associated with erythema nodosum, febrile arthralgia often involving particularly the ankles, or constitutional symptoms with low fever. This initial illness, if there is one, is generally selfterminating. In the majority of cases, the BHL subsides within 6 months to 2 years. In some cases, about two-fifths in my experience, BHL is followed by a widespread pulmonary infiltration causing generalized mottled shadowing in the chest radiograph. In a high proportion of cases, this prefibrotic infiltration in its turn resolves either completely or leaving minor presumably fibrotic residues. Among patients who presented with BHL and no radiographic changes in the lungs when first seen, I found that 8% of those without symptoms or with erythema nodosum showed some lung fibrosis 2 years later, but only one-third of these, about one in forty of the total group, had respiratory symptoms. A higher proportion, one in four, of the small number who at the onset had respiratory or constitutional symptoms, without erythema nodosum, were left with some residual fibrosis, though in most instances this produced only slight or no symptoms. The time-scale of the sequence BHL-infiltrationresolution with or without some residual fibrosis is very variable. The whole process may be completed to resolution within one year; most frequently it takes 2-3 years; but occasionally it is much slower, as in the case illustrated in Figs Many patients show pulmonary infiltration as the first observed evidence of sarcoidosis. In my experience about equal numbers of those presenting in this way have and have not evidence of past or present BHL. It is only occasionally possible to be sure that a patient presenting without BHL has not passed through a phase of BHL; but it is significant that patients in whom there is no record of BHL
2 FIG. 1 (top left). BHL in a symptomless man, aged 19, in March It was known to have been present for nearly 3 years. The Kveim test was positive. FIG. 3 (bottom left). The same, August Still symptom-free. Objective tests showed only a slight restrictive ventilatory defect, and CO transfer factor in the normal range (26-5 ml/min/mmhg by the steady state method). differ from those with evidence of BHL in having a lower incidence of evident extrathoracic sarcoidosis The late stages ofpulmonary sarcoidosis 531 and a rather higher incidence of subsequent fibrosis. Of eighty-seven patients with prefibrotic sarcoidosis of the lungs, with or without BHL, I found that twenty-five had evidence of some permanent fibrosis after 5 years' observation, though only a minority of these had appreciable disability (Scad- FIG. 2 (top right). The same, May Still symptomfree, playing Rugby football. Maximum voluntary ventilation 172 1/min. FIG. 4 (bottom right). The same, December The dense infiltration shown in Fig. 3 has resolved without 'treatment' at any time, leaving radiological evidence of slight fibrosis in the left middle zone. CO transfer factor 27-5 ml/min/mmhg. ding, 1967). Thus the proportion of patients with intrathoracic sarcoidosis in England who develop disabling fibrosis is small. It is necessary to specify the place where the observations were made, since the prognosis of sarcoidosis varies in different populations; in particular, north American Negroes tend to have more extensive and florid disease than those of Caucasian stock and a correspondingly worse prognosis.
3 532 J. G. Scadding In a few patients, a prefibrotic infiltration remains non-progressive for prolonged periods. If such a patient has no symptoms, substantial resolution with only minor radiographic residues and no disability can still occur, no matter how long the infiltration has been present. For instance, the irregular densities shown in Fig. 5 were present for 5 years in a woman in the late twenties, without symptoms, but eventually resolved spontaneously, leaving almost clear lung-fields..~~:1:::... F _.: :. ::.::e: Sarcoid infiltration of the lungs, locally confluent FIG. 5. in the right upper/middle zone, in a symptomless woman aged 27. It persisted for 5 years before clearing spontaneously, leaving only a minor linear 'scar' at the site of the confluent infiltration. A high proportion of those developing fibrosis show a rather characteristic radiographic appearance. In the earlier stage, mottled opacities are densest in the middle or the middle and adjacent parts of the upper zones of the lungs, the lower and, usually less strikingly, the upper zones being clearer. Irregular linear shadows appear to extend out from the hila (Fig. 6). When fibrosis is established, the hilar shadows are often raised, with corresponding distortion of the vascular pattern; mottling tends to disappear, the linear shadows already mentioned become more prominent, and there may be localized dense shadows, presumably of confluent fibrosis (Fig. 7). The lower and sometimes the upper zones of the lungs show areas of transradiancy suggesting emphysema, sometimes bullous; and air-containing ~i:~:iaii:i~?~!~iii ii ii iiiiii-i~l~iii i~,~ii!!~!~!~?~...:. i~i:i~i~ '! iii~~ ii~d;iii: i~ ~'iiii ~'ili :ef-~'i.':i :-1:e:;:..:. :,...~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.::l'l:ili i:.::!~ FIG. 6. A characteristic pattern of developing middlezone fibrosis in a man. Widespread mottling had first been observed 18 months earlier. Note the concentration of mottling in the middle zone and the adjacent part of the upper zone, and the tendency to a linear pattern of shadowing from the hila into these densely involved areas. ~~~~~~~~~~iiiiiiiid i :: i,::iei:,i:ei-i:e:i-i:;i : ""~~~~~~~~~~~~~... i '::: :I"::I'::;:::;::;:. ':' i:ii FIG. 7. Confluent shadows, principally in the middle zones of the lungs in a woman aged 39 who had had BHL 10 years earlier, and whose disease had progressed to the stage shown through a widespread infiltration of the lungs.
