Clinical White Paper
|
|
|
- Mae Johnston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical White Paper
2 Table of Contents 1 Abstract 1 2 High Efficiency Aerosol Drug Delivery During Ventilation 2 3 A Lung Recruitment Strategy for Patients with Respiratory Failure utilising Aerogen 5 4 Comparison of Aerogen with MDIs 5 5 Superior Drug Deposition During HFOV 6 6 Optimal Drug Delivery During NIV & HFNC 7 7 Aerogen Aerosol Drug Delivery Technology for Non-Vented Patients 12 8 Aerogen Improves Clinical Outcomes in the Emergency Department 16 9 Aerogen in the OR Summary References 19
3 1 Abstract Aerogen s vibrating mesh technology, available within the Aerogen Solo, Aerogen Pro and NIVO has been adopted for use across many areas of the hospital during a variety of ventilatory support including conventional mechanical ventilation, high frequency oscillatory ventilation, non-invasive ventilation and high flow nasal cannula. Clinical researchers have established its superior performance in bench and imaging studies Aerogen devices can provide the patient with up to 9 fold higher drug dose than a standard small volume nebuliser (SVN) during mechanical ventilation 2. In paediatric patients in respiratory failure Aerogen aerosolised Salbutamol resulted in improved lung recruitment 14. It is also cost effective, as shown by multiple hospitals in the US switching to Aerogen and observing significant savings compared to MDIs The Aerogen technology is not only available for use during both invasive and non-invasive ventilation but can be used with spontaneously breathing patients with mouthpieces and masks throughout the acute care setting where Aerogen Ultra enables effective aerosol therapy of up to 35% inhaled dose available to the patient 19. Recent clinical data have shown significant improvements in clinical outcomes and reduced drug dose in the ED for all patients requiring Salbutamol via the Aerogen Ultra 37. Key Take Away Points Aerogen s vibrating mesh technology has been adopted across the hospital and used during MV, HFOV, NIV, HFNC and with spontaneous breathing patients. Aerogen technology enables optimal aerosol therapy across all ventilatory support. Substantial cost savings have been observed in comparison to MDIs in the US. Improved lung recruitment compared to baseline can be achieved with Aerogen aerosolised Salbutamol in paediatric respiratory failure patients. Bench, imaging and case studies all provide evidence of the superior performance of the Aerogen aerosol drug delivery devices. Improved clinical outcomes observed with use of the Aerogen Ultra in the ED. Clinical White Paper 1
4 2 High Efficiency Aerosol Drug Delivery During Ventilation Aerogen devices are highly efficient vibrating mesh aerosol drug delivery systems which can be used inline during any type of respiratory support including mechanical ventilation, high frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV), non-invasive ventilation (NIV), continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) 1-4, 7, 20, 23. The Aerogen Solo utilises active vibrating mesh technology, where energy applied to the vibrational element, causes vibration of each of the 1000 funnel shaped apertures within the mesh. The mesh acts as a micropump drawing liquid through the holes producing a low velocity aerosol optimised for targeted drug delivery to the lungs. The Aerogen device can deliver 9 times more aerosol dose compared to standard small volume nebuliser during mechanical ventilation 2, and outperforms all standard small volume nebulisers when positioned at both the wye (proximal to the patients in the inspiratory limb) and before the humidifier 2 (Figure 1). While the Ultrasonic nebuliser efficiency is comparable to the Aerogen Solo at the Y, there are many limitations with the device which include an inability to aerosolise viscous solutions, heat generation which can degrade some solutions and large residual volumes 21. Furthermore the use of ultrasonic nebulisers is now minimal in the hospitals. This difference in aerosol deposition related to positioning was originally studied by Ari et al. and demonstrated improved deposition when the Aerogen Solo was placed before the humidifier compared to at the wye with both adult and paediatric settings when utilising a bias flow 1 ; without bias flow improved aerosol deposition was noted when the nebuliser was positioned closer to the patient 22. 2
5 Aerogen Drug Dose, % * * * * * SVN (Hudson) SVN (Salter) USN Prior to the Humidifier At the Wye Figure 1 Comparison of drug deposition after aerosol therapy through a ventilation circuit with standard small volume nebulisers, ultrasonic and the Aerogen Solo. The position of the nebuliser tested included: at the wye and before the humidifier (closer to the ventilator). In this paediatric model of mechanical ventilation with bias flow the Aerogen Solo outperforms both small volume nebulisers in both positions in the ventilator circuit. *p< Adapted from 2. Clinical White Paper 3
6 Physiological lung dose was studied in an infant animal model, where quantification of radiolabelled aerosol was measured after inhalation through a ventilator circuit, tested with both a small volume nebuliser and the Aerogen Pro. The Aerogen Pro demonstrated a 25 fold higher deposition of aerosol in the lungs compared to a standard small volume nebuliser 13. The Aerogen Pro achieved a lung dose of 13% and the difference in aerosol deposition between the two systems can be clearly observed in the scintigraphy pictures below (Figure 2) 13. The superior drug deposition available with Aerogen is associated with the minimal residual volume left in the device after nebulisation. Standard small volume nebulisers on average leave up to half of the drug behind which can be quite costly when using more expensive drugs 24. Dubus et al. observed that the standard small volume nebuliser has a residual volume of 1.1 ml after nebulisation of 3-mL of solution. In contrast the Aerogen Pro had a residual volume of 0.1 ml after 0.5-mL 13. Small Volume Nebuliser Aerogen Pro Figure 2 Lung Scintigraphy images of a ventilated infant animal model after inhalation of radiolabelled aerosol using either a small volume nebuliser or the Aerogen Pro. The Aerogen Pro delivered a significantly greater lung dose than the small volume nebuliser. Adapted from 13. 4
7 3 Lung Recruitment Strategy for Patients with Respiratory Failure utilising Aerogen Strategies to improve lung recruitment in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and respiratory failure can include the use of B-agonists. These drugs are used extensively to treat hypoxemic ventilated patients even without a confirmed clinical benefit. A recent study has investigated whether providing inhaled Salbutamol delivered by Aerogen technology can improve the lung function of paediatric patients 14. Compared 4 that to baseline, aerosolised Salbutamol improved the functional residual capacity of critically ill children with respiratory failure. This study provides new evidence for the use of aerosolised B-agonists as another strategy to improve lung recruitment with ARDS 14. Comparison of Aerogen with MDIs Although drug delivery efficiency has been shown to be similar between a pressurised metered dose inhaler (pmdi) and Aerogen 22, the actual dose emitted from the pmdis (e.g, 100µg per actuation with Salbutamol) is much lower than the typical 2.5mg dose used with Aerogen. In addition, pmdis aren t without difficulties as failure to synchronise actuations with inspiration has been shown to reduce the aerosol drug delivery 25. It is also important to ensure canisters are shaken before use as the dose may vary due to separation from the propellant 26. There are several studies, which provide evidence the cost savings of switching from combivent MDI to the Aerogen Solo is significant 15-18, 27. Blake et al. discussed substantial cost savings in conjunction with staff satisfaction after switching and a potential system wide annual saving of up to $1.74 million across 105 hospitals 15. Loborec et al. investigated the financial impact of replacing ipratropium-albuterol MDIs for Aerogen and calculated a three month cost saving of $99,359 and projected yearly saving of $397, Clinical White Paper 5
