Bronchodilator and Cardiac Effects of Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Aerosols in Asthma
|
|
|
- Cynthia Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1971, 46, 52. Bronchodilator and Cardiac Effects of Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Aerosols in Asthma A. D. MILNER and D. INGRAM From The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London Milner, A. D., and Ingram, D. (1971). Archives of Diseases in Childhood, 46, 52. Bronchodilator and cardiac effects of isoprenaline, orciprenaline, and salbutamol aerosols in asthma. The bronchodilator and cardiac effects of -5% isoprenaline, 2 5% orciprenaline, and -5% salbutamol, and a placebo solution inhaled as a nebulized mist from a Wright nebulizer were compared with the help of 12 asthmatic children. All three active drugs produced similar relief of bronchoconstriction, but salbutamol was followed by only a 13% increase in heart rate compared with 26% after orciprenaline and 29% after isoprenaline, and only a 9% increase in systolic blood pressure compared to 13% after orciprenaline and 15% after isoprenaline. For many years nebulized isoprenaline solutions have proved useful in the treatment of asthmatic children admitted with severe bronchoconstriction. Their use gives the child some relief from his symptoms but almost always is accompanied by tachycardia, and may actually cause a fall in arterial Po2 by augmenting ventilation/perfusion mismatch (Palmer and Diament, 1967). Three bronchodilators-isoprenaline, orciprenaline, and salbutamol-were investigated to see which produced most relief of bronchospasm with least cardiac disturbance. Subjects The 12 children (6 boys and 6 girls) all attended the asthma clinic of The Hospital for Sick Children. Their ages ranged from 1 years 6 months to 14 years 4 months, with a mean of 11 years 9 5 months. All the children had had symptoms of asthma for over 7 years, and 1 had been on steroids for at least 6 months at some time. At the time of the trial 3 were on steroids and 11 were on disodium cromoglycate, with or without isoprenaline (Intal co. and Intal). Six of the children were below the 3rd centile for height. Procedure Each child attended on four occasions. The visits tended to be at irregular intervals but each child was kept to a morning or afternoon session to reduce errors from fluctuations in airways resistance during the day (Lewinsohn, Capel, and Smart, 196). The parent was Received 18 January asked not to give the child any bronchodilator or isoprenaline on the day of the test but steroids were not discontinued. On arrival, lung function was assessed from measurements of the forced vital capacity (FVC) and the forced expiratory volume over 75 sec (FEVO.75) using a reverse plethysmograph. The FEVo.75 was measured rather than the FEV1. because some young healthy children are able to breathe out their FVC in 1 second (Lunn, 1965). The reverse plethysmograph consists of a rigid container, volume 1,5 litre (Fig. 1). The REVERSE PLETHYSMOGRAPH SYSTEM FIG. 1.-The reverse plethysmograph.
2 Brontchodilator and Cardiac Effects of Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Aerosols 53 3.,- s placebo x, isoprenal ine a : orf iprenaline a saobutamol I 2 4 6b FIG. 2.-Mean values for vital capacity before and after inhalation of isoprenaline, orciprenaline, salbutamol, and placebo. child blows into the container which causes pressure changes in it of the order of 7 cmh2 per litre of air expired. The changes are relayed to a fast hot wire Devices recorder by an Ether strain gauge transducer situated in the base of the tank. The system was calibrated against a 5 ml syringe on each occasion. The advantage of this system over wet and dry spirometers is that it has no moving parts and is, therefore, not liable to errors from inertial drag and overswing. The system will detect 1 ml volume changes and the standard error on repeated measurements of 5 ml volumes delivered by a glass syringe was 1 68 ml. The best of three attempts was selected on each occasion and these results are expressed at ambient temperature and pressure. The pulse rate was measured using a Devices ECG preamplifier and recorder. The systolic and diastolic blood pressures were measured using a sphygmomanometer. The child then breathed from a face mask connected to a Wright nebulizer containing 1 5 ml active drug or placebo (distilled water). A compressed air cylinder provided a flow of 8 l./min to the nebulizer. The child continued to breathe from this system until the nebulizer ceased to produce a mist, usually after 2 to 3 minutes. Initial experiments had shown that at this stage approximately 1 ml solution had been nebulized, 5 ml remaining on the walls of the nebulizer. Lung function tests, pulse and blood pressure measurements were repeated at 5, 1, 15, 3, 45, 6, 9, 12, and 15 minutes after administration of the mist. Statistical Analysis The measurements of lung and heart function that were made after taking each treatment were used to assess four characteristics of the response. These are as follows: I Peak effect, i.e. maximum effect minus basal value. II Time to peak, i.e. number of minutes after dosing at which peak occurred. III Total effect, i.e. area under the response-time 'curve' above basal value. IV Duration, i.e. duration of average effect. Each of these aspects was