4 spaces may be evident, especially on tomography, in in the densely opaque areas. These have been shown in some instances at necropsy to have dense fibrous tissue walls, without specific granulomatous or other changes or epithelial lining (Figs. 8 and 9). FIG. 8 (top). Fibrotic stage of pulmonary sarcoidosis in a man aged 42, in whom a widespread fine mottled infiltration had first been observed 9 years earlier. FIG. 9 (bottom). Tomogram of middle zone of the left lung, 12 cm from the back, in the same patient, showing irregular cavities in confluent fibrosis. The late stages ofpulmonary sarcoidosis 533 Occasionally, these air-containing spaces, like those of other origin, become colonized by the common mould Aspergillus, usually the species.fumigatus. This results in the development of a 'fungus ball', presenting a characteristic radiographic appearance (Figs. 10 and 11). The usual pattern of functional defect consists in a restrictive ventilatory defect (small total lung capacity with proportionate reduction in its subdivisions, possibly diminished compliance, and normal airways resistance) and a gas transfer defect (reduced transfer factor, tendency to arterial oxygen desaturation at rest and increasing on exercise, with normal or slightly low CO2 pressure). At the stage of prefibrotic infiltration, the results of all these tests may be within normal limits, in spite of a gross radiographic abnormality; if they are abnormal, ventilatory restriction is generally more prominent than gas transfer defect. With the development of fibrosis, the gas transfer defect becomes more prominent. Chronic bronchitis is so frequent in a cigarette-smoking population that it is not surprising that a proportion of patients show an additional obstructive ventilatory defect from this cause. Not all those patients developing fibrosis show the 'middle zone' pattern described above. In a few, a widespread granulomatous infiltration appears to undergo focal fibrosis, without confluence or evident distortion of macroscopic lung architecture. In these, the mottling becomes less dense in the radiograph, individual elements diminishing in size, and perhaps giving place to a fine reticular pattern; but disability increases, and objective tests show deterioration in transfer factor and in restrictive ventilatory defect. An even rarer development is airways obstruction with grossly overdistended lungs, suggestive of emphysema. I have seen only one example of this. The patient was a woman who was a non-smoker and had no evidence of chronic bronchitis at any time. At the onset, she showed radiographic evidence of BHL with widespread infiltration (Fig. 12); over the next 2 years she became increasingly breathless on exertion, with increased density of the mottling in the lung fields. At this time the FEV, was only 800 ml, constituting 47% of the FVC, and the gas transfer factor was only moderately lowered, to about two-thirds of the predicted value. In view of her symptoms, she was treated with corticotrophin, with symptomatic and radiographic improvement, but persistence of airways obstruction. The infiltration reappeared on cessation of the corticotrophin treatment after 18 months, but subsequently disappeared spontaneously, leaving persistent airways obstruction, very low gas transfer factor not increasing on exercise, and radiographic evidence of overdistended abnormally transradiant lungs (Fig. 13).