8 5 Superior Drug Deposition during HFOV HFOV has historically been a challenge for aerosol administration. It represents another ventilation mode where aerosol can be delivered during the therapy with Aerogen technology. In an in vitro model of adult, paediatric and infant ventilation, Fang et al. compared drug deposition during HFOV with the Aerogen Solo in comparison to a standard small volume nebuliser 3. Drug deposition was minimal with both devices during HFOV when the nebuliser was placed back at the humidifier. Conversely, the deposition of aerosol in all simulated lung models was significantly higher with the Aerogen Solo compared to standard ventilation when the Aerogen Solo was placed proximal to the patient (Figure 3) p=0.010 Aerogen SVN 1400 Drug Drug Mass, µg p<0.001 p= p=0.164 p=0.029 N/A 0 Distal Proximal Distal Proximal Distal Proximal Adult Paediatric Infant Figure 3 Aerosol delivery during HFOV using the Aerogen Solo compared to a standard small volume nebuliser. Positioning of the Aerogen Solo closer to the patient provided a higher drug deposition. Adapted from 3. 6
9 6 Optimal Drug Delivery During NIV & HFNC The Aerogen device can also be connected to a NIV circuit and can deliver aerosol during NIV and CPAP. Studies have shown that aerosol deposition with the Aerogen Pro connected into the circuit, patient side of the leak valve, provided 2-3 fold more inhaled drug than a standard small volume nebuliser in the same position. The importance of positioning of the nebuliser is observed in this study as the Aerogen Pro efficiency of 51% is reduced to 19% if connected before the leak valve (Figure 4) % Aerogen SVN Drug Deposition, µg % 18.7% 6.8% 0 Patient side of the leak port Ventilator side of the leak port Figure 4 Aerosol dose at the patient side and ventilator side of the leak port during NIV. The Aerogen Pro provided increased dose both at the patient and ventilator side of the leak port in comparison to the SVN. Aerosol dose is higher when either nebuliser is positioned patient side of the leak port. Adapted from 4. Clinical White Paper 7
10 Additional studies have confirmed these data with the NIVO, which fits directly into an NIV mask 6, 28. In an in vitro comparison of a vibrating mesh (NIVO) vs a small volume nebuliser during NIV, a similar difference in inhaled drug was noted (Figure 5) 6. It is also important to note that the efficiency of the Aerogen Solo and NIVO has been directly compared and similar aerosol deposition has been reported 29. Inhaled Aerosol During CPAP & Bi-Level NIV (% of Initial Charge) Legend Each data point represents the mean of two test runs. Inhaled Aerosol (% of Initial Charge) NIVO CPAP = 5 NIVO S/T = 15/8 NIVO S/T = 10/5 SVN CPAP = 5 SVN S/T = 15/8 SVN S/T = 10/ Treatment Time (minutes) Figure 5 Aerosol deposition during NIV using the NIVO and a small volume nebuliser. During both BIPAP and CPAP aerosol deposition was higher with the NIVO compared to the small volume nebuliser. Adapted from 6. 8
11 Lung dose correlates directly to these in vitro studies. Galindo-Filho et al. completed a scintigraphy study with healthy patients using the NIVO during NIV and quantified the inhaled dose to be 23.1% for the vibrating mesh and 6.1% with the small volume nebuliser. A lung dose of 5.5% was measured with the vibrating mesh, which was 3-4 fold greater than the 1.5% measured with a standard small volume nebuliser (Figure 6) 5. NIVO SVN Figure 6 Distribution of aerosol in the lungs of healthy patients after nebulisation with a SVN and NIVO. Lung deposition is significantly greater with the NIVO. Adapted from 5. Clinical White Paper 9
12 Aerosol therapy during the use of High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) can be provided by the Aerogen Solo inline with a variety of HFNC systems, delivering aerosol directly through the nasal cannula. This technique allows aerosol delivery without interruption of oxygen flow and pressure and is more effective than placement of an aerosol mask over the nasal cannula. Preliminary studies have demonstrated sub-optimal delivery of aerosol with the placement of aerosol masks over the cannula compared to taking the cannula off to administer aerosol therapy 30. Initial studies have demonstrated that the Aerogen Solo can provide effective aerosol therapy through the cannula of a HFNC system 7, 31, 32. Ari et al. studied aerosol delivery in paediatric patients and showed that an inhaled dose of 11% was achievable at a gas flow rate of 3L/min. The effect of flow and gas type does modify the aerosol deposition where heliox and lower flow rates have a favourable effect on aerosol dose 7. More recent research into adult HFNC showed that placing the Aerogen Solo before the humidifier provided optimal aerosol therapy in comparison to two small volume nebulisers 8. Reminiac at al. commented that the Aerogen Solo was associated with high nebulisation efficiency, a high fraction of aerosol made of particle with a diameter of 0.4 to 4.4 µm, a shorter nebulisation duration, and the absence of added gas flow which could potentially influencing the inspired oxygen fraction 8. A lung dose of between 2-10% were achieved at flows rates 30, 45, and 60 L/min and aerosol delivered was greater with distressed breathing than with normal breathing. This may be due to the higher inspiratory flow and volumes, allowing more of the aerosol to be inhaled (Figure 7) * 30 l/min * 45 l/min Respirable Mass, % 10 5 * 60 l/min 0 Quiet Respiratory Distress Simulated Breathing Pattern Figure 7 Respirable dose measured at three flow rates of 30, 45 and 60 L/min and with two different breathing patterns; quiet and respiratory distress. Increasing flow rate results in a decrease in respirable mass. Elevated aerosol was delivered with distressed breathing than with normal breathing. Adapted from 8. 10
13 Alcoforado et al. have recently studied the effect of flow rate on aerosol deposition during adult HFNC in healthy patients 33. The study results correlated with previous in vitro data demonstrating higher aerosol deposition is achieved at lower flow rates (Figure 8). 10L/min 30L/min 50L/min Lung Dose (%) 10.6 ± ± ± 0.8 Figure 8 Actual lung deposition in health patients during HFNC at flow rates of 10, 30 and 50 L/min. A lung dose of 10.6% is achievable at a flow rate of 10L/min. Lower flow rates correlate with higher drug deposition. Adapted from 33. Clinical White Paper 11
14 7Aerogen Aerosol Drug Delivery Technology For Non-Vented Patients The Aerogen Ultra, which can be used with the Aerogen Solo provides a platform to deliver aerosolised drugs to spontaneously breathing patients with mouthpiece and mask for use across the entire acute care setting. The Aerogen Ultra connects to low flow oxygen and can be used for both intermittent and continuous treatments in both paediatric and adult patients (Figure 9). The device is composed of a valved collection chamber, which connects the Aerogen Solo and a mouthpiece or facemask (Figure 9). The innovative design of the device s valved system controls the flow of air through the aerosol chamber. On inhalation, the air is drawn through the inlet valve on the base of the device creating a flow of air or oxygen through the device. This purges the aerosol chamber of aerosol and delivers drug to the patient via the mouthpiece. When the patient breaths out, the inlet valve closes and the exhalation valve on the mouthpiece opens. This allows the patient to exhale through the port on the mouthpiece while the aerosol chamber is refilled by the Aerogen Solo. Valved Mask Mouth Piece Exhalation Valve Inlet Valve Aerogen Solo Figure 9 Aerogen Ultra O 2 Port 12