examined by analysis of covariance to make allowance for the difference in basal value that were observed (Quenouille, 1953). Drugs The three bronchodilator drugs, 5% isoprenaline, 2-5% orciprenaline, and 5% salbutamol, and the placebo (distilled water) were prepared in individual vials and coded by random selection by Allen and Hanburys Ltd. Benzalkanonium chloride, -1%, was added to all samples as a preservative. Each sample was identified by a number relating to the patient and a letter identifying the solution within. Thus, each child received each of the four solutions under doubleblind control conditions. Results Bronchodilator effect of drugs. The mean results of the improvement in FVC and the FEVo. 75 after inhalation of the three active drugs and placebo are shown in Figs. 2 and 3. There was response to all solutions including the placebo. The peak effects of the three active solutions were very similar and only the difference in peak vital capacity between salbutamol and the placebo was statistically significant (Tables I and II). In 1 of the 12 children, the FEV.75 rose by more than 25% from control levels after inhalation of the placebo. There was no significant difference in the rate of rise or the duration of effect over the I
3 54 E U- 2,- - r1 Milner and Ingram X =placebo x =isoprenaline =orc ipre no line. =salbutamol bo FIG. 3.-Mean values for FEVo7.5 before and after inhalation of isoprenaline, orciprenaline, salbutamol, and placebo. TABLE I Mean Changes in Forced Vital Capacity after Inhalation of Placebo, Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Basal eak Time to Dura- Treatment Value (ml)* Peak Aa n tion (ml) m)* (min) (1.imin) Placebo Isoprenaline Orciprenaline Salbutamol significance (P = -5) *Significantly related to basal values., and adjusted accordingly. period of the investigation as judged by the FVC, but the total effect of salbutamol, as measured by integration of the area under the curve, was significantly larger than the placebo. 2. Cardiac effects of drugs. All four solutions were followed by an increase in the pulse rate 2 TABLE II Mean Changes in FEVo.75 after Inhalation of Placebo, Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Basal Time of Dura- Treatment Value Peak Peak Are tion (ml)* (1 n (Ml) (mi)n m) (min) Placebo Isoprenaline Orciprenaline Salbutamol significance (P = 5) *Significantly related to basal value, and adjusted to allow for variation among the four mean basal values. (Fig. 4). This was very small after the placebo (+3%) and relatively small after salbutamol (+13%) but was significantly larger after isoprenaline (+29%) than after salbutamol and placebo, and significantly larger after orciprenaline (+26%) than after the placebo (Table III). The tachycardia after salbutamol lasted significantly Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 August Downloaded from c 5 4- D@ 1- c L) 5.placebo =isoprenal ine L=orciprenaline.=salbutamol _ 2 4 b6 8 IO FIG. 4.-Mean values for pu!se rate before and after inhalation of isoprenaline, orciprenaline, salbutamol, and placebo. on 2 September 218 by guest. Protected by
4 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~diastolic Bronchodilator and Cardiac Effects of Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Aerosols 55 TABLE III TABLE IV Mean Changes in Pulse after Inhalation of Placebo, Mean Changes in Systolic Blood Pressure after Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Inhalation of Placebo, Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Basal Peak Time to Area Dura- Treatment (beats! (beats/ Peak (beats/ tion Basal Time to Ara Duramin) min) (min) min) (min) Treatment Value Peak (mg (mm min)* tion (m(mmhg)mmhg) (min) (min)* Placebo Placebo Isoprenaline Orciprenaline Isoprenaline Salbutamol Orciprenaline Salbutamol significance (P =-.5) significance (P - 5) *Significantly related basal value, and adjusted accordingly. longer than after isoprenaline. Orciprenaline had the largest effect on the heart rate as judged by the 'area under the curve', but this only reached significance when compared to placebo (Table III). TABLE V Only the placebo solution produced no rise in Mean Changes in Diastolic Blood Pressure after systolic blood pressure (Fig. 5) but the effect of Inhalation of Placebo, Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, salbutamol was slight. Isoprenaline and orciprenaline were both followed by significant increases and Salbutamol compared to the placebo solution (Table IV and V). Basal Pa Time to Area Dura- Orciprenaline again had the largest total effect. Treatment Value Peak Peak (mm.min)* tion (mmhg) (mmhg)* (min) (min)* As regards diastolic pressure, only isoprenaline had an appreciable effect, causing a 13% increase. Placebo Isoprenaline Orciprenaline Order of drug administration. The results Salbutamol were also examined to see whether there was any difference in the cardiovascular and bronchodilator response between the first and subsequent significance (P = 5) sessions, as it was felt that on the initial visit the *Significantly related basal value, and adjusted accordingly I--. systolic 1- E 8- E L- ' a-() SO - O 4- o = placebo x.isoprenaline a.orciprenaline *. -sa buta mol IbO FIG. 5.-Mean values for systolic and diastolic blood pressure before and after inhalation of isoprenaline, orciprenaline, salbutamol, and placebo.