5 534 J. G. Scadding Involvement of main, lobar, segmental and large sub-segmental bronchi in sarcoidosis is well recognized. This occasionally gives rise in the later stage to bronchial narrowings; these have a rather characteristic distribution affecting the proximal parts of segmental or subsegmental bronchi, though occasionally main bronchi may show long smooth narrowings (Fig. 14). Clinically, this produces dyspnoea with a pattern of inspiratory as well as expiratory obstruction, causing prolongation and noisiness of both inspiration and expiration (Citron & Scadding, 1957). Another feature of the late stage of intrathoracic sarcoidosis the frequency of which has only recently been recognized is the development of calcification, typically in symmetrical fashion in the hilar lymphnodes, and less frequently in small foci in the lungs. In the hilar nodes, it occurs only, in my experience, in patients who have also had a pulmonary infiltration; I found that it developed in 5% of such patients, observed for periods ranging from 5 to 20 years (Scadding, 1961, 1968a). The pattern of discrete symmetrical calcifications in the hilar and sometimes paratracheal regions, corresponding to the distribution of the early enlargement of hilar nodes, is very characteristic (Fig. 15). Occasionally, the nodes are calcified in 'egg-shell' fashion, showing a well-defined radio-opaque linear outline. There is evidence that the calcification develops in the ischaemic featureless fibrous tissue into which sarcoid tubercles are converted if they do not resolve. Finally, it must be noted that in the latest stages of sarcoid fibrosis of the lungs, the specific granuloma may be no longer convincingly demonstrable (Scadding, 1968b). In such cases, there is much featureless hyaline fibrosis in lymph-nodes, lungs, spleen and sometimes other organs; groups of Schaumann conchoidal bodies may be found in this, though careful search may be required; and the few epithelioid cells that remain no longer show a follicular arrangement. In such cases, although the pathologist may remain unconvinced, the physician may legitimately conclude, from knowledge of the clinical course and earlier history of the case, that a diagnosis of sarcoidosis is justified, since he can FIG. 10 (top). Fibrotic stage of pulmonary sarcoidosis in a woman aged 59: duration unknown, since she came under observation with established fibrosis. In the upper half of the right lung, there is a thick-walled cavity. She also had a plaque-like sarcoid of the skin of the right forearm, and sarcoid infiltration of some old scars. FIG. 11 (bottom). Tomogram of the upper half of the right lung in the same patient: the well-defined opacity in the cavity was shown to be an aspergilloma by the finding of A. fumigatus in the sputum, and the presence of precipitins, giving multiple strong lines in gel diffusion tests, in the blood serum.
6 .;di.ii. : "::; : The late stages ofpulmonary sarcoidosis 535 iiiiiiiii : :. : ;:d. '.'.:..: i: : ': '' ''. i:::;. ; ;. :::s:: J:i : ::t i :. : - ::i:...:-:..:;,,...,...:..., ::.:. -n::- : :...liiiiiiiiiii:liiiii.jail ili: :..:.:..:..i i : : ::.. :I:r::,r:, :: ::r :.:i: ' : :" ::. :. :: : :: :r : ::i;iiiii ': :i: :. : : -a :";":".;?. ;I - ::. : : :. : iiii;ii ii-i::i;-;:ii:iii:pjii.i:.i :::i i ::ii::.: " ; : I:e::. :.. nqii:;. : ::::: i:iil.j. :; : :... ":' ':.a. : ::ir :ijjjjj :,,., :.i.: "! : : : i:l: :...I : : : i i I '' ':'i ':':: :i :' la:.iiii: i...l- iii i: Iliixi ::i :: '':'i.: ';;f6.. l i ' : :.:..: ::.:i :: ii.a.p.8.g.e.i d --.rr.g;w.7ei::::.:. li: i.': " I I:.kr.s.lg... ' '' i i i : :::.:b ::: ; Llr.i.i.hl: ":' FIG. 12. BHL and widespread infiltration of the lungs in a woman aged 40: see text. ILPiiir iii : : : ii. : ' : :: :I ii.;c;iz :i,;iiiiviaiiii : :: :; :Ii :' iiii :i:i : Pdl.i.a.e%C 1-9. P.Li..i.B.eP8esll1p ;:: ::,: Zi:; :l.b..811 : ::s:::::w: i. : I:.... 1:.I. : ' i' ": :'' FIG. 14. Bronchogram showing narrowing of main bronchi by fibrosing sarcoid infiltration in a man aged 38 years. :: ::!::-::- :' :?:':' :..:.:: i i(ifli: ::: I :i.:: :;i:: j:: 'P: :, FIG. 13. The same, 11 years later. The lungs appear over-distended; there was severe airways obstruction and low gas-transfer factor. i:ii.i?.i. "ildihi :;ii. :':'' i,iiili;diii :. I: :: :::.. fii. :::. ::::: i,.,:..gy.e :: ij:'ii. I.:::: i: i:i::r:: i : '.:.:.;i.:: ::.. : : '.' I:.I i :; I:..:.: :;li : : -;: ;; : i::.:... :...:.: :;;:;;: ' ' '':'':::::19li..:.. : ::::i:::1: il :: l:ii:jjjjj.lii.i.l.itlz!ii:.l:b:' : : p:l:n::- : - :.:. I. :.:..:.Tj:K: :i ) R$:i: I: : : ;:;: :; : :''"'"''' ''':' I':l"ls:'iiiii:..il.i.8.fiiil i.iiiiiiiiil..,,,l,,,,,,.lici:llx a::;::!::.i..iiiiiiii.klliiiii.iil;i;':;:.il:':l:iiiii :i:.iiiiia!ra..el.lp;iii:i:i::i;;.:i; :i :'l l: 'i:.i:i::i: : LliiIiiiiii;lii iiiiiiiriiiiiii!iiic!8il :...:.. '::Ciiiiiigili.li : : i : : ii :dicii-f." I.8 ';:''I.: :.i ;::.... : : :: :: ::: ::. :::, ml::: :..':.".: ' i:::: i:.. : : : iii:. I ' :l l:.:::::i ::.. :...::.i.. : i :::i ': :.::.,:' : i::i::s lililiili 'i! iiiiiliiiii:iil:i: :: 'I' ilijl!ilp LI:: : I ':::: il:tl: ::' : :::: I; I:::::.:. :.. :. :i. II%I: :..'iiiil i:;i:::::;:i:li:iiil I:i:l::::;i:::: :iaiii. I:iilliij :.r.. qi.ilciiig.i e::. : 'ai : I.i.i ;ii.ii iiipir : ':i is ilfitii Fii:;iiiii 8:.i.aii.ii. "I: ::.:I:"i:R : ::. i:l.f li :. I::iiS eii:i:i iiii. iz :.il :.. i :i aili.iiiiiii:i:. a:r : l : iii::l;:i":: :::iif i: : ' :.'ls ii iliiiiiii'ii:ii,': :; : :: : :.::i r i:.. ; ; :L::'i::r::, :,:,:. ililii:i :ii-i i:9 - gilil.l.it: : :.P:.l:::;ia ii... il.i.i.il iii Symmetrical calcification in hilar lymph-nodes. had been followed by widespread infiltration in the lungs. FIG. 15. Sarcoid BHL had been discovered 13 years earlier and i:.iii
7 536 J. G. Scadding deduce that in the active stage the defining characteristics of sarcoidosis, non-caseating epithelioid-cell tubercules in several organs, were present. This illustrates the general rule that although the definition of sarcoidosis is in histological terms, its diagnosis depends in practice almost always upon the correlation of evidence derived from several relevant fields of study. References CITRON, K.M. & SCADDING, J.G. (1957) Stenosing noncaseating tuberculosis (sarcoidosis) of the bronchi. Thorax, 12, 10. SCADDING, J.G. (1961) Calcification in sarcoidosis. Tubercle, 42, 121. SCADDING, J.G. (1967) Sarcoidosis. Eyre & Spottiswoode, London. SCADDING, J.G. (1968a) Further observations on calcification in sarcoidosis. Scandinavian Journal ofrespiratory Diseases, suppl. 65, 235. SCADDING, J.G. (1968b) A 'burnt-out' case of sarcoidosis. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 44, 105. Postgrad Med J: first published as /pgmj on 1 August Downloaded from on 26 October 2018 by guest. Protected by
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Localised airway narrowing in sarcoidosis
 Thorax 1982;37:443-447 JW HADFIELD, RL PAGE, CDR FLOWER, JE STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge, and Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge ABSTRACr Four patients developed multiple narrowings
Thorax 1982;37:443-447 JW HADFIELD, RL PAGE, CDR FLOWER, JE STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge, and Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge ABSTRACr Four patients developed multiple narrowings
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
INTRATHORACIC SARCOIDOSIS
 268 -- INTRATHORACIC SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a systemic disease in which the lungs and intrathoracic lymph nodes are frequently involved. Although the clinical features of patients with sarcoidosis
268 -- INTRATHORACIC SARCOIDOSIS Sarcoidosis is a systemic disease in which the lungs and intrathoracic lymph nodes are frequently involved. Although the clinical features of patients with sarcoidosis
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
Chest radiograph of an. asymptomatic man. Case report. Case history
 Eleftheria Chaini 1, Niki Giannakou 2, Dimitra Haini 3, Anna Maria Athanassiadou 4, Angelos Tsipis 4, Nikolaos D. Hainis 5 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Kontokali, Greece.
Eleftheria Chaini 1, Niki Giannakou 2, Dimitra Haini 3, Anna Maria Athanassiadou 4, Angelos Tsipis 4, Nikolaos D. Hainis 5 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Kontokali, Greece.
Value of measuring serum angiotensin I converting enzyme and serum lysozyme in the
 Value of measuring serum angiotensin I converting enzyme and serum lysozyme in the management of sarcoidosis C W G TURTON,1 GRUNDY,2 G FIRTH,2 D MITCHLL,' B G RIGDN,2 AND M TURNR-WARWICK' Thorax, 1979,
Value of measuring serum angiotensin I converting enzyme and serum lysozyme in the management of sarcoidosis C W G TURTON,1 GRUNDY,2 G FIRTH,2 D MITCHLL,' B G RIGDN,2 AND M TURNR-WARWICK' Thorax, 1979,
Prolonged treatment of pulmonary sarcoidosis
 Thorax (1967), 22, 519. Prolonged treatment of pulmonary sarcoidosis with corticosteroids CLIFFORD HOYLE, HUGH SMYLLIE1, AND DAVID LEAK From King's College Hospital, London The results are described of
Thorax (1967), 22, 519. Prolonged treatment of pulmonary sarcoidosis with corticosteroids CLIFFORD HOYLE, HUGH SMYLLIE1, AND DAVID LEAK From King's College Hospital, London The results are described of
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry
 Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Bronchography in chronic bronchitis
 Bronchography in chronic bronchitis A. G. OGILVIE Wood Cottage, Thropton, Morpeth, Northumnberland Thorax (1975), 30, 631. Ogilvie, A. G. (1975). Thorax, 30, 631-635. Bronchography in chronic bronchitis.