15 Initial bench testing has demonstrated the aerosol drug deposition of this new offering compared with small volume nebulisers is highly efficient providing an inhaled dose available to the patient of up to 35% with no added flow 19 (Figure 10). In addition, as the Aerogen Solo has minimal residual volume remaining after aerosol treatments, more drug will therefore be available to the patient compared to a standard small volume nebuliser 12, 24. Even with the addition of 2 litre per minute of flow through the device, 15% inhaled dose is still achievable with the Aerogen Ultra with a mouthpiece or valved face mask (Figure 10) 19. Aerogen Ultra SVN 40 p= Inhaled Mass, % p=0.014 p= p= Mouthpiece Valved Mask Open Mask Mouthpiece (no oxygen) Figure 10 Inhaled dose of the Aerogen Ultra compared to a standard small volume nebuliser with 2 litres per minute of flow through the device. The mouthpiece, a valved and open mask were tested where an enhanced efficiency was noted with mouth piece or valved mask. When no flow is utilised, 35% inhaled dose can be achieved with the mouthpiece. Adapted from 19. Clinical White Paper 13
16 The Aerogen Ultra also provides a more efficient delivery of medication in a shorter period of time as observed by Hickin et al. (Figure 11): Our labbased study has shown that a vibrating mesh system is quicker and more effective than a small volume nebuliser, delivering more Salbutamol over a shorter period of time. Initial data on the device performance has supported their hypothesis that a mesh nebuliser is a more effective method of delivering inhaled bronchodilators to patients with respiratory disease as the study demonstrated that in a COPD model the device provides more than 8 times the medication in nearly half the time (Figure 11) Aerogen Ultra 140 SVN 120 COPD Breathing Pattern Dose Rate, µg/min Nebulisation Time (mins: secs) Respirable Dose (% of total dose) Aerogen Ultra Jet Nebuliser % 1.6% COPD * Residual Volume (%) 0.9% 42.9% Figure 11 The dose rate of the Aerogen Ultra compared to a small volume nebuliser and the nebulisation time, respirable dose and residual volume. The Aerogen Ultra provides a superior dose in a shorter period of time with minimal residual volume left in the nebuliser. Adapted from
17 Multiple scintigraphy studies have determined the pulmonary aerosol deposition in healthy adults and demonstrated a 4-6 fold significant rise in drug entering the lungs using the Aerogen Ultra with a mouth piece compared to a standard small volume nebuliser (Figure 12) 9, 11. In addition to this, experience of using Aerogen in the Emergency department by Baystate hospital both with spontaneously breathing patients and with HFNC led to a performance improvement plan for paediatric patient in respiratory distress 34. The goal was to improve the clinical outcome of these patients with the least invasive methods. The improvements included use of Aerogen and HFNC. The plan resulted in a positive impact on clinical outcomes and staff and patient satisfaction. The same hospital has already noted in two case studies describing their experience with the Aerogen Ultra, that the use of the device with a mouthpiece or valved mask improved clinical response in paediatric patients with asthma exacerbations and potentially prevented escalation of care 35, 36. a Aerogen Ultra Small Volume Nebuliser b Figure 12 Scintigraphic images of the lung deposition of aerosol using the Aerogen Ultra or a small volume nebuliser. (a) Alcoforado et al. 9 and (b) Dugernier et al. 11 In both studies the lung deposition was significantly higher with the use of the Aerogen Ultra (left images) compared to the small volume nebuliser (right images). Clinical White Paper 15
18 8Aerogen Improves Clinical Outcomes in the Emergency Department The Aerogen Ultra has demonstrated improved inhaled dose and superior lung deposition compared to standard SVNs in multiple bench and imaging studies. Although it s important to note the improved efficiency of the Aerogen Ultra, clinical outcome data in patients is essential to support healthcare and economic arguments for use of this device. A retrospective chart review was recently completed comparing emergency department (ED) patients who received aerosolised bronchodilator treatments. The review compared the hospital standard practice with an SVN to implementation of the Aerogen Ultra. A total of 1594 patients were included in the study. When compared to the standard SVN treatment the admission rate of patients into the hospital was 32% lower with the Aerogen Ultra. Discharges home from the ED were 30% higher with the Aerogen Ultra and the median length of stay in the ED was 37 minutes less per patient 37. Furthermore, the Salbutamol dose required to alleviate symptoms was significantly lower when the Aerogen Ultra was used (Figure 13). This retrospective study has shown significant improvements in clinical outcomes and reduced drug dose for all patients requiring Salbutamol in the ED when delivery was via the Aerogen Ultra 37. These data confirm the health and economic impact of using Aerogen technology in the ED. 16
19 a b 50 p<0.05 % Admission Rates % 41% % Discharge Rates % p< % 0 Aerogen Ultra SVN 0 Aerogen Ultra SVN c LOS (hours) Median = 4.17 hrs p= Median = 4.79 hrs d 5 mg 15% 2.5 mg 85% Aerogen Ultra 400 mg 1% > 7.5 mg 23% 5 mg 29% SVN 2.5 mg 47% p< Aerogen Ultra SVN Figure 13 Retrospective chart review of patients in the ED requiring bronchodilator treatment. (a) Admission rate into the hospital was 32% lower when compared to the standard SVN treatment. (b) Discharges home from the ED were 30% higher with the Aerogen Ultra when compared to the standard SVN treatment. (c) Median length of stay in the ED was 37 minutes less per patient with Aerogen Ultra when compared to the standard SVN treatment. (d) Salbutamol dose was significantly lower with the Aerogen Ultra when compared to the standard SVN treatment 37. Clinical White Paper 17
20 9 Aerogen in the OR The Aerogen Solo can also be used during surgery in the presence of general anaesthesia in line with the limits outlined in the instructions for use. A case study published in 2012 described an intraoperative bronchospasm of a 3 year old asthmatic patient admitted for dental restorations under general anaesthetic 38. The bronchospasm was relieved with the use of the Aerogen Pro after MDI, small volume nebuliser and other pharmacologic interventions failed Summary Aerogen provides superior aerosol therapy within the intensive care environment during ventilation, NIV, HFNC and with spontaneously breathing patients. In addition to the optimal performance, substantial cost savings have also been acknowledged when hospitals make the transition to the device. This advanced aerosol delivery is now available across the acute care setting delivering optimal aerosol treatments to all respiratory patients. 18
21 11References 1 Ari A, Atalay OT, Harwood R, Sheard MM, Aljamhan EA and Fink JB. Influence of nebulizer 7 Ari A, Harwood R, Sheard M, Dailey P and Fink JB. In vitro comparison of heliox and oxygen in type, position, and bias flow on aerosol drug aerosol delivery using pediatric high flow nasal delivery in simulated pediatric and adult lung cannula. Pediatric pulmonology. 2011;46: models during mechanical ventilation. Respiratory care. 2010;55: Berlinski A and Willis JR. Albuterol delivery by 4 different nebulizers placed in 4 different positions in a pediatric ventilator in vitro model. Respiratory 8 Reminiac F, Vecellio L, Heuze-Vourc h N, Petitcollin A, Respaud R, Cabrera M, Le Pennec D, Diot P and Ehrmann S. Aerosol Therapy in Adults Receiving High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy. Journal of aerosol medicine and pulmonary drug delivery. care. 2013;58: Fang TP, Lin HL, Chiu SH, Wang SH, DiBlasi RM, Tsai YH and Fink JB. Aerosol Delivery Using Jet 9 Alcoforado L, de Melo Barcelar J, Castor Galindo V, Cristina S. Brandão S, Fink J, B. and Dornelas Nebulizer and Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer During de Andrade A. Analysis of Deposition Radioaerosol High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation: An In Vitro Nebulizers Membrane in Healthy Subjects. ISAM Comparison. Journal of aerosol medicine and poster presentation pulmonary drug delivery Abdelrahim ME, Plant P and Chrystyn H. In-vitro characterisation of the nebulised dose during 10 Ari A, de Andrade A, Sheard M, AlHamad B and Fink JB. Performance Comparisons of Jet and Mesh Nebulizers Using Different Interfaces non-invasive ventilation. The Journal of pharmacy in Simulated Spontaneously Breathing Adults and pharmacology. 2010;62: and Children. Journal of aerosol medicine and 5 Galindo-Filho VC, Ramos ME, Rattes CS, Barbosa AK, Brandao DC, Brandao SC, Fink JB and de Andrade AD. Radioaerosol Pulmonary Deposition 11 pulmonary drug delivery Dugernier J, Reychler G, Depoortere V, Roeseler J, Michotte JB, Laterre PF, Jamar F and Hesse M. Using Mesh and Jet Nebulizers During Noninvasive Tomoscintigraphiccomparison of lung deposition Ventilation in Healthy Subjects. Respiratory care. with a vibrating-mesh and a jet nebulizer. ERS 2015;60: conference poster McPeck M. Improved Aerosol Drug Delivery with an Electronic Mesh Nebulizer during Non-invasive 12 Hickin S, Mac Loughlin R, Sweeney L, Tatham A and Gidwani S. Comparison of mesh nebuliser Ventilation AARC poster versus jet nebuliser in simulated adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Poster at the College of Emergency Medicine Clinical Excellence Conference Clinical White Paper 19