5 56 Milner and Ingram children might be more anxious and less able to The cardiac effects of the drugs showed greater achieve their best results. Analysis showed that variation. As was expected, isoprenaline caused an the improvement in forced vital capacity as judged increase in heart rate of up to 7 %; in only two by its total effect was significantly less on the first children was the increase less than 2%. The than on subsequent occasions. No significant effect on the cardiovascular system was also differences could be detected from examination reflected in the increase in systolic and diastolic of the pulse record. pressure. Rather more surprising was the tachycardia and increase in systolic blood pressure Four children received salbutamol, 4 isoprenaline 3 placebo, and 1 orciprenaline on their first visit. associated with the orciprenaline. These changes Side effects. Two children felt dizzy after isoprenaline and one felt dizzy after orciprenaline. Discussion One of the main problems in any trial designed to compare bronchodilator drugs is the dose selection. In this trial we selected doses which we hoped would be equipotent as regards relief of bronchoconstriction, so that we could then compare the cardiac effects. However, the information available on dose relation is contradictory. Some workers, e.g. Cullum et al. (1969) using cats and dogs, and Grant (1969), Choo-Kang, Simpson, and Grant (1969), Kamburoff and Prime (197), and Riding, Dinda, and Chatterjee (197), with normal and asthmatic adults, found that dose for dose salbutamol was several times more potent than isoprenaline. However, Warrell et al. (197), using more sophisticated techniques, obtained very similar response curves for the two drugs, and Riding, Chatterjee, and Dinda (1969) found very similar relief of bronchoconstriction in asthmatic adults after the inhalation of * 5% salbutamol and -5% isoprenaline delivered by an ultrasonic nebulizer. Hambleton and Shinebourne (197) reported that 1 [±g doses of isoprenaline and salbutamol delivered as an aerosol produced very similar relief of airways obstruction in 1 children with asthma, but that the effect of salbutamol was more prolonged. When compared to salbutamol, orciprenaline was less effective in relieving bronchospasm even with six times the dose (Kennedy and Simpson, 1969), but it was not felt justified to exceed the relatively high concentration of 2 5% in these children. Our results showed very similar improvements in FEV.75 and FVC after all three active drugs. However, they were less striking than in the other series, partly because these children have had severe asthma for many years and now have some permanent underlying lung damage. The response to placebo was striking, with 1 of the children showing an obvious improvement in FEVO.75, again illustrating the need for good controls when assessing any treatment in asthma. persisted for longer than the changes after isoprenaline. Salbutamol did produce an increase in the heart rate which persisted for significantly longer than after isoprenaline, but the increase was much less marked than after the other two drugs. Riding et al. (1969) found a similar rise in the pulse rate after the inhalation of a nebulized solution of -5% in adults. However, Kennedy and Simpson (1969) found no change in pulse and blood pressure after the inhalation of 4,ug salbutamol from an aerosol, and Riding et al. (197) actually observed a fall after 2.tg. It is possible that a similar degree of bronchodilatation could have been achieved with a considerably lower dose, but we were anxious to reproduce the doses likely to be given to a child admitted to the ward in severe bronchospasm. In conclusion, a * 5% salbutamol solution delivered by a Wright nebulizer is as effective a bronchodilator agent as 5% isoprenaline or 2 5% orciprenaline, but had considerably less effect on the cardiovascular system and thus should be used in place of isoprenaline for children with severe bronchoconstriction. We wish to thank Dr. A. P. Norman and Dr. D. Hull for their advice and encouragement, and Allen and Hanburys Ltd. who supplied the samples and carried out the statistical analysis. Financial support was provided by the Asthma Research Council. REPERNCES Capel, L. H., and Fletcher, E. C. (1964). Spirometric integrals after isoprenaline and atropine in asthma. British journal of Diseases of the Chest, 58, 174. Choo-Kang, Y. F. J., Simpson, W. T., and Grant, I. W. B. (1969). Controlled comparison of the bronchodilator effects of three,3-adrenergic stimulant drugs administered by inhalation to patients with asthma. British Medical Journal, 2, 287. Cullum, V. A., Farmer, J. B., Jack, D., and Levy, G. P. (1969). Salbutamol: a new, selective,3-adrenoceptive receptor stimulant. British journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy, 35, 141. Grant, I. W. B. (1969). Bronchodilator aerosols. In New ideas in asthma and its management: Proceedings of the Chest and Heart Association Conference p. 48. Chest and Heart Association, London. Hambleton, G., and Shinebourne, E. (197). Evaluation of the effects of isoprenaline and salbutamol aerosols on airways obstruction and pulse rates of children with asthma. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 45, 766. Kamburoff, P. L., and Prime, F. J. (197). Oral and inhaled salbutamol as a bronchodilator. British J3ournal of Diseases of the Chest., 64, 46.