Bronchography in chronic bronchitis A. G. OGILVIE Wood Cottage, Thropton, Morpeth, Northumnberland Thorax (1975), 30, 631. Ogilvie, A. G. (1975). Thorax, 30, 631-635. Bronchography in chronic bronchitis.
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 396-401 Treatment of rapidly progressive rheumatoid pneu moconiosis DEWI DAVI ES Ransom Hospital, Mansfield, Nottinghamshire Davies, D. (1973). British
Case of the Day Chest
 Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Inspiratory crackles-early and late
 Inspiratory crackles-early and late A. R. NATH and L. H. CAPEL The London Chest Hospital, Bonner Road, London E2 Thorax (1974), 29, 223. Nath, A. R. and Capel, L. H. (1974). Thorax, 29, 223-227. Inspiratory
Inspiratory crackles-early and late A. R. NATH and L. H. CAPEL The London Chest Hospital, Bonner Road, London E2 Thorax (1974), 29, 223. Nath, A. R. and Capel, L. H. (1974). Thorax, 29, 223-227. Inspiratory
PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
 Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH MILIARY OPACITIES.
 DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO MILIARY OPACITIES. 1 INTRODUCTION The term miliary derives from the radiographic picture of diffuse, discrete, nodular shadows about the size of a millet seed (~2mm). 2 CHEST X-RAY
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH TO MILIARY OPACITIES. 1 INTRODUCTION The term miliary derives from the radiographic picture of diffuse, discrete, nodular shadows about the size of a millet seed (~2mm). 2 CHEST X-RAY
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of. Pulmonary Mycetoma. Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu***
 Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
Sarcoidosis Registry Proforma
 Patient Demographics Patient Data Has a patient consent form been completed? 1.1 Title Mr 1.2 1.3 Forename(s) PlainText Surname PlainText 1.4 Gender Male 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Mrs Ms Miss Dr Other
Patient Demographics Patient Data Has a patient consent form been completed? 1.1 Title Mr 1.2 1.3 Forename(s) PlainText Surname PlainText 1.4 Gender Male 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Mrs Ms Miss Dr Other
Typical and atypical findings of pulmonary sarcoidosis at high resolution CT
 Typical and atypical findings of pulmonary sarcoidosis at high resolution CT Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Raposo Rodríguez, C. Mejía, B. Escobar Mallada,
Typical and atypical findings of pulmonary sarcoidosis at high resolution CT Poster No.: C-0169 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Raposo Rodríguez, C. Mejía, B. Escobar Mallada,
CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1956, 13, 24. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, the United
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1956, 13, 24. CARDIAC HYPERTROPHY IN COALWORKERS' PNEUMOCONIOSIS BY W. R. L. JAMES and ARTHUR J. THOMAS Welsh National School of Medicine, Cardiff, and Llandough Hospital, the United
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
A Case of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis with Endobronchial Nodular Involvement
 http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.6.274 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2013;74:274-279 CopyrightC2013. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2013.74.6.274 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2013;74:274-279 CopyrightC2013. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis
 www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
Swyer-James Syndrome: An Infrequent Cause Of Bronchiectasis?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 12 Number 1 Swyer-James Syndrome: An Infrequent Cause Of Bronchiectasis? A Huaringa, S Malek, M Haro, L Tapia Citation A Huaringa, S Malek, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 12 Number 1 Swyer-James Syndrome: An Infrequent Cause Of Bronchiectasis? A Huaringa, S Malek, M Haro, L Tapia Citation A Huaringa, S Malek, M
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Radiology of uncomplicated asthma
 Thorax (1974), 29, 296. Radiology of uncomplicated asthma MARGARET E. HODSON, G. SIMON, and J. C. BATTEN Brompton Hospital, London Hodson, Margaret E., Simon, G., and Batten, J. C. (1974). Thorax, 29,
Thorax (1974), 29, 296. Radiology of uncomplicated asthma MARGARET E. HODSON, G. SIMON, and J. C. BATTEN Brompton Hospital, London Hodson, Margaret E., Simon, G., and Batten, J. C. (1974). Thorax, 29,
Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging
 July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
Typical and Atypical Manifestations of Intrathoracic Sarcoidosis
 Typical and typical Manifestations of Intrathoracic Sarcoidosis Hyun Jin Park, MD 1 Jung Im Jung, MD 1 Myung Hee Chung, MD 1 Sun Wha Song, MD 1 Hyo Lim Kim, MD 1 Jun Hyun aik, MD 1 Dae Hee Han, MD 1 Ki