22 13 Dubus JC, Vecellio L, De Monte M, Fink JB, Grimbert D, Montharu J, Valat C, Behan N and 19 Ari A, de Andrade AD, Sheard M, AlHamad B and Fink JB. Performance Comparisons of Jet and Mesh Diot P. Aerosol deposition in neonatal ventilation. Nebulizers Using Different Interfaces in Simulated Pediatric research. 2005;58:10-4. Spontaneously Breathing Adults and Children. 14 Ramsi MA, Henry M, Milla CE and Cornfield DN. Inhaled beta2-agonist Therapy Increases Functional Residual Capacity in Mechanically Ventilated Children With Respiratory Failure. 20 Journal of aerosol medicine and pulmonary drug delivery. 2015;28: Reminiac F, Vecellio L, Heuze-Vourc h N, Petitcollin A, Respaud R, Cabrera M, Pennec DL, Diot P and Pediatric critical care medicine : a journal of the Ehrmann S. Aerosol Therapy in Adults Receiving Society of Critical Care Medicine and the World High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy. Journal Federation of Pediatric Intensive and Critical Care of aerosol medicine and pulmonary drug delivery. Societies. 2015;16:e ;29: Blake G, Yaklic J and Cobb J. Transition from ipratropium/albuterol inhaler to nebulizer on quality 21 Ari A and Fink JB. Guidelines for aerosol devices in infants, children and adults: which to choose, and cost savings in ventilated patients. Poster why and how to achieve effective aerosol therapy. presentation at American Society of Health-System Expert review of respiratory medicine. 2011;5:561- Pharmacists McDaniel C, Glynn G, Gudowski S, Pezzano T and Weibel S. Conversion of pressurized Metered-Dose 22 Ari A, Areabi H and Fink JB. Evaluation of aerosol generator devices at 3 locations in humidified and Inhaler to Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer Administered non-humidified circuits during adult mechanical Medications. Poster presentation at the Society of ventilation. Respiratory care. 2010;55: Critical Care Medicine Streepy KS, Dawson AM, Grigonis AM, Hammerman SI and Snyder LK. Conversion from metered dose 23 Sidler-Moix AL, Di Paolo ER, Dolci U, Berger- Gryllaki M, Cotting J and Pannatier A. Physicochemical aspects and efficiency of inhalers to a vibrating mesh nebulizer in long albuterol nebulization: comparison of three term acute care hospitals: cost effectiveness and aerosol types in an in vitro pediatric model. respiratory staff perception Poster presentation at Respiratory care. 2015;60: American Society of Health-System Pharmacists Ari A, Fink JB and Dhand R. Inhalation Therapy 18 Loborec SM, Johnson SE and Keating EA. Financial effect of converting ipratropium-albuterol in Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation: An Update. Journal of aerosol medicine and pulmonary drug delivery therapy from inhalers to nebulizer treatments at an academic health system. American journal of health-system pharmacy : AJHP : official 25 Diot P, Morra L and Smaldone GC. Albuterol delivery in a model of mechanical ventilation. Comparison journal of the American Society of Health-System of metered-dose inhaler and nebulizer efficiency. Pharmacists. 2016;73: American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 1995;152:
23 26 Everard ML, Devadason SG, Summers QA and Le Souef PN. Factors affecting total and respirable 33 Alcoforado L, Ari A, De Melo Barcelar J, Brandao SS, Fink JB and Dornelas De Andrade A. dose delivered by a salbutamol metered dose Comparison of Aerosol Deposition with Heated inhaler. Thorax. 1995;50: and Unheated High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) in Healthy Adults. Poster presentation at ATS Emberger J. Cost Reduction using Aeroneb Solo in a Medical ICU Ventilator Population.. Respiratory Care, Christiana Care Health System, Newark, 34 Dailey P, Tina T, Santos J and Gurung P. Performance Improvement Plan for Pediatric 2011 OPEN FORUM Abstracts Patients in Respiratory Distress: Clinical Experience. Respiratory Therapy. 2015;10: White CC, Crotwell DN, Shen S, Salyer J, Yung D, Zheng J and DiBlasi RM. Bronchodilator delivery during simulated pediatric noninvasive ventilation. 35 Newsome T, Thayer T and Lieberman S. Pediatric Patient with Severe Asthma Treated with a Respiratory care. 2013;58: Vibrating Mesh with Valved Adapter. Respiratory Therapy Case Study. 2015;10: AlQuaimi M, Fink JB, Harwood R, Sheard M, Bryant L and Ari A. The effect of nebulizer type and mask design on aerosol delivery during 36 Thayer T, Hodgens E and Lieberman S. A Case Study: Use of Vibrating Mesh with a Valved noninvasive positive pressure ventilation of an Adapter in a Pediatric Patient with a Severe adult lung model. AARC poster Asthma Exacerbation. Respiratory Therapy Case 30 Alalwan M, Ari A, Fink J, Harwood R, Bryant L and Sheard M. Delivery of albuterol by pressurized metered-dose inhaler and jet nebulizer via mask 37 Study. 2016;11:52. Dunne R, Shortt SA and Dailey PA. Comparison of bronchodilator administration with vibrating mesh with high flow nasal cannula in place reduces with adapter and jet nebulizer in the emergency aerosol delivery. AARC Open Forum Abstract. department AARC Open Forum Abstract Bhashyam AR, Wolf MT, Marcinkowski AL, Saville A, Thomas K, Carcillo JA and Corcoran TE. Aerosol 38 Golden LR, Desimone HA, Yeroshalmi F, Pranevicius M and Saraghi M. Severe intraoperative bronchospasm treated with a vibrating-mesh delivery through nasal cannulas: an in vitro study. nebulizer. Anesthesia progress. 2012;59: Journal of aerosol medicine and pulmonary drug delivery. 2008;21: MacLoughlin R, Power P, Wolny M and Duffy C. Evaluation of vibrating mesh nebulizer performance during nasal high flow therapy. Poster Presentation at International Society of Aerosols in Medicine Clinical White Paper 21
24 Aerogen Ltd. Galway Business Park, Dangan, Galway, Ireland. INTL. US (886) PM349
Frequently Asked Questions.
 Frequently Asked Questions www.aerogen.com 1 FAQs Frequently asked questions are answered below and specifically for each of our products. If you have a question that is not listed, please feel free to
Frequently Asked Questions www.aerogen.com 1 FAQs Frequently asked questions are answered below and specifically for each of our products. If you have a question that is not listed, please feel free to
Dolci U 1, Sidler-Moix AL 1, Di Paolo ER 1,Berger- Gryllaki 1 M, Pannatier A 1, Cotting J 2
 SALBUTAMOL DELIVERY IN AN IN VITRO PAEDIATRIC VENTILATOR-LUNG MODEL: COMPARISON OF JET, ULTRASONIC AND MESH NEBULISERS Dolci U 1, Sidler-Moix AL 1, Di Paolo ER 1,Berger- Gryllaki 1 M, Pannatier A 1, Cotting
SALBUTAMOL DELIVERY IN AN IN VITRO PAEDIATRIC VENTILATOR-LUNG MODEL: COMPARISON OF JET, ULTRASONIC AND MESH NEBULISERS Dolci U 1, Sidler-Moix AL 1, Di Paolo ER 1,Berger- Gryllaki 1 M, Pannatier A 1, Cotting
Effective Aerosol Delivery in Acute Care
 Effective Aerosol Delivery in Acute Care Jim Fink, RRT, PhD, FAARC, FCCP Chief Science Officer, Aerogen Pharma Corp., San Mateo, CA USA Visiting Professor, Dept of Physical therapy, Universidade Federal
Effective Aerosol Delivery in Acute Care Jim Fink, RRT, PhD, FAARC, FCCP Chief Science Officer, Aerogen Pharma Corp., San Mateo, CA USA Visiting Professor, Dept of Physical therapy, Universidade Federal
Pediatrics in mechanical ventilation
 Pediatrics Optimization Intitulé du cours of aerosol therapy in mechanical ventilation Thèmes donnés Ermindo Di Paolo, PhD Departments of Pharmacy and Pediatrics Lausanne University Hospital Switzerland