6 Bronchodilator and Cardiac Effects of Isoprenaline, Orciprenaline, and Salbutamol Aerosols 57 Kennedy, M. C. S., and Simpson, W. T. (1969). Human pharmacological and clinical studies on salbutamol: a specific,- adrenergic bronchodilator. British Journal of Diseases of the Chest, 63, 165. Lewinsohn, H. C., Capel, L. H., and Smart, J. (196). Changes in forced expiratory volumes throughout the day. British Medical Journal, 1, 462. Lunn, J. E. (1965). Respiratory measurements of 3556 Sheffield schoolchildren. British Journal of Preventive and Social Medicine, 19, 115. Palmer, K. N. V., and Diament, M. L. (1967). Effect of aerosol isoprenaline on blood-gas tensions in severe bronchial asthma. Lancet, 2, Quenouille, M. H. (1953). The Design and Analysis of Experiment, p. 9. Griffin, London. Riding, W. D., Chatterjee, S. S., and Dinda, P. (1969). Clinical trial of a new (3-adrenergic stimulant in asthma. British 3rournal of Clinical Practice, 23, 217. Riding, W. D., Dinda, P., and Chatterjce, S. S. (197). The bronchodilator and cardiac effects of five pressure-packed aerosols in asthma. British Journal of Diseases of the Chest, 64, 37. Warrell, D. A., Robertson, D. G., Newton-Howes, J., Conolly, M. E., Paterson, J. W., Beilin, L. J., and Dollery, C. T. (197). Comparison of cardiorespiratory effects of isoprenaline and salbutamol in patients with bronchial asthma. British Medical Journal, 1, 65. Correspondence to Dr. A. D. Milner, The Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London W.C.1. Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 August Downloaded from on 2 September 218 by guest. Protected by
Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma
 Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
Time factor in the measurement of response
 Thorax (1967), 22, 538. Time factor in the measurement of response to bronchodilators G. J. MUSHIN From Pritnce Heairv's Hospital, Melbournie, A ustralia Trhe measurement of response to bronchodilators
Thorax (1967), 22, 538. Time factor in the measurement of response to bronchodilators G. J. MUSHIN From Pritnce Heairv's Hospital, Melbournie, A ustralia Trhe measurement of response to bronchodilators
Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1971, 28, 159-163 Peak flow rate in relation to forced expiratory volume in hemp workers v v I E. ZUSKIN and F. VALIC Department of Occupational Health, Andrija Stampar School of
Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients
 Thorax 1988;43:674-678 Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients ANDERS ULLMAN, NILS SVEDMYR From the Department of Clinical
Thorax 1988;43:674-678 Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients ANDERS ULLMAN, NILS SVEDMYR From the Department of Clinical
Air or oxygen as driving gas for nebulised salbutamol
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 9-94 Air or oxygen as driving gas for nebulised salbutamol J G A GLEESON, S GREEN, AND J F PRICE Paediatric Respiratory Laboratory, Department of Thoracic Medicine,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 9-94 Air or oxygen as driving gas for nebulised salbutamol J G A GLEESON, S GREEN, AND J F PRICE Paediatric Respiratory Laboratory, Department of Thoracic Medicine,
Bronchial lability in cystic fibrosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1973, 48, 355. Bronchial lability in cystic fibrosis GILLIAN DAY* and MARGARET B. MEARNS From Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London Day, G., and Mearns, M. (1973).
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1973, 48, 355. Bronchial lability in cystic fibrosis GILLIAN DAY* and MARGARET B. MEARNS From Queen Elizabeth Hospital for Children, London Day, G., and Mearns, M. (1973).
INTRAVENOUS INFUSION OF SALB UTAM OL I N TH E TR EATM ENT OF ASTH MA
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1975), 2, 53-58 INTRAVNOUS INFUSION OF SALB UTAM OL I N TH TR ATM NT OF ASTH MA C.S. MAY & J.W. PATRSON Asthma Research Council Clinical Pharmacology Unit, Department of Medicine,
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1975), 2, 53-58 INTRAVNOUS INFUSION OF SALB UTAM OL I N TH TR ATM NT OF ASTH MA C.S. MAY & J.W. PATRSON Asthma Research Council Clinical Pharmacology Unit, Department of Medicine,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
Bronchoconstriction in potroom workers
 British Journal of Inidustrial Medicine, 1979, 36, 211-215 M. SARIC, E. ZUSKIN*, AND M. GOMZI From the Institute for Meclical Research and Occupational Health, Zagreb and the *Andrija Stampar School of
British Journal of Inidustrial Medicine, 1979, 36, 211-215 M. SARIC, E. ZUSKIN*, AND M. GOMZI From the Institute for Meclical Research and Occupational Health, Zagreb and the *Andrija Stampar School of
Credential Maintenance Program
 First Quarter of the Calendar 5 I. INSTRUMENTATION / EQUIPMENT 1 4 5 A. Set Up, Maintain, Calibrate 1 2 3 1. Blood gas analyzers 2. CO-oximeters / hemoximeters 3. Spirometers (for example, diagnostic,
First Quarter of the Calendar 5 I. INSTRUMENTATION / EQUIPMENT 1 4 5 A. Set Up, Maintain, Calibrate 1 2 3 1. Blood gas analyzers 2. CO-oximeters / hemoximeters 3. Spirometers (for example, diagnostic,
Treatment of acute asthmatic exacerbations with an increased dose of inhaled steroid
 12 Paediatrics and Child Health, Dunedin School of Medicine, PO Box 913, University of Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand J Garrett Preventive and Social Medicine, Dunedin School of Medicine S
12 Paediatrics and Child Health, Dunedin School of Medicine, PO Box 913, University of Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand J Garrett Preventive and Social Medicine, Dunedin School of Medicine S
Dose-response comparison of ipratropium bromide from a metered-dose inhaler and by jet nebulisation
 Thorax 1983;38:297-301 Dose-response comparison of ipratropium bromide from a metered-dose inhaler and by jet nebulisation SA GOMM, NP KEANEY, LP HUNT, SC ALLEN, TB STRETTON From the Department ofrespiratory
Thorax 1983;38:297-301 Dose-response comparison of ipratropium bromide from a metered-dose inhaler and by jet nebulisation SA GOMM, NP KEANEY, LP HUNT, SC ALLEN, TB STRETTON From the Department ofrespiratory
controlled trial of prednisone, in low dosage, in patients with chronic airways obstruction.