Typical and typical Manifestations of Intrathoracic Sarcoidosis Hyun Jin Park, MD 1 Jung Im Jung, MD 1 Myung Hee Chung, MD 1 Sun Wha Song, MD 1 Hyo Lim Kim, MD 1 Jun Hyun aik, MD 1 Dae Hee Han, MD 1 Ki
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I. December 5, 2012
 SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
SESSION IV: MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS PULMONARY PATHOLOGY I December 5, 2012 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic and pathophysiologic changes in various conditions
Clinical- Pathologic Conference
 Clinical- Pathologic Conference Clinical-pathologic conference in general thoracic surgery: Bilateral lung transplantation for sarcoidosis with aspergilloma G. Alexander Patterson, MD From the Washington
Clinical- Pathologic Conference Clinical-pathologic conference in general thoracic surgery: Bilateral lung transplantation for sarcoidosis with aspergilloma G. Alexander Patterson, MD From the Washington
380 Annals New York Academy of Sciences
 11. A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF OBSERVER VARIATION IN THE CLASSIFICATION OF RADIOGRAPHS OF ASBESTOS- EXPOSED WORKERS AND THE RELATION OF PATHOLOGY AND X-RAY APPEARANCES A. Caplan," J. C. Gilson,t K. F. W. Hinson,$
11. A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF OBSERVER VARIATION IN THE CLASSIFICATION OF RADIOGRAPHS OF ASBESTOS- EXPOSED WORKERS AND THE RELATION OF PATHOLOGY AND X-RAY APPEARANCES A. Caplan," J. C. Gilson,t K. F. W. Hinson,$
Chief Complain. For chemotherapy
 Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Imaging of sarcoidosis of the airways and lung parenchyma and correlation with lung function
 Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 750 765 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00025212 CopyrightßERS 2012 SERIES SARCOIDOSIS FROM BENCH TO BEDSIDE Edited by V. Cottin and J. Müller-Quernheim Number 3 in this Series Imaging of
Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 750 765 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00025212 CopyrightßERS 2012 SERIES SARCOIDOSIS FROM BENCH TO BEDSIDE Edited by V. Cottin and J. Müller-Quernheim Number 3 in this Series Imaging of
Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 402. Inhaled Foreign Bodies in Children An analysis of 40 cases CONSTANCE M. DAVIS From the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital and Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Lofgren's syndrome A case report
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Lofgren's syndrome A case report Volume 3 (2017) Issue 24 ISSN 2379-1039 Mohammad Iqbal KM; Thara Pratap; Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal*; Chippy Eldhose; Shani
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Lofgren's syndrome A case report Volume 3 (2017) Issue 24 ISSN 2379-1039 Mohammad Iqbal KM; Thara Pratap; Muhammed Jasim Abdul Jalal*; Chippy Eldhose; Shani
Pulmonary sarcoidosis with an alveolar radiographic
 Thorax 1982;37:448-452 Pulmonary sarcoidosis with an alveolar radiographic pattern JP BATTESTI, G SAUMON, D VALEYRE, J AMOUROUX, B PECHNICK, D SANDRON, R GEORGES From the Service de Pneumologie, H6pital
Thorax 1982;37:448-452 Pulmonary sarcoidosis with an alveolar radiographic pattern JP BATTESTI, G SAUMON, D VALEYRE, J AMOUROUX, B PECHNICK, D SANDRON, R GEORGES From the Service de Pneumologie, H6pital
Sarcoidosis: the clinical problem
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 531-535 Sarcoidosis: the clinical problem Edmund Neville St Mary's Hospital, Portsmouth P03 6AD, UK. Summary: This paper reviews the clinical manifestations of acute
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 531-535 Sarcoidosis: the clinical problem Edmund Neville St Mary's Hospital, Portsmouth P03 6AD, UK. Summary: This paper reviews the clinical manifestations of acute
Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi
 Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
Thorax 1983;38: 373-377 Clinical review of pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium xenopi MJ SMITH, KM CITRON From the Cardiothoracic Institute, Brompton Hospital, London ABSTRACT Mycobacterium xenopi
David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids
 Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Thorax (1972), 27, 156. Pulmonary aspergiliomas treated with corticosteroids DEWI DAVIES and ALAN R. SOMNER Ransom Hospital, Mansfield and the Chest Clinic, Wallsend-on-Tyne The development of an aspergilloma
Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases
 CASE REPORT Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases Nobuhiko Nagata 1, Kentaro Watanabe 2, Michihiro Yoshimi 3, Hiroshi Okabayashi 4, Katsuo Sueishi 5, Kentaro