Pediatrics Optimization Intitulé du cours of aerosol therapy in mechanical ventilation Thèmes donnés Ermindo Di Paolo, PhD Departments of Pharmacy and Pediatrics Lausanne University Hospital Switzerland
NIV and Aerosoltherapy
 NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU
 Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
600 RESPIRATORY CARE MAY 2016 VOL 61 NO 5
 Quantifying Aerosol Delivery in Simulated Spontaneously Breathing Patients With Tracheostomy Using Different Humidification Systems With or Without Exhaled Humidity Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Robert
Quantifying Aerosol Delivery in Simulated Spontaneously Breathing Patients With Tracheostomy Using Different Humidification Systems With or Without Exhaled Humidity Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Robert
Aerosol Delivery Through Adult High Flow Nasal Cannula With Heliox and Oxygen
 Aerosol Delivery Through Adult High Flow Nasal Cannula With Heliox and Oxygen Patricia A Dailey RRT, Robert Harwood MSA RRT-NPS FAARC, Kyle Walsh, James B Fink PhD RRT FAARC, Tina Thayer RRT, Greg Gagnon,
Aerosol Delivery Through Adult High Flow Nasal Cannula With Heliox and Oxygen Patricia A Dailey RRT, Robert Harwood MSA RRT-NPS FAARC, Kyle Walsh, James B Fink PhD RRT FAARC, Tina Thayer RRT, Greg Gagnon,
In Vitro Determination of the Main Effects in the Design of High-Flow Nasal Therapy Systems with Respect to Aerosol Performance
 Pulm Ther (2018) 4:73 86 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41030-018-0054-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH In Vitro Determination of the Main Effects in the Design of High-Flow Nasal Therapy Systems with Respect to Aerosol
Pulm Ther (2018) 4:73 86 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41030-018-0054-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH In Vitro Determination of the Main Effects in the Design of High-Flow Nasal Therapy Systems with Respect to Aerosol
Archives of Pulmonology and Respiratory Care
 v Clinical Group Archives of Pulmonology and Respiratory Care DOI CC By Marwa Mohsen 1, Ahmed A Elberry 2, Abeer Salah Eldin 3, Raghda RS Hussein 1 and Mohamed EA Abdelrahim 1,4 * Research Article Effects
v Clinical Group Archives of Pulmonology and Respiratory Care DOI CC By Marwa Mohsen 1, Ahmed A Elberry 2, Abeer Salah Eldin 3, Raghda RS Hussein 1 and Mohamed EA Abdelrahim 1,4 * Research Article Effects
High-Flow Nasal Cannula and Aerosolized Agonists for Rescue Therapy in Children With Bronchiolitis: A Case Series
 High-Flow Nasal Cannula and Aerosolized Agonists for Rescue Therapy in Children With Bronchiolitis: A Case Series Sherwin E Morgan RRT, Steve Mosakowski RRT, Patti Solano RRT, Jesse B Hall MD, and Avery
High-Flow Nasal Cannula and Aerosolized Agonists for Rescue Therapy in Children With Bronchiolitis: A Case Series Sherwin E Morgan RRT, Steve Mosakowski RRT, Patti Solano RRT, Jesse B Hall MD, and Avery
In Vitro Evaluation of Radio-Labeled Aerosol Delivery Via a Variable-Flow Infant CPAP System
 In Vitro Evaluation of Radio-Labeled Aerosol Delivery Via a Variable-Flow Infant CPAP System Kimberly D Farney RRT, Brandon T Kuehne RRT MBA, Laurie A Gibson RT (N), Leif D Nelin MD, and Edward G Shepherd
In Vitro Evaluation of Radio-Labeled Aerosol Delivery Via a Variable-Flow Infant CPAP System Kimberly D Farney RRT, Brandon T Kuehne RRT MBA, Laurie A Gibson RT (N), Leif D Nelin MD, and Edward G Shepherd
Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience
 Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience 8th Annual North Regional Respiratory Care Conference Minnesota & Wisconsin Societies for Respiratory Care Mayo Civic
Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience 8th Annual North Regional Respiratory Care Conference Minnesota & Wisconsin Societies for Respiratory Care Mayo Civic
Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer Compared With Metered-Dose Inhaler in Mechanically Ventilated Subjects
 Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer Compared With Metered-Dose Inhaler in Mechanically Ventilated Subjects Meagan N Dubosky MSc RRT, Yi-Fan Chen PhD, Mary E Henriksen MSc RRT, and David L Vines MHS RRT FAARC BACKGROUND:
Vibrating Mesh Nebulizer Compared With Metered-Dose Inhaler in Mechanically Ventilated Subjects Meagan N Dubosky MSc RRT, Yi-Fan Chen PhD, Mary E Henriksen MSc RRT, and David L Vines MHS RRT FAARC BACKGROUND:
Simone Gambazza, PT Cystic Fibrosis Centre, Milan Fondazione I.R.C.C.S. Cà Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico
 Simone Gambazza, PT Cystic Fibrosis Centre, Milan Fondazione I.R.C.C.S. Cà Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Aerosol Deposition and Particles Sizes þ Inertial impaction It occurs with larger (>3µm)
Simone Gambazza, PT Cystic Fibrosis Centre, Milan Fondazione I.R.C.C.S. Cà Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Aerosol Deposition and Particles Sizes þ Inertial impaction It occurs with larger (>3µm)
Factors affecting bronchodilator delivery in mechanically ventilated adults
 LITERATURE REVIEW Factors affecting bronchodilator delivery in mechanically ventilated adults Arzu Ari and James B Fink ABSTRACT Background: Bronchodilators are increasingly being used in patients undergoing
LITERATURE REVIEW Factors affecting bronchodilator delivery in mechanically ventilated adults Arzu Ari and James B Fink ABSTRACT Background: Bronchodilators are increasingly being used in patients undergoing
Pediatric Aerosol Therapy
 Pediatric Aerosol Therapy Ariel Berlinski MD Introduction Delivery Device Selection for the Treatment of Acute Pediatric Asthma Transnasal Aerosol Delivery in Pediatric Patients Delivery Device Selection
Pediatric Aerosol Therapy Ariel Berlinski MD Introduction Delivery Device Selection for the Treatment of Acute Pediatric Asthma Transnasal Aerosol Delivery in Pediatric Patients Delivery Device Selection
Respiratory Care in PICU Aerosol Therapy ส พ ชชา ชา แสงโขต โรงพยาบาลสมเด จพระป นเกล า
 Respiratory Care in PICU Aerosol Therapy น.อ.หญ ง ส พ ชชา ชา แสงโขต โรงพยาบาลสมเด จพระป นเกล า Aerosol liquid droplets or solid particles suspended in a gas(air) visible like fog Aerosol vs Humidity Humidity
Respiratory Care in PICU Aerosol Therapy น.อ.หญ ง ส พ ชชา ชา แสงโขต โรงพยาบาลสมเด จพระป นเกล า Aerosol liquid droplets or solid particles suspended in a gas(air) visible like fog Aerosol vs Humidity Humidity
In Vitro Comparison of Aerosol Delivery Using Different Face Masks and Flow Rates With a High-Flow Humidity System
 In Vitro Comparison of Aerosol Delivery Using Different Face Masks and Flow Rates With a High-Flow Humidity System Hui-Ling Lin MSc RRT RN FAARC, Robert J Harwood MSA RRT FAARC, James B Fink PhD RRT FAARC,
In Vitro Comparison of Aerosol Delivery Using Different Face Masks and Flow Rates With a High-Flow Humidity System Hui-Ling Lin MSc RRT RN FAARC, Robert J Harwood MSA RRT FAARC, James B Fink PhD RRT FAARC,
Reliability of Vibrating Mesh Technology
 Reliability of Vibrating Mesh Technology Ashwin A Gowda DO, Ann D Cuccia MPH RRT-NPS RPFT, and Gerald C Smaldone MD PhD BACKGROUND: For delivery of inhaled aerosols, vibrating mesh systems are more efficient
Reliability of Vibrating Mesh Technology Ashwin A Gowda DO, Ann D Cuccia MPH RRT-NPS RPFT, and Gerald C Smaldone MD PhD BACKGROUND: For delivery of inhaled aerosols, vibrating mesh systems are more efficient
Articles. The Advantages of Nebulization in the Treatment of Mechanically Ventilated Neonates. Kristin Smith, RRT-NPS
 Articles The Advantages of Nebulization in the Treatment of Mechanically Ventilated Neonates Kristin Smith, RRT-NPS A major goal in the care of premature babies is growth, and so all therapies are applied
Articles The Advantages of Nebulization in the Treatment of Mechanically Ventilated Neonates Kristin Smith, RRT-NPS A major goal in the care of premature babies is growth, and so all therapies are applied
I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI)
 I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) II. Policy: Aerosol medication administration by metered dose inhaler will be performed upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel.