 Thorax (1974), 29, 401. A controlled trial of prednisone, in low dosage, in patients with chronic airways obstruction J. A. EVANS', I. M. MORRISON2, and K. B. SAUNDERS3 Departments of Medicine and of Thoracic
Thorax (1974), 29, 401. A controlled trial of prednisone, in low dosage, in patients with chronic airways obstruction J. A. EVANS', I. M. MORRISON2, and K. B. SAUNDERS3 Departments of Medicine and of Thoracic
normal and asthmatic males
 Lung volume and its subdivisions in normal and asthmatic males MARGARET I. BLACKHALL and R. S. JONES1 Thorax (1973), 28, 89. Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children's Hospital,
Lung volume and its subdivisions in normal and asthmatic males MARGARET I. BLACKHALL and R. S. JONES1 Thorax (1973), 28, 89. Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, Alder Hey Children's Hospital,
Standardization of Exercise Tests in Asthmatic Children
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 882. Standardization of Exercise Tests in Asthmatic Children M. SILVERMAN and SANDRA D. ANDERSON with the assistance of Tina Andrea From the Department of Paediatrics,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1972, 47, 882. Standardization of Exercise Tests in Asthmatic Children M. SILVERMAN and SANDRA D. ANDERSON with the assistance of Tina Andrea From the Department of Paediatrics,
Significance of effect of beta blockade on ventilatory
 Thorax (1972), 27, 572. Significance of effect of beta blockade on ventilatory function in normal and asthmatic subjects R. S. JONES Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, lder Hey Children's
Thorax (1972), 27, 572. Significance of effect of beta blockade on ventilatory function in normal and asthmatic subjects R. S. JONES Institute of Child Health, University of Liverpool, lder Hey Children's
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Influence of mist tent therapy on sputum viscosity and water content in cystic fibrosis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 66. Influence of mist tent therapy on sputum viscosity and water content in cystic fibrosis M. ROSNBLUTH and V. CHRNICK From the Department ofpaediatrics, University
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1974, 49, 66. Influence of mist tent therapy on sputum viscosity and water content in cystic fibrosis M. ROSNBLUTH and V. CHRNICK From the Department ofpaediatrics, University
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY. A. Definition of Spirometry
 UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory symptoms and ventilatory function
 Thorax (1972), 27, 454. Respiratory symptoms and ventilatory function changes in relation to length of exposure to cotton dust E. ZUgKIN and F. VALIC Andrija Stampar School of Public Health, Zagreb University,
Thorax (1972), 27, 454. Respiratory symptoms and ventilatory function changes in relation to length of exposure to cotton dust E. ZUgKIN and F. VALIC Andrija Stampar School of Public Health, Zagreb University,
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators
 I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
Some patients with chronic airways obstruction. develop pulmonary hypertension secondary to. chronic hypoxaemia. If terbutaline causes vasodilatation
 Thorax, 1977, 32, 601-605 Effect of intravenous terbutaline on arterial blood gas tensions, ventilation, and pulmonary circulation in patients with chronic bronchitis and cor pulmonale R. A. STOCKLEY,
Thorax, 1977, 32, 601-605 Effect of intravenous terbutaline on arterial blood gas tensions, ventilation, and pulmonary circulation in patients with chronic bronchitis and cor pulmonale R. A. STOCKLEY,
Relationship of exercise-induced asthma to clinical asthma in childhood
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 450-454 Relationship of exercise-induced asthma to clinical asthma in childhood LIONEL BALFOUR-LYNN, MARIAN TOOLEY, AND SIMON GODFREY Department of Paediatrics
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 450-454 Relationship of exercise-induced asthma to clinical asthma in childhood LIONEL BALFOUR-LYNN, MARIAN TOOLEY, AND SIMON GODFREY Department of Paediatrics
SPIROMETRY. Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: Copyright CARE Medical ltd
 SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
Pulmonary Function Technologists (PFT) Detailed Content Outline
 I. INSTRUMENTATION / EQUIPMENT 7 15 8 30 A. Set Up, Maintain, Calibrate 3 5 2 10 1. Blood gas analyzers 2. CO-oximeters / hemoximeters 3. Spirometers (for example, diagnostic, screening, portable) 4. Peak
I. INSTRUMENTATION / EQUIPMENT 7 15 8 30 A. Set Up, Maintain, Calibrate 3 5 2 10 1. Blood gas analyzers 2. CO-oximeters / hemoximeters 3. Spirometers (for example, diagnostic, screening, portable) 4. Peak
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES:
 TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
Asthma and the competitive swimmer
 Asthma and the competitive swimmer Introduction: One in seven children and one in 25 adults in Great Britain have asthma and the number is growing. Thus every swim squad or club will have a number of asthmatics
Asthma and the competitive swimmer Introduction: One in seven children and one in 25 adults in Great Britain have asthma and the number is growing. Thus every swim squad or club will have a number of asthmatics
effects of intravenous labetalol
 Pharmacological basis for antihypertensive effects of intravenous labetalol D. A. RICHARDS,' B. N. C. PRICHARD, A. J. BOAKES, J. TUCKMAN, AND E. J. KNIGHT2 From the Department of Clinical Pharmacology,
Pharmacological basis for antihypertensive effects of intravenous labetalol D. A. RICHARDS,' B. N. C. PRICHARD, A. J. BOAKES, J. TUCKMAN, AND E. J. KNIGHT2 From the Department of Clinical Pharmacology,
THE ACUTE AND CHRONIC BRONCHODILATOR
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1975), 2, 533-537 THE ACUTE AND CHRONIC BRONCHODILATOR EFFECTS OF EPHEDRINE IN ASTHMATIC PATIENTS C.S. MAY, M.E. PICKUP & J.W. PATERSON Asthma Research Council Clinical Pharmacology
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1975), 2, 533-537 THE ACUTE AND CHRONIC BRONCHODILATOR EFFECTS OF EPHEDRINE IN ASTHMATIC PATIENTS C.S. MAY, M.E. PICKUP & J.W. PATERSON Asthma Research Council Clinical Pharmacology