CASE REPORT Combined Unclassifiable Interstitial Pneumonia and Emphysema: A Report of Two Cases Nobuhiko Nagata 1, Kentaro Watanabe 2, Michihiro Yoshimi 3, Hiroshi Okabayashi 4, Katsuo Sueishi 5, Kentaro
Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
Thorax (1965), 20, 118. Total collapse of the lung in aspergillosis R. H. ELLIS From the Gloucestershire Royal Hospital, Pulmonary aspergillosis can be divided conveniently into two main types, allergic
ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN COALWORKERS BY ARTHUR J. THOMAS AND W. R. L. JAMES From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals) and the Department of Pathology, Welsh National
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
Thorax, 1980, 35, 936-940 Lung folding simulating peripheral pulmonary neoplasm (Blesovsky's syndrome) C R PAYNE, P JAQUES, AND I From the Brompton Hospital, London H KERR ABSTRACT Six cases are reported
THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS
 Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
Thorax (1956), 11, 241. THE RADIOTHERAPEUTIC AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF RADIATION FIBROSIS OF THE LUNGS* BY WILLIAM M. ROSS From Newcastle Regional Hospital Board (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 23,
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS
 Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
NONE OVERVIEW FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF (UIP) FOR PATHOLOGISTS. IPF = Idiopathic UIP Radiologic UIP Path UIP
 UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
UPDATE ON IDIOPATHIC PULMONARY FIBROSIS/IPF () FOR PATHOLOGISTS Thomas V. Colby, M.D. Professor of Pathology (Emeritus) Mayo Clinic Arizona FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES NONE OVERVIEW IPF Radiologic Dx Pathologic
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P
 Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
Dr.kassim.m.sultan F.R.C.P inflammatory disorder of the lung, involving alveolar walls and terminal airways, that is induced, in a susceptible host, by repeated inhalation of a variety of organic agents.
RESEARCH ARTICLE. The Relationship between Sarcoidosis of Intrathoracic Lymph Nodes and Digestive System Diseases: A Comparative Observation
 ISSN 0975-8542 Journal of Global Pharma Technology Available Online at www.jgpt.co.in RESEARCH ARTICLE The Relationship between Sarcoidosis of Intrathoracic Lymph Nodes and Digestive System Diseases: A
ISSN 0975-8542 Journal of Global Pharma Technology Available Online at www.jgpt.co.in RESEARCH ARTICLE The Relationship between Sarcoidosis of Intrathoracic Lymph Nodes and Digestive System Diseases: A
Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma
 Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD
 COPD DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD Confirm Diagnosis Presence and history of symptoms: Shortness of breath Cough
COPD DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD Confirm Diagnosis Presence and history of symptoms: Shortness of breath Cough
PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA
 Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
Thor-ax (1954), 9, 304. PULMONARY INFARCTS ASSOCIATED WITH BRONCHOGENIC CARCINOMA W. J. HANBURY, R. J. R. CURETON, AND G. SIMON From St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London BY (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION JUNE
CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT
 Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction
 Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction Poster No.: C-0143 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Kahkouee, R. Pourghorban, M. Bitarafan,
Isolated anthracosis: benign but neglected cause of bronchial stenosis and obstruction Poster No.: C-0143 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Kahkouee, R. Pourghorban, M. Bitarafan,
Surgical treatment of bullous lung disease
 Surgical treatment of bullous lung disease PD POTGIETER, SR BENATAR, RP HEWITSON, AD FERGUSON Thorax 1981 ;36:885-890 From the Respiratory Clinic, Groote Schuur Hospita', and Departments of Medicine, Anaesthetics,
Surgical treatment of bullous lung disease PD POTGIETER, SR BENATAR, RP HEWITSON, AD FERGUSON Thorax 1981 ;36:885-890 From the Respiratory Clinic, Groote Schuur Hospita', and Departments of Medicine, Anaesthetics,
PATTERNS OF DISTURBED LUNG FUNCTION IN PATIENTS
 Thorax (1959), 14, 216 PATTERNS OF DISTURBED LUNG FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMATOUS BULLAE BY COLIN OGILVIE AND MARY CATTERALL From the London Hospital In a previous publication (Ogilvie, 1959) an
Thorax (1959), 14, 216 PATTERNS OF DISTURBED LUNG FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH EMPHYSEMATOUS BULLAE BY COLIN OGILVIE AND MARY CATTERALL From the London Hospital In a previous publication (Ogilvie, 1959) an
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis?
 Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN
 THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
THE IMPORTANCE OF BRONCHOSCOPY IN THE RECOGNITION OF NON-OPAQUE FOREIGN BODY IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN BY N. ASHERSON, M.A., M.B., B.S., F.R.C.S. Surgeon to the Central London Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital
TESTS IN CLINICAL MEDICINE
 274 THE PLACE OF RESPIRATORY FUNCTION TESTS IN CLINICAL MEDICINE D. V. BATES, M.D., M.R.C.P. First Assistant, Mledical Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London, E.C.i Introduction It is difficult to settle
274 THE PLACE OF RESPIRATORY FUNCTION TESTS IN CLINICAL MEDICINE D. V. BATES, M.D., M.R.C.P. First Assistant, Mledical Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital, London, E.C.i Introduction It is difficult to settle
Radiological Features of Mycobacterium tuberculosis TUBERCULE BACILLUS TUBERCULE BACILLUS DIAGNOSIS. Guy Richards. PATHOGENESIS of TUBERCULOSIS
 Radiological Features of Guy Richards Department of critical care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa TUBERCULE BACILLUS Discovery
Radiological Features of Guy Richards Department of critical care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa TUBERCULE BACILLUS Discovery
CLINICAL VIGNETTE Sarcoidosis: A Case Study Gloria Kim, M.D.
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE Sarcoidosis: A Case Study Gloria Kim, M.D. Case Report A 56-year-old female presented to her primary care physician with complaints of dyspnea on exertion and increasing cough. She reported
CLINICAL VIGNETTE Sarcoidosis: A Case Study Gloria Kim, M.D. Case Report A 56-year-old female presented to her primary care physician with complaints of dyspnea on exertion and increasing cough. She reported
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA
 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA INTRODUCTION In this lecture we will discuss atelectasis which is a complication of several medical and surgical
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 2: ATELECTASIS AND EMPHYSEMA INTRODUCTION In this lecture we will discuss atelectasis which is a complication of several medical and surgical
Imaging Features of Sarcoidosis on MDCT, FDG PET, and PET/CT
 AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Imaging Features of Sarcoidosis on MDCT, FDG PET, and PET/CT Hima B. Prabhakar 1, Chad B. Rabinowitz 1, Fiona K. Gibbons 2, Walter J. O Donnell 2,
AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Imaging Features of Sarcoidosis on MDCT, FDG PET, and PET/CT Hima B. Prabhakar 1, Chad B. Rabinowitz 1, Fiona K. Gibbons 2, Walter J. O Donnell 2,
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
COUGH Dr. A m A it i e t sh A g A garwa w l Le L ctu t rer Departm t ent t o f f M e M dic i in i e
 COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
Right infrahilar nodule
 Right infrahilar nodule Search Infrahilar nodule Nov 9, 2015.. CT chest showed a right infrahilar mass 3.5 2.5 cm along with multiple bilateral lung nodules of size 9 to 11 mm. Bronchoscopy. Jun 13, 2015.
Right infrahilar nodule Search Infrahilar nodule Nov 9, 2015.. CT chest showed a right infrahilar mass 3.5 2.5 cm along with multiple bilateral lung nodules of size 9 to 11 mm. Bronchoscopy. Jun 13, 2015.
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
CORRELATION OF CERTAIN BRONCHOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES SEEN IN CHRONIC BRONCHITIS WITH THE PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES
 Thorax (1955), 10, 199. CORRELATION OF CERTAIN BRONCHOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES SEEN IN CHRONIC BRONCHITIS WITH THE PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES BY LYNNE M. REID From the Institute of Diseases of the Chest, Brompton
Thorax (1955), 10, 199. CORRELATION OF CERTAIN BRONCHOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES SEEN IN CHRONIC BRONCHITIS WITH THE PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES BY LYNNE M. REID From the Institute of Diseases of the Chest, Brompton
Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT
 Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT Alan S. Brody, MD Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief, Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio, USA Pediatric High-Resolution CT Short
Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT Alan S. Brody, MD Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief, Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio, USA Pediatric High-Resolution CT Short
Thoracic Sarcoidosis Imaging Updated: Jul 19, 2013
 Thoracic Sarcoidosis Imaging Updated: Jul 19, 2013 Overview Radiography Computed Tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging Nuclear Imaging Show All Multimedia Library References Overview For patients with
Thoracic Sarcoidosis Imaging Updated: Jul 19, 2013 Overview Radiography Computed Tomography Magnetic Resonance Imaging Nuclear Imaging Show All Multimedia Library References Overview For patients with