I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) II. Policy: Aerosol medication administration by metered dose inhaler will be performed upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel.
It is recommended that a mask and protective eyewear be worn when providing care to a patient with a cough
 UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
Intracheal antibiotics administration
 Intracheal antibiotics administration Jean Chastre, M.D. www.reamedpitie.com Disclosure Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Bayer, Pfizer, Cubist/Merck, Basilea, Kenta/Aridis, Roche, AstraZeneca/Medimmune
Intracheal antibiotics administration Jean Chastre, M.D. www.reamedpitie.com Disclosure Conflicts of interest: Consulting or Lecture fees: Bayer, Pfizer, Cubist/Merck, Basilea, Kenta/Aridis, Roche, AstraZeneca/Medimmune
Misty Max 10 nebulizer
 AirLife brand Misty Max 10 nebulizer Purpose Introduction Delivery of nebulized medication to the lungs is a complex process dependant upon a variety of clinical and device-related variables. Patient breathing
AirLife brand Misty Max 10 nebulizer Purpose Introduction Delivery of nebulized medication to the lungs is a complex process dependant upon a variety of clinical and device-related variables. Patient breathing
Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment (Hand-Held)
 Small Volume Aerosol Treatment Page 1 of 6 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment To standardize the delivery of inhalation aerosol drug therapy via small volume (hand-held)
Small Volume Aerosol Treatment Page 1 of 6 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment To standardize the delivery of inhalation aerosol drug therapy via small volume (hand-held)
8/13/11. RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3. Humidification Equipment. Aerosol Therapy
 1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
1 RSPT 1410 Humidity & Aerosol Therapy Part 3 Wilkins: Chapter 35, p. 775-799 Cairo: Chapter 4, p. 88-143 2 Humidification Equipment A humidifier is a device that adds molecular liquid (e.g. water vapor)
Effects of Heat and Moisture Exchangers and Exhaled Humidity on Aerosol Deposition in a Simulated Ventilator-Dependent Adult Lung Model
 Effects of Heat and Moisture Exchangers and Exhaled Humidity on Aerosol Deposition in a Simulated Ventilator-Dependent Adult Lung Model Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Khalid S Alwadeai MSc RRT-NPS, and
Effects of Heat and Moisture Exchangers and Exhaled Humidity on Aerosol Deposition in a Simulated Ventilator-Dependent Adult Lung Model Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Khalid S Alwadeai MSc RRT-NPS, and
Radioaerosol Pulmonary Deposition Using Mesh and Jet Nebulizers During Noninvasive Ventilation in Healthy Subjects
 Radioaerosol Pulmonary Deposition Using Mesh and Jet Nebulizers During Noninvasive Ventilation in Healthy Subjects Valdecir C Galindo-Filho PhD, Maria Eveline Ramos PT, Catarina SF Rattes MSc, Antônio
Radioaerosol Pulmonary Deposition Using Mesh and Jet Nebulizers During Noninvasive Ventilation in Healthy Subjects Valdecir C Galindo-Filho PhD, Maria Eveline Ramos PT, Catarina SF Rattes MSc, Antônio
NebuTech nebulizer from Salter. Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION. To help you and your patients. easy. breathe
 nebulizer from Salter To help you and your patients breathe easy Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION nebulizer from Salter Let go to work for you and your patients today. Performance Versatility
nebulizer from Salter To help you and your patients breathe easy Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION nebulizer from Salter Let go to work for you and your patients today. Performance Versatility
OPTIMISING ANALYTICAL STRATEGIES FOR THE DEMONSTRATION OF BIOEQUIVALENCE IN A GENERIC NEBULISER
 OPTIMISING ANALYTICAL STRATEGIES FOR THE DEMONSTRATION OF BIOEQUIVALENCE IN A GENERIC NEBULISER US FDA guidance for the in vitro demonstration of bioequivalence in a generic nebuliser directly references
OPTIMISING ANALYTICAL STRATEGIES FOR THE DEMONSTRATION OF BIOEQUIVALENCE IN A GENERIC NEBULISER US FDA guidance for the in vitro demonstration of bioequivalence in a generic nebuliser directly references
Delay Between Actuation and Shaking of a Hydrofluoroalkane Fluticasone Pressurized Metered-Dose Inhaler
 Delay Between Actuation and Shaking of a Hydrofluoroalkane Fluticasone Pressurized Metered-Dose Inhaler Ariel Berlinski MD, Dirk von Hollen, John N Pritchard PhD, and Ross HM Hatley PhD BACKGROUND: Inhaled
Delay Between Actuation and Shaking of a Hydrofluoroalkane Fluticasone Pressurized Metered-Dose Inhaler Ariel Berlinski MD, Dirk von Hollen, John N Pritchard PhD, and Ross HM Hatley PhD BACKGROUND: Inhaled
The Impact of Aerosol Devices and Delivery Interfaces on Aerosol Deposition in Children Receiving Noninvasive Ventilation
 Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Respiratory Therapy Theses Department of Respiratory Therapy Spring 4-4-2018 The Impact of Aerosol Devices and Delivery Interfaces on Aerosol
Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Respiratory Therapy Theses Department of Respiratory Therapy Spring 4-4-2018 The Impact of Aerosol Devices and Delivery Interfaces on Aerosol
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators
 I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre
 PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
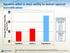 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Albuterol Delivery via Intrapulmonary Percussive Ventilator and Jet Nebulizer in a Pediatric Ventilator Model
 Albuterol Delivery via Intrapulmonary Percussive Ventilator and Jet Nebulizer in a Pediatric Ventilator Model Ariel Berlinski MD and J Randy Willis RRT-NPS BACKGROUND: In-line administration of bronchodilators
Albuterol Delivery via Intrapulmonary Percussive Ventilator and Jet Nebulizer in a Pediatric Ventilator Model Ariel Berlinski MD and J Randy Willis RRT-NPS BACKGROUND: In-line administration of bronchodilators
Important Principles of Aerosol Therapy for Your Patients
 Important Principles of Aerosol Therapy for Your Patients Disclaimer Appendix 3 Declaration of Vested Interest Form Name of presenter: David Henry RRT Name of employer: DeVilbiss Healthcare Inc. Definition:
Important Principles of Aerosol Therapy for Your Patients Disclaimer Appendix 3 Declaration of Vested Interest Form Name of presenter: David Henry RRT Name of employer: DeVilbiss Healthcare Inc. Definition:
University of Groningen. Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne
 University of Groningen Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Technology in practice Lexmond, Anne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
GE Healthcare. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator. Relief, Relax, Recovery
 GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
JAMES B. FINK, RAJIV DHAND, JERRY GRYCHOWSKI, PATRICK J. FAHEY, and MARTIN J. TOBIN
 Reconciling In Vitro and In Vivo Measurements of Aerosol Delivery from a Metered-Dose Inhaler during Mechanical Ventilation and Defining Efficiency-enhancing Factors JAMES B. FINK, RAJIV DHAND, JERRY GRYCHOWSKI,
Reconciling In Vitro and In Vivo Measurements of Aerosol Delivery from a Metered-Dose Inhaler during Mechanical Ventilation and Defining Efficiency-enhancing Factors JAMES B. FINK, RAJIV DHAND, JERRY GRYCHOWSKI,
Rush University, College of Health Sciences
 Rush University, College of Health Sciences An Evaluation of the Prototype OxyMulti Mask Prototype Compared to the Oxymask Aerosol, OxyMulti Mask and Airlife Aerosol Mask for Aerosol Delivery in Adults
Rush University, College of Health Sciences An Evaluation of the Prototype OxyMulti Mask Prototype Compared to the Oxymask Aerosol, OxyMulti Mask and Airlife Aerosol Mask for Aerosol Delivery in Adults
experiences that matter
 Salter Labs Product Catalog Aerosol Delivery Products International 2015 Distinct products experiences that matter International 2015 Aerosol delivery NebuTech Nebulisers...B2 T-Piece Nebulisers...B5