AIRNERGY REPORT. May Dr Nyjon Eccles BSc MBBS PhD MRCP The Chiron Clinic, Harley St, London, England W1G 6AX Tel:
 AIRNERGY REPORT May 2004 Dr Nyjon Eccles BSc MBBS PhD MRCP The Chiron Clinic, Harley St, London, England W1G 6AX Tel: 0207 2244622 Abstract Six volunteers were recruited for a study of the effect of 4
AIRNERGY REPORT May 2004 Dr Nyjon Eccles BSc MBBS PhD MRCP The Chiron Clinic, Harley St, London, England W1G 6AX Tel: 0207 2244622 Abstract Six volunteers were recruited for a study of the effect of 4
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of the Dossier. Volume:
 Final Report M/100977/21Final Version () 2. SYNOPSIS A Title of Study: A PHASE IIa, RANDOMISED, DOUBLE-BLIND, MULTIPLE DOSE, PLACEBO CONTROLLED, 3 PERIOD CROSS-OVER, ASCENDING DOSE CLINICAL TRIAL TO ASSESS
Final Report M/100977/21Final Version () 2. SYNOPSIS A Title of Study: A PHASE IIa, RANDOMISED, DOUBLE-BLIND, MULTIPLE DOSE, PLACEBO CONTROLLED, 3 PERIOD CROSS-OVER, ASCENDING DOSE CLINICAL TRIAL TO ASSESS
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ]
![NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ] NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ]](/thumbs/76/73199826.jpg) s@lm@n NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ] https://certkill.com NBRC RPFT : Practice Test Question No : 1 Using a peak
s@lm@n NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ] https://certkill.com NBRC RPFT : Practice Test Question No : 1 Using a peak
Oral Prophylaxis of Bronchial Asthma in Children
 Abstract Oral Prophylaxis of Bronchial Asthma in Children Pages with reference to book, From 90 To 93 M.A. Arif, S.Q. Nizami ( National Institute of Child Health, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi.
Abstract Oral Prophylaxis of Bronchial Asthma in Children Pages with reference to book, From 90 To 93 M.A. Arif, S.Q. Nizami ( National Institute of Child Health, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre, Karachi.
BETTER SPIROMETRY. Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: Copyright CARE Medical ltd
 BETTER SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual
BETTER SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual
VENTOLIN. About your Ventolin Respirator Solution. Read all of this leaflet carefully before you use your medicine
 Patient Information VENTOLIN About your Ventolin Respirator Solution Read all of this leaflet carefully before you use your medicine This leaflet does not have the complete information about your medicine.
Patient Information VENTOLIN About your Ventolin Respirator Solution Read all of this leaflet carefully before you use your medicine This leaflet does not have the complete information about your medicine.
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients
 Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
A total of 3061 children, 1528 boys and 1533 girls. aged 4-19 years, were included in the analysis. Table 1. Does your child have: 1 Asthma ( ) ( )
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 96-102 Growth and other factors flow rate affecting peak expiratory J W K CARSON,* H HOEY,*t AND M R H TAYLOR*t *National Children's Hospital and tdepartment
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 96-102 Growth and other factors flow rate affecting peak expiratory J W K CARSON,* H HOEY,*t AND M R H TAYLOR*t *National Children's Hospital and tdepartment
FEVI before (5% predicted) 62 (49-77) 59 (44-77) FEV, after (% predicted) 92 (84-108) 89 (69-107) to the entire group received aerosol isoprenaline.
 Tl.orax, 1980, 35, 298-302 Lung elastic recoil and reduced airflow in clinically stable asthma D S McCARTHY AND M SIGURDSON From the Department of Medicine, University ofmanitoba, Respiratory Division,
Tl.orax, 1980, 35, 298-302 Lung elastic recoil and reduced airflow in clinically stable asthma D S McCARTHY AND M SIGURDSON From the Department of Medicine, University ofmanitoba, Respiratory Division,
Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 22-26 Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an acute asthmatic attack D. DaCRUZ & C. HOLBURN Accident and Emergency Department,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1989, 6, 22-26 Serum potassium responses to nebulized salbutamol administered during an acute asthmatic attack D. DaCRUZ & C. HOLBURN Accident and Emergency Department,
bronchoconstriction Inhaled antihistamines- bronchodilatation and effects on histamine- and methacholine-induced Thorax, 1978, 33,
 Thorax, 1978, 33, 700-704 Inhaled antihistamines- bronchodilatation and effects on histamine- and methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction S G NOGRADY AND C BEVAN From the Welsh National School of Medicine
Thorax, 1978, 33, 700-704 Inhaled antihistamines- bronchodilatation and effects on histamine- and methacholine-induced bronchoconstriction S G NOGRADY AND C BEVAN From the Welsh National School of Medicine
Spirometry in primary care
 Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test
 powder for solution, for inhalation Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test Provocholine is a registered trademark of Methapharm Inc. Copyright Methapharm Inc. 2016. All rights reserved. Healthcare professionals
powder for solution, for inhalation Performing a Methacholine Challenge Test Provocholine is a registered trademark of Methapharm Inc. Copyright Methapharm Inc. 2016. All rights reserved. Healthcare professionals
Cystic fibrosis, atopy, and airways lability
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1978, 53, 873-877 Cystic fibrosis, atopy, and airways lability M. SILVERMAN, F. D. R. HOBBS, I. R. S. GORDON, AND F. CARSWELL From the Departments of Child Health and
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1978, 53, 873-877 Cystic fibrosis, atopy, and airways lability M. SILVERMAN, F. D. R. HOBBS, I. R. S. GORDON, AND F. CARSWELL From the Departments of Child Health and
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
Smith, Miller and Grab er(4) state that the maintenance of an efficient
 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
Study of dynamic lung parameters in bronchial Asthma
 20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic
 Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Relevant Papers: eight relevant articles were found, but four were reviewed because they were most directly related to the topic
 Topic: Prehospital use of bromide paired with salbutamol as treatment for shortness of breath. Author: Lisa Henderson Clinical Scenario: Two primary care paramedics respond code 4 for a 55 year old male
Topic: Prehospital use of bromide paired with salbutamol as treatment for shortness of breath. Author: Lisa Henderson Clinical Scenario: Two primary care paramedics respond code 4 for a 55 year old male
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(4): 353-59 Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma Praveen Aggarwal*, Onkar Singh**, Jyoti P Wali***, Rohini Handa*, Sada N Dwivedi****, Ashutosh Biswas*****,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(4): 353-59 Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma Praveen Aggarwal*, Onkar Singh**, Jyoti P Wali***, Rohini Handa*, Sada N Dwivedi****, Ashutosh Biswas*****,
Effect of an extension tube on the bronchodilator efficacy of terbutaline delivered from a metered dose inhaler
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 552-556 Effect of an extension tube on the bronchodilator efficacy of terbutaline delivered from a metered dose inhaler S A GOMM, N P KEANEY, N J P WINSEY, AND T B STRETTON From the Department
Thorax, 1980, 35, 552-556 Effect of an extension tube on the bronchodilator efficacy of terbutaline delivered from a metered dose inhaler S A GOMM, N P KEANEY, N J P WINSEY, AND T B STRETTON From the Department
Pulmonary Function Tests. Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist
 Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
G. Boyd on behalf of a UK Study group
 Eur Respir J, 1995, 8, 1494 1498 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.95.08091494 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1995 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Salmeterol xinafoate in
Eur Respir J, 1995, 8, 1494 1498 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.95.08091494 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1995 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Salmeterol xinafoate in
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 2/5/2019
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
Effect of long-term ionized air treatment on patients with bronchial asthma
 Thorax (1976), 31, 428. Effect of long-term ionized air treatment on patients with bronchial asthma D. P. JONES, S. A. O'CONNOR, J. V. COLLINS, and B. W. WATSON Departments of Medicine and Medical Electronics,
Thorax (1976), 31, 428. Effect of long-term ionized air treatment on patients with bronchial asthma D. P. JONES, S. A. O'CONNOR, J. V. COLLINS, and B. W. WATSON Departments of Medicine and Medical Electronics,
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Total body potassium in cor pulmonale
 Thorax (1976), 31, 708. Total body potassium in cor pulmonale A. D. HOWIE', A. I. PACK', K. BODDY2, and MAUREEN MAHAFFEY2 Centre for Respiratory Investigation, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow G4 OSF1
Thorax (1976), 31, 708. Total body potassium in cor pulmonale A. D. HOWIE', A. I. PACK', K. BODDY2, and MAUREEN MAHAFFEY2 Centre for Respiratory Investigation, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow G4 OSF1
Subcutaneous adrenaline versus terbutaline in the
 Thorax 1988;43:19-23 Subcutaneous adrenaline versus terbutaline in the treatment of acute severe asthma M A SPITERI, A B MILLAR, D PAVIA, S W CLARKE From the Department of Thoracic Medicine, Royal Free
Thorax 1988;43:19-23 Subcutaneous adrenaline versus terbutaline in the treatment of acute severe asthma M A SPITERI, A B MILLAR, D PAVIA, S W CLARKE From the Department of Thoracic Medicine, Royal Free
Radiology of uncomplicated asthma
 Thorax (1974), 29, 296. Radiology of uncomplicated asthma MARGARET E. HODSON, G. SIMON, and J. C. BATTEN Brompton Hospital, London Hodson, Margaret E., Simon, G., and Batten, J. C. (1974). Thorax, 29,
Thorax (1974), 29, 296. Radiology of uncomplicated asthma MARGARET E. HODSON, G. SIMON, and J. C. BATTEN Brompton Hospital, London Hodson, Margaret E., Simon, G., and Batten, J. C. (1974). Thorax, 29,
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment (Hand-Held)
 Small Volume Aerosol Treatment Page 1 of 6 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment To standardize the delivery of inhalation aerosol drug therapy via small volume (hand-held)
Small Volume Aerosol Treatment Page 1 of 6 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment To standardize the delivery of inhalation aerosol drug therapy via small volume (hand-held)
Asthma is global health problem in children,
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 52 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Efficacy of salbutamol-ipratropium bromide nebulization compared to salbutamol alone in children with mild to moderate asthma attacks Matahari
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 52 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Efficacy of salbutamol-ipratropium bromide nebulization compared to salbutamol alone in children with mild to moderate asthma attacks Matahari
This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist, District Early Intervention Programme National Health Mission, Ambikapur, Chattisgarh, India
 (Volume2, Issue6) Available online at www.ijarnd.com Evaluation of Peak Expiratory Flow Rate and Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second in Indian Children with Suspected Asthma Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist,
(Volume2, Issue6) Available online at www.ijarnd.com Evaluation of Peak Expiratory Flow Rate and Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second in Indian Children with Suspected Asthma Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist,
Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD
 Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1014 1020 Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD J.F. Donohue a, *, S. Menjoge b, S. Kesten b a University of North Carolina School of Medicine, 130
Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1014 1020 Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD J.F. Donohue a, *, S. Menjoge b, S. Kesten b a University of North Carolina School of Medicine, 130
Sample Case Study. The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on
 Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
The optimal particle size for beta-adrenergic aerosols in mild asthmatics*
 The optimal particle size for beta-adrenergic aerosols in mild asthmatics* Introduction The treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) has improved considerably with the introduction
The optimal particle size for beta-adrenergic aerosols in mild asthmatics* Introduction The treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) has improved considerably with the introduction
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness. treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years
 The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 3/12/2018
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
P01. Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) P01 Guideline for Peak flow recording
 Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for Peak flow recording Caroline Youle,
Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for Peak flow recording Caroline Youle,
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN DISKS
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN DISKS APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol sulphate B.P. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder. It is soluble in 4 parts
PRODUCT INFORMATION VENTOLIN DISKS APPROVED NAME: Salbutamol sulphate B.P. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Salbutamol sulphate is a white or almost white odourless powder. It is soluble in 4 parts
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP)
 Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
JANUARY Guide to the WADA Prohibited List and Therapeutic Use Exemptions
 JANUARY 2018 Guide to the WADA Prohibited List and Therapeutic Use Exemptions Contents The WADA Prohibited List 3 Therapeutic Use Exemptions (TUEs) 5 Requirements for asthma TUEs 9 2 The WADA Prohibited
JANUARY 2018 Guide to the WADA Prohibited List and Therapeutic Use Exemptions Contents The WADA Prohibited List 3 Therapeutic Use Exemptions (TUEs) 5 Requirements for asthma TUEs 9 2 The WADA Prohibited
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium budesonide/formoterol 100/6, 200/6 turbohaler (Symbicort SMART ) No. (362/07) Astra Zeneca UK Limited 9 March 2007 (Issued May 2007) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC)
Scottish Medicines Consortium budesonide/formoterol 100/6, 200/6 turbohaler (Symbicort SMART ) No. (362/07) Astra Zeneca UK Limited 9 March 2007 (Issued May 2007) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC)
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
It is recommended that a mask and protective eyewear be worn when providing care to a patient with a cough
 UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
Transit-time analysis of the forced expiratory spirogram during clinical remission in juvenile asthma
 Thorax, 1979, 34, 194-199 Transit-time analysis of the forced expiratory spirogram during clinical remission in juvenile asthma A LIANG, A E MACFIE, E A HARRIS, AND R M L WHITLOCK From the Clinical Physiology
Thorax, 1979, 34, 194-199 Transit-time analysis of the forced expiratory spirogram during clinical remission in juvenile asthma A LIANG, A E MACFIE, E A HARRIS, AND R M L WHITLOCK From the Clinical Physiology
NEBULIZED SALBUTAMOL WITH & WITHOUT IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE SEVERE ASTHMA
 NEBULIZED SALBUTAMOL WITH & WITHOUT IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE SEVERE ASTHMA Naveed Inayat*, Riaz Hussain Shah**, Qurban Ali Rahu***, Rubina Sahito* ORIGINAL ARTICLE *Department of Pulmonology,
NEBULIZED SALBUTAMOL WITH & WITHOUT IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE SEVERE ASTHMA Naveed Inayat*, Riaz Hussain Shah**, Qurban Ali Rahu***, Rubina Sahito* ORIGINAL ARTICLE *Department of Pulmonology,
Formoterol (OXIS s ) Turbuhaler s as a rescue therapy compared with salbutamol pmdi plus spacer in patients with acute severe asthma
 Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1067 1074 Formoterol (OXIS s ) Turbuhaler s as a rescue therapy compared with salbutamol pmdi plus spacer in patients with acute severe asthma W. Boonsawat*, S. Charoenratanakul,
Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1067 1074 Formoterol (OXIS s ) Turbuhaler s as a rescue therapy compared with salbutamol pmdi plus spacer in patients with acute severe asthma W. Boonsawat*, S. Charoenratanakul,
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
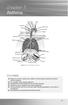 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Spirometry: FEVER DISEASE DIABETES HOW RELIABLE IS THIS? 9/2/2010 BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools
 SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
punctiform type of coalworkers' In 1958 a stratified random sample of 300 miners and a private census in the Rhondda Fach in Glamorgan
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1974, 31, 196-200 Mortality in pneumoconiosis punctiform type of coalworkers' W. E. WATERS1, A. L. COCHRANE, and F. MOORE Medical Research Council's Epidemiology
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1974, 31, 196-200 Mortality in pneumoconiosis punctiform type of coalworkers' W. E. WATERS1, A. L. COCHRANE, and F. MOORE Medical Research Council's Epidemiology
responsiveness in asthmatic patients and smokers
 63 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma G H Koeter Th W van der Mark Department of Allergology J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 973 EZ Groningen, The Netherlands Reprint requests to: Professor
63 Department of Pulmonology B Auffarth D S Postma G H Koeter Th W van der Mark Department of Allergology J G R de Monchy University Hospital, 973 EZ Groningen, The Netherlands Reprint requests to: Professor
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse
 Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