Salter Labs Product Catalog Aerosol Delivery Products International 2015 Distinct products experiences that matter International 2015 Aerosol delivery NebuTech Nebulisers...B2 T-Piece Nebulisers...B5
Inhaled Medication Delivery in Mechanically Ventilated Patients
 Inhaled Medication Delivery in Mechanically Ventilated Patients Saving money and Quality can co-exist Return to another time, Back to the Future, or a work in Progress? William R Howard MBA, RRT NCSRC
Inhaled Medication Delivery in Mechanically Ventilated Patients Saving money and Quality can co-exist Return to another time, Back to the Future, or a work in Progress? William R Howard MBA, RRT NCSRC
Guidelines and Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide
 Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS
 NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
2008 IPAC-RS Conference Doing the Right Thing Science, Quality and Patient Focus
 2008 IPAC-RS Conference Doing the Right Thing Science, Quality and Patient Focus Patient Perspective Alpha-1 1 Foundation John W. Walsh Patient Focus Personal perspective Challenges and lessons Importance
2008 IPAC-RS Conference Doing the Right Thing Science, Quality and Patient Focus Patient Perspective Alpha-1 1 Foundation John W. Walsh Patient Focus Personal perspective Challenges and lessons Importance
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES
 AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
Latex Free. An affordable, easy to use, high density, small volume nebulizer with a breath enhanced design! Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer
 Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients alike. This
Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients alike. This
Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma
 Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma Talk Outline Case Delivery of bronchodilators Meter-dose inhalers and spacers Continuous nebulization
Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma Talk Outline Case Delivery of bronchodilators Meter-dose inhalers and spacers Continuous nebulization
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities
 Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
NOVEMBER 2015 AN INDEPENDENT SUPPLEMENT DISTRIBUTED IN THE GUARDIAN ON BEHALF OF MEDIAPLANET, WHO TAKE SOLE RESPONSIBILITY FOR ITS CONTENTS
 NOVEMBER 2015 AN INDEPENDENT SUPPLEMENT DISTRIBUTED IN THE GUARDIAN ON BEHALF OF MEDIAPLANET, WHO TAKE SOLE RESPONSIBILITY FOR ITS CONTENTS Respiratory Health HEALTHAWARENESS.CO.UK Ching-He Huang on why
NOVEMBER 2015 AN INDEPENDENT SUPPLEMENT DISTRIBUTED IN THE GUARDIAN ON BEHALF OF MEDIAPLANET, WHO TAKE SOLE RESPONSIBILITY FOR ITS CONTENTS Respiratory Health HEALTHAWARENESS.CO.UK Ching-He Huang on why
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices
 Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Paediatric pulmonary drug delivery: considerations in asthma treatment
 Review Paediatric pulmonary drug delivery: considerations in asthma treatment 1. Introduction 2. Guideline recommendations 3. Factors affecting drug delivery to the lung 4. Nebulisers 5. Metered-dose inhalers
Review Paediatric pulmonary drug delivery: considerations in asthma treatment 1. Introduction 2. Guideline recommendations 3. Factors affecting drug delivery to the lung 4. Nebulisers 5. Metered-dose inhalers
A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO nebulization
 A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO nebulization therapy a initiative This book is based on sources believed to be reliable in providing information that is complete and generally in accordance with the standards accepted
A PRACTICAL GUIDE TO nebulization therapy a initiative This book is based on sources believed to be reliable in providing information that is complete and generally in accordance with the standards accepted
Physicochemical Aspects and Efficiency of Albuterol Nebulization: Comparison of Three Aerosol Types in an In Vitro Pediatric Model
 Physicochemical Aspects and Efficiency of Albuterol Nebulization: Comparison of Three Aerosol Types in an In Vitro Pediatric Model Anne-Laure Sidler-Moix PhD, Ermindo R Di Paolo PhD, Ugo Dolci RPh, Markoulina
Physicochemical Aspects and Efficiency of Albuterol Nebulization: Comparison of Three Aerosol Types in an In Vitro Pediatric Model Anne-Laure Sidler-Moix PhD, Ermindo R Di Paolo PhD, Ugo Dolci RPh, Markoulina
Aerosol delivery to ventilated newborn infants: historical challenges and new directions
 Eur J Pediatr (2011) 170:433 444 DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1292-6 REVIEW Aerosol delivery to ventilated newborn infants: historical challenges and new directions Jan Mazela & Richard A. Polin Received: 14
Eur J Pediatr (2011) 170:433 444 DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1292-6 REVIEW Aerosol delivery to ventilated newborn infants: historical challenges and new directions Jan Mazela & Richard A. Polin Received: 14
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
Redefining Continuous Aerosol Drug Delivery PM223
 Redefining Continuous Aerosol Drug Delivery PM223 Explanation of Continuous via Traditional Small Volume (Jet) Nebulizer Traditional small volume (jet) nebulizers require compressed gas to aerosolize medication
Redefining Continuous Aerosol Drug Delivery PM223 Explanation of Continuous via Traditional Small Volume (Jet) Nebulizer Traditional small volume (jet) nebulizers require compressed gas to aerosolize medication
Redefining Continuous Aerosol Drug Delivery 2015 PM223
 Redefining Continuous Aerosol Drug Delivery 2015 PM223 Explanation of Continuous via Traditional Small Volume (Jet) Nebulizer Traditional small volume (jet) nebulizers require compressed gas to aerosolize
Redefining Continuous Aerosol Drug Delivery 2015 PM223 Explanation of Continuous via Traditional Small Volume (Jet) Nebulizer Traditional small volume (jet) nebulizers require compressed gas to aerosolize
Oxygen administration and inhaled bronchodilators. Aerosol Therapy in Adults Receiving High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy
 JOURNAL OF AEROSOL MEDICINE AND PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY Volume 28, Number 0, 2015 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 1 8 DOI: 10.1089/jamp.2015.1219 Aerosol Therapy in Adults Receiving High Flow Nasal Cannula
JOURNAL OF AEROSOL MEDICINE AND PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY Volume 28, Number 0, 2015 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 1 8 DOI: 10.1089/jamp.2015.1219 Aerosol Therapy in Adults Receiving High Flow Nasal Cannula
Basic Techniques for Aerosol Delivery During Mechanical Ventilation. Rajiv Dhand MD
 Symposium Papers Basic Techniques for Aerosol Delivery During Mechanical Ventilation Rajiv Dhand MD Introduction Factors That Influence Aerosol Delivery During Mechanical Ventilation Methods to Assess
Symposium Papers Basic Techniques for Aerosol Delivery During Mechanical Ventilation Rajiv Dhand MD Introduction Factors That Influence Aerosol Delivery During Mechanical Ventilation Methods to Assess
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution
 Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
AARC Clinical Practice Guideline
 AARC Clinical Practice Guideline Aerosol Delivery Device Selection for Spontaneously Breathing Patients: 2012 Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC and Ruben D Restrepo MD RRT FAARC Using an electronic literature
AARC Clinical Practice Guideline Aerosol Delivery Device Selection for Spontaneously Breathing Patients: 2012 Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC and Ruben D Restrepo MD RRT FAARC Using an electronic literature
Characterizing the Performance of Metered Dose Inhalers with Add-On Devices: New Methods For Clinically Relevant Testing
 INSTRUMENTATION» Characterizing the Performance of Metered Dose Inhalers with Add-On Devices: New Methods For Clinically Relevant Testing Mark Copley Director Copley Scientific The recent introduction
INSTRUMENTATION» Characterizing the Performance of Metered Dose Inhalers with Add-On Devices: New Methods For Clinically Relevant Testing Mark Copley Director Copley Scientific The recent introduction
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither?
 Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
Combining imaging techniques and CFD to model lung deposition in various age classes of the paediatric population
 Combining imaging techniques and CFD to model lung deposition in various age classes of the paediatric population Contents: Motivation: Why modelling the paediatric dose to lung via in-vitro and in-silico
Combining imaging techniques and CFD to model lung deposition in various age classes of the paediatric population Contents: Motivation: Why modelling the paediatric dose to lung via in-vitro and in-silico
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Nebulizers. Small Volume Nebulizers
 Small Volume MICRO MIST Nebulizer The MICRO MIST small volume nebulizer is designed for performance and economy and includes the design features needed by today s respiratory care practitioners. It can
Small Volume MICRO MIST Nebulizer The MICRO MIST small volume nebulizer is designed for performance and economy and includes the design features needed by today s respiratory care practitioners. It can
Revision 2. Improving Aerosol Drug Delivery During Invasive Mechanical Ventilation with Redesigned Components
 Revision 2 Improving Aerosol Drug Delivery During Invasive Mechanical Ventilation with Redesigned Components P. Worth Longest, Ph.D., 1,2* Mandana Azimi, Pharm.D., 2 Laleh Golshahi, Ph.D., 2 and Michael
Revision 2 Improving Aerosol Drug Delivery During Invasive Mechanical Ventilation with Redesigned Components P. Worth Longest, Ph.D., 1,2* Mandana Azimi, Pharm.D., 2 Laleh Golshahi, Ph.D., 2 and Michael
Effect of mask dead space and occlusion of mask holes on delivery of nebulized albuterol. Ariel Berlinski, MD 1,2. Little Rock, Arkansas.
 Effect of mask dead space and occlusion of mask holes on delivery of nebulized albuterol Ariel Berlinski, MD 1,2 1 University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Department of Pediatrics, Pulmonology Section
Effect of mask dead space and occlusion of mask holes on delivery of nebulized albuterol Ariel Berlinski, MD 1,2 1 University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Department of Pediatrics, Pulmonology Section
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) NICU POCKET GUIDE
 Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
An update on inhalation devices
 OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
Special Problems in Aerosol Delivery: Artificial Airways
 Special Problems in Aerosol Delivery: Artificial Airways Rajiv Dhand MD Introduction Factors Influencing Aerosol Delivery through Endotracheal Tubes Endotracheal Tube Size Endotracheal Tube Material/Design
Special Problems in Aerosol Delivery: Artificial Airways Rajiv Dhand MD Introduction Factors Influencing Aerosol Delivery through Endotracheal Tubes Endotracheal Tube Size Endotracheal Tube Material/Design
Latex Free. An affordable, easy to use, high density, small volume nebulizer with a revolutionary breath enhanced design!
 Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a revolutionary breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients
Latex Free Breath Enhanced High Density Jet Nebulizer The NebuTech HDN nebulizer, a revolutionary breath enhanced design, by Salter Labs is quickly becoming the product of choice for caregivers and patients
ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS. Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK
 THE PRESS-AND-BREATHE pmdi ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK steve.newman@physics.org Compact, portable, convenient Asthma
THE PRESS-AND-BREATHE pmdi ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK steve.newman@physics.org Compact, portable, convenient Asthma
Respiratory Drug Delivery. Be inspired. Nebulizer and compressor catalog
 Respiratory Drug Delivery Be inspired Nebulizer and compressor catalog Introduction Inspiring innovation Philips is committed to enhancing patients lives by delivering cost-effective solutions that drive
Respiratory Drug Delivery Be inspired Nebulizer and compressor catalog Introduction Inspiring innovation Philips is committed to enhancing patients lives by delivering cost-effective solutions that drive
Aerosol Delivery Devices
 Aerosol Delivery Devices Judy Bielenda LRRT Respiratory Therapy Clinical Specialist Pediatric Asthma Education Coordinator University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children s and Von Voigtlander Women s Hospital
Aerosol Delivery Devices Judy Bielenda LRRT Respiratory Therapy Clinical Specialist Pediatric Asthma Education Coordinator University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children s and Von Voigtlander Women s Hospital
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC)
 Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
. Type of solution/medication. Amount/dose to be delivered. Frequency/duration. Mode of administration.
 Page 1 of 9 (Large, Medium Volume, and Aerogen Continuous Nebulizer) Purpose Scope Physician's Order To standardize the use of continuous aerosol therapy as a modality used for the rescue of patients with
Page 1 of 9 (Large, Medium Volume, and Aerogen Continuous Nebulizer) Purpose Scope Physician's Order To standardize the use of continuous aerosol therapy as a modality used for the rescue of patients with
Confidence in your patient s comfort. Respironics patient interfaces and circuits for noninvasive ventilation
 Confidence in your patient s comfort Respironics patient interfaces and circuits for noninvasive ventilation Delivering exceptional NIV Philips Respironics masks are designed to support enhanced NIV. From
Confidence in your patient s comfort Respironics patient interfaces and circuits for noninvasive ventilation Delivering exceptional NIV Philips Respironics masks are designed to support enhanced NIV. From
Continuous Aerosol Therapy
 PROCEDURE - : Page 1 of 5 Purpose Policy Physician's Order To standardize the administration of continuous aerosol therapy. Respiratory Care Services provides equipment and therapy according to physician
PROCEDURE - : Page 1 of 5 Purpose Policy Physician's Order To standardize the administration of continuous aerosol therapy. Respiratory Care Services provides equipment and therapy according to physician
Albuterol Delivery via Facial and Tracheostomy Route in a Model of a Spontaneously Breathing Child
 Albuterol Delivery via Facial and Tracheostomy Route in a Model of a Spontaneously Breathing Child Brandy Cooper and Ariel Berlinski MD BACKGROUND: Some pediatric patients receiving therapeutic aerosols
Albuterol Delivery via Facial and Tracheostomy Route in a Model of a Spontaneously Breathing Child Brandy Cooper and Ariel Berlinski MD BACKGROUND: Some pediatric patients receiving therapeutic aerosols
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
In Vitro Evaluation of Positive Expiratory Pressure Devices Attached to Nebulizers
 In Vitro Evaluation of Positive Expiratory Pressure Devices Attached to Nebulizers Ariel Berlinski MD BACKGROUND: Patients with cystic fibrosis perform airway clearance techniques and receive nebulized
In Vitro Evaluation of Positive Expiratory Pressure Devices Attached to Nebulizers Ariel Berlinski MD BACKGROUND: Patients with cystic fibrosis perform airway clearance techniques and receive nebulized
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
acapella vibratory PEP Therapy System Maximizing Therapy Effectiveness, Empowering Patient Compliance
 acapella vibratory PEP Therapy System Maximizing Therapy Effectiveness, Empowering Patient Compliance Investigating Questions Each acapella vibratory PEP therapy system uniquely provides PEP therapy by
acapella vibratory PEP Therapy System Maximizing Therapy Effectiveness, Empowering Patient Compliance Investigating Questions Each acapella vibratory PEP therapy system uniquely provides PEP therapy by
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
C l i n i c a lcpap. Advanced Solutions in Acute Respiratory Care
 C l i n i c a lcpap Advanced Solutions in Acute Respiratory Care This is tex which explains in moderate clinicsal detail, the background and structure of the patient indication for CPAP. This is tex which
C l i n i c a lcpap Advanced Solutions in Acute Respiratory Care This is tex which explains in moderate clinicsal detail, the background and structure of the patient indication for CPAP. This is tex which
NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP)
 Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
LRI Children s Hospital
 LRI Children s Hospital Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHFNC) Oxygen Therapy Staff relevant to: Medical and Nursing staff Team approval date: 5.01.18 Version: 1 Revision due: January 2020 Written
LRI Children s Hospital Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHFNC) Oxygen Therapy Staff relevant to: Medical and Nursing staff Team approval date: 5.01.18 Version: 1 Revision due: January 2020 Written
ADASUVE (LOXAPINE) INHALATION POWDER. EDUCATION PROGRAM for HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
 ADASUVE (LOXAPINE) INHALATION POWDER EDUCATION PROGRAM for HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS August2017 December 2012 PMR-JUN-2017-0017 ADASUVE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Education Program Content
ADASUVE (LOXAPINE) INHALATION POWDER EDUCATION PROGRAM for HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS August2017 December 2012 PMR-JUN-2017-0017 ADASUVE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Education Program Content
High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC. Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand
 786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Effect of Mask Dead Space and Occlusion of Mask Holes on Delivery of Nebulized Albuterol
 Effect of Mask Dead Space and Occlusion of Mask Holes on Delivery of Nebulized Albuterol Ariel Berlinski MD BACKGROUND: Infants and children with respiratory conditions are often prescribed bronchodilators.
Effect of Mask Dead Space and Occlusion of Mask Holes on Delivery of Nebulized Albuterol Ariel Berlinski MD BACKGROUND: Infants and children with respiratory conditions are often prescribed bronchodilators.